Case Study of High Level Synthesis on Path Planning Algorithm
-
摘要: 随着机器人自动导航技术的快速发展,基于软件实现的路径规划算法在实时性上已无法满足许多应用场景的需求,这就要求对算法进行快速高效的硬件定制,从而获得低延时的性能加速。该文以机器人路径规划中的经典A*算法为对象,通过构建面向硬件设计的C/C++数据结构和函数流程优化,采用高层综合(HLS)实现快速的硬件架构探索和选取较优的设计方案,并完成硬件FPGA综合。实验数据表明,相较于传统寄存器传输级(RTL)开发模式,基于HLS开发模式的路径规划算法在FPGA实现上在开发效率、硬件性能和资源占用率上都有显著提升,验证了高层综合在硬件定制中的可行性和成本优势。Abstract: With the advancement of robot automatic navigation technology, software-based path planning algorithms can no longer satisfy the needs in scenarios of many real-time applications. Fast and efficient hardware customization of the algorithm is required to achieve low-latency performance acceleration. In this work, High Level Synthesis (HLS) of classic A* algorithm is studied. Hardware-oriented data structure and function optimization, varying design constraints are explored to pick the right architecture, which is then followed by FPGA synthesis. Experimental results show that, compared to the conventional Register Transfer Level (RTL) method, the HLS-based FPGA implementation of the A* algorithm can achieve better productivity, improved hardware performance and resource utilization efficiency, which demonstrates the advantages of high level synthesis in hardware customization in algorithm-centric applications.
-
1 A*算法的基本流程
(1)初始化开启列表和关闭列表为空 (2)将七点插入开启列表中 (3)while(开启列表不为空) (4) 从开启列表中取出最小F值的格点作为当前格点,并将之加
入关闭列表(5) foreach(当前格点的相邻格点) (6) if(该格点在关闭列表中或是故障格点) then(跳过该格点) (7) elsif(该格点在开启列表中) then(比较通过当前格点计算
得出的F值是否更小,若更小则更新该格点的F值,设其
父节点为当前节点,并将之插入开启列表)(8) elsif(该格点不在开启列表中) then(通过当前节点计算该
节点的F值,设其父亲节点为当前节点,并将之插入开启
列表)(9) elsif(该格点为终点) then(设其父节点为当前节点,并通
过追踪父节点链条至起点,输出起点到终点的路径,算
法结束)(10) end_foreach (11)end_while (12)if(开启列表为空) then(路径搜索失败) 表 1 SOC FPGA 芯片 PL 资源
资源名称 总数 逻辑单元 LUT 87 840 LUTRAM 57 600 触发器 Flip-flop(FF) 175 680 BRAM 128 I/O 引脚 256 全局时钟缓冲器 BUFG 352 表 2 15×15地图下不同开启列表优化比较
数据结构 LUT个数 FF个数 BRAM个数 运行时长(ns) 优先队列 2 485 2 807 3.0 18 598 队列 2 137 2 755 2.5 44 325 堆栈 2 148 2 739 2.5 38 779 表 3 使用优先队列数据结构的HLS和RTL开发模式比较
FPGA开发模式 运行时间(ns) LUT个数 FF个数 BRAM个数 HLS 483 445 3 208 3 303 34.5 RTL 523 046 7 253 7 161 59.5 表 4 使用堆栈数据结构的HLS和RTL开发模式比较
FPGA开发模式 运行时间(ns) LUT个数 FF个数 BRAM个数 HLS 3 305 830 1 669 1 523 25 RTL 5 987 348 7 313 7 065 56 表 5 使用队列数据结构的HLS和RTL开发模式比较
FPGA开发模式 运行时间(ns) LUT个数 FF个数 BRAM个数 HLS 3 389 425 1 756 1 555 25 RTL 5 598 080 7 317 7 053 56 -
[1] 郑岩. 改进势场蚁群算法的机器人自主导航应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆三峡学院, 2020. doi: 10.27883/d.cnki.gcqsx.2020.000061.ZHENG Yan. Application of improved potential field ant colony algorithm for autonomous robot navigation[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing Three Gorges University, 2020. doi: 10.27883/d.cnki.gcqsx.2020.000061. [2] 郭炜, 魏继增, 郭筝, 等. SoC设计方法与实现[M]. 3版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2017: 23–24.GUO Wei, WEI Jizeng, GUO Zheng, et al. SoC Design Methodology and Implementation[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2017: 23–24. [3] 陈志盛, 朱予涵, 刘耿耿, 等. 考虑流端口数量约束下的连续微流控生物芯片流路径规划算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(9): 3321–3330. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221168.CHEN Zhisheng, ZHU Yuhan, LIU Genggeng, et al. Flow-path planning algorithm for continuous-flow microfluidic biochips with strictly constrained flow ports[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(9): 3321–3330. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221168. [4] CORMEN T H, LEISERSON C E, RIVEST R L, 等, 殷建平, 徐云, 王刚, 等. 译. 算法导论[M]. 3版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2013: 374–376.CORMEN T H, LEISERSON C E, RIVEST R L, et al, YIN Jianping, XU Yun, WANG Gang, et al. translation. Introduction to Algorithms[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2013: 374–376. [5] ABDOKASEB. A C Program to implement A* Search Algorithm[EB/OL]. https://github.com/abdokaseb/AStar-C/, 2022. [6] Mentor, A Siemens Business. HLS Bluebook[M]. Software Version v10. 5b, 2020. [7] ALTOYAN W and ALONSO J J. Investigating performance losses in high-level synthesis for stencil computations[C]. 2020 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines, Fayetteville, USA, 2020: 195–203. doi: 10.1109/FCCM48280.2020.00034. [8] 潘妍, 程岳, 高雅濛. 面向FPGA的高层次综合技术综述[J]. 信息技术与信息化, 2022(3): 96–99. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9528.2022.03.024.PAN Yan, CHENG Yue, and GAO Yameng. An overview of high-level synthesis techniques for FPGAs[J]. Information Technology and Informatization, 2022(3): 96–99. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9528.2022.03.024. [9] 石添介, 刘飞阳, 田径, 等. 基于高层次综合的FPGA循环神经网络加速器设计[J]. 信息技术与信息化, 2022(1): 151–153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9528.2022.01.042.SHI Tianjie, LIU Feiyang, TIAN Jing, et al. Design of FPGA recurrent neural network accelerator based on high-level synthesis[J]. Information Technology and Informatization, 2022(1): 151–153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9528.2022.01.042. [10] 叶海雄, 陶宁蓉, 匡兴红, 等. 基于Catapult C高层次综合工具平台优化运动检测算法的研究[J]. 电子设计工程, 2017, 25(14): 1–4. doi: 10.14022/j.cnki.dzsjgc.2017.14.001.YE Haixiong, TAO Ningrong, KUANG Xinghong, et al. Optimization motion detection algorithm based on Catapult C high-level synthesis tool platform[J]. Electronic Design Engineering, 2017, 25(14): 1–4. doi: 10.14022/j.cnki.dzsjgc.2017.14.001. [11] 徐瑞帆, 肖有为, 罗进, 等. 高层次综合综述[J]. 微纳电子与智能制造, 2021, 3(2): 74–79. doi: 10.19816/j.cnki.10-1594/tn.2021.02.074.XU Ruifan, XIAO Youwei, LUO Jin, et al. The overview of high-level synthesis[J]. Micro/Nano Electronics and Intelligent Manufacturing, 2021, 3(2): 74–79. doi: 10.19816/j.cnki.10-1594/tn.2021.02.074. [12] PANDA P R, SHARMA N, KURRA S, et al. Exploration of loop unroll factors in high level synthesis[C]. 2018 31st International Conference on VLSI Design and 2018 17th International Conference on Embedded Systems. Pune, India, 2018: 465–466. doi: 10.1109/VLSID.2018.115. [13] 谢晓燕, 张玉婷, 刘镇弢. 高层次综合特征检测算法的FPGA实现[J]. 实验室研究与探索, 2018, 37(1): 93–97,117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2018.01.023.XIE Xiaoyan, ZHANG Yuting, and LIU Zhentao. FPGA implementation of feature detection algorithm based on high level synthesis[J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 2018, 37(1): 93–97,117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2018.01.023. [14] 申懿鑫, 韩跃平, 唐道光. 高层次综合的SM4算法硬件实现与优化[J]. 单片机与嵌入式系统应用, 2023, 23(8): 11–14.SHEN Yixin, HAN Yueping, and TANG Daoguang. hardware implementation and optimization of SM4 algorithm based on high-level synthesis[J]. Microcontrollers & Embedded Systems, 2023, 23(8): 11–14. [15] 周成瑞, 杨玲玲. 基于A星算法的全向移动机器人仿真研究[J]. 电脑与信息技术, 2023, 31(3): 29–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1228.2023.03.008.ZHOU Chengrui and YANG Lingling. Simulation research on omnidirectional mobile robot based on A* algorithm[J]. Computer and Information Technology, 2023, 31(3): 29–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1228.2023.03.008. [16] 王小丽. 基于Vivado HLS雾天图像预处理IP核设计[J]. 电脑编程技巧与维护, 2023(4): 158–161. doi: 10.16184/j.cnki.comprg.2023.04.020.WANG Xiaoli. Vivado HLS foggy sky image preprocessing IP core based design[J]. Computer Programming Skills & Maintenance, 2023(4): 158–161. doi: 10.16184/j.cnki.comprg.2023.04.020. [17] 韦苏伦, 陶青川. 基于HLS的MobileNet加速器实现[J]. 现代计算机, 2023, 29(8): 91–97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2023.08.015.WEI Sulun and TAO Qingchuan. Realization of MobileNet accelerator based on HLS[J]. Modern Computer, 2023, 29(8): 91–97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1423.2023.08.015. -






 下载:
下载:
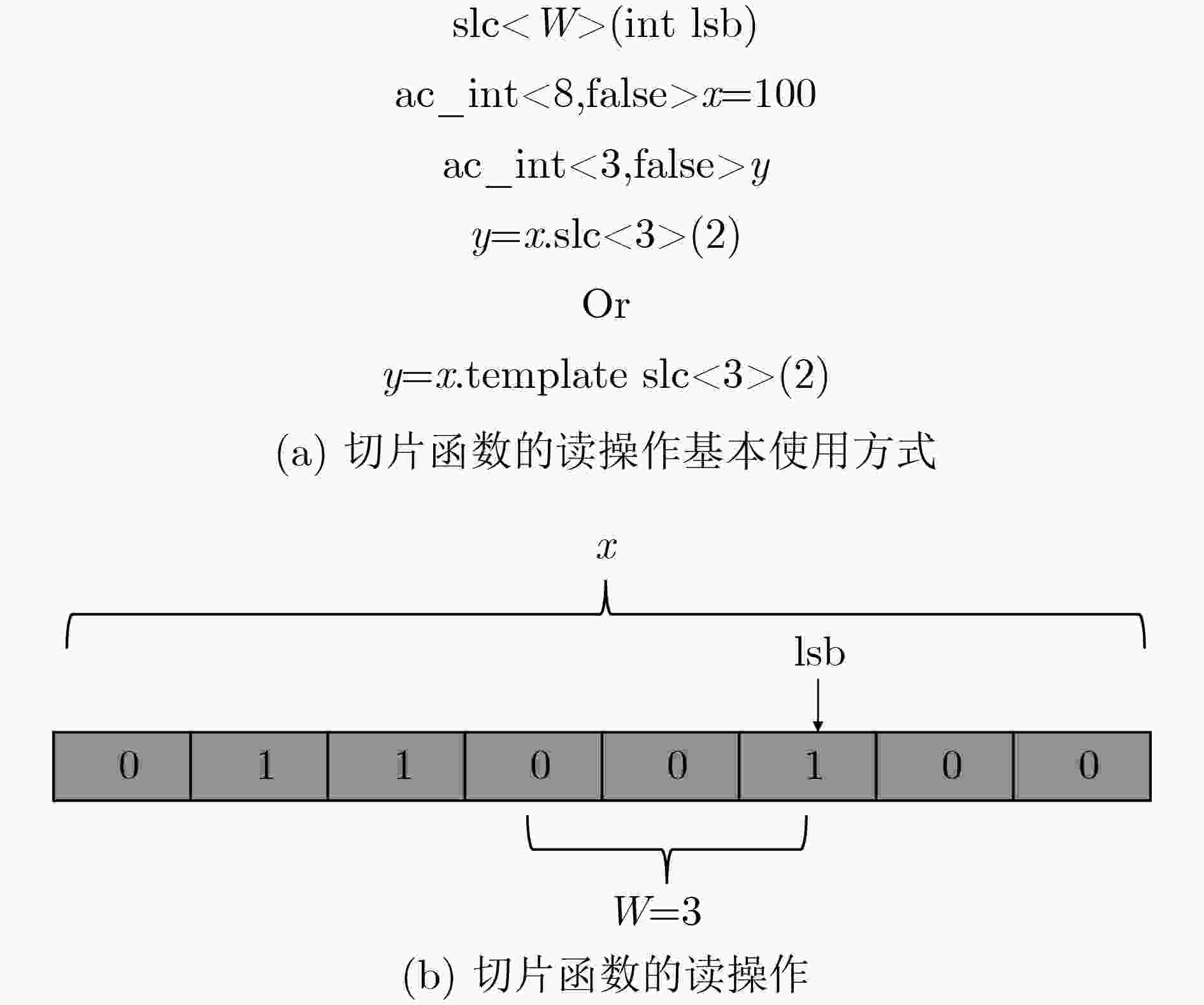


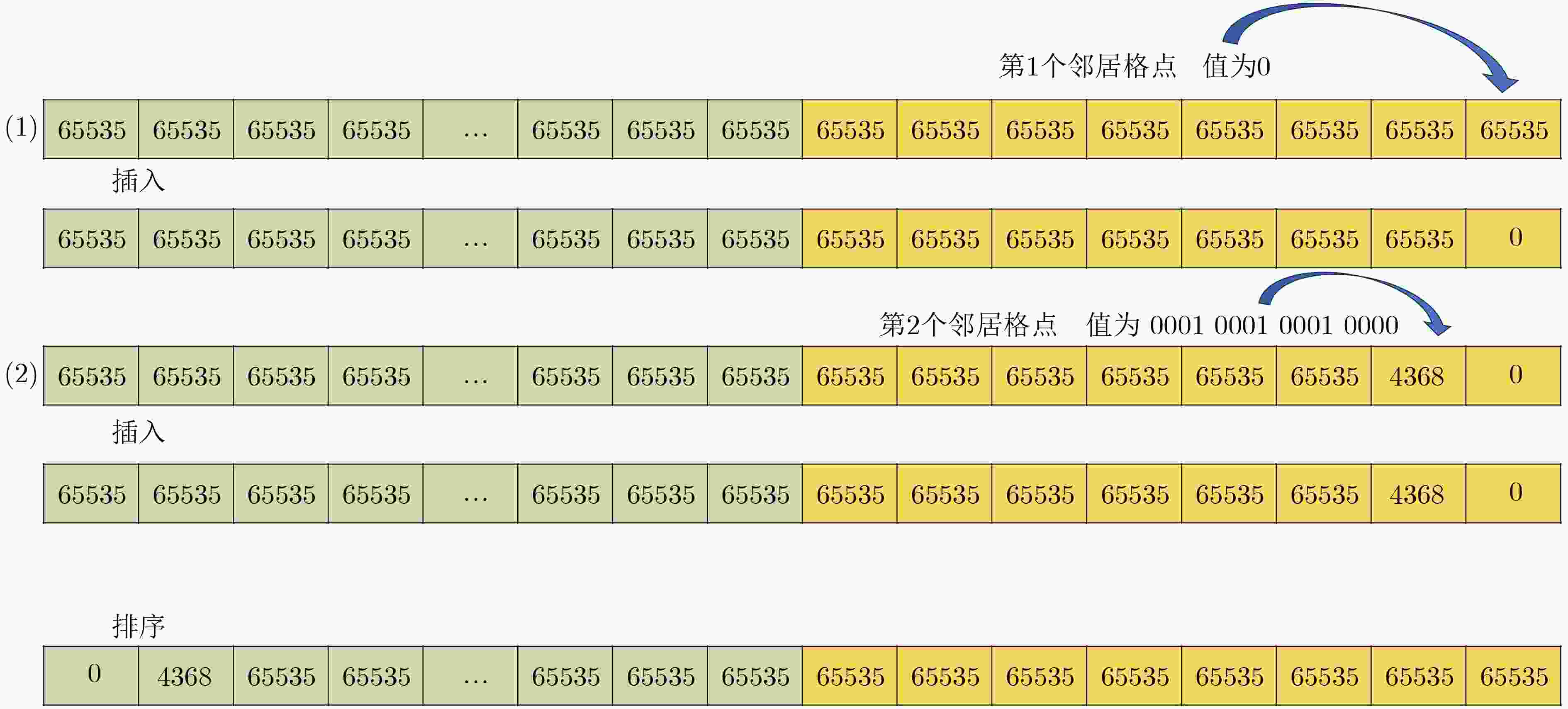
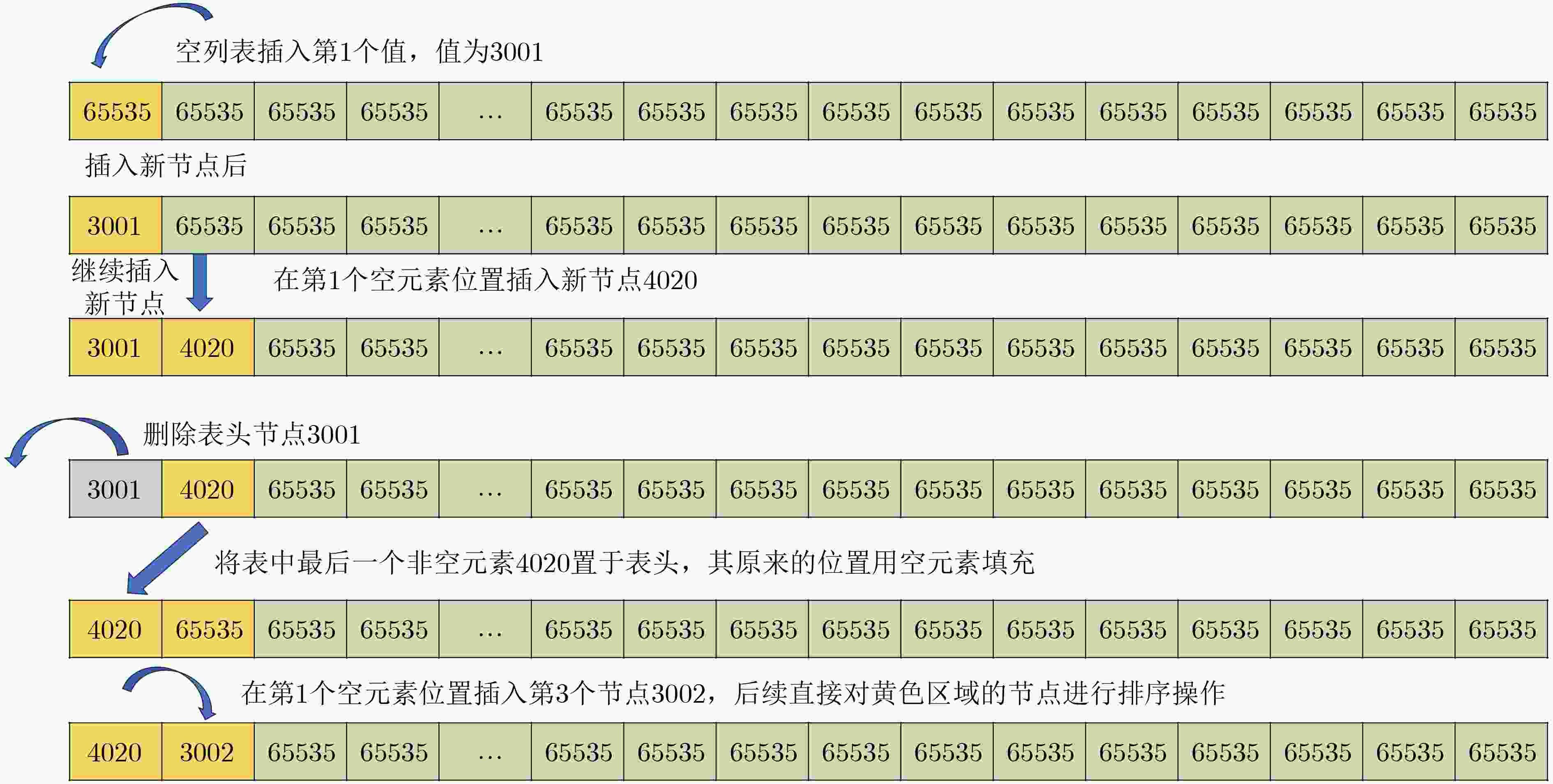









 下载:
下载:
