Small Object Detection Algorithm for UAV Aerial Images in Complex Environments
-
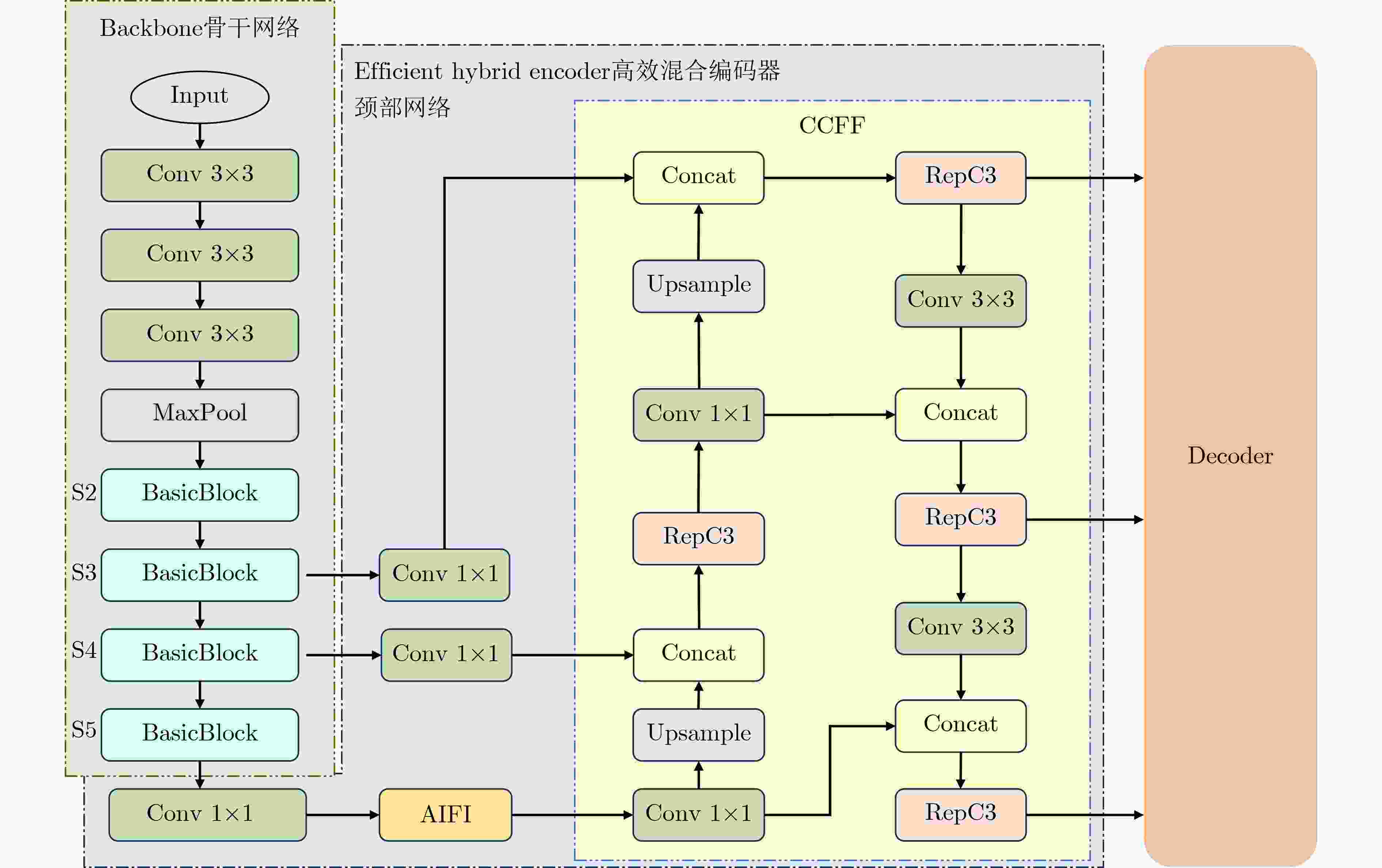
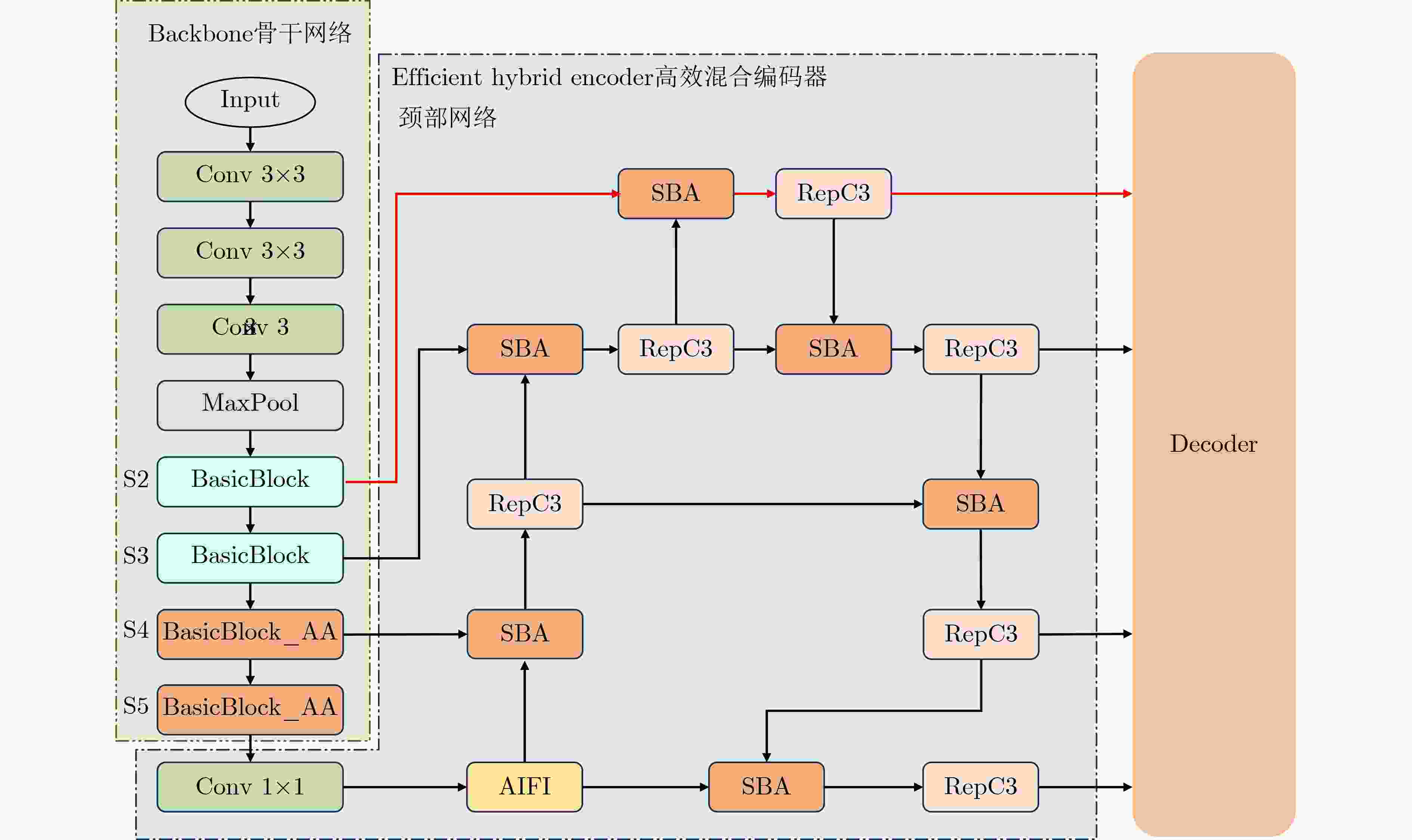
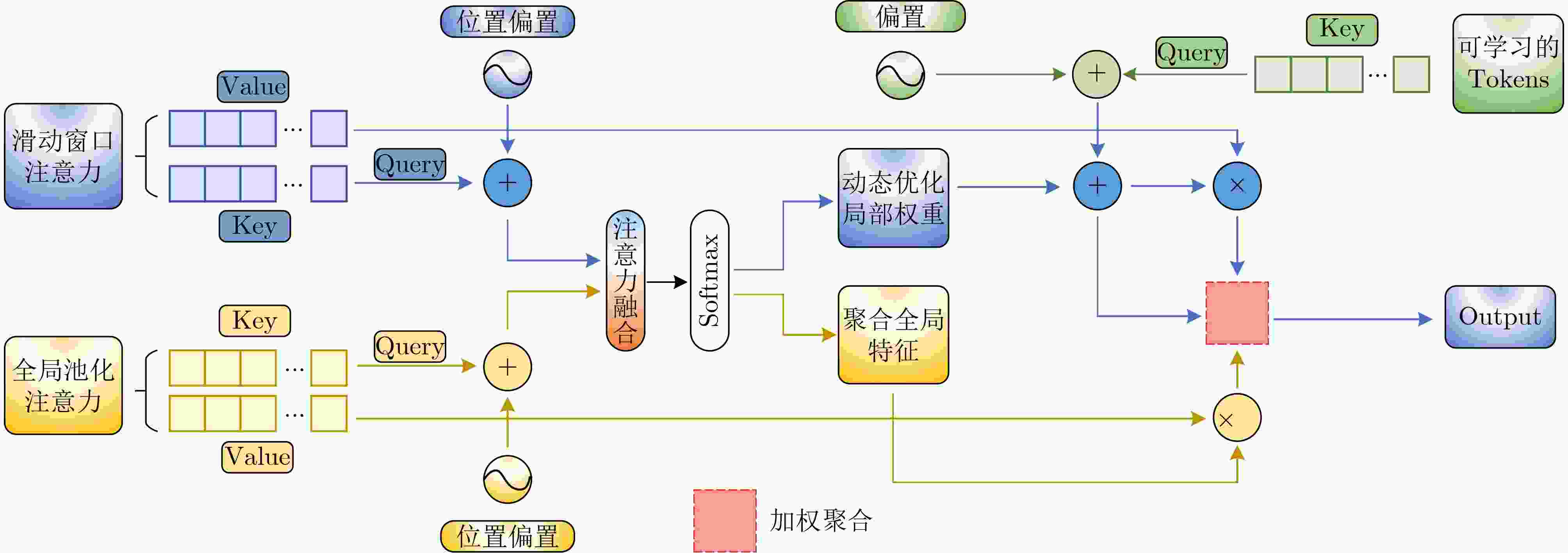
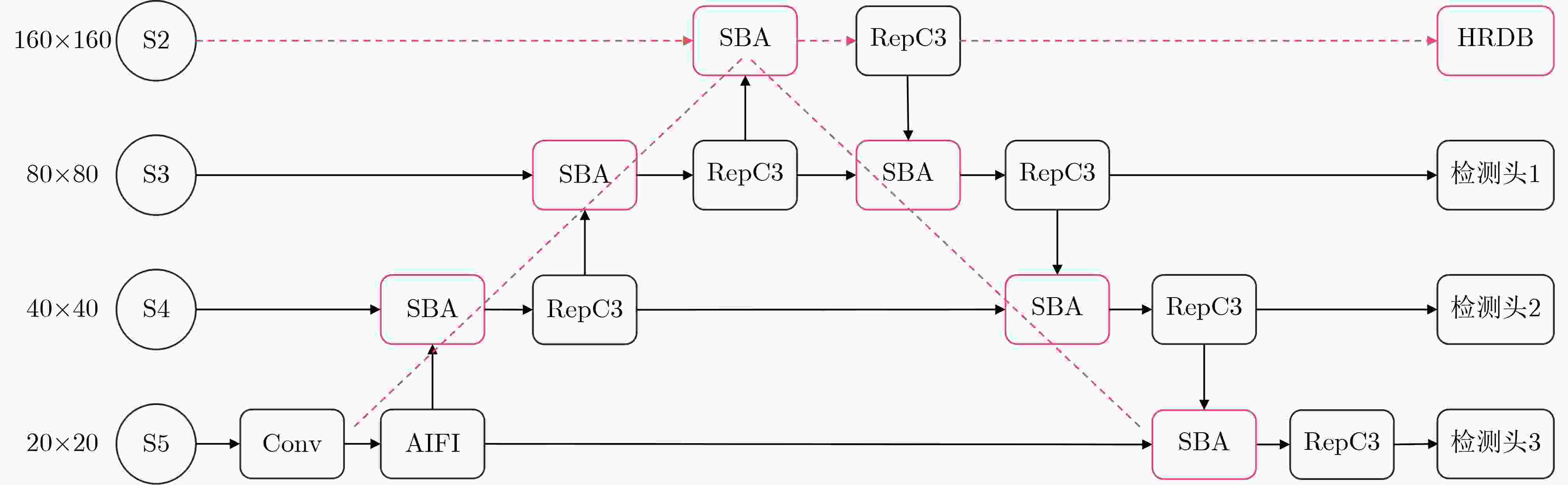
摘要: 无人机航拍图像因其分辨率高、视角广、部署灵活的特点,在智能交通领域得到广泛应用。针对无人机航拍图像中目标尺度变化大、背景复杂、小目标密集等问题,提出一种面向复杂环境的无人机航拍目标检测算法HAR-DETR。首先,对骨干网络的最后两层BasicBlock重新设计,添加聚合感知注意力以提取目标的多尺度特征,增大了感受野和对细粒度目标的感知效果;其次,设计高分辨率检测分支,提高模型对小目标检测的敏感度。最后,提出基于特征金字塔的重校准特征融合网络(RFF-FPN),将小目标的浅层边界特征与深层语义特征结合,更好地捕捉多尺度目标的语义信息,同时简化颈部网络的结构。实验结果表明,在VisDrone2019数据集上,HAR-DETR算法的mAP50相比原RT-DETR模型提升3.8%,mAP50-95提升3.2%。在RSOD数据集上展现出良好的泛化性能,在小目标检测任务中表现优异,具有较强的实用价值和推广前景。Abstract:
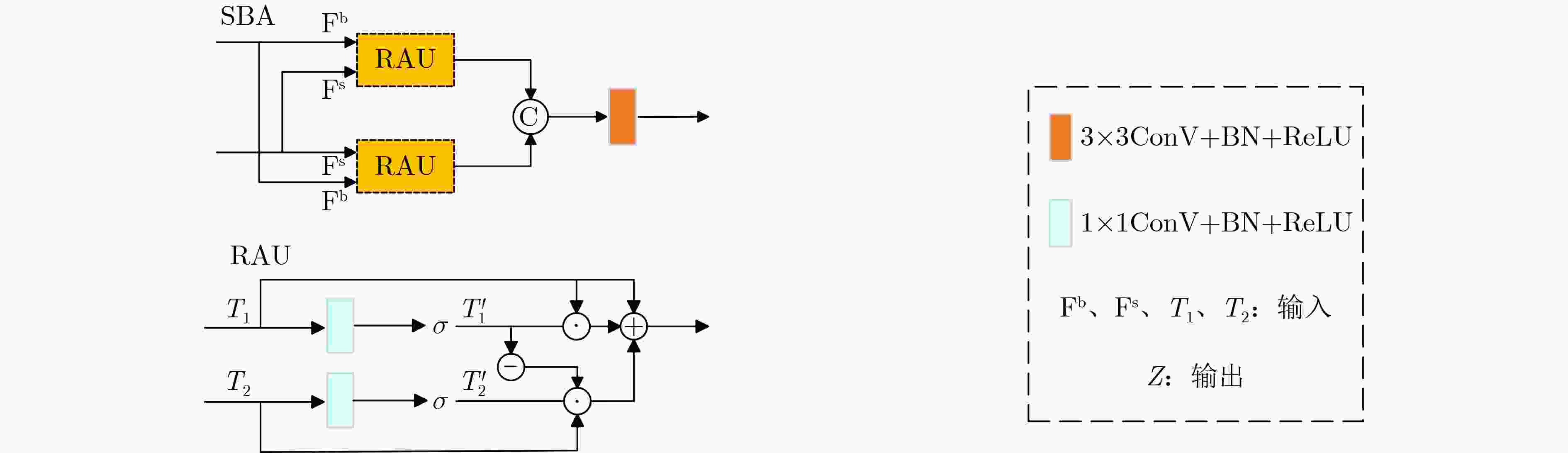
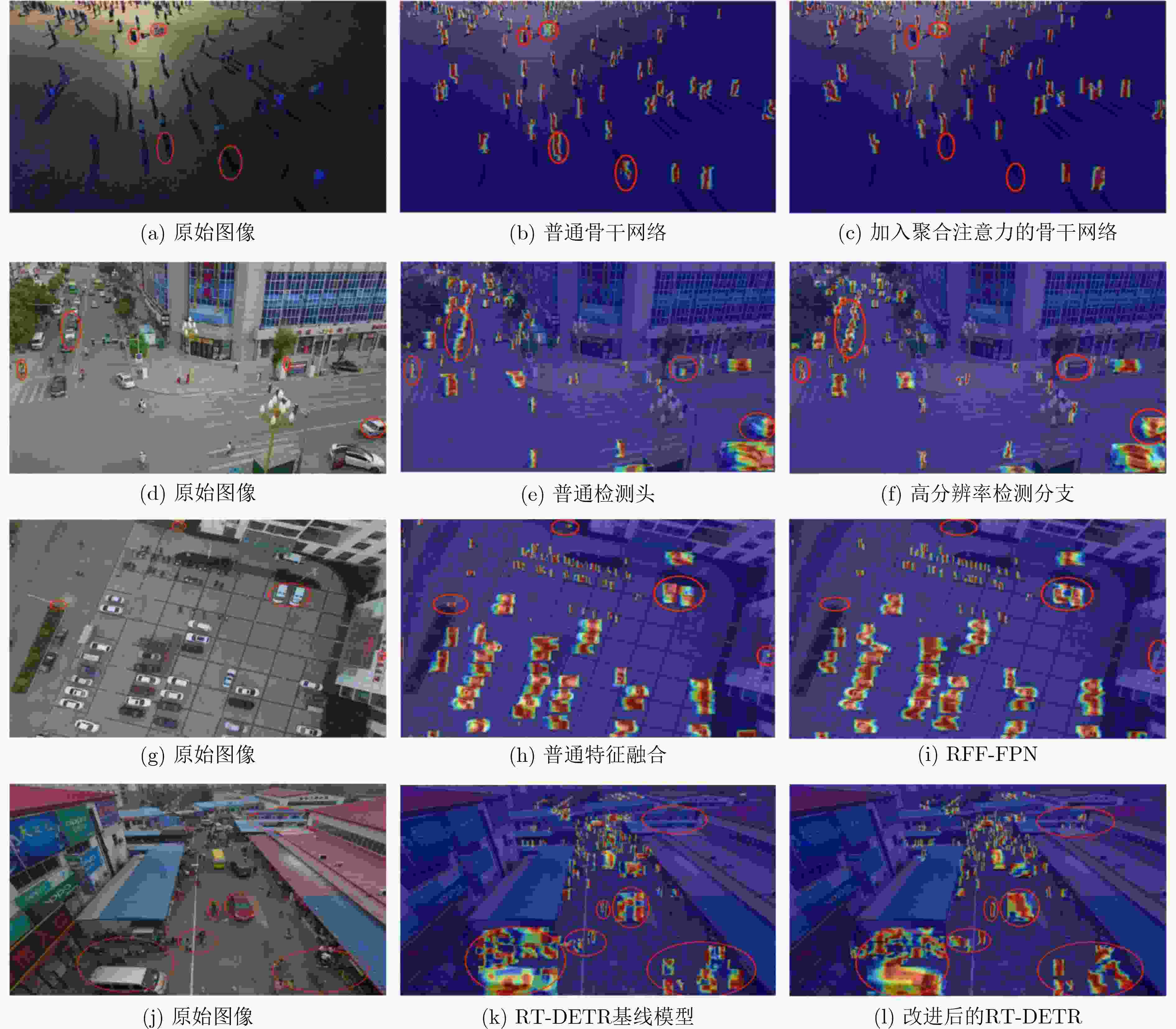
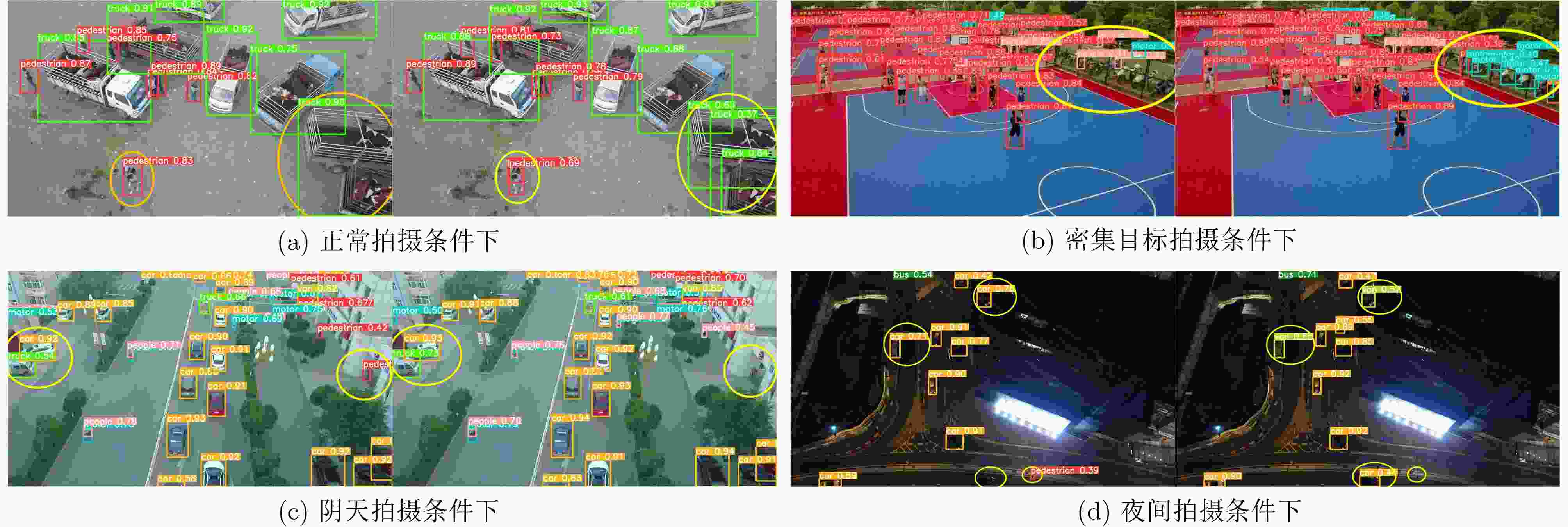
Objective Small object detection plays a critical role in practical applications such as UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) inspection and intelligent transportation systems, where precise perception of diminutive targets is essential for operational reliability and safety. It enables the automated identification and tracking of challenging targets. However, the limited pixel size of small objects, coupled with their tendency to be obscured or integrated with complex backgrounds, results in strong background noise, leading to poor performance and elevated false-negative rates in existing detection models. To address this issue and achieve high-performance, high-precision detection of small objects in complex environments, this study proposes HAR-DETR, an enhancement over the RT-DETR baseline model, aimed at improving the detection accuracy for small objects. Methods HAR-DETR is proposed for small object detection in aerial images, incorporating three key improvements: Aggregated Attention, RFF-FPN (Recalibrated Feature Fusion Network-FPN), and a high-resolution detection branch. In the backbone network, Aggregated Attention enhances the model's ability to focus on relevant features of small objects. By expanding the receptive field, the model captures more detailed edge and texture information, thereby enabling more effective extraction of multi-scale features of the targets. During the feature fusion phase, RFF-FPN selectively integrates high-level and low-level features, allowing the network to retain critical spatial information and context. This facilitates the refinement of the edges and contours of small objects, improving the accuracy of localization and recognition, especially when object details may be obscured by background clutter or varying lighting conditions. The high-resolution detection head places greater emphasis on the edge features of small objects, providing enhanced small object perception capabilities, and further improving the model's robustness and precision. Results and Discussions A comparative analysis is conducted with several widely used object detection models, including YOLOv5, YOLOv8, YOLOv10 and so on, to evaluate the performance of the model in small object detection using precision, recall, and mAP metrics. Experimental results show that the HAR-DETR model outperforms other comparative models in terms of precision, recall, and mAP on the VisDrone2019 dataset ( Table 1 ). The mAP50 and mAP50-95 are improved by 3.8% and 3.2%, respectively, compared to the baseline model (Table 2 ). This demonstrates that the HAR-DETR model offers superior performance in detecting small objects in aerial images under complex environments. Heatmaps generated using GradCAM are utilized for comparative analysis of the proposed improvements, showing better detection results for all improvements compared to the baseline model (Fig. 6 ). In the generalization performance experiment, the VisDrone2019 validation set and RSOD dataset are used under identical training conditions. The experimental results indicate that HAR-DETR exhibits strong generalization ability across heterogeneous tasks (Tables 3 and4 ).Conclusions This paper addresses the issues of false positives and false negatives in small object detection within aerial images captured in complex environments by utilizing the HAR-DETR model. Aggregated Attention is introduced in the backbone feature extraction phase to expand the receptive field and enhance global feature extraction capabilities. In the feature fusion phase, the RFF-FPN structure is proposed to enrich the feature representations. Additionally, a high-resolution detection head is introduced to make the model more sensitive to the edge textures of small objects. The model is evaluated using the Visdrone2019 and RSOD datasets, and the results demonstrate the following: (1) The proposed method improves the small object detection metrics, mAP50 and mAP50-95, by 3.8% and 3.2%, respectively, compared to the baseline model, achieving 51.2% and 32.1%, and mitigating the issues of false negatives and false positives; (2) In comparison with other mainstream object detection models, HAR-DETR exhibits the best performance in small object detection, thereby fully validating the effectiveness of the model; (3) The HAR-DETR model achieves high accuracy in cross-dataset training, demonstrating its excellent generalization performance. These results indicate that HAR-DETR possesses stronger semantic expression and spatial awareness capabilities, making it adaptable to various aerial perspectives and target distribution patterns, thus providing a more versatile solution for UAV visual perception systems in complex environments. -
Key words:
- Small object detection /
- RT-DETR /
- Feature fusion /
- Aerial images
-
表 1 对比实验结果
算法名称 PM GFLOPs P/% R/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% FPS YOLOv5m 25.2 64.0 52.1 41.2 41.6 25.0 124.5 YOLOv5l 53.1 134.7 54.5 42.9 43.8 26.7 83.0 YOLOv8m 25.8 78.7 53.1 41.2 41.9 25.4 114.5 YOLOv8l 43.5 164.9 55.0 42.7 43.8 26.6 86.2 YOLOv10m 16.7 63.4 54.2 40.9 42.1 26.2 110.3 YOLOv10l 25.7 126.4 55.3 42.5 44.3 27.6 82.6 YOLOv12m 20.1 67.2 53.7 42.0 43.4 26.3 112.9 YOLOv12l 26.3 88.6 56.1 43.0 44.9 27.8 85.1 Gold-YOLO-s 21.5 46.0 - - 34.3 19.8 102.0 Efficient DETR 32.0 159.0 49.5 36.1 36.7 22.0 19.7 Deformable DETR 41.2 173.1 - - 43.1 27.1 16.4 RT-DETR-R18 20.0 57.0 62.2 46.6 47.4 28.9 45.8 RT-DETR-R34 31.1 88.8 63.1 45.7 48.6 29.8 25.4 文献[15] - 52.4 - - 49.4 30.2 40.6 文献[16] 14.6 49.6 64.3 48.8 50.8 31.7 54.6 HAR-DETR 22.8 84.4 64.5 49.0 51.2 32.1 37.8 表 2 消融实验结果
模型 P/% R/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% Baseline 62.2 46.6 47.4 28.9 +AA 62.0 46.2 47.7 29.3 +HRDB 61.9 46.8 48.8 30.6 +RFF-FPN 61.7 46.3 47.5 29.0 +RFF-FPN+HRDB 62.4 48.1 49.7 31.3 +AA+ HRDB 62.7 48.6 50.3 31.7 +AA+HRDB+RFF-FPN 64.5 49.0 51.2 32.1 表 3 Visdrone2019测试集实验结果
模型 P/% R/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% Baseline 55.7 39.5 37.9 21.9 HAR-DETR 58.3 40.9 40.4 24.0 表 4 RSOD数据集实验结果
模型 P/% R/% mAP50/% mAP50-95/% Baseline 95.3 95.6 97.4 71.4 HAR-DETR 95.2 96.1 97.5 73.6 -
[1] 张志豪, 杜丽霞, 侯越, 等. 跨层注意力交互下的多特征交叉无人机图像检测[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2024, 32(24): 3616–3631. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20243224.3616.ZHANG Zhihao, DU Lixia, HOU Yue, et al. Multi-feature cross UAV image detection algorithm under cross-layer attentional interaction[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2024, 32(24): 3616–3631. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20243224.3616. [2] 孙叶美, 桑学婷, 张艳, 等. 基于超图计算的高效传递多尺度特征小目标检测算法[J]. 光电工程, 2025, 52(5): 250061. doi: 10.12086/oee.2025.250061.SUN Yemei, SANG Xueting, ZHANG Yan, et al. Hypergraph computed efficient transmission multi-scale feature small target detection algorithm[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2025, 52(5): 250061. doi: 10.12086/oee.2025.250061. [3] KONG Yaning, SHANG Xiangfeng, and JIA Shijie. Drone-DETR: Efficient small object detection for remote sensing image using enhanced RT-DETR model[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(17): 5496. doi: 10.3390/s24175496. [4] 李凯璇, 刘晓锋, 陈强, 等. YOLOv8-GAIS: 一种改进的无人机航拍目标检测算法[J]. 光电工程, 2025, 52(4): 240295. doi: 10.12086/oee.2025.240295.LI Kaixuan, LIU Xiaofeng, CHEN Qiang, et al. YOLOv8-GAIS: Improved object detection algorithm for UAV aerial photography[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2025, 52(4): 240295. doi: 10.12086/oee.2025.240295. [5] HUANG Ji and LI Tianrui. Small object detection by DETR via information augmentation and adaptive feature fusion[C]. Proceedings of 2024 ACM ICMR Workshop on Multimodal Video Retrieval, New York, USA, 2024: 39–44. doi: 10.1145/3664524.3675362. [6] 张明明, 郑光迪, 万鸣, 等. 一种基于YOLOv5的改进航拍图像识别算法[J/OL]. 激光技术, 1–20. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/51.1125.TN.20250918.1341.012, 2025.ZHANG Mingming, ZHENG Guangdi, WAN Ming, et al. An improved aerial image recognition algorithm based on YOLOv5[J/OL]. Laser Technology, 1–20. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/51.1125.TN.20250918.1341.012, 2025. [7] 杨智能, 钟小勇, 李华耀, 等. 改进YOLOv8n的航拍小目标检测算法[J]. 电光与控制, 2025, 32(7): 27–32,78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2025.07.005.YANG Zhineng, ZHONG Xiaoyong, LI Huayao, et al. Aerial small target detection based on improved YOLOv8n algorithm[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2025, 32(7): 27–32,78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2025.07.005. [8] LU Yanfeng, GAO Jingwen, YU Qian, et al. A cross-scale and illumination invariance-based model for robust object detection in traffic surveillance scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(7): 6989–6999. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3264573. [9] WU Dangxuan, LI Xiuhong, LI Boyuan, et al. A lightweight two-level nested FPN network for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 6011505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3412244. [10] SHI Jianyu, JIA Yuan, ZHOU Gang, et al. Small target insect detection based on improved YOLOv8n[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 2025: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49660.2025.10890801. [11] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 213–229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13. [12] 戴铮, 刘骁佳, 潘泉. 基于改进DETR算法的焊缝缺陷检测方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(7): 2298–2307. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241009.DAI Zheng, LIU Xiaojia, and PAN Quan. Research on weld defect detection method based on improved DETR[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(7): 2298–2307. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241009. [13] ZHU Xizhou, SU Weijie, LU Lewei, et al. Deformable DETR: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. (查阅网上资料, 未找到对应的出版地信息, 请确认补充). [14] 沈靖夫, 张元良, 刘飞跃, 等. 基于深度学习的水面无人清理船目标检测综述[J]. 价值工程, 2024, 43(13): 157–160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2024.13.044.SHEN Jingfu, ZHANG Yuanliang, LIU Feiyue, et al. A review of target detection for unmanned surface cleaning ships based on deep learning[J]. Value Engineering, 2024, 43(13): 157–160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4311.2024.13.044. [15] 胡佳乐, 周敏, 申飞. 面向无人机小目标的RTDETR改进检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(20): 198–206. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2404-0114.HU Jiale, ZHOU Min, and SHEN Fei. Improved detection algorithm of RTDETR for UAV small target[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(20): 198–206. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2404-0114. [16] 程鑫淼, 张雪松, 曹冰洁, 等. 改进RT-DETR的小目标检测方法研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2025, 61(15): 144–155. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2501-0293.CHENG Xinmiao, ZHANG Xuesong, CAO Bingjie, et al. Research on small object detection method of improved RT-DETR[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2025, 61(15): 144–155. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2501-0293. [17] ZHAO Yian, LV Wenyu, XU Shangliang, et al. DETRs beat YOLOs on real-time object detection[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 16965–16974. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01605. [18] 庞玉东, 李志星, 刘伟杰, 等. 基于改进实时检测Transformer的塔机上俯视场景小目标检测模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2024, 44(12): 3922–3929. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023121796.PANG Yudong, LI Zhixing, LIU Weijie, et al. Small target detection model in overlooking scenes on tower cranes based on improved real-time detection transformer[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2024, 44(12): 3922–3929. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023121796. [19] LIU Ruoyuan, ZHANG Xizheng, JIN Shengwei, et al. A small target detection model based on an improved RT-DETR[C]. 2024 4th International Conference on Industrial Automation, Robotics and Control Engineering (IARCE), Chengdu, China, 2024: 434–438. doi: 10.1109/IARCE64300.2024.00086. [20] 王满利, 窦泽亚, 蔡明哲, 等. 基于高分辨扩展金字塔的场景文本检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(7): 2334–2346. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241017.WANG Manli, DOU Zeya, CAI Mingzhe, et al. Scene text detection based on high resolution extended pyramid[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(7): 2334–2346. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241017. [21] 邵延华, 张铎, 楚红雨, 等. 基于深度学习的YOLO目标检测综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(10): 3697–3708. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210790.SHAO Yanhua, ZHANG Duo, CHU Hongyu, et al. A review of YOLO object detection based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(10): 3697–3708. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210790. [22] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.74. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
