Reconfigurable Intelligence Surface Assisted Key Generation Resistant to Signal Injection Attacks
-
摘要: 针对智能超表面(Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces, RIS)辅助下的密钥生成技术,从攻击与防御双视角开展研究。首先,基于攻击方视角提出了一种改进的联合密钥推测攻击策略,主动窃听者可结合注入信号和信道空间相关性进行联合密钥推测,显著加剧密钥生成过程的安全威胁;其次,从防御方视角提出了一种利用RIS随机化信道的抗注入式攻击密钥生成方案,合法用户通过调控RIS,在每个探测回合中主动随机化信道状态信息,迫使窃听者无法有效实施信号注入式攻击,从而降低密钥泄露风险并抑制密钥推测概率;进一步地;推导了该方案合法信道密钥容量和窃听信道密钥容量的理论表达式,定量分析了信噪比和窃听信道功率占比对合法信道密钥容量和窃听信道密钥容量的影响。仿真结果表明,相比现有方案,所提方案在克服准静态场景信道变化缓慢的基础上,提升了密钥生成系统的安全性。即使窃听者增大注入信号功率,窃听信道的密钥容量也呈现基本不变的趋势,有效抵御了信号注入式攻击的威胁。Abstract:
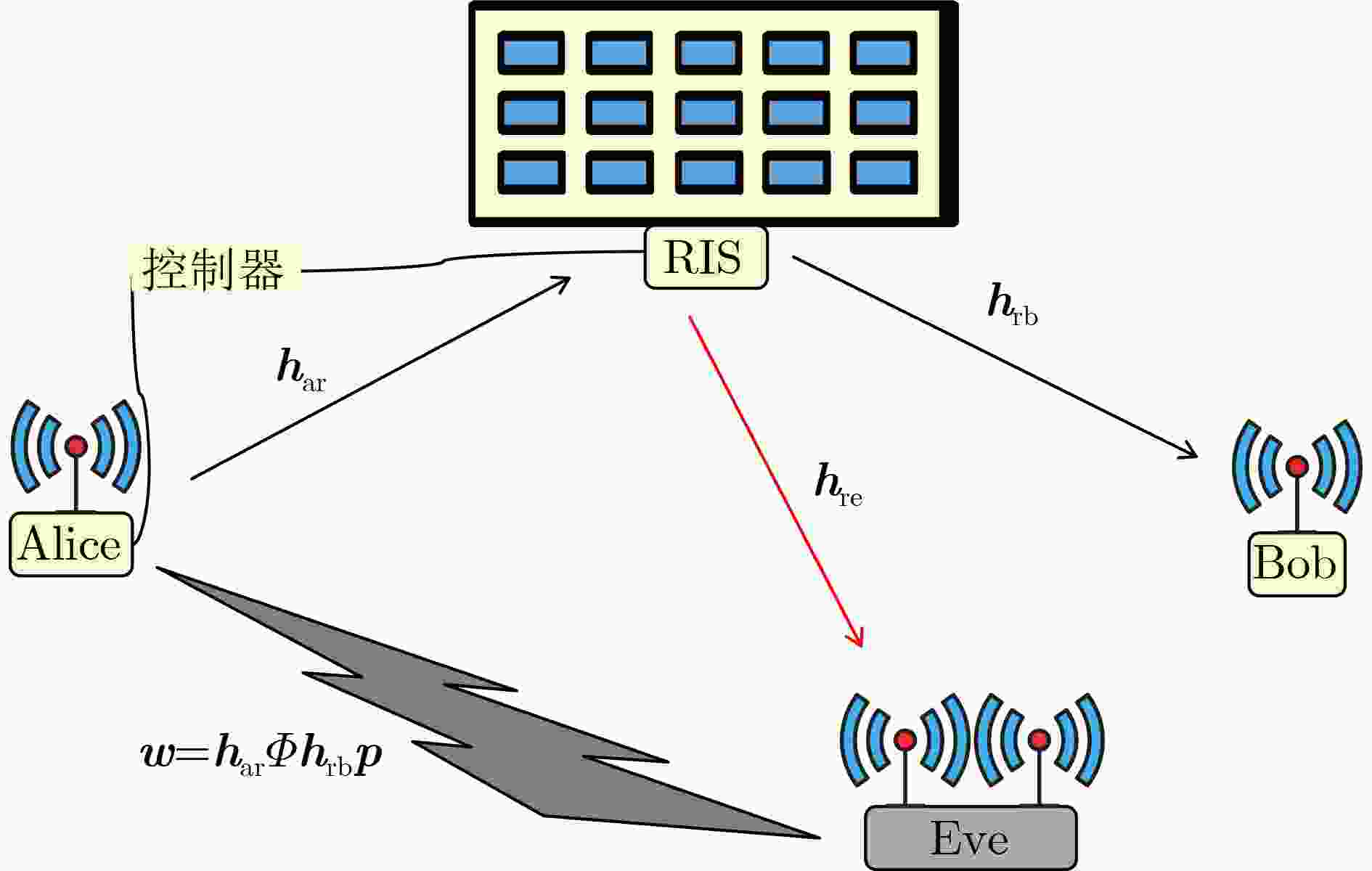
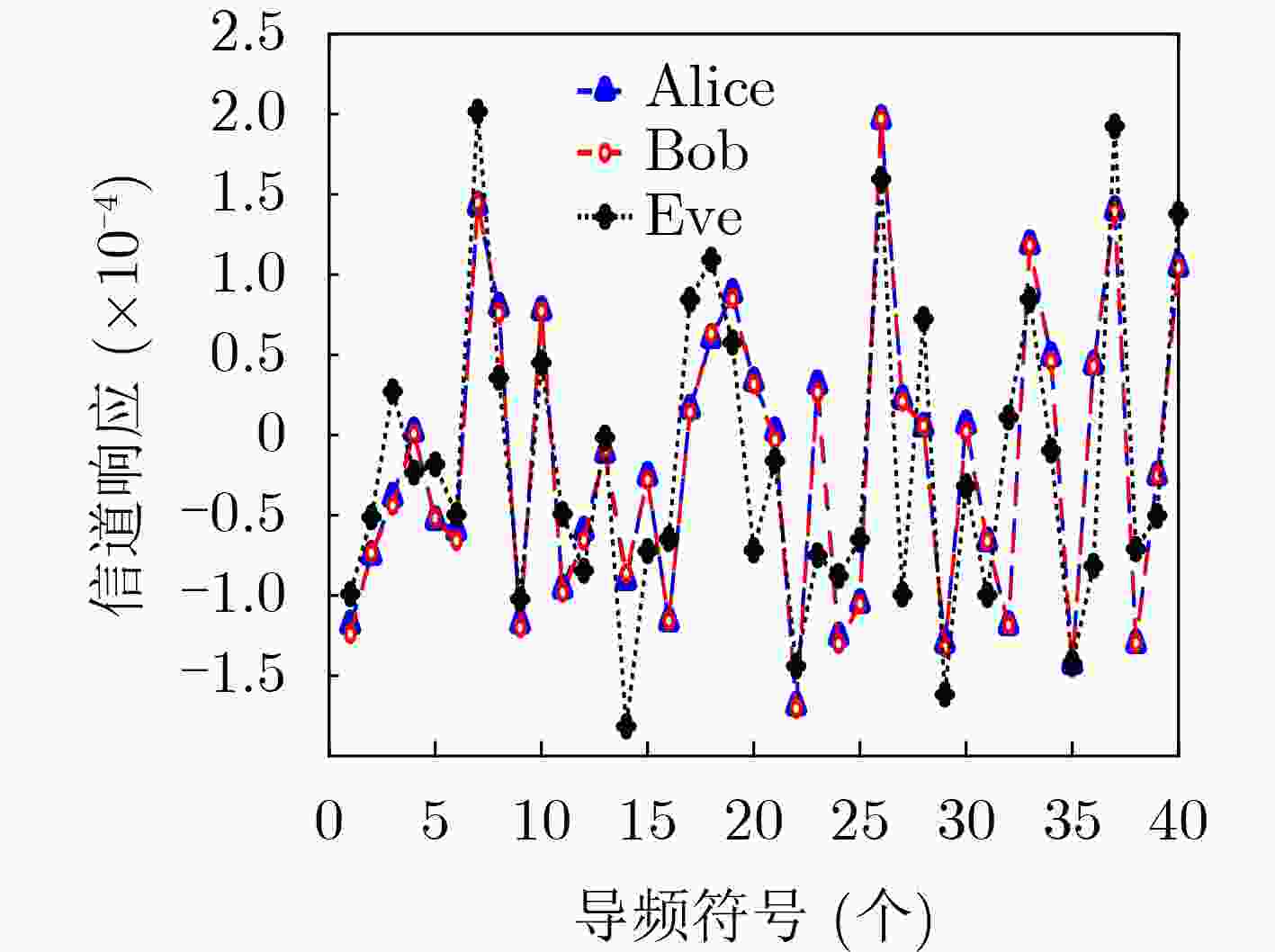
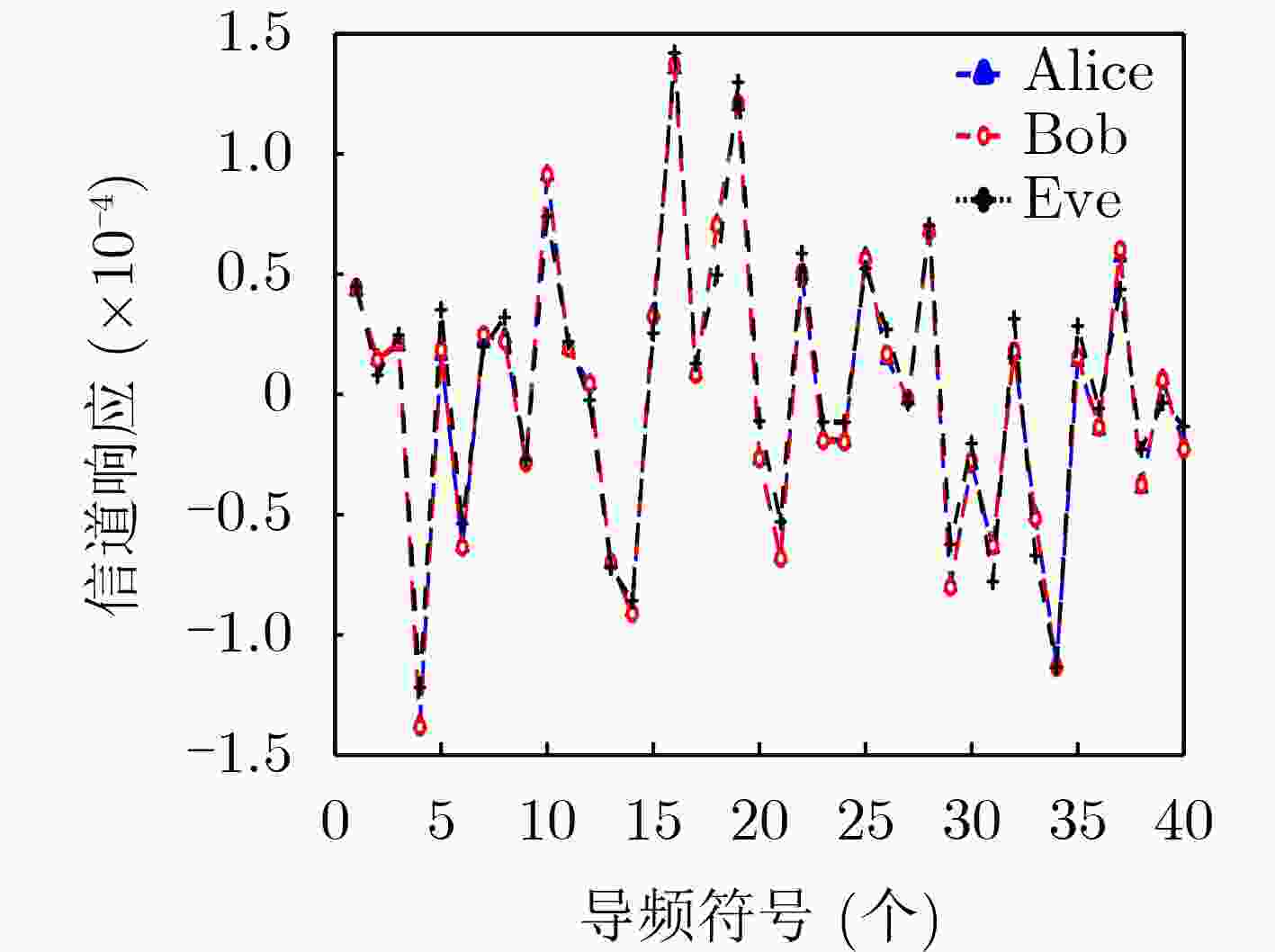
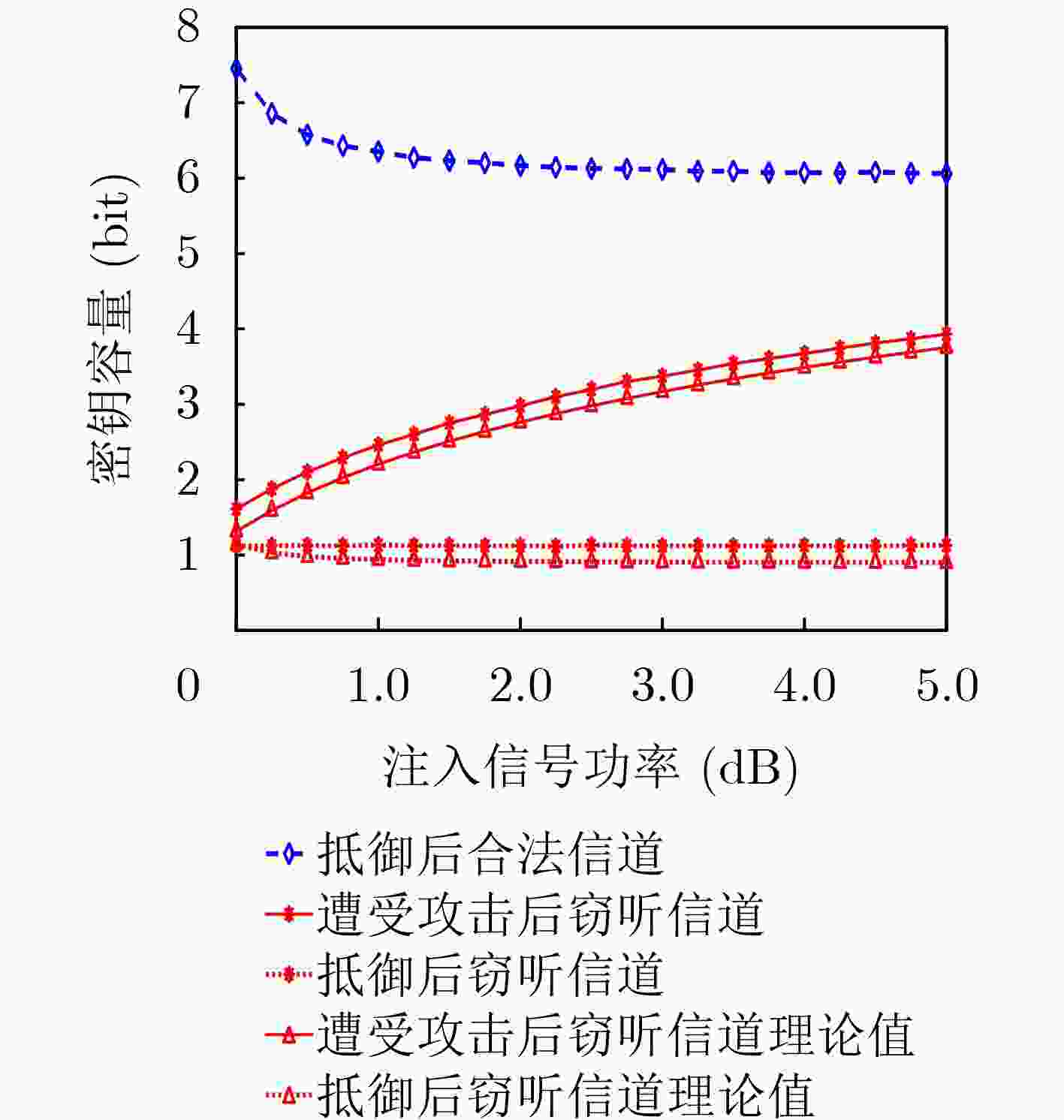
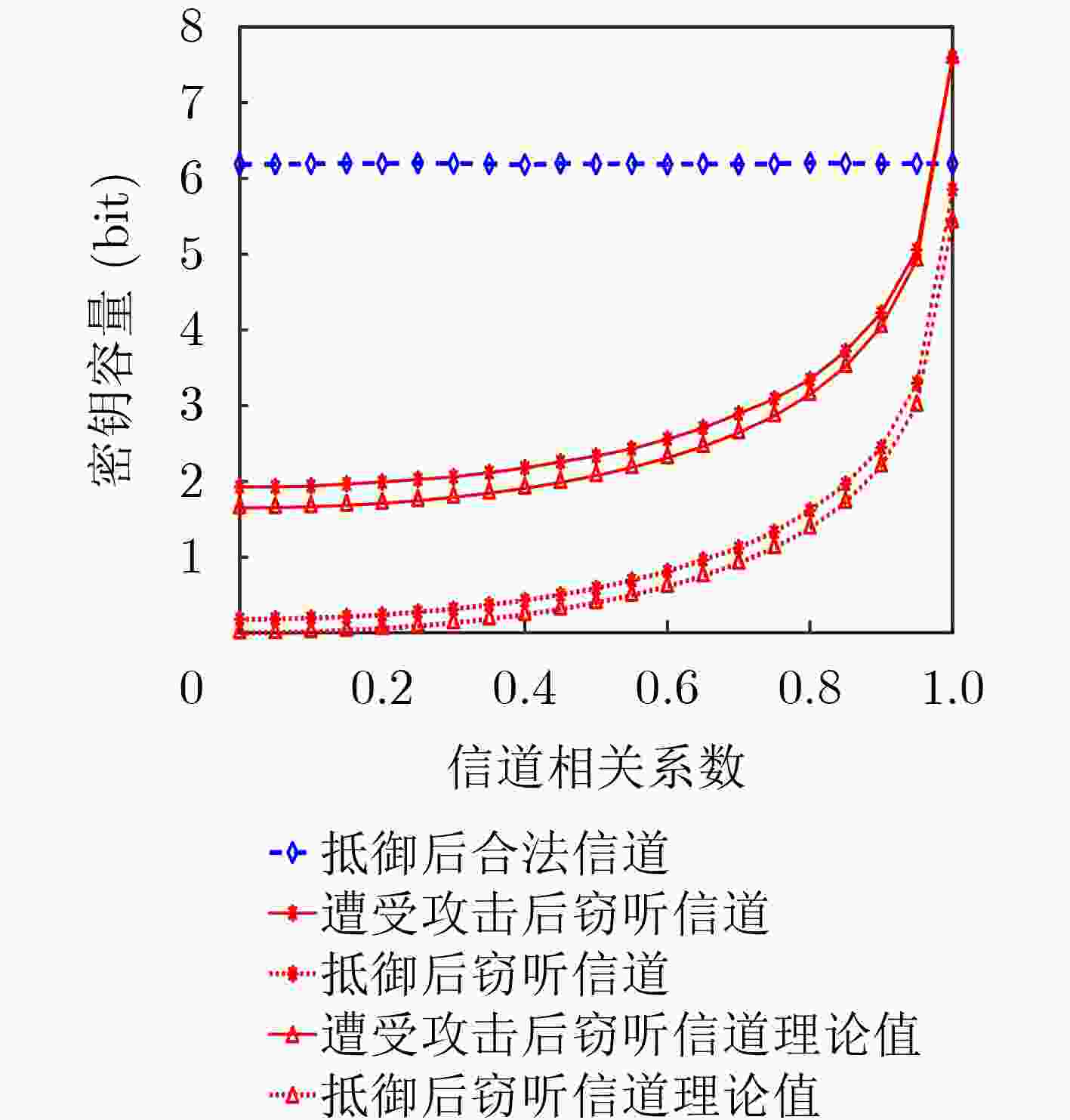
Objective This work investigates the potential threat of signal injection attacks to physical layer key generation (PLKG) in reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-assisted wireless systems, which can be particularly impactful in quasi-static channels where the channel state remains highly correlated across multiple probing rounds. From both attack and defense perspectives, the study clarifies how the spatial correlation between RIS reflection channels and eavesdropping channels may be exploited to enhance key inference, and designs a channel-randomization mechanism that leverages the controllability of RIS to suppress key leakage, reduce the eavesdropper’s key capacity, and improve the security of RIS-assisted PLKG for future 6G scenarios. It further provides quantitative insights into the interplay among injection power, SNR, and spatial correlation, which may serve as a useful reference for future studies on robust RIS configuration and secure system design in practice. Methods A RIS-assisted TDD system is considered where single-antenna Alice and Bob generate symmetric keys from a reciprocal channel, while a two-antenna active eavesdropper Eve injects signals using previously observed CSI ( Fig. 1 ). The links follow quasi-static Rayleigh block fading, and CSI for Alice/Bob/Eve is specified per time slot in a coherence interval. We model a conventional injection attack in which Eve estimates the eavesdropping channel in one slot, precodes an injected waveform, and contaminates the next probing at Alice and Bob, partly steering their key source. We then present a joint key-inference strategy that exploits spatial correlation between RIS reflection and eavesdropping channels and the common RIS-induced subchannel shared by legitimate and eavesdropping links (Table 1 ). As a defense, we propose channel-randomization PLKG: Alice randomly reconfigures RIS coefficients at each probing round so the Alice–Bob, Alice–Eve, and Bob–Eve effective channels vary independently across rounds while Alice–Bob reciprocity within a round remains. Eve’s injection, precoded with outdated CSI, then appears as uncorrelated interference. We derive mutual-information-based bounds on secret-key capacity to obtain key capacities, define Eve’s key recovery rate (KRR), and validate results via 10,000-trial MATLAB Monte Carlo simulations using an information-theoretic estimator toolbox under varying SNR, injection power, and spatial correlation (Figs. 2 –5 ,Table 2 ).Results and Discussions Analysis of the conventional injection attack without RIS defense shows that at high SNR, due to channel reciprocity, Alice and Bob observe nearly identical reciprocal channels, while Eve’s injected-signal-based estimate follows a similar trend with noticeable mismatch ( Fig. 2 ). Thus, Eve recovers some key bits but with notable errors and only still moderate KRR. With the proposed joint key inference strategy, Eve’s reconstructed channel matches the legitimate response more closely (Fig. 3 ), since RIS-assisted PLKG causes legitimate and eavesdropping links to share an RIS-induced subchannel, introducing exploitable spatial correlation beyond the known injected signal; consequently, Eve’s key capacity and KRR increase significantly, further highlighting a stronger RIS-specific threat. At fixed SNR (Fig. 4 ), Eve’s key capacity without defense rises rapidly with injection power and can approach or exceed the legitimate capacity, whereas under RIS randomization the legitimate capacity degrades slightly and Eve’s remains small and nearly constant, indicating that randomization converts structured injection into noise. Spatial-correlation results inFig. 5 show that Eve’s capacity without defense grows quickly and becomes critical near correlation one, while with RIS randomization it increases slowly and can be near zero at moderate correlation.Table 2 further confirms these trends in KRR: about 50% with no correlation and no injection; about 62.5% with injection but zero correlation while defense stays near random; and over 80% with higher correlation and injection, reduced to roughly 57%–66% by the defense.Conclusions The study investigates the dual role of RIS in PLKG security, showing that RIS can act both as a vulnerability amplifier and as a defensive tool. By exploiting the correlation between RIS reflection channels and eavesdropping channels, an improved joint key inference attack is developed, which increases the eavesdropper’s key capacity and recovery rate compared with conventional injection attacks, thus revealing a new attack vector for RIS-assisted systems. By harnessing the dynamic controllability of RIS, a channel-randomization PLKG scheme is then proposed, in which RIS is used to shorten the effective coherence time to a single probing round and to decorrelate successive channel realizations from the attacker’s perspective. Theoretical derivations and Monte Carlo simulations demonstrate that this defense scheme transforms malicious injection signals into uncorrelated interference, reduces the eavesdropping key capacity, and pushes the eavesdropper’s KRR close to that of random guessing, even under high SNR, strong spatial correlation, and large injection power. The proposed mechanism achieves these security enhancements with low hardware overhead compared with reconfigurable antenna-based solutions, since RISs are already envisioned as key infrastructure elements in 6G networks. The insights gained from this work provide guidelines for the secure design of RIS-assisted PLKG, suggesting that the controllable nature of RIS should further effectively be exploited for both performance enhancement and security hardening. -
表 1 信号注入式攻击时隙分配对比
攻击方案 相干时间 Eve操作 是否进行密钥推测 推测依据 信号注入式攻击 时隙$ t $ 观测窃听信道 否 无 时隙$ t+1 $ 进行信号注入 是 注入信号 本文方案 时隙$ t $ 观测窃听信道 是 窃听信道 时隙$ t+1 $ 进行信号注入 是 窃听信道+注入信号 表 2 不同条件下的密钥恢复率
随机密钥推测 经典密钥推测 改进联合推测 RIS抵御联合推测 $ \rho =0 $;$ {P}_{\text{E}}=0 $(%) 0.4999 0.4995 0.5027 0.4996 $ \rho =0 $;$ {P}_{\text{E}}=1 $ (%) 0.5010 0.6250 0.6256 0.5009 $ \rho =0.4 $;$ {P}_{\text{E}}=5 $(%) 0.4986 0.6816 0.7462 0.5746 $ \rho =0.8 $;$ {P}_{\text{E}}=10 $(%) 0.4996 0.7152 0.8485 0.6573 -
[1] 杨立君, 陈子硕, 陆海涛, 等. RIS辅助通信场景中一种基于展开信道的物理层密钥生成方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(2): 449–457. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240988.YANG Lijun, CHEN Zishuo, LU Haitao, et al. An unfolded channel-based physical layer key generation method for reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted communication systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(2): 449–457. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240988. [2] 杨立君, 孔文杰, 陆海涛, 等. 原子空间稀疏分解驱动的RIS辅助毫米波MIMO系统密钥生成机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(4): 1066–1075. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240885.YANG Lijun, KONG Wenjie, LU Haitao, et al. A key generation method based on atomic norm minimization for reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted millimeter wave MIMO communication systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(4): 1066–1075. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240885. [3] KAPETANOVIC D, ZHENG Gan, and RUSEK F. Physical layer security for massive MIMO: An overview on passive eavesdropping and active attacks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2015, 53(6): 21–27. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2015.7120012. [4] JAKES W C and COX D C. Microwave Mobile Communications[M]. New York: Wiley-IEEE Press, 1994: 60–65. (查阅网上资料, 出版地信息不确定, 请确认). [5] LI Guyue, STAAT P, LI Haoyu, et al. RIS-jamming: Breaking key consistency in channel reciprocity-based key generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 5090–5105. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2024.3389569. [6] LI Guyue, HU Lei, STAAT P, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface for physical layer key generation: Constructive or destructive?[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2022, 29(4): 146–153. doi: 10.1109/MWC.007.2100545. [7] WEI Zhuangkun, HU Wenxiu, ZHANG Junqing, et al. Explainable adversarial learning framework on physical layer key generation combating malicious reconfigurable intelligent surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025, 24(4): 3529–3545. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3531799. [8] PHAM T M, MITEV M, CHORTI A, et al. Pilot randomization to protect MIMO secret key generation systems against injection attacks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(7): 1234–1238. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3268714. [9] XIA Enjun, HU Binjie, and SHEN Qiaoqiao. Secret key generation with intelligent reflecting surface under the pilot contamination attack[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2024, 13(1): 213–217. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3325361. [10] TAN Haijun, LI Zhuoyuan, XIE Ning, et al. Detection of jamming attacks for the physical-layer authentication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(12): 9579–9594. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3272337. [11] EBERZ S, STROHMEIER M, WILHELM M, et al. A practical man-in-the-middle attack on signal-based key generation protocols[C]. 17th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, Pisa, Italy, 2012: 235–252. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33167-1_14. [12] JIN Rong and ZENG Kai. Physical layer key agreement under signal injection attacks[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), Florence, Italy, 2015: 254–262. doi: 10.1109/CNS.2015.7346835. [13] MITEV M, CHORTI A, BELMEGA E V, et al. Man-in-the-middle and denial of service attacks in wireless secret key generation[C]. 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM38437.2019.9013816. [14] MITEV M, CHORTI A, BELMEGA E V, et al. Protecting physical layer secret key generation from active attacks[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23(8): 960. doi: 10.3390/e23080960. [15] PAN Yanjun, XU Ziqi, LI Ming, et al. Man-in-the-middle attack resistant secret key generation via channel randomization[C]. The 22nd International Symposium on Theory, Algorithmic Foundations, and Protocol Design for Mobile Networks and Mobile Computing, Shanghai, China, 2021: 231–240. doi: 10.1145/3466772.3467052. [16] 唐杰, 文红, 宋欢欢, 等. 基于智能反射表面辅助的MIMO无线通信密钥快速生成[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(7): 2264–2272. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210442.TANG Jie, WEN Hong, SONG Huanhuan, et al. MIMO fast wireless secret key generation based on intelligent reflecting surface[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(7): 2264–2272. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210442. [17] YANG Lijun, ZHU Tiancheng, CHEN Zishuo, et al. Secret key generation assisted by reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for quasi-static channel[C]. 2023 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2023: 1856–1861. doi: 10.1109/GCWkshps58843.2023.10464734. [18] 马向进, 韩家奇, 乐舒瑶, 等. 可重构智能超表面设计及其无线通信系统应用[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2022, 48(2): 258–268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.02.008.MA Xiangjin, HAN Jiaqi, YUE Shuyao, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent metasurface design and applications in wireless communication systems[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2022, 48(2): 258–268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.02.008. [19] LI Guyue, SUN Chen, XU Wei, et al. On maximizing the sum secret key rate for reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted multiuser systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 211–225. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3138612. [20] MATHUR S, TRAPPE W, MANDAYAM N, et al. Radio-telepathy: Extracting a secret key from an unauthenticated wireless channel[C]. Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, San Francisco, USA, 2008: 128–139. doi: 10.1145/1409944.1409960. [21] THAI B N, TIEN T N, MINH K D, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: A hardware-centric review of structures, implementation, evaluation, and integration with UAV and machine learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 96564–96588. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3575583. [22] MAURER U M. Secret key agreement by public discussion from common information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1993, 39(3): 733–742. doi: 10.1109/18.256484. [23] ROTTENBERG F, NGUYEN T H, DRICOT J M, et al. CSI-based versus RSS-based secret-key generation under correlated eavesdropping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(3): 1868–1881. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3040434. [24] SZABÓ Z. Information theoretical estimators toolbox[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 283–287. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
