The Power Suppression Techniques for the DPA-resistant RISC-V CPU Core Based on WDDL
-
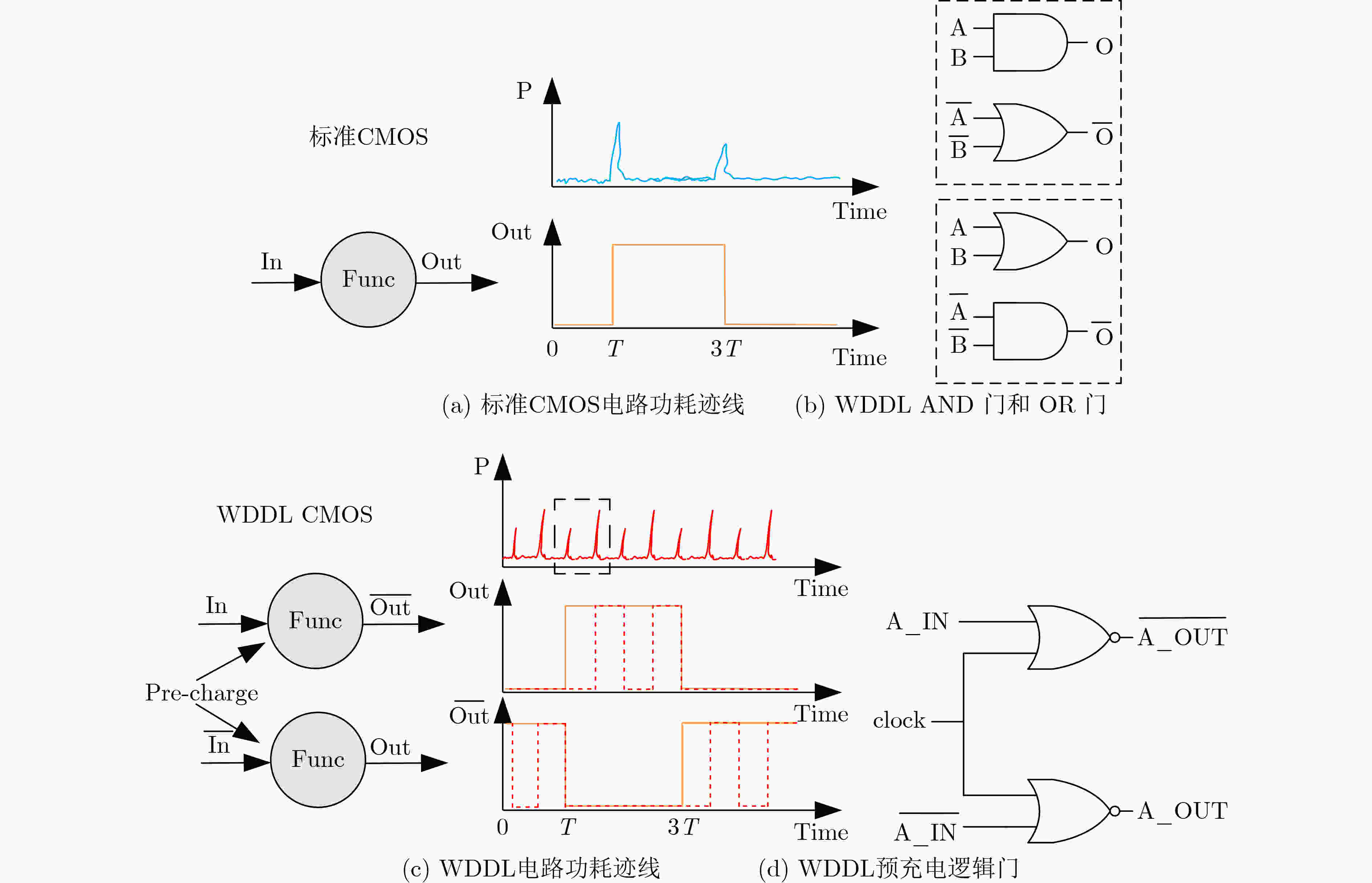
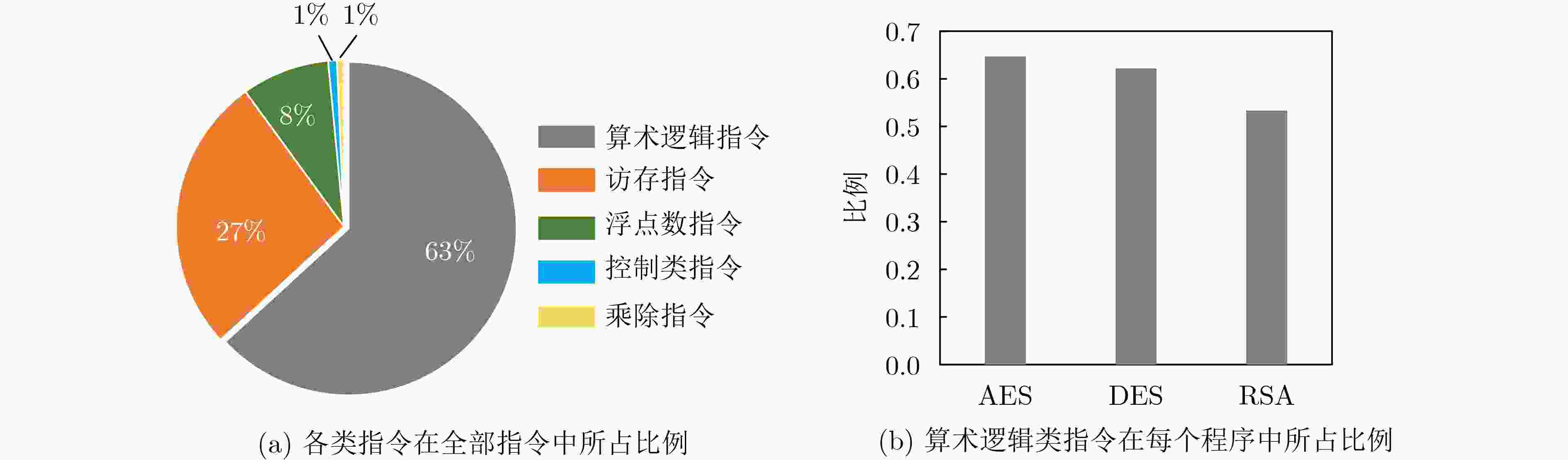
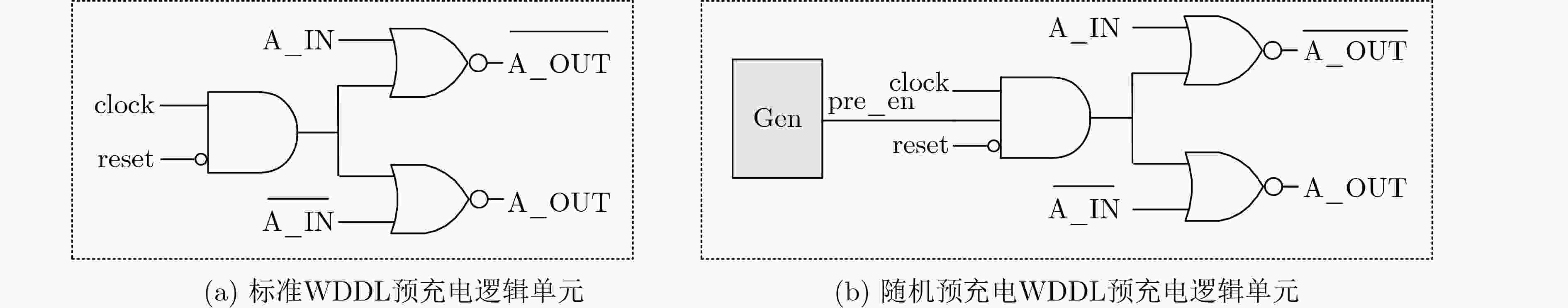
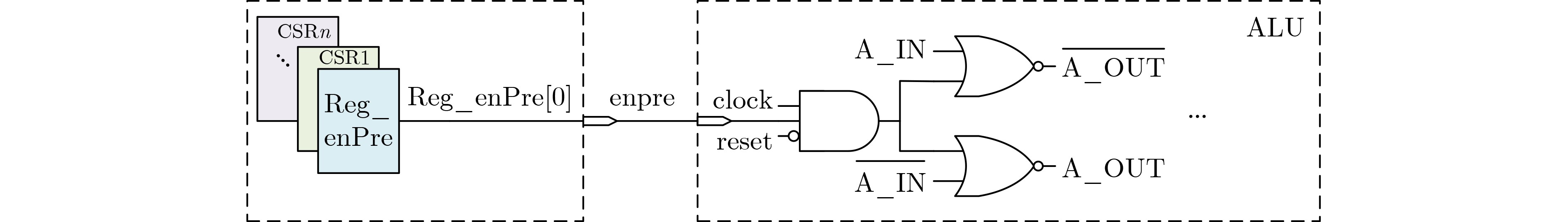
摘要: 差分功耗分析(DPA)攻击不仅威胁加密硬件,对加密软件的安全性也构成严重挑战。将波动动态差分逻辑(WDDL)技术应用在RISC-V指令集的处理器芯核上可减少功耗信息的泄露。但是,WDDL技术会给电路引入巨大的功耗开销。该文针对基于WDDL的RISC-V处理器芯核提出两种功耗抑制方法。虽然随机预充电使能技术与指令无关,而预充电使能指令技术需要扩充指令集,但这两种方法都是属于轻量级的设计改进。仿真结果表明,采用了随机预充电使能技术和预充电使能指令技术的Rocket 芯核的电路功耗分别是原始的WDDL Rocekt 芯核功耗的42%和36.4%。Abstract: Differential Power Analysis (DPA) is a serious threat to cryptographic hardware and software. The RISC-V processor core based on Wave Dynamic Differential Logic (WDDL) is implemented to mitigate the power leakage. However, the WDDL technique results in a dramatic increase in circuit power. For WDDL-based RISC-V CPU cores, two power suppression techniques are proposed in the paper. Both of them are lightweight solutions. The simulation results show that the circuit power of the DPA-resistant Rocket core with the random precharge enabling technique and the precharge enabling instruction technique can be reduced to 42% and 36.4% of that of the original WDDL based counterpart, respectively.
-
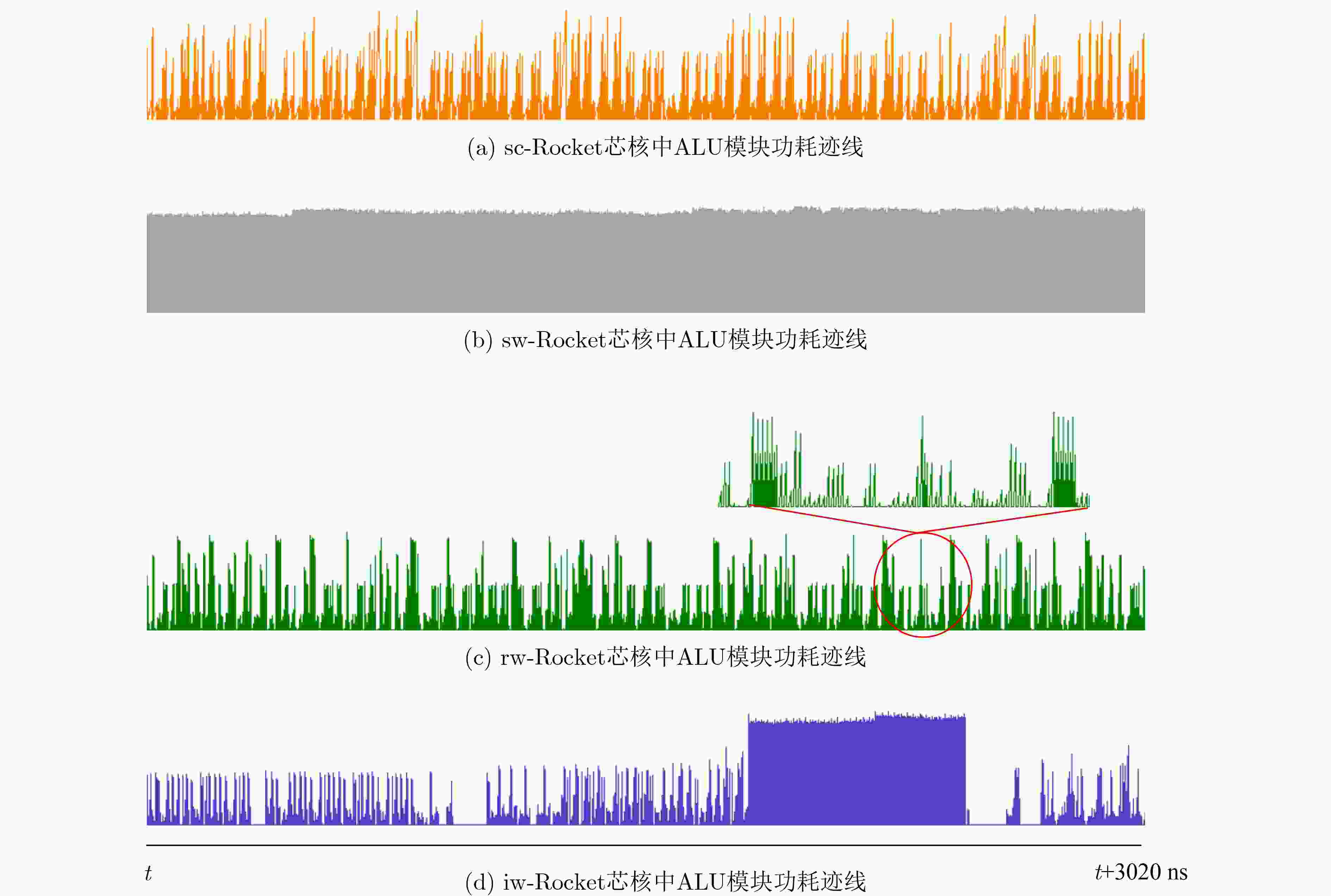
表 1 不同程序的功耗比较(mW)
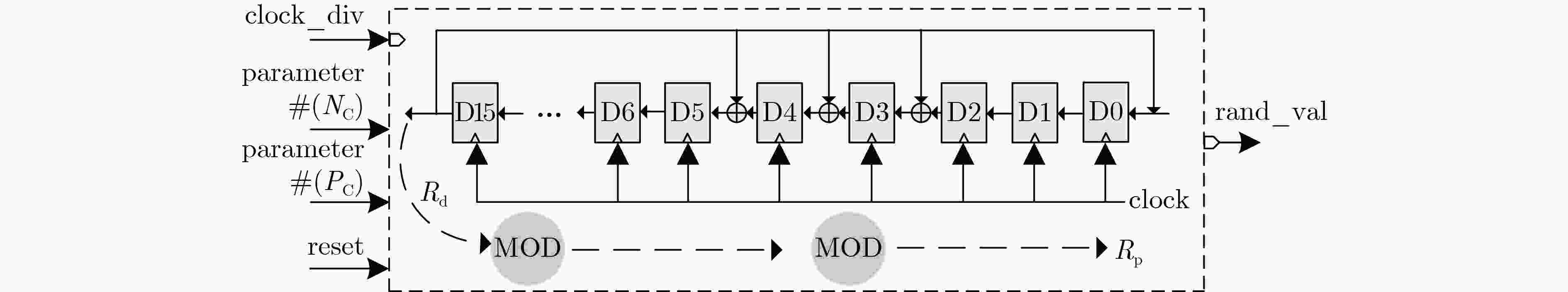
sc-Rocket sw-Rocket Rocket ALU Rocket ALU Helloworld 1.55 0.04 5.60(×3.6) 4.09(×102.3) DES 2.16 0.13 6.14(×2.8) 4.12(×31.6) AES 1.94 0.11 5.93(×3.1) 4.11(×37.4) RSA 1.72 0.05 5.77(×3.4) 4.09(×81.8) 表 2 随机预充电发生器的面积和功耗开销
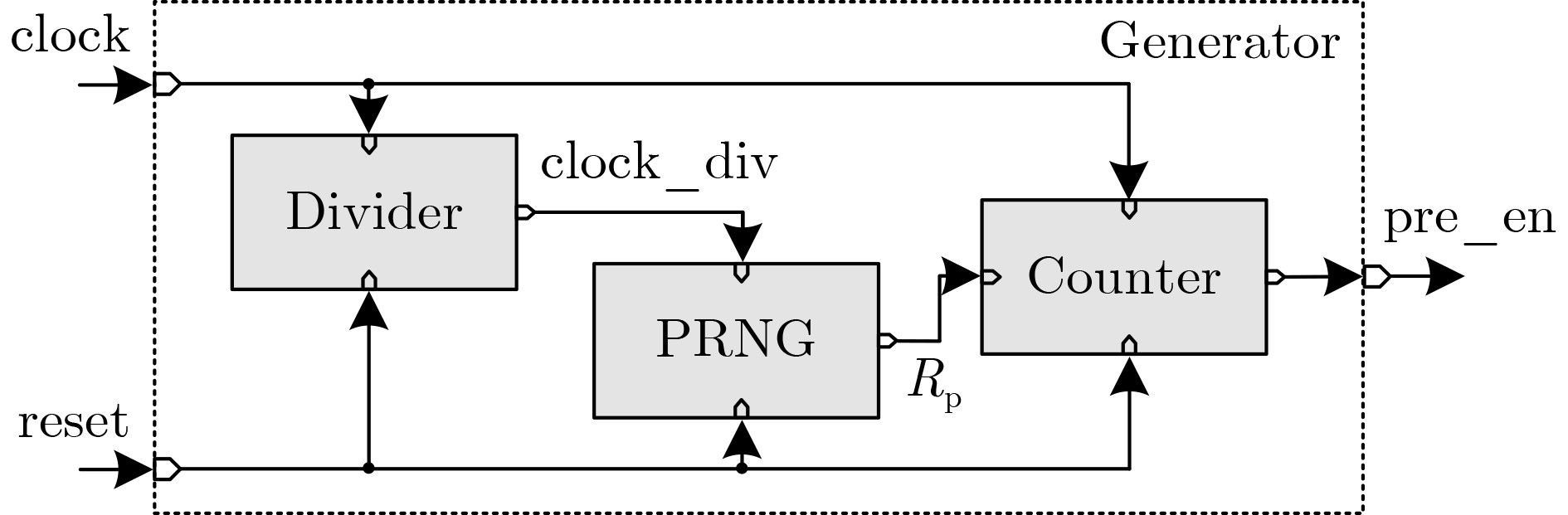
NC PC 面积(μm2) 功耗(μW) Divider PRNG Generator Generator 8 2 33.1 270.4 346.7 26.6 6 33.1 354.6 436.7 27.7 16 5 46.4 271.0 372.2 31.3 8 46.4 400.0 517.3 31.4 16 46.4 451.8 579.2 31.7 32 5 58.7 272.0 398.2 35.8 10 58.7 453.2 597.6 35.6 16 58.7 453.6 604.8 35.7 30 58.7 465.5 615.9 36.3 64 6 71.6 356.8 519.8 40.6 8 71.6 402.5 571.0 40.6 16 71.6 457.2 632.9 40.8 30 71.6 466.9 642.6 40.9 64 71.6 520.6 709.6 41.0 表 3 不同Rocket核心的面积开销(μm2)
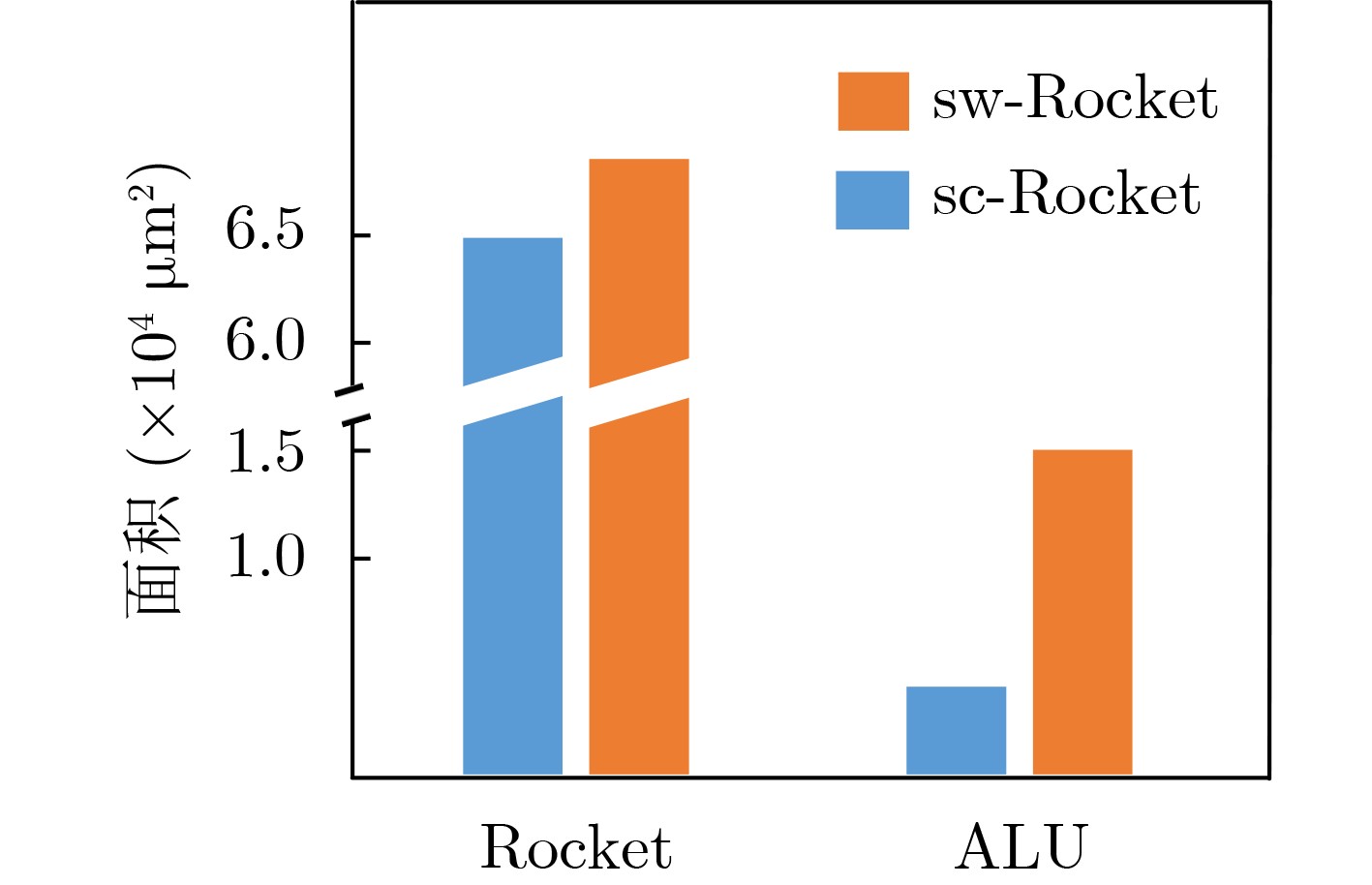
sc-Rocket sw-Rocket rw-Rocket iw-Rocket Rocket 74644.2 85620.6 86020.9 86252.8 ALU 4063.0 15039.4 15439.7 15010.9 CSRFile 15794.3 15794.3 15794.3 16426.1 表 4 不同Rocket核心运行AES-128程序的功耗开销(mW)
sw-Rocket rw-Rocket iw-Rocket Rocket 5.93 2.49 2.16 ALU 4.11 0.67 0.33 CSRFile 0.24 0.24 0.26 -
[1] KOCHER P, JAFFE J, and JUN B. Differential power analysis[C]. The 19th Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 1999: 388–397. [2] ORS S B, GURKAYNAK F, OSWALD E, et al. Power-analysis attack on an ASIC AES implementation[C]. The International Conference on Information Technology: Coding and Computing, Las Vegas, USA, 2004: 546–552. [3] CHEN Juncheng, NG J S, KYAW N A, et al. Normalized differential power analysis - for ghost peaks mitigation[C]. 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Daegu, Korea, 2021: 1–5. [4] DEN BOER B, LEMKE K, and WICKE G. A DPA attack against the modular reduction within a CRT implementation of RSA[C]. The 4th International Workshop Redwood Shores, Redwood Shores, USA, 2003: 228–243. [5] FAN Junfeng and VERBAUWHEDE I. An updated survey on secure ECC implementations: Attacks, countermeasures and cost[M]. NACCACHE D. Cryptography and Security: From Theory to Applications. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012: 265–282. [6] MPALANE K, TSAGUE H D, GASELA N, et al. Bit-level differential power analysis attack on implementations of advanced encryption standard software running inside a PIC18F2420 microcontroller[C]. 2015 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence, Las Vegas, USA, 2015: 42–46. [7] PETRVALSKY M, DRUTAROVSKY M, and VARCHOLA M. Differential power analysis of advanced encryption standard on accelerated 8051 processor[C]. 2013 23rd International Conference Radioelektronika, Pardubice, Czech Republic, 2013: 334–339. [8] PETRVALSKY M, DRUTAROVSKY M, and VARCHOLA M. Differential power analysis attack on ARM based AES implementation without explicit synchronization[C]. 2014 24th International Conference Radioelektronika, Bratislava, Slovakia, 2014: 1–4. [9] DE MULDER E, GUMMALLA S, and HUTTER M. Protecting RISC-V against side-channel attacks[C]. The 56th Annual Design Automation Conference, Las Vegas, USA, 2019: 45. [10] AKKAR M L and GIRAUD C. An implementation of DES and AES, secure against some attacks[C]. The 3rd International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Paris, France, 2001: 309–318. [11] LU Tong, ZHOU Fang, WU Ning, et al. Implementation of SM4 based on random state to resist DPA[C]. 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Electronics Technology, Chengdu, China, 2021: 717–721. [12] TIRI K and VERBAUWHEDE I. A logic level design methodology for a secure DPA resistant ASIC or FPGA implementation[C]. The Design, Automation and Test in Europe Conference and Exhibition, Paris, France, 2004: 246–251. [13] BUCCI M, GIANCANE L, LUZZI R, et al. Three-phase dual-rail pre-charge logic[C]. The 8th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Yokohama, Japan, 2006: 232–241. [14] BELLIZIA D, BONGIOVANNI S, OLIVIERI M, et al. SC-DDPL: A novel standard-cell based approach for counteracting power analysis attacks in the presence of unbalanced routing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2020, 67(7): 2317–2330. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2020.2979831 [15] BAYRAK A G, VELICKOVIC N, IENNE P, et al. An architecture-independent instruction shuffler to protect against side-channel attacks[J]. ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code Optimization, 2012, 8(4): 20. doi: 10.1145/2086696.2086699 [16] BRUGUIER F, BENOIT P, TORRES L, et al. Cost-effective design strategies for securing embedded processors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2016, 4(1): 60–72. doi: 10.1109/tetc.2015.2407832 [17] DAO B A, HOANG T T, LE A T, et al. Correlation power analysis attack resisted cryptographic RISC-V SoC with random dynamic frequency scaling countermeasure[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 151993–152014. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3126703 [18] ANTOGNAZZA F, BARENGHI A, and PELOSI G. Metis: An integrated morphing engine CPU to protect against side channel attacks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 69210–69225. doi: 10.1109/access.2021.3077977 [19] LEPLUS G, SAVRY O, and BOSSUET L. Insertion of random delay with context-aware dummy instructions generator in a RISC-V processor[C]. 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust, McLean, USA, 2022: 81–84. [20] STANGHERLIN K and SACHDEV M. Design and implementation of a secure RISC-V microprocessor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2022, 30(11): 1705–1715. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2022.3203307 [21] TENA-SÁNCHEZ E, POTESTAD-ORDÓÑEZ F E, JIMÉNEZ-FERNÁNDEZ C J, et al. Gate-level hardware countermeasure comparison against power analysis attacks[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(5): 2390. doi: 10.3390/app12052390 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
