Robust Adaptive Beamforming Algorithm Based on Dominant Eigenvector Extraction and Orthogonal Projection
-
摘要: 该文针对传统自适应波束成形算法对信号到达角(DOA)失配敏感的问题,提出一种能有效抑制功率压制型干扰的稳健自适应波束成形算法。首先分析了DOA失配情况下的接收端波束成形输出信干噪比,基于正交投影理论提出一种能实现方向图精确控制的理想波束成形器。然后,通过干扰信号到达角扇区的功率谱积分构造协方差矩阵,分析了矩阵主空间与实际干扰导向矢量列空间的等价性,提出一种正交投影矩阵生成方法,能够提升波束成形器对干扰信号DOA失配的鲁棒性。同理,在期望信号到达角扇区进行功率谱积分,利用所得矩阵的主空间与实际期望信号导向矢量列空间的等价性来估计期望信号导向矢量。最后,基于生成的正交投影矩阵和估计的期望信号导向矢量提出一种能有效抑制干扰的稳健自适应波束成形器。仿真结果表明,所提算法在不存在失配、DOA失配、导向矢量失配等情况下都展现出比传统算法更优的空域抗干扰性能和鲁棒性。Abstract:
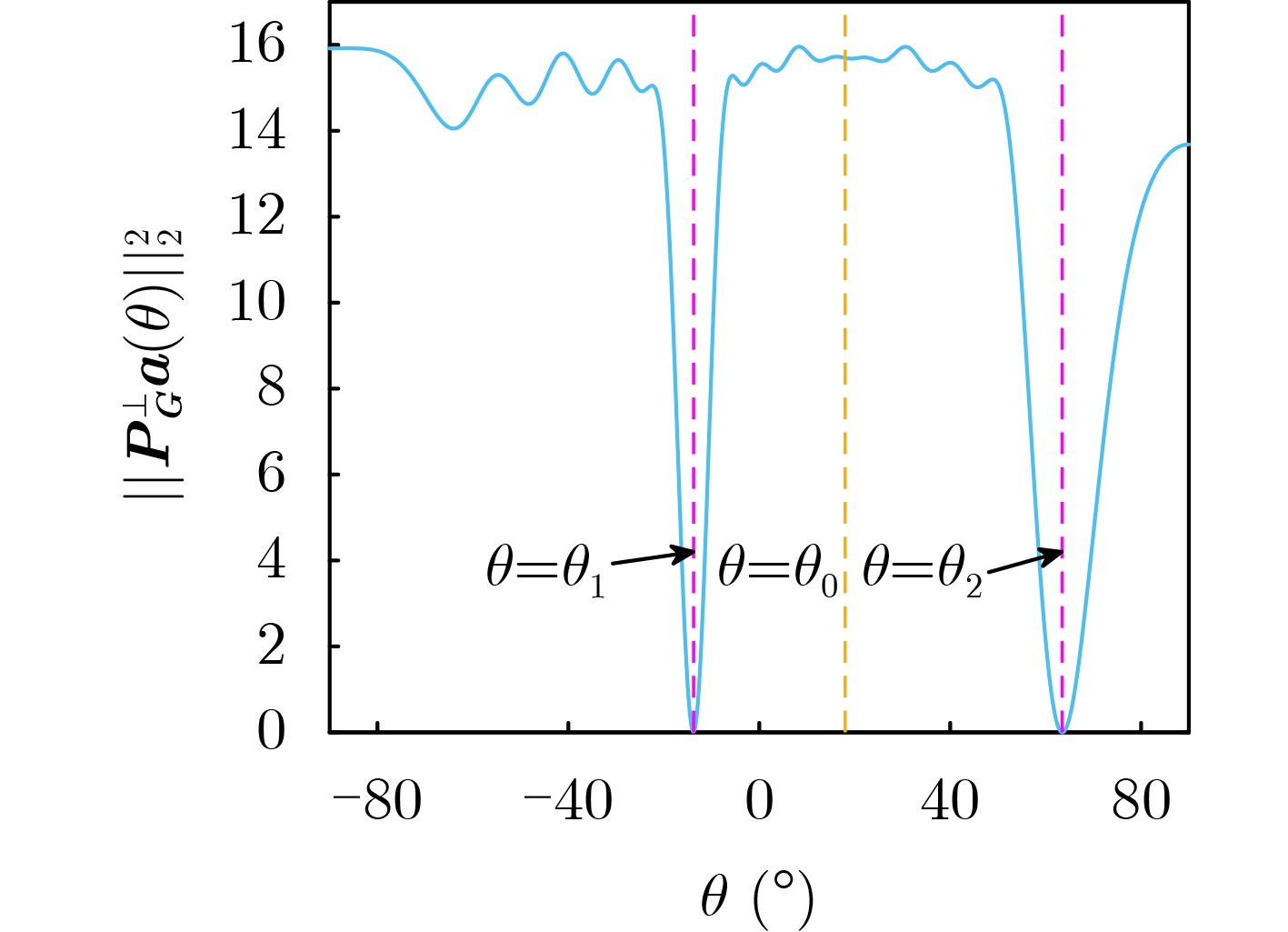
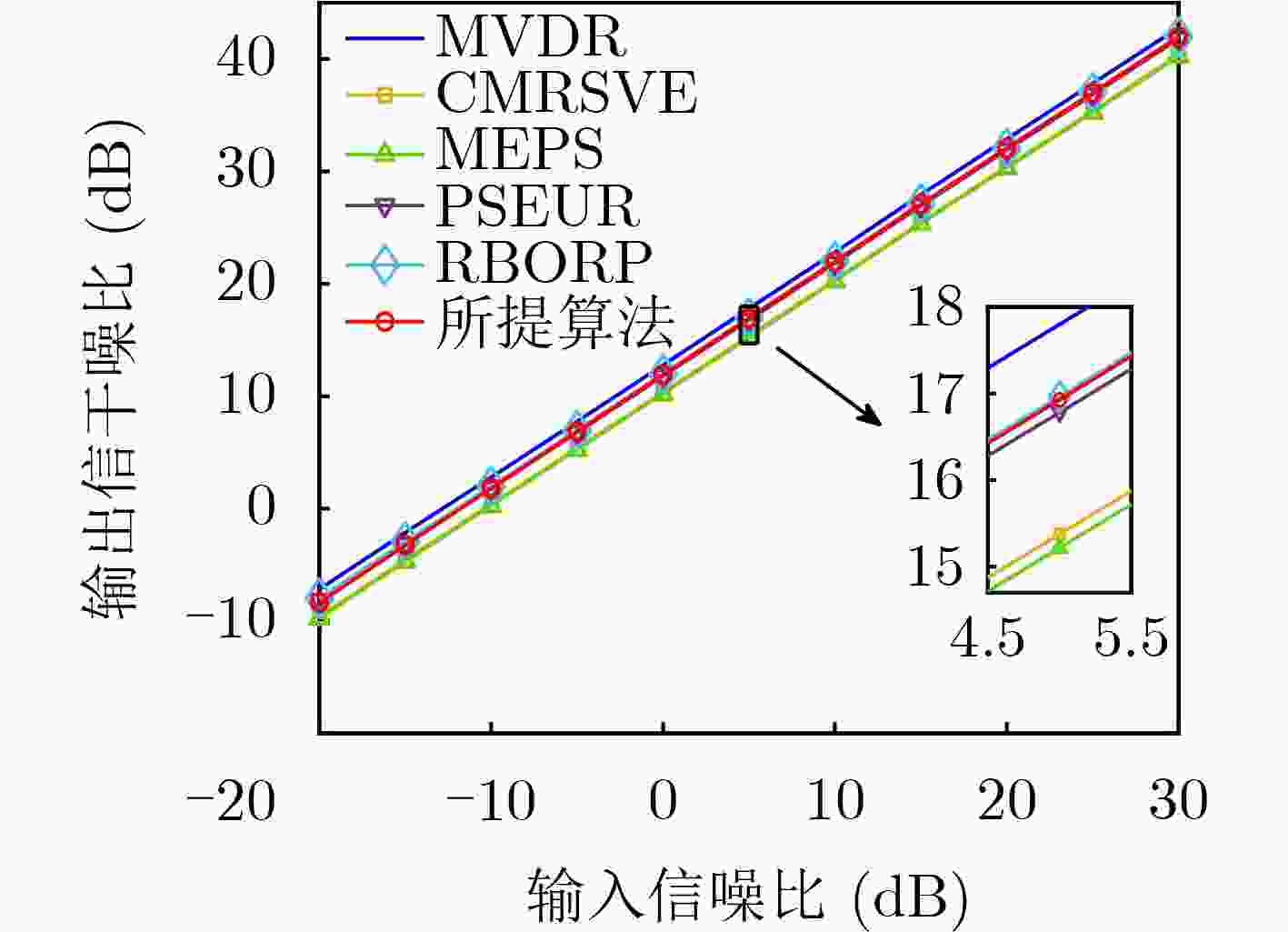
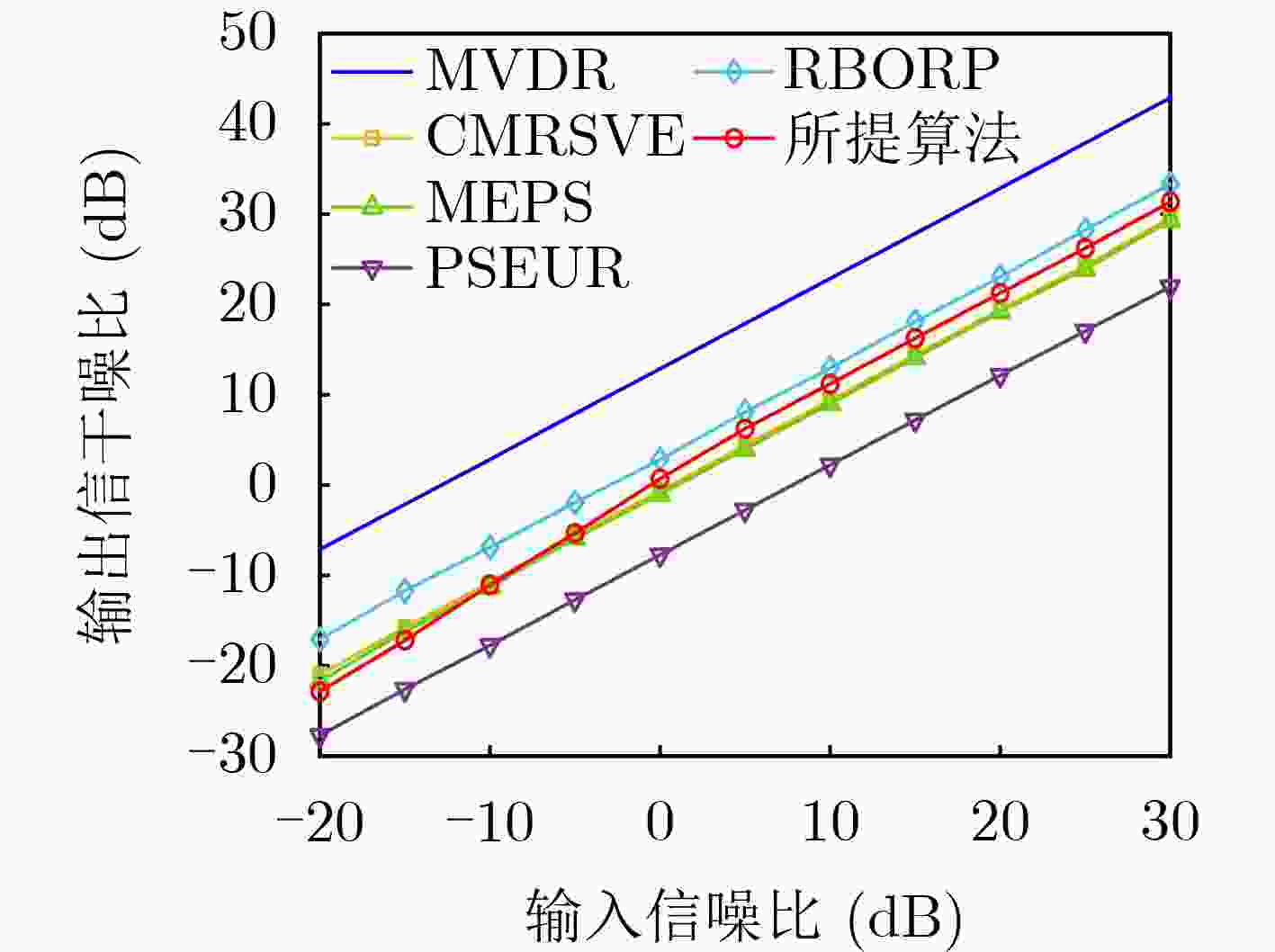
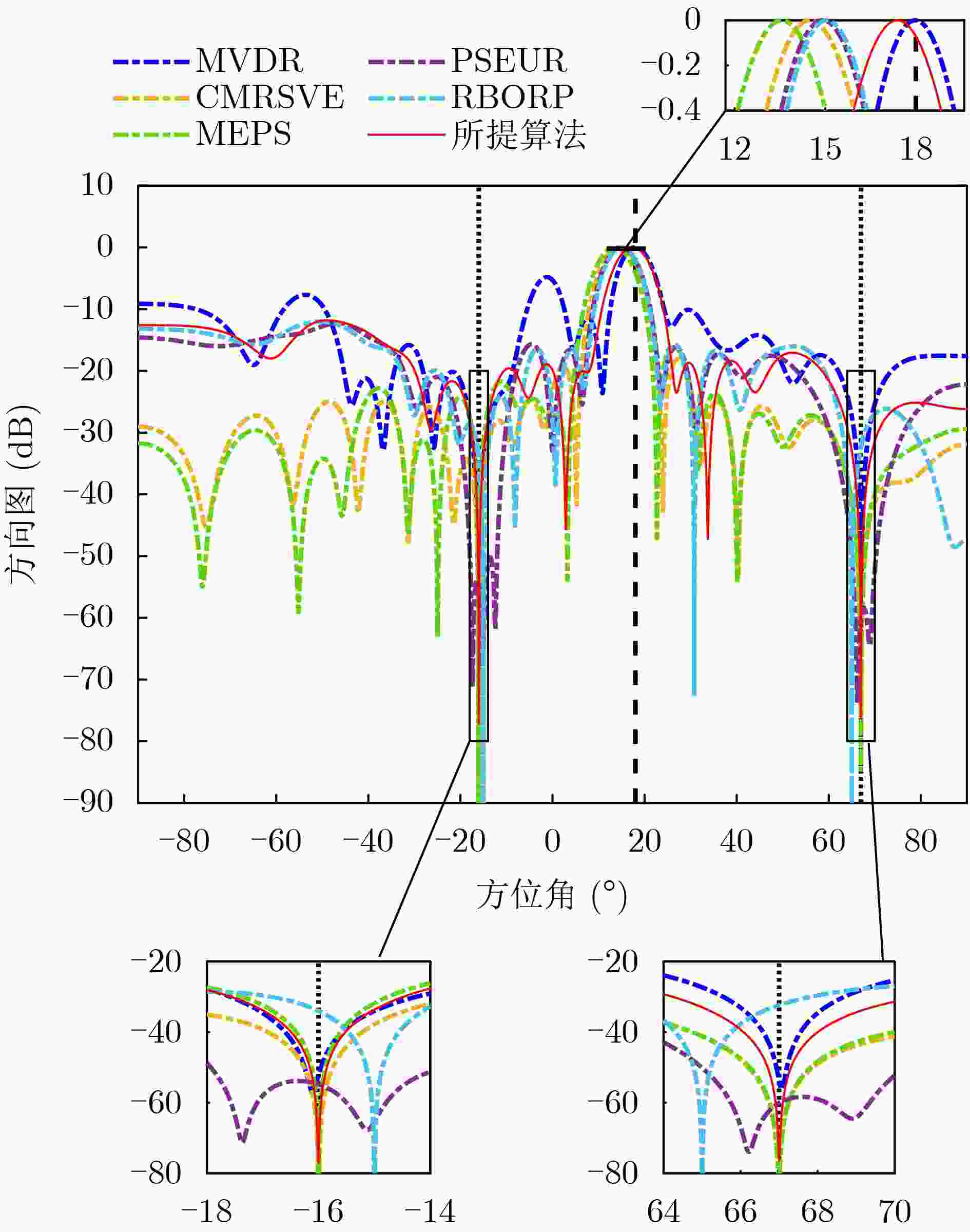
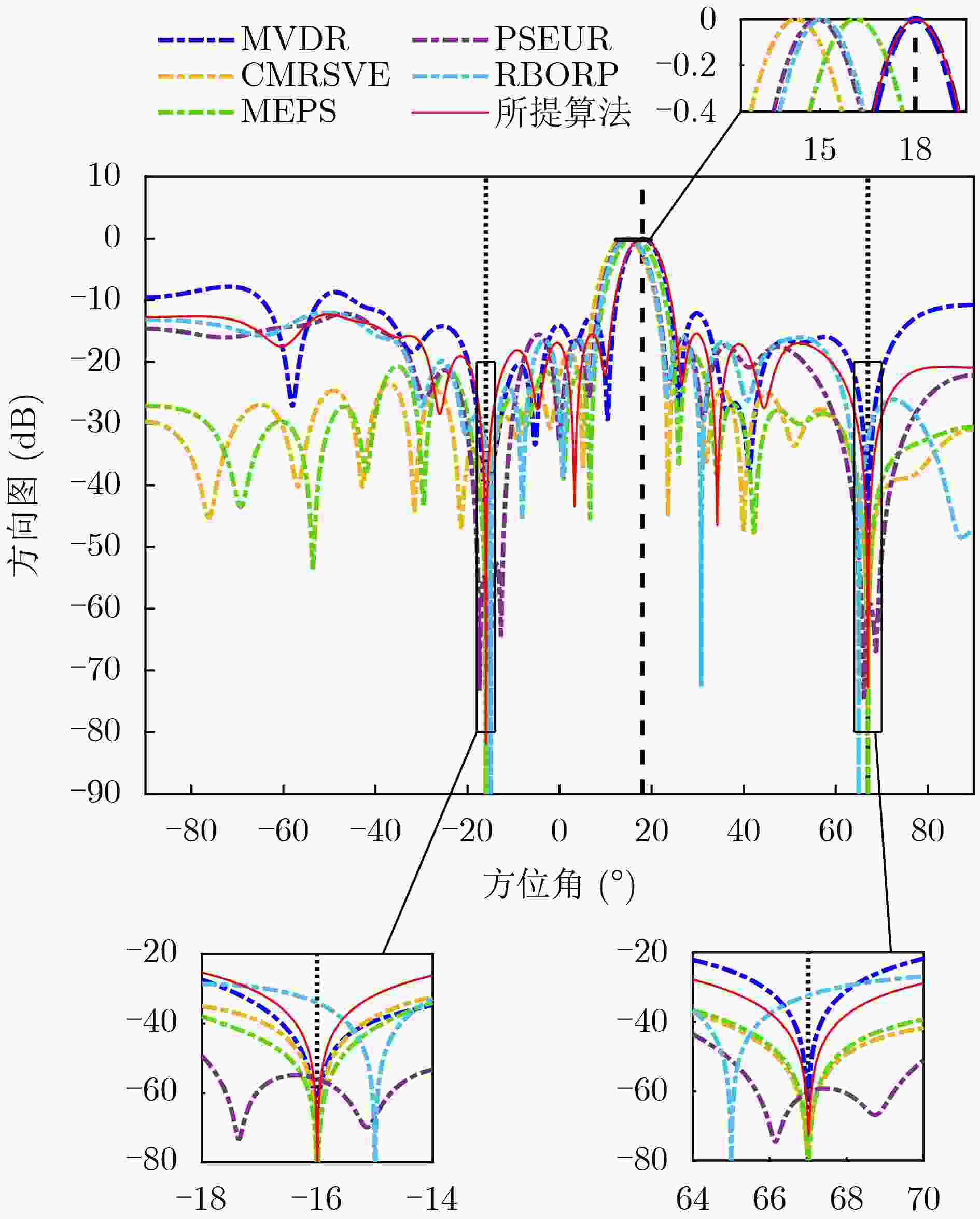
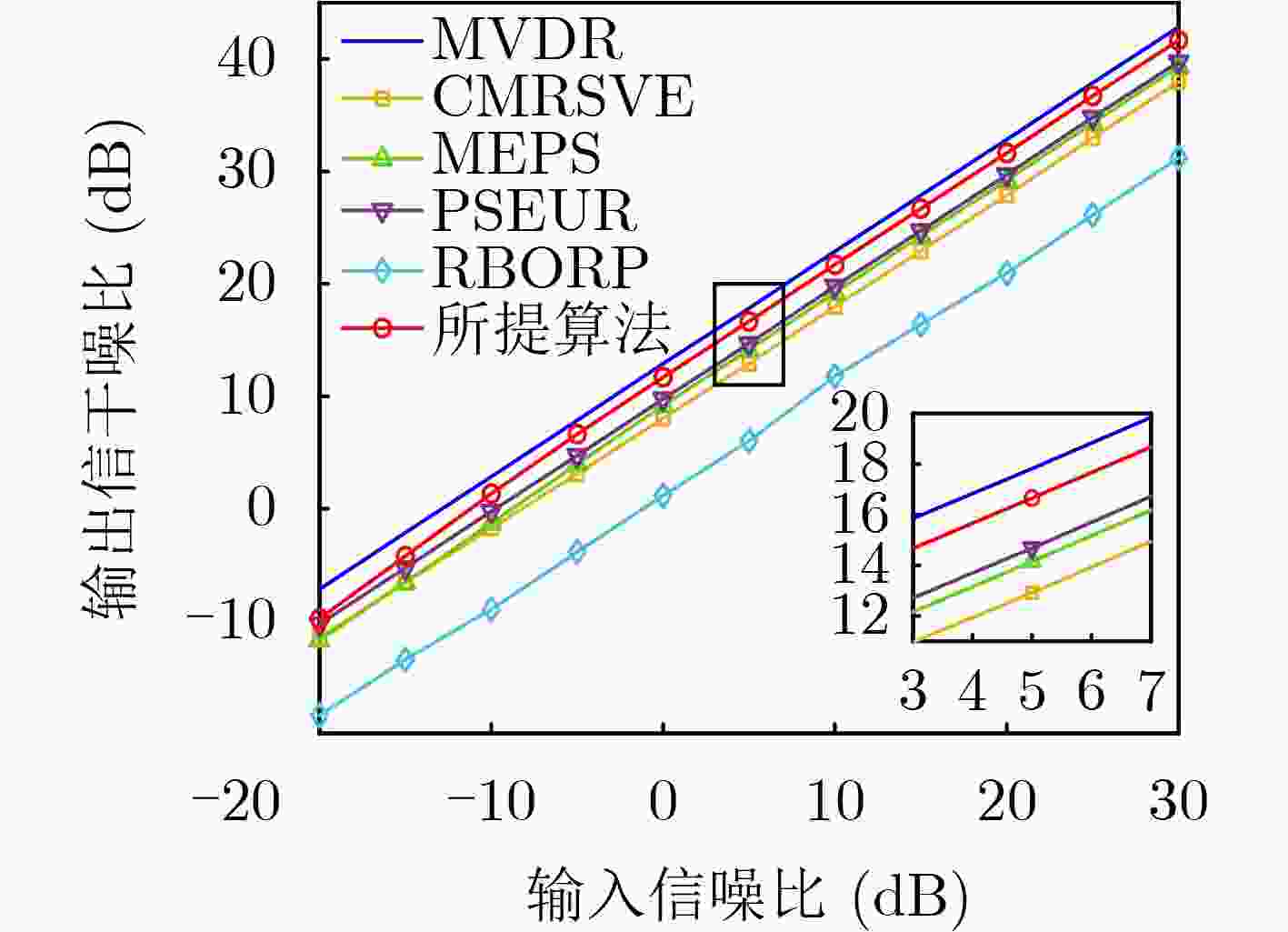
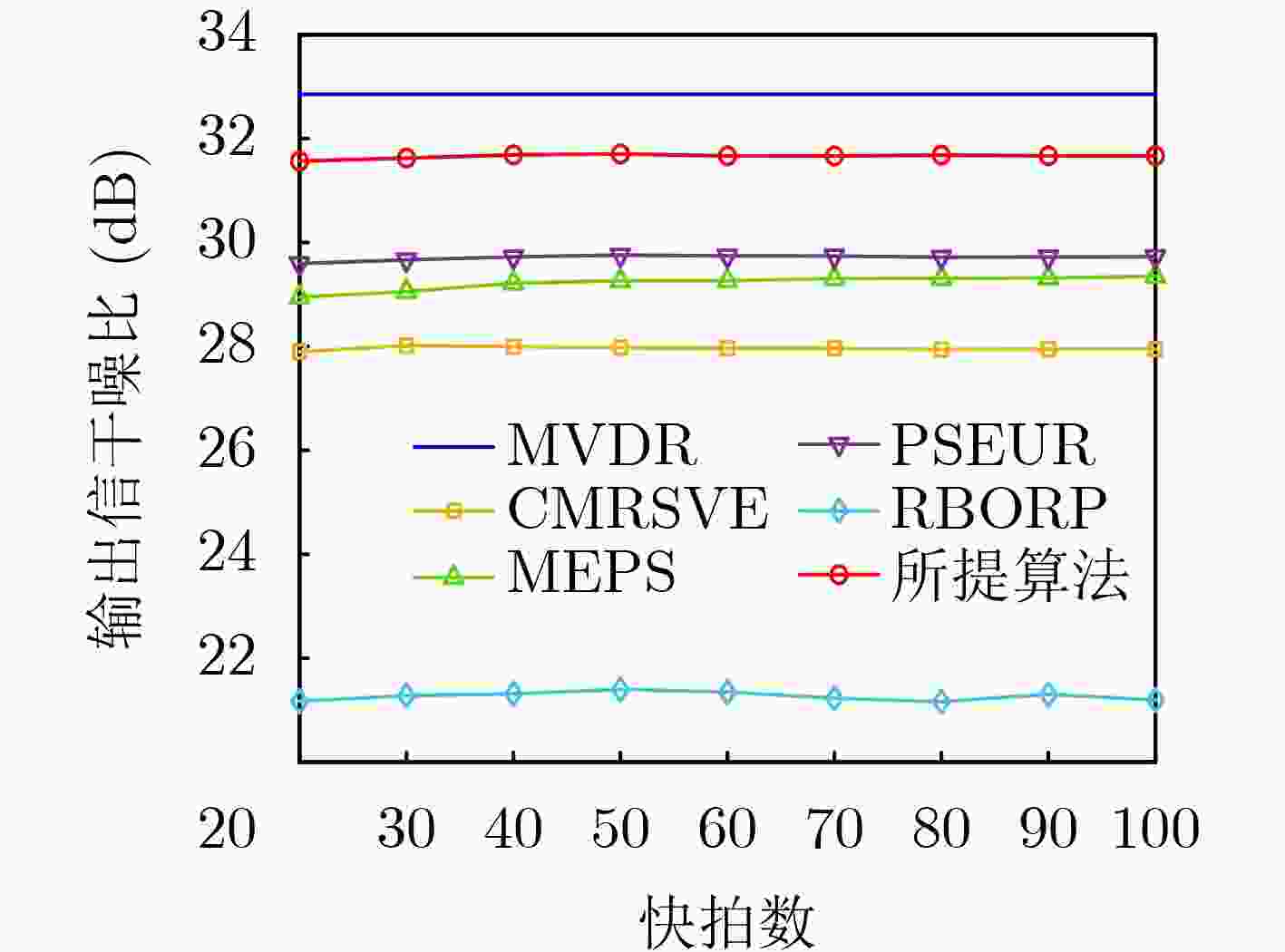
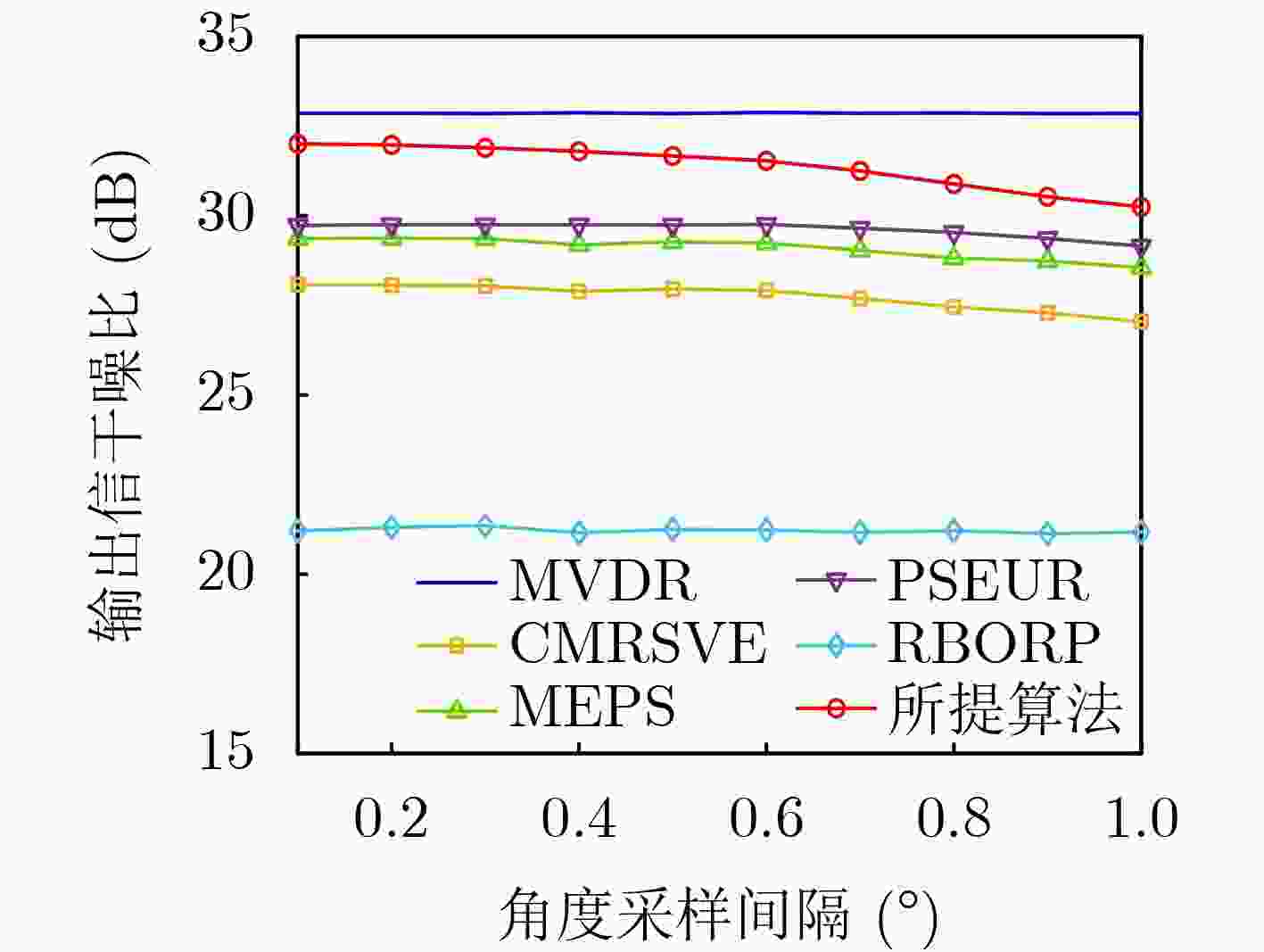
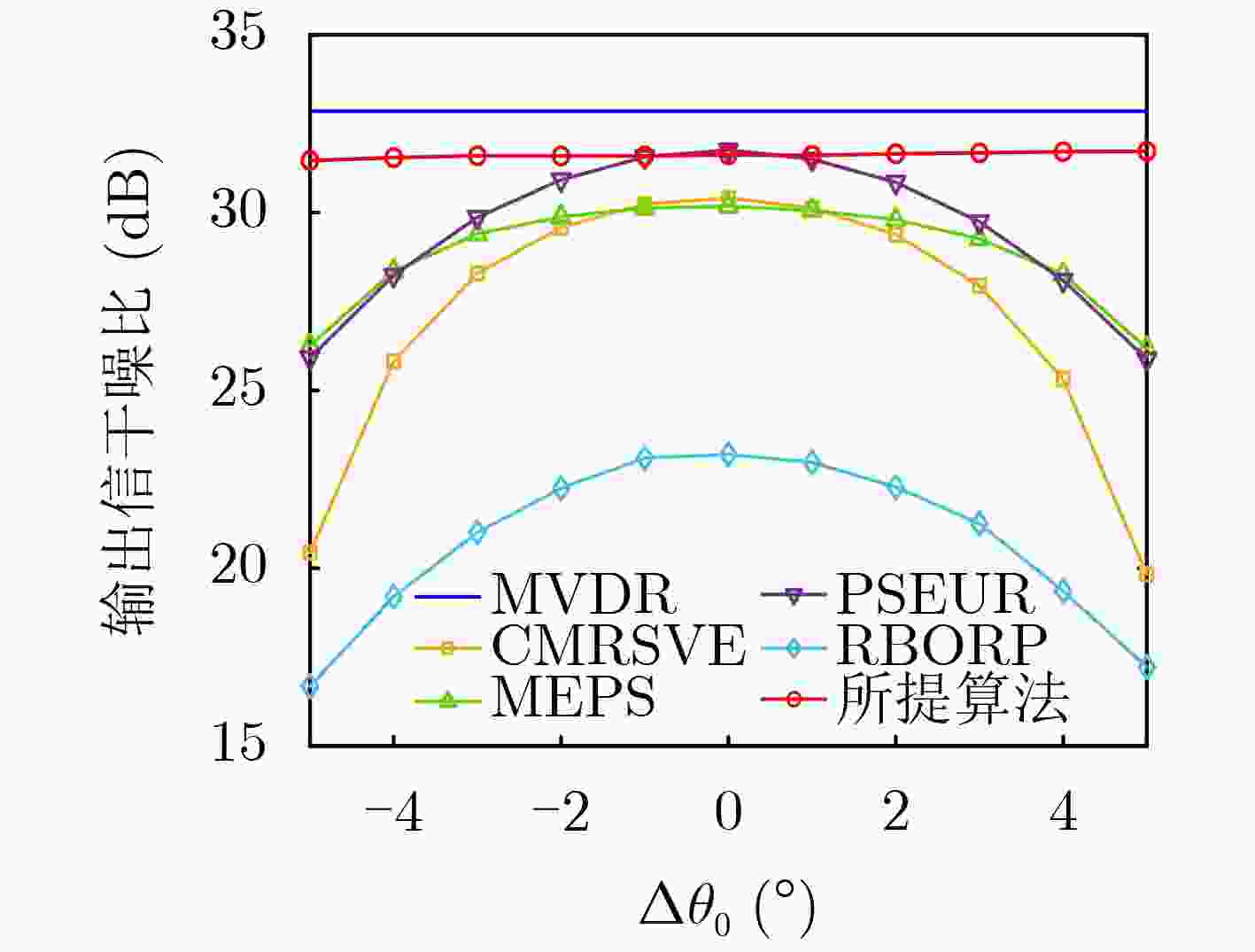
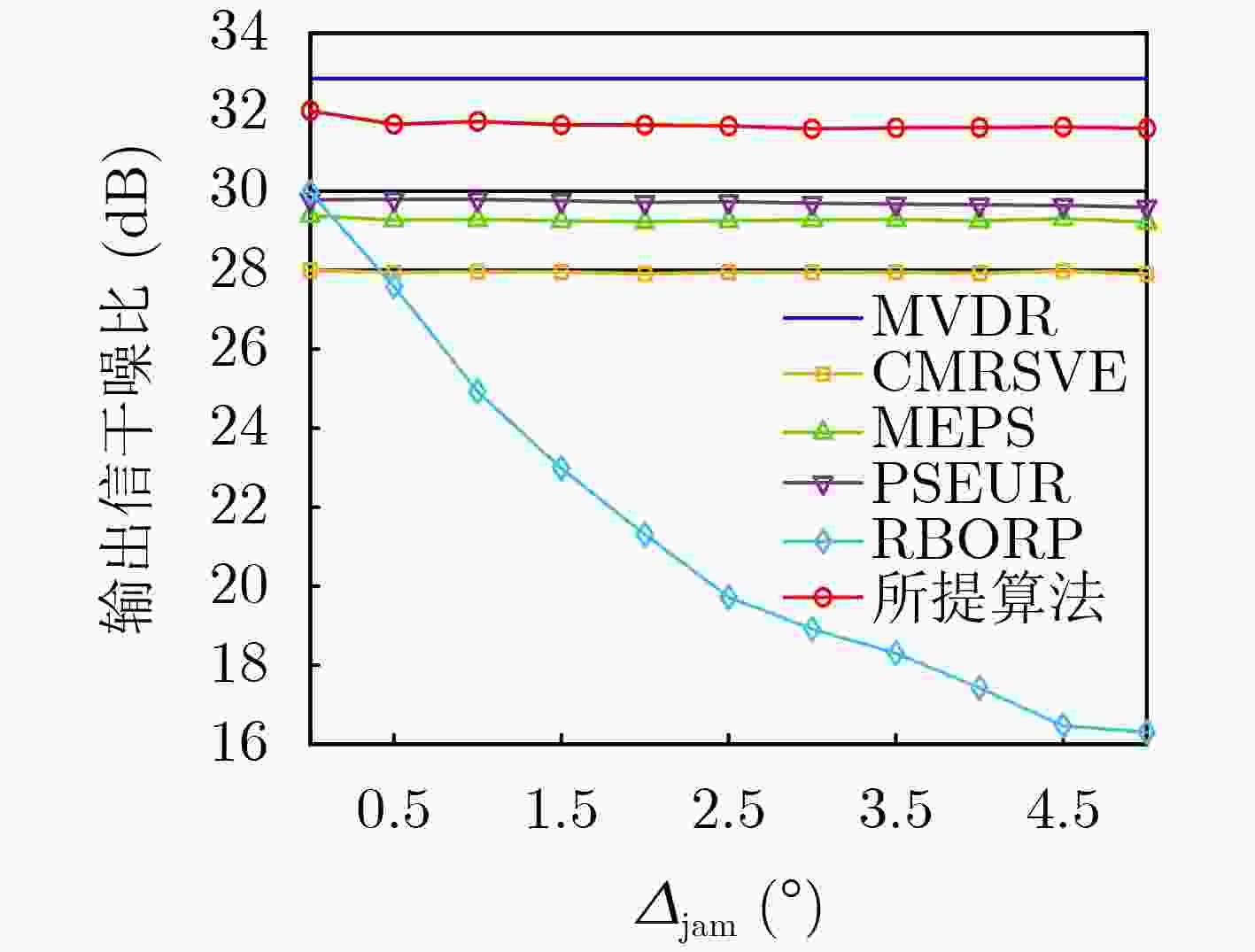
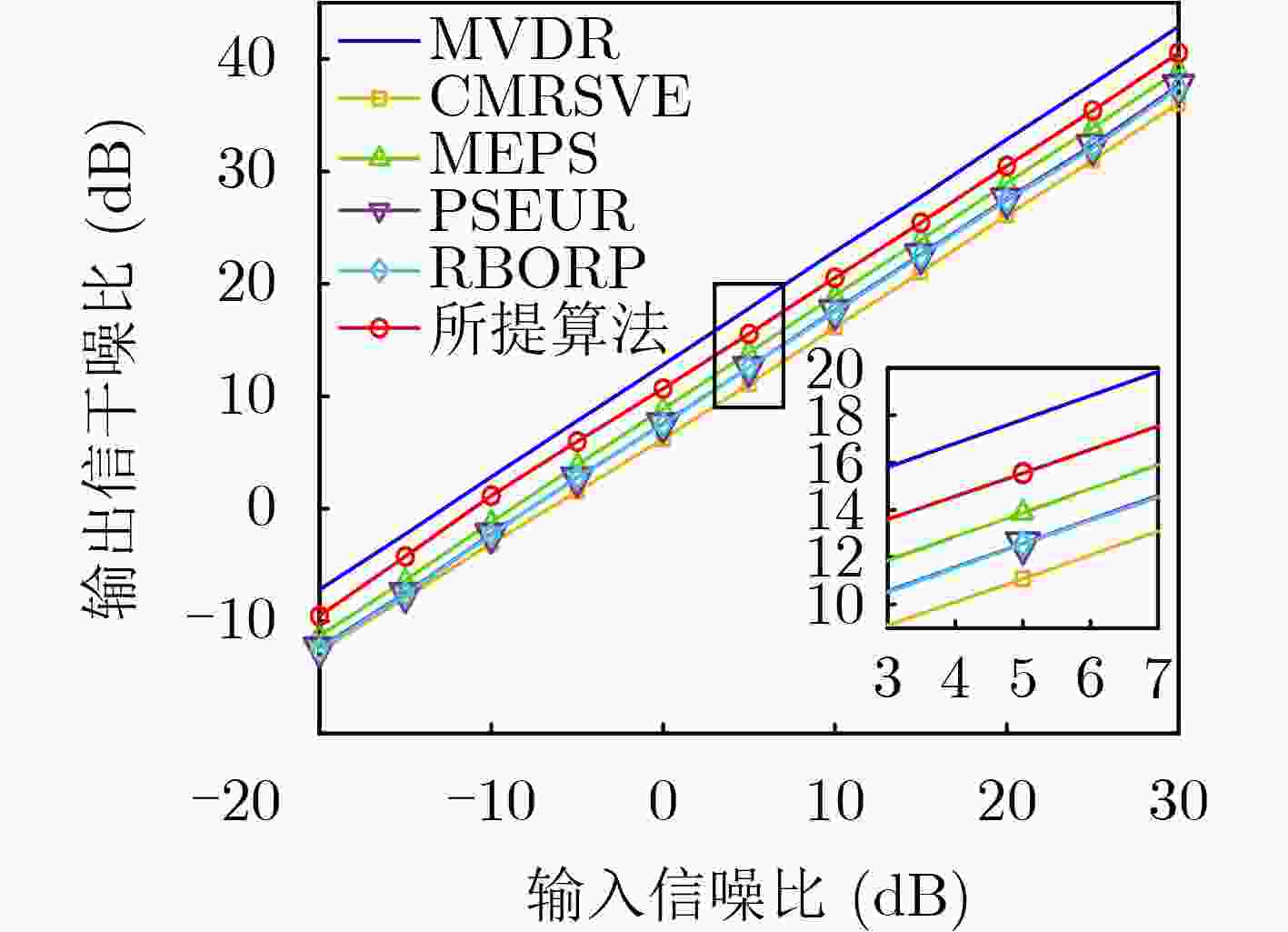
Objective In practical applications, the spatial anti-jamming performance of adaptive beamformers is often degraded by mismatches in the Directions Of Arrival (DOAs) of signals. Some robust adaptive beamforming algorithms reduce the error between the estimated signal steering vector and the actual steering vector by solving a Quadratic Constrained Quadratic Programming (QCQP) problem. This strategy significantly increases hardware cost. In addition, traditional adaptive beamforming algorithms often exhibit beampattern distortion under non-ideal conditions, such as DOA mismatch. The objective of this paper is to design a robust adaptive beamformer that effectively suppresses jamming signals under different mismatch scenarios. Methods A robust adaptive beamforming algorithm for spatial anti-jamming is proposed. First, the actual output Signal-to-Jamming-plus-Noise Ratio (SJNR) in the presence of DOA mismatch is analyzed. An ideal beamformer based on orthogonal projection is then proposed to achieve accurate beampattern control and maximize the practical output SJNR. To improve anti-jamming robustness in mismatch environments, the signal steering vector is estimated through covariance matrix construction and dominant eigenvector extraction. The beamforming weight vector is obtained by constructing an orthogonal projection matrix. Results and Discussions The proposed adaptive beamforming algorithm effectively suppresses jamming signals in mismatch environments. Numerical results show that the algorithm achieves good spatial anti-jamming performance in an ideal scenario without mismatch ( Fig. 3 ) and in a scenario with steering vector mismatch (Fig. 4 ). In DOA mismatch scenarios, the proposed algorithm demonstrates superior beampattern performance (Fig. 5 ,Fig. 6 ) and output SJNR performance (Fig. 7 ,Fig. 8 ,Fig. 9 ). The results also indicate stronger robustness to DOA mismatch (Fig. 10 ,Fig. 11 ). Effective jamming suppression is maintained even when the incoming directions of the jamming signals are closely spaced (Fig. 12 ).Conclusions This paper proposes a robust adaptive beamforming algorithm for suppressing power suppressive jamming signals. An ideal beamformer is first developed to achieve precise beampattern control and maximize the actual output SJNR. A robust adaptive beamforming algorithm is then constructed through covariance matrix construction, dominant eigenvector extraction, and orthogonal projection. Numerical results show that the proposed algorithm provides strong spatial anti-jamming performance in ideal scenarios without mismatch and in scenarios with DOA mismatch or steering vector mismatch. -
1 基于主特征向量提取与正交投影的稳健自适应波束成形算法
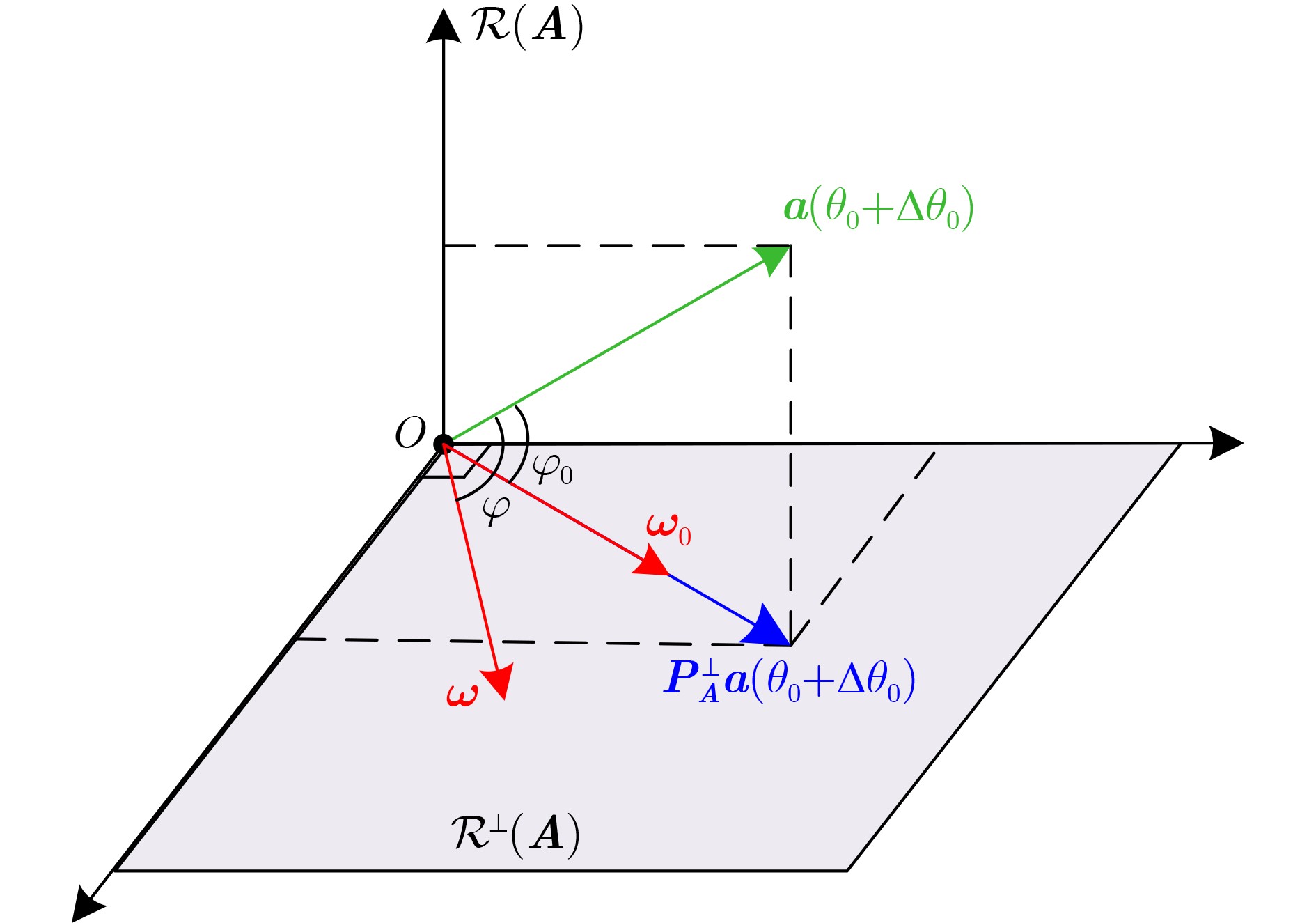
输入:接收端阵列采样数据$ \{\boldsymbol{x}(k)\}_{k=1}^{K} $ 1:得到采样协方差矩阵$ \hat{\boldsymbol{R}}=(1\text{/}K)\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{k=1}^{K}\boldsymbol{x}(k){\boldsymbol{x}}^{\mathrm{H}}(k) $; 2:在干扰信号角扇区$ {\varTheta }_{\text{jam}} $内进行Capon功率谱积分构造矩阵
$ {\overline{\boldsymbol{R}}}_{\mathrm{jam}} $;3:对矩阵$ {\overline{\boldsymbol{R}}}_{\mathrm{jam}} $进行特征值分解$ {\overline{\boldsymbol{R}}}_{\mathrm{jam}}=\boldsymbol{U}{{\boldsymbol{\varLambda}} }{\boldsymbol{U}}^{\mathrm{H}} $; 4:计算参数$ {T}_{0} $,并构造矩阵
$ \boldsymbol{G}=[{\boldsymbol{u}}_{1},{\boldsymbol{u}}_{2},\cdots ,{\boldsymbol{u}}_{{{T}_{0}}}] $;5:得到正交投影矩阵$ \boldsymbol{P}_{\boldsymbol{G}}^{\bot }=\boldsymbol{I}-\boldsymbol{G}{({{\boldsymbol{G}}^{\mathrm{H}}}\boldsymbol{G})}^{-1}{\boldsymbol{G}}^{\mathrm{H}} $; 6:在期望信号角扇区$ {\varTheta }_{\text{s}} $内进行Capon功率谱积分构造矩阵$ \tilde{\boldsymbol{R}} $; 7:对矩阵$ \tilde{\boldsymbol{R}} $进行特征值分解$ \tilde{\boldsymbol{R}}=\boldsymbol{V}\boldsymbol{Z}{\boldsymbol{V}}^{\mathrm{H}} $,并估计期望信号导
向矢量$ \hat{\boldsymbol{a}}({\theta }_{0})=\sqrt{M}{\boldsymbol{v}}_{1} $;8:得到所提波束成形器$ {\boldsymbol{w}}_{\text{prop}}=\boldsymbol{P}_{\boldsymbol{G}}^{\bot }\hat{\boldsymbol{a}}({\theta }_{0}) $; 表 1 线性阵列的阵元位置分布表
m $ {z}_{m}/\varepsilon $ m $ {z}_{m}/\varepsilon $ m $ {z}_{m}/\varepsilon $ m $ {z}_{m}/\varepsilon $ 1 0 5 2.35 9 4.04 13 5.75 2 0.45 6 2.67 10 4.48 14 6.24 3 1.18 7 3.35 11 4.76 15 6.57 4 1.73 8 3.71 12 5.48 16 7.25 -
[1] CAI Lingyi, WANG Jiacheng, ZHANG Ruichen, et al. Secure physical layer communications for low-altitude economy networking: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2026, 28: 2497–2530. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2025.3634768. [2] 张君彪, 吴静, 赵飞, 等. 俄乌冲突中无人机作战运用情况及启示[J]. 现代防御技术, 2025, 53(6): 37–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2025.06.005.ZHANG Junbiao, WU Jing, ZHAO Fei, et al. Application and enlightenment of UAV in the Russia-Ukraine conflict[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2025, 53(6): 37–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2025.06.005. [3] 范旭慧, 王宇翼, 王安义, 等. 鲁棒自适应稀疏阵列波束形成[J]. 电子与信息学报. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250952.FAN Xuhui, WANG Yuyi, WANG Anyi, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming for sparse arrays[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250952. [4] 李振东, 巴建乐, 苏洲, 等. 可移动天线赋能的ISAC系统中波束赋形与天线位置联合优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(10): 3482–3491. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250146.LI Zhendong, BA Jianle, SU Zhou, et al. Joint beamforming and antenna position optimization in movable antenna empowered ISAC systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(10): 3482–3491. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250146. [5] 邓志祥, 张志威. 近场ISAC多用户安全通信波束设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(11): 4166–4175. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250462.DENG Zhixiang and ZHANG Zhiwei. Secure beamforming design for multi-user near-field ISAC systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(11): 4166–4175. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250462. [6] CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278. [7] LI Jian, STOICA P, and WANG Zhisong. On robust capon beamforming and diagonal loading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2003, 51(7): 1702–1715. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2003.812831. [8] VOROBYOV S A, GERSHMAN A B, and LUO Zhiquan. Robust adaptive beamforming using worst-case performance optimization: A solution to the signal mismatch problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2003, 51(2): 313–324. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2002.806865. [9] NAI S E, SER W, YU Zhuliang, et al. Iterative robust minimum variance beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(4): 1601–1611. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2096222. [10] YANG Feixue, REN Wen, ZHANG Zhenyu, et al. Diagonal loading method with small snapshot number and steering vector errors[C]. 2024 7th International Conference on Information Communication and Signal Processing, Zhoushan, China, 2024: 206–210. doi: 10.1109/ICICSP62589.2024.10809253. [11] DU Lin, LI Jian, and STOICA P. Fully automatic computation of diagonal loading levels for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(1): 449–458. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5417174. [12] ZHANG Ming, CHEN Xiaoming, and ZHANG Anxue. A simple tridiagonal loading method for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 157: 103–107. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.11.019. [13] ZHOU Chengwei, GU Yujie, HE Shibo, et al. A robust and efficient algorithm for coprime array adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 1099–1112. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2704610. [14] LAN Zhengfeng, ZHENG Chichao, WANG Yuanguo, et al. Adaptive threshold for eigenspace-based minimum variance beamformer for dark region artifacts elimination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 4507516. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3127627. [15] YANG Jian, TU Yuwei, LU Jian, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming based on subspace decomposition, steering vector estimation and correction[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(12): 12260–12268. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3174848. [16] CHEN Peng, YANG Yixin, WANG Yong, et al. Adaptive beamforming with sensor position errors using covariance matrix construction based on subspace bases transition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(1): 19–23. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2878948. [17] HUANG Fei, SHENG Weixing, and MA Xiaofeng. Modified projection approach for robust adaptive array beamforming[J]. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(7): 1758–1763. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.01.015. [18] GU Yujie and LESHEM A. Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix reconstruction and steering vector estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(7): 3881–3885. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2194289. [19] RUAN Hang and DE LAMARE R C. Robust adaptive beamforming using a low-complexity shrinkage-based mismatch estimation algorithm[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2014, 21(1): 60–64. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2013.2290948. [20] RUAN Hang and DE LAMARE R C. Robust adaptive beamforming based on low-rank and cross-correlation techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(15): 3919–3932. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2550006. [21] ZHANG Zhenyu, LIU Wei, LENG Wen, et al. Interference-plus-noise covariance matrix reconstruction via spatial power spectrum sampling for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(1): 121–125. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2504954. [22] HUANG Lei, ZHANG Jing, XU Xu, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming with a novel interference-plus-noise covariance matrix reconstruction method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(7): 1643–1650. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2396002. [23] MOHAMMADZADEH S, NASCIMENTO V H, DE LAMARE R C, et al. Maximum entropy-based interference-plus-noise covariance matrix reconstruction for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 845–849. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2994527. [24] ZHENG Zhi, ZHENG Yan, WANG Wenqin, et al. Covariance matrix reconstruction with interference steering vector and power estimation for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(9): 8495–8503. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2849646. [25] ZHENG Zhi, YANG Tong, WANG Wenqin, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming via simplified interference power estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3139–3152. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2899796. [26] MOHAMMADZADEH S, NASCIMENTO V H, DE LAMARE R C, et al. Covariance matrix reconstruction based on power spectral estimation and uncertainty region for robust adaptive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 3848–3858. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3232100. [27] 吕岩, 曹菲, 杨剑, 等. 基于导向矢量双层估计和协方差矩阵重构的稳健波束形成算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(12): 4159–4167. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211120.LÜ Yan, CAO Fei, YANG Jian, et al. Robust beamforming algorithm based on double-layer estimation of steering vector and covariance matrix reconstruction[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(12): 4159–4167. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211120. [28] LIU Yiyuan, WANG Jinlong, ZHANG Xiaokai, et al. Spatial anti-jamming based on low complexity robust beamforming via orthogonal projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(8): 13190–13195. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3553109. [29] ZHANG Xuejing, HE Zishu, LIAO Bin, et al. A2RC: An accurate array response control algorithm for pattern synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(7): 1810–1824. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2649487. [30] ZHOU Yuehai, WANG Rong, YANG Xiaoyu, et al. Orthogonal projection and distributed compressed sensing-based impulsive noise estimation for underwater acoustic OSDM communication[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(24): 22279–22293. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3303182. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
