Deep Image Prior Denoising Model Using Relatively Clean Image Space Search
-
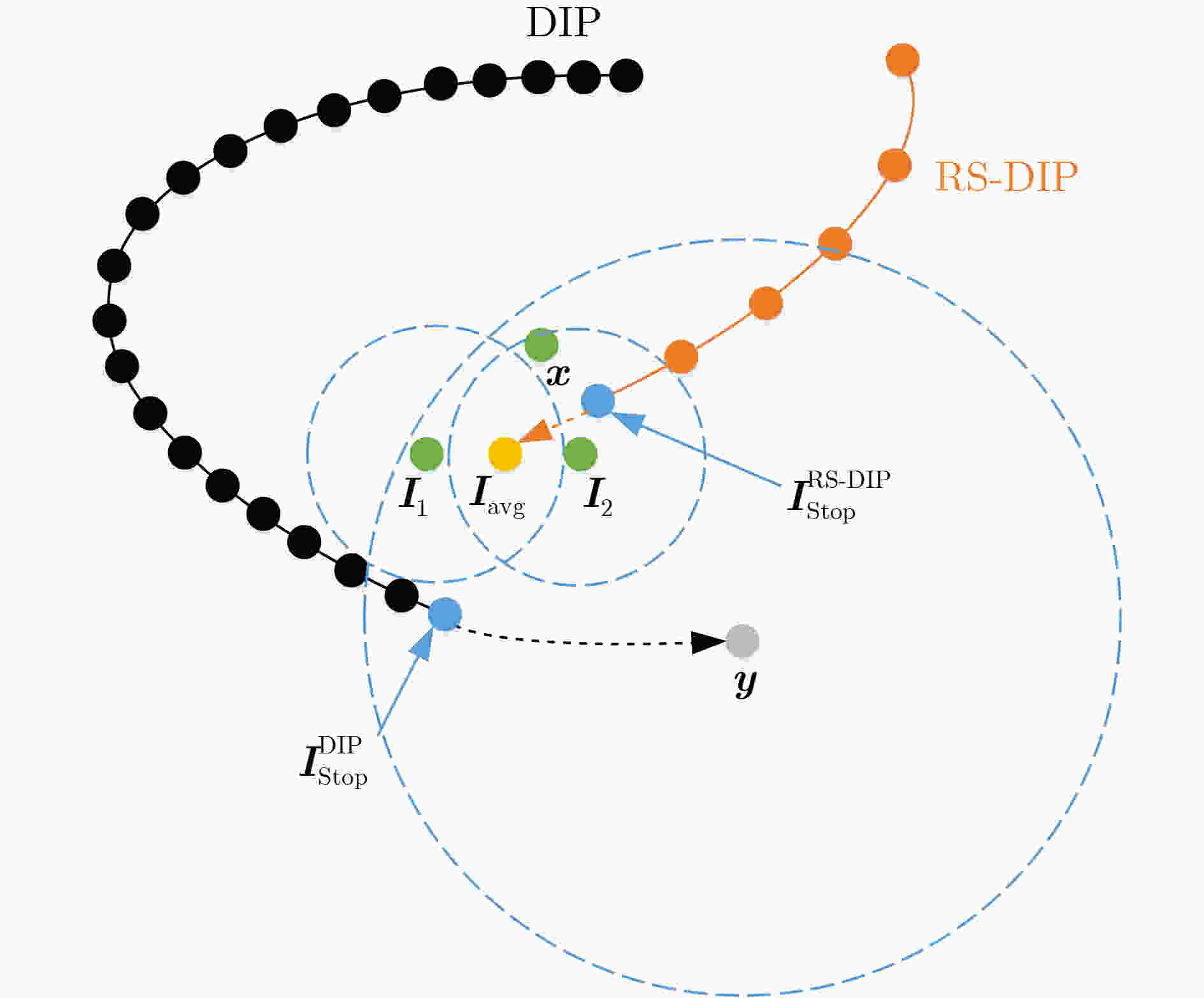
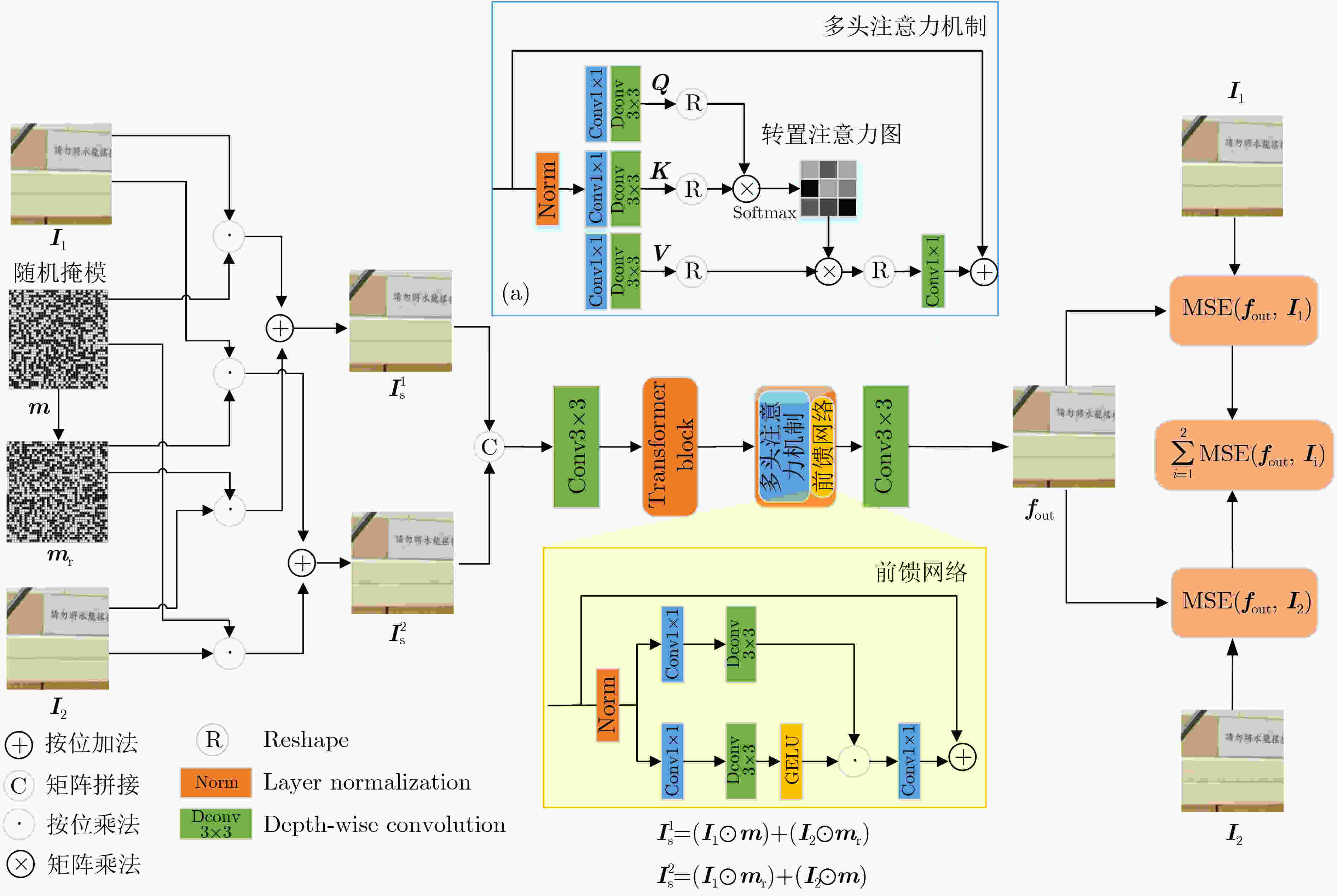
摘要: 鉴于深度图像先验(DIP)降噪模型的性能高度依赖于目标图像所确定的搜索空间,该文提出一种新的基于近清图像空间搜索策略的改进降噪模型。首先,使用当前两种主流有监督降噪模型对同一场景下两张噪声图像分别进行降噪,所获得两张降噪后图像称为近清图像;其次,采用随机采样融合法将两张近清图像融合后作为网络输入,同时以两张近清图像替换噪声图像作为双目标图像以更好地约束搜索空间,进而在更为接近参考图像的空间范围内搜索可能的图像作为降噪后图像;最后,将原DIP模型的多尺度UNet网络简化为单尺度模式,同时引入Transformer模块以增强网络对长距离像素点之间的建模能力,从而在保证网络搜索能力的基础上提升模型的执行效率。实验结果表明:所提改进模型在降噪效果和执行效率两个方面显著优于原DIP模型,在降噪效果方面也超过了主流有监督降噪模型。Abstract: Given that the performance of the Deep Image Prior (DIP) denoising model highly depends on the search space determined by the target image, a new improved denoising model called RS-DIP (Relatively clean image Space-based DIP) is proposed by comprehensively improving its network input, backbone network, and loss function.Initially, two state-of-the-art supervised denoising models are employed to preprocess two noisy images from the same scene, which are referred to as relatively clean images. Furthermore, these two relatively clean images are combined as the network input using a random sampling fusion method. At the same time, the noisy images are replaced with two relatively clean images, which serve as dual-target images. This strategy narrows the search space, allowing exploration of potential images that closely resemble the ground-truth image. Finally, the multi-scale U-shaped backbone network in the original DIP model is simplified to a single scale. Additionally, the inclusion of Transformer modules enhances the network’s ability to effectively model distant pixels. This augmentation bolsters the model’s performance while preserving the network’s search capability. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed denoising model exhibits significant advantages over the original DIP model in terms of both denoising effectiveness and execution efficiency. Moreover, regarding denoising effectiveness, it surpasses mainstream supervised denoising models.
-
表 1 不同降噪模型组合对降噪性能的影响(dB)
算法组合 Restormer+
DnCNNRestormer+
FFDNetRestormer+
DAGLDAGL+
DnCNNDAGL+
FFDNetDAGL+
SwinIRRestormer+
SwinIR1 36.33 36.29 35.79 36.19 35.77 36.08 36.44 2 36.74 36.64 36.06 36.43 36.14 36.48 36.84 3 35.25 34.78 34.78 34.78 35.57 35.28 35.03 4 31.33 31.49 31.48 31.55 31.56 31.62 31.58 5 38.41 37.00 37.57 38.21 36.86 37.30 37.31 6 38.51 40.11 38.53 38.40 39.72 39.82 40.23 7 30.19 30.27 30.02 29.58 29.78 29.77 30.32 8 34.52 34.69 34.17 33.78 33.98 34.03 34.70 9 35.83 35.41 34.79 34.53 34.81 34.80 35.50 10 36.65 36.38 36.04 36.14 35.85 35.94 36.48 平均值 35.27 35.31 34.98 34.96 35.00 35.11 35.44 表 2 随机采样操作对模型降噪性能的影响比较(dB)
对比算法 RS-DIP-1 RS-DIP 1 36.42 36.44 2 36.90 36.84 3 34.93 35.03 4 31.59 31.58 5 37.18 37.31 6 40.14 40.23 7 30.30 30.32 8 34.70 34.70 9 35.49 35.50 10 36.36 36.48 平均值 35.40 35.44 表 3 简化骨干网络对模型降噪性能的影响(dB)
对比算法 RS-DIP-2 RS-DIP 1 36.22 36.44 2 36.79 36.84 3 35.07 35.03 4 31.48 31.58 5 36.83 37.31 6 40.21 40.23 7 30.31 30.32 8 34.54 34.70 9 35.43 35.50 10 36.20 36.48 平均值 35.31 35.44 表 4 各对比方法在各真实噪声数据集上所获得的PSNR值比较(dB)
数据集 PolyU NIND SIDD BM3D 33.90 32.87 38.00 DnCNN 33.28 31.33 32.84 FFDNet 34.25 32.72 37.54 DAGL 33.44 32.10 42.47 Restormer* 33.47 35.20 44.17 SwinIR* 34.45 33.84 37.24 DIP 34.43 33.79 39.42 RS-DIP 35.44 35.46 44.60 *表示该模型被用于处理噪声图像,在NIND和PolyU数据集上分别使用Restormer和SwinIR作为预处理算法处理不同的噪声图像,而在SIDD数据集上仅使用Restormer作为预处理算法处理两张噪声图像。 -
[1] JIN Xin, ZHANG Li, SHAN Chaowei, et al. Dual prior learning for blind and blended image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 1042–1056. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3135482. [2] 白勇强, 禹晶, 李一秾, 等. 基于深度先验的盲图像去模糊算法[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(4): 1050–1067. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211483.BAI Yongqiang, YU Jing, LI Yinong et al. Deep prior-based blind image deblurring[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(4): 1050–1067. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20211483. [3] DABOV K, FOI A, KATKOVNIK V, et al. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(8): 2080–2095. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901238. [4] GOYAL B, DOGRA A, AGRAWAL S, et al. Image denoising review: From classical to state-of-the-art approaches[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 55: 220–244. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.09.003. [5] 周建新, 周凤祺. 基于改进协同量子粒子群的小波去噪分析研究[J]. 电光与控制, 2022, 29(1): 47–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.01.010.ZHOU Jianxin and ZHOU Fengqi. Wavelet denoising analysis based on cooperative quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2022, 29(1): 47–50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2022.01.010. [6] 曾理, 熊西林, 陈伟. 低剂量CT图像降噪的深度图像先验的目标偏移加速算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(6): 2188–2196. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220551.ZENG Li, XIONG Xilin, and CHEN Wei. Deep image prior acceleration method for target offset in low-dose CT images denoising[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(6): 2188–2196. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220551. [7] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, CHEN Yunjin, et al. Beyond a Gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142–3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206. [8] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, and ZHANG Lei. FFDNet: Toward a fast and flexible solution for CNN-based image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9): 4608–4622. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2839891. [9] GUO Shi, YAN Zifei, ZHANG Kai, et al. Toward convolutional blind denoising of real photographs[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1712–1722. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00181. [10] ANWAR S and BARNES N. Real image denoising with feature attention[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3155–3164. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00325. [11] LEHTINEN J, MUNKBERG J, HASSELGREN J, et al. Noise2Noise: Learning image restoration without clean data[C]. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 2965–2974. [12] KRULL A, BUCHHOLZ T O, and JUG F. Noise2void-learning denoising from single noisy images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2124–2132. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00223. [13] HUANG Tao, LI Songjiang, JIA Xu, et al. Neighbor2Neighbor: Self-supervised denoising from single noisy images[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 14776–14785. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01454. [14] LEMPITSKY V, VEDALDI A, and ULYANOV D. Deep image prior[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9446–9454. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00984. [15] HENDRYCKS D and GIMPEL K. Gaussian error linear units (GELUs)[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.08415, 2023. [16] XU Jun, LI Hui, LIANG Zhetong, et al. Real-world noisy image denoising: A new benchmark[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02603, 2018. [17] YANG Yu, XU Haifeng, QI Bin, et al. Stroke screening data modeling based on openEHR and NINDS Stroke CDE[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioMedicine (BIBM), Seoul, Korea (South), 2020: 2147–2152. doi: 10.1109/BIBM49941.2020.9313127. [18] ABDELHAMED A, LIN S, and BROWN M S. A high-quality denoising dataset for smartphone cameras[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1692–1700. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00182. [19] 徐胜军, 杨华, 李明海, 等. 基于双频域特征聚合的低照度图像增强[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(12): 230225. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230225.XU Shengjun, YANG Hua, LI Minghai, et al. Low-light image enhancement based on dual-frequency domain feature aggregation[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2023, 50(12): 230225. doi: 10.12086/oee.2023.230225. [20] SOH J W, CHO S, and CHO N I. Meta-transfer learning for zero-shot super-resolution[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 3513–3522. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00357. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
