Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks-based Channel Estimation for ISAC-RIS System
-
摘要: 通感一体化(Integrated Sensing and Communication, ISAC)技术作为未来无线通信发展的关键趋势,旨在通过频谱资源的高效利用,实现通信与感知功能的融合与协同。当智能反射表面(Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces, RIS)被引入ISAC系统后,可重构无线传播环境,从而显著提升通信质量及感知精度。然而,准确的信道估计对于保障可靠运行是至关重要的。尽管传统的深度学习方法在一定程度上能够应对信道估计问题,但在面对多用户复杂信道环境时,其泛化能力和估计精度仍存在不足。针对上述问题,本文对于RIS辅助多用户ISAC系统提出了一种基于条件生成对抗网络(Conditional Generative Adversarial Network, CGAN)的两阶段信道估计方法。该方法通过调整RIS的开关状态,分阶段完成对直射信道与反射信道的估计,以提高信道估计的准确性和稳定性。通过生成网络与判别网络的对抗训练,不仅能够学习观测信号与真实信道之间的映射关系,还能根据判别网络的反馈来不断优化输出,从而有效提升训练效率与估计精度。仿真结果表明,与传统深度学习方法相比,所提基于CGAN的方案在信道估计性能上均表现出显著优势。该结果验证了CGAN方法在RIS辅助ISAC系统下信道估计的应用潜力,并为实现更精准和可靠的系统部署奠定了基础。Abstract:
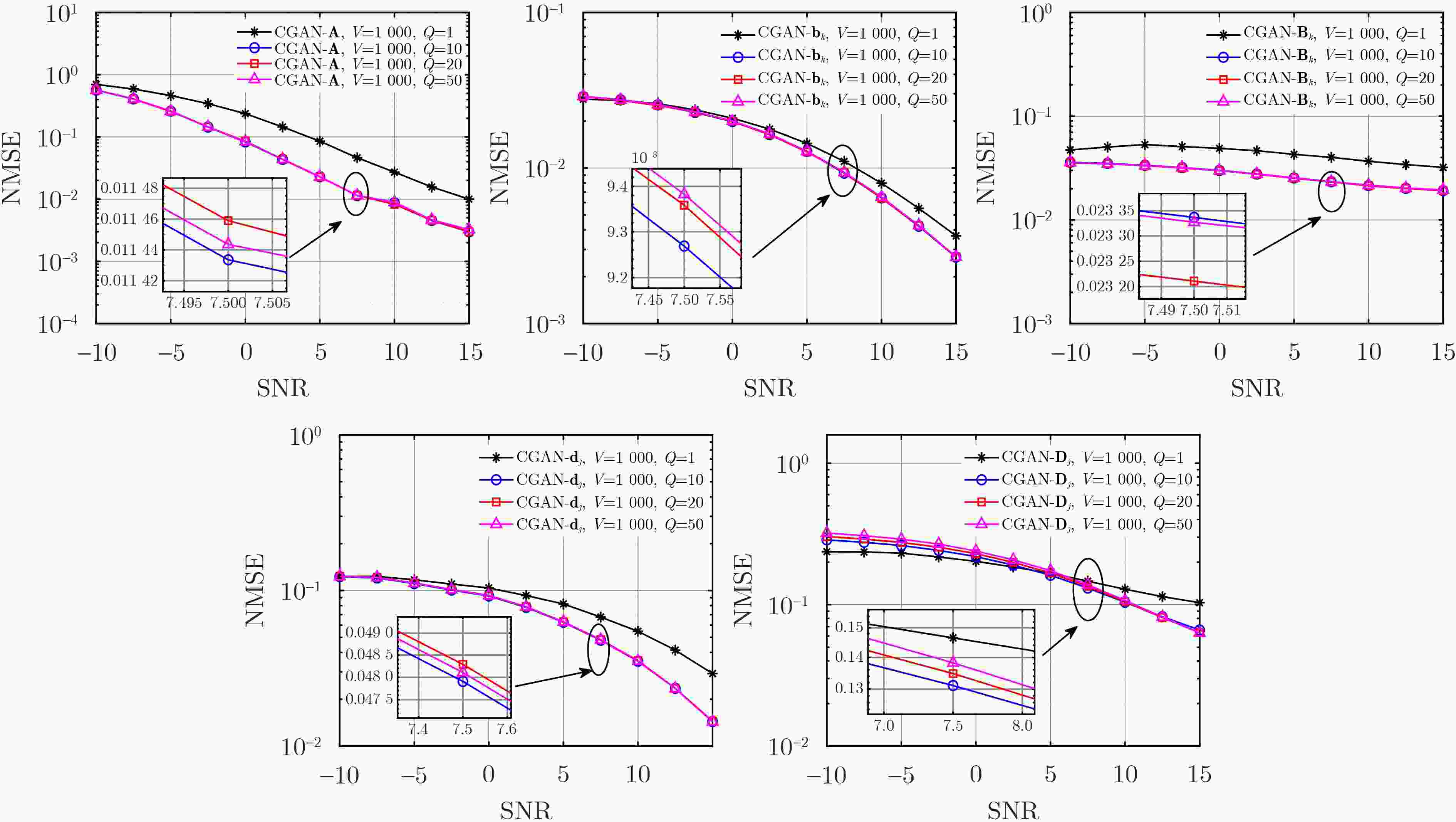
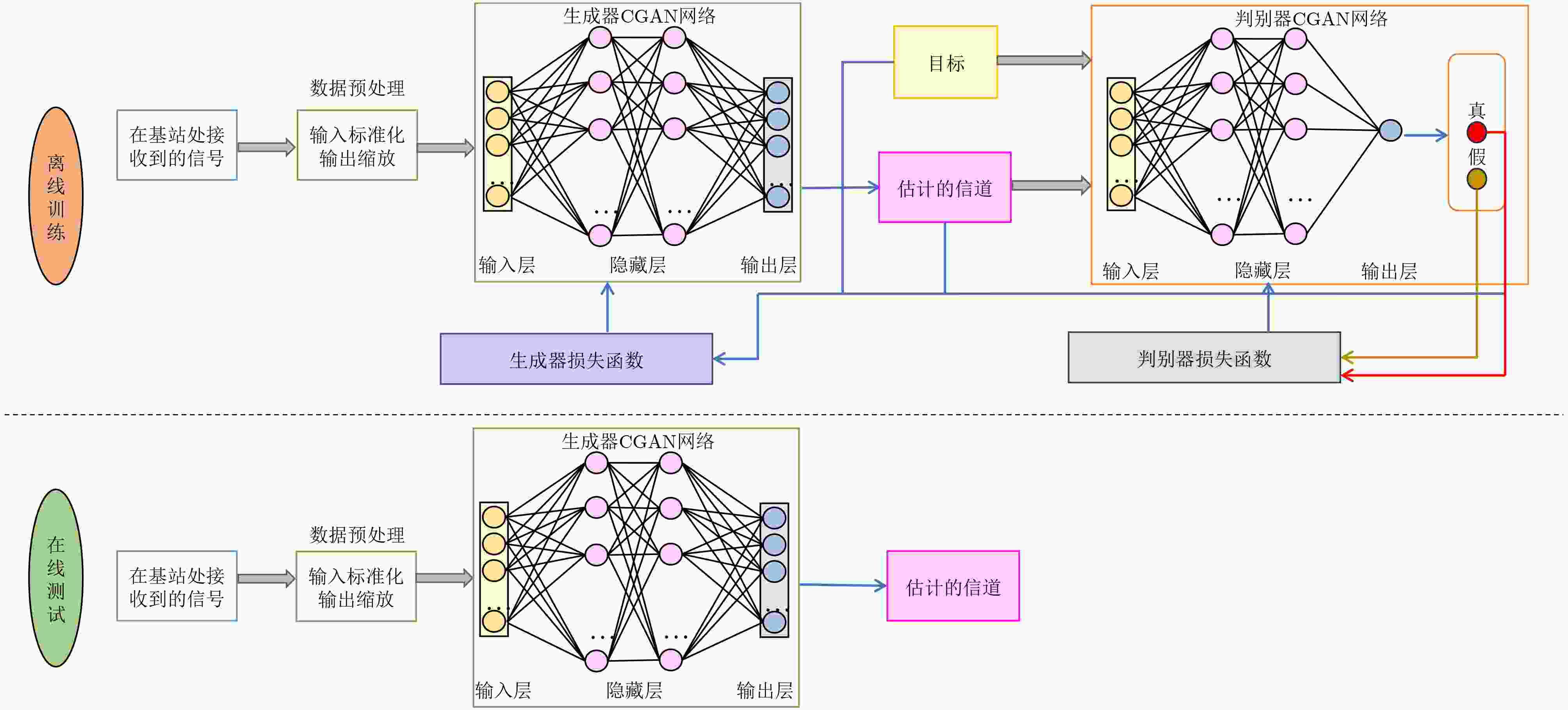
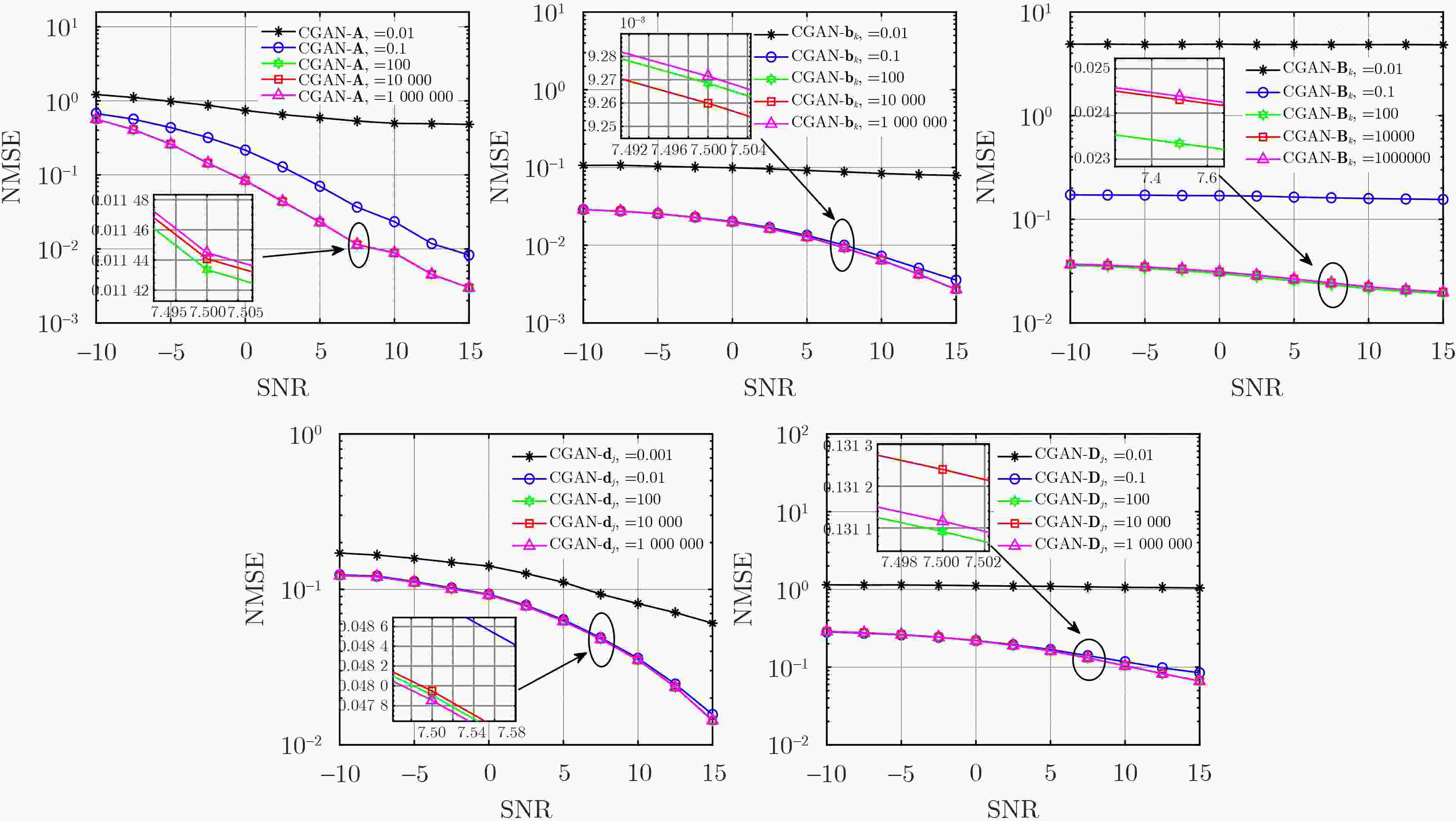
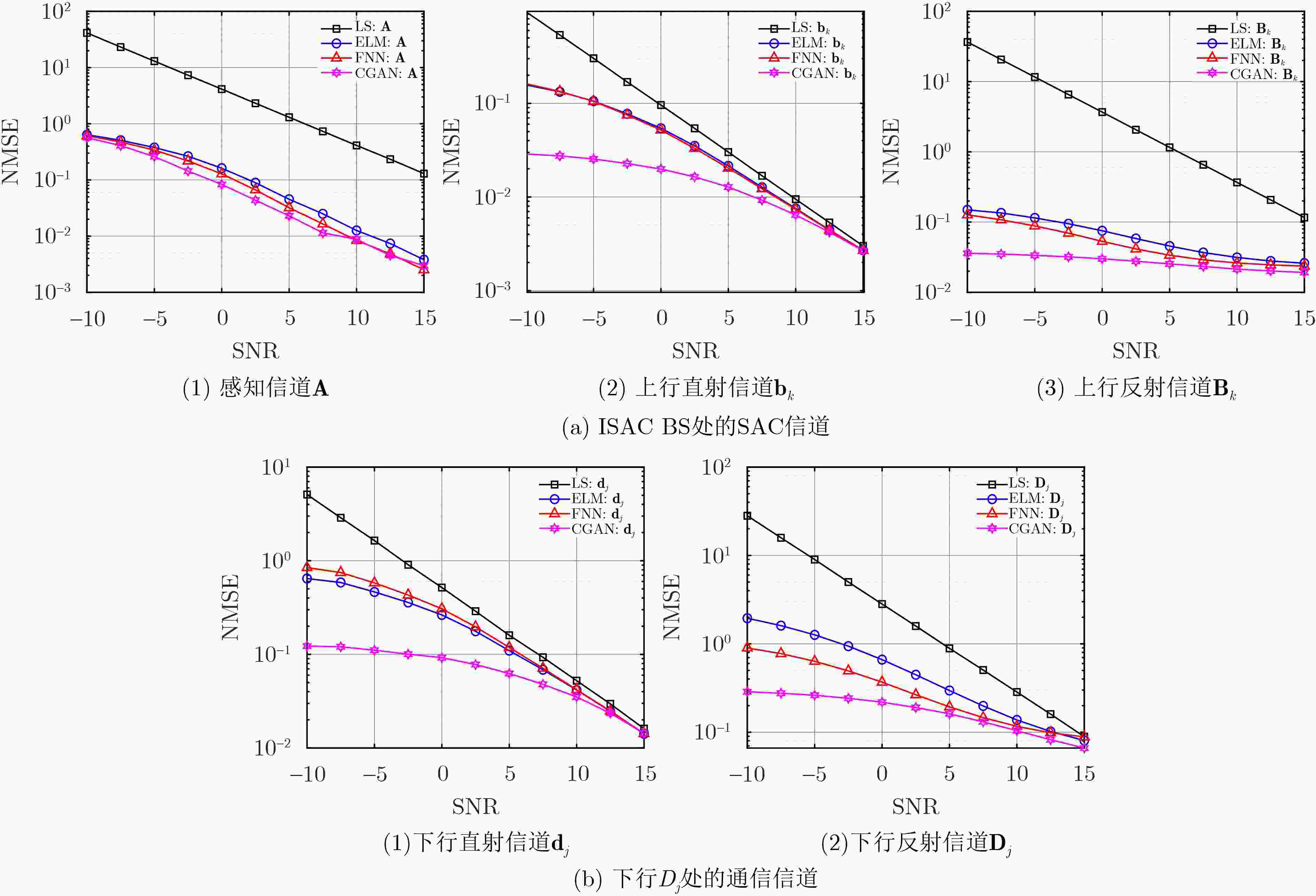
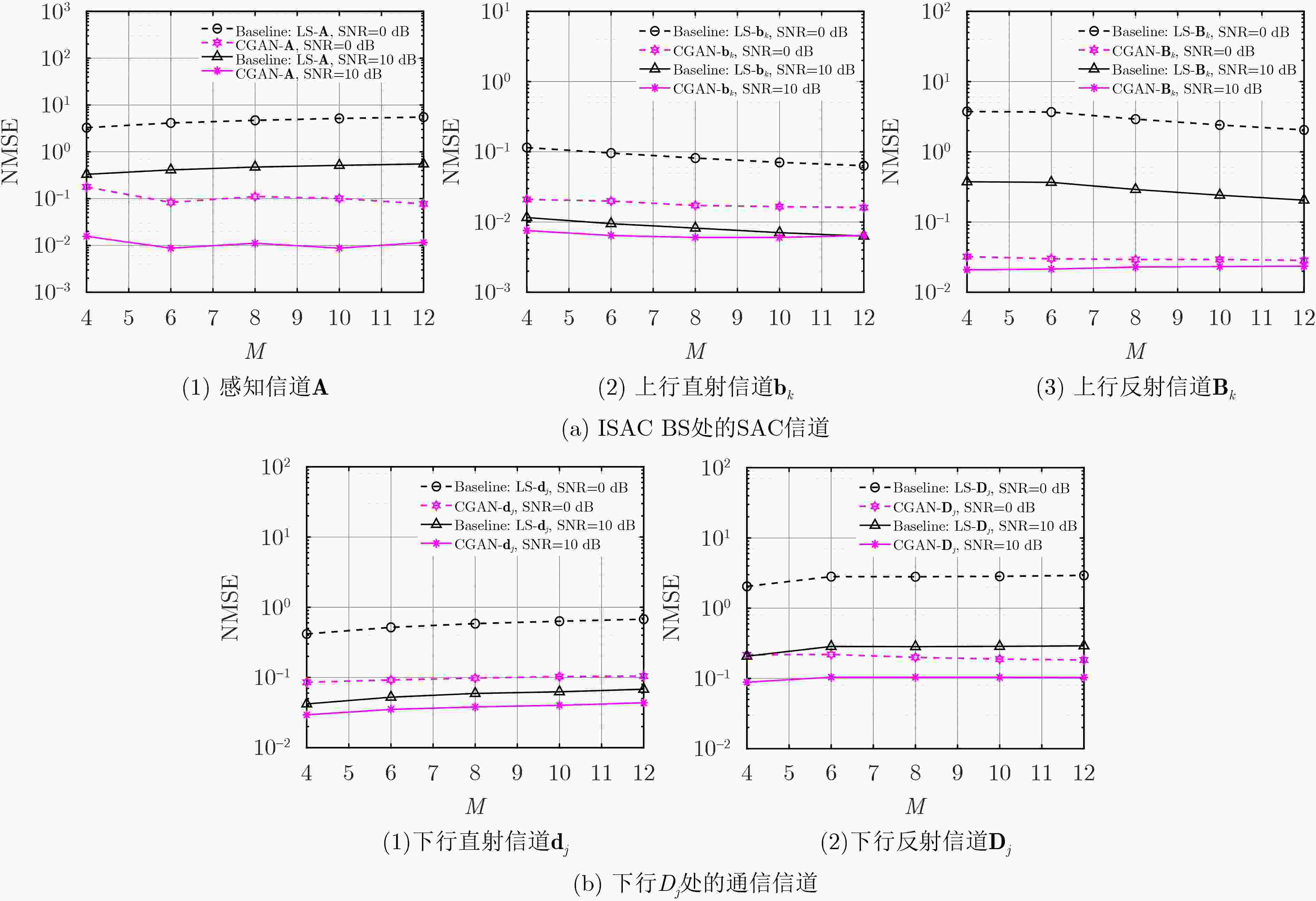
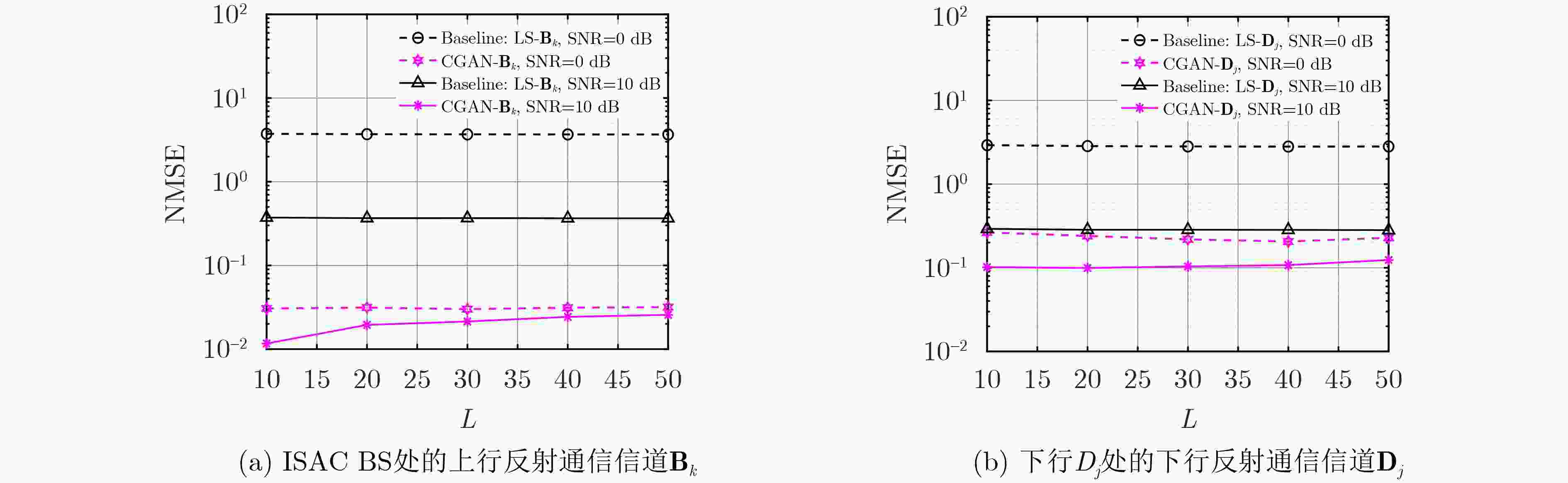
Objective In RIS-assisted ISAC systems, accurate channel estimation is crucial to ensure reliable operation. Although traditional deep learning methods can partially address the channel estimation problem, their generalization ability and estimation accuracy remain limited in complex multi-user channel environments. To tackle these challenges, this paper proposes a two-stage channel estimation method based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Network(CGAN) for RIS-assisted multi-user ISAC systems, aiming to enhance both the accuracy and stability of channel estimation. Methods This paper proposes a two-stage channel estimation method based on CGAN for estimating the SAC channels in RIS-assisted multi-user ISAC systems. By adjusting the switching states of the RIS, the overall estimation problem is decomposed into subproblems, enabling sequential estimation of the direct and reflected channels. Within the proposed CGAN framework, the adversarial training between the generator and discriminator allows the model not only to learn the mapping relationship between the observed signals and the true channels but also to optimize the output according to the discriminator’s feedback, thereby effectively improving both training efficiency and estimation accuracy. Results and Discussions Extensive simulation experiments were conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. First, the estimation performance of the SAC channel under different SNR conditions was compared. The results demonstrate that the proposed CGAN-based method achieves significantly better NMSE performance than the LS benchmark and traditional models such as FNN and ELM ( Fig. 4 ). Then, the impact of increasing the number of antennas and RIS elements on SAC channel estimation performance was investigated. Compared with the LS benchmark, the proposed CGAN method consistently maintains superior performance under various SNR conditions (Figs. 5 and6 ).Conclusions This paper investigates the channel estimation problem in RIS-assisted multi-user ISAC systems and proposes a two-stage channel estimation method based on CGAN. By adjusting the switching states of the RIS and employing adversarial training between the generator and discriminator networks, the proposed method achieves accurate estimation of the SAC channel. Simulation results demonstrate that, under various SNR conditions and channel dimensions, the CGAN-based estimation method exhibits strong generalization capability and significantly outperforms the benchmark schemes in estimation accuracy. Therefore, it shows great potential as an effective solution for enhancing system stability and efficiency. -
表 1 CGAN网络的具体参数
模型 网络 层 大小 激活函数 CGAN 生成器 输入层 $ 2M{P}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{l}}} $ - FFL 100 LeakyReLU FFL 200 LeakyReLU 输出层 $ 2{M}^{2} $ - 判别器 输入层 $ 2{M}^{2} $ - FFL 100 LeakyReLU FFL 200 LeakyReLU 输出层 1 - 表 2 两个阶段的子帧持续时间
时隙持续时间 时隙个数 子帧持续时间 子帧个数 两个阶段的总子帧持续时间 S1 TP=0.52 μs $ {P}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{1}}} $=M+K=12 $ \begin{aligned}T_{\mathrm{F}}^{{\mathrm{S}}_{1}}&={T}_{\mathrm{P}}{P}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{1}}}\\&=6.24 \;{\text{μs}}\end{aligned} $ $ {C}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{1}}} $ $ \begin{aligned}{T}_{\mathrm{E}}&={C}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{1}}}T_{\mathrm{F}}^{{\mathrm{S}}_{1}}+\left({C}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{2}}}-{C}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{1}}}\right)\\T_{\mathrm{F}}^{{\mathrm{S}}_{2}}&=99.84 \;{\text{μs}}\end{aligned} $ $ {\mathrm{S}}_{2} $ $ {T}_{\mathrm{P}}=0.52 \;{\text{μs}} $ $ {P}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{2}}}=\max \left\{M,K\right\}=6 $ $ \begin{aligned}T_{\mathrm{F}}^{{\mathrm{S}}_{2}}&={T}_{\mathrm{P}}{P}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{2}}}\\&=3.12 \;{\text{μs}}\end{aligned} $ $ {C}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{2}}}-{C}^{{{\mathrm{S}}_{1}}} $ 表 3 SAC信道的路径损耗
距离 路径损耗指数 路径损耗 BS-目标-BS链路 $ {d}_{\mathrm{S}}=150\mathrm{m} $ $ {\beta }_{\mathrm{S}}=3 $ $ {\xi }_{\mathrm{S}}={\xi }_{0}{\left({d}_{\mathrm{S}}/{d}_{0}\right)}^{-{{\beta }_{\mathrm{S}}}} $ RIS-BS链路 $ {d}_{\mathrm{IB}}=50\mathrm{m} $ $ {\beta }_{\mathrm{IB}}=2.3 $ $ {\xi }_{\mathrm{IB}}={\xi }_{0}{\left({d}_{\mathrm{IB}}/{d}_{0}\right)}^{-{{\beta }_{\mathrm{IB}}}} $ $ {U}_{k} $-BS链路 $ {d}_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{B}}=50\mathrm{m} $ $ {\beta }_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{B}}=3.5 $ $ {\xi }_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{B}}={\xi }_{0}{\left({d}_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{B}}/{d}_{0}\right)}^{-{{\beta }_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{B}}}} $ BS-$ {D}_{j} $链路 $ {d}_{\mathrm{B}{{D}_{j}}}=50\mathrm{m} $ $ {\beta }_{\mathrm{B}{{D}_{j}}}=3.5 $ $ {\xi }_{\mathrm{B}{{D}_{j}}}={\xi }_{0}{\left({d}_{\mathrm{B}{{D}_{j}}}/{d}_{0}\right)}^{-{{\beta }_{\mathrm{B}{{D}_{j}}}}} $ $ {U}_{k} $-RIS链路 $ {d}_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{I}}=2\mathrm{m} $ $ {\beta }_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{I}}=2 $ $ {\xi }_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{I}}={\xi }_{0}{\left({d}_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{I}}/{d}_{0}\right)}^{-{{\beta }_{{{U}_{k}}\mathrm{I}}}} $ RIS-$ {D}_{j} $链路 $ {d}_{\mathrm{I}{{D}_{j}}}=2\mathrm{m} $ $ {\beta }_{\mathrm{I}{{D}_{j}}}=2 $ $ {\xi }_{\mathrm{I}{{D}_{j}}}={\xi }_{0}{\left({d}_{\mathrm{I}{{D}_{j}}}/{d}_{0}\right)}^{-{{\beta }_{\mathrm{I}{{D}_{j}}}}} $ 表 4 训练时间(s)
训练时间 ELM FNN CGAN ISAC BS $ {\mathrm{S}}_{1} $:$ \bf{A} $,$ {\bf{b}}_{k} $ 2.54 10.31 436.09 $ {\mathrm{S}}_{2} $:$ {\bf{B}}_{k} $ 14.76 485.26 618.24 下行$ {D}_{j} $ $ {\mathrm{S}}_{1} $:$ {\bf{d}}_{j} $ 2.38 3.94 493.52 $ {\mathrm{S}}_{2} $:$ {\bf{D}}_{j} $ 9.41 88.82 522.06 -
[1] BARNETO C B, LIYANAARACHCHI S D, HEINO M, et al. Full duplex radio/radar technology: The enabler for advanced joint communication and sensing[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(1): 82–88. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000220. [2] BOZORGI F, SEN P, BARRETO A N, et al. RF front-end challenges for joint communication and radar sensing[C]. Proceedings of 2021 1st IEEE International Online Symposium on Joint Communications & Sensing (JC&S), Dresden, Germany, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/JCS52304.2021.9376387. [3] HAN Liang and WU Ke. Multifunctional transceiver for future intelligent transportation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2011, 59(7): 1879–1892. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2138156. [4] DONG Fuwang, LIU Fan, CUI Yuanhao, et al. Sensing as a service in 6G perceptive networks: A unified framework for ISAC resource allocation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(5): 3522–3536. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2022.3219463. [5] ZHAO Bo, WANG Ming, XING Zeng, et al. Integrated sensing and communication aided dynamic resource allocation for random access in satellite terrestrial relay networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(2): 661–665. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3227594. [6] HE Zhenyao, XU Wei, SHEN Hong, et al. Full-duplex communication for ISAC: Joint beamforming and power optimization[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2023, 41(9): 2920–2936. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2023.3287540. [7] LE Q N, NGUYEN V D, DOBRE O A, et al. RIS-assisted full-duplex integrated sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(10): 1677–1681. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2023.3285391. [8] LI Hongyu, SHEN Shanpu, NERINI M, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces 2.0: Beyond diagonal phase shift matrices[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2024, 62(3): 102–108. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2300019. [9] CHU Jinjin, LU Zhiping, LIU Rang, et al. Joint beamforming and reflection design for secure RIS-ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(3): 4471–4475. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3328192. [10] JIANG Chengjun, ZHANG Chensi, HUANG Chongwen, et al. RIS-assisted ISAC systems for robust secure transmission with imperfect sense estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025, 24(5): 3979–3992. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2025.3534439. [11] 陈真, 杜晓宇, 唐杰, 等. 基于深度强化学习的RIS辅助通感融合网络: 挑战与机遇[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(9): 3467–3473. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240086.CHEN Zhen, DU Xiaoyu, TANG Jie, et al. DRL-based RIS-assisted ISAC network: Challenges and opportunities[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(9): 3467–3473. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240086. [12] LIU Yu, AL-NAHHAL I, DOBRE O A, et al. Deep-learning channel estimation for IRS-assisted integrated sensing and communication system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(5): 6181–6193. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3231727. [13] LIU Yu, AL-NAHHAL I, DOBRE O A, et al. Extreme learning machine-based channel estimation in IRS-assisted multi-user ISAC system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(12): 6993–7007. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3308150. [14] WANG Yang, XU Yin, ZHANG Cixiao, et al. Channel estimation for RIS-assisted mmWave systems via diffusion models[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2025, 30: 597–601. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2025.3645078. [15] WU Qingying, BAO Junqi, XU Hui, et al. A convolutional-transformer residual network for channel estimation in intelligent reflective surface aided MIMO systems[J]. Sensors, 2025, 25(19): 5959. doi: 10.3390/s25195959. [16] FAISAL A, AL-NAHHAL I, LEE K, et al. Conditional generative adversarial networks for channel estimation in RIS-assisted ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2025, 73(9): 7828–7841. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2025.3541047. [17] ELSAYED M, EL-BANNA A A A, DOBRE O A, et al. Hybrid-layers neural network architectures for modeling the self-interference in full-duplex systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(6): 6291–6307. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3159535. [18] ELSAYED M, EL-BANNA A A A, DOBRE O A, et al. Full-duplex self-interference cancellation using dual-neurons neural networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(3): 557–561. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3136030. [19] ELSAYED M, EL-BANNA A A A, DOBRE O A, et al. Low complexity neural network structures for self-interference cancellation in full-duplex radio[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(1): 181–185. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3024063. [20] 3GPP. 3GPP TS 36.211 Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Physical channels and modulation[S]. 2016. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版信息, 请确认). [21] XIAO Zhiqiang and ZENG Yong. Waveform design and performance analysis for full-duplex integrated sensing and communication[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(6): 1823–1837. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155509. [22] MA Jianpeng, ZHANG Shun, LI Hongyan, et al. Sparse bayesian learning for the time-varying massive MIMO channels: Acquisition and tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(3): 1925–1938. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2855197. [23] SHORTEN C and KHOSHGOFTAAR T M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2019, 6(1): 60. doi: 10.1186/s40537-019-0197-0. [24] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. [25] BISWAS S, MASOUROS C, and RATNARAJAH T. Performance analysis of large multiuser MIMO systems with space-constrained 2-D antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(5): 3492–3505. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2522419. [26] LIU Fan, MASOUROS C, PETROPULU A P, et al. Joint radar and communication design: Applications, state-of-the-art, and the road ahead[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(6): 3834–3862. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2973976. [27] FAISAL A, AL-NAHHAL I, DOBRE O A, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for optimizing RIS-assisted HD-FD wireless systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(12): 3893–3897. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3117929. [28] LIU Yu, AL-NAHHAL I, DOBRE O A, et al. Deep-learning channel estimation for IRS-assisted integrated sensing and communication system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(5): 6181–6193. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3231727. (查阅网上资料,本条文献与第12条文献重复,请确认). -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
