Lightweight Integrity Verification Scheme for Outsourced Medical Data in Cloud Storage Supporting Conditional Identity Anonymity
-
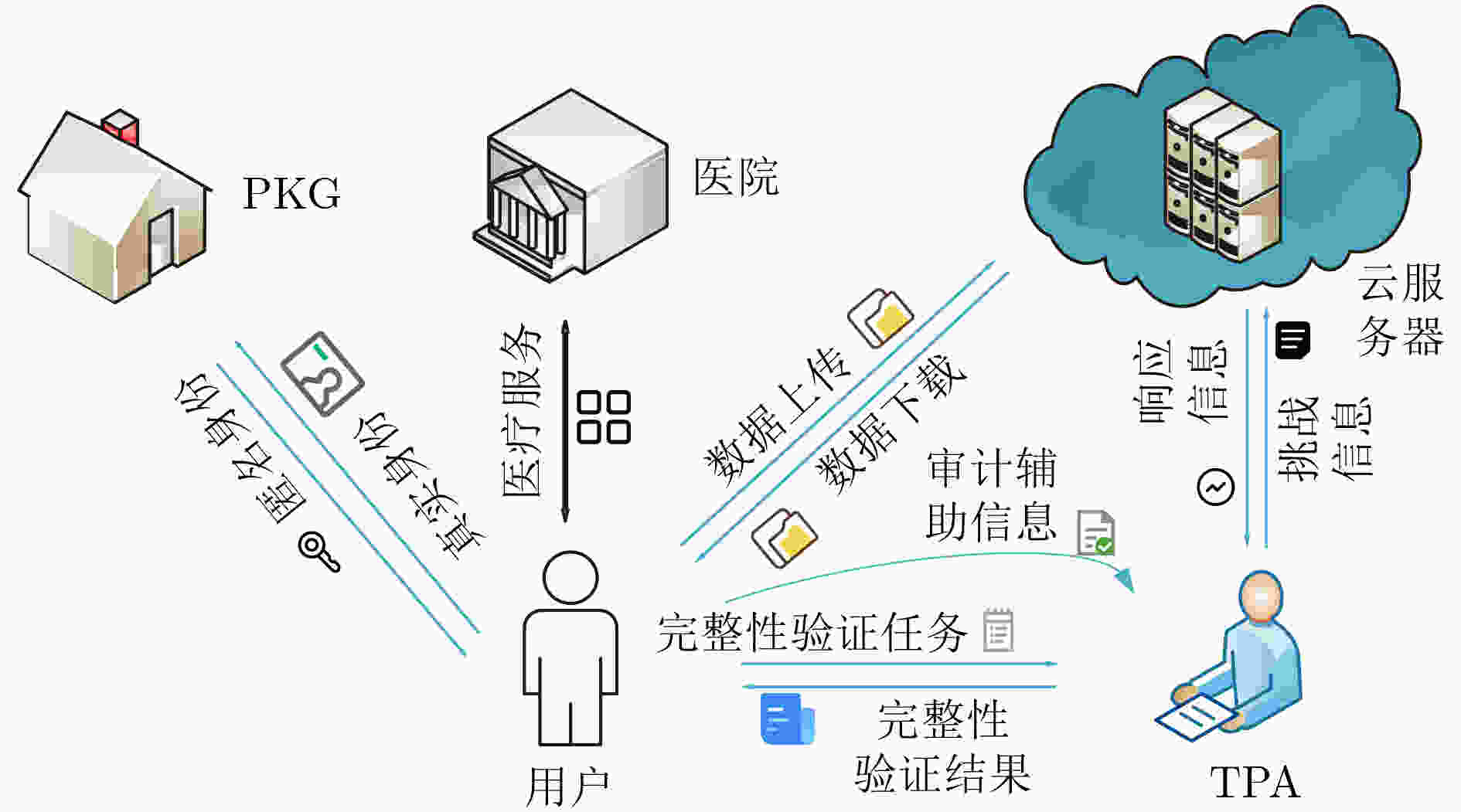
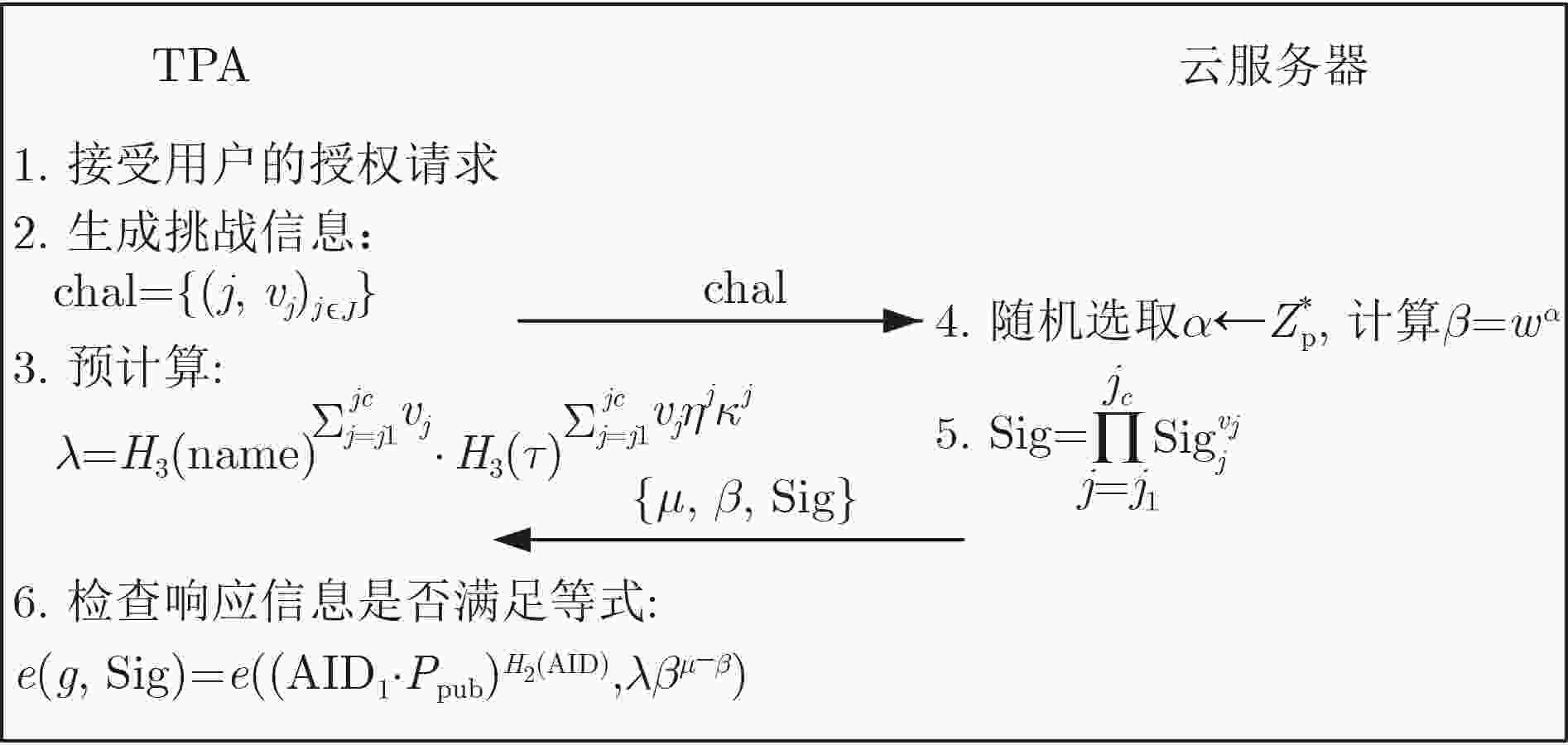
摘要: 医疗云存储服务是云计算技术的一个重要应用,同时外包医疗数据的完整性和用户的身份隐私保护已变得越来越重要。该文提出适用于无线医疗传感器网络的支持条件身份匿名的外包云存储医疗数据轻量级完整性验证方案。方案结合同态哈希函数设计了聚合签名,通过第三方审计者(TPA)对外包云存储医疗数据进行完整性验证,在TPA端存放审计辅助信息,利用同态哈希函数的同态性质将TPA端的计算优化为常量运算,大大降低了第三方审计者的计算开销,同时支持TPA对多个数据文件执行批量验证,其验证开销几乎是恒定的,与医疗数据文件的数量无关。方案有效防止了第三方审计者通过求解线性方程恢复原始医疗数据,并且设计了条件身份匿名算法,密钥生成中心(PKG)根据用户唯一标识的身份信息为用户生成匿名身份及对应的签名私钥。即使攻击者截获到用户传输的医疗数据,也无法获知拥有此数据的真实身份,有效避免了对公钥证书的复杂管理,同时使得密钥生成中心可以有效追踪医疗信息系统中具有恶意行为的用户。安全性分析与性能评估结果表明该方案能够安全高效地部署在云辅助无线医疗传感器网络。Abstract: Medical cloud storage service is one of the most significant applications in cloud computing. Simultaneously, the integrity of outsourced medical data and users’ identity privacy-preservation have been more and more important. To this end, an outsourced cloud storage medical data lightweight integrity verification scheme is proposed for wireless medical sensor networks, supporting conditional identity anonymity. The scheme combines the homomorphic hash function to design an aggregated signature to enable a Third Party Auditor (TPA) to check the integrity of outsourced medical data effectively. The scheme stores auditing auxiliary information on TPA side and uses the homomorphic property of the homomorphic hash function to optimize the calculations on TPA side to a constant, which reduces greatly the computational costs of TPA. The scheme enables TPA to perform batch verification on multiple data files, and the verification costs are nearly constant, independent of the number of data files. In addition, this scheme prevents effectively TPA from recovering the original medical data by solving the linear equations, and a conditional identity anonymous algorithm is designed, thus the Private Key Generator (PKG) could generate the anonymous identity of a user and corresponding singing key. Even if the attacker intercepts the medical data transmitted by the user, it can not know the real identity of the data. In addition, the complex certificates management is efficiently avoided, and PKG could also trace and revoke the real identities of misbehaved users efficiently. The security analysis and performance evaluation demonstrate that this scheme could be securely and efficiently deployed in wireless medical sensor networks.
-
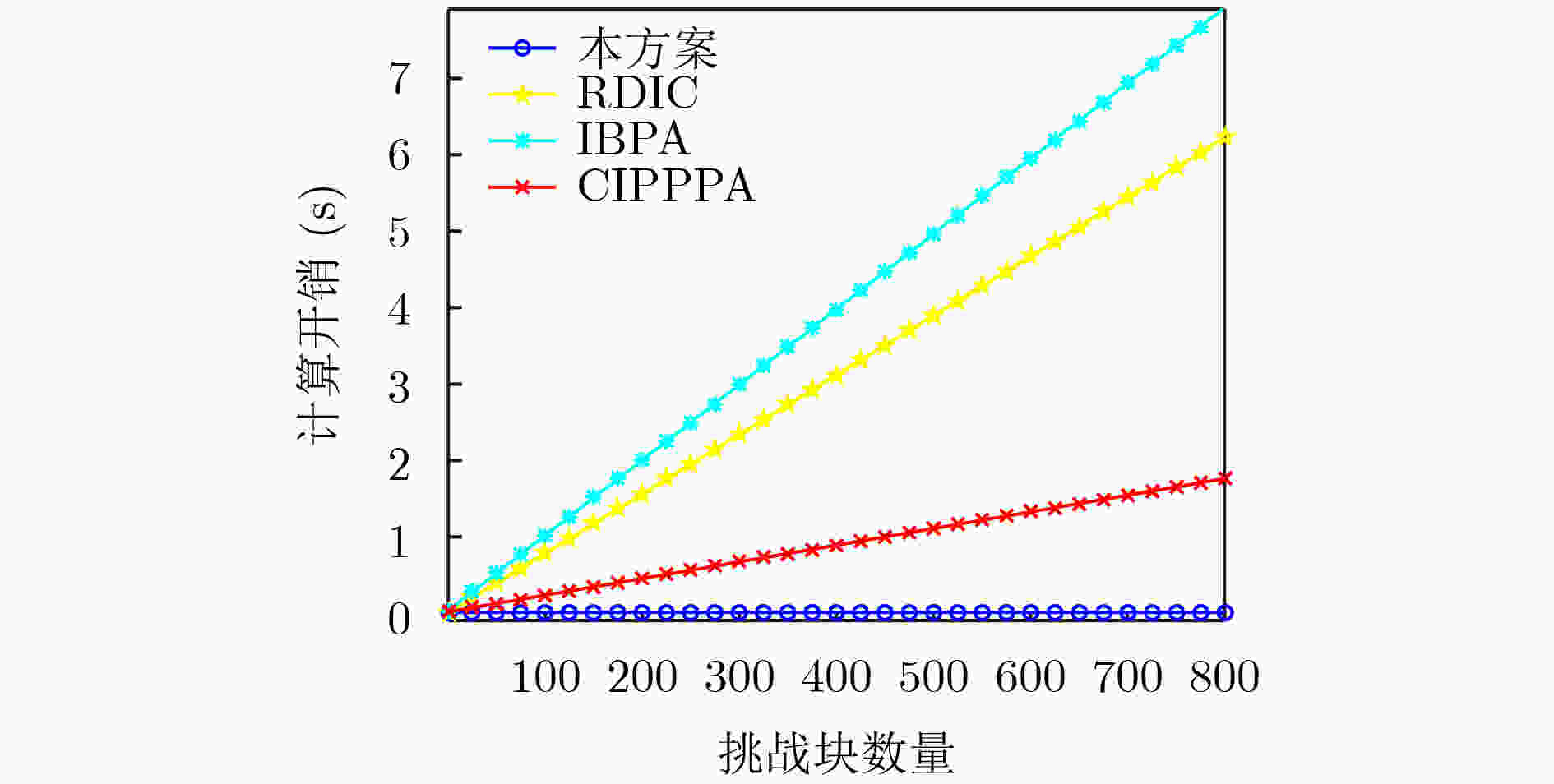
表 1 完整性验证计算开销比较
方案 完整性验证计算开销 RDIC $ (2c + 6) \cdot {\text{Exp}} + (c + 1) \cdot {\text{Pair + }}c \cdot {\text{mult}} $ IBPA $ \begin{aligned}& (2c + 4) \cdot {\text{Mult} } + 3{\text{Pair} } + (2c - 1) \cdot {\text{Add} } \\& \quad + (c{ { + 2} }) \cdot {\text{Ha} } + (c + 1) \cdot {\text{ha} } \end{aligned}$ CIPPPA $ (c + 2) \cdot {\text{Mult}} + 3{\text{Pair}} + (c - 1) \cdot {\text{Add}} + c \cdot {\text{Ha}} + {\text{ha}} $ 本文 $ 2{\text{Exp + }}2{\text{Pair}} + 2 \cdot {\text{mult}} + {\text{ha}} $ 表 2 完整性验证通信开销比较
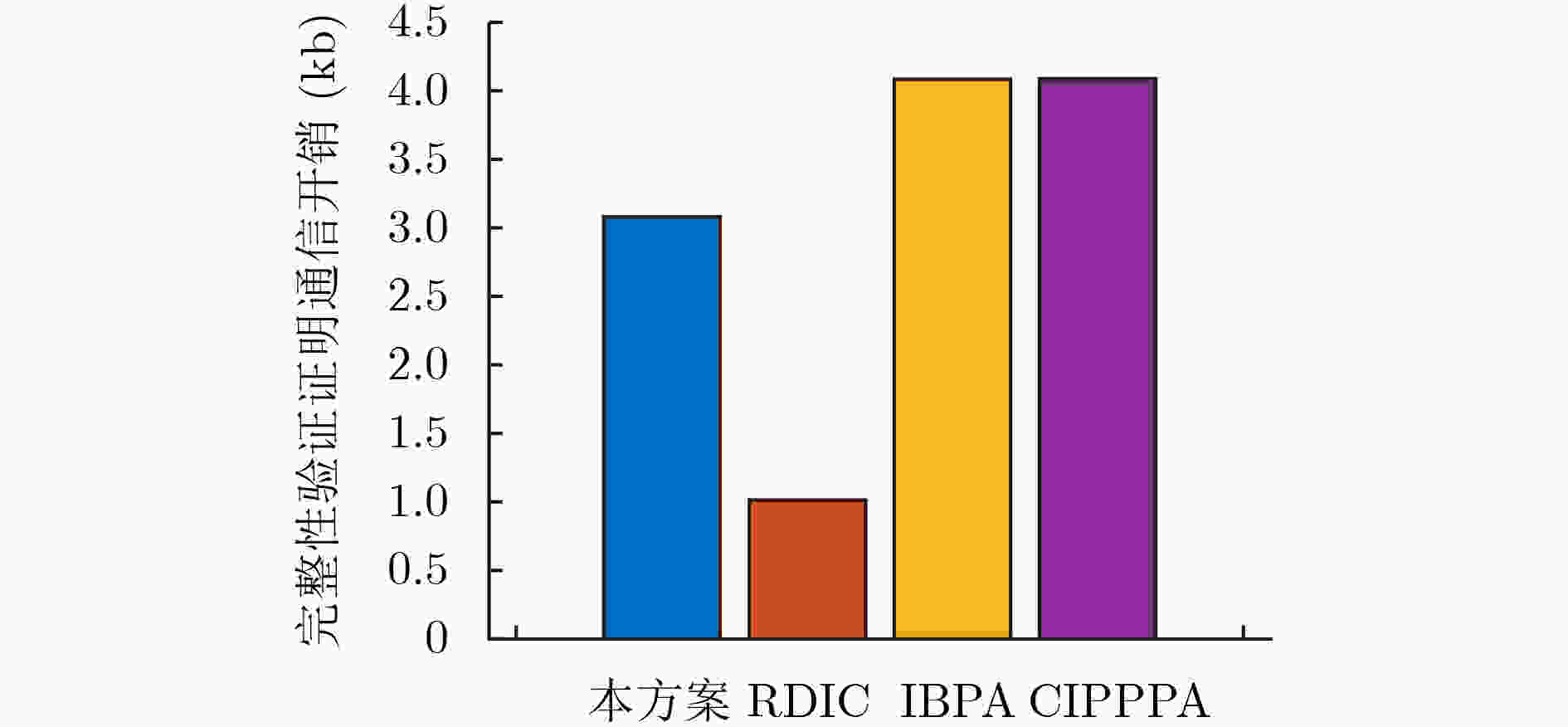
方案 挑战信息 完整性验证证明信息 RDIC $ c \cdot (|n| + |p|) + |{\text{pf}}| + 2|G| $ $ 3\left| G \right| $ IBPA $ c \cdot (|n| + |p|) $ $ 3\left| G \right| + \left| p \right| $ CIPPPA $ c \cdot (|n| + |p|) $ $ 3\left| G \right| + \left| p \right| $ 本文 $ c \cdot (|n| + |p|) $ $ 2|G| + \left| p \right| $ -
[1] BARATI M, AUJLA G S, LLANOS J T, et al. Privacy-aware cloud auditing for GDPR compliance verification in online healthcare[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(7): 4808–4819. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3100152 [2] NAYAK S K and TRIPATHY S. SEPDP: Secure and efficient privacy preserving provable data possession in cloud storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2021, 14(3): 876–888. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2018.2820713 [3] LI Hongzhi, HAN Dezhi, and TANG Mingdong. A privacy-preserving storage scheme for logistics data with assistance of blockchain[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(6): 4704–4720. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3107846 [4] SUBRAMANI J, MARIA A, RAJASEKARAN A S, et al. Lightweight privacy and confidentiality preserving anonymous authentication scheme for WBANs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(5): 3484–3491. doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3097759 [5] REN Kui, WANG Cong, and WANG Qian. Security challenges for the public cloud[J]. IEEE Internet Computing, 2012, 16(1): 69–73. doi: 10.1109/MIC.2012.14 [6] SUN Jinyuan, FANG Yuguang, and ZHU Xiaoyan. Privacy and emergency response in e-healthcare leveraging wireless body sensor networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2010, 17(1): 66–73. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2010.5416352 [7] ATENIESE G, BURNS R, CURTMOLA R, et al. Provable data possession at untrusted stores[C]. The 14th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Alexandria, USA, 2007: 598–609. [8] JUELS A and KALISKI B S. PORs: Proofs of retrievability for large files[C]. The 14th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Alexandria, USA, 2007: 584–597. [9] WANG Cong, CHOW S S M, WANG Qian, et al. Privacy-preserving public auditing for secure cloud storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2013, 62(2): 362–375. doi: 10.1109/TC.2011.245 [10] 马华, 党乾龙, 王剑锋, 等. 基于属性加密的高效密文去重和审计方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 355–361. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170935MA Hua, DANG Qianlong, WANG Jianfeng, et al. Efficient ciphertext deduplication and auditing scheme with attribute-based encryption[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 355–361. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170935 [11] YEH L Y, CHIANG P Y, TSAI Y L, et al. Cloud-based fine-grained health information access control framework for LightweightIoT devices with dynamic auditing and attribute revocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2018, 6(2): 532–544. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2015.2485199 [12] HAHN C, KWON H, KIM D, et al. Enabling fast public auditing and data dynamics in cloud services[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2022, 15(4): 2047–2059. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2020.3030947 [13] 田俊峰, 井宣. 多方参与高效撤销组成员的共享数据审计方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1534–1541. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190468TIAN Junfeng and JING Xuan. Shared data auditing scheme for efficient revocation of group members via multi-participation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1534–1541. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190468 [14] SHAMIR A. Identity-based cryptosystems and signature schemes[C]. Workshop on the Theory and Application of Cryptographic Techniques, Santa Barbara, USA, 1984: 47–53. [15] NI Jianbing, ZHANG Kuan, YU Yong, et al. Identity-based provable data possession from RSA assumption for secure cloud storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(3): 1753–1769. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2020.3036641 [16] ZHANG Xiaojun, ZHAO Jie, XU Chunxiang, et al. CIPPPA: Conditional identity privacy-preserving public auditing for cloud-based WBANs against malicious auditors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, 2021, 9(4): 1362–1375. doi: 10.1109/TCC.2019.2927219 [17] GAO Xiang, YU Jia, CHANG Yan, et al. Checking only when it is necessary: Enabling integrity auditing based on the keyword with sensitive information privacy for encrypted cloud data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2021, 19(6): 3774–3789. [18] XUE Jingting, XU Chunxiang, ZHAO Jining, et al. Identity-based public auditing for cloud storage systems against malicious auditors via blockchain[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2019, 62(3): 32104. doi: 10.1007/s11432-018-9462-0 [19] ALI S T, SIVARAMAN V, OSTRY D, et al. Securing first-hop data provenance for bodyworn devices using wireless link fingerprints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2014, 9(12): 2193–2204. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2014.2357998 [20] ZHANG Yinghui, ZHANG Tiantian, GUO Rui, et al. Traceable dynamic public auditing with identity privacy preserving for cloud storage[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2019, 13(11): 5653–5672. doi: 10.3837/tiis.2019.11.021 [21] YU Yong, AU M H, ATENIESE G, et al. Identity-based remote data integrity checking with perfect data privacy preserving for cloud storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(4): 767–778. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2615853 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
