Deadlock Avoidance of Advanced eXtensible Interface Interconnection Networks in Modular System-on-Chips
-
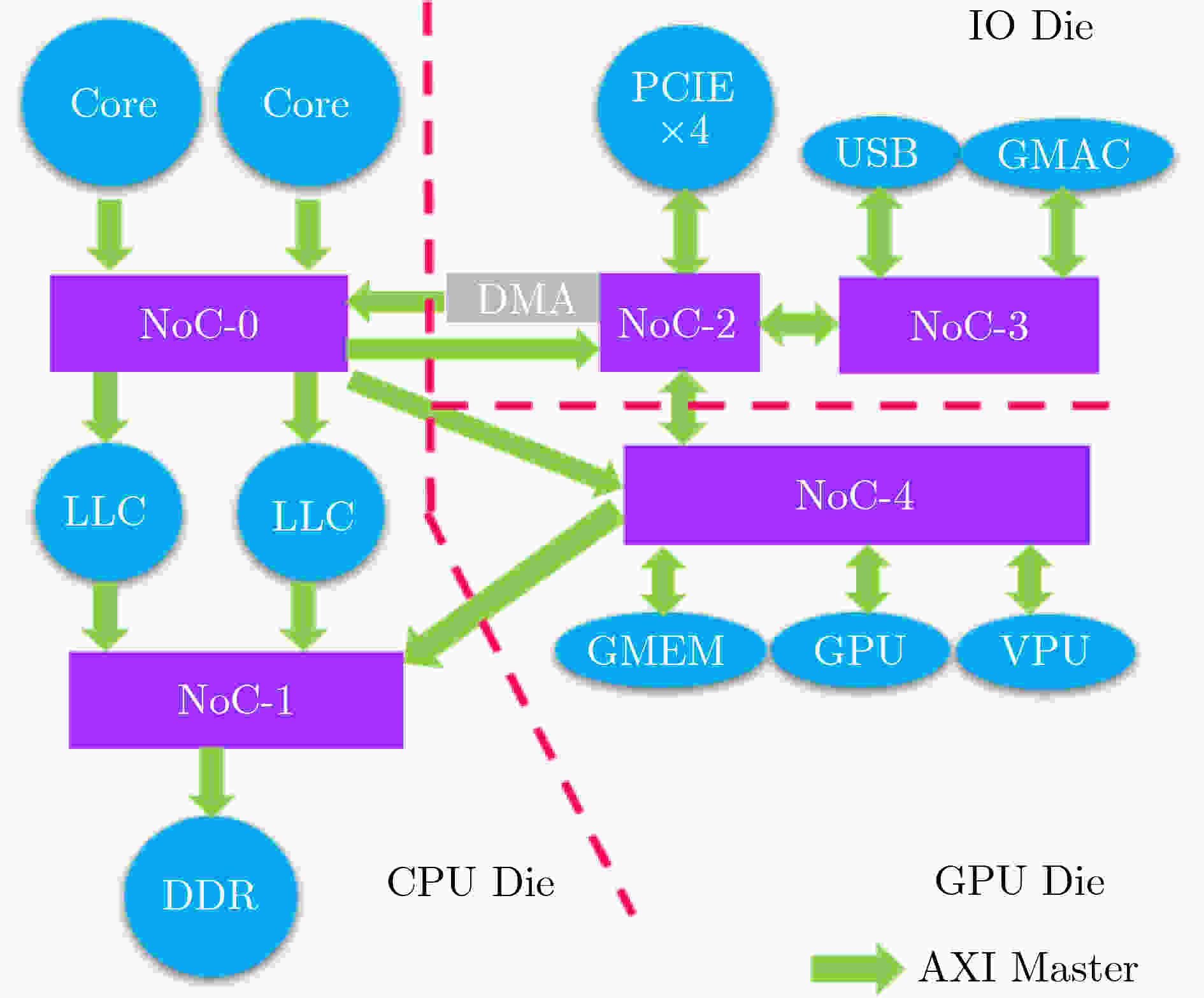
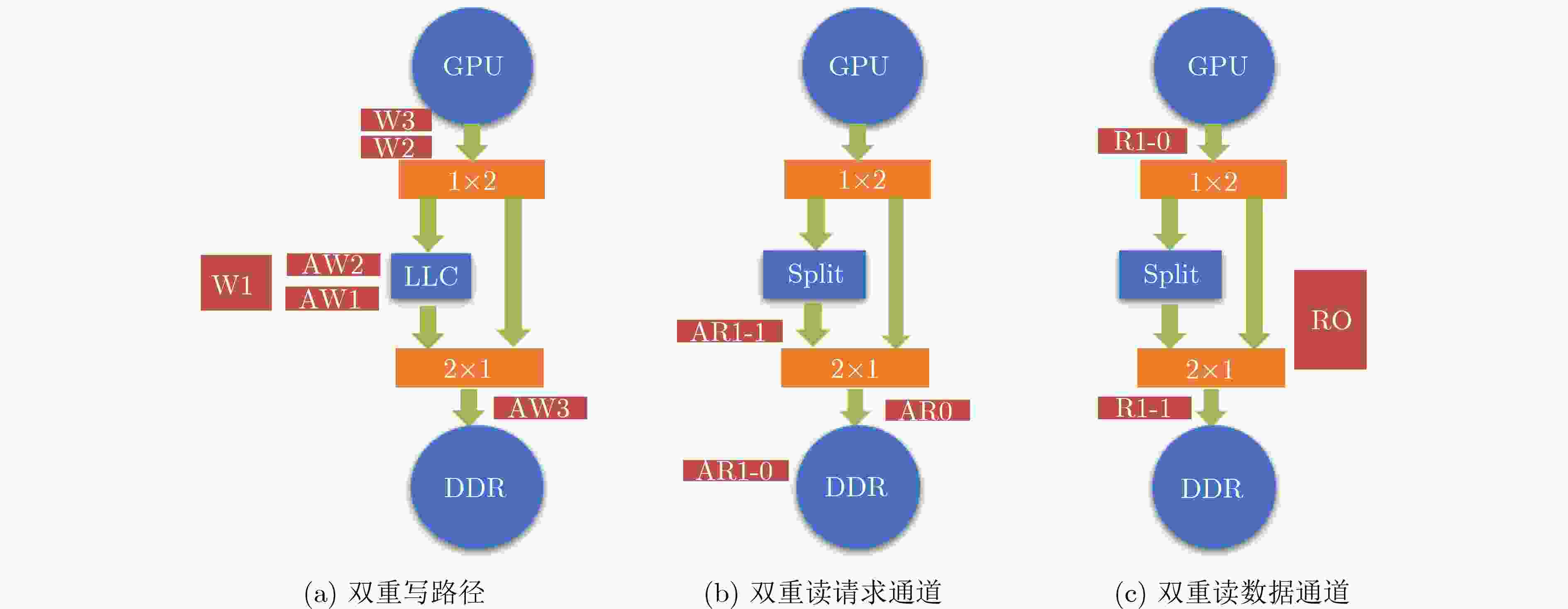
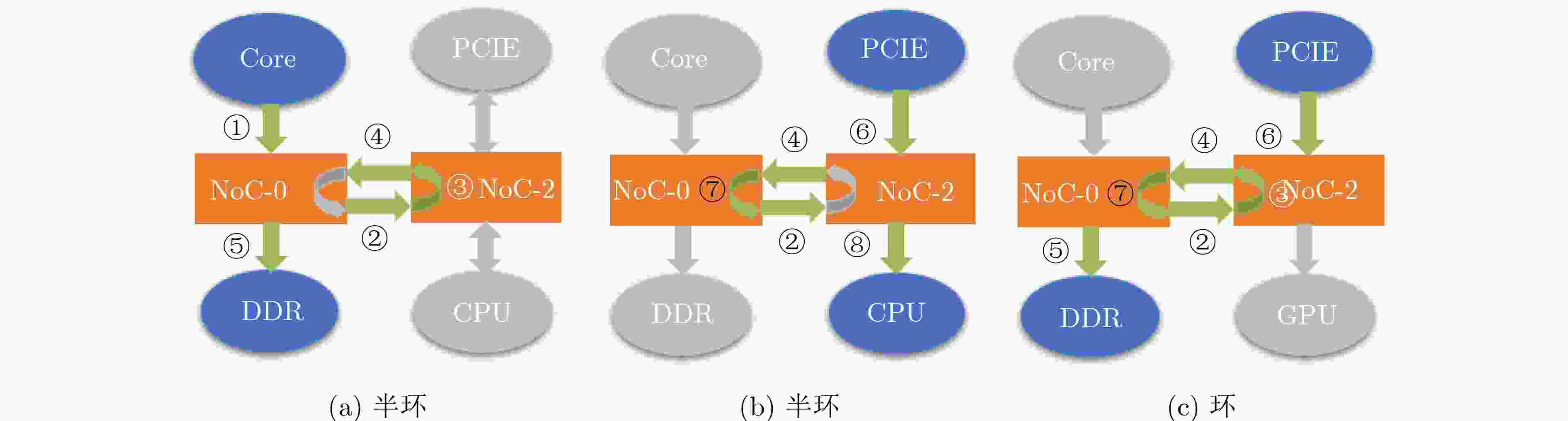
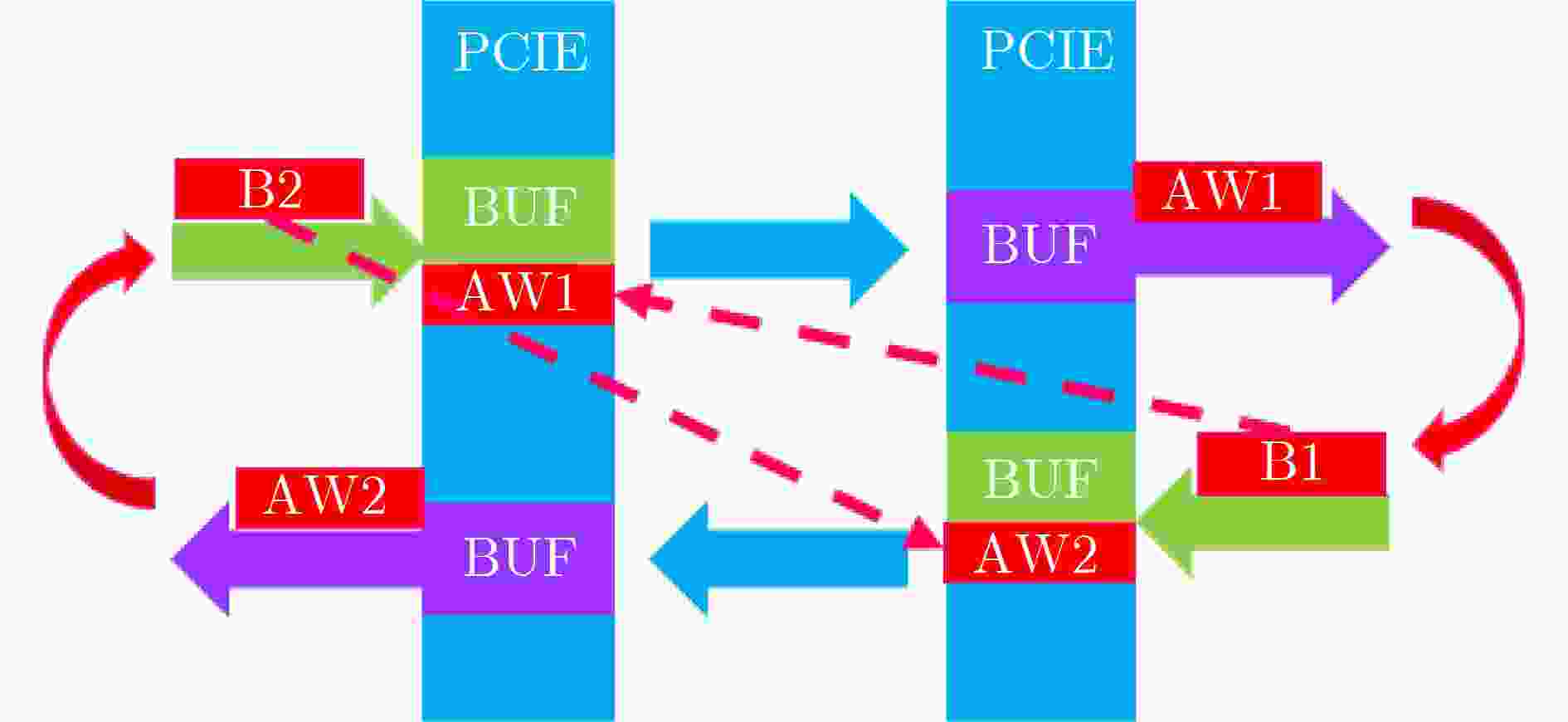
摘要: 模块化片上系统(MSoC)包含多个独立的IP组件及多个可能的子网络,这种异构集成的方式往往为片上网络(NoC)引入潜在的死锁。该文基于模块化异构系统MSoC研究了使用高级可扩展接口(AXI)协议的片上网络中3种类型的死锁。MSoC包含多种常见的异构组件,以及由多个独立子网络集成的片上网络,能够充分反映真实芯片的复杂性和不规则性。该文发现除环形通道导致的死锁外,基于AXI的片上网络还涉及双重路径死锁和桥接死锁。该文还提出一种两阶段算法检测片上网络中可能存在的这3种死锁。相比于通用验证方法学(UVM)随机验证,使用该算法可以将检测时长从几个月缩短到几个小时,提高片上网络的可靠性和鲁棒性。Abstract: Modular System-on-Chips (MSoC) contain several distinct IP components with possibly multiple sub-networks, resulting in potential deadlock situations for the Network on Chip (NoC). A MSoC is developed, and three deadlock cases in Advanced eXtensible Interface (AXI)-based network-on-chip are studied. MSoC consists of various common heterogeneous components, and NoC integrated by multiple independent subnetworks. MSoC can fully reflect the complexity and irregularity of real chips. NoC based on AXI is found toface double-path deadlock and bridge deadlock in addition to loop-path deadlock. A two-stage algorithm is proposed to detect those three cases. Compared to Universal Verification Methodology(UVM) random verification, this method can reduce detection time from months to hours, improving the reliability and robustness of the on-chip network.
-
表 1 近年发布的多款处理器芯片的IP组件情况
表 2 死锁避免机制比较
算法1 FTLR算法 输入:拓扑结构图G,路由规则集F。 输出:潜在死锁依赖P。 变量:中间结果集合M。 步骤1 读入G,检测G中是否存在环。如果存在,则将其加入到M中。 步骤2 遍历G中所有Master到Slave的数据通路,加入到M中,并标识拆包模块和桥接模块。 步骤3 遍历F中所有Master到Slave的路由通路,如果与M中某一数据通路组合满足死锁发生条件,则输出该路径。 表 3 互连网络死锁检测方法对比
方法 双重通道死锁 环形通道死锁 桥接死锁 检测效率 建模难度 检测时间 CDG × √ × 并行 困难 几天 UVM √ √ √ 串行 一般 几周 FTLR √ √ √ 并行 简单 几小时 -
[1] NAFFZIGER S, BECK N, BURD T, et al. Pioneering chiplet technology and design for the AMD EPYC™ and Ryzen™ processor families: Industrial product[C]. 2021 ACM/IEEE 48th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Valencia, Spain, 2021: 57–70. [2] BECK N, WHITE S, PARASCHOU M, et al. ‘Zeppelin’: An SoC for multichip architectures[C]. 2018 IEEE International Solid - State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2018: 40–42. [3] ARUNKUMAR A, BOLOTIN E, CHO B, et al. MCM-GPU: Multi-chip-module GPUs for continued performance scalability[C]. The 44th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Toronto, Canada, 2017: 320–332. [4] VIJAYARAGHAVAN T, ECKERT Y, LOH G H, et al. Design and analysis of an APU for exascale computing[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Austin, USA, 2017: 85–96. [5] MA Xiaohan, WANG Ying, WANG Yujie, et al. Survey on chiplets: Interface, interconnect and integration methodology[J]. CCF Transactions on High Performance Computing, 2022, 4(1): 43–52. doi: 10.1007/s42514-022-00093-0 [6] WANG Mengdi, WANG Ying, LIU Cheng, et al. Network-on-interposer design for agile neural-network processor chip customization[C]. 2021 58th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, USA, 2021: 49–54. [7] FENG Yinxiao and MA Kaisheng. Chiplet actuary: A quantitative cost model and multi-chiplet architecture exploration[C]. The 59th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2022: 121–126. [8] TALPES E, SARMA D D, VENKATARAMANAN G, et al. Compute solution for Tesla's full self-driving computer[J]. IEEE Micro, 2020, 40(2): 25–35. doi: 10.1109/MM.2020.2975764 [9] [EB/OL].https://www.anandtech.com/show/17019/apple-announced-m1-pro-m1-max-giant-new-socs-with-allout-performance. [10] STILES D. The hardware security behind azure sphere[J]. IEEE Micro, 2019, 39(2): 20–28. doi: 10.1109/MM.2019.2898633 [11] BISWAS A. Sapphire rapids[C]. 2021 IEEE Hot Chips 33 Symposium (HCS), Palo Alto, USA, 2021: 1–22. [12] ROTEM E, MANDELBLAT Y, BASIN V, et al. Alder lake architecture[C]. 2021 IEEE Hot Chips 33 Symposium (HCS), Palo Alto, USA, 2021: 1–23. [13] JACOBI C. Real-time AI for enterprise workloads: The IBM Telum processor[C]. 2021 IEEE Hot Chips 33 Symposium (HCS), Palo Alto, USA, 2021: 1–22. [14] ZHENG Hao, WANG Ke, and LOURI A. Adapt-NoC: A flexible network-on-chip design for heterogeneous manycore architectures[C]. 2021 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Seoul, Korea, 2021: 723–735. [15] MAJUMDER P, KIM S, HUANG J, et al. Remote control: A simple deadlock avoidance scheme for modular systems-on-chip[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2021, 70(11): 1928–1941. doi: 10.1109/TC.2020.3029682 [16] DALLY W J and TOWLES B. Principles and Practices of Interconnection Networks[M]. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2004. [17] EBRAHIMI M and DANESHTALAB M. EbDa: A new theory on design and verification of deadlock-free interconnection networks[C]. The 44th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Toronto, Canada, 2017: 703–715. [18] LI Ming, ZENG Qing’an, and JONE W B. DyXY: A proximity congestion-aware deadlock-free dynamic routing method for network on chip[C]. The 43rd Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2006: 849–852. [19] FU Binzhang, HAN Yinhe, MA Jun, et al. An abacus turn model for time/space-efficient reconfigurable routing[C]. The 38th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, San Jose, USA, 2011: 259–270. [20] SAMIH A, WANG Ren, KRISHNA A, et al. Energy-efficient interconnect via router parking[C]. 2013 IEEE 19th International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Shenzhen, China, 2013: 508–519. [21] WANG Ling, WANG Yadong, and WANG Xiaohang. An approximate multiplane network-on-chip[C]. 2020 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 2020: 234–239. [22] RAMRAKHYANI A and KRISHNA T. Static bubble: A framework for deadlock-free irregular on-chip topologies[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Austin, USA, 2017: 253–264. [23] XIA Jing, CHENG Chuanning, ZHOU Xiping, et al. Kunpeng 920: The first 7-nm chiplet-based 64-core ARM SoC for cloud services[J]. IEEE Micro, 2021, 41(5): 67–75. doi: 10.1109/MM.2021.3085578 [24] DUBOIS F, SHEIBANYRAD A, PÉTROT F, et al. Elevator-first: A deadlock-free distributed routing algorithm for vertically partially connected 3D-NoCs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2013, 62(3): 609–615. doi: 10.1109/TC.2011.239 [25] WANG Tianqi, FENG Fan, XIANG Shaolin, et al. Application defined on-chip networks for heterogeneous chiplets: An implementation perspective[C]. 2022 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Seoul, Korea, 2022: 1198–1210. [26] HU Xing, STOW D, and XIE Yuan. Die stacking is happening[J]. IEEE Micro, 2018, 38(1): 22–28. doi: 10.1109/MM.2018.011441561 [27] LANKES A, WILD T, HERKERSDORF A, et al. Comparison of deadlock recovery and avoidance mechanisms to approach message dependent deadlocks in on-chip networks[C]. 2010 Fourth ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Networks-on-Chip, Grenoble, France, 2010: 17–24. [28] ANJAN K V and PINKSTON T M. An efficient, fully adaptive deadlock recovery scheme: DISHA[C]. The 22nd Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Santa Margherita Ligure, Italy, 1995: 201–210. [29] RAMRAKHYANI A, GRATZ P V, and KRISHNA T. Synchronized progress in interconnection networks (SPIN): A new theory for deadlock freedom[C]. 2018 ACM/IEEE 45th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Los Angeles, USA, 2018: 699–711. [30] PARASAR M, FARROKHBAKHT H, JERGER N E, et al. DRAIN: Deadlock removal for arbitrary irregular networks[C]. 2020 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), San Diego, USA, 2020: 447–460. [31] PARASAR M, JERGER N E, GRATZ P V, et al. SWAP: Synchronized weaving of adjacent packets for network deadlock resolution[C]. The 52nd Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Columbus, USA, 2019: 873–885. [32] JERGER N E, KRISHNA T, and PEH L S. On-Chip Networks[M]. 2nd ed. Cham: Springer, 2017. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
