FPGA Implementation of Direction of Arrival Estimation Method for Polarization Sensitive Array
-
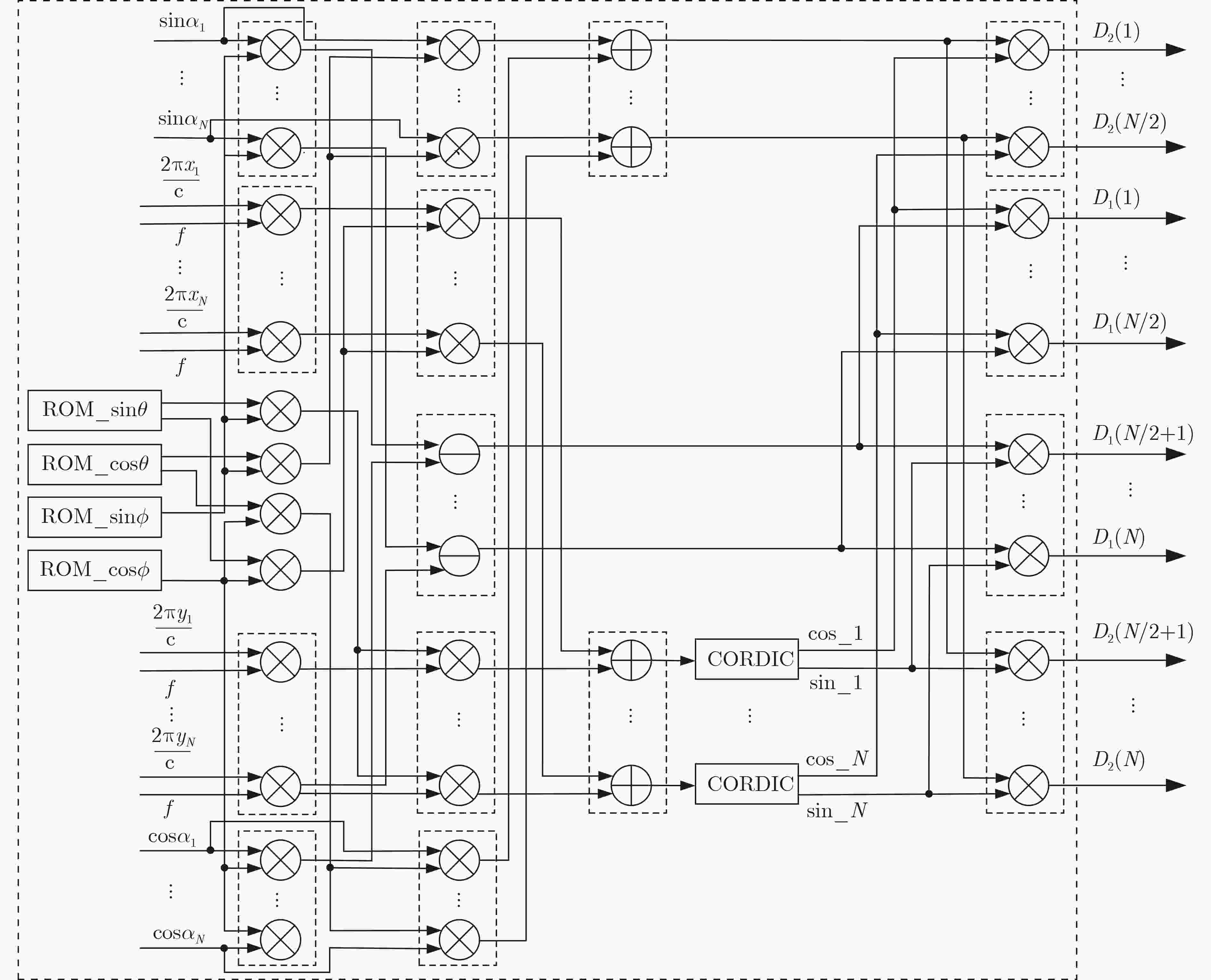
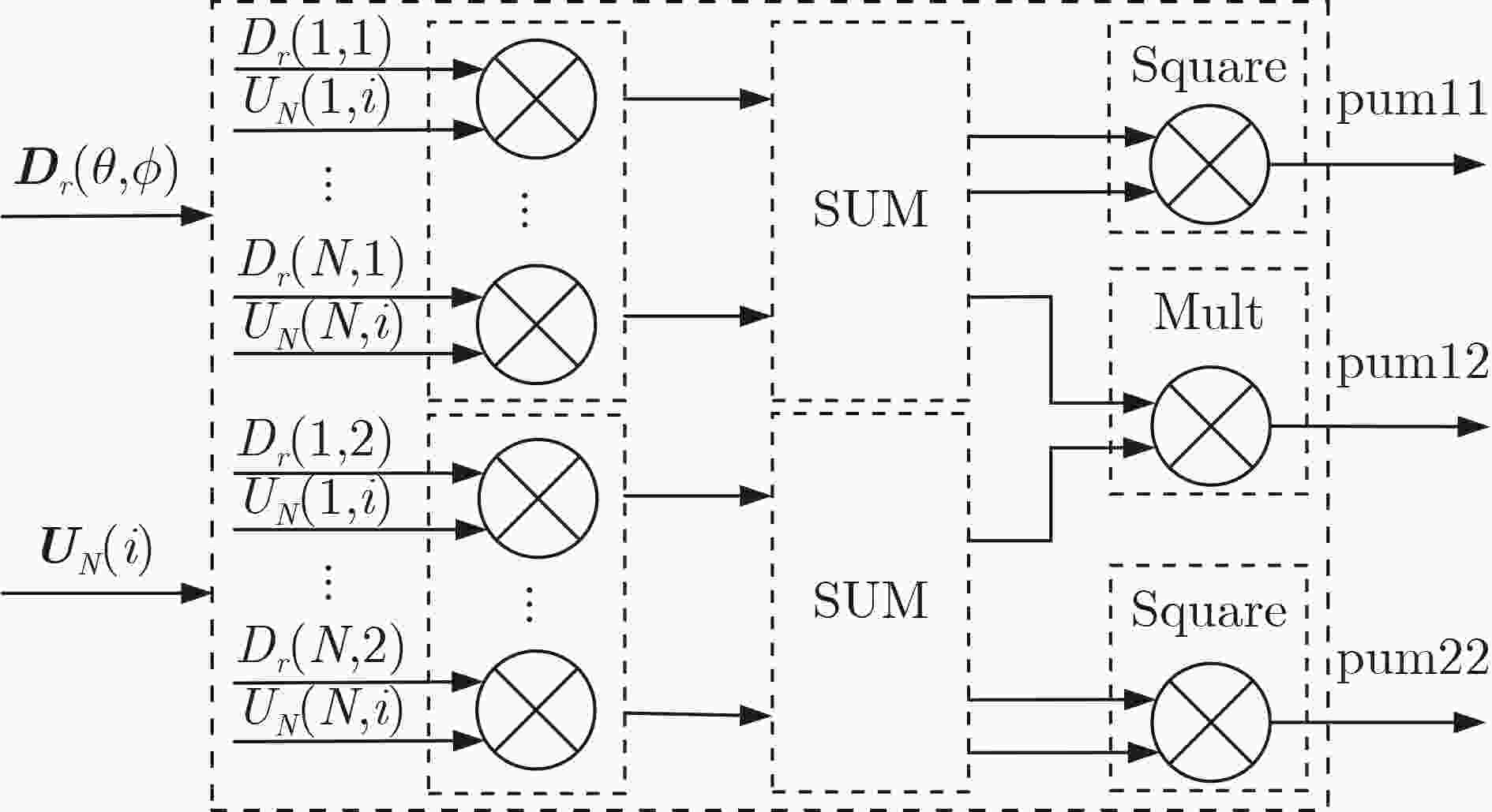
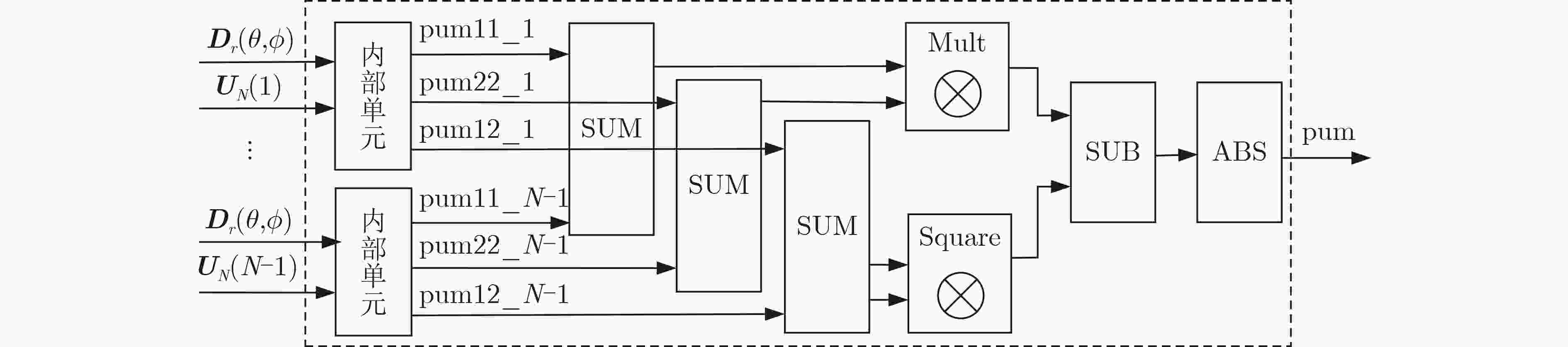
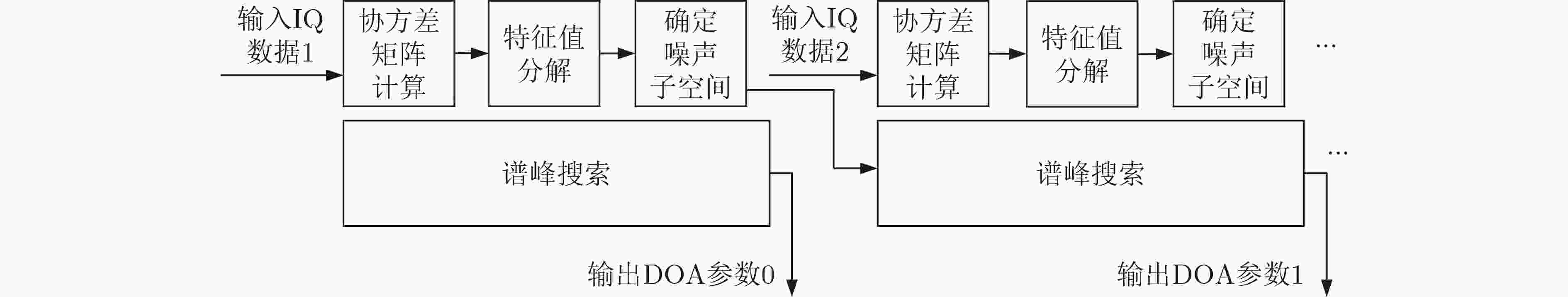
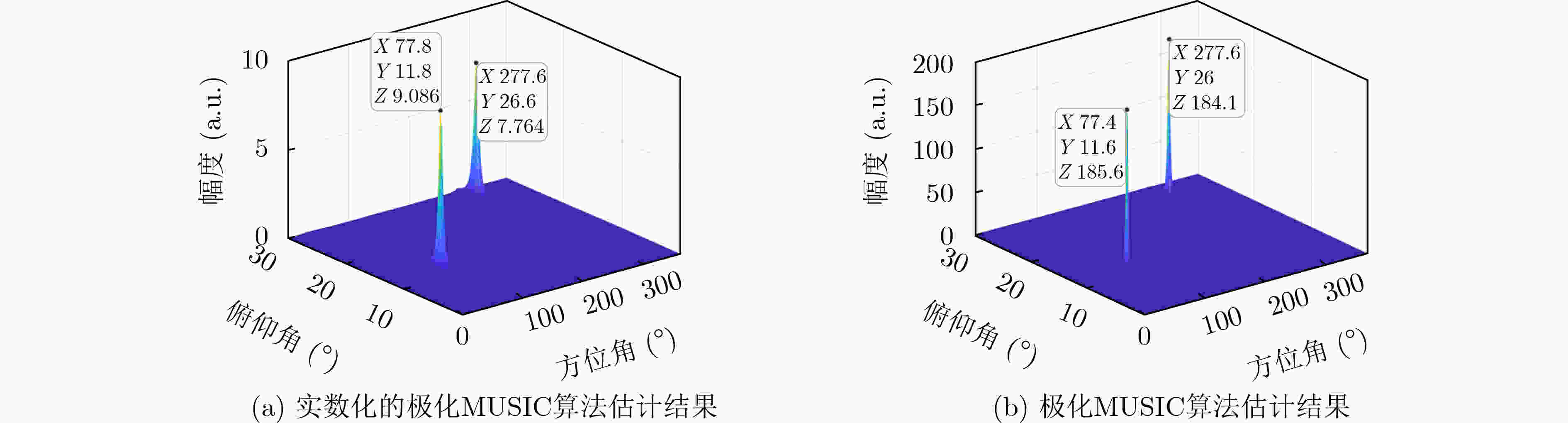
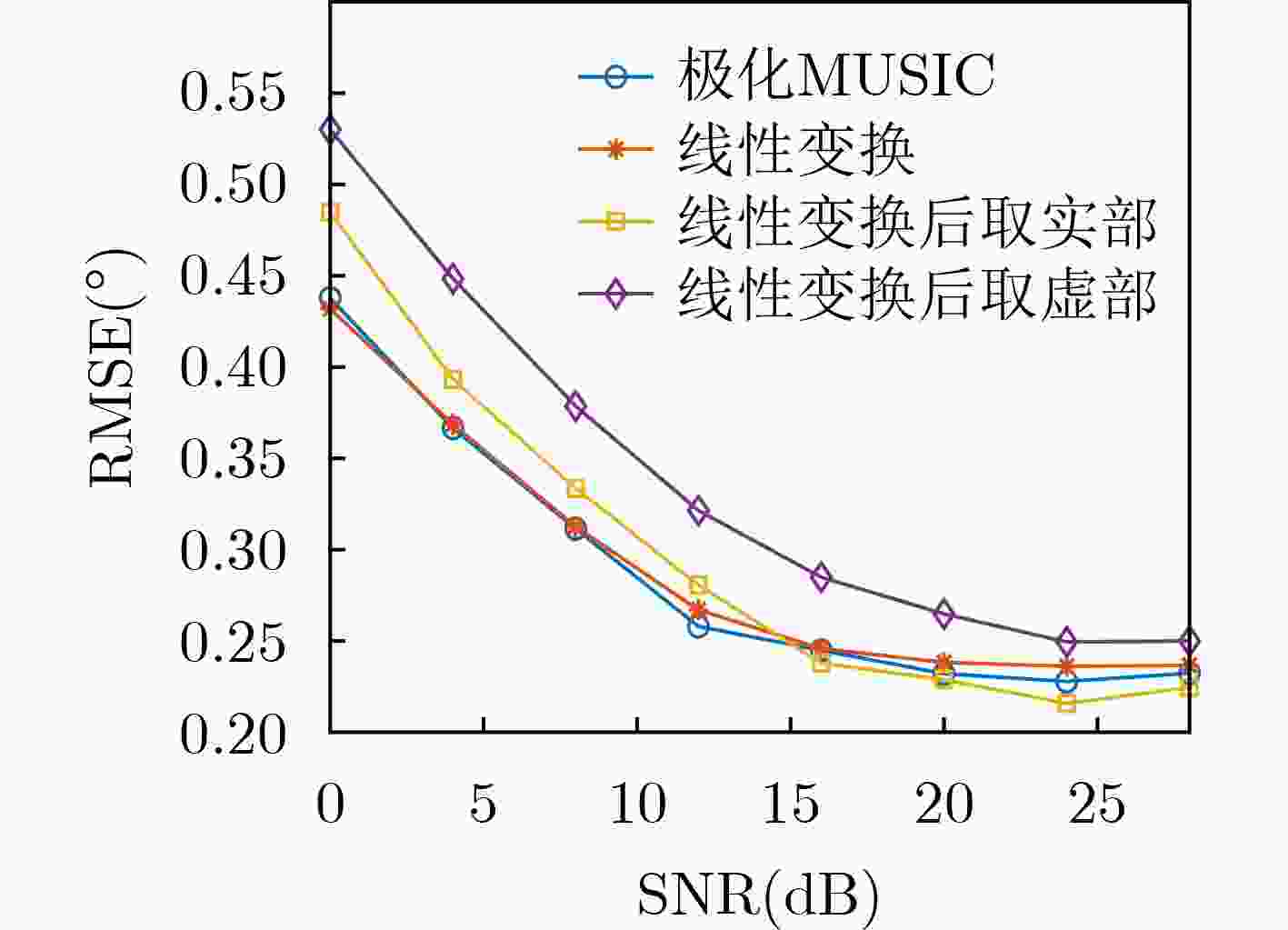
摘要: 针对将传统的复数多重信号分类(MUSIC)算法直接嵌入现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)将消耗大量硬件资源和计算时间的问题,该文提出基于极化敏感阵列的实数化的MUSIC算法的FPGA实现方案。利用圆形分布极化敏感阵列的中心对称特性,提出一种实数化预处理方法,该方法直接对接收信号做线性变换,从而简化极化MUSIC算法的后续计算。该FPGA方案通过协方差矩阵模块并行计算、特征值分解模块采用多级清扫的并行Jacobi算法、多尺度谱峰搜索和各个模块的流水线工作来减少算法耗时。试验结果表明,与复数极化MUSIC算法相比,该方案大大降低了硬件资源消耗和时间消耗。Abstract: To solve the problem that embedding the traditional complex MUlti SIgnal Classification (MUSIC) algorithm directly into the Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) will consume a lot of hardware resources and computing time, a FPGA implementation scheme of real MUSIC based on polarization sensitive array is proposed. A real value preprocessing method is proposed based on the centrosymmetric property of circular distributed polarization sensitive array. The proposed approach introduces linear transformation on the received signal, thus simplifying the subsequent calculation of polarization MUSIC algorithm. The FPGA scheme reduces the time consumption of the algorithm through the parallel calculation of the covariance matrix module, the parallel Jacobi algorithm of multi-level sweeping in the eigenvalue decomposition module, the multi-scale spectral peak search and the pipeline work of each module. The experimental results show that compared with complex polarization MUSIC, this scheme reduces greatly the hardware resource consumption and time consumption.
-
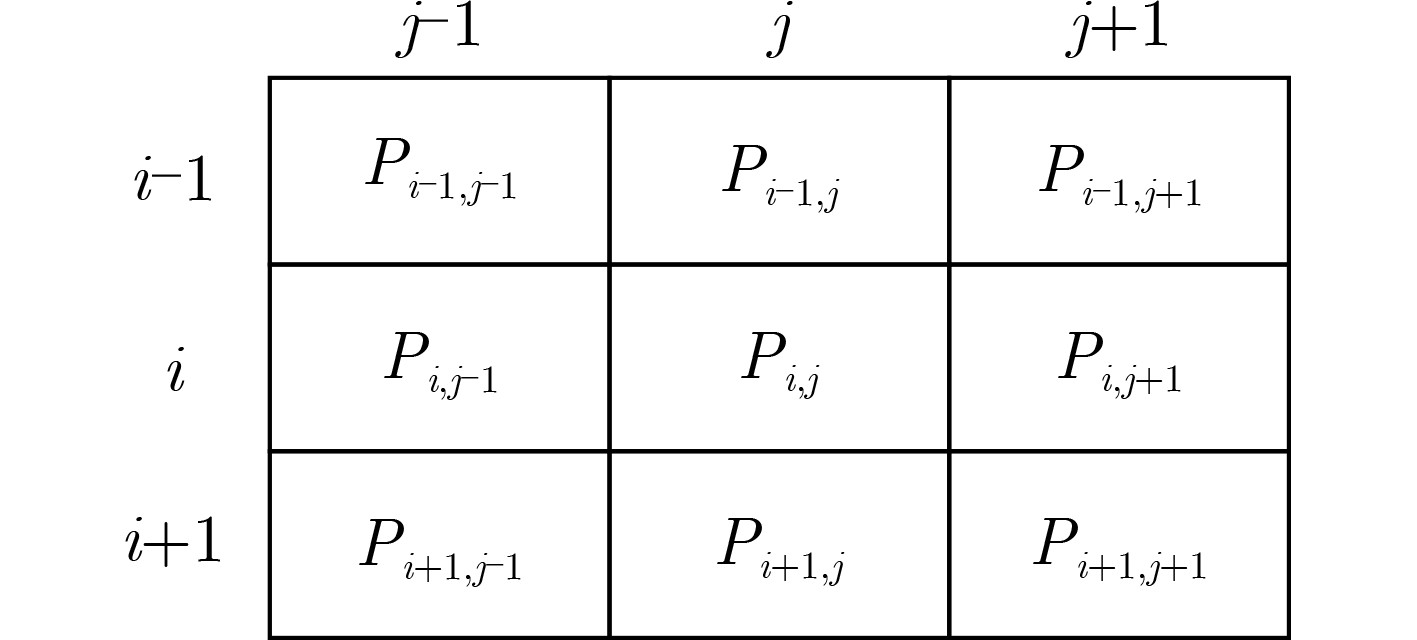
表 1 10×10矩阵的并行Jacobi分组
序号 分组 S1 {(1,2)(3,4)(5,6)(7,8)(9,10)} S2 {(1,4)(2,6)(3,8)(5,10)(7,9)} S3 {(1,6)(4,8)(2,10)(3,9)(5,7)} S4 {(1,8)(6,10)(4,9)(2,7)(3,5)} S5 {(1,10)(8,9)(6,7)(4,5)(2,3)} S6 {(1,9)(10,7)(8,5)(6,3)(4,2)} S7 {(1,7)(9,5)(10,3)(8,2)(6,4)} S8 {(1,5)(7,3)(9,2)(10,4)(8,6)} S9 {(1,3)(5,2)(7,4)(9,6)(10,8)} 表 2 资源占用情况
资源 可利用 实数化的极化MUSIC算法 极化MUSIC算法 占用 占比(%) 占用 占比(%) LUT 433 200 84 658 19.54 268 978 62.09 查找表随机存取存储器(LookUp Table Random Access Memory, LUTRAM) 174 200 439 0.25 346 0.20 FF 866 400 95 185 10.99 214 345 24.74 块随机存取存储器(Block Random Access Memory, BRAM) 1 470 7 0.48 6 0.41 DSP 3 600 1 311 36.42 2 979 82.75 表 3 各模块消耗时间
模块 实数化的极化MUSIC算法 极化MUSIC算法 消耗周期(个) 消耗时间(μs) 消耗周期(个) 消耗时间(μs) 协方差矩阵计算模块 105 1.05 105 1.05 特征值分解模块 1 769 17.69 2 939 29.39 确定噪声子空间模块 17 0.17 23 0.23 谱峰搜索模块 3 460 34.60 3 472 34.72 总计 5 396 53.96 6 539 65.39 -
[1] 王琦森, 余华, 李杰, 等. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的空间紧邻信号DOA估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 708–716. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200656WANG Qisen, YU Hua, LI Jie, et al. Sparse Bayesian learning based algorithm for DOA estimation of closely spaced signals[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 708–716. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200656 [2] ZHENG Hang, SHI Zhiguo, ZHOU Chengwei, et al. Coupled coarray tensor CPD for DOA estimation with coprime L-shaped array[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1545–1549. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3099074 [3] 马健钧, 魏少鹏, 马晖, 等. 基于ADMM的低仰角目标二维DOA估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2859–2866. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210582MA Jianjun, WEI Shaopeng, MA Hui, et al. Two-dimensional DOA estimation for low-angle target based on ADMM[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2859–2866. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210582 [4] 王炜彤, 杨健, 郭晓冉, 等. 基于压缩感知的正交偶极子阵列信号参数估计[J]. 中国舰船研究, 2022, 17(1): 221–226,234. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02262WANG Weitong, YANG Jian, GUO Xiaoran, et al. Joint estimation for DOA and polarization parameters of orthogonal dipole array based on compressive sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2022, 17(1): 221–226,234. doi: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.02262 [5] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830 [6] 庄钊文. 极化敏感阵列信号处理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2005: 200–213.ZHUANG Zhaowen. Signal Processing of Polarization Sensitive Array[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2005: 200–213. [7] 徐友根, 刘志文, 龚晓峰. 极化敏感阵列信号处理[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2013: 2–3.XU Yougen, LIU Zhiwen, and GONG Xiaofeng. Signal Processing of Polarization Sensitive Array[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology Press, 2013: 2–3. [8] BUTT U M, KHAN S A, ULLAH A, et al. Towards low latency and resource-efficient FPGA implementations of the MUSIC algorithm for direction of arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2021, 68(8): 3351–3362. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2021.3083280 [9] HUANG Kai, SHA Jin, SHI Wei, et al. An efficient FPGA implementation for 2-D MUSIC algorithm[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2016, 35(5): 1795–1805. doi: 10.1007/s00034-015-0144-z [10] XU Dechen, LIU Zhiwen, QI Xiaodong, et al. A FPGA-based implementation of MUSIC for centrosymmetric circular array[C]. 2008 9th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 2008: 490–493. [11] SHI Zhiguo, HE Qianwen, and LIU Ying. Accelerating parallel Jacobi method for matrix eigenvalue computation in DOA estimation algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(6): 6275–6285. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2984705 [12] HUSSAIN A A, TAYEM N, and SOLIMAN A H. Matrix decomposition methods for efficient hardware implementation of DOA estimation algorithms: A performance comparison[C]. 2019 4th International Conference and Workshops on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering (ICRAIE), Kedah, Malaysia, 2019: 1–7. [13] 王永良. 空间谱估计理论与算法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004: 83–85.WANG Yongliang. Theory and Algorithm of Spatial Spectrum Estimation[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004: 83–85. [14] 蒋驰, 王文晴, 张晓丽, 等. 基于空间域补偿的极化敏感阵列MUSIC测向算法[J]. 制导与引信, 2021, 42(4): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0576.2021.04.001JIANG Chi, WANG Wenqing, ZHANG Xiaoli, et al. MUSIC direction finding algorithm of polarization sensitive array based on spatial domain compensation[J]. Guidance &Fuze, 2021, 42(4): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0576.2021.04.001 [15] SHI Haoqiang, JIANG Zhanjun, LIU Qianru, et al. An efficient FPGA parallel implementation for 2-D MUSIC algorithm[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 252(3): 032168. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/252/3/032168 [16] BRENT R P, LUK F T, and VAN LOAN C. Computation of the generalized singular value decomposition using mesh-connected processors[C]. The 27th Annual Technical Symposium on Real-Time Signal Processing VI, San Diego, USA, 1983: 66–71. -






 下载:
下载:
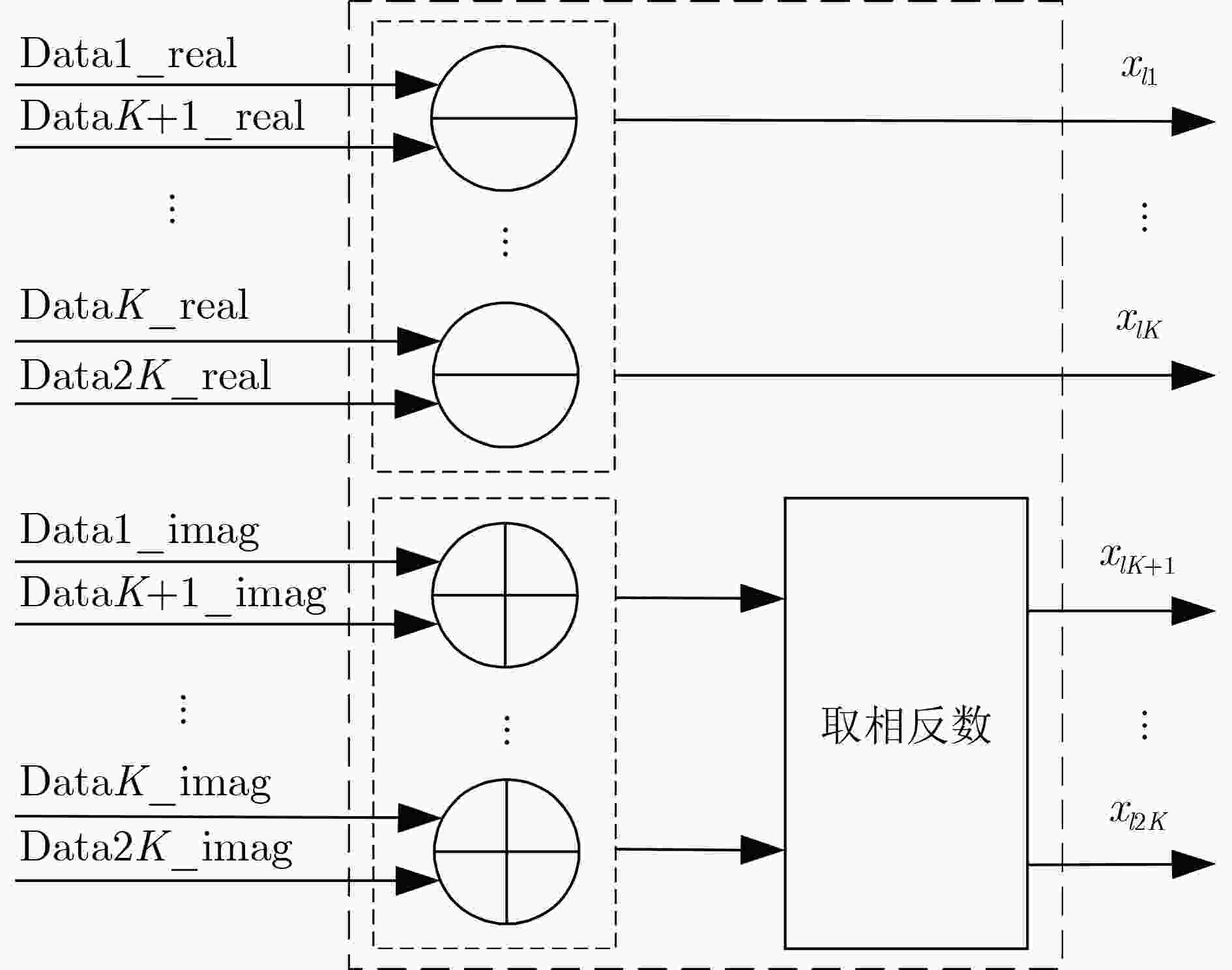
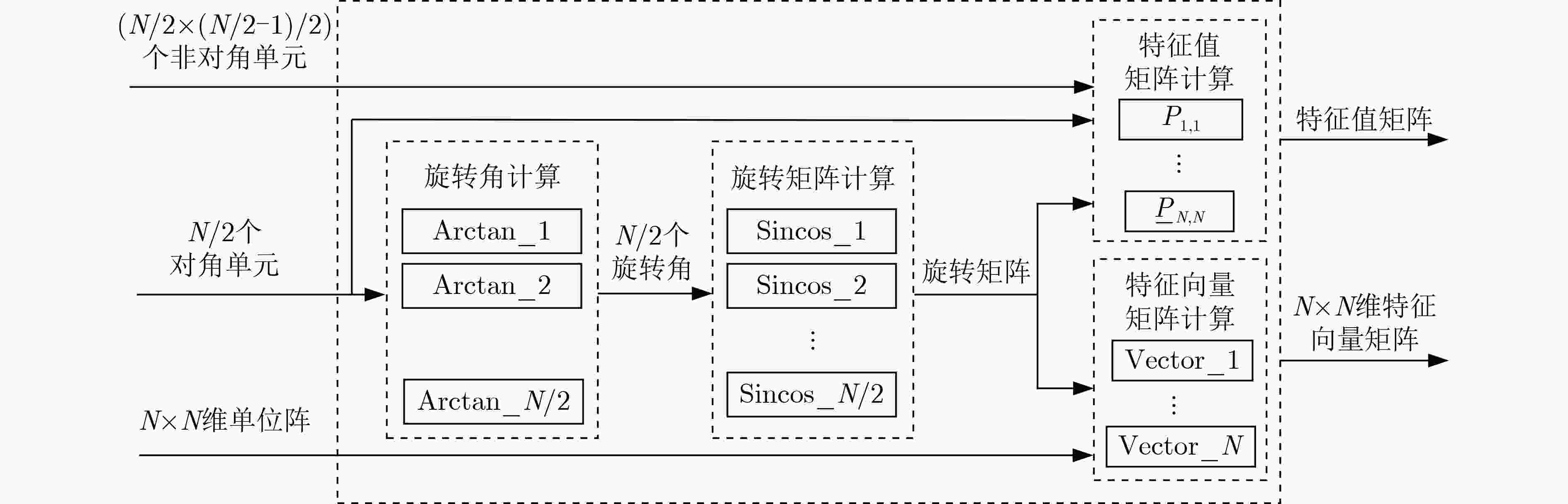
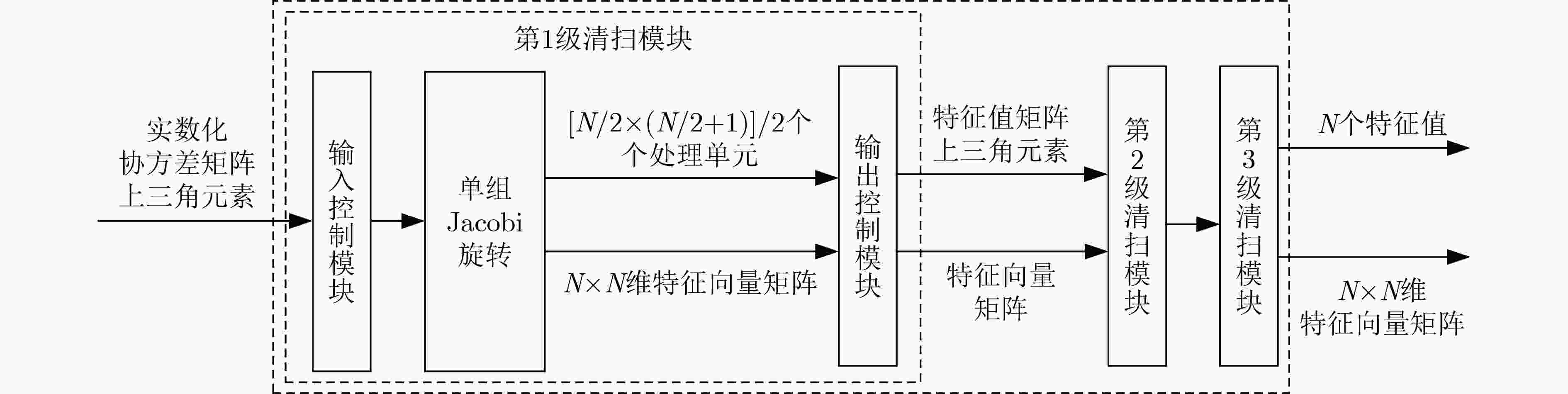
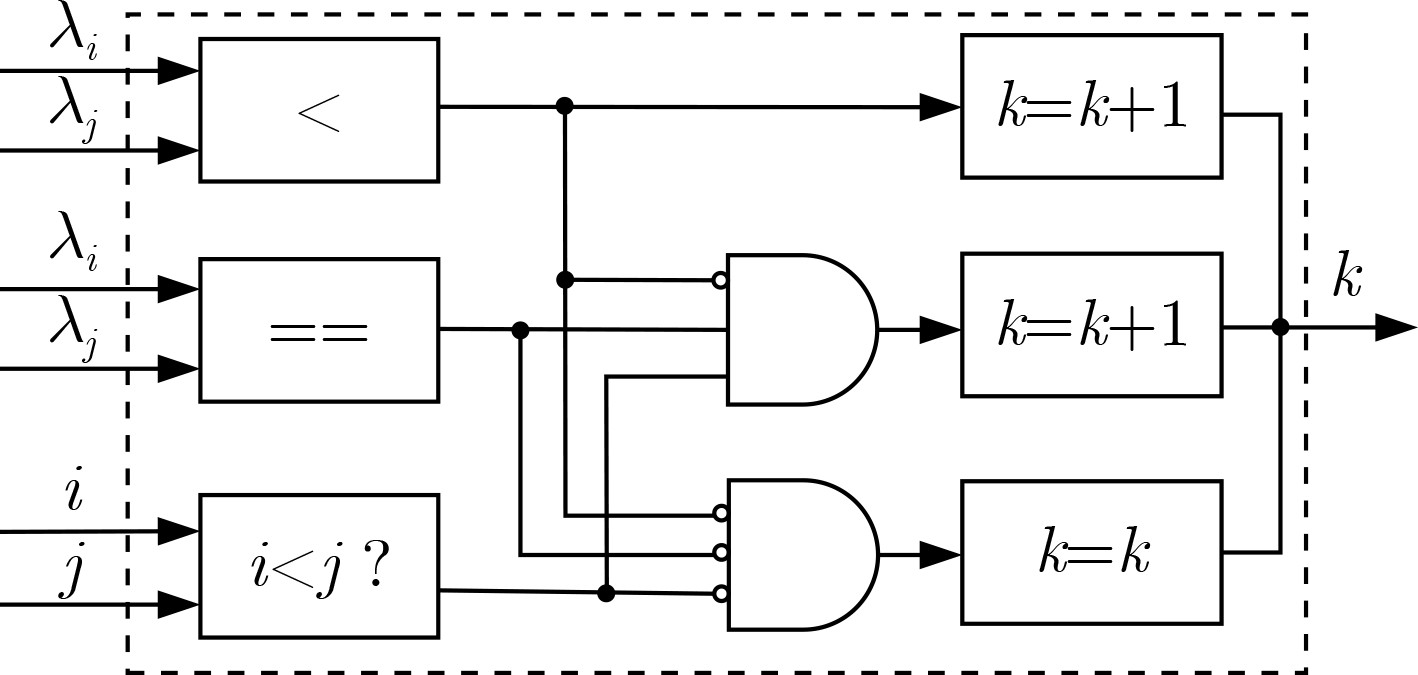


 下载:
下载:
