Manifold Transformation-based Information Geometry Radar Target Detection Method
-
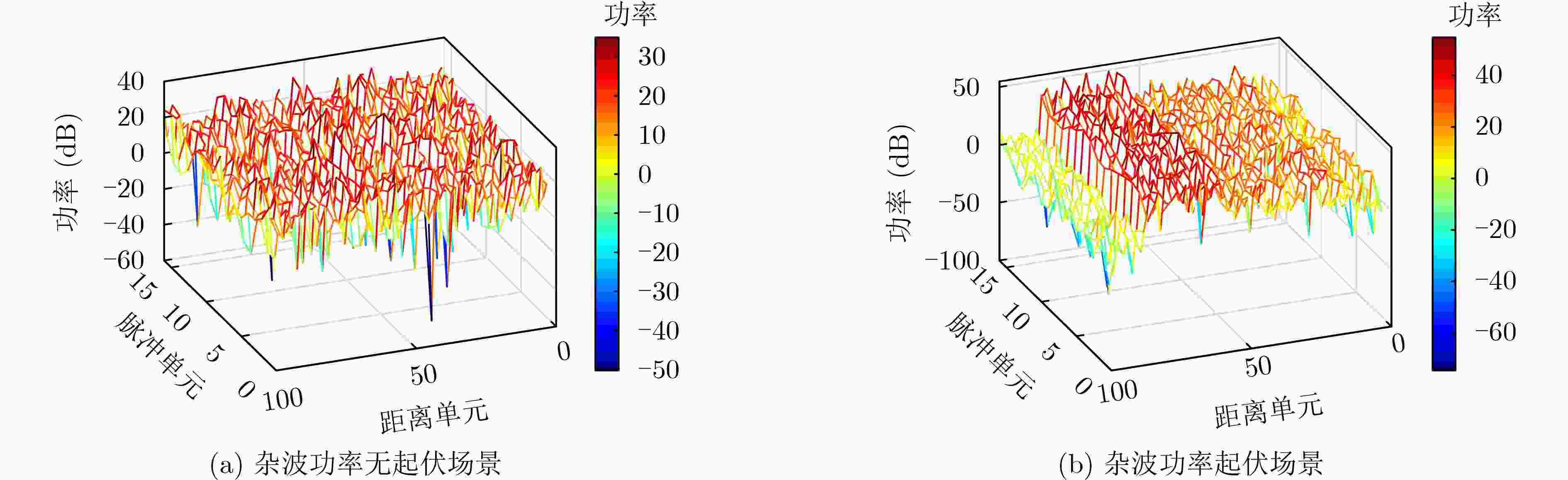
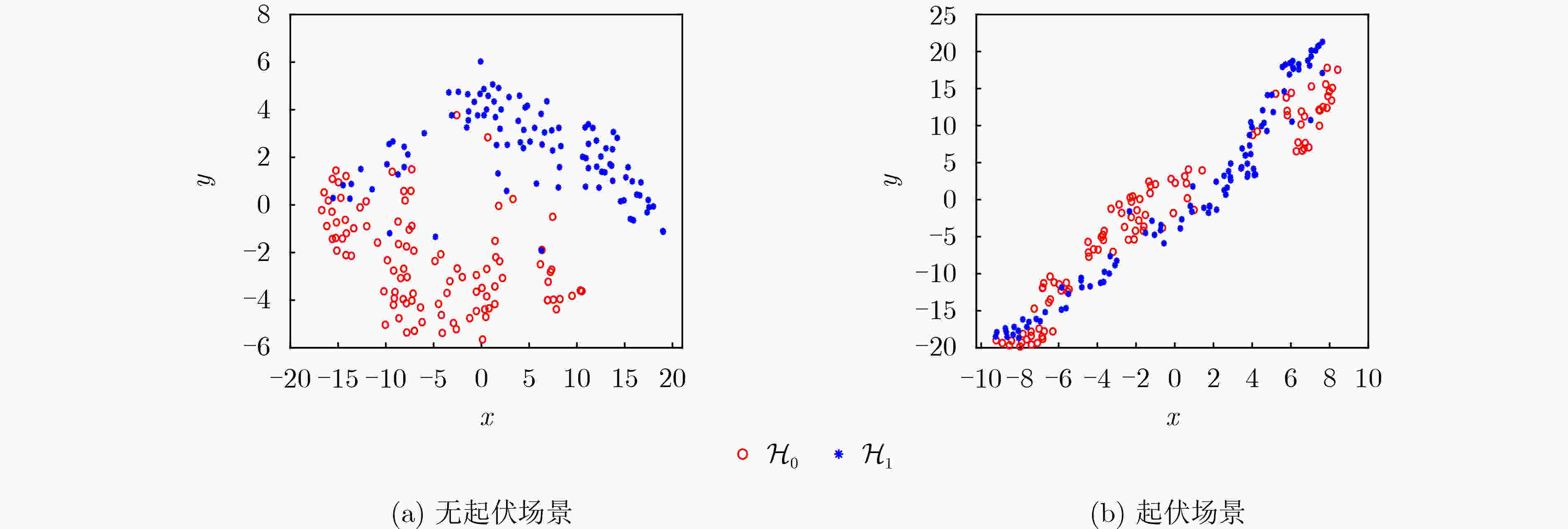
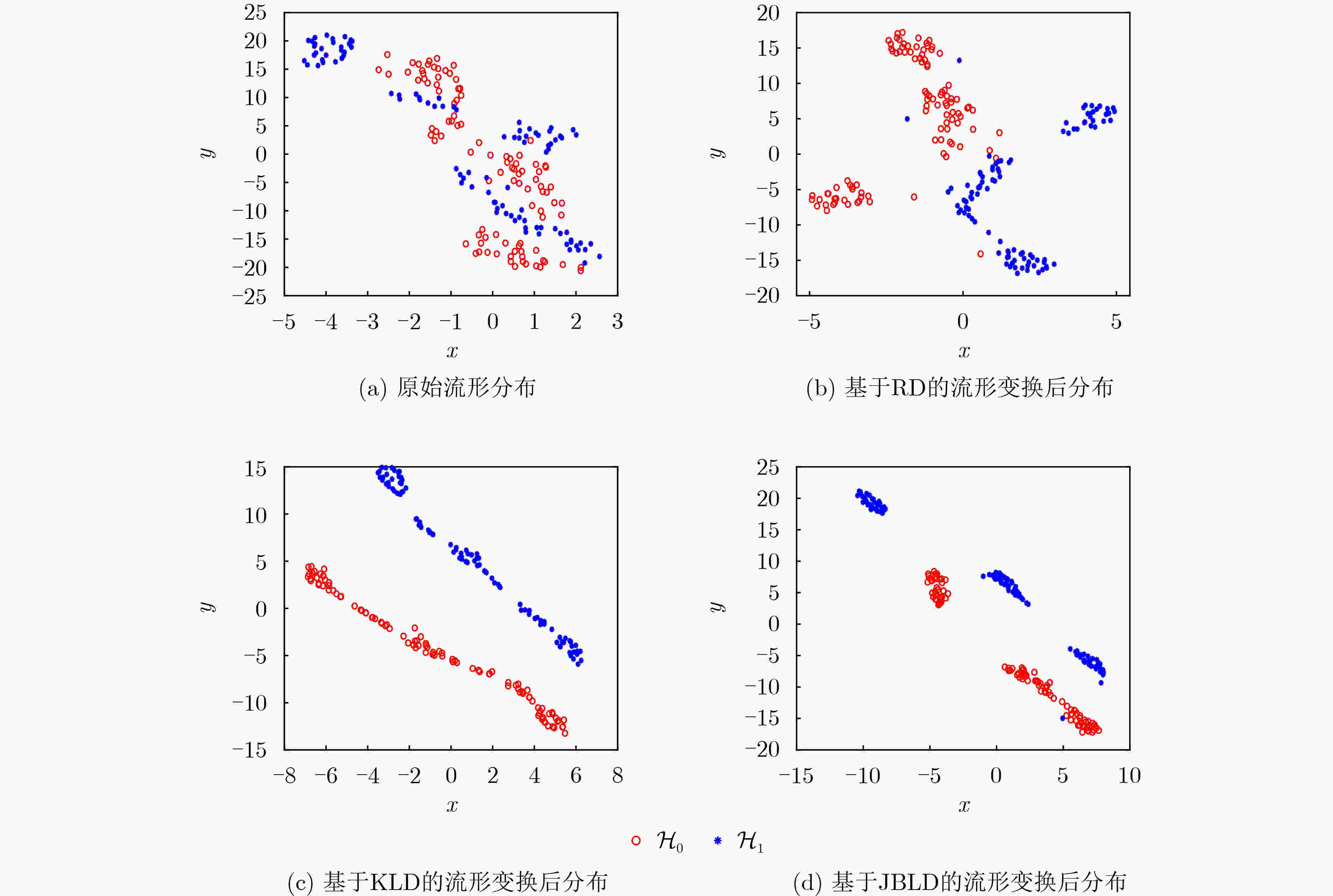
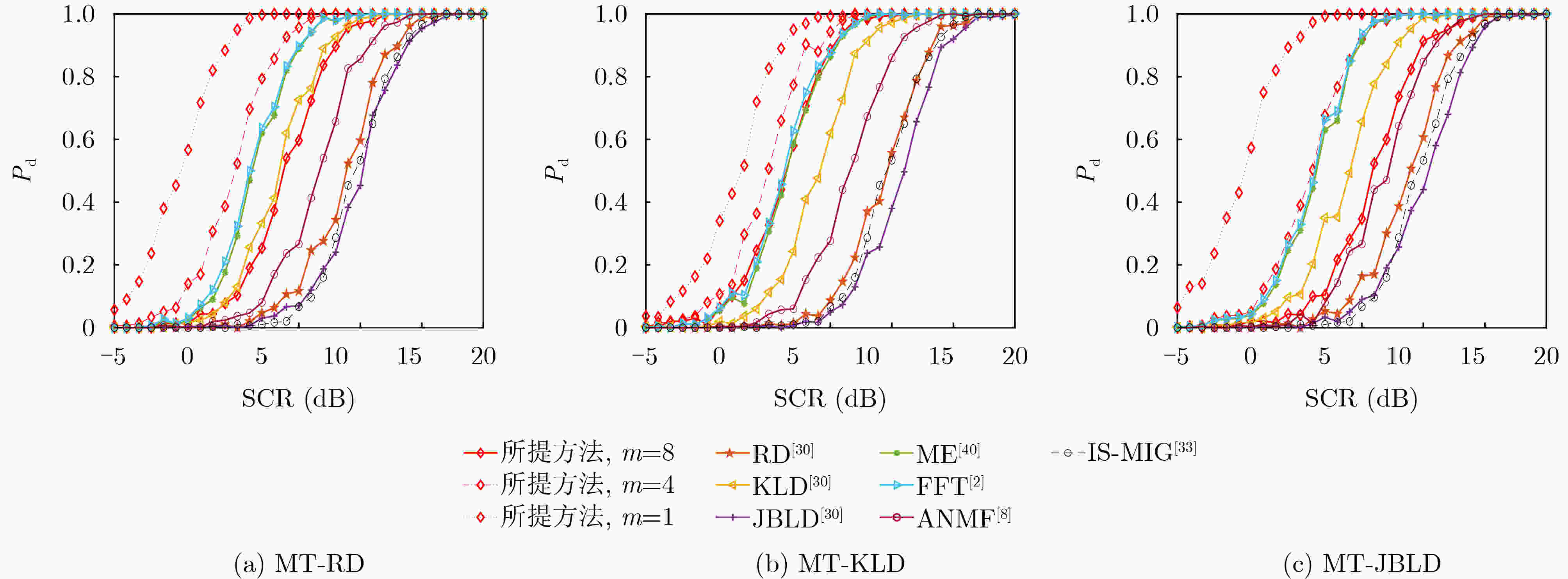
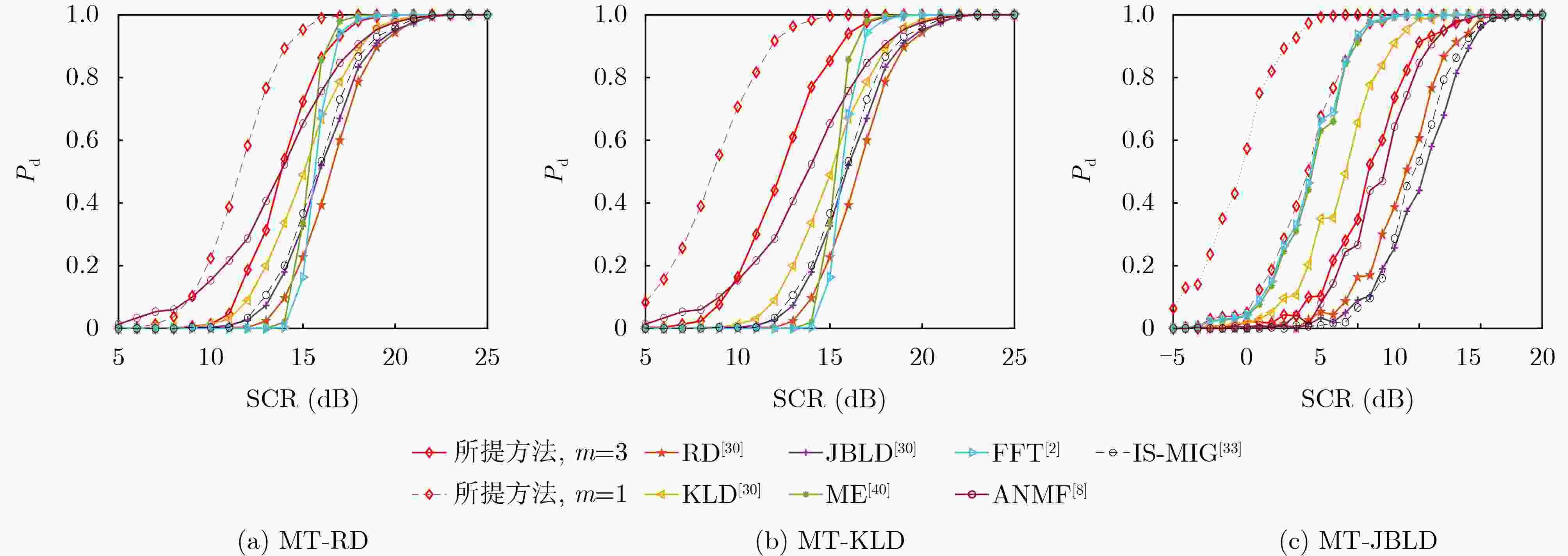
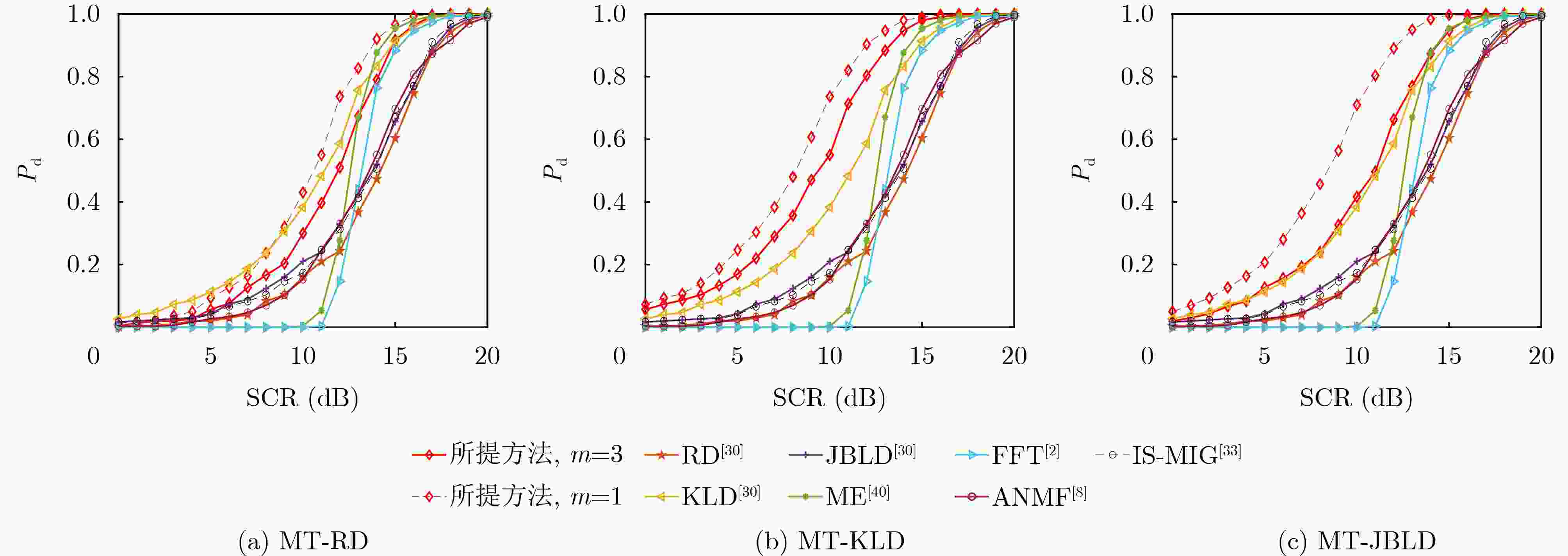
摘要: 基于信息几何的目标检测方法为解决雷达目标检测问题提供了新的技术途径。该文以矩阵信息几何理论为基础,考虑复杂非均匀环境下,回波信杂比低,目标与杂波在矩阵流形上区分性差,导致传统信息几何检测器性能受限的问题,提出一种基于流形变换的信息几何检测器。具体地,该文建立了流形到流形映射变换,并提出待检测单元与杂波中心的几何距离联合优化方法,从而增强变换后流形上目标与杂波的区分性。通过仿真和实测数据验证,所提方法具有较好检测性能。基于仿真数据实验,当信杂比高于1 dB时,所提方法的检测概率可以达到60%以上,同时,实测数据验证结果表明,当检测概率达到80%时,相较于传统信息几何检测器,该文所提检测器能够提升检测信杂比为3~6 dB。Abstract: A novel and effective information geometry-based method for detecting radar targets is proposed based on the theory of matrix information geometry. Due to the poor discriminative power between the target and the clutter on matrix manifold under complex heterogeneous clutter background with low Signal-to-Clutter Ratio (SCR), in this study, the problem of unsatisfactory performance for the conventional information geometry detector is considered, therefore, to address this issue, a manifold transformation-based information geometry detector is proposed. Concretely, a manifold-to-manifold mapping scheme is designed, and a joint optimization method based on the geometric distance between the Cell Under Test (CUT) and the clutter centroid is presented to enhance the discriminative power between the target and the clutter on the mapped manifold. Finally, the superior performance of the proposed method is evaluated using simulated and real clutter data. The results of simulated data show that the detection probability of the proposed method is over 60% when the SCR exceeds 1 dB. Meanwhile, the real data results confirm that the proposed method can achieve SCR improvement about 3~6 dB compared with the conventional information geometry detector.
-
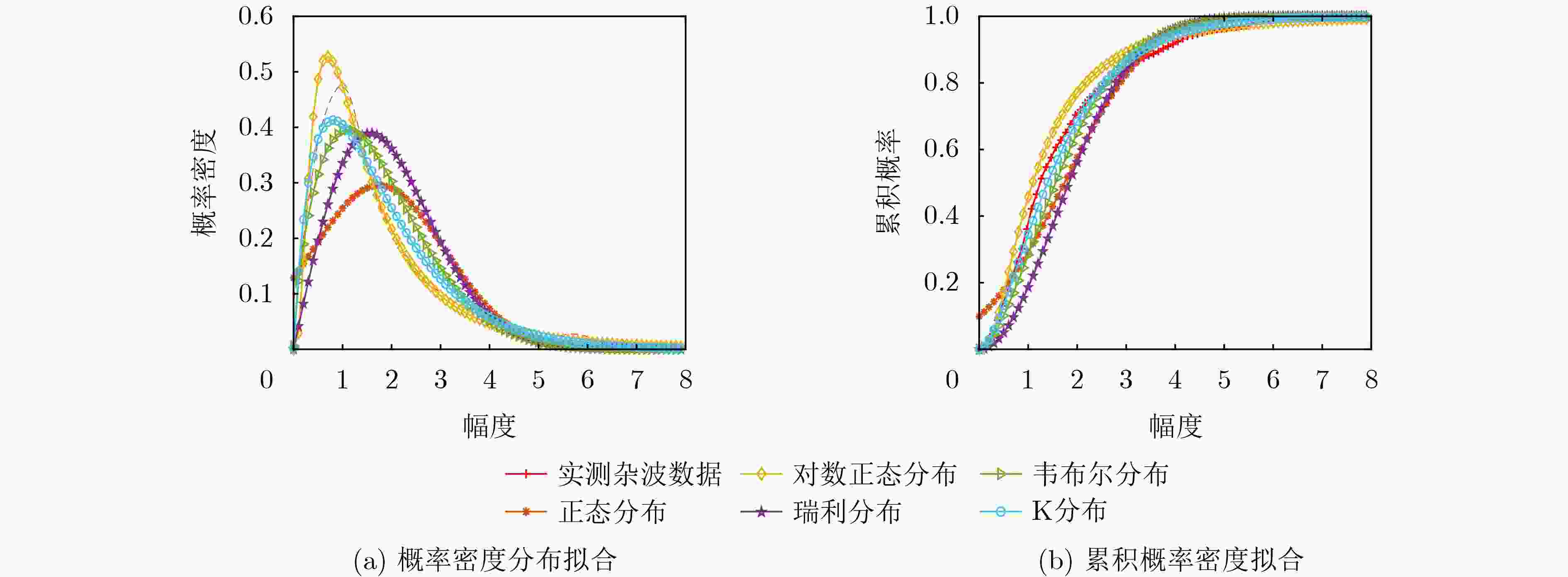
表 1 实测杂波数据拟合优度检验结果
统计分布模型 KL距离 KS统计量 正态分布 2.33 0.16 对数正态分布 0.94 0.11 瑞利分布 4.78 0.23 韦布尔分布 1.56 0.12 K分布 0.78 0.06 表 2 IPIX雷达数据信息
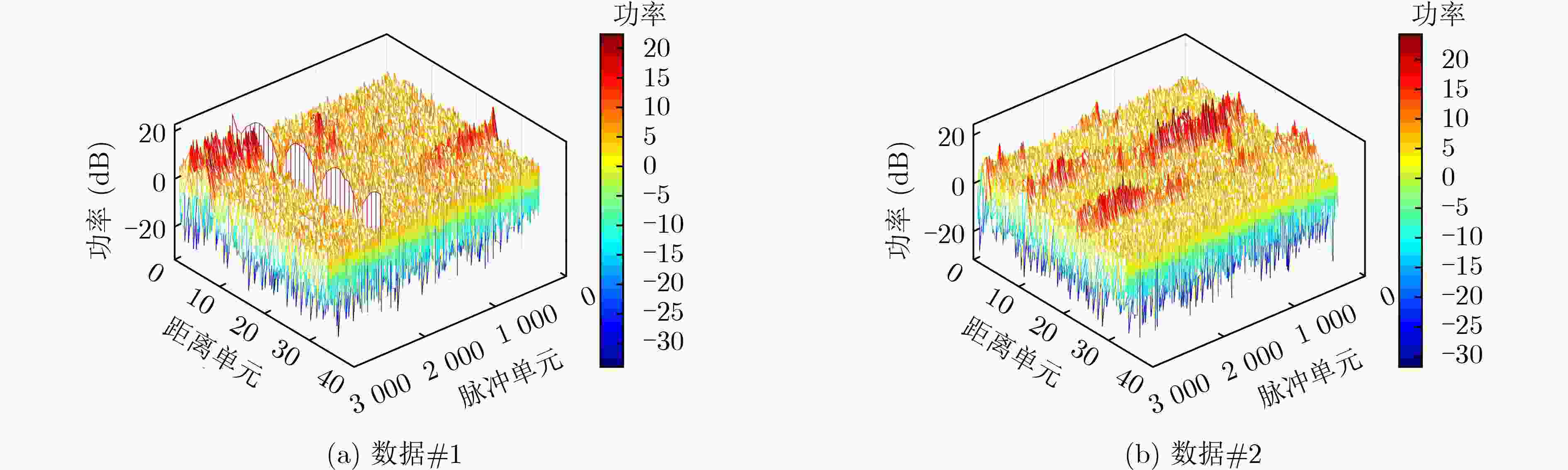
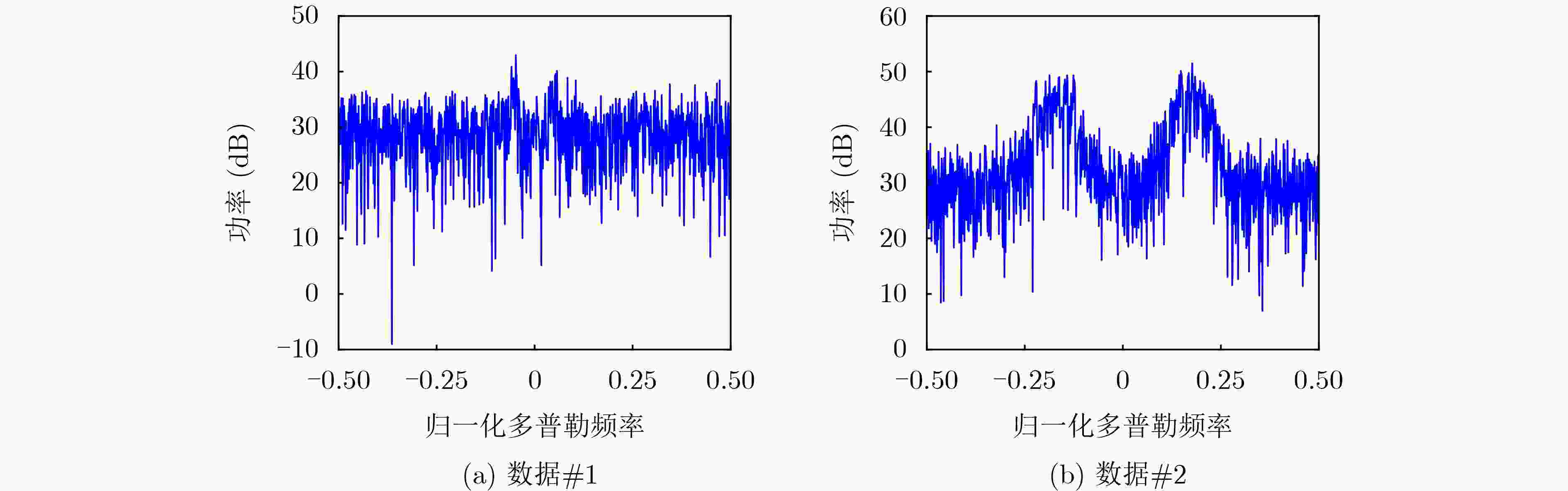
数据号 文件名 距离单元数 脉冲数 数据 #1 19980223 _190901 _ANTSTEP.CDF34 60000 数据 #2 19980223 _191339 _ANTSTEP.CDF34 60000 -
[1] WATTS S. Cell-averaging CFAR gain in spatially correlated K-distributed clutter[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1996, 143(5): 321–327. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19960745. [2] WANG Sichun, INKOL R, RAJAN S, et al. Performance analysis of the FFT filter bank-based summation CFAR detector[C]. 2008 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Victoria, Canada, 2008: 452–456. doi: 10.1109/IMTC.2008.4547078. [3] KELLY E J. An adaptive detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1986, AES-22(2): 115–127. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1986.310745. [4] LIU Weijian, LIU Jun, HAO Chengpeng, et al. Multichannel adaptive signal detection: Basic theory and literature review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2022, 65(2): 121301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3211-8. [5] 薛健, 朱圆玲, 潘美艳. 基于海杂波先验知识的雷达目标自适应Rao检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(11): 3839–3847. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221216.XUE Jian, ZHU Yuanling, and PAN Meiyan. Adaptive Rao detection of radar targets based on the priori-knowledge of sea clutter[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(11): 3839–3847. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221216. [6] ROBEY F C, FUHRMANN D R, KELLY E J, et al. A CFAR adaptive matched filter detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1992, 28(1): 208–216. doi: 10.1109/7.135446. [7] COLUCCIA A, FASCISTA A, and RICCI G. CFAR feature plane: A novel framework for the analysis and design of radar detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 3903–3916. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3000952. [8] CONTE E, LOPS M, and RICCI G. Asymptotically optimum radar detection in compound-Gaussian clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1995, 31(2): 617–625. doi: 10.1109/7.381910. [9] 许述文, 白晓惠, 郭子薰, 等. 海杂波背景下雷达目标特征检测方法的现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084.XU Shuwen, BAI Xiaohui, GUO Zixun, et al. Status and prospects of feature-based detection methods for floating targets on the sea surface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084. [10] 许述文, 焦银萍, 白晓惠, 等. 基于频域多通道图特征感知的海面小目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(5): 1567–1574. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220188.XU Shuwen, JIAO Yinping, BAI Xiaohui, et al. Small target detection based on frequency domain multichannel graph feature perception on sea surface[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(5): 1567–1574. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220188. [11] WU Xijie, DING Hao, LIU Ningbo, et al. A method for detecting small targets in sea surface based on singular spectrum analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5110817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3138488. [12] GUO Juan, HAO Guocheng, YU Jiantao, et al. Floating target detection in sea clutter via deshape multiple synchrosqueezing transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 4285–4294. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3373717. [13] 尹鹏智, 戴恩泽. 基于变换域分形的海面小目标快速检测[J]. 电光与控制, 2022, 29(9): 17–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.09.004.YIN Pengzhi and DAI Enze. Fast sea surface small target detection based on transform domain fractal[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2022, 29(9): 17–21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.09.004. [14] 董云龙, 张兆祥, 刘宁波, 等. 海杂波多普勒谱Hurst指数特性分析及目标检测[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2023, 21(4): 355–363,374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2023.04.001.DONG Yunlong, ZHANG Zhaoxiang, LIU Ningbo, et al. Characteristic analysis on Hurst index of sea clutter Doppler spectrum and target detection[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2023, 21(4): 355–363,374. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2023.04.001. [15] BAI Xiaohui, XU Shuwen, ZHU Jianan, et al. Floating small target detection in sea clutter based on multifeature angle variance[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 9422–9436. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3321998. [16] 陈小龙, 何肖阳, 邓振华, 等. 雷达微弱目标智能化处理技术与应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2024, 13(3): 501–524. doi: 10.12000/JR23160.CHEN Xiaolong, HE Xiaoyang, DENG Zhenhua, et al. Radar intelligent processing technology and application for weak target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 501–524. doi: 10.12000/JR23160. [17] CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, HUANG Yong, et al. False-alarm-controllable radar detection for marine target based on multi features fusion via CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9099–9111. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054744. [18] 苏宁远, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于深度学习的海上目标一维序列信号目标检测方法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 1987–1997. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.004.SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. One-dimensional sequence signal detection method for marine target based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1987–1997. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.004. [19] 黎湘, 程永强, 王宏强, 等. 信息几何理论与应用研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2013, 43(6): 707–732. doi: 10.1360/112012-424.LI Xiang, CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. Progress in theory and applications of information geometry[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2013, 43(6): 707–732. doi: 10.1360/112012-424. [20] CHENG Yongqiang, HUA Yongqiang, WANG Yongqiang, et al. The geometry of signal detection with applications to radar signal processing[J]. Entropy, 2016, 18(11): 381. doi: 10.3390/e18110381. [21] CHEN Xixi, CHENG Yongqiang, WU Hao, et al. Heterogeneous clutter suppression via affine transformation on Riemannian manifold of HPD matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5109813. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3147494. [22] WU Hao, CHENG Yongqiang, CHEN Xixi, et al. Information geometry-based track-before-detect algorithm for slow-moving fluctuating target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023, 71: 1833–1848. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2023.3277205. [23] ARNAUDON M, BARBARESCO F, and YANG Le. Riemannian medians and means with applications to radar signal processing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(4): 595–604. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2261798. [24] YANG Zheng, CHENG Yongqiang, WU Hao, et al. Manifold projection-based subband matrix information geometry detection for radar targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5110415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3323663. [25] WU Hao, CHENG Yongqiang, CHEN Xixi, et al. Geodesic normal coordinate-based manifold filtering for target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5114615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3183432. [26] 杨政, 程永强, 吴昊, 等. 基于正交投影的子带信息几何雷达弱小目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 776–792. doi: 10.12000/JR23079.YANG Zheng, CHENG Yongqiang, WU Hao, et al. Subband information geometry detection method based on orthogonal projection for weak radar targets[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 776–792. doi: 10.12000/JR23079. [27] BARBARESCO F and MEIER U. Radar monitoring of a wake vortex: Electromagnetic reflection of wake turbulence in clear air[J]. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2010, 11(1): 54–67. doi: 10.1016/j.crhy.2010.01.001. [28] HUA Xiaoqiang, ONO Y, PENG Linyu, et al. Target detection within nonhomogeneous clutter via total bregman divergence-based matrix information geometry detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 4326–4340. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3095725. [29] HUA Xiaoqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Yongqiang, et al. Robust covariance estimators based on information divergences and Riemannian manifold[J]. Entropy, 2018, 20(4): 219. doi: 10.3390/e20040219. [30] HUA Xiaoqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. Geometric means and medians with applications to target detection[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2017, 11(6): 711–720. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0547. [31] HUA Xiaoqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, WANG Hongqiang, et al. Matrix CFAR detectors based on symmetrized Kullback–Leibler and total Kullback–Leibler divergences[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 69: 106–116. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2017.06.019. [32] 赵文静, 金明录, 刘文龙. 基于谱范数的矩阵CFAR检测器[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(9): 1951–1956. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.09.019.ZHAO Wenjing, JIN Minglu, and LIU Wenlong. Matrix CFAR detector based on matrix spectral norm[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(9): 1951–1956. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.09.019. [33] 王宏强, 程永强, 华小强, 等. 基于流形等距映射的矩阵信息几何检测方法[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2023, 21(4): 523–529. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2023039.WANG Hongqiang, CHENG Yongqiang, HUA Xiaoqiang, et al. Matrix information geometry method based on manifold ISOMAP[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2023, 21(4): 523–529. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2023039. [34] HUA Xiaoqiang, PENG Linyu, LIU Weijian, et al. LDA-MIG detectors for maritime targets in nonhomogeneous sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5101815. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3250990. [35] IPIX RADAR FILE. IPIX radar dataset files in Grimsby on the shores of Lake Ontari[EB/OL]. http://soma.mcmaster.ca/ipix.php, 2003. [36] DO T N, KADDOUM G, NGUYEN T L, et al. Multi-RIS-aided wireless systems: Statistical characterization and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(12): 8641–8658. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3117599. [37] VAN DER MAATEN L and HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(86): 2579–2605. [38] UDRIŞTE C. Convex Functions and Optimization Methods on Riemannian Manifolds[M]. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer, 1994. doi: 10.1007/978-94-015-8390-9. [39] ABSIL P A, MAHONY R, and SEPULCHRE R. Optimization Algorithms on Matrix Manifolds[M]. Princeton, USA: Princeton University Press, 2008. doi: 10.1515/9781400830244. [40] ZHAO Wenjing, LIU Chang, LIU Wenlong, et al. Maximum eigenvalue-based target detection for the K-distributed clutter environment[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(11): 1294–1306. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5229. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
