Split-architecture Non-contact Optical Seismocardiography Triggering System for Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
-
摘要: 心脏磁共振(CMR)对心动与呼吸极为敏感,稳定可靠的门控是保证成像质量与量化准确性的关键。针对高磁场环境下心电门控易受磁流体力学与梯度噪声干扰的问题,该文提出一种面向复杂电磁环境的CMR非接触光学心振触发方案。具体地,提出一种“近机光学采集-远机计算与触发”的分体式架构:近机端以离焦散斑成像捕获胸壁微振,远机端进行方向自适应位移合成、漂移屏蔽基线回正及因果多项式局部回归平滑,实现主动脉瓣开放等机械事件的实时触发。在20名健康志愿者、3类线圈遮挡条件下进行评估:在无线圈与超柔性体线圈条件下,心振信号相对同搏R波的后向生理延迟分别为44.7±24.8 ms与45.1±26.7 ms,拍间抖动通常为20~30 ms;可用率分别为95.7%与97.6%,F1分数分别为0.921与0.912。结果表明,良好的线圈-胸壁耦合与视野通畅对非接触机械门控至关重要;相较外周光体积信号与雷达门控,心振信号作为“近源”机械标记可显著缩短触发相位滞后,相较外周光体积信号与门控,更适用于高心率或时序约束更严格的CMR序列。总体而言,所提方案为高场环境下实现非接触、低延迟CMR门控提供了工程化实现路径。Abstract:
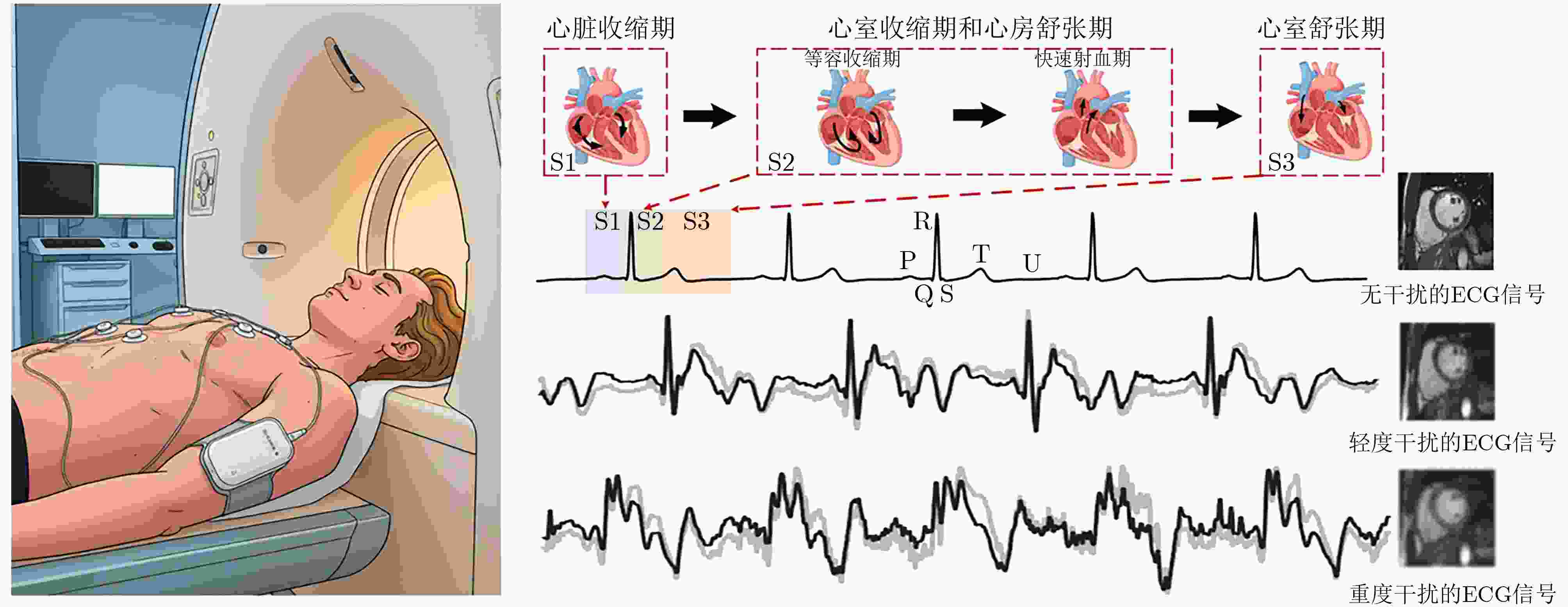
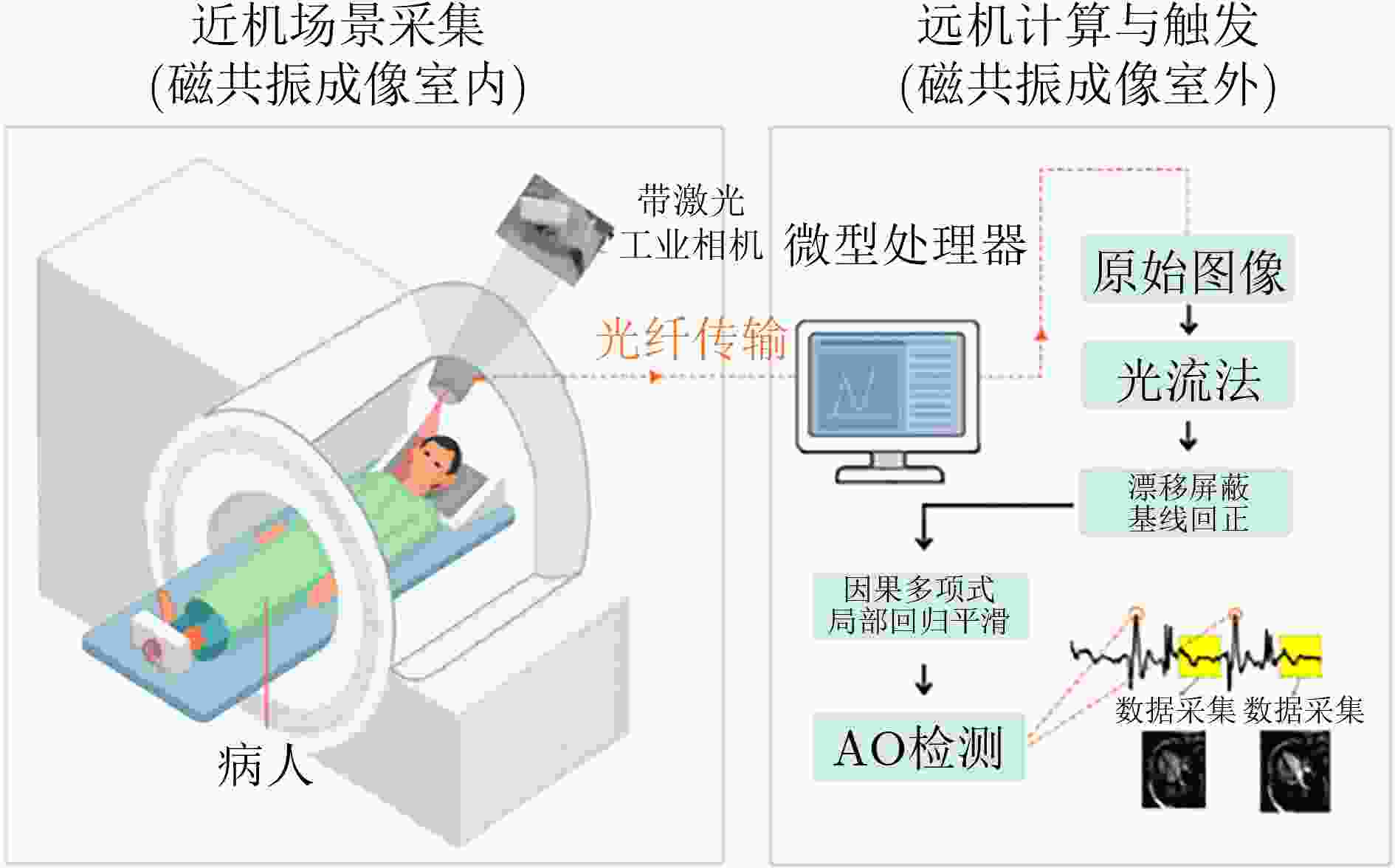
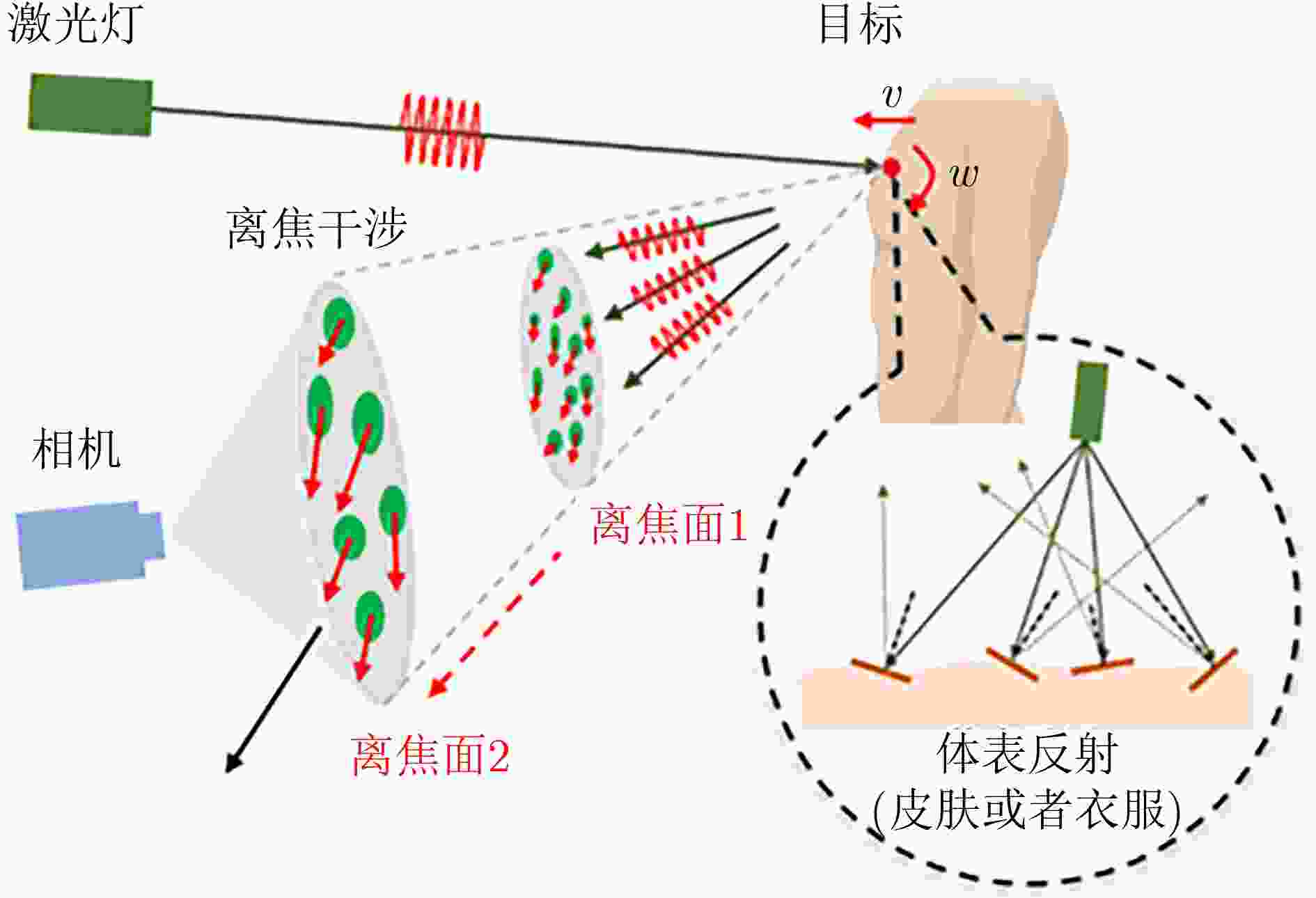
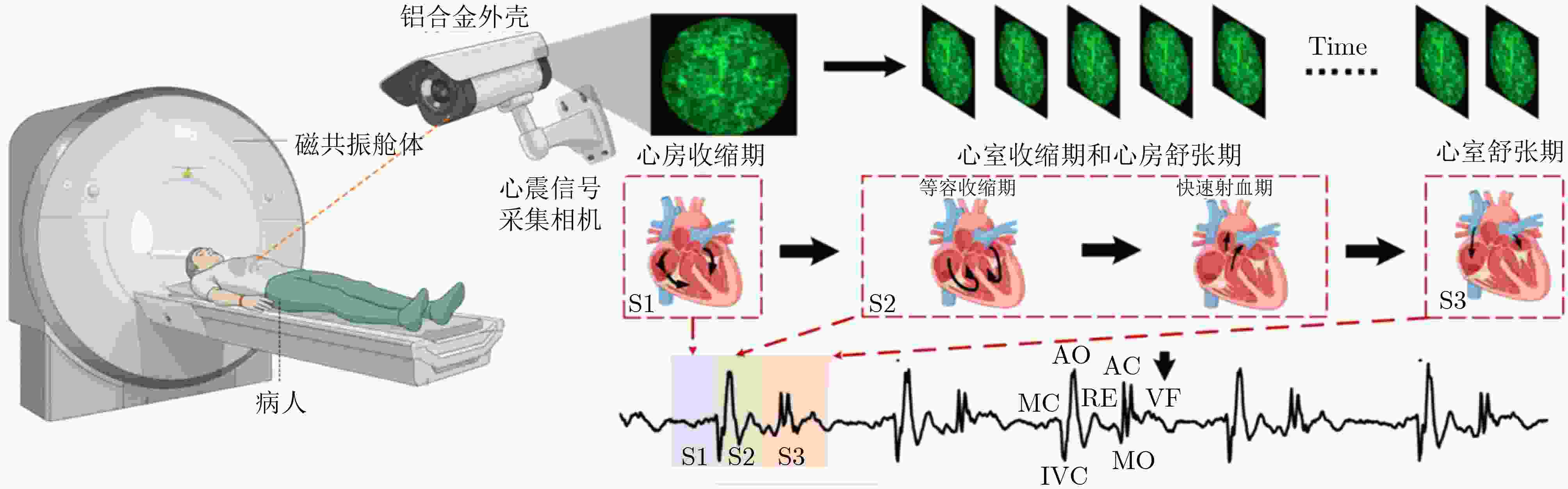
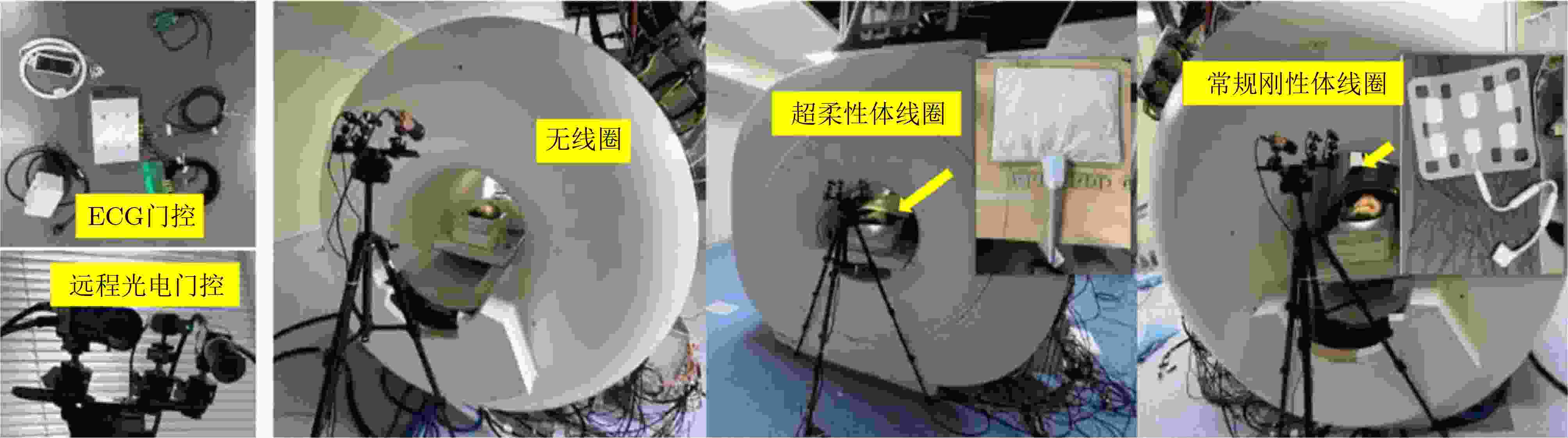
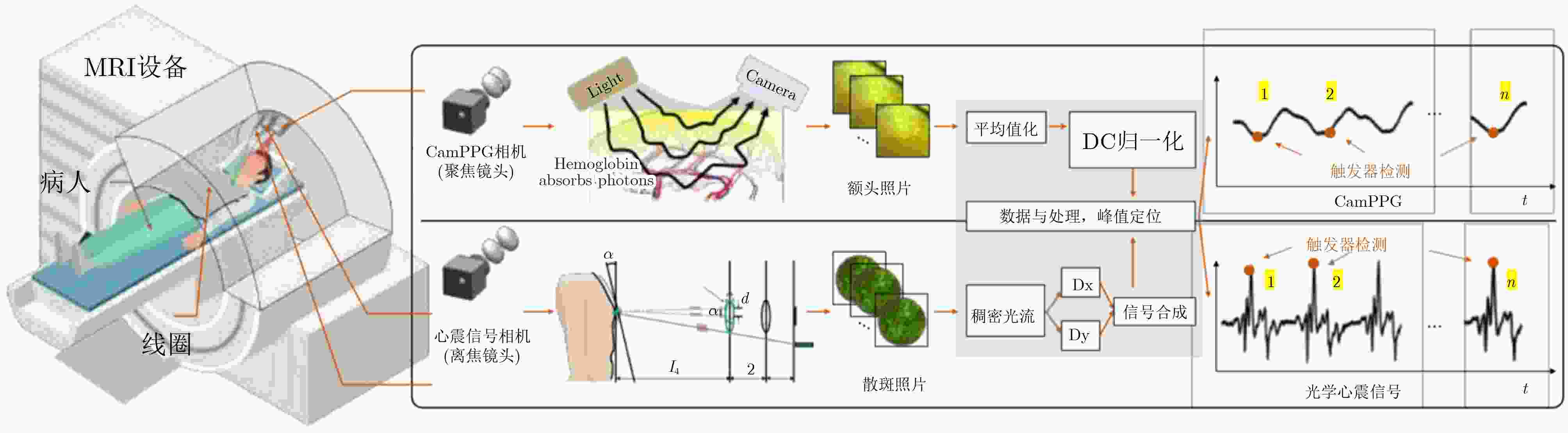
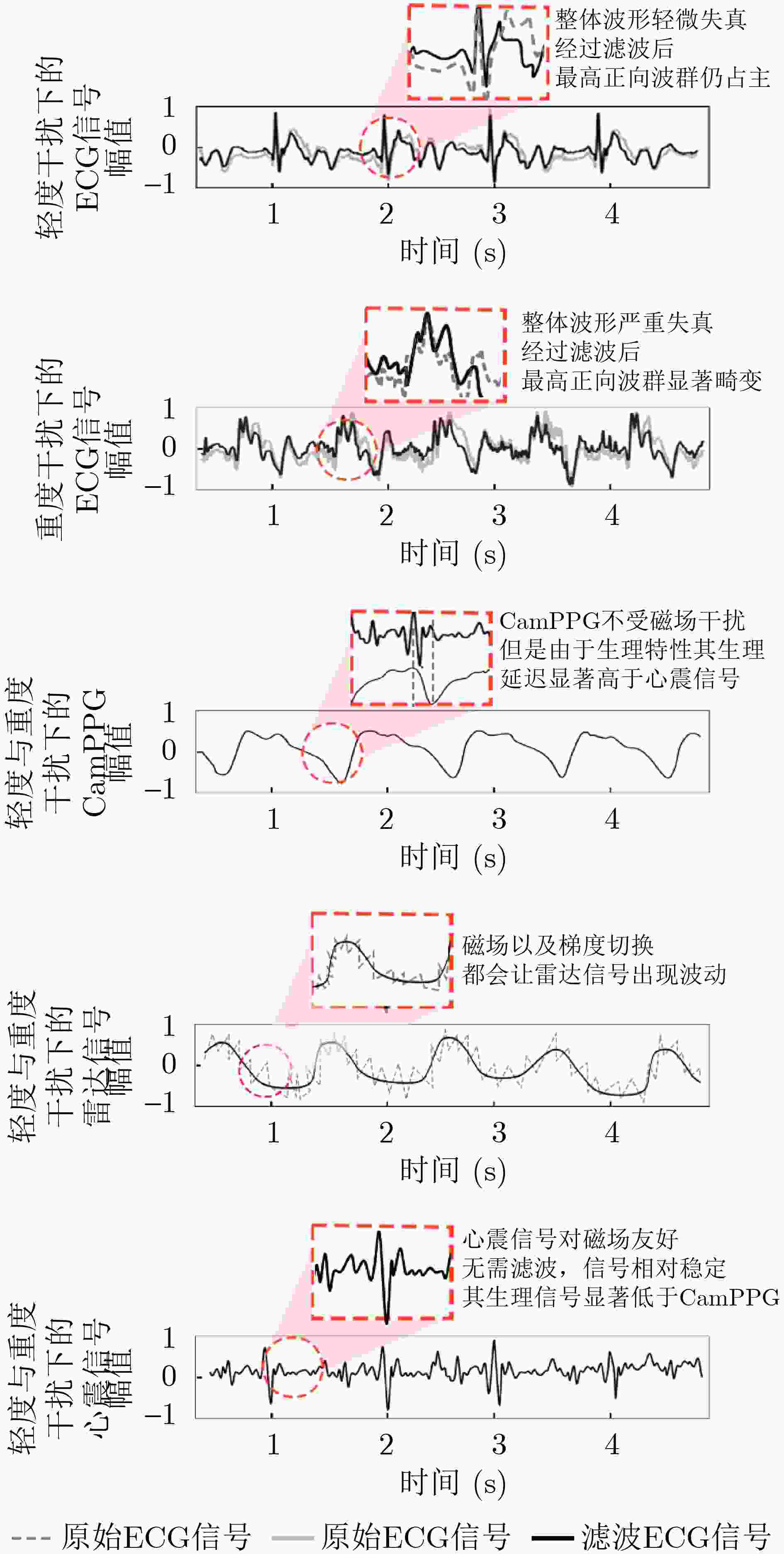
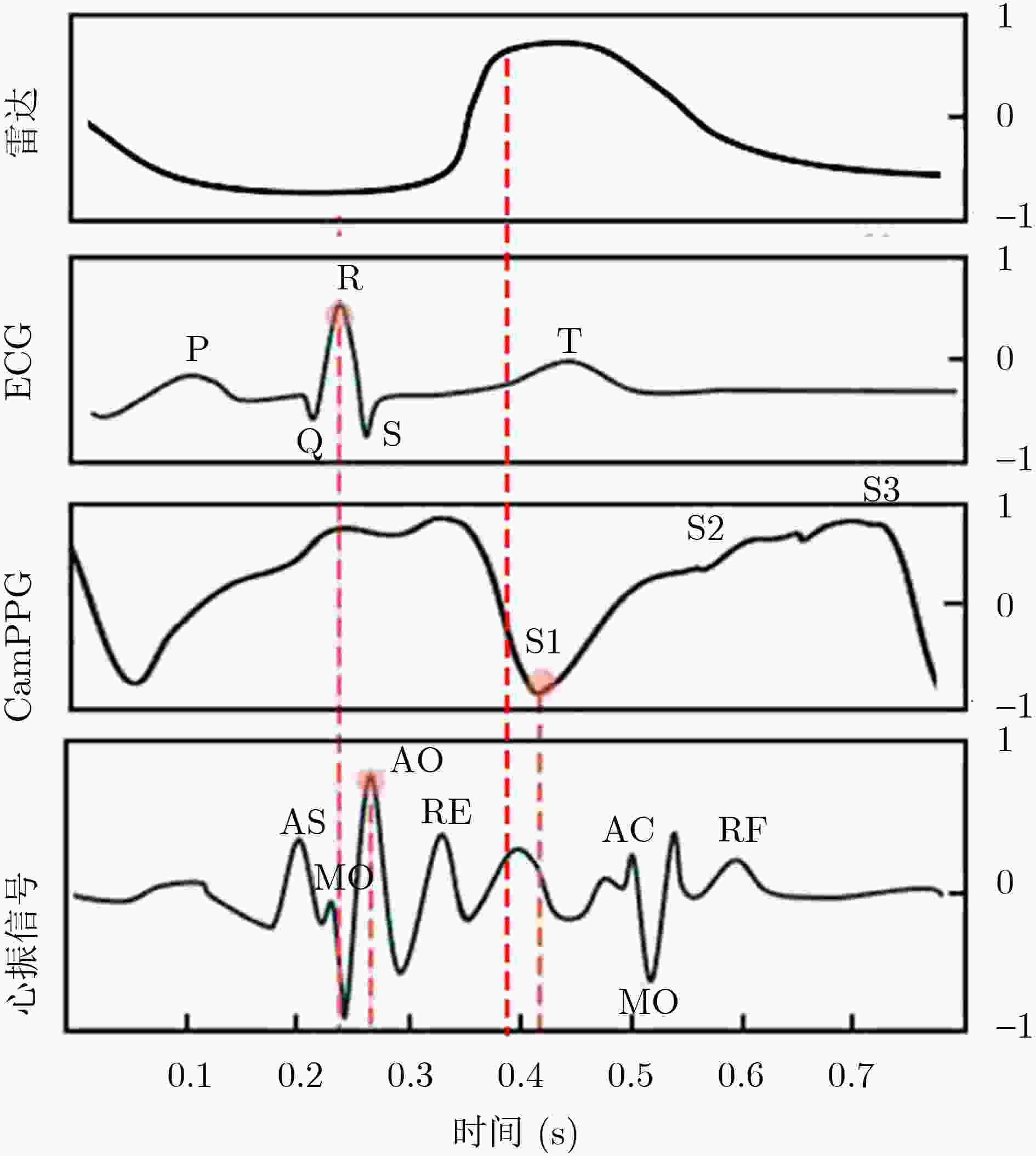
Objective Cardiac-cycle synchronization is required in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) to reduce motion artifacts and preserve quantitative accuracy. At high field strengths, the ElectroCardioGram (ECG) trigger is affected by magnetohydrodynamic effects and scanner-generated ElectroMagnetic Interference (EMI). Electrode placement and lead routing add setup burden. Contact-based mechanical sensors still require skin contact, and optical photoplethysmography introduces long physiological delay. A fully contactless and EMI-robust mechanical surrogate is therefore needed. This study develops a split-architecture, non-contact optical SeismoCardioGraphy (SCG) triggering system for CMR and evaluates its availability, beatwise detection performance, and timing characteristics under practical body-coil coverage. Methods The split-architecture system consists of a near-magnet optical acquisition unit and a far-magnet computation-and-triggering unit connected by fiber-optic links to minimize conductive pathways near the scanner ( Fig. 2 ). The acquisition unit uses a defocused industrial camera and laser illumination to record speckle-pattern dynamics on the anterior chest without physical contact (Fig. 3 ). Dense optical flow is computed in a chest region of interest, and the displacement field is projected onto a principal motion direction to form a one-dimensional SCG sequence (Fig. 4 ). Drift suppression, smoothing, and short-window normalization are applied. Trigger timing is refined with a valley-constrained gradient search within a physiologically bounded window to reduce spurious detections and improve temporal consistency (Fig. 4 ). A benchmark dataset is acquired from 20 healthy volunteers under three coil configurations: no body coil, an ultra-flexible body coil, and a rigid body coil (Fig. 5 ,Fig. 6 ,Table 3 ). ECG serves as the reference, and CamPPG and radar are recorded for comparison. Beatwise precision, recall, and F1 score are computed against ECG R peaks, and availability is reported as the fraction of usable segments under unified quality criteria (Table 4 ). Backward and forward physiological delays and delay variability are summarized across subjects and coil conditions (Table 5 ,Table 6 ). Key windowing and refractory parameters are tested for sensitivity (Table 2). Runtime is measured to assess real-time feasibility, including the cost of dense optical flow and the overhead of one-dimensional processing and triggering (Table 7 ).Results and Discussions Under no-coil and ultra-flexible-coil conditions, the optical SCG trigger achieves high availability (about 97.6%) and strong beatwise performance. F1 reaches about 0.91 under the ultra-flexible coil ( Table 4 ,Table 5 ). The backward physiological delay remains on the order of several tens of milliseconds, and delay jitter is generally within a few tens of milliseconds (Table 5 ,Table 6 ). Under the rigid body coil, performance decreases markedly. Mechanical decoupling between the coil surface and the chest wall weakens and distorts the vibration signature, which blurs AO-related features and increases false triggers (Fig. 1 ). This effect appears as lower precision and F1 and as a shift toward longer and more variable delays compared with the other conditions (Table 4 ,Table 6 ). Compared with CamPPG, which reflects peripheral blood-volume dynamics and typically lags further behind the ECG R peak, the optical SCG surrogate provides a more proximal mechanical marker with reduced trigger phase lag (Fig. 8 ,Table 5 ). EMI robustness is supported by representative segments: ECG waveforms show visible distortion under interference, whereas the optical SCG surrogate remains interpretable because acquisition and transmission near the scanner are fully optical and electrically isolated (Fig. 8 ). Parameter analysis supports a moderate processing window and a 0.5 s minimum interbeat interval as a stable choice across subjects (Table 2 ). Runtime analysis shows that dense optical flow dominates computational cost, whereas one-dimensional processing and triggering add little overhead. Throughput exceeds the acquisition frame rate, supporting real-time triggering (Table 7 ).Conclusions A split-architecture, non-contact optical SCG triggering system is developed and validated under three representative body-coil configurations. Fiber-optic separation between near-magnet acquisition and far-magnet processing improves EMI robustness while maintaining real-time trigger output. High availability, strong beatwise performance, and short physiological delay are demonstrated under no-coil and ultra-flexible-coil conditions ( Table 4 ,Table 5 ). Rigid-coil coverage exposes a clear limitation caused by reduced mechanical coupling, which motivates further optimization for mechanically decoupled or heavily occluded scenarios (Fig. 1 ,Table 6 ). -
表 1 替代门控路径对比信息汇总
方法 准确性 抗干扰 复杂度 局限性 电生理门控[4,5] 高 中 需要电极与导线管理,
操作复杂需防高电压感应/安全问题 自门控[6,7] 中 高 软件仿真不需要额外硬件,
重建链路复杂心肌收缩幅度很轻、高心率、
前瞻触发时受限光电脉搏波门控[8,9] 低 高 需要相机或指夹式传感器,
操作适中运动伪影;生理延迟长 超声多普勒门控[10,11] 中 高 需要超声前端与探头固定,
操作适中延迟长;与患者接触困难;
心脏异常时受影响心源性
机械门控[8, 11–13]接触式
近心机械振动高 中 需要固定CMR兼容线缆,
操作复杂传导/处理造成的较长延迟 非接触
光学心震信号(本文)高 高 仅需红外摄像头,
操作简单研究处于起步阶段,
尚未覆盖心律失常表 2 参数鲁棒性验证
固定变量 自变量 精准率 召回率 可用率 最小峰间距
0.5 s平滑窗口
1 000 ms0.724 0.754 0.826 平滑窗口
200 ms0.872 0.852 90.8 平滑窗口
600 ms0.901 0.908 92.4 平滑窗口
500 ms最小峰间距
0.7 s0.846 0.849 82.5 最小峰间距
0.2 s0.482 0.435 96.8 最小峰间距
0.5 s0.912 0.927 95.7 表 3 志愿者相关统计信息
性别 人数 年龄 身高(cm) 体重(kg) 男 10 25±6.7 175±8.5 64.9±20.3 女 10 24±3.6 159±8.7 58.9±11.1 表 4 3种线圈条件下检测模式的精度、召回率和F1分数
模态 指标 条件 无线圈 软线圈 硬线圈 远程光电脉搏波 精确率 0.900 0.854 0.878 召回率 0.938 0.967 0.959 F1 0.919 0.907 0.917 雷达 精确率 0.894 0.834 0.078 召回率 0.923 0.922 0.659 F1 0.901 0.907 0.167 心振信号 精确率 0.912 0.861 0.097 召回率 0.927 0.969 0.702 F1 0.921 0.912 0.170 表 5 3种线圈条件下的延迟与可用率
模型 前向延迟(ms)MAE±STD 后向延迟(ms)MAE±STD 可用率(%) 无线圈 软线圈 硬线圈 无线圈 软线圈 硬线圈 无线圈 软线圈 硬线圈 远程光电脉搏波 107.3±39.3 114.4±46 121.7±58.5 797±78 795.9±78 762±78 94.9 97.5 96.5 雷达 56.3±48.3 61.1±51.3 132±72.5 767±78 775.9±78 762±78 92.9 95.3 86.2 心振信号 44.7±24.8 45.1±26.7 126.1±59.2 751.3±78 750±66 758.9±88 95.7 97.6 90.2 表 6 男女评价指标对比
性别 前向延迟 精确率 召回率 可用率(%) 男 41.6±22.9 0.908 0.933 96.8 女 47.8±26.7 0.916 0.922 94.6 表 7 模块开销
模块 时间复杂度 相对计算开销 稠密光流估计 O(N) 主要开销 方向自适应位移合成 O(N) 较小 一维预处理(基线、平滑、归一化) O(L) 很小 峰值检测与门控调度 O(L) 可忽略 -
[1] BARNWELL J D, KLEIN J L, STALLINGS C, et al. Image-guided optimization of the ECG trace in cardiac MRI[J]. The International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging, 2012, 28(3): 587–593. doi: 10.1007/s10554-011-9865-7. [2] 国家药监局. 国家药监局关于发布优化全生命周期监管支持高端医疗器械创新发展有关举措的公告[A/OL]. (2025-07-05). https://www.nmpa.gov.cn/xxgk/ggtg/ylqxggtg/ylqxqtggtg/20250703163951182.html, 2025.National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). Announcement on issuing measures to optimize whole-life-cycle regulation to support the innovative development of high-end medical devices[A/OL]. (2025-07-05). https://www.nmpa.gov.cn/xxgk/ggtg/ylqxggtg/ylqxqtggtg/20250703163951182.html, 2025. [3] 上海市人民政府. 上海市促进高端医疗器械产业全链条发展行动方案[A/OL]. (2025-09-15). https://www.shanghai.gov.cn/nw12344/20250915/91ccfe1a601d40ecbb579034a030cfa8.html, 2025.Shanghai Municipal People’s Government. Action plan for promoting the full-chain development of the high-end medical device industry[A/OL]. (2025-09-15). https://www.shanghai.gov.cn/nw12344/20250915/91ccfe1a601d40ecbb579034a030cfa8.html, 2025. [4] SNYDER C J, DELABARRE L, METZGER G J, et al. Initial results of cardiac imaging at 7 tesla[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2009, 61(3): 517–524. doi: 10.1002/mrm.21895. [5] KRUG J, ROSE G, STUCHT D, et al. Limitations of VCG based gating methods in ultra high field cardiac MRI[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 2013, 15(S1): W19. doi: 10.1186/1532-429X-15-S1-W19. [6] ZHOU Zhiqin, HUANG Jia, LI Haozhe, et al. Camera seismocardiogram based monitoring of left ventricular ejection time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2025, 72(9): 2609–2622. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2025.3548090. [7] WANG Zi, XIAO Min, ZHOU Yirong, et al. Deep separable spatiotemporal learning for fast dynamic cardiac MRI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2025, 72(12): 3642–3654. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2025.3574090. [8] LARSON A C, WHITE R D, LAUB G, et al. Self-gated cardiac cine MRI[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2004, 51(1): 93–102. doi: 10.1002/mrm.10664. [9] LIU Lin, YU Dongfang, LU Hongzhou, et al. Camera-based seismocardiogram for heart rate variability monitoring[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2024, 28(5): 2794–2805. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2024.3370394. [10] ZHU Y, LAI H, MO H, et al. Camera-SCG based cardiac gating for magnetic resonance imaging: A feasibility study[J]. [11] WANG Wenjin, WEISS S, DEN BRINKER A C, et al. Fundamentals of camera-PPG based magnetic resonance imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2022, 26(9): 4378–4389. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3136603. [12] LI Ning, TOUS C, DIMOV I P, et al. Design of a low-cost, self-adaptive and MRI-compatible cardiac gating system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2023, 70(11): 3126–3136. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2023.3280348. [13] KORDING F, SCHOENNAGEL B, LUND G, et al. Doppler ultrasound compared with electrocardiogram and pulse oximetry cardiac triggering: A pilot study[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2015, 74(5): 1257–1265. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25502. [14] TASDELEN B, YAGIZ E, CINBIS B R, et al. Contactless cardiac gating at 0.55T using high-amplitude pilot tone with interference cancellation (HAPTIC)[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2025, 94(3): 1182–1190. doi: 10.1002/mrm.30528. [15] ROSENZWEIG S, SCHOLAND N, HOLME H C M, et al. Cardiac and respiratory self-gating in radial MRI using an adapted singular spectrum analysis (SSA-FARY)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(10): 3029–3041. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.2985994. [16] CROWE M E, LARSON A C, ZHANG Qiang, et al. Automated rectilinear self-gated cardiac cine imaging[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2004, 52(4): 782–788. doi: 10.1002/mrm.20212. [17] NIJM G M, SAHAKIAN A V, SWIRYN S, et al. Comparison of self-gated cine MRI retrospective cardiac synchronization algorithms[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2008, 28(3): 767–772. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21514. [18] ZHU Yingen, GE Yao, WEI Qiang, et al. Camera-based Bi-modal PPG-SCG: Sleep privacy-protected contactless vital signs monitoring[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(4): 4375–4389. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3484752. [19] VOLLBRECHT T M, BISSELL M M, KORDING F, et al. Fetal cardiac MRI using Doppler US gating: Emerging technology and clinical implications[J]. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, 2024, 6(2): e230182. doi: 10.1148/ryct.230182. [20] MARTINEK R, BRABLIK J, KOLARIK J, et al. A low-cost system for seismocardiography-based cardiac triggering: A practical solution for cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging at 3 tesla[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 118608–118629. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2936184. [21] ADCOX K, ADLER S S, AFANASIEV S, et al. Formation of dense partonic matter in relativistic nucleus-nucleus collisions at RHIC: Experimental evaluation by the PHENIX collaboration[J]. Nuclear Physics A, 2005, 757(1/2): 184–283. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2005.03.086. [22] SPICHER N, MADERWALD S, LADD M E, et al. Heart rate monitoring in ultra-high-field MRI using frequency information obtained from video signals of the human skin compared to electrocardiography and pulse oximetry[J]. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering, 2015, 1(1): 69–72. doi: 10.1515/cdbme-2015-0018. [23] DONG Zhekang, JI Xiaoyue, LAI C S, et al. Design and implementation of a flexible neuromorphic computing system for affective communication via memristive circuits[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2023, 61(1): 74–80. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2200272. [24] GANTI V G, GAZI A H, AN S, et al. Wearable seismocardiography-based assessment of stroke volume in congenital heart disease[J]. Journal of the American Heart Association, 2022, 11(18): e026067. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026067. [25] DONG Zhekang, ZHU Liyan, ZHOU Shiqi, et al. FE-SpikeFormer: A camera-based facial expression recognition method for hospital health monitoring[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2025: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2025.3589267. [26] 董哲康, 杜晨杰, 林辉品, 等. 基于多通道忆阻脉冲耦合神经网络的多帧图像超分辨率重建算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 835–843. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190868.DONG Zhekang, DU Chenjie, LIN Huipin, et al. Multi-channel memristive pulse coupled neural network based multi-frame images super-resolution reconstruction algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 835–843. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190868. [27] 董哲康, 钱智凯, 周广东, 等. 基于忆阻的全功能巴甫洛夫联想记忆电路的设计、实现与分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(6): 2080–2092. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210376.DONG Zhekang, QIAN Zhikai, ZHOU Guangdong, et al. Memory circuit design, implementation and analysis based on memristor full-function Pavlov associative[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(6): 2080–2092. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210376. [28] 周师琦, 王俊帆, 赖俊升, 等. 结合贝叶斯Autoformer的多维自适应短期电力负荷概率预测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(12): 4432–4440. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240398.ZHOU Shiqi, WANG Junfan, LAI Junsheng, et al. Multi-view adaptive probabilistic load forecasting combing Bayesian Autoformer network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(12): 4432–4440. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240398. [29] SPICHER N, KUKUK M, MADERWALD S, et al. Initial evaluation of prospective cardiac triggering using photoplethysmography signals recorded with a video camera compared to pulse oximetry and electrocardiography at 7T MRI[J]. Biomedical Engineering Online, 2016, 15(1): 126. doi: 10.1186/s12938-016-0245-3. [30] LADROVA M, MARTINEK R, NEDOMA J, et al. Monitoring and synchronization of cardiac and respiratory traces in magnetic resonance imaging: A review[J]. IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 15: 200–221. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2021.3055550. [31] TOGAWA T, OKAI O, and OSHIMA M. Observation of blood flow E. M. F. in externally applied strong magnetic field by surface electrodes[J]. Medical and Biological Engineering, 1967, 5(2): 169–170. doi: 10.1007/BF02474505. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
