A Software Watermarking Method Based on Program Execution Time
-
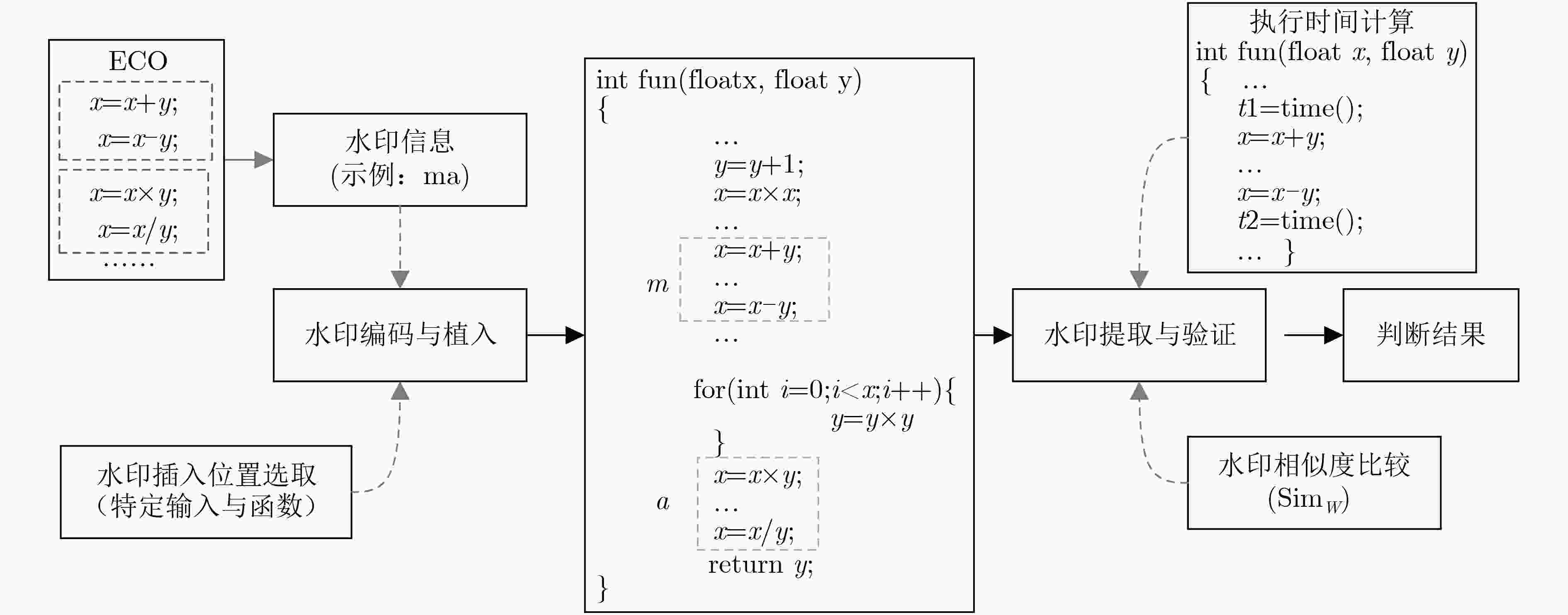
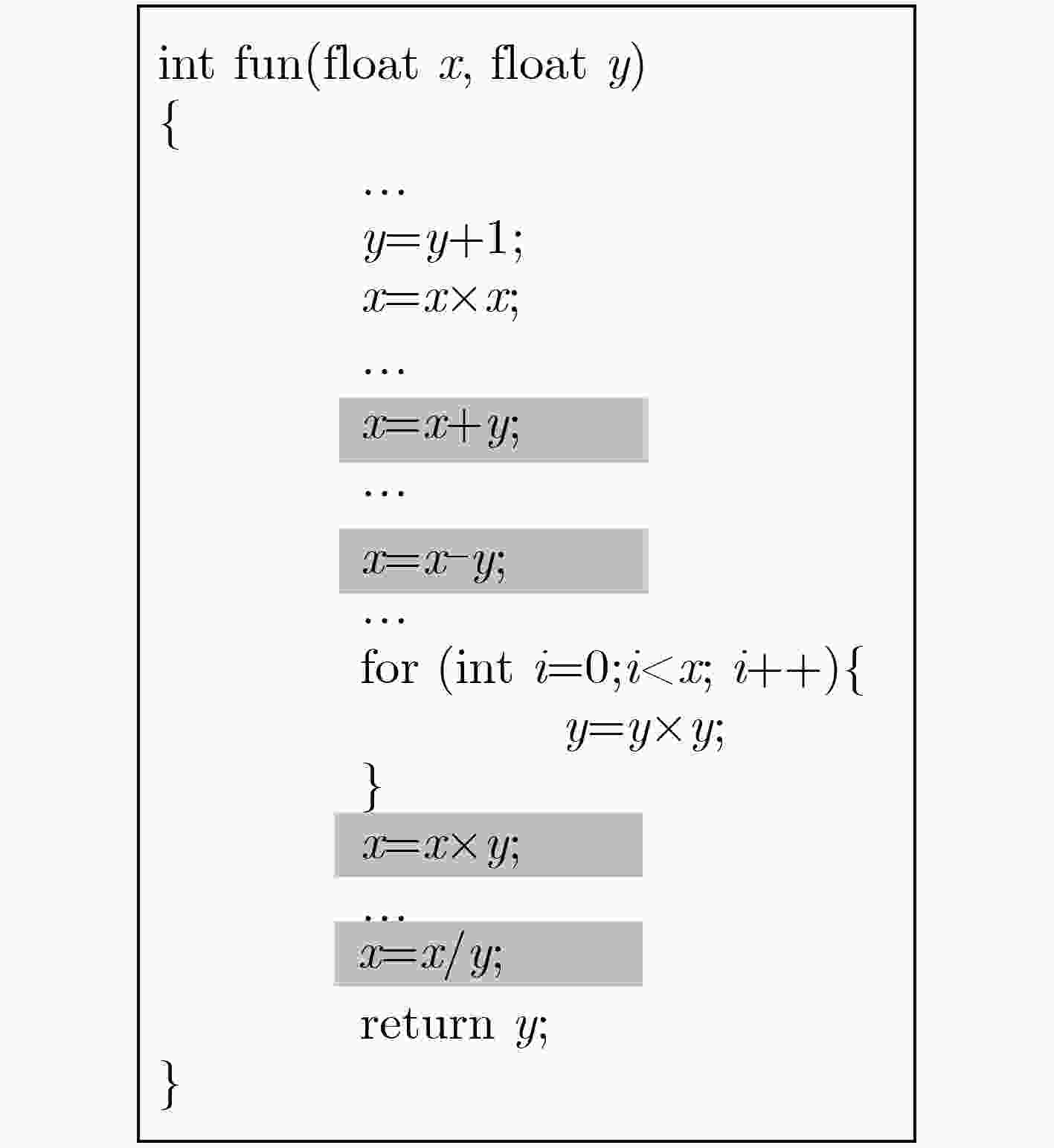
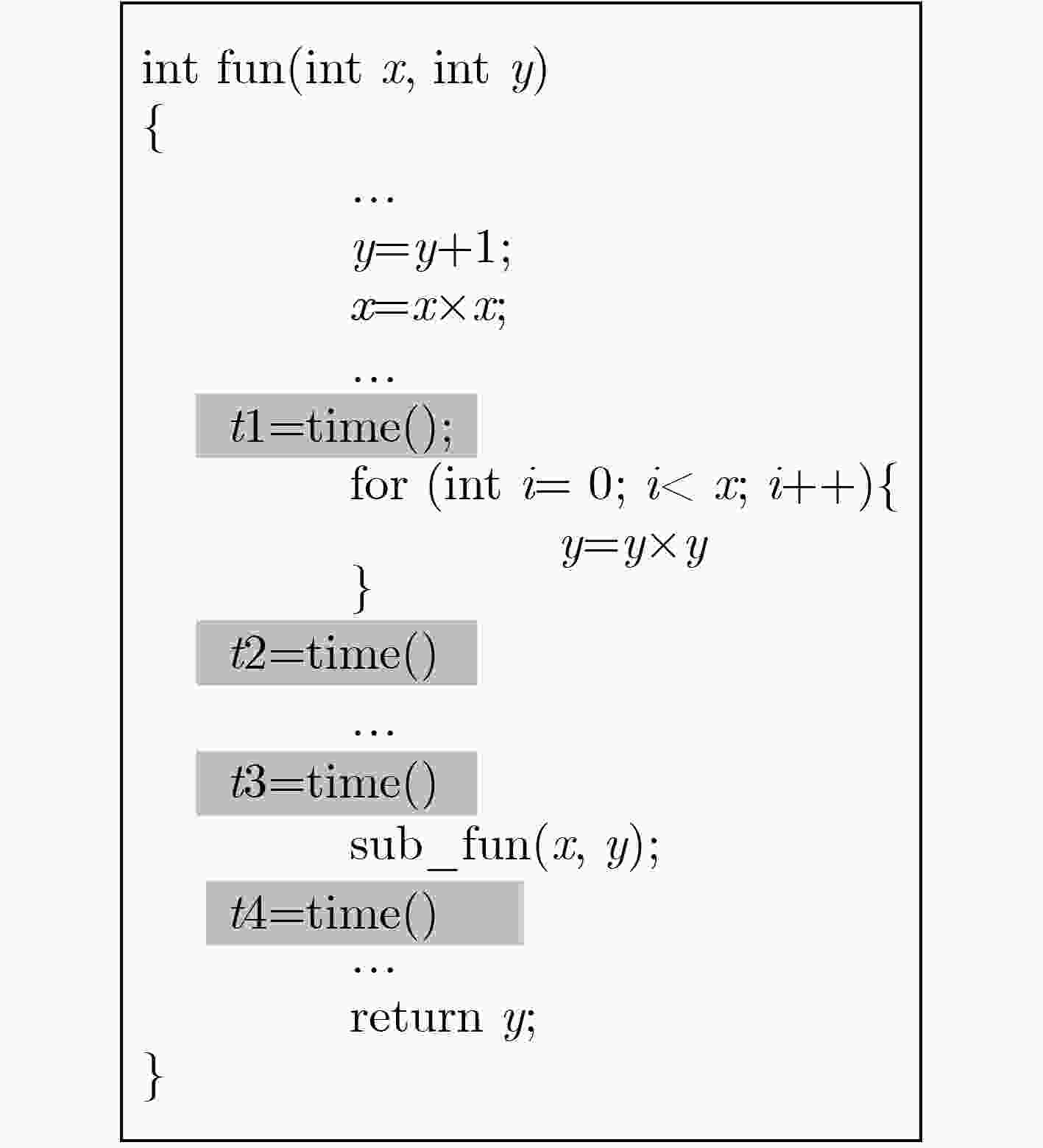
摘要: 当前,应用软件面临的重要问题是不法分子通过软件剽窃、重打包等技术,将恶意负载或广告加载到合法应用软件中,并形成新软件进行发布,给用户和应用软件作者的合法权益带来威胁。为了实现对应用软件剽窃、重打包等安全风险的测评,该文提出一种基于程序执行时间量化分析的软件水印方法(SW_PET)。通过生成多种相互抵消功能的操作组,实现对水印信息的时间化编码,并植入应用软件中;在检测过程中,需要提取相应的水印信息,对照之前的时间编码对应的原始水印,比较不同操作的执行时间,判断水印相似度,进而判别原始水印的存在性,完成应用软件合法性的判断。该方法也可以与其它类型的水印信息相结合,增强水印的鲁棒性。最后,通过搭建仿真模拟器,实现对不同应用软件水印信息的比较和判断,验证该方法的有效性。Abstract: Currently, a main problem in software is repackaging or plagiarization, which means attackers can add malicious payloads or advertisements into legitimate APPs through piggybacking, it greatly threatens the users and original developers. In this paper, a novel Software Watermarking method based on Program Execution Time (SW_PET) is proposed. By generating a variety of effect-canceling operations, the watermark information can be encoded into the form of program execution time, and can be embedded into Android APPs. In the detection process, the watermark information is extracted and compared with the original watermark to check whether the APP is repackaged. This method can be combined with other types of watermarks (e.g., picture-based watermarks) in order to enhance the robustness. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed approach is verified, and the overhead introduced by the watermark is measured, which is demonstrated to be minimal.
-
Key words:
- Software watermarking /
- Program execution /
- Watermark encoding
-
表 1 主要操作类型表
操作类型 操作 示例 算术操作 加法 x = x + y, x = x + C,等 减法 x = x – y, x = x - C,等 乘法 x = x × y, x = x × C,等 除法 x = x / y, x = x / C,等 逻辑操作 逻辑与 x = x && y, x = x && C,等 逻辑或 x = x || y, x = x || C,等 逻辑非 x =!x 比特位操作 比特and操作 x = x & y, x = x & C,等 比特or操作 x = x | y, x = x | C,等 移位操作 左移位 x = x << y, x = x << C,等 右移位 x = x >> y, x = x >> C,等 表 2 mark的时间编码序列
水印字母 操作代码 m x = x + y; x = x – y a x = x × y; x = x / y r x = x + y; x = x – y; x = x × y; x = x / y k y = x; x = (x>>2); y = x & 0 × 3; x = (x<<2)|y 表 3 mark的时间编码序列
水印字母 操作代码 时间(μs) m x = x + y; x = x – y 2.14 a x = x × y; x = x / y 4.04 r x = x + y; x = x – y; x = x × y; x = x / y 7.14 k y = x; x = (x>>2); y = x & 0x3; x = (x<<2)|y 6.19 -
林迪. 2018年中国App下载量排名全球第一: 占全球50%[EB/OL]. https://www.sohu.com/a/289551518_162522, 2019. ZHOU Wu, ZHANG Xinwen, and JIANG Xuxian. AppInk: Watermarking android apps for repackaging deterrence[C]. The 8th ACM SIGSAC Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security. Hangzhou, China, 2013: 1–12. doi: 10.1145/2484313.2484315. ZHOU Wu, ZHOU Yajin, JIANG Xuxian, et al. Detecting repackaged smartphone applications in third-party android marketplaces[C]. The 2nd ACM Conference on Data and Application Security and Privacy. San Antonio, United States, 2012: 317–326. doi: 10.1145/2133601.2133640. Arxan Technologies. State of security in the App Economy: Mobile apps under attack[EB/OL]. http://www.arxan.com/assets/1/7/state-of-security-appeconomy.pdf, 2012. CHEN Kai, ZHANG Yingjun, and LIU Peng. Leveraging information asymmetry to transform android apps into self-defending code against repackaging attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(8): 1879–1893. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2017.2782249 CHEN Kai, LIU Peng, and ZHANG Yingjun. Achieving accuracy and scalability simultaneously in detecting application clones on android markets[C]. The 36th International Conference on Software Engineering. Hyderabad, India, 2014: 175–186. doi: 10.1145/2568225.2568286. CRUSSELL J, GIBLER C, and CHEN Hao. AnDarwin: Scalable detection of semantically similar android applications[C]. The 18th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security on Computer Security. Egham, UK, 2013: 182–199. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-40203-6_11. Guardsquare. Proguar[EB/OL]. http://proguard.sourceforge.net/, 2013. Guardsquare. A specialized optimizer and obfuscator for android[EB/OL]. http://www.saikoa.com/dexguard, 2013. 陈明奇, 钮心忻, 杨义先. 数字水印的攻击方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2001, 23(7): 705–711.CHEN Mingqi, NIU Xinyi, and YANG Yixian. The attack methods of digital watermarking[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2001, 23(7): 705–711. 毛琼, 陈明奇, 夏光升, 等. 安全数字水印体系的研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2001, 23(9): 833–840.MAO Qiong, CHEN Mingqi, XIA Guangsheng, et al. The research of secure digital watermarking architecture[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2001, 23(9): 833–840. HAMILTON J and DANICIC S. A survey of static software watermarking[C]. 2011 World Congress on Internet Security. London, UK, 2011: 100–107. doi: 10.1109/worldcis17046.2011.5749891. MONDEN A, IIDA H, MATSUMOTO K, et al. A practical method for watermarking java programs[C]. The 24th Annual International Computer Software and Applications Conference. Taipei, China, 2000: 191–197. doi: 10.1109/CMPSAC.2000.884716. VENKATESAN R, VAZIRANI V, and SINHA S. A graph theoretic approach to software watermarking[C]. The 4th International Workshop on Information Hiding. Pittsburgh, USA, 2001: 157–168. doi: 10.1007/3-540-45496-9_12. COUSOT P and COUSOT R. An abstract interpretation-based framework for software watermarking[C]. The 31st ACM SIGPLAN-SIGACT Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages. Venice, Italy, 2004: 173–185. doi: 10.1145/964001.964016. NAGRA J and THOMBORSON C. Threading software watermarks[C]. The 6th International Workshop on Information Hiding. Toronto, Canada, 2004: 208–223. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-30114-1_15. COLLBERG C, HUNTWORK A, CARTER E, et al. More on graph theoretic software watermarks: Implementation, analysis, and attacks[J]. Information and Software Technology, 2009, 51(1): 56–67. doi: 10.1016/j.infsof.2008.09.016 COLLBERG C, CARTER E, DEBRAY S, et al. Dynamic path-based software watermarking[J]. ACM Sigplan Notices, 2004, 39(6): 107–118. doi: 10.1145/996893.996856 COLLBERG C, CARTER E, DEBRAY S, et al. Dynamic path-based software watermarking[C]. The 2004 ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation, Washington, USA, 2004: 107–118. doi: 10.1145/996841.996856. ZENG Lingling, REN Wei, LEI Min, et al. DroidMark: A lightweight android text and space watermark scheme based on semantics of XML and DEX[C]. The 5th International Conference on Emerging Internetworking. Wuhan, China, 2017: 756–766. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-59463-7_75. COLLBERG C and THOMBORSON C. Software watermarking: Models and dynamic embedding[C]. The 26th ACM SIGPLAN-SIGACT Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages. San Antonio, USA, 1999: 311–324. doi: 10.1145/292540.292569. ZHANG Yingjun and CHEN Kai. AppMark: A picture-based watermark for android apps[C]. The 8th International Conference on Software Security and Reliability (SERE). San Francisco, USA, 2014: 58–67. doi: 10.1109/SERE.2014.19. 王叶茂, 车生兵. 软件水印及其研究现状概述[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2015, 32(4): 6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2015.04.002WANG Yemao and CHE Shengbing. Summary on software watermarking and its research progress[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2015, 32(4): 6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2015.04.002 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
