Adversarial Attacks on 3D Target Recognition Driven by Gradient Adaptive Adjustment
-
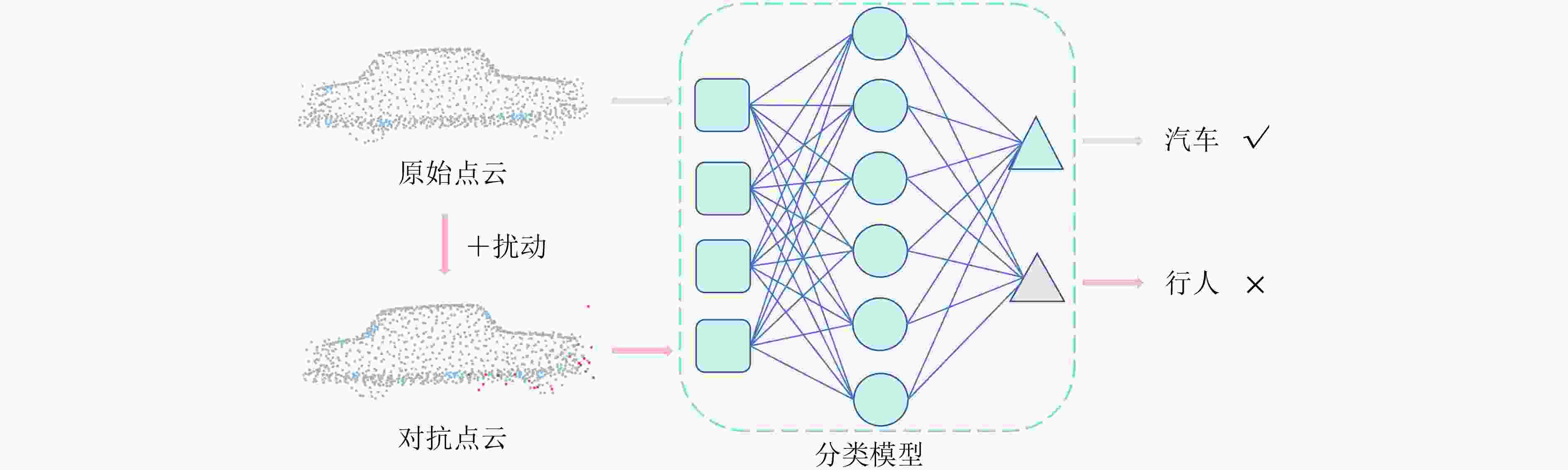
摘要: 人工智能与光电感知技术的深度融合,有力推动了智能驾驶的发展。激光雷达作为核心光电传感器,能够获取高精度三维点云,已成为环境感知不可或缺的数据来源。然而,基于深度学习的点云识别模型在对抗样本面前表现脆弱,易受微小扰动影响而导致识别性能显著下降,对智能驾驶光电感知系统的安全构成了严峻挑战。现有攻击方法虽能实现一定攻击效果,但往往扰动明显、隐蔽性不足,且易产生离群点,难以在实际光电感知场景中有效应用。为此,该文提出一种基于梯度自适应调整驱动的点云对抗攻击方法(GAA)。该方法首先分析三维点云分类网络的决策脆弱性,筛选对模型输出影响显著的关键点集;进而结合各点的局部曲率信息自适应调整梯度权重,并在主曲率方向的几何约束下优化扰动生成,从而在保证较高攻击成功率的同时,有效维持对抗点云的几何一致性与视觉自然性。在多个公开数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在实现高攻击成功率的同时,显著降低了扰动强度,以ModelNet40数据集为例,在PointNet模型上平均仅扰动28个点便可达到97.69%的攻击成功率,显著优于现有对比方法,为评估和提升智能驾驶光电感知系统的安全性提供了有效工具。Abstract:
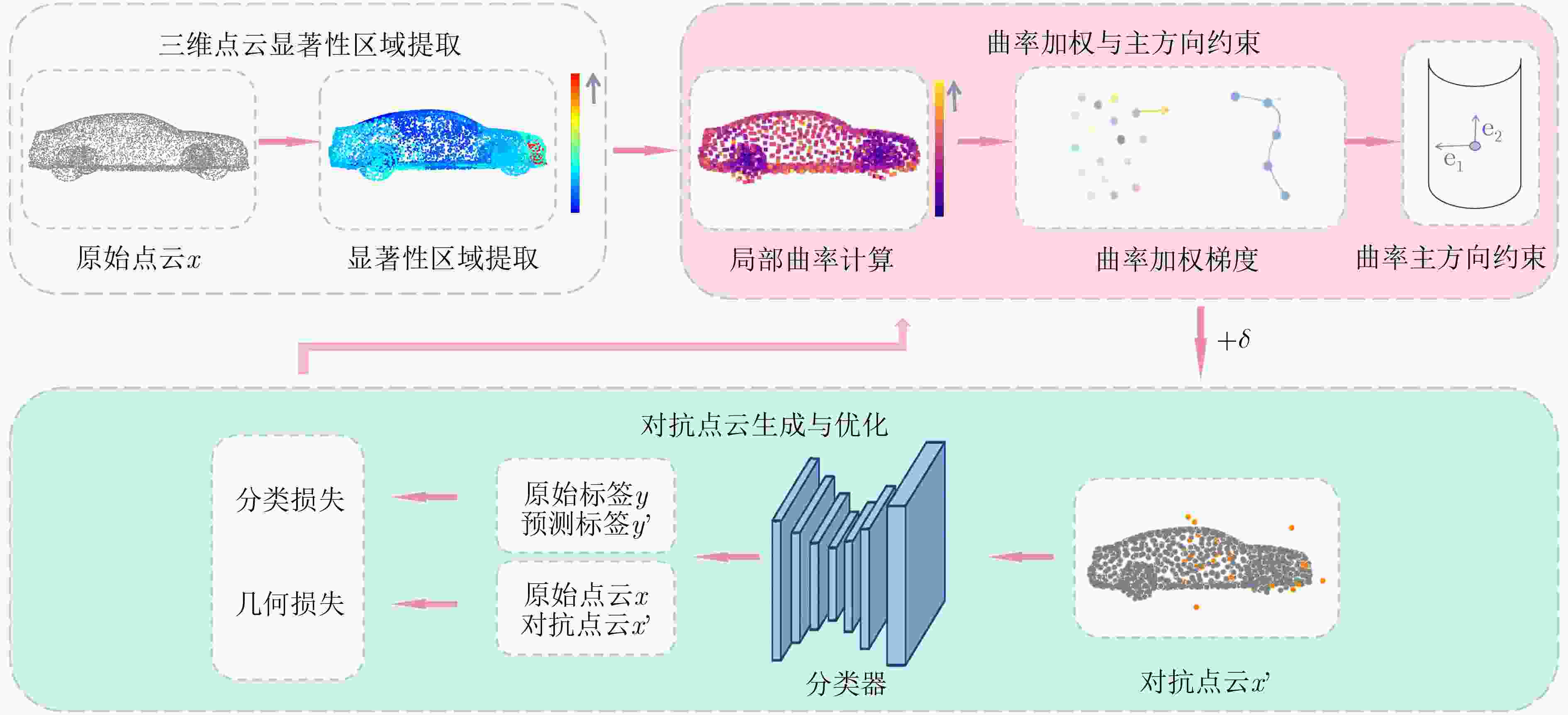
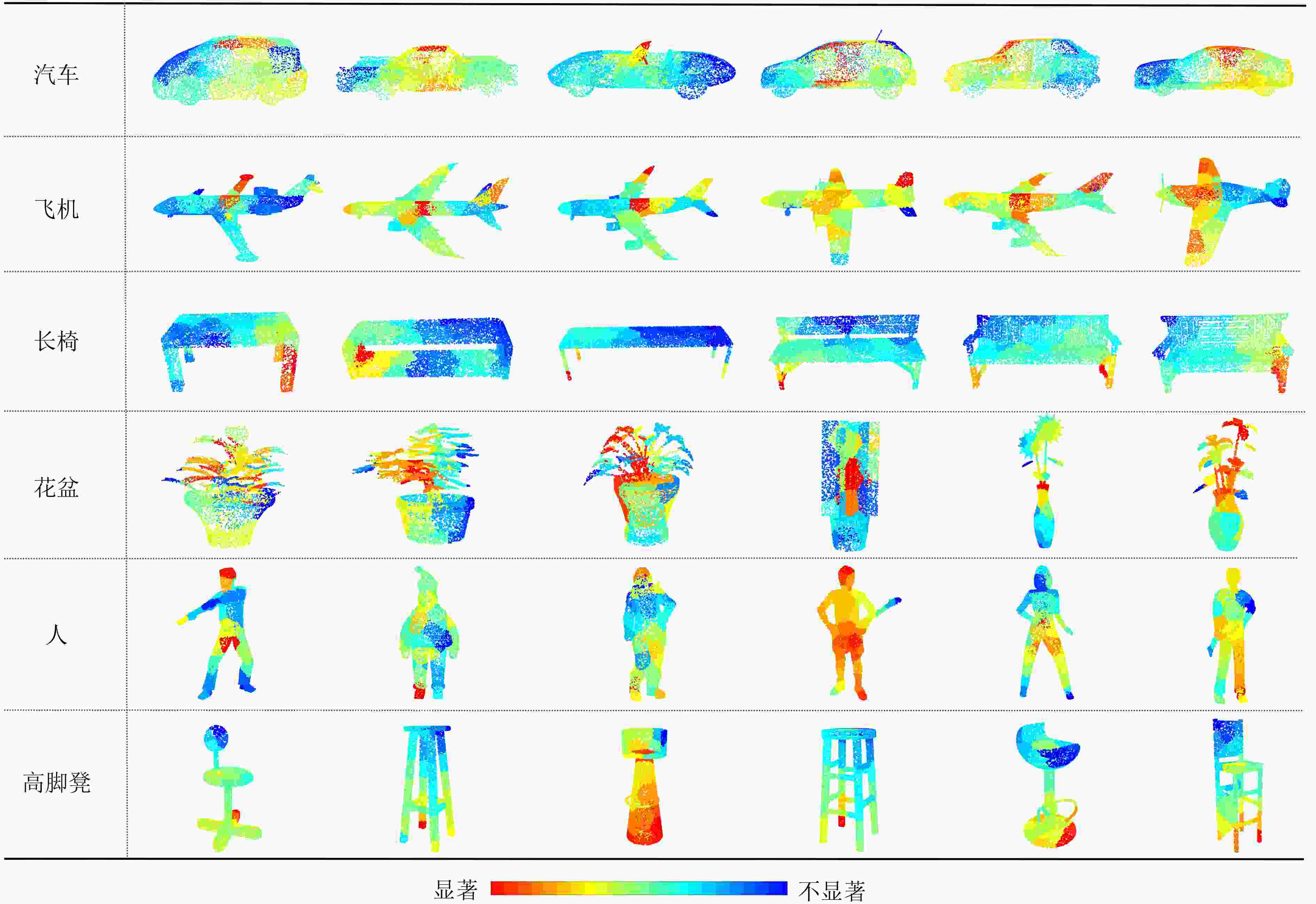
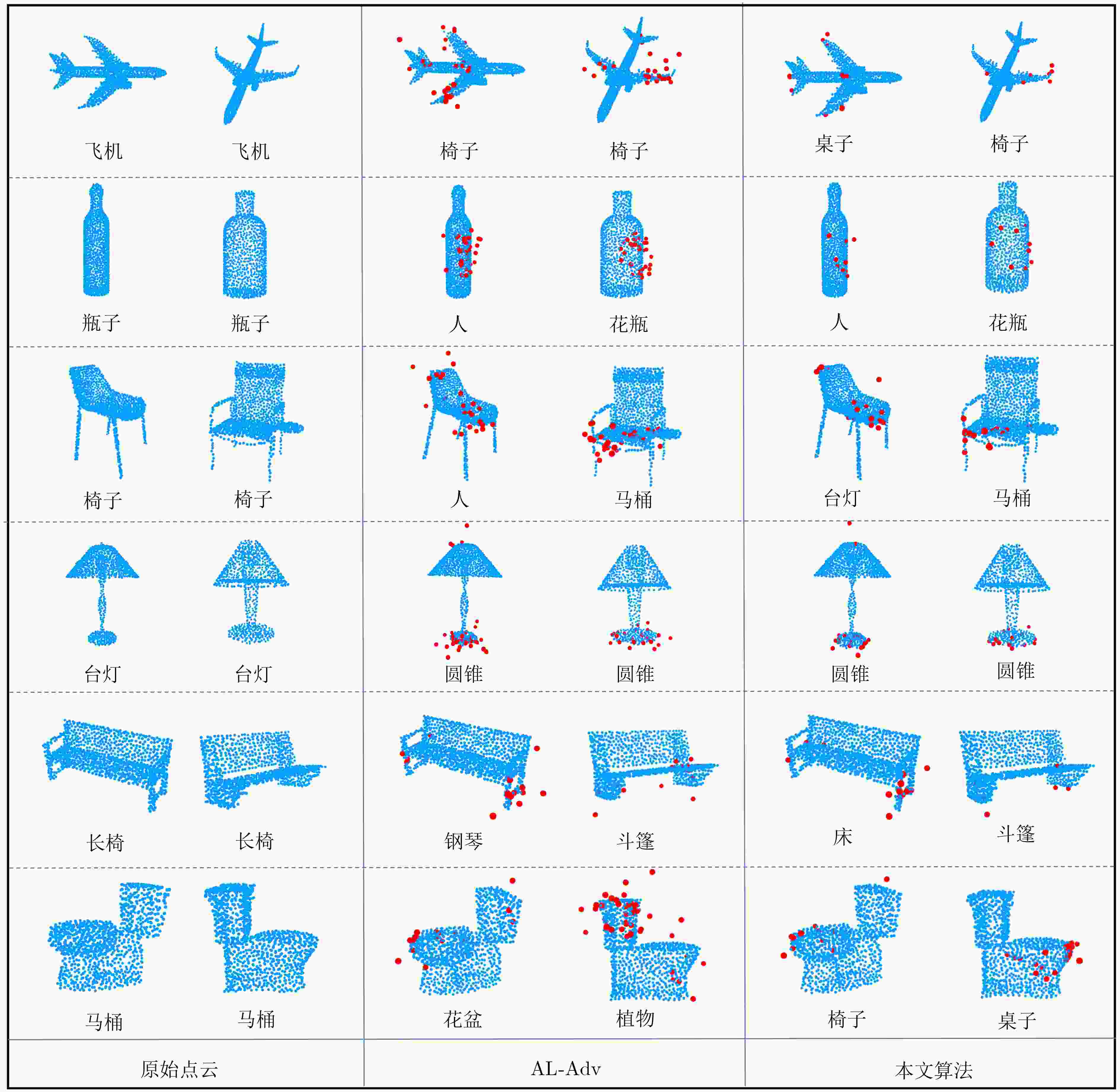
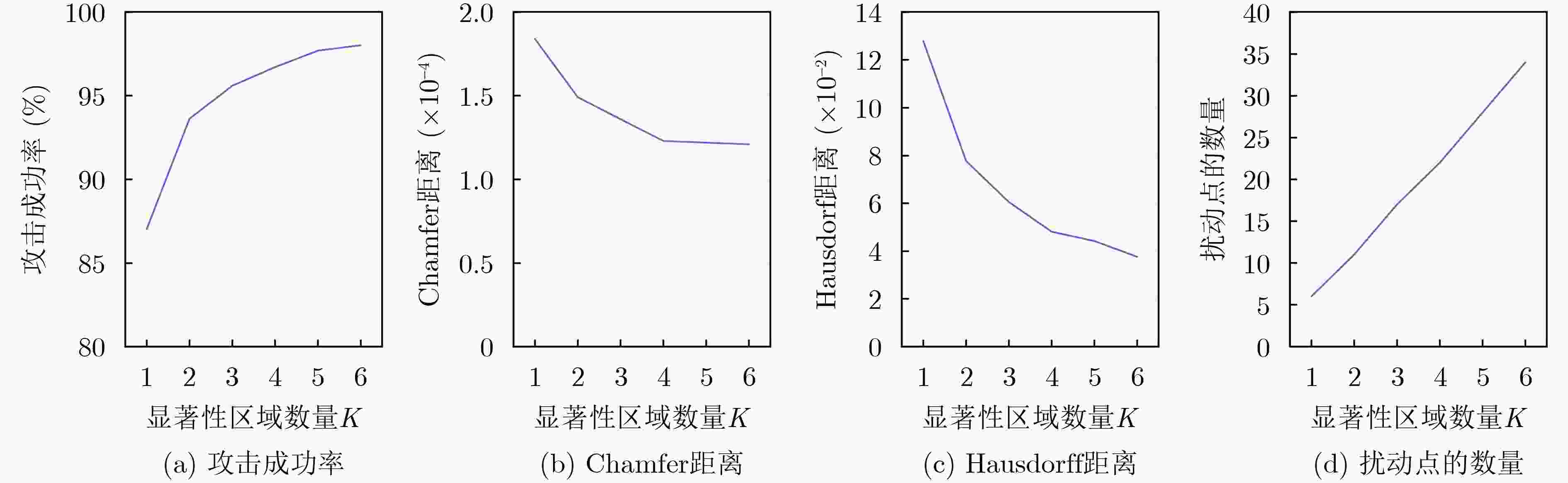
Objective Robust environmental perception is essential for intelligent driving systems. Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) provides high-resolution 3D point cloud data and serves as a core information source for object detection and recognition. However, deep learning models for 3D point cloud recognition show notable vulnerability to adversarial attacks. Small, imperceptible perturbations can cause severe classification errors and threaten system safety. Existing attack methods have improved the Attack Success Rate (ASR), but the perturbations they generate often lack concealment, create outliers, and show poor imperceptibility because they do not adequately preserve the geometric structure of point clouds. This reduces their suitability for realistic security evaluation of optoelectronic perception systems. Developing an attack method that maintains a high success rate while preserving geometric consistency and imperceptibility is therefore critical. This study addresses this need by proposing a framework that incorporates point cloud geometry into perturbation generation. Methods A Gradient Adaptive Adjustment (GAA) adversarial attack method for 3D point cloud recognition is proposed. The framework (Fig. 2) includes three coordinated modules. The 3D Point Cloud Salient Region Extraction module evaluates decision-level vulnerability using Shapley value analysis to identify and rank point subsets with the strongest influence on classifier output. Perturbations are then concentrated in these sensitive regions. A Curvature-Weighted Gradient Mechanism integrates local geometric priors. For each point in the salient region, a local covariance matrix is computed from its k-nearest neighbors. Principal component analysis generates eigenvalues and eigenvectors, which are used to compute a curvature measure. A Gaussian kernel function produces curvature-dependent weights that are applied to backpropagated gradients. This suppresses perturbations in high-curvature areas and encourages them in low-curvature regions to preserve local shape morphology. A Principal Curvature Direction Constrained Optimization module further refines the perturbation direction. The weighted gradient is projected onto the principal curvature directions, and the projection components are fused using coefficients derived from the corresponding eigenvalues. This aligns the perturbation with natural geometric trends and avoids unnatural deformation. An Adaptive Optimization Algorithm then minimizes a multi-objective loss balancing attack success, geometric similarity (via Chamfer Distance and Hausdorff Distance), and perturbation sparsity. The adversarial point cloud is iteratively updated based on the saliency map, curvature-weighted gradients, and principal direction constraints. Results and Discussions Experiments on ModelNet40, ShapeNetPart, and KITTI were conducted using PointNet, DGCNN, and PointConv. The GAA method showed strong performance. On ModelNet40 with PointNet, it achieved a 97.69% ASR with an average of 28 perturbed points, outperforming ten baselines such as AL-Adv (92.92% ASR, 40 points) and Kim et al. (89.38% ASR, 36 points) ( Table 1 ). It also produced lower geometric distortion, as indicated by smaller Chamfer Distance and Hausdorff Distance values. Visual results (Fig. 4 ) show that GAA produces fewer outliers and more natural adversarial point clouds compared with methods such as AL-Adv. The method generalized well across architectures, reaching 99.78% ASR on DGCNN and 96.91% on PointConv (Table 2 ), with similar performance on ShapeNetPart (Table 3 ). Ablation experiments on the number of salient regions (K) showed consistent improvements in ASR and reduced geometric distortion as K increased from 1 to 6 (Table 4 ,Fig. 5 ), confirming the advantage of targeting multiple critical regions. Tests on the KITTI dataset demonstrated strong performance in real-world, noisy environments. The method maintained high ASRs, such as 99.33% on PointNet, with limited perturbations (Table 5 ). An ablation study on K indicated that K=4 offers an effective balance between success rate and perturbation cost for PointNet (Table 6 ).Conclusions This study presents a GAA method for adversarial attacks on 3D point cloud recognition. By combining a Shapley value-based saliency analyzer, a curvature-weighted gradient mechanism, and a principal curvature direction constraint, the method generates adversarial examples that achieve high attack success while preserving geometric consistency. Experiments show that GAA minimizes perceptual distortion and perturbs fewer points across datasets and models. The method provides a practical tool for vulnerability analysis and supports the development of more robust and secure optoelectronic perception systems for intelligent driving. Future work will examine robustness under adverse conditions and assess physical-world implications. -
Key words:
- 3D point cloud /
- Target recognition /
- Adversarial attack
-
图 4 ModelNet40[19]中的对抗点云可视化
对抗攻击方法 攻击成功率(%) Chamfer距离(×10–4) Hausdorff距离(×10–3) 扰动点数 Jaeyeon Kim[10] 89.38 1.55 18.80 36 Xiang et al. [8] 85.9 1.77 23.80 967 Adversarial sink[25] 88.30 76.50 192.00 1024 Adversarial stick[25] 83.70 49.30 149.00 210 Random selection[26] 55.56 7.47 2.49 413 Critical selectio[26] 18.99 1.15 9.39 50 Saliency map/critical frequency[11] 63.18 5.72 2.50 303 Saliency map/low-score[11] 55.97 6.47 25.00 358 Saliency map/high-score[11] 58.39 7.52 2.48 424 AL-Adv[27] 92.92 2.36 46.60 40 GAA(本文) 97.69 1.22 0.44 28 表 2 ModelNet40[19]数据集上攻击不同的三维网络模型
表 3 在ShapeNetPart[20]数据集上攻击不同的三维网络模型
K 攻击成功率(%) Chamfer距离(×10–4) Hausdorff距离(×10–2) 扰动点数 1 87.03 1.84 12.80 6 2 93.63 1.49 7.77 11 3 95.60 1.36 6.06 17 4 96.70 1.23 4.81 22 5 97.69 1.22 4.42 28 6 98.02 1.21 3.76 34 表 5 在Kitti[21]数据集上攻击不同的三维网络模型
-
[1] LIU Weiquan, XIE Min, HUANG Xingwang, et al. Generating transferable traffic object adversarial 3D point clouds via momentum-based decompose perturbation[J]. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2025, X-1/W2-2025: 83–89. doi: 10.5194/isprs-annals-X-1-W2-2025-83-2025. [2] CAO Yulong, XIAO Chaowei, CYR B, et al. Adversarial sensor attack on LiDAR-based perception in autonomous driving[C]. The 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, New York, USA, 2019: 2267–2281. doi: 10.1145/3319535.3339815. [3] ZHENG Shijun, LIU Weiquan, GUO Yu, et al. A new adversarial perspective for LiDAR-based 3D object detection[C]. The 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence), Philadelphia, USA, 2025: 10608–10616. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v39i10.33152. [4] 吴涛, 纪琼辉, 先兴平, 等. 信息熵驱动的图神经网络黑盒迁移对抗攻击方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(10): 3814–3825. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250303.WU Tao, JI Qionghui, XIAN Xingping, et al. Information entropy-driven black-box transferable adversarial attack method for graph neural networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(10): 3814–3825. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250303. [5] 刘伟权, 郑世均, 郭宇, 等. 三维点云目标识别对抗攻击研究综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 1645–1657. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231188.LIU Weiquan, ZHENG Shijun, GUO Yu, et al. A survey of adversarial attacks on 3D point cloud object recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 1645–1657. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231188. [6] LIU D, YU R, and SU Hao. Extending adversarial attacks and defenses to deep 3D point cloud classifiers[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, China, 2019: 2279–2283. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2019.8803770. [7] DONG Xiaoyi, CHEN Dongdong, ZHOU Hang, et al. Self-robust 3D point recognition via gather-vector guidance[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11513–11521. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01153. [8] XIANG Chong, QI C R, and LI Bo. Generating 3D adversarial point clouds[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9128–9136. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00935. [9] GUO Yu, LIU Weiquan, XU Qingshan, et al. Boosting adversarial transferability through augmentation in hypothesis space[C]. 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2025: 19175–19185. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52734.2025.01786. [10] KIM J, HUA B S, NGUYEN D T, et al. Minimal adversarial examples for deep learning on 3D point clouds[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 7777–7786. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00770. [11] ZHENG Tianhang, CHEN Changyou, YUAN Junsong, et al. PointCloud saliency maps[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 1598–1606. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00168. [12] ZHENG Shijun, LIU Weiquan, GUO Yu, et al. SR-Adv: Salient region adversarial attacks on 3D point clouds for autonomous driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(10): 14019–14030. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3406153. [13] ZHANG Jianping, GU Wenwei, HUANG Yizhan, et al. Curvature-invariant adversarial attacks for 3D point clouds[C]. The 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 7142–7150. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v38i7.28542. [14] ZHANG Zihao, SANG Nan, WANG Xupeng, et al. SC-Net: Salient point and curvature based adversarial point cloud generation network[C]. ICASSP 2023 – IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10094878. [15] 钱亚冠, 孔亚鑫, 陈科成, 等. 利用频谱衰减增强深度神经网络对抗迁移攻击[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(10): 3847–3857. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250157.QIAN Yaguan, KONG Yaxin, CHEN Kecheng, et al. Adversarial transferability attack on deep neural networks through spectral coefficient decay[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(10): 3847–3857. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250157. [16] KUHN H W. Classics in Game Theory[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1997. doi: 10.2307/j.ctv173f1fh. [17] LIU Weiquan, LIU Minghao, ZHENG Shijun, et al. Interpreting hidden semantics in the intermediate layers of 3D point cloud classification neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2025, 27: 965–977. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3345147. [18] CARLINI N and WAGNER D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, USA, 2017: 39–57. doi: 10.1109/SP.2017.49. [19] WU Zhirong, SONG Shuran, KHOSLA A, et al. 3D ShapeNets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1912–1920. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298801. [20] CHANG A X, FUNKHOUSER T, GUIBAS L, et al. ShapeNet: An information-rich 3D model repository[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1512.03012, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1512.03012. [21] GEIGER A, LENZ P, and URTASUN R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 3354–3361. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248074. [22] QI C R, SU Hao, KAICHUN M, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 77–85. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.16. [23] WANG Yue, SUN Yongbin, LIU Ziwei, et al. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2019, 38(5): 146. doi: 10.1145/3326362. [24] WU Wenxuan, QI Zhongang, and LI Fuxin. PointConv: Deep convolutional networks on 3D point clouds[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9613–9622. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00985. [25] LIU D, YU R, and SU Hao. Adversarial shape perturbations on 3D point clouds[C]. European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 88–104. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-66415-2_6. [26] WICKER M and KWIATKOWSKA M. Robustness of 3D deep learning in an adversarial setting[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 11759–11767. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.01204. [27] ZHENG Shijun, LIU Weiquan, SHEN Siqi, et al. Adaptive local adversarial attacks on 3D point clouds[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 144: 109825. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109825. [28] 陈卓, 江辉, 周杨. 一种面向联邦学习对抗攻击的选择性防御策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 1119–1127. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230137.CHEN Zhuo, JIANG Hui, and ZHOU Yang. A selective defense strategy for federated learning against attacks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 1119–1127. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230137. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
