Joint Suppression of Range-Ambiguous Clutter and Mainlobe Deceptive Jammer with Subarray FDA-MIMO Radar
-
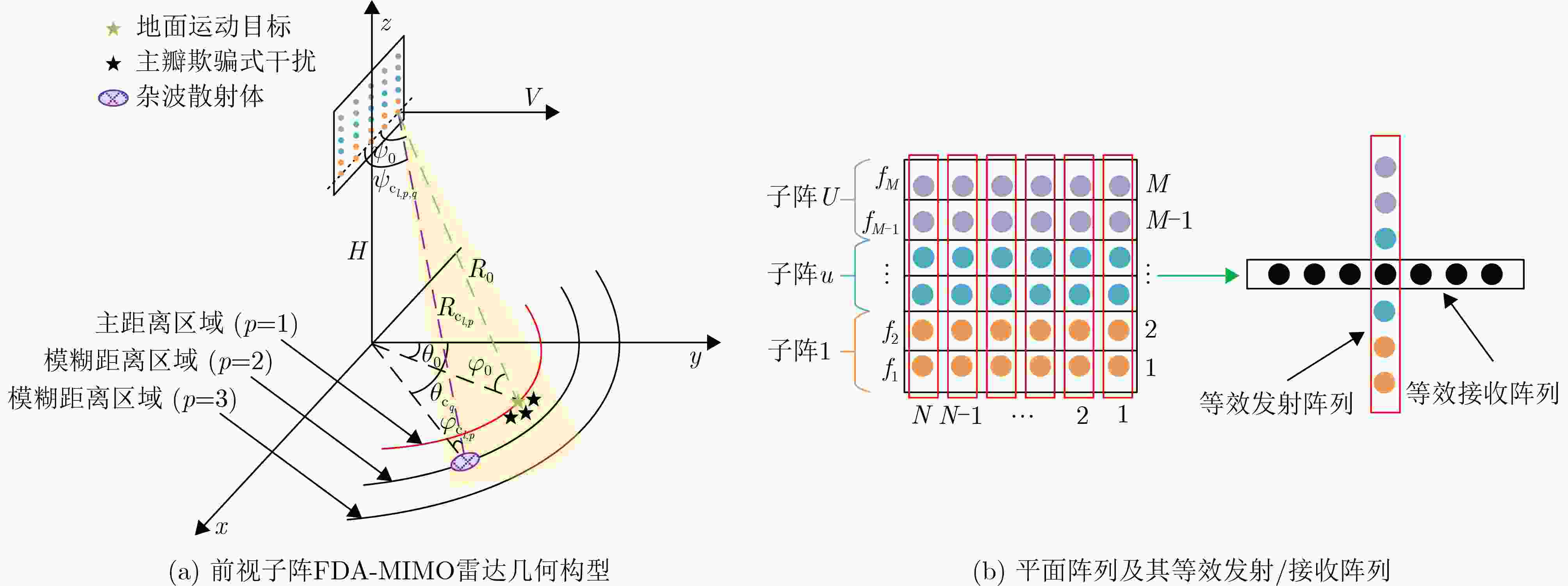
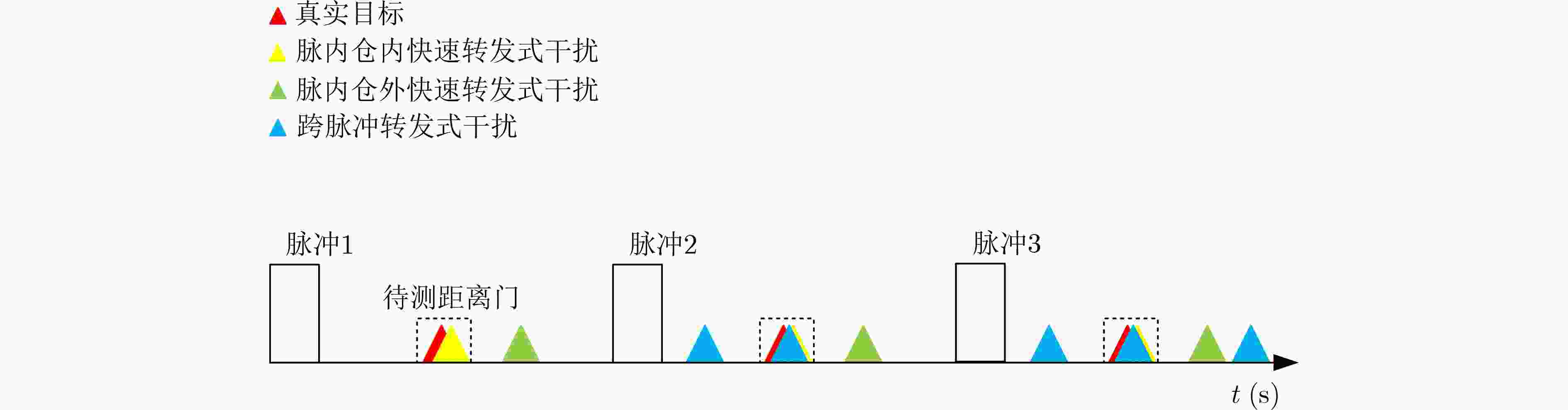
摘要: 距离模糊杂波与主瓣欺骗式干扰严重制约了雷达空时自适应处理(STAP)的性能。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于子阵频率分集阵列多输入多输出(FDA-MIMO)雷达的杂波与干扰联合抑制方法。具体而言,通过在发射子阵内和子阵间分别引入小频率增量和大频率增量,子阵FDA-MIMO雷达具备了子阵内与子阵间两级距离自由度(DOFs)。通过距离依赖补偿,可在发射空间频域实现真实目标与距离模糊杂波、跨脉冲转发式干扰以及脉内快速转发式干扰的有效分离。随后,在子阵内发射维设计预STAP滤波器,以抑制距离模糊杂波与跨脉冲转发式干扰。最后,采用基于子空间投影的三维(3-D)STAP方法同时抑制本地杂波与脉内快速转发式干扰。仿真实验验证了所提联合抑制方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 子阵频率分集阵列MIMO雷达 /
- 距离模糊杂波与主瓣欺骗式干扰联合抑制 /
- 跨脉冲转发式干扰 /
- 脉内快速转发式干扰 /
- 空时自适应处理
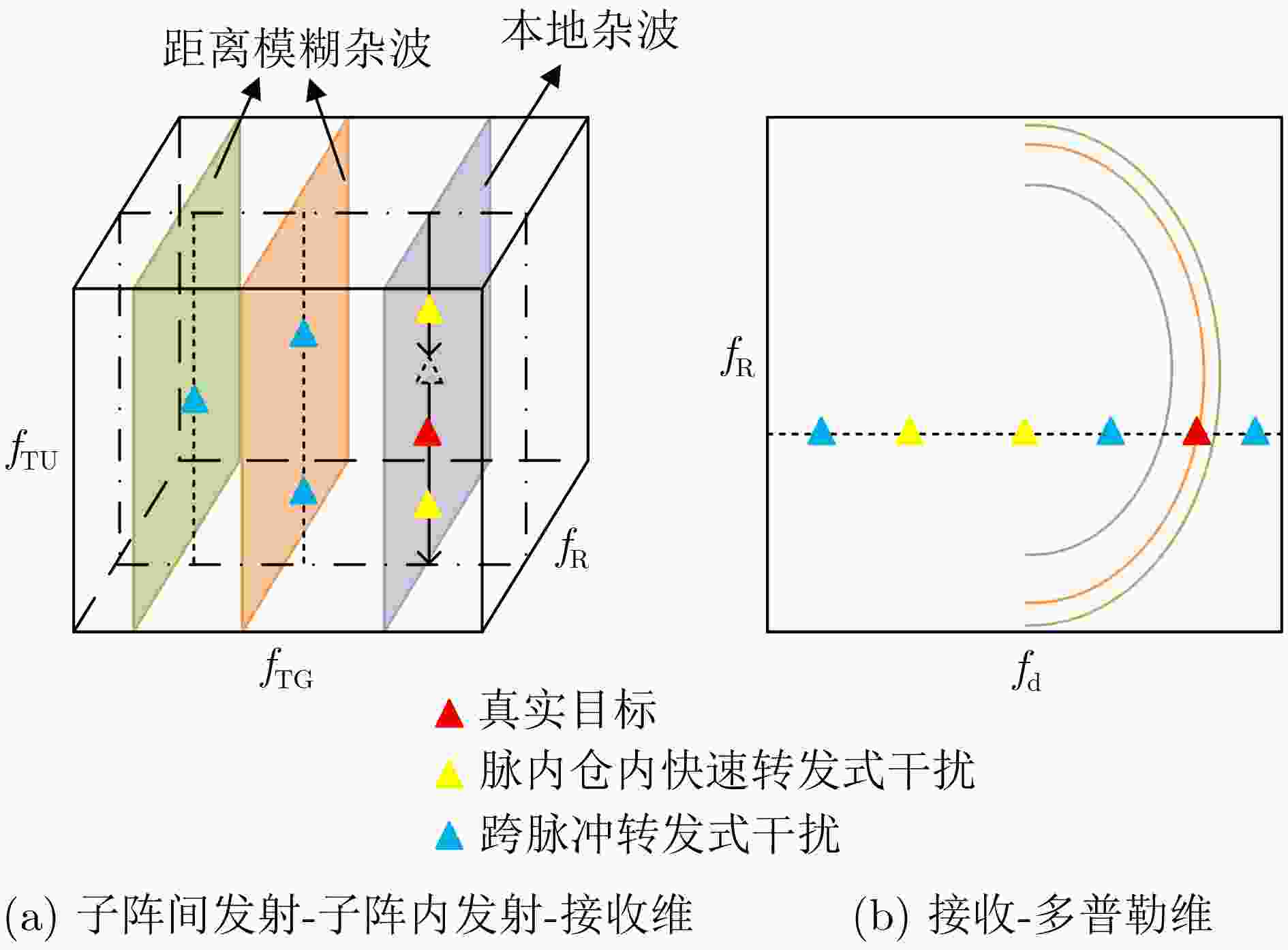
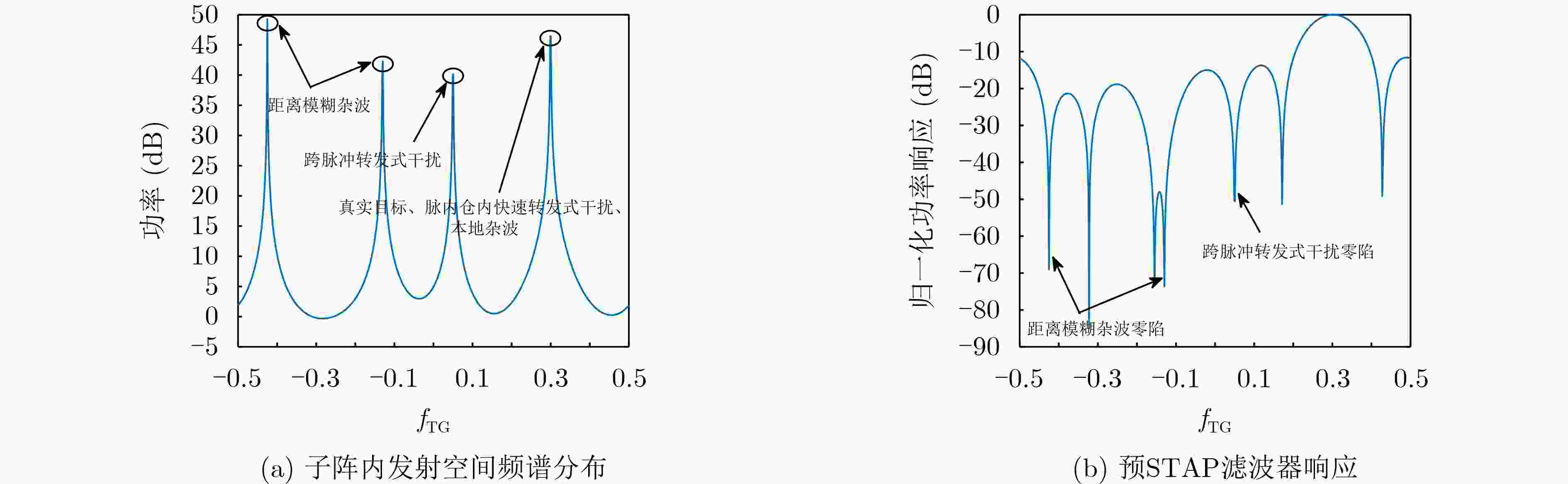
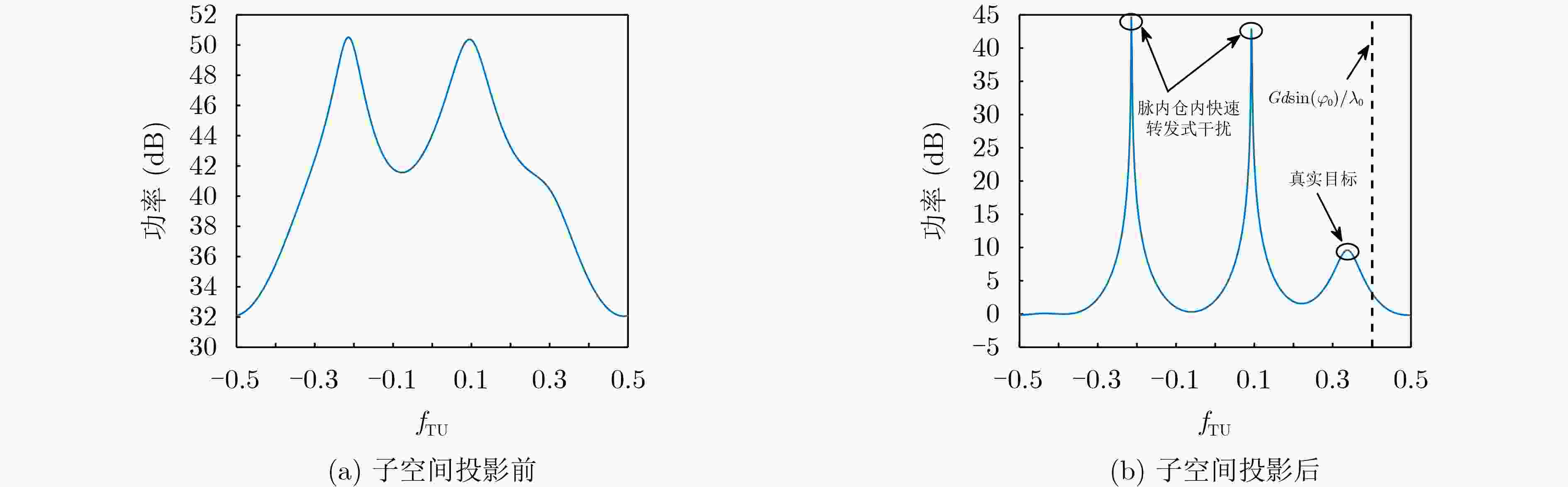
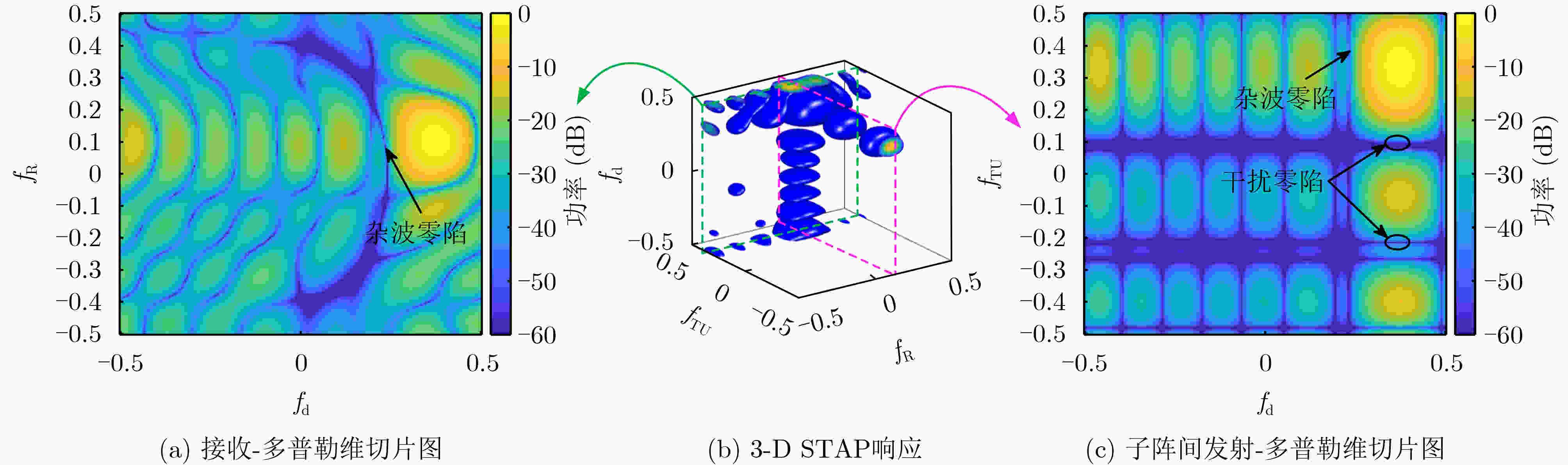
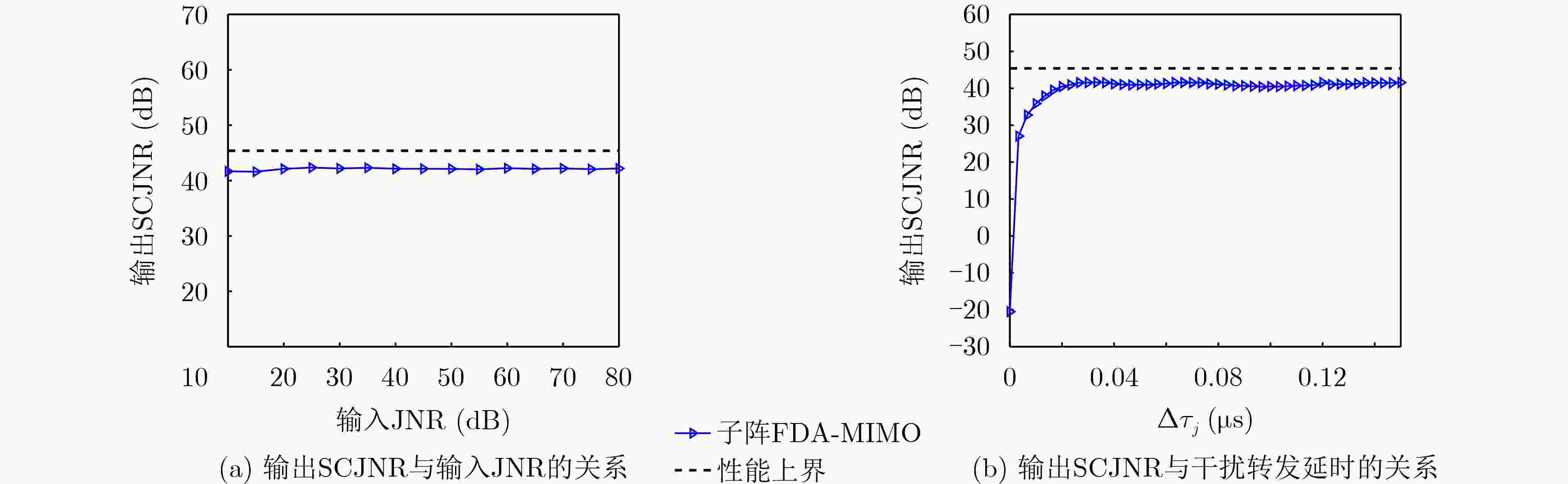
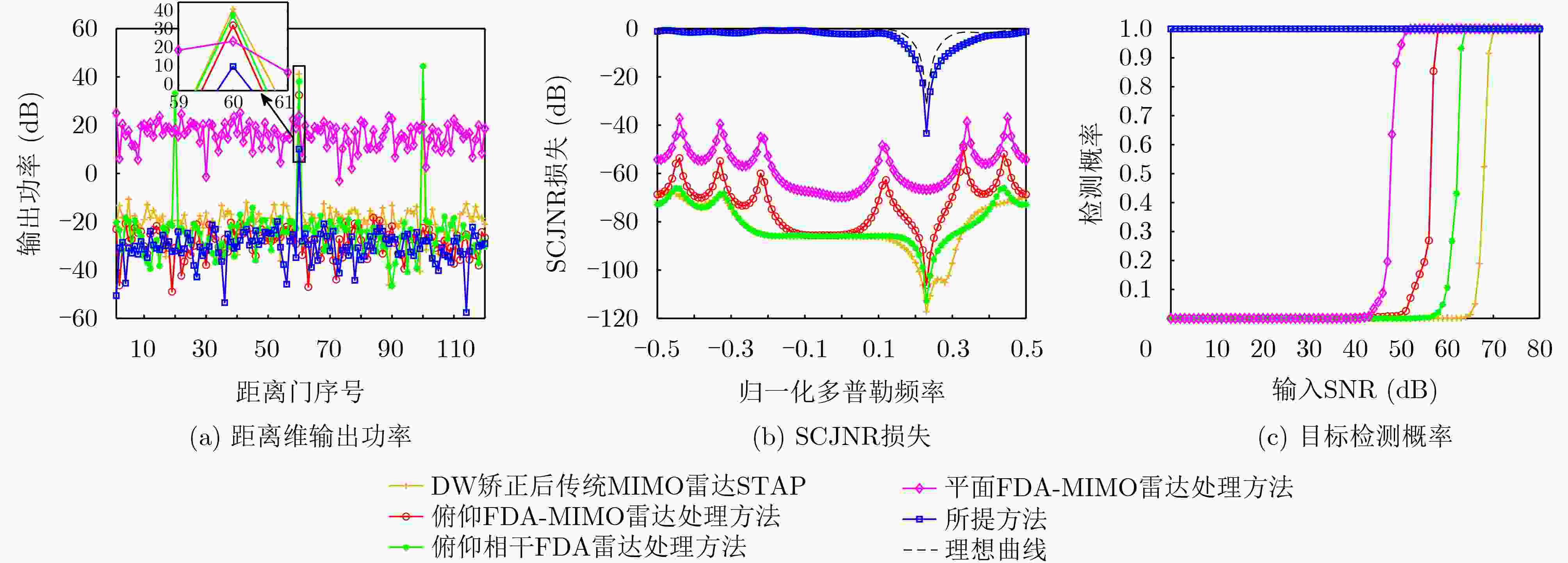
Abstract:Objective In the downward-looking mode, airborne radar systems face the dual challenge of mitigating strong clutter and mainlobe deceptive jammers in increasingly complex electromagnetic environments. Clutter exhibiting both range ambiguity and range dependence constrains of Moving Target Detection (MTD) in high Pulse Repetition Frequency (PRF) radars with non-side-looking configurations. Mainlobe deceptive jammers further increase the difficulty of detecting the true target. By exploiting controllable range Degrees Of Freedom (DOFs), Waveform Diverse Array (WDA) radars, such as Frequency Diverse Array Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (FDA-MIMO) radar and Element Pulse Coding Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (EPC-MIMO) radar, show clear advantages in suppressing mainlobe deceptive jammers. However, existing WDA-based techniques are limited to suppressing false targets whose delays exceed one Pulse Repetition Interval (PRI) relative to the true target, referred to as cross-pulse repeater jammers. With advances in Digital Radio Frequency Memory (DRFM) technology, the delay of false targets is reduced, enabling the generation of false targets that share the same number of delayed pulses as the true target, referred to as intra-PRI rapid repeater jammers. Furthermore, most anti-jamming methods are developed under Gaussian white noise assumptions and do not consider practical clutter environments. Therefore, a joint suppression framework is required to simultaneously handle range-ambiguous clutter and multiple types of mainlobe deceptive jammer. Methods A joint suppression framework based on a subarray FDA-MIMO radar is proposed for scenarios with coexisting range-ambiguous clutter, cross-pulse repeater jammers, and intra-PRI rapid repeater jammers. Compared with conventional FDA-MIMO radar, the subarray FDA-MIMO configuration employs small frequency increments within transmit subarrays and large frequency increments across subarrays, which provides two-level range DOFs at the intra-subarray and inter-subarray scales. First, a Range-Dependent Compensation (RDC) technique is applied to separate the true target from echoes contaminated by clutter and jammers in the joint intra-subarray and inter-subarray transmit spatial frequency domain. Next, a pre-Space-Time Adaptive Processing (STAP) filter is designed by exploiting range DOFs in the intra-subarray transmit dimension to suppress range-ambiguous clutter and cross-pulse repeater jammers. Finally, subspace projection-based three-Dimensional (3-D) STAP is applied to suppress local clutter and intra-PRI rapid repeater jammers. Results and Discussions After RDC, the true target is effectively separated from ambiguous clutter and jammers in the joint intra-subarray and inter-subarray transmit spatial frequency domain ( Fig. 3 ). By exploiting range DOFs in the intra-subarray transmit dimension, the pre-STAP filter achieves effective suppression of range-ambiguous clutter and cross-pulse repeater jammers (Fig. 4 ). Local clutter in the inter-subarray transmit spatial frequency domain is suppressed by using clutter distribution characteristics in the receive-doppler domain combined with subspace projection (Fig. 5 ). This enables accurate estimation of the Jammer Covariance Matrix (JCM) for intra-PRI-inner-bin rapid repeater jammers. Subsequently, 3-D STAP suppresses local clutter and intra-PRI-inner-bin rapid repeater jammers (Fig. 6 ,Fig. 7 ). Comparative simulation results show that the proposed framework achieves significantly improved suppression performance under the considered complex scenario (Fig. 8 ).Conclusions The problem of MTD in scenarios with simultaneous range-ambiguous clutter, cross-pulse repeater jammers, and intra-PRI-inner-bin rapid repeater jammers is addressed. A joint suppression framework based on subarray FDA-MIMO radar is proposed, in which small frequency increments are used within transmit subarrays and large increments across subarrays to enable flexible utilization of range DOFs. RDC achieves effective separation of the target from ambiguous clutter and jammers in the joint transmit spatial frequency domain. By exploiting intra-subarray range DOFs, a pre-STAP filter suppresses range-ambiguous clutter and cross-pulse repeater jammers. To mitigate the Inner-Bin Range Dependence (IRD) effect of clutter, a subspace projection method is developed to recover the JCM for intra-PRI-inner-bin rapid repeater jammers from clutter-contaminated data. Finally, 3-D STAP in the inter-subarray transmit-receive-Doppler domain suppresses local clutter and intra-PRI-inner-bin rapid repeater jammers. Numerical simulations verify the effectiveness of the proposed joint suppression framework. -
表 1 子阵FDA-MIMO雷达系统参数
参数 参数值 参数 参数值 子阵内发射阵元数 8 阵元间距 0.05 m 子阵数 6 距离区域数 3 接收阵元数 8 平台高度 6 km 脉冲数 9 平台速度 150 m/s 参考载波频率 3 GHz 信号带宽 6 MHz 脉冲重复间隔 100 μs 信噪比 10 dB 子阵内频率增量 2.5 kHz 干噪比 50 dB 子阵间频率增量 4.6 MHz 杂噪比 50 dB 表 2 真/假目标参数
参数 真实目标参数值 假目标1参数值 假目标2参数值 假目标3参数值 假目标4参数值 假目标5参数值 俯仰角(°) 36.86 36.86 36.86 36.86 36.86 36.86 方位角(°) 15 15 15 15 15 15 等效距离(m) 10002 10010 10020 24000 25000 41000 所在距离区域 1 1 1 2 2 3 所在距离门序号 60 60 60 20 60 100 归一化多普勒频率 0.36 –0.1 0 0.1 –0.2 0.3 -
[1] 李海, 张强, 周桉宇, 等. 卷积神经网络STAP低空风切变风速估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(8): 3193–3201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231335.LI Hai, ZHANG Qiang, ZHOU Anyu, et al. Convolutional neural network STAP low level wind shear wind speed estimation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(8): 3193–3201. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231335. [2] LIU Zhixin, ZHU Shengqi, XU Jingwei, et al. Range-ambiguous clutter suppression for STAP-based radar with vertical coherent frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5106517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3291738. [3] VARADARAJAN V and KROLIK J L. Joint space-time interpolation for distorted linear and bistatic array geometries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 848–860. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.862941. [4] KREYENKAMP O and KLEMM R. Doppler compensation in forward-looking STAP radar[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2001, 148(5): 253–258. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20010557. [5] HIMED B, ZHANG Yuhong, and HAJJARI A. STAP with angle-Doppler compensation for bistatic airborne radars[C]. 2002 IEEE Radar Conference (IEEE Cat. No. 02CH37322), Long Beach, CA, USA, 2002: 311–317. doi: 10.1109/NRC.2002.999737. [6] GERLACH K and ANDREWS G A. Cascaded detector for multiple high-PRF pulse Doppler radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1990, 26(5): 754–767. doi: 10.1109/7.102711. [7] MENG Xiangdong, WANG Tong, WU Jianxin, et al. Short-range clutter suppression for airborne radar by utilizing prefiltering in elevation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 268–272. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2012126. [8] 兰宇, 周剑雄. 一种空域线性调频加权的空时联合频控阵雷达波形[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(11): 4340–4350. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250561.LAN Yu and ZHOU Jianxiong. A space-time joint waveform for frequency diverse array radar with spatial linear frequency modulation weighting[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(11): 4340–4350. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250561. [9] 谢宁波, 欧阳缮, 廖可非, 等. 基于图信号处理的频控阵雷达目标定位方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(5): 1559–1566. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220970.XIE Ningbo, OUYANG Shan, LIAO Kefei, et al. A novel target localization method for frequency diverse array based on graph signal processing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(5): 1559–1566. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220970. [10] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, and SO H C. Space-time adaptive processing with vertical frequency diverse array for range-ambiguous clutter suppression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5352–5364. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2561308. [11] YANG Xingjia, DUAN Keqing, QIU Zizhou, et al. Range-ambiguous clutter suppression with cascaded FDA-MIMO STAP for bistatic space-based early warning radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(6): 7754–7770. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3420258. [12] SOUMEKH M. SAR-ECCM using phase-perturbed LFM chirp signals and DRFM repeat jammer penalization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 191–205. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603414. [13] BANDIERA F, ORLANDO D, and RICCI G. A subspace-based adaptive sidelobe blanker[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(9): 4141–4151. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.926193. [14] ZHU Jiahua, CHU Ning, SONG Yongping, et al. Alternative signal processing of complementary waveform returns for range sidelobe suppression[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 159: 187–192. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.02.012. [15] ZHU Quanjiang, YANG Shiwen, ZHENG Li, et al. Design of a low sidelobe time modulated linear array with uniform amplitude and sub-sectional optimized time steps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 60(9): 4436–4439. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2012.2207082. [16] LAN Lan, XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, et al. Suppression of mainbeam deceptive jammer with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11584–11598. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3014689. [17] WU Zhixia, ZHU Shengqi, XU Jingwei, et al. Interference suppression with MR-FDA-MIMO radar using virtual samples based beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 5211–5225. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3386884. [18] LAN Lan, ZHANG Yitao, XU Jingwei, et al. Suppressing mainlobe deceptive jammers via two-low-rank matrix decomposition in FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 2885–2898. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3480030. [19] LIU Feilong, ZHU Shengqi, XU Jingwei, et al. Fast repeater deception jamming suppression with DFI-FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 4271–4284. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3374711. [20] ZHANG Mengdi, LU Jiahao, XU Jingwei, et al. Mainlobe deceptive interference suppression with planar frequency diverse array MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(3): 7626–7638. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3540823. [21] 兰岚, 张翔, 许京伟, 等. 阵列雷达时空多维域编码抗主瓣转发式欺骗干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2025, 14(2): 439–455. doi: 10.12000/JR24229.LAN Lan, ZHANG Xiang, XU Jingwei, et al. Main-lobe deceptive jammers with array radars using space-time multidimensional coding[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(2): 439–455. doi: 10.12000/JR24229. [22] GAO Jie, ZHU Shengqi, LAN Lan, et al. Joint deceptive jammer and clutter suppression via 3-D-ANM with EPC-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 1487–1504. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3456755. [23] WANG Keyi, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Multi-scale moving target detection with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2024, 216: 109301. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2023.109301. [24] GU Yujie and LESHEM A. Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix reconstruction and steering vector estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(7): 3881–3885. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2194289. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
