A Spatio-Temporal Feature Fusion LSTM Relaxation Measurement Method for LEO Satellites
-
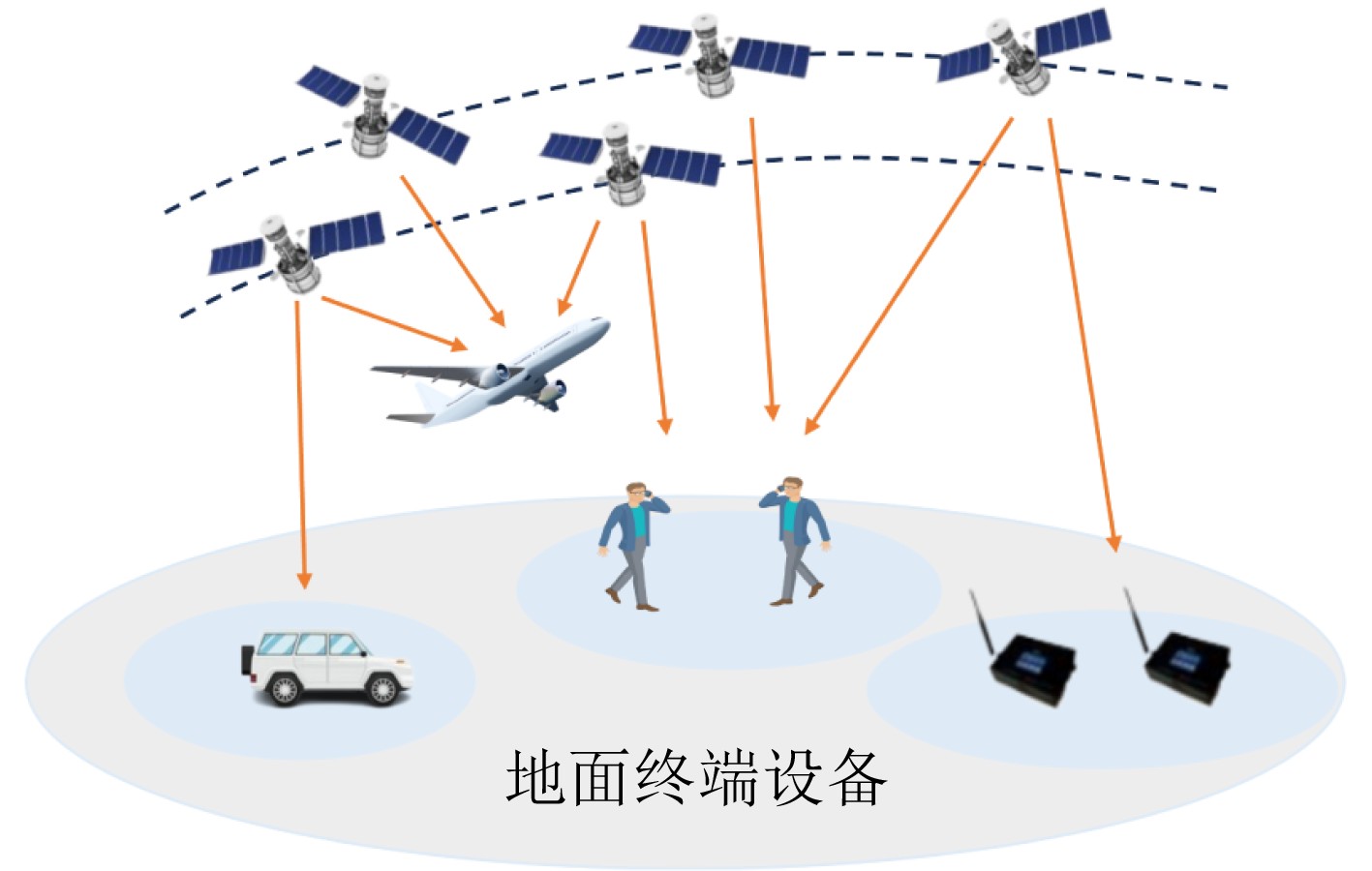
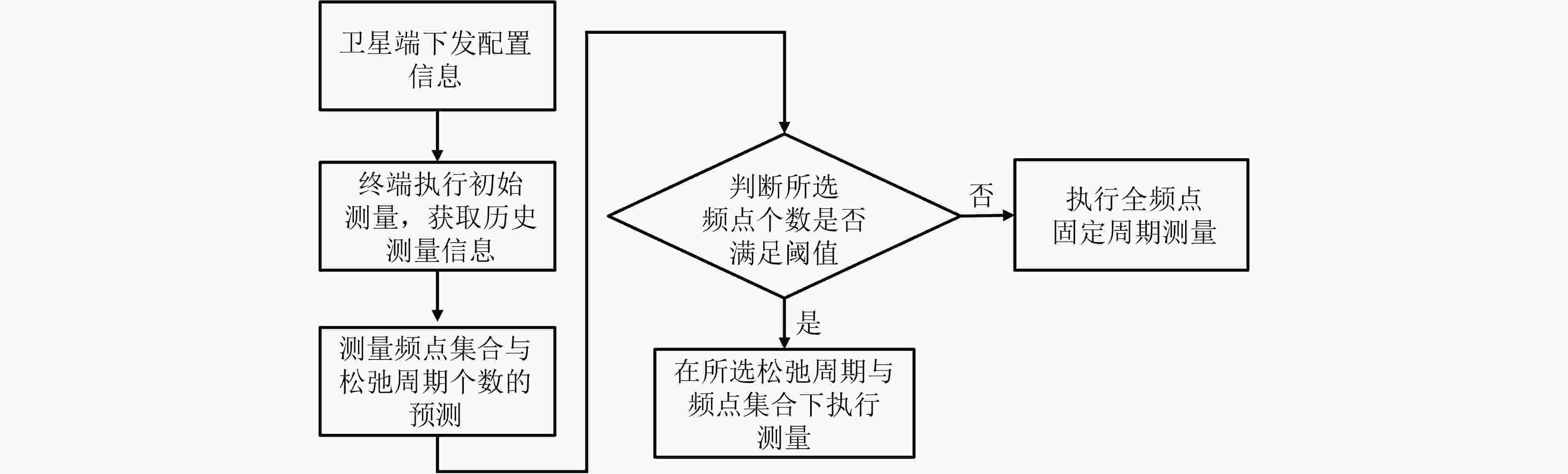
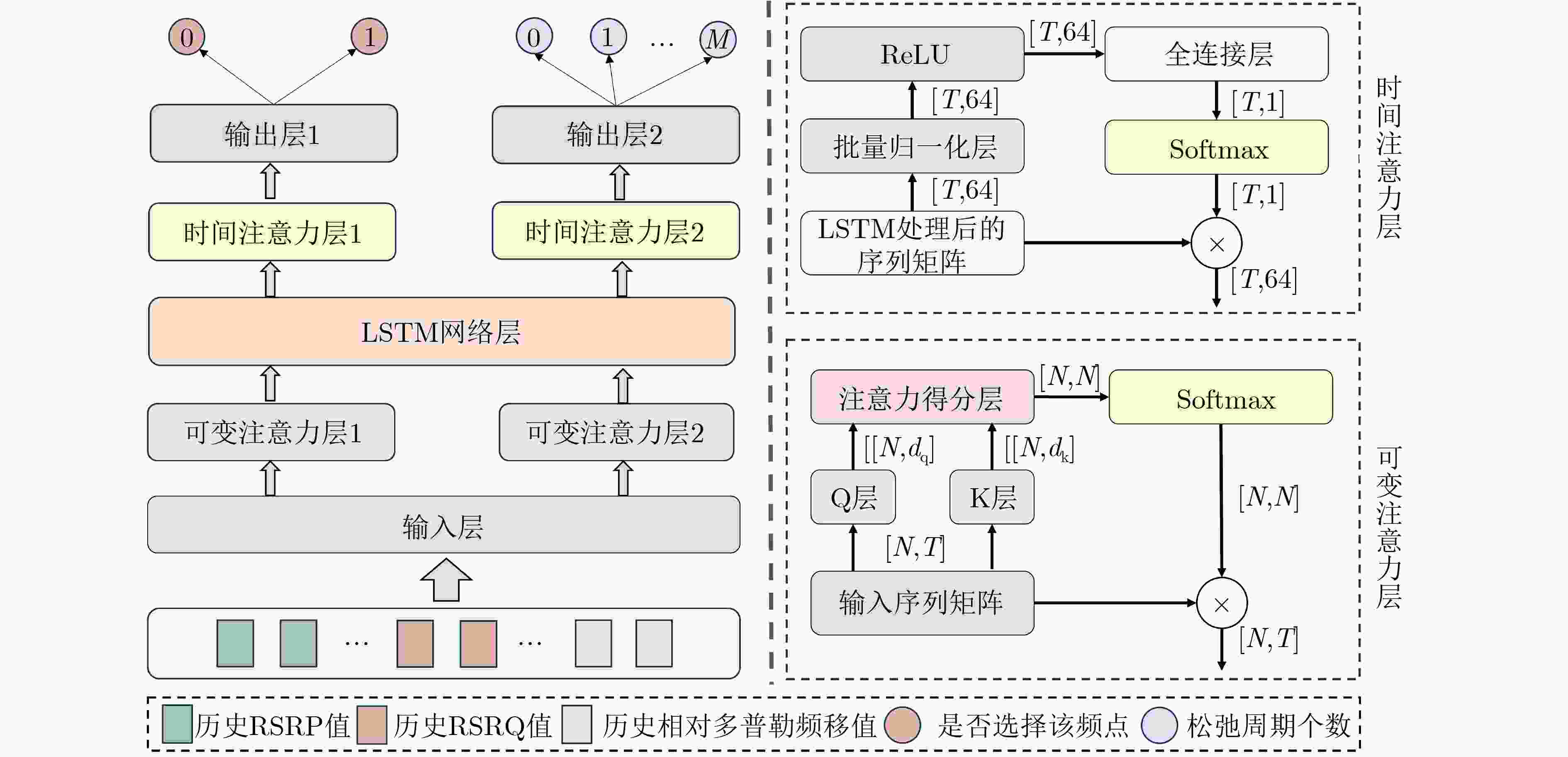
摘要: 为降低低轨(LEO)卫星系统的高动态性导致的终端频繁链路测量,现有松弛测量方案主要采用基于静态阈值或常规的时空预测模型的方法。然而,卫星的高动态性导致不同历史时刻的测量数据和不同测量指标的重要性随之动态演化,而传统方法难以捕获这种时空重要性的动态变化。为此,针对上述挑战,该文提出一种面向低轨卫星的时空特征融合长短期记忆递归神经网络(LSTM)松弛测量方法。首先,建立了LEO卫星通信系统模型,以获取所需要的历史测量数据。然后,构建了集成双重注意力机制的LSTM预测模型,实现对关键历史时刻与动态重要特征的精准聚焦,从而完成对测量频点集合与测量周期的精准预测。最后,在选择的测量频点集合和松弛周期下,执行自适应的链路测量。仿真结果表明,相较于基线方法,该文所提松弛测量方案在确保链路可靠性的同时,可以显著降低终端的测量频次。与基线相比,在更大的速度和松弛周期下,具有更强的自适应性。Abstract:
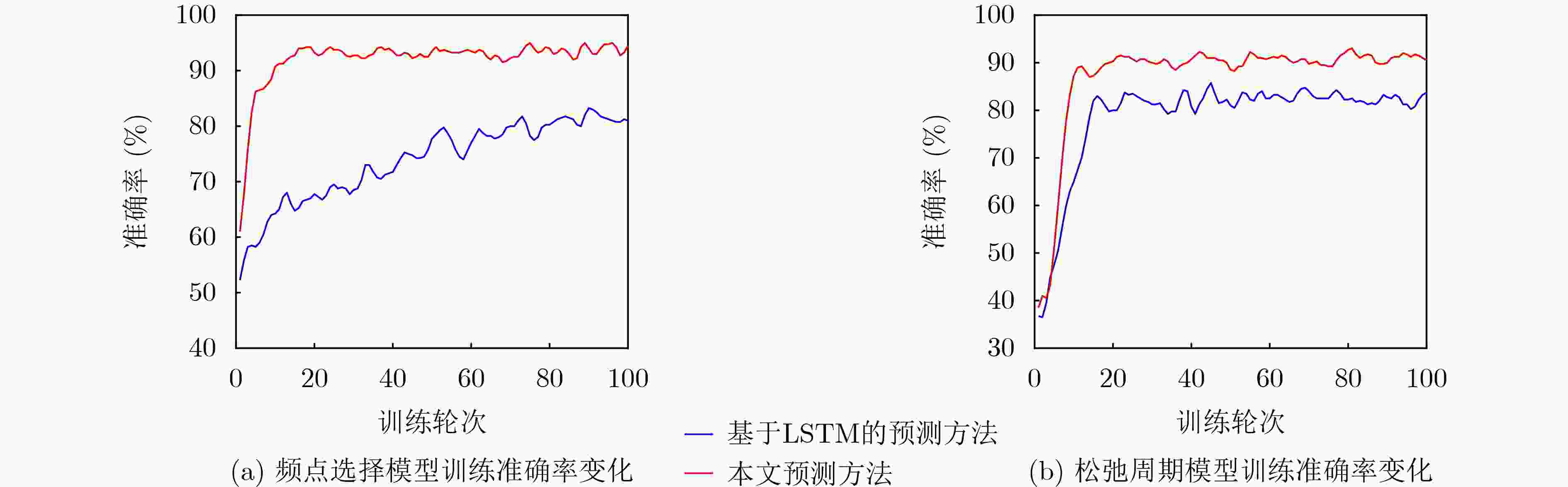
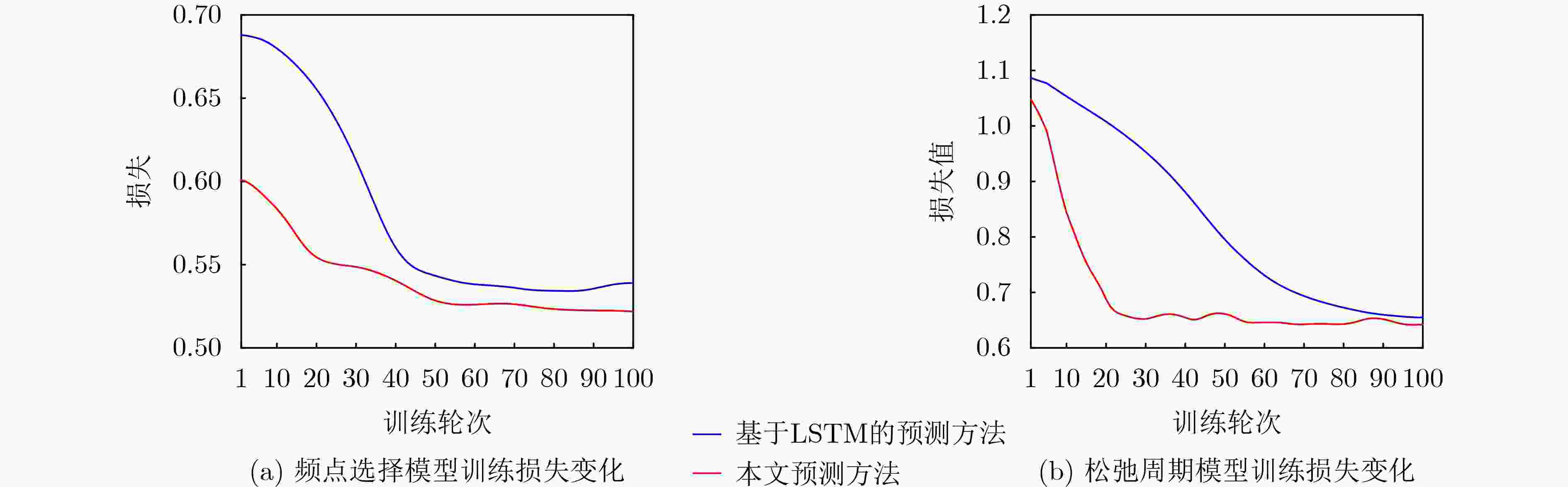
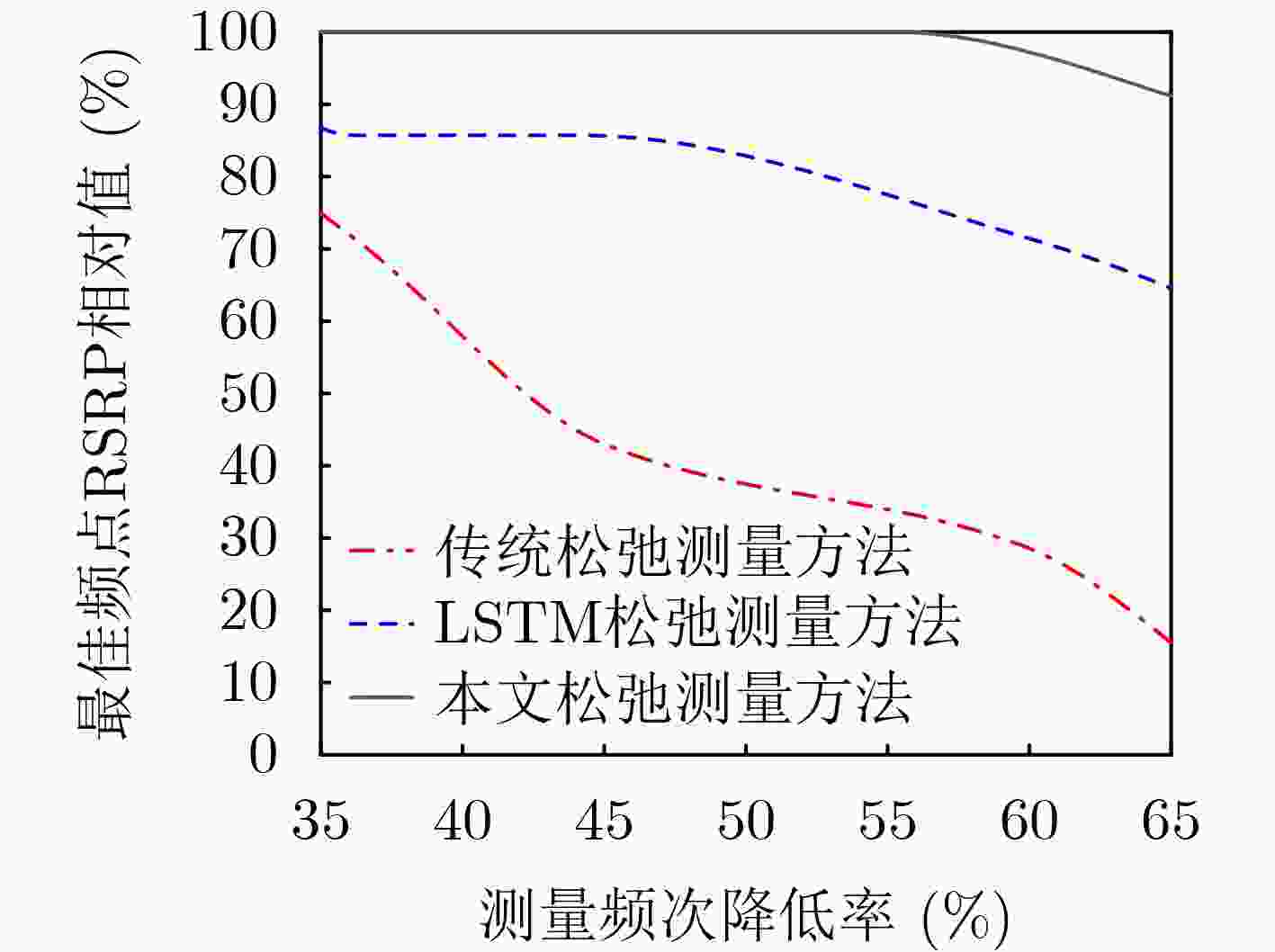
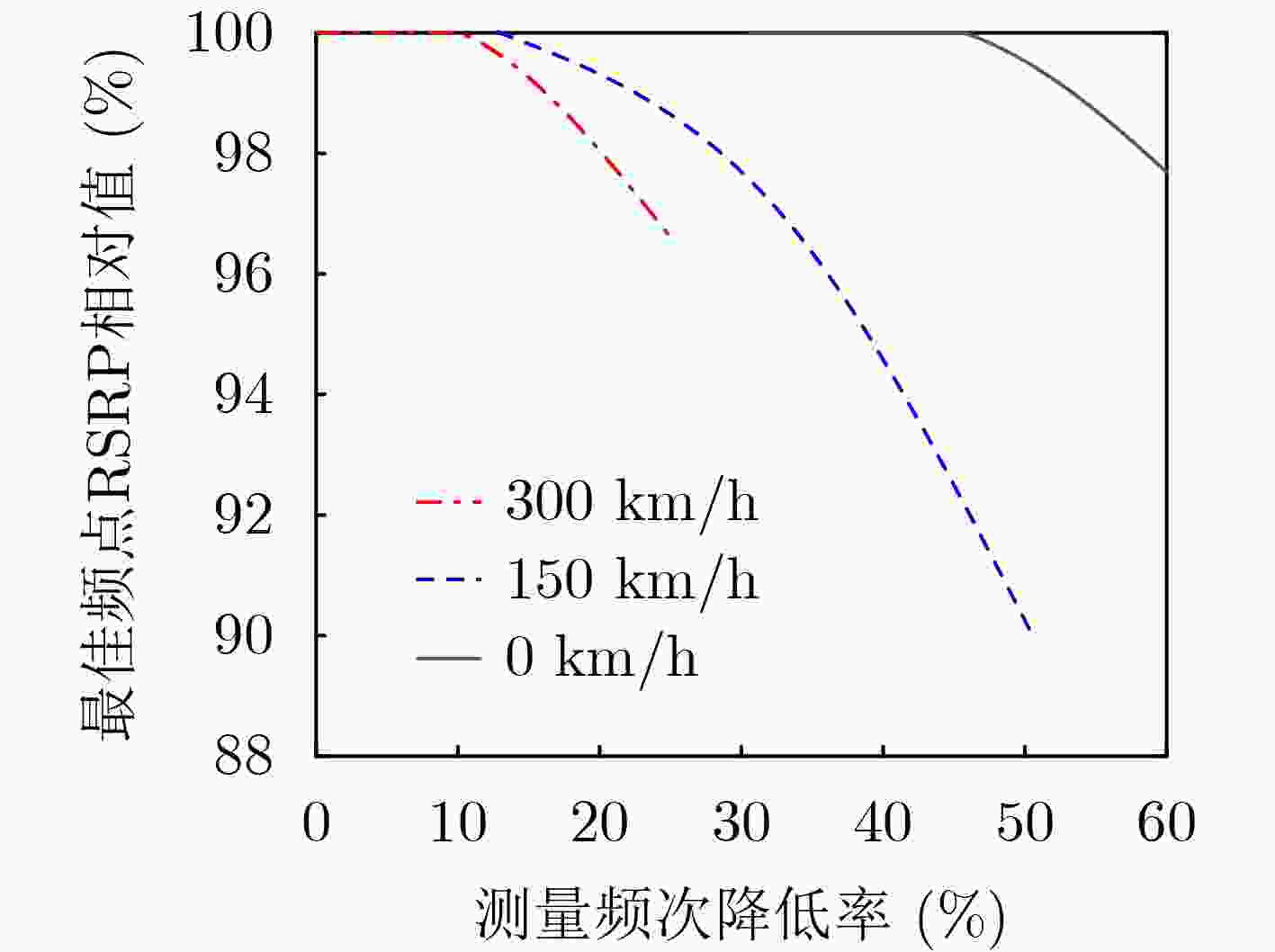
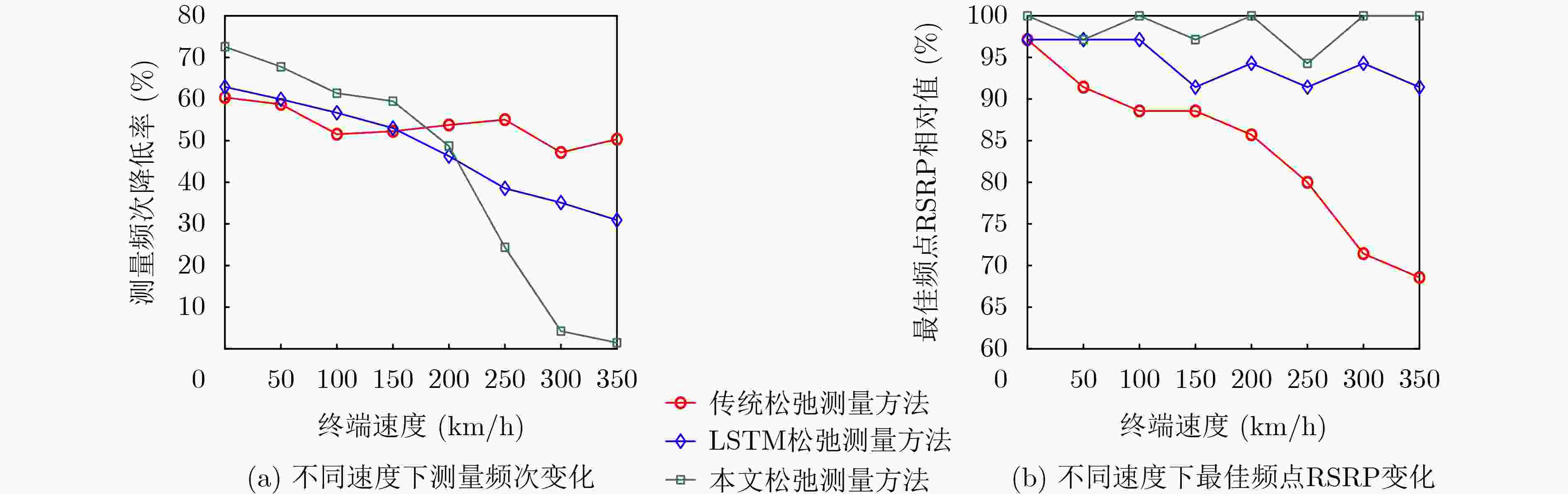
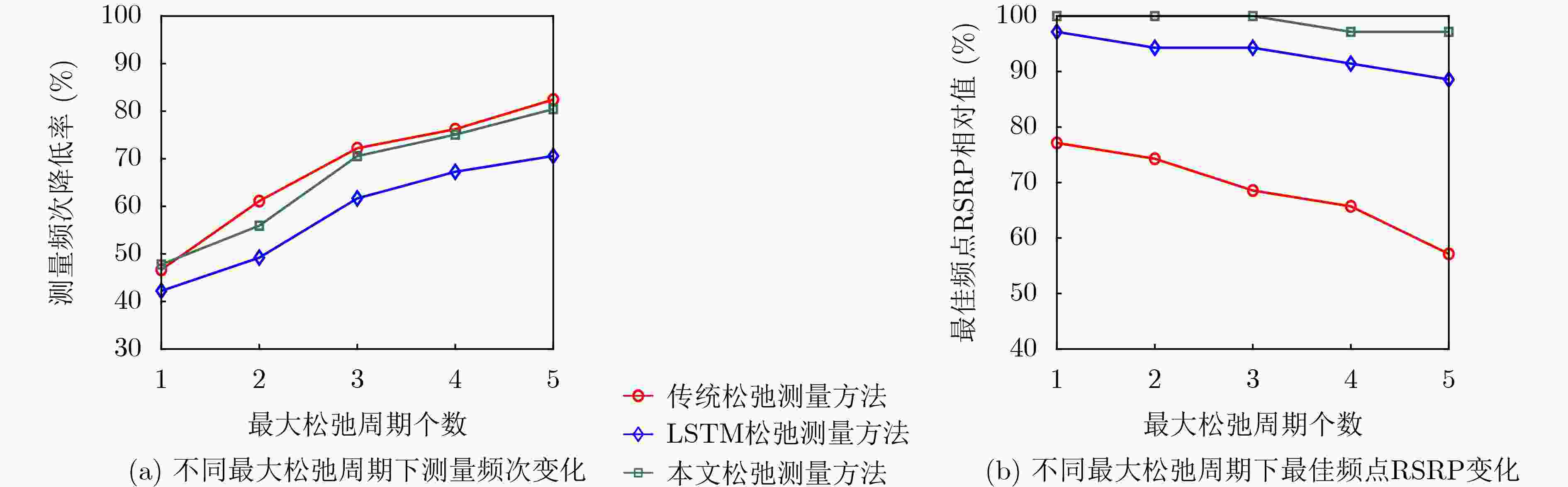
Objective The high dynamics of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite communication systems cause frequent link measurements. Existing schemes mainly adopt threshold-based or standard spatio-temporal prediction-based relaxation measurement strategies to mitigate this issue. However, these approaches do not effectively capture the dynamic evolution of the importance of historical data and multiple measurement metrics induced by satellite mobility. Therefore, adaptation to highly time-varying satellite-ground link environments remains limited. To address this problem, a spatio-temporal feature fusion relaxation measurement method based on a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network is proposed for LEO satellite communication. An LSTM recurrent neural network integrated with a dual-attention mechanism is constructed. The LSTM extracts correlations among historical measurement data, whereas temporal attention and variable attention focus on key time instants and significant features, respectively. On this basis, the measurement frequency point set and the number of relaxation periods are jointly predicted. Intelligent link measurement is then performed using the selected frequency point set and relaxation period, enabling adaptive and energy-efficient link monitoring in LEO satellite systems. Methods The proposed spatio-temporal feature fusion LSTM-based relaxation measurement method employs a Dual-Attention LSTM (DA-LSTM) model to reduce measurement overhead while maintaining reliable link monitoring. Historical link quality indicators, including Reference Signal Receiving Power (RSRP), Reference Signal Receiving Quality (RSRQ), and Doppler shift, together with satellite ephemeris information, are used as model inputs. These features capture temporal and spatial variations and support the joint prediction of a subset of measurement frequency points and their corresponding relaxation periods. Based on the predicted results, the terminal performs adaptive frequency point selection and dynamic relaxation period adjustment or executes full-band measurements with a fixed measurement period. This process enables adaptive and energy-efficient link monitoring while preserving communication performance in LEO satellite systems. Results and Discussions The proposed relaxation measurement method applies the DA-LSTM model to predict measurement frequency points and the number of relaxation periods using historical link quality information. Simulation results show higher convergence efficiency, higher training accuracy, and lower loss for both frequency point selection and relaxation period selection compared with baseline methods ( Fig. 4 andFig. 5 ). The proposed measurement algorithm achieves an average measurement frequency below 30% with minimal performance degradation (Table 3 ). This result is attributed to the adaptive selection of high-quality frequency points and dynamic adjustment of the measurement period. The trade-off between measurement frequency and communication performance is further examined (Fig. 6 andFig. 7 ), indicating that the proposed method achieves a better balance than baseline methods under different terminal speeds. Additional simulations under different terminal speeds (Fig. 8 ) and different maximum relaxation periods (Fig. 9 ) further confirm that high energy efficiency and communication performance are maintained under diverse operational conditions.Conclusions This work addresses the challenge of dynamic spatio-temporal importance evolution caused by satellite mobility, which limits the effectiveness of existing relaxation measurement strategies. A DA-LSTM-based relaxation measurement algorithm is proposed to predict both the measurement frequency point set and the number of relaxation periods by extracting spatio-temporal correlations from historical link quality data. Simulation results under various scenarios show that: (1) the proposed algorithm achieves higher convergence efficiency and training accuracy than baseline methods; (2) adaptive selection of high-quality frequency points and dynamic adjustment of relaxation periods maintain a favorable balance between measurement frequency and communication reliability; and (3) the method remains effective across different terminal speeds and maximum relaxation periods, indicating good scalability and robustness in dynamic operational environments. The current study is limited to simulations and does not consider hardware constraints, atmospheric effects, or real-time processing requirements. These factors should be investigated in future work. -
表 1 具体仿真参数配置
系统参数 参数设置 轨道面数、每个轨道卫星数 6,10 相位因子 1,2 倾角 55°,89° 卫星频段 n510,n511,n512 偏心率 0.001020 轨道高度 875 km, 925 km 天线增益、带宽B 16 dBi, 380 MHz 表 2 神经网络模型参数
系统参数 参数设置 损失函数 均方误差(MSE) 优化器 Adam 激活函数 ReLU, Softmax 可学习参数量 308.5 k 学习率 0.00001 表 3 终端测量平均性能(%)
传统松弛测量方法 LSTM松弛测量方法 本文松弛测量方法 测量频次降低率 60.38 62.92 72.57 最佳频点RSRP相对值 97.57 97.68 99.89 -
[1] 何元智, 肖永伟, 张世杰, 等. 全球泛在连接新模式: 手机直连卫星关键技术及挑战[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 1591–1603. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240032.HE Yuanzhi, XIAO Yongwei, ZHANG Shijie, et al. A novel pattern for global ubiquitous interconnection: Key technologies and challenges of direct-to-smartphone[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 1591–1603. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240032. [2] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 6G总体愿景与潜在关键技术白皮书[R]. 2021. IMT-2030(6G) Promotion Group. 6G overall vision and potential key technology white paper[R]. 2021. [3] 苏昭阳, 刘留, 艾渤, 等. 面向低轨卫星的星地信道模型综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 1684–1702. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230941.SU Zhaoyang, LIU Liu, AI Bo, et al. Survey of satellite-ground channel models for low earth orbit satellites[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 1684–1702. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230941. [4] YUE Pingyue, AN Jianping, ZHANG Jiankang, et al. Low earth orbit satellite security and reliability: Issues, solutions, and the road ahead[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2023, 25(3): 1604–1652. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2023.3296160. [5] 3GPP. TR 38.331-2022 NR Radio Resource Control (RRC) protocol specification[S]. Sophia Antipolis, France: 3GPP. 2022. [6] 3GPP. TR 38.821-2020 Solutions for NR to support non-terrestrial networks (NTN)[S]. Sophia Antipolis, France: 3GPP. 2020. [7] PARK S and KIM J. Trends in LEO satellite handover algorithms[C]. 2021 Twelfth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Jeju Island, Korea, 2021: 422–425. doi: 10.1109/ICUFN49451.2021.9528738. [8] JUAN E, LAURIDSEN M, WIGARD J, et al. Handover solutions for 5G low-earth orbit satellite networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 93309–93325. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3203189. [9] Nokia Siemens Networks and Nokia Corporation. Small cell signal based control of inter-frequency measurements[R]. TSG-RAN WG2 Meeting #77bis, 2012. [10] 郑景仁. NTN中的测量和小区重选[P]. 中国, 118216179A, 2024.ZHENG Jingren. Measurement and cell reselection in NTN[P]. CN, 118216179A, 2024. [11] 孔繁华, 邝奕如, 徐海博, 等. 测量放松方法及装置[P]. 中国, 115460660A, 2022.KONG Fanhua, KUANG Yiru, XU Haibo, et al. Measurement relaxation method and device[P]. CN, 115460660A, 2022. [12] LUO Hejia, WANG Yu, WANG Xiaolu, et al. The present application provides a communication method and apparatus, relates to the technical field of wireless[P]. CN, WO2023061166A1, 2023. [13] 何燃燃, 张艳霞, 肖潇. 测量控制方法、终端及网络侧设备[P]. 中国, 117440395A, 2024.HE Ranran, ZHNAG Yanxia, and XIAO Xiao. Measurement control method, terminal and network side equipment[P]. CN, 117440395A, 2024. [14] 胡奕, 李海涛. NTN中非连接态终端的RRM测量方式确定方法、装置及介质[P]. 中国, 202180101902.2, 2024.HU Yi and LI Haitao. Method and device for determining RRM (Radio Resource Management) measurement mode of non-connected terminal in NTN (Network Temporary Network), and medium[P]. CN, 202180101902.2, 2024. [15] WANG Juan, SUN Lijuan, ZHOU Jian, et al. An adaptive dynamic channel allocation algorithm based on a temporal–spatial correlation analysis for LEO satellite networks[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(21): 10939. doi: 10.3390/app122110939. [16] 李学华, 廖海龙, 张贤, 等. 面向低轨卫星通信网络的联邦深度强化学习智能路由方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(8): 2652–2664. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250072.LI Xuehua, LIAO Hailong, ZHANG Xian, et al. Federated deep reinforcement learning-based intelligent routing design for LEO satellite networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(8): 2652–2664. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250072. [17] 彭亮, 闫杰, 魏鹏, 等. 低轨卫星网络中基于时空相关性的不完全时间序列流量预测[J]. 信息与电子工程前沿(英文版), 2025, 26(5): 788–804. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2300873.PENG Liang, YAN Jie, WEI Peng, et al. Spatio-temporal correlation-based incomplete time-series traffic prediction for LEO satellite networks[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2025, 26(5): 788–804. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2300873. [18] ORTIZ F, VASQUEZ-PERALVO J A, QUEROL J, et al. Harnessing supervised learning for adaptive beamforming in multibeam satellite systems[C]. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning for Communication and Networking (ICMLCN), Stockholm, Sweden, 2024: 386–392. doi: 10.1109/ICMLCN59089.2024.10624792. [19] SU Yongtao, LIU Yaoqi, ZHOU Yiqing, et al. Broadband LEO satellite communications: Architectures and key technologies[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(2): 55–61. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2019.1800299. [20] 王瀚萱, 陈子博, 孙耀华. 低轨卫星通信中的波束跳变和频率复用方法研究[J]. 电子技术应用, 2023, 49(5): 24–29. doi: 10.16157/j.issn.0258-7998.233990.WANG Hanxuan, CHEN Zibo, and SUN Yaohua. Study on beam hopping and frequency reuse in LEO satellite communication[J]. Application of Electronic Technique, 2023, 49(5): 24–29. doi: 10.16157/j.issn.0258-7998.233990. [21] 3GPP. TR 38.811-2018 Study on New Radio (NR) to support non-terrestrial networks[S]. 2018. [22] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. doi: 10.5555/3295222.3295349. [23] 张弓, 马福建, 聂欣, 等. PULSAR低轨卫星导航星座性能分析研究[J]. 航天器工程, 2024, 33(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2024.01.001.ZHANG Gong, MA Fujian, NIE Xin, et al. Study on performance of PULSAR low earth orbit constellation satellite for navigation[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2024, 33(1): 1–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2024.01.001. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
