Crosstalk-Free Frequency-Spin Multiplexed Multifunctional Device Realized by Nested Meta-Atoms
-
摘要: 电磁波的多种物理自由度为实现超高信息容量的多功能超表面提供了广阔的维度复用空间。然而,现有的多维度复用超表面通常依赖复杂的多层设计或空间划分,导致器件制备成本较高,且信道间往往存在不可避免的串扰。为简化设计并提高信道隔离度,该研究提出了一种基于嵌套式双光谱超原子的无串扰频率-自旋复用单层超表面。通过精心设计,无串扰双光谱超原子的物理结构和电磁响应能够同时巧妙地表示为两个单光谱超原子的线性叠加,显著降低了复用设计的复杂度。作为概念验证,设计并制备了两款超表面器件,分别在由两个频率和两个自旋态组成的4个信道中实现了独立且无串扰的涡旋光束生成和全息成像功能。实验结果验证了多维复用超表面优异的信道隔离性能。该方法为超表面在提升信息容量方面提供了一种简单、低成本且无串扰的解决方案,并在6G多通道无线通信和全息成像等领域展现出广阔的应用前景。Abstract:
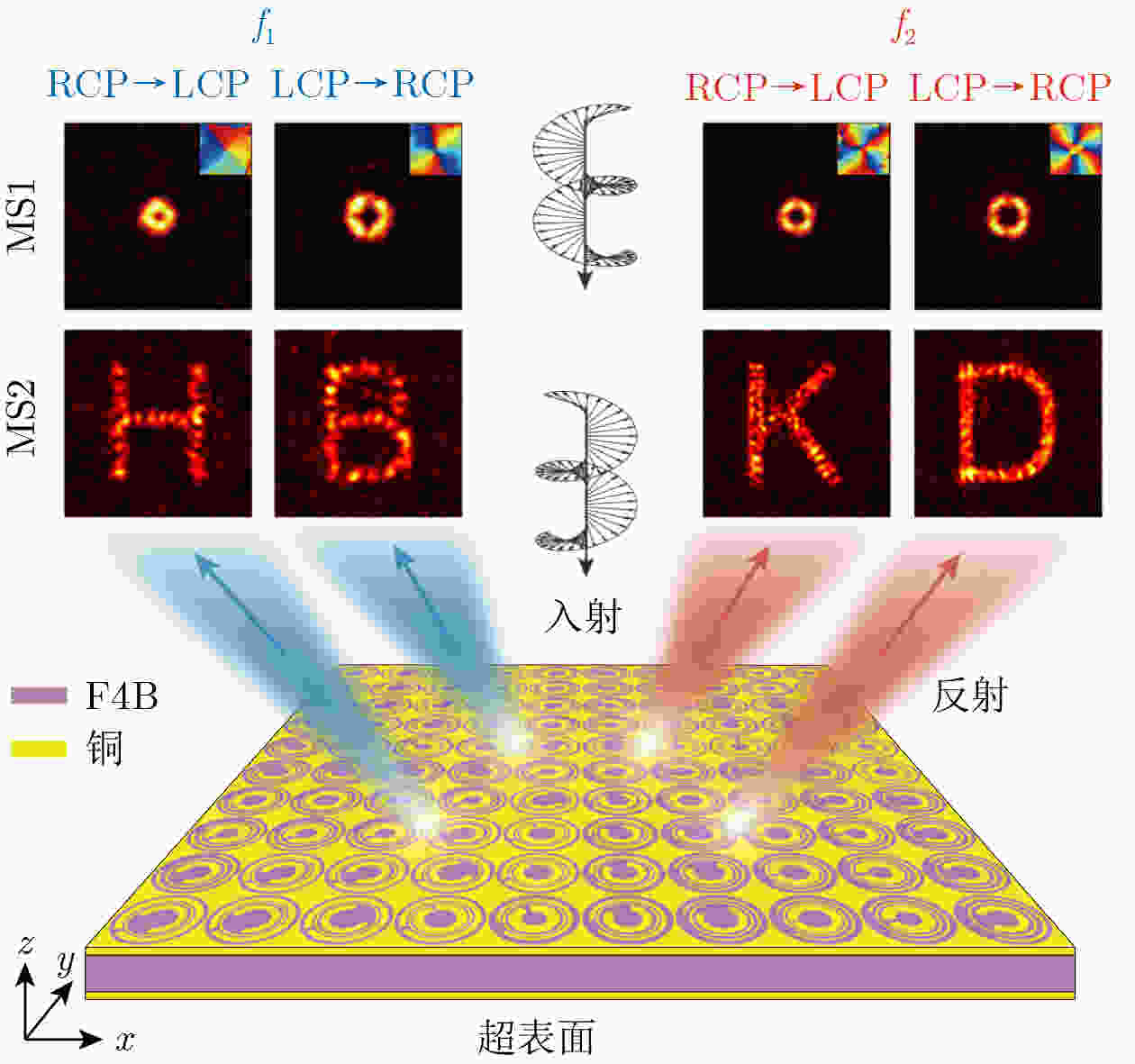
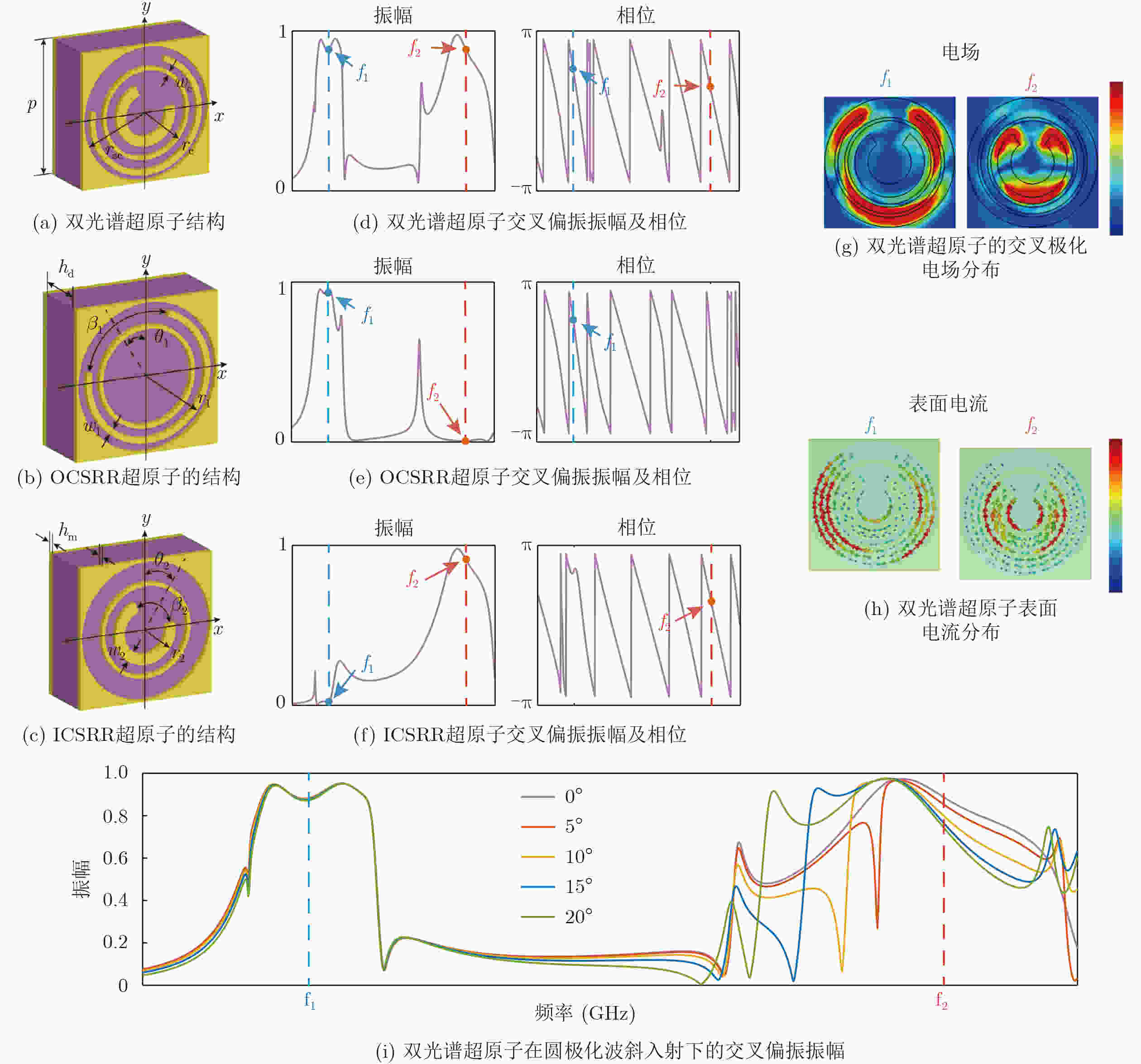
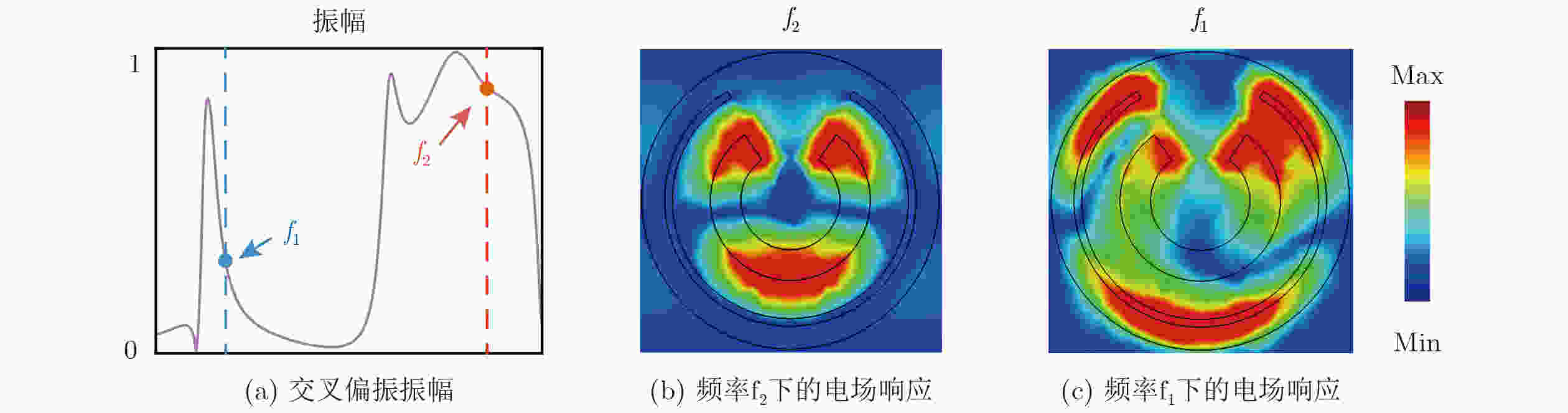
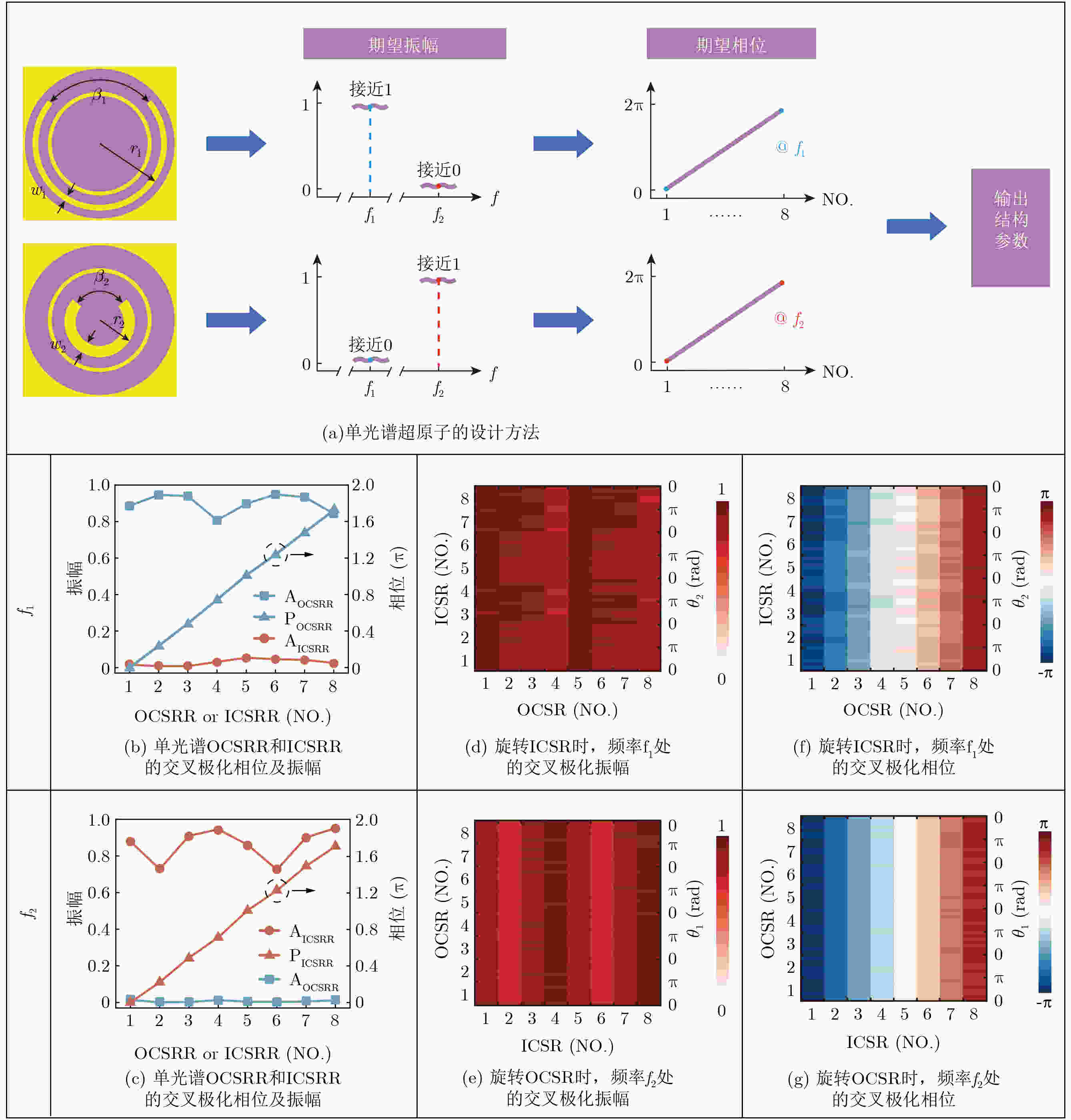
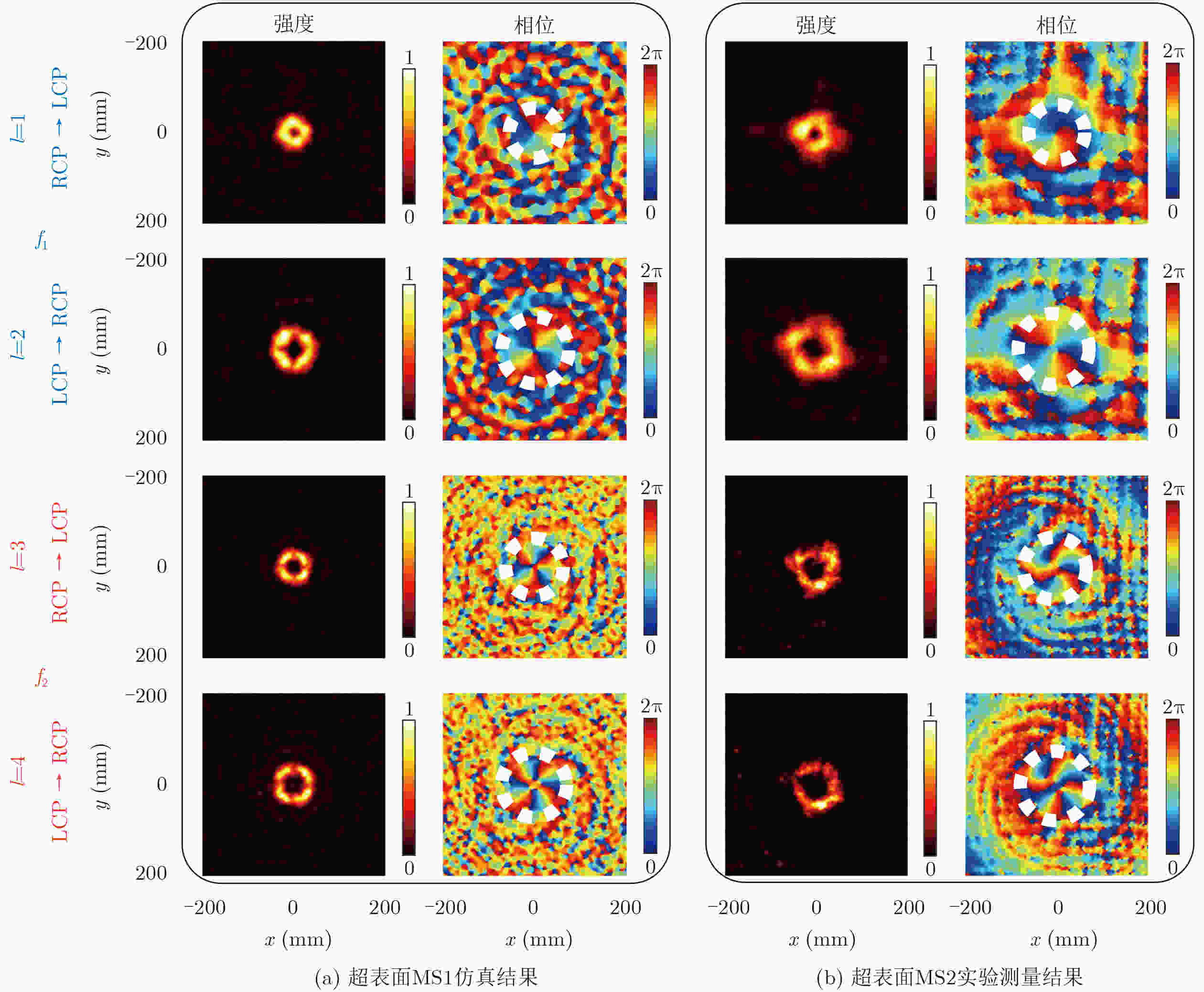
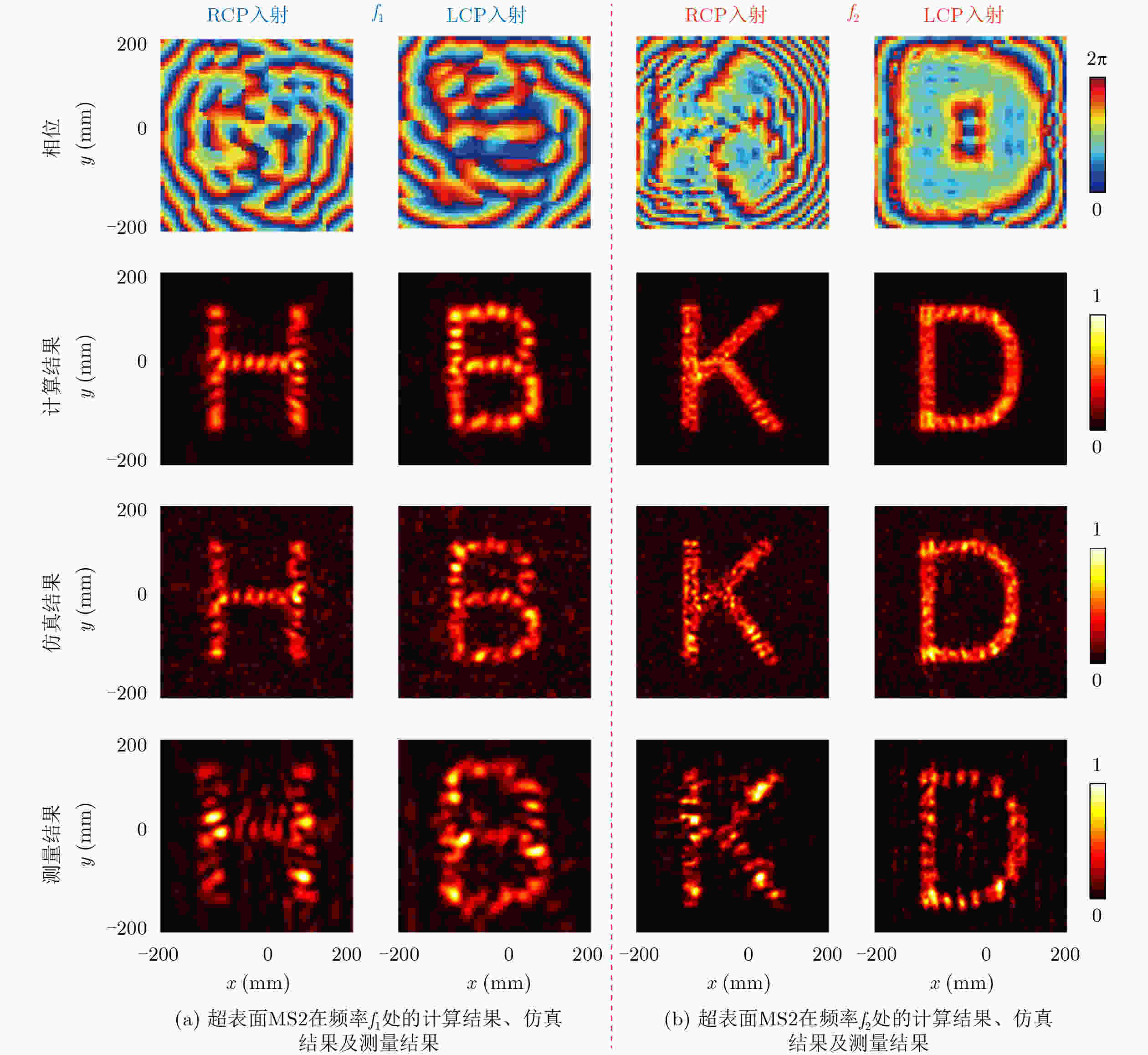
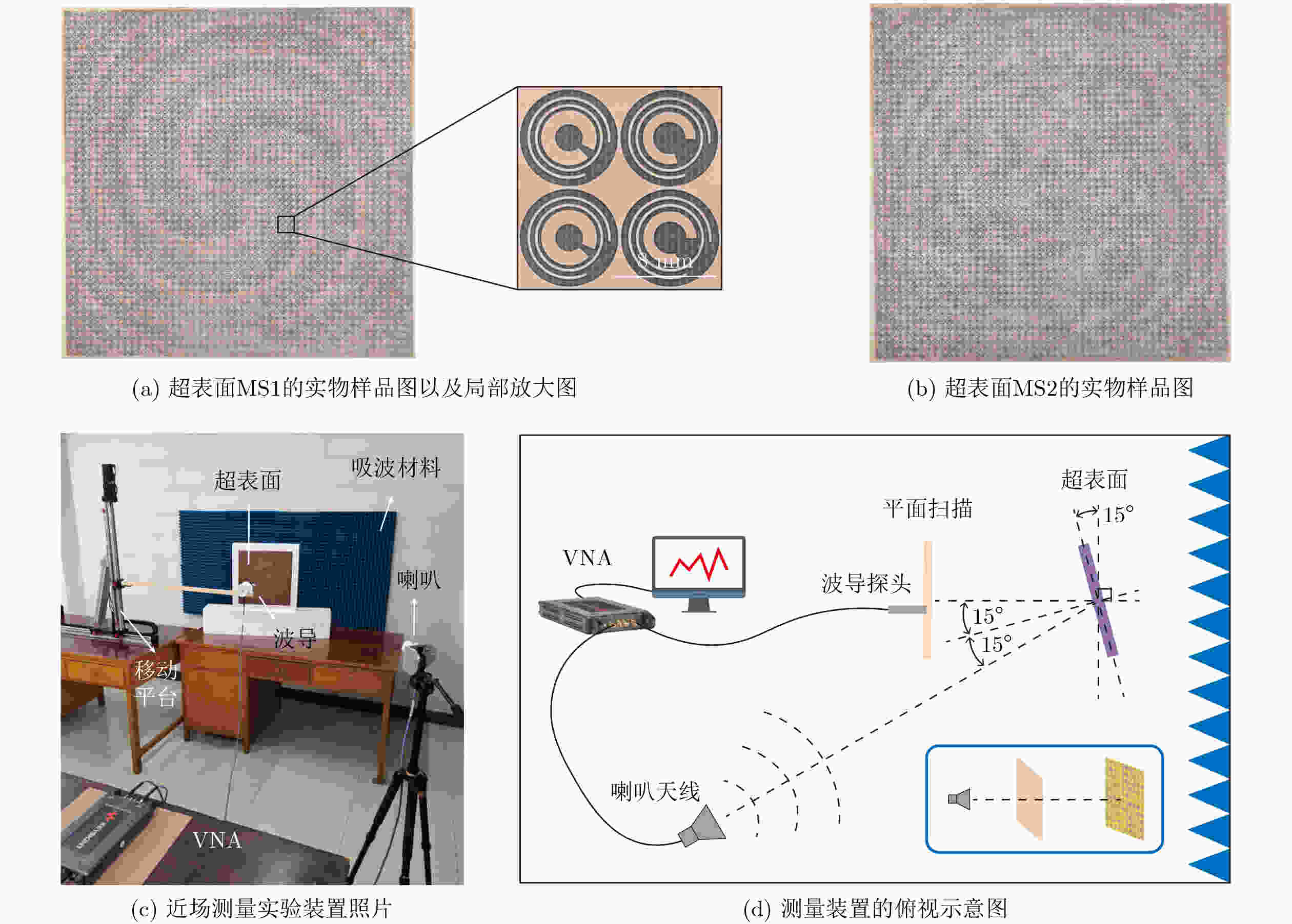
Objective To address high fabrication costs and signal crosstalk in existing multidimensional multiplexed metasurfaces, a crosstalk-free, frequency-spin multiplexed single-layer metasurface based on nested bi-spectral meta-atoms is proposed. Two C-shaped split-ring resonators are physically superimposed to target the Ku band (12.5 GHz) and the K band (22 GHz). This configuration enables four fully independent information channels, defined by two frequencies and two spin states, without spatial division or multilayer stacking. The objective is to demonstrate independent, high-performance vortex beam generation and holographic imaging, providing a simplified and cost-effective solution for advanced 6G communication and sensing systems. Methods A reflective metal–dielectric–metal metasurface architecture is adopted, in which each unit cell integrates an Outer C-Shaped Split-Ring Resonator (OCSRR) and an Inner C-Shaped Split-Ring Resonator (ICSRR). Parameter sweeps performed using CST Microwave Studio are used to select structures that provide high cross-polarization conversion at the target frequencies while maintaining negligible responses in non-target bands. Independent spin multiplexing is achieved through the combined use of transmission phase and geometric phase, controlled by resonator rotation. Two prototypes are fabricated using printed circuit board technology. MS1 is designed for focused vortex beam generation with topological charges l = +1, +2, +3, and +4, whereas MS2 is designed for holographic imaging of the letters “H”, “B”, “K”, and “D”. Device performance is validated by near-field scanning measurements under oblique incidence using a vector network analyzer. Results and Discussions Simulation and experimental results confirm strong frequency selectivity and effective spin decoupling enabled by the nested meta-atom design. The OCSRR and ICSRR dominate the electromagnetic responses at 12.5 GHz and 22 GHz, respectively, and exhibit linear superposition behavior with minimal crosstalk. MS1 generates four focused vortex beams with clearly separated topological charges, achieving an average mode purity of 88.25%. MS2 reconstructs four independent and well-defined holographic images with high channel isolation. The close agreement between measured and simulated results demonstrates the robustness of the device and validates the effectiveness of the crosstalk-free design strategy under practical illumination conditions. Conclusions A reliable approach for realizing crosstalk-free frequency-spin multiplexed metasurfaces using nested meta-atoms is demonstrated. Simultaneous and independent manipulation of electromagnetic waves across four channels is achieved on a single metasurface layer, substantially reducing design complexity and fabrication cost. The successful demonstration of multi-channel vortex beam generation and holographic imaging indicates strong potential for integrated multifunctional applications in next-generation wireless communication and optical systems. -
Key words:
- Metasurface /
- Frequency-spin multiplexing /
- Crosstalk-free /
- Bi-spectral meta-atoms
-
表 1 八个OCSRR超原子和八个ICSRR超原子的结构参数
参数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 r1 (mm) 3.5 3.3 3.3 3.5 3.5 3.3 3.3 3.5 w1 (mm) 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.3 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.3 β1 (°) 10 30 60 100 10 30 60 100 θ1 (°) 0 0 0 0 90 90 90 90 r2 (mm) 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.2 w2 (mm) 0.9 1.1 0.8 0.7 0.9 1.1 0.8 0.7 β2 (°) 8 20 70 100 8 20 70 100 θ2 (°) 0 0 0 0 90 90 90 90 -
[1] YU Nanfang, GENEVET P, KATS M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: Generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333–337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713. [2] KIM T T, KIM H, KENNEY M, et al. Amplitude modulation of anomalously refracted terahertz waves with gated-graphene metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2018, 6(1): 1700507. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700507. [3] GRADY N K, HEYES J E, CHOWDHURY D R, et al. Terahertz metamaterials for linear polarization conversion and anomalous refraction[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6138): 1304–1307. doi: 10.1126/science.1235399. [4] CHEN H T, TAYLOR A J, and YU Nanfang. A review of metasurfaces: Physics and applications[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 2016, 79(7): 076401. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/79/7/076401. [5] LI Junhao, LIU Wenwei, XU Haofei, et al. An RGB-achromatic aplanatic metalens[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2024, 18(4): 2300729. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202300729. [6] PENG Yuyan, ZHANG Jiawei, ZHOU Xiongtu, et al. Metalens in improving imaging quality: Advancements, challenges, and prospects for future display[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2024, 18(4): 2300731. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202300731. [7] YANG Hui, OU Kai, WAN Hengyi, et al. Metasurface-empowered optical cryptography[J]. Materials Today, 2023, 67: 424–445. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2023.06.003. [8] CHEN Chen, LIU Wenyuan, XIAO Likun, et al. Encrypted metasurfaces with inherent asymmetric-like digitized keys under decoupled near-field parameters[J]. Communications Physics, 2025, 8(1): 64. doi: 10.1038/s42005-025-01994-6. [9] YIN Yongyao, JIANG Qiang, WANG Hongbo, et al. Multi-dimensional multiplexed metasurface holography by inverse design[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(21): 2312303. doi: 10.1002/adma.202312303. [10] PARK C, JEON Y, and RHO J. 36-channel spin and wavelength co-multiplexed metasurface holography by phase-gradient inverse design[J]. Advanced Science, 2025, 12(28): 2504634. doi: 10.1002/advs.202504634. [11] ATALOGLOU V G, TARAVATI S, and ELEFTHERIADES G V. Metasurfaces: Physics and applications in wireless communications[J]. National Science Review, 2023, 10(8): nwad164. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwad164. [12] CHEN Xiaoqing, ZHANG Lei, ZHENG Yining, et al. Integrated sensing and communication based on space-time-coding metasurfaces[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16(1): 1836. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57137-6. [13] IQBAL S, RAJABALIPANAH H, ZHANG Lei, et al. Frequency-multiplexed pure-phase microwave meta-holograms using bi-spectral 2-bit coding metasurfaces[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(3): 703–714. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2019-0461. [14] XIE Rensheng, XIN Minbo, CHEN Shiguo, et al. Frequency-multiplexed complex-amplitude meta-devices based on bispectral 2-bit coding meta-atoms[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2020, 8(24): 2000919. doi: 10.1002/adom.202000919. [15] ZHANG Runzhe, GUO Yinghui, ZHANG Fei, et al. Dual-layer metasurface enhanced capacity of polarization multiplexing[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2024, 18(9): 2400126. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202400126. [16] LIU Yu, HUO Xingyuan, XIAO Yutong, et al. Metasurface-based non-orthogonal tri-channel polarization multiplexing for optical encryption[Invited][J]. Optical Materials Express, 2025, 15(3): 565–575. doi: 10.1364/OME.549304. [17] XU Hexiu, HU Guangwei, JIANG Menghua, et al. Wavevector and frequency multiplexing performed by a spin-decoupled multichannel metasurface[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2020, 5(1): 1900710. doi: 10.1002/admt.201900710. [18] WANG Zhenxu, FU Xinmin, LIANG Jian’gang, et al. Spin-decoupled metasurface by hybridizing curvature- and rotation-induced geometrical phases[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2024, 18(9): 2400184. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202400184. [19] WANG Yue, YAO Zhenyu, CUI Zijian, et al. Orbital angular momentum multiplexing holography based on multiple polarization channel metasurface[J]. Nanophotonics, 2023, 12(23): 4339–4349. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2023-0550. [20] KAMALI S M, ARBABI E, ARBABI A, et al. Angle-multiplexed metasurfaces: Encoding independent wavefronts in a single metasurface under different illumination angles[J]. Physical Review X, 2017, 7(4): 041056. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.7.041056. [21] CHEN Shuqi, LIU Wenwei, LI Zhancheng, et al. Metasurface-empowered optical multiplexing and multifunction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(3): 1805912. doi: 10.1002/adma.201805912. [22] ZHU Lei, WEI Jinxu, DONG Liang, et al. Four-channel meta-hologram enabled by a frequency-multiplexed mono-layered geometric phase metasurface[J]. Optics Express, 2024, 32(3): 4553–4563. doi: 10.1364/OE.513920. [23] GOU Yue, MA Huifeng, WU Liangwei, et al. Non-interleaved polarization-frequency multiplexing metasurface for multichannel holography[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2022, 10(22): 2201142. doi: 10.1002/adom.202201142. [24] HE Guoli, ZHENG Yaqin, ZHOU Changda, et al. Multiplexed manipulation of orbital angular momentum and wavelength in metasurfaces based on arbitrary complex-amplitude control[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2024, 13(1): 98. doi: 10.1038/s41377-024-01420-6. [25] LIU Wanying, JIANG Xiaohan, XU Qaun, et al. All-dielectric terahertz metasurfaces for multi-dimensional multiplexing and demultiplexing[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2024, 18(8): 2301061. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202301061. [26] QU Kai, CHEN Ke, HU Qi, et al. Deep-learning-assisted inverse design of dual-spin/frequency metasurface for quad-channel off-axis vortices multiplexing[J]. Advanced Photonics Nexus, 2023, 2(1): 016010. doi: 10.1117/1.apn.2.1.016010. [27] XU Hexiu, HU Guangwei, KONG Xianghong, et al. Super-reflector enabled by non-interleaved spin-momentum-multiplexed metasurface[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2023, 12(1): 78. doi: 10.1038/s41377-023-01118-1. [28] SUN Shi, GOU Yue, CUI Tiejun, et al. High-security nondeterministic encryption communication based on spin-space-frequency multiplexing metasurface[J]. PhotoniX, 2024, 5(1): 38. doi: 10.1186/s43074-024-00154-3. [29] ZHANG Fei, PU Mingbo, LUO Jun, et al. Symmetry breaking of photonic spin-orbit interactions in metasurfaces[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(3): 319–325. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.03.006. [30] DING Guowen, CHEN Ke, LUO Xinyao, et al. Dual-helicity decoupled coding metasurface for independent spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2019, 11(4): 044043. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.11.044043. [31] BAI Xudong, ZHANG Fuli, SUN Li, et al. Dynamic millimeter-wave OAM beam generation through programmable metasurface[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(7): 1389–1399. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0790. [32] CHONG Mingzhe, ZHOU Yiwen, ZHANG Zongkun, et al. Generation of polarization-multiplexed terahertz orbital angular momentum combs via all-silicon metasurfaces[J]. Light: Advanced Manufacturing, 2024, 5(3): 38. doi: 10.37188/lam.2024.038. [33] JIANG Yuying, LI Shuying, CHEN Xinlei, et al. Frequency-polarization multiplexing reflective metasurface for orbital angular momentum generation[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2024, 124(22): 221701. doi: 10.1063/5.0207349. [34] XU Quan, SU Xiaoqiang, ZHANG Xueqian, et al. Mechanically reprogrammable pancharatnam-berry metasurface for microwaves[J]. Advanced Photonics, 2022, 4(1): 016002. doi: 10.1117/1.AP.4.1.016002. [35] ZHAO Fengtao, DONG Peng, LI Kang, et al. Inverse design of terahertz metasurfaces for multi-channel holographic imaging based on the modified gradient descent method[J]. Optics Express, 2025, 33(8): 18005–18016. doi: 10.1364/OE.560396. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
