Natural Computing Method Based on Nonlinear Dimension Reduction
-
摘要:
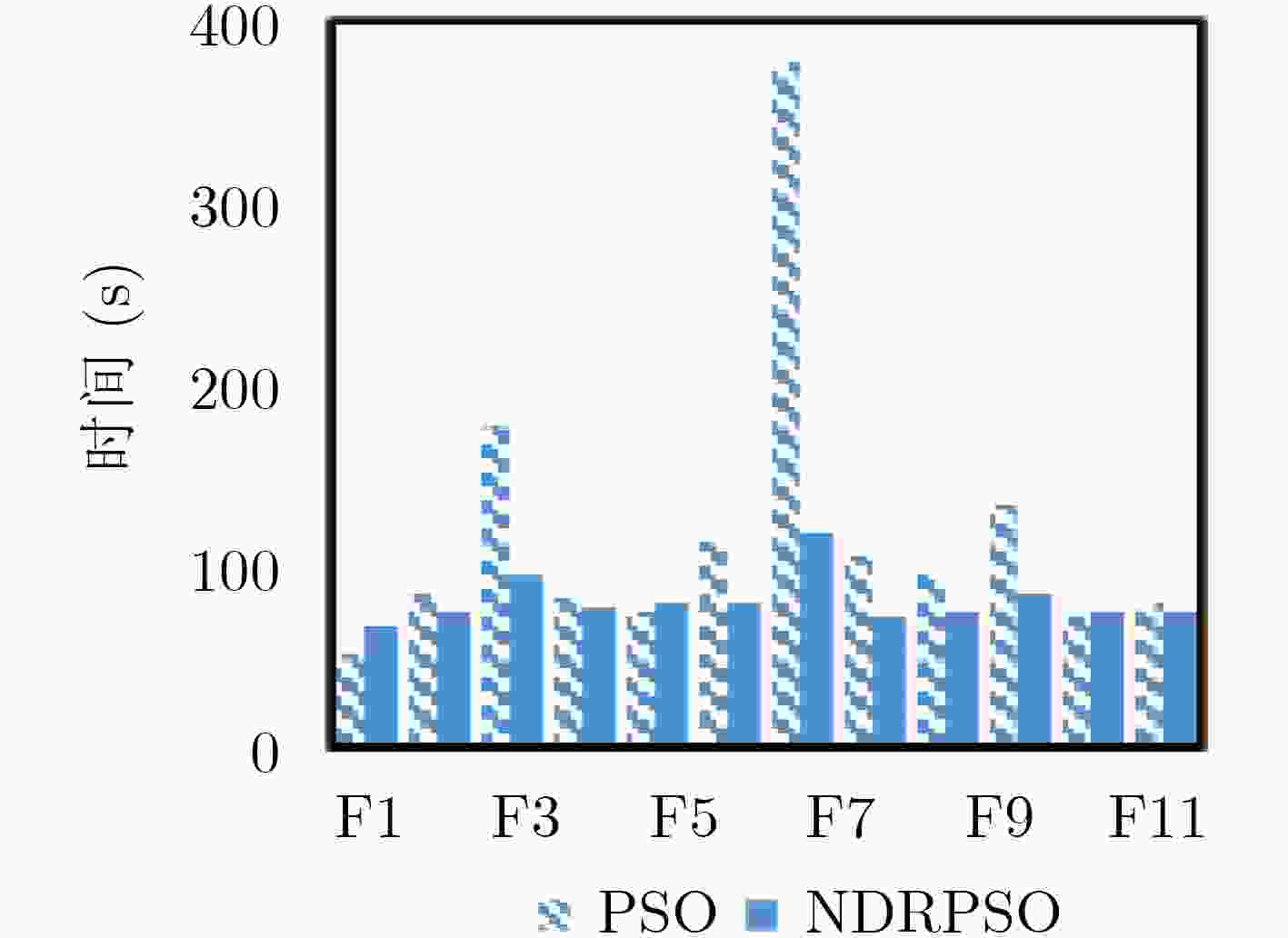
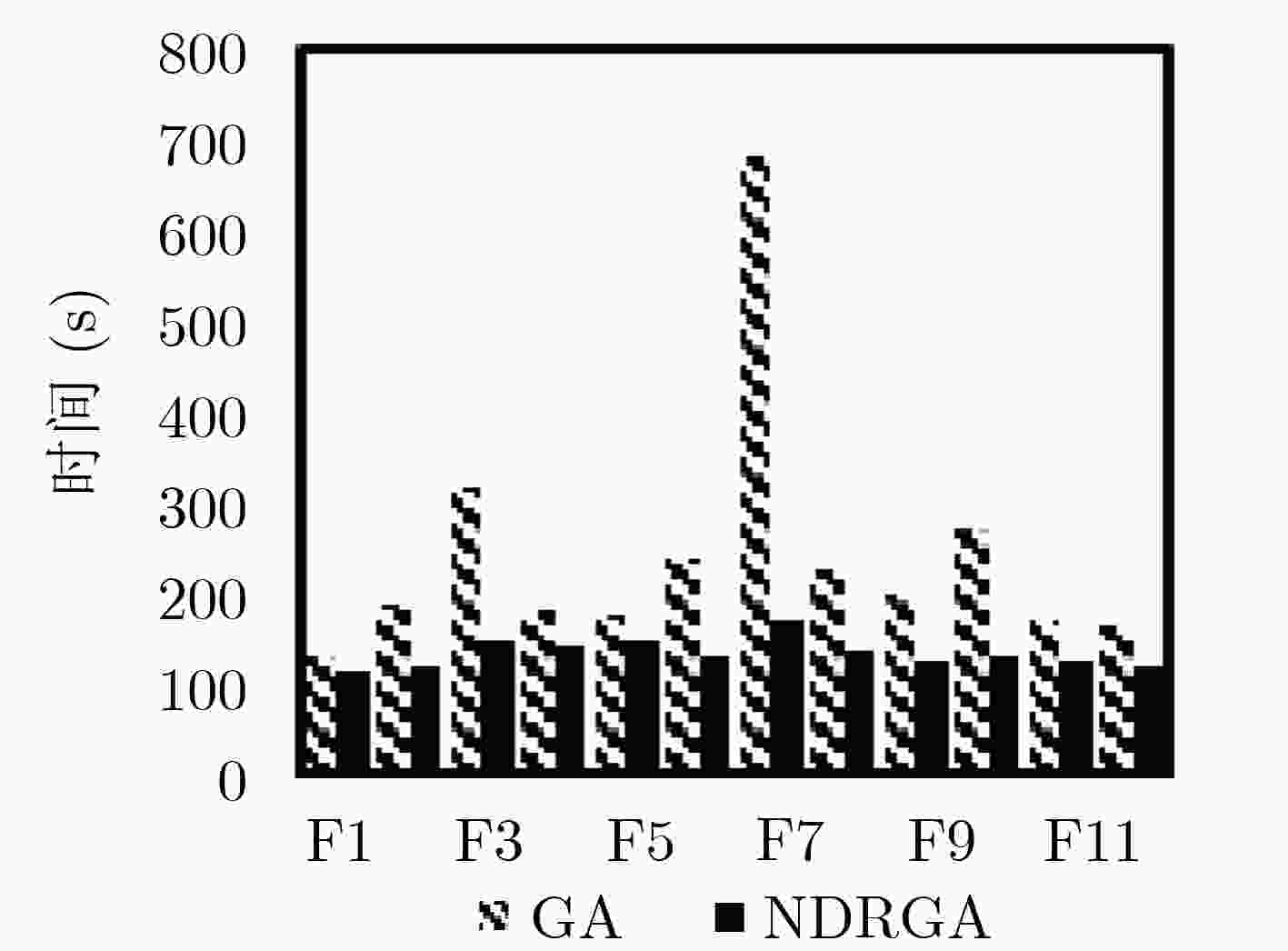
随着人工智能的发展,许多优化问题发展为高维的大规模优化问题。在自然计算方法中,针对高维问题虽然能避免算法陷入局部最优,但是在收敛速度和时间可行性上却不占优势。该文在传统自然计算方法的基础上,提出了非线性降维的自然计算方法(NDR),该策略不依赖具体的算法,具有普适性。该方法将初始化的N个个体看做一个N行D列的矩阵,然后对矩阵的列向量求最大线性无关组,从而减少矩阵的冗余度,达到降低维度的目的。在此过程中,由于剩余的任意列向量组均可由最大线性无关组表示,所以通过对最大线性无关组施加一个随机系数来维持种群的多样性和完整性。将该文所提策略分别应用到标准遗传算法(GA)和粒子群优化算法(PSO)中,并与标准粒子群算法、遗传算法以及目前主流的对维数进行优化的4个算法对比,实验证明,改进的算法对大部分标准测试函数都具有很强的全局收敛能力,其寻优能力超过了上述6个算法,同时改进后的算法在运行时间上远优于对比算法。
Abstract:Many optimization problems develop into high-dimensional large-scale optimization problems in the process of the development of artificial intelligence. Although the high-dimensional problem can avoid the algorithm falling into local optimum, it has no advantage in convergence speed and time feasibility. Therefore, the natural computing method for Nonlinear Dimension Reduction (NDR) is proposed. This strategy does not depend on specific algorithm and has universality. In this method, the initialized N individuals are regarded as a matrix of N rows and D columns, and then the maximum linear independent group is calculated for the column vector of the matrix, so as to reduce the redundancy of the matrix and reduce the dimension. In this process, since any remaining column vector group can be represented by the maximum linearly independent group, a random coefficient is applied to the maximum linearly independent group to maintain the diversity and integrity of the population. The standard genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization using NDR strategy compare with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Genetic Algorithm (GA) and the four mainstream algorithms for dimension optimization. Experiments show that the improved algorithm has strong global convergence ability and better time complexity for most standard test functions.
-
Key words:
- Natural computing method /
- Optimization /
- Dimension reduction /
- Nonlinearity
-
表 1 非线性降维的自然计算方法(NDR)
种群规模为N,终止进化代数为G,测试次数为T (1) 初始化N, G, T 等参数,随机产生第1代种群$\bf{pop}$; (2) 将生成的种群$\bf{pop}$做线性变换,求得列向量的最大线性无关
组,即为新的种群$\bf{newpop}$;(3) 对新种群$\bf{newpop}$的各维乘以随机系数${r_i}$,更新$\bf{newpop}$; (4) 将得到的$\bf{newpop}$使用基于种群的自然计算方法进化; (5) 结束。 表 2 标准测试函数
测试函数 维数 可行解空间 ${F_1} = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D { {x_i}^2} $ 1000 [–100, 100]n ${F_2} = {\left( { {x_1} - 1} \right)^2} + {\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D {i\cdot \left( {2{x_i}^2 - {x_{i - 1} } } \right)} ^2}$ 1000 [–10, 10]n ${F_3} = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D { { {\left| { {x_i} } \right|}^{i + 1} } }$ 1000 [–1, 1]n $\begin{array}{l}{F_4} = - a\cdot\exp \left( { - b\sqrt {\dfrac{1}{D}\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D { {x_i}^2} } } \right) - \exp \left( {\dfrac{1}{D}\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D {\cos \left( {c{x_i} } \right)} } \right) + a + \exp \left( 1 \right), a = 20,b = 0.2,c = 2\pi \end{array}$ 1000 [–32.768, 32.768]n ${F_5} = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D {({x_i}^2 - 10 \cos (2 \pi {x_i})} + 10)$ 1000 [–5.12, 5.12]n ${F_6} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^D {\frac{ { {x_i}^2} }{ {4000} } - \prod\limits_{i = 1}^D {\cos \left( {\frac{ { {x_i} } }{ {\sqrt i } } } \right)} } + 1$ 1000 [–600,600]n $\begin{array}{l}{F_7} = {\sin ^2}\left( {\pi {\omega _1} } \right) + {\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{D - 1} {\left( { {\omega _i} - 1} \right)} ^2}\left[ {1 + 10{ {\sin }^2}\left( {\pi {\omega _i} + 1} \right)} \right]\\ \quad\ \ + {\left( { {\omega _D} - 1} \right)^2}\left[ {1 + { {\sin }^2}\left( {2\pi {\omega _D} } \right)} \right]{\omega _i} = 1 + \dfrac{ { {\omega _i} - 1} }{4}\end{array}$ 1000 [–10, 10]n ${F_8} = 418.9829D - \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D { {x_i}\sin \left( {\sqrt {\left| { {x_i} } \right|} } \right)}$ 1000 [–500, 500]n ${F_9} = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{D - 1} {\left[ {100{ {\left( { {x_{i + 1} } - x_i^2} \right)}^2} + { {\left( { {x_i} - 1} \right)}^2} } \right]} $ 1000 [–5, 10]n ${F_{10} } = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^{D/4} {\left[ { { {\left( { {x_{4i - 3} } + 10{x_{4i - 2} } } \right)}^2} + 5{ {\left( { {x_{4i - 1} } - {x_{4i} } } \right)}^2} + { {\left( { {x_{4i - 2} } - 2{x_{4i - 1} } } \right)}^4} + 10{ {\left( { {x_{4i - 3} } - {x_{4i} } } \right)}^4} } \right]} $ 1000 [–4, 5]n ${F_{11} }{\rm{ = } }\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D {ix_i^2} $ 1000 [–10, 10]n ${F_{12} } = \displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D {x_i^2 + { {\left( {\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D {0.5i{x_i} } } \right)}^2} + { {\left( {\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^D {0.5i{x_i} } } \right)}^4} } $ 1000 [–5, 10]n 表 3 各算法对12个标准测试函数进行优化结果
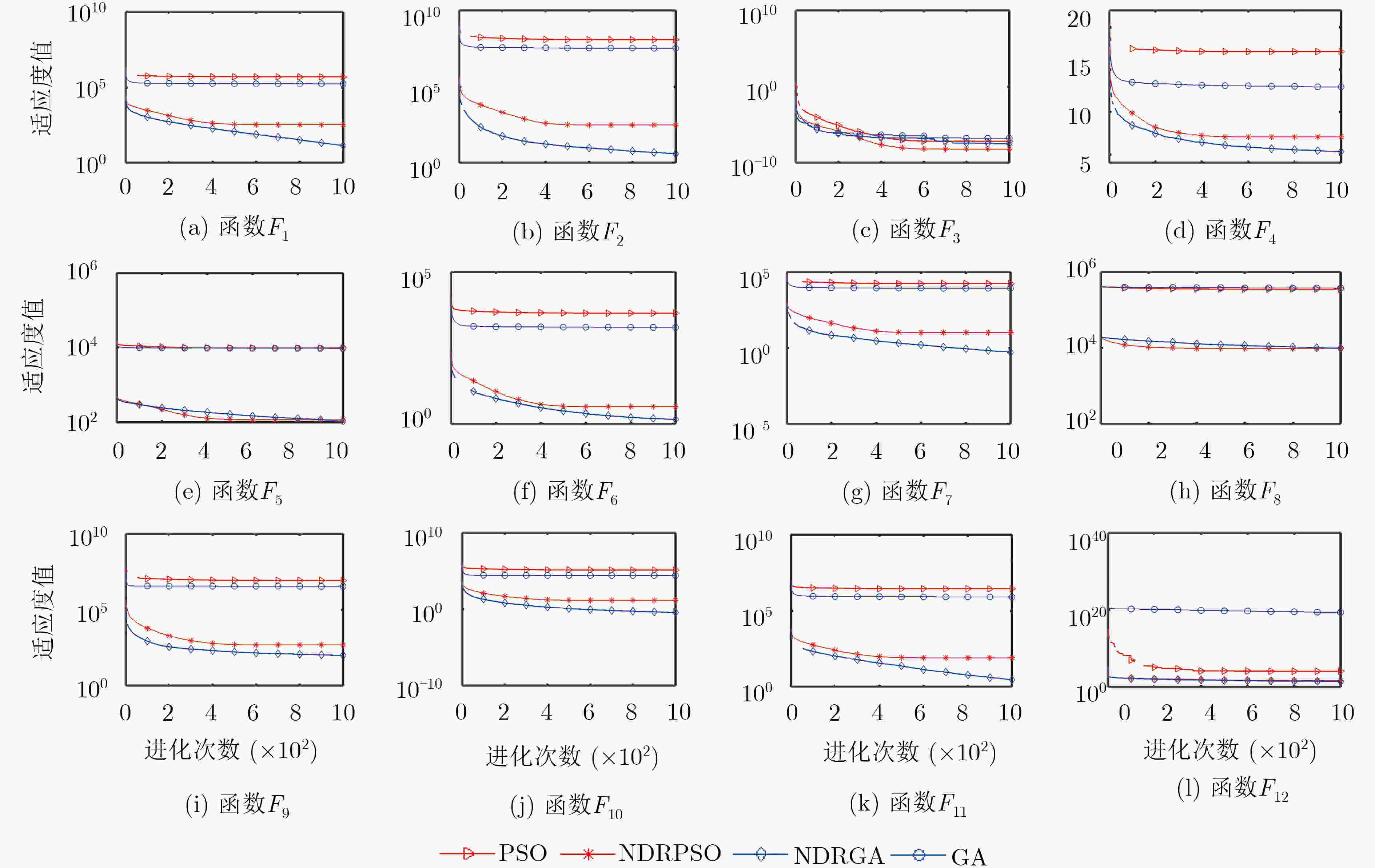
函数 平均结果及标准方差 PSO NDRPSO GA NDRGA F1 4.92e+05±5.09e+04 345.2211±96.7891 1.78e+05±6.12e+03 12.7059±3.2681 F2 1.18e+08±2.47e+07 301.8188±114.0539 3.65e+07±1.85e+06 3.8379±2.8421 F3 6.71e-08±7.10e-08 6.48e-09±8.88e-09 1.11e-07±1.84e-07 3.17e-08±4.51e-08 F4 17.1198±0.5185 7.0752±0.7417 13.2492±0.1323 5.2058±0.5977 F5 9.72e+03±464.6314 115.6225±21.7166 9.68e+03±86.5390 104.5187±18.5246 F6 4.34e+03±366.1741 3.6991±0.7714 1.61e+03±64.0915 1.4019±0.1196 F7 1.66e+04±1.45e+03 13.0269±5.8130 8.62e+03±366.1671 0.4960±0.1577 F8 3.47e+05±7.50e+03 9.58e+03±866.1230 3.70e+05±2.42e+03 9.92e+03±619.0421 F9 9.20e+06±2.18e+06 694.6303±588.9850 3.48e+06±2.40e+05 103.1690±45.9190 F10 1.16e+05±1.50e+04 14.2205±5.1053 2.48e+04±1.50e+03 0.3623±0.2182 F11 2.82e+06±2.62e+05 80.1161±31.8298 7.96e+05±2.70e+04 2.8521±1.2240 F12 1.31e+04±3.41e+03 53.57±12.84 2.18e+19±3.03e+09 27.9986±12.1954 表 4 各算法的实验对比结果
${F_1}$ ${F_3}$ ${F_4}$ ${F_5}$ ${F_6}$ ${F_8}$ DMS-CC best 13.2 5.88e+05 1.60e+14 2.30e+06 2.20e+04 2.00e+11 SLPSO best 4.78e-14 3.82e+06 1.90e+14 5.15e+09 9.42e+06 – DMS-PSO best 1.66e+01 1.14e+08 4.36e+07 1.68e+09 9.23e+04 4.51e+10 CSO best 2.43e-09 3.71e+06 4.61e+14 3.25e+09 9.68e+06 2.13e+11 NDRPSO best 6.54 1.11e-08 2.89 12.91 0.88 2.02e+03 -
DE CASTRO L N. Fundamentals of natural computing: An overview[J]. Physics of Life Reviews, 2007, 4(1): 1–36. doi: 10.1016/j.plrev.2006.10.002 刘鑫, 李大海. 基于遗传算法的相位差异技术图像恢复[J]. 四川大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 55(4): 745–751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0490-6756.2018.04.015LIU Xin and LI Dahai. Recovering image using a genetic algorithm based phase diversity technology[J]. Journal of Sichuan University:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 55(4): 745–751. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0490-6756.2018.04.015 魏鹏, 罗红波, 赵康, 等. 基于蚁群算法的运动时间优化算法研究[J]. 四川大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 55(6): 1171–1179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0490-6756.2018.06.008WEI Peng, LUO Hongbo, ZHAO Kang, et al. Optimization of multi-joint robot motion of hydraulic drilling vehicle based on ant colony algorithm[J]. Journal of Sichuan University:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 55(6): 1171–1179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0490-6756.2018.06.008 邓昌明, 李晨, 邓可君, 等. 基因遗传算法在文本情感分类中的应用[J]. 四川大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 56(1): 45–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0490-6756.2019.01.010DENG Changming, LI Chen, DENG Kejun, et al. Application of genetic algorithm in text sentiment classification[J]. Journal of Sichuan University:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 56(1): 45–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0490-6756.2019.01.010 王蓉芳, 焦李成, 刘芳, 等. 自适应动态控制种群规模的自然计算方法[J]. 软件学报, 2012, 23(7): 1760–1772. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2012.04151WANG Rongfang, JIAO Licheng, LIU Fang, et al. Nature computation with self-adaptive dynamic control strategy of population size[J]. Journal of Software, 2012, 23(7): 1760–1772. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1001.2012.04151 SUN Wei, LIN Anping, YU Hongshan, et al. All-dimension neighborhood based particle swarm optimization with randomly selected neighbors[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 405: 141–156. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.04.007 刘云, 易松. 双变换算法在多维序列数据分析中的优化研究[J]. 四川大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 56(4): 633–638. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0490-6756.2019.04.009LIU Yu and YI Song. Research on optimization of double transform algorithm in multidimensional sequence data analysis[J]. Journal of Sichuan University:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 56(4): 633–638. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0490-6756.2019.04.009 贺毅朝, 王熙照, 张新禄, 等. 基于离散差分演化的KPC问题降维建模与求解[J]. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(10): 267–2280.HE Yichao, WANG Xizhao, ZHANG Xinlu, et al. Modeling and solving by dimensionality reduction of kpc problem based on discrete differential evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(10): 267–2280. WANG Xuesong, KONG Yi, CHENG Yuhu, et al. Dimensionality reduction for hyperspectral data based on sample-dependent repulsion graph regularized auto-encoder[J]. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2017, 26(6): 1233–1238. doi: 10.1049/cje.2017.07.012 XU Guiping, CUI Quanlong, SHI Xiaohu, et al. Particle swarm optimization based on dimensional learning strategy[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 45: 33–51. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2018.12.009 WEI Jingxuan and WANG Yuping. A dynamical particle swarm algorithm with dimension mutation[C]. 2006 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Guangzhou, China, 2006: 254–257. doi: 10.1109/ICCIAS.2006.294131. 纪震, 周家锐, 廖惠莲, 等. 智能单粒子优化算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2010, 33(3): 556–561. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2010.00556JI Zhen, ZHOU Jiarui, LIAO Huilian, et al. A novel intelligent single particle optimizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2010, 33(3): 556–561. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1016.2010.00556 拓守恒, 邓方安, 周涛. 一种利用膜计算求解高维函数的全局优化算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2011, 47(19): 27–30. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.19.009TUO Shouheng, DENG Fang’an, and ZHOU Tao. Algorithm for solving global optimization problems of multi-dimensional function based on membrane computing[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2011, 47(19): 27–30. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.19.009 CERVANTE L, XUE Bing, SHANG Lin, et al. A dimension reduction approach to classification based on particle swarm optimisation and rough set theory[C]. The 25th Australasian Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Sydney, Australia, 2012: 313–325. 拓守恒. 一种基于人工蜂群的高维非线性优化算法[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2012, 29(7): 42–46. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2012.07.010TUO Shouheng. A new high-dimensional nonlinear optimization algorithm based on artificial bee colony[J]. Microelectronics &Computer, 2012, 29(7): 42–46. doi: 10.19304/j.cnki.issn1000-7180.2012.07.010 JIN Xin, LIANG Yongquan, TIAN Dongping, et al. Particle swarm optimization using dimension selection methods[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2013, 219(10): 5185–5197. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2012.11.020 梁静, 刘睿, 于坤杰, 等. 求解大规模问题协同进化动态粒子群优化算法[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(9): 2595–2605. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005398LIANG Jing, LIU Run, YU Kunjie, et al. Dynamic multi-swarm particle swarm optimization with cooperative coevolution for large scale global optimization[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(9): 2595–2605. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005398 YANG Chenghong, YANG Huaishuo, CHUANG L, et al. PBMDR: A particle swarm optimization-based multifactor dimensionality reduction for the detection of multilocus interactions[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2019, 461: 68–75. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.10.012 宋丹, 石勇, 邓宸伟. 一种结合PCA与信息熵的SIFT特征向量自适应降维算法[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2017, 38(7): 1636–1641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2017.07.039SONG Dan, SHI Yong, DENG Chenwei, et al. Self -adaptive descending dimension algorithm of sift feature vector combined with PCA and information entropy[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2017, 38(7): 1636–1641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2017.07.039 CHEN Sibao, DING C H O, and LUO Bin. Linear regression based projections for dimensionality reduction[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 467: 74–86. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.07.066 ARIYARATNE M K A, FERNANDO T G I, and WEERAKOON S. Solving systems of nonlinear equations using a modified firefly algorithm (MODFA)[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 48: 72–92. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2019.03.010 刘振焘, 徐建平, 吴敏, 等. 语音情感特征提取及其降维方法综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(12): 2833–2851. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.02833LIU Zhentao, XU Jianping, WU Min, et al. Review of emotional feature extraction and dimension reduction method for speech emotion recognition[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(12): 2833–2851. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.02833 孟凡超, 初佃辉, 李克秋, 等. 基于混合遗传模拟退火算法的SaaS构件优化放置[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(4): 916–932. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.004965MENG Fanchao, CHU Dianhui, LI Keqiu, et al. Solving SaaS components optimization placement problem with hybird genetic and simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(4): 916–932. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.004965 KENNEDY J and EBERHART E. Particle swarm optimization[C]. 1995 International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 1995: 1942–1948. CHENG Ran and JIN Yaochu. A social learning particle swarm optimization algorithm for scalable optimization[J]. Information Sciences, 2015, 291: 43–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.039 SABAR N R, ABAWAJY J, and YEARWOOD J. Heterogeneous cooperative co-evolution memetic differential evolution algorithm for big data optimization problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2017, 21(2): 315–327. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2016.2602860 CHENG Ran and JIN Yaochu. A competitive swarm optimizer for large scale optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(2): 191–204. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2322602 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
