A Review of Research on Voiceprint Fault Diagnosis of Transformers
-
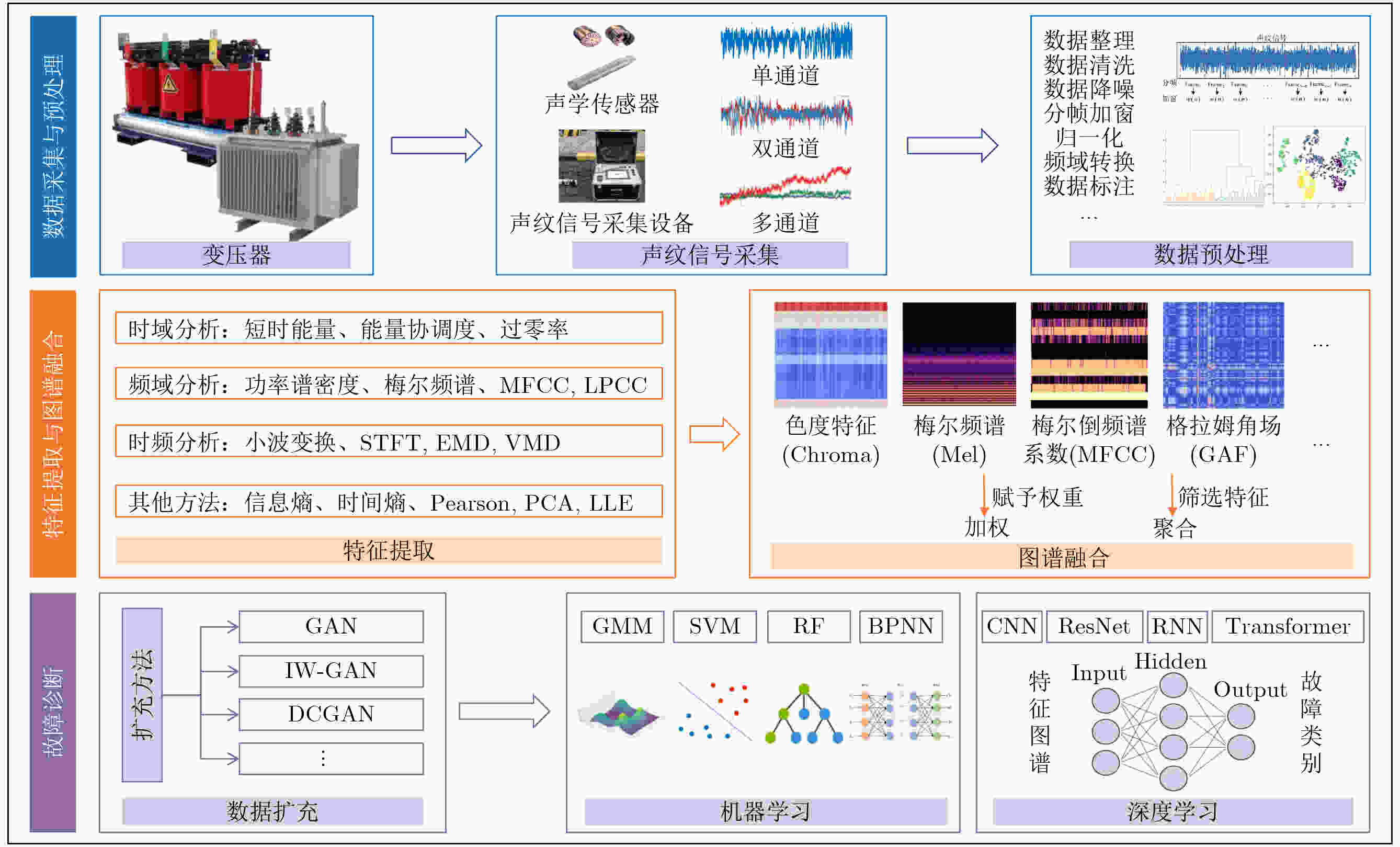
摘要: 变压器作为电网的核心枢纽设备,其运行状态直接影响电力系统的安全性与稳定性。传统监测技术存在依赖人工经验、实时性不足等问题,声纹故障诊断技术凭借非接触式监测等优势成为当前变压器故障诊断领域的研究热点。该文梳理了变压器声纹故障诊断领域的研究进展,明晰变压器主要故障类型与监测技术差异,归纳时域、频域及时频域3类声纹特征提取方法,剖析主流机器学习与深度学习模型的优劣势及适用场景等,并针对当前研究中存在的噪声鲁棒性不足、样本分布不平衡、模型可解释性差、标准化体系缺失、跨模态融合不足等关键问题深入分析,展望未来研究方向,以期为该领域的理论研究与工程应用提供系统性参考。Abstract:
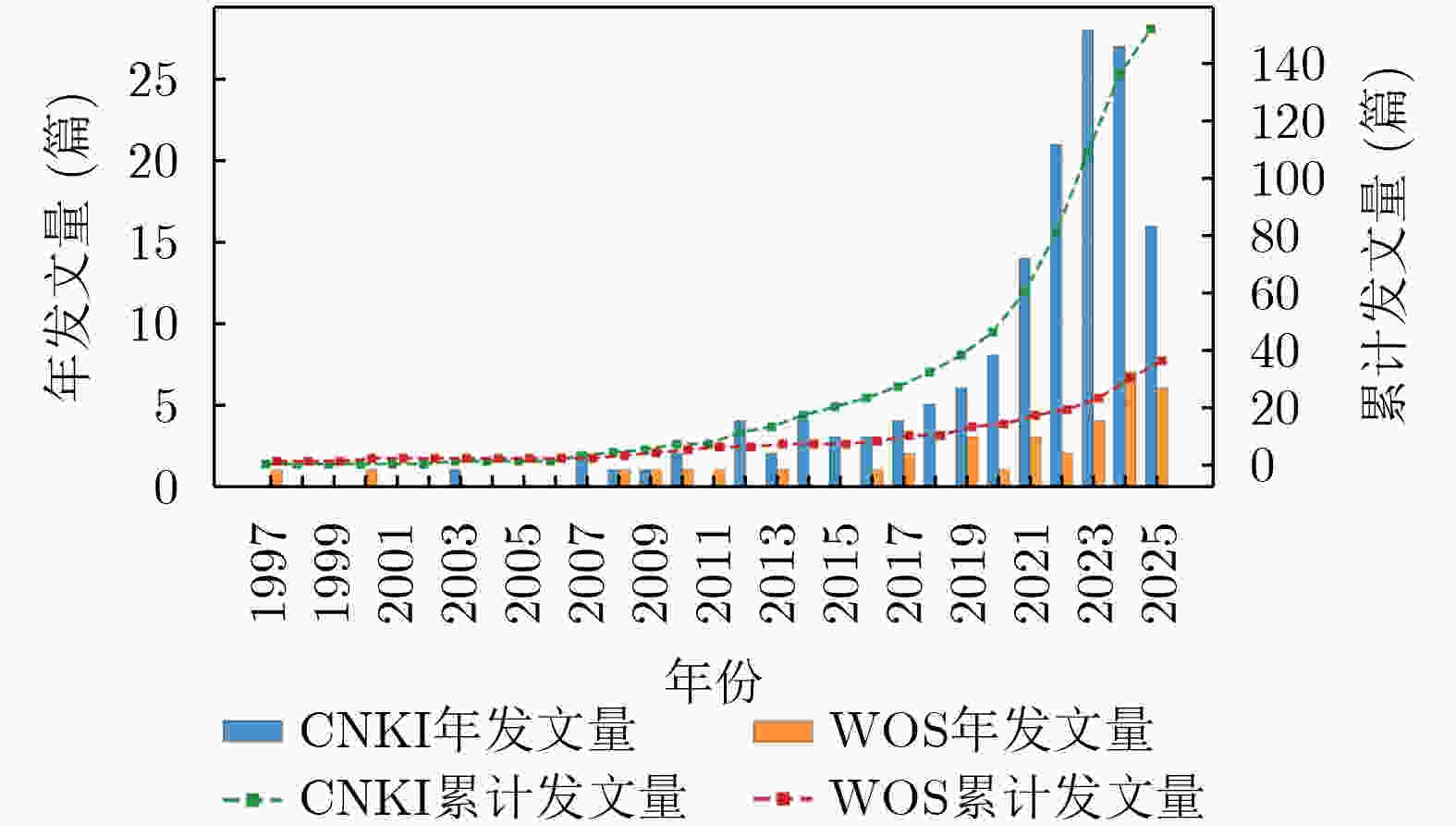
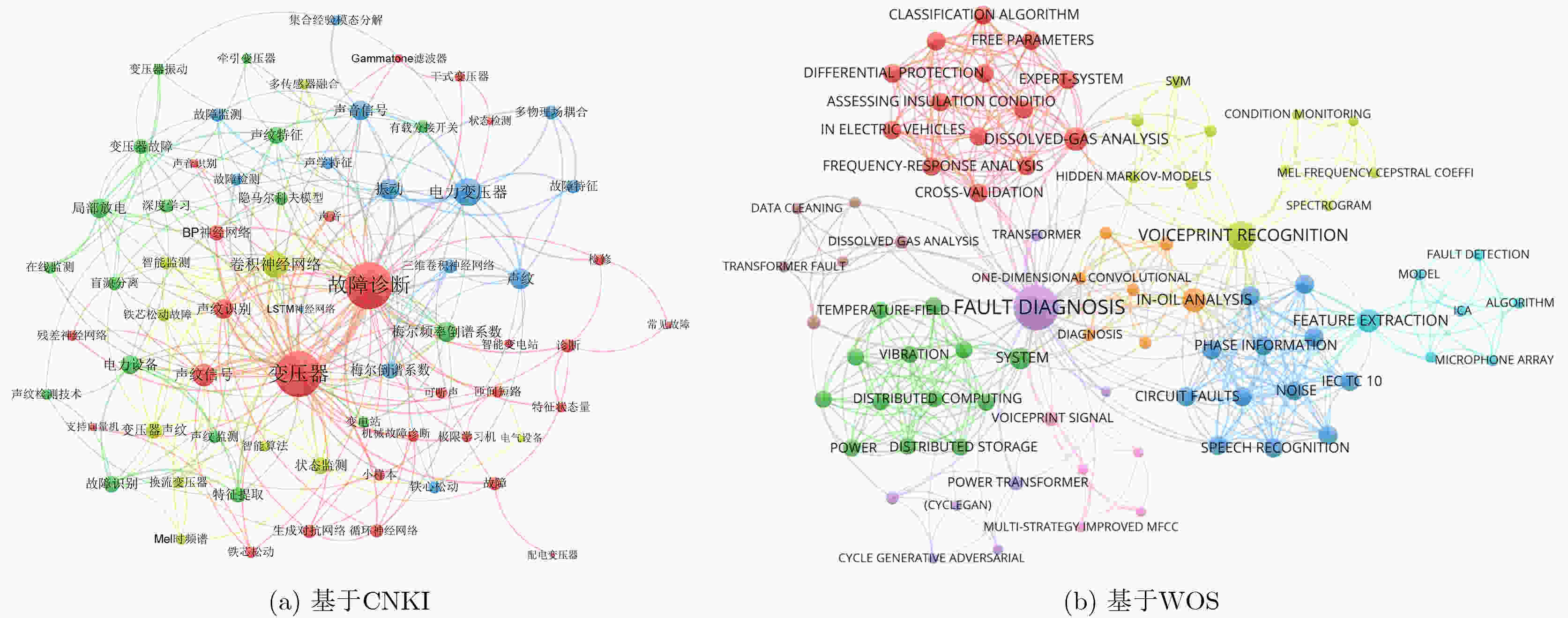
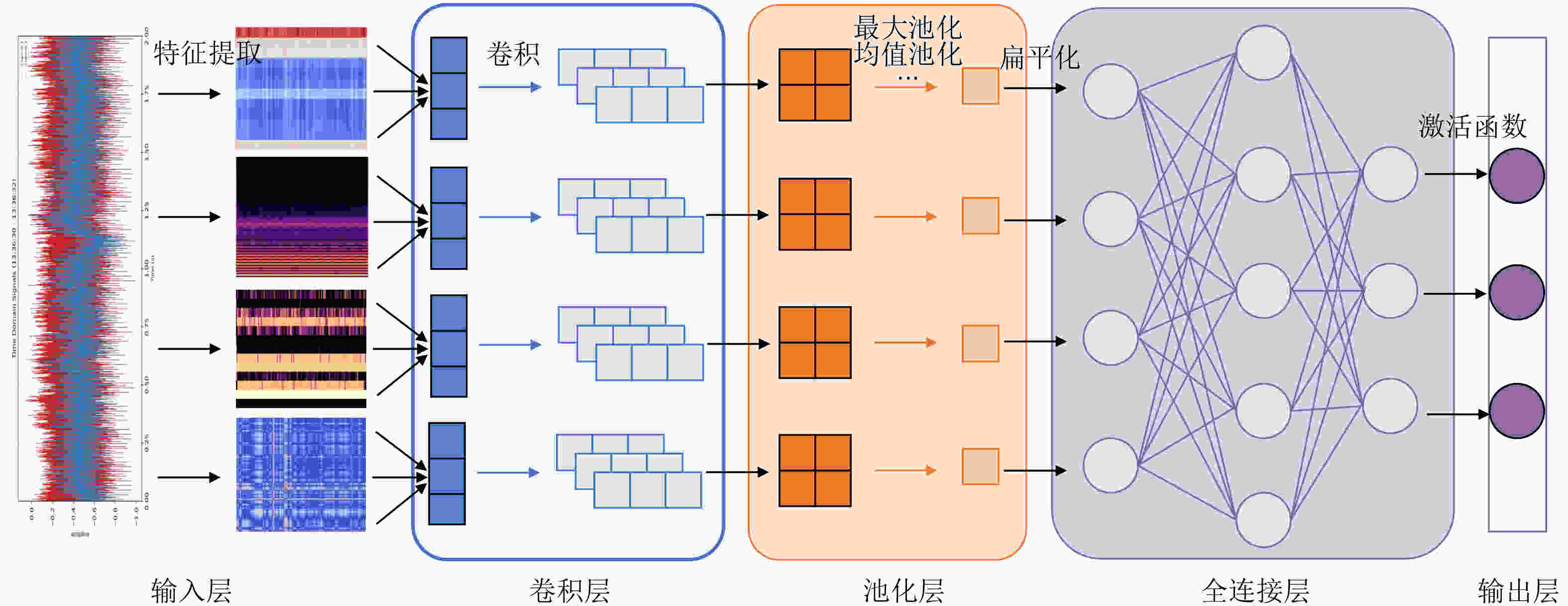
Significance Voiceprint fault diagnosis of transformers has become an active research area for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of power systems. Traditional monitoring methods, such as dissolved gas analysis, infrared temperature measurement, and online partial discharge monitoring, exhibit limited real-time capability and rely heavily on expert experience. These limitations hinder effective detection of early-stage faults. Voiceprint fault diagnosis captures operational voiceprint signals from transformers and enables non-contact monitoring for early anomaly warning. This approach offers advantages in real-time performance, sensitivity, and fault coverage. This review systematically traces the technological evolution from traditional signal analysis to deep learning and compares the advantages, limitations, and application scenarios of different models across multiple dimensions. Key challenges are identified, including limited robustness to noise and imbalanced datasets. Potential research directions are proposed, including integration of physical mechanisms with data-driven methods and improvement of diagnostic transparency and interpretability. These analyses provide theoretical support and practical guidance for promoting the transition of voiceprint fault diagnosis from laboratory research to engineering applications. Progress Research on voiceprint fault diagnosis of transformers has progressed from traditional signal analysis to an intelligent recognition paradigm based on deep learning, reflecting a clear technological evolution. A bibliometric analysis of 188 papers from the CNKI and Web of Science databases shows that annual publications remained at 1–10 papers between 1997 and 2020, corresponding to an exploratory stage. Studies during this period focused mainly on fundamental voiceprint signal processing methods, including acoustic wave detection, wavelet transform, and Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD). After 2020, Variational Modal Decomposition (VMD), Mel spectrum, and Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC) were gradually applied to voiceprint feature extraction. Since 2021, publication output has increased rapidly and reached a historical peak in 2023. This growth was driven by advances in image and speech processing technologies. Early studies emphasized time-domain and frequency-domain analysis of voiceprint signals. Recent research increasingly converts voiceprint signals into two-dimensional time–frequency spectrogram representations. Model architectures have evolved from single-channel feature inputs with single-model outputs to complex frameworks with multi-channel feature extraction and multi-model fusion. Classical machine learning models, including Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), and Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN), form the foundation of voiceprint fault diagnosis but are limited in handling high-dimensional features. Deep learning models, such as Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Residual Neural Network (ResNet), Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), and Transformer, demonstrate advantages in automatic feature extraction and complex pattern recognition, although they require substantial computational resources. Conclusions This review summarizes the technological development of transformer voiceprint fault diagnosis from machine learning to deep learning. Although deep learning methods achieve high recognition accuracy for complex voiceprint signals, five major challenges remain. These challenges include limited robustness to noise in non-stationary environments, severe data imbalance caused by scarce fault samples, the black-box nature of deep learning models, fragmented evaluation systems resulting from inconsistent data acquisition standards, and insufficient cross-modal fusion of multi-source data. Sensitivity to environmental noise limits diagnostic performance under varying operating conditions. Data imbalance reduces recognition accuracy for rare fault types. Limited interpretability restricts fault mechanism analysis and diagnostic credibility. Inconsistent sensor placement and sampling parameters lead to poor comparability across datasets. Single-modal voiceprint analysis restricts effective utilization of complementary information from other data sources. Addressing these challenges is essential for advancing voiceprint fault diagnosis from laboratory validation to field deployment. Prospects Future research should focus on five directions. First, noise-robust voiceprint feature extraction methods based on physical mechanisms should be developed to address non-stationary interference in complex operating environments. Second, the lack of real-world fault data should be alleviated by constructing electromagnetic field–structural mechanics–acoustic coupling models of transformers to generate high-fidelity voiceprint fault samples, while unsupervised clustering methods should be applied to improve annotation efficiency and quality. Third, explainable deep learning architectures for voiceprint fault diagnosis that incorporate physical mechanisms should be designed. Attention mechanisms combined with SHapley Additive exPlanations, Grad-CAM, and physical equations can support process-level and post hoc interpretation of diagnostic results. Fourth, industry-wide collaboration is required to establish standardized voiceprint data acquisition protocols, benchmark datasets, and unified evaluation systems. Fifth, cross-modal fusion models based on multi-channel and multi-feature analysis should be developed to enable integrated transformer fault diagnosis through comprehensive utilization of multi-source information. -
Key words:
- Transformer /
- Voiceprint recognition /
- Fault diagnosis /
- Deep learning
-
表 1 监测技术原理及应用场景
监测技术 监测原理 核心优势 主要局限 应用场景 油色谱
分析检测绝缘油中溶解气体的
成分与含量能有效诊断内部绝缘过热、
放电等潜伏性故障响应滞后,无法定位故障点,对突发性及机械类故障不敏感 适用于定期巡检与绝缘状态长期趋势评估,内部故障诊断 红外测温 利用红外热像仪探测设备
表面的温度分布非接触,成像直观,
能快速扫描大面积设备仅检测表面温度,难察内部过热,受环境干扰,价值发挥晚 巡视电气连接部位、排查冷却系统异常及局部过热缺陷 局部放电在线监测 捕捉设备因内部绝缘缺陷产生的瞬时电磁波或超声波信号 灵敏度高,能发现微小的绝缘缺陷,可结合放电图谱进行模式识别 成本高,安装复杂,受现场电磁干扰,对抗噪能力要求严苛 重点应用于新设备验收及存在绝缘隐患设备的长期跟踪监测 声纹故障诊断 分析运行时声纹信号的
时频域特征变化非接触,实时性强,成本低廉,
部署灵活易受噪声干扰,缺乏统一标准与可解释性 可监测机械及电气类故障,适用于日常巡检与快速筛查 表 2 主要故障类型及其声学特性
故障类 具体故障 声学产生机理 典型声学特性 机械类 组件松动 组件因电磁场变化发生不规则振动,产生异常噪声 间歇性的不均匀敲击声或振动声,并持续存在 风机老化 长期工作导致轴承损坏老化、叶片生锈变形,影响正常运转 转动噪音增大,转动速率下降 冷凝器异响 风扇、油泵等冷却系统运转异常 异常且连续的机械振动声或空气流动声 电气类 重过载 电磁力增强,使得铁芯和绕组的振动增强 “嗡嗡”声或“咯咯”声,声音更响亮且连续 直流偏磁 电磁力分布不均,使得铁芯和绕组产生额外的振动 产生异常的“嗡嗡”声,音调尖锐刺耳 短路冲击 产生巨大的电流和热量,伴随油温升高和油位异常等现象 突发异常的“砰”声或“水沸腾” 局部放电 放电过程产生气体冲击、电弧等现象,伴随特定声音产生 忽大忽小的高频“吱吱”或“哼哼”声 表 3 常用声学传感器类型及特性
传感器类型 工作原理 优点 缺点 适用性分析 动圈式传声器 基于电磁感应原理的声电转换设备 成本低,结构坚固,适用面广,
使用方便,不需极化电压,
能耐高声压灵敏度低,频响窄,瞬态响应慢,易受现场电磁环境干扰 适用于工业现场稳定、噪声强度高、环境恶劣的长期监测,对精度要求不高但需高可靠性的场景 电容式传声器 利用电容量变化引起声电转换作用 灵敏度高,频响宽,本体噪声低,可保证振幅固定 成本较高,需要极化电压,
系统较复杂,使用不太方便,
对潮湿环境敏感性能优异,能满足变压器声纹采集对高灵敏度和宽频响的要求,是实验室和高精度测量的理想选择 驻极体传声器 已注入电荷而被极化的驻极体代替极化电源 无需极化电压,结构简单,重量轻,体积小,成本低且便携,
动态范围广,抗电磁干扰能力强长期稳定性较差,温湿度敏感,
耐高温能力弱综合性能与便捷性较佳,适合在
变电站复杂电磁环境下进行现场
监测,是变压器可听声诊断的
理想选择数字传声器 集成声学传感器和ADC芯片,直接输出数字信号 微型化,抗干扰能力强,功耗低,支持降噪、回声消除等内部处理 成本较高,依赖数字接口与
主控芯片,维修不便适用于构建分布式、智能化的在线监测节点,是实现变压器声纹诊断系统嵌入式部署的未来方向 表 4 不同类型变压器的声纹监测差异
变压器类型 主要特点 监测方式 诊断方法核心要求 干式变压器 无绝缘油,铁芯绕组暴露于空气中,空气散热,声源铁芯绕组振动、有载分接开关动作 电容式或驻极体传声器布置于距本体
1 m处,高度居中高保真声纹特征提取能力 油浸式变压器 含绝缘油,铁芯绕组密封于金属油箱内,
冷却方式多样,声源铁芯绕组动、
冷却系统噪声,有载分接开关动作驻极体或数字传声器布置于距本体
0.3 m处,高度位于1/3 油箱高强噪声下异常检测能力 牵引变压器 用于电气化铁路牵引供电系统,频繁启停,
负载波动,具有非线性、冲击性、不对称性,
油浸式,少数为干式电容式或驻极体传声器布置于距本体
0.3 m处,高度位于牵引变压器整体
1/2 处动态适应性,强鲁棒性 换流变压器 用于高压直流输电,高谐波电流,
直流分量侵入,油浸式驻极体传声器布置于距本体 0.5 m,
高度位于换流变压器整体 1/2处非平稳线性信号去噪能力 表 5 变压器声纹特征提取方法对比
分析域 分析方法 优势 劣势 适用场景 动态工况适用性 时域 时域波形 计算简单,物理意义直观,
能直接捕捉瞬时异常对细微的频率特征不敏感,
难直接用于诊断故障短路冲击、有载调压等产生的暂态振动 弱:仅反映幅值突变,无法
解析频率成分的时变规律频域 梅尔频谱 能有效突出低频信息、
抑制高频噪声仍是全局平均频谱,
暂态特性表征能力弱铁芯、绕组松动等机械故障 弱:难以跟踪动态频率演化 MFCC 能有效表征声纹频谱包络,对稳态噪声的特征提取鲁棒性高,识别效果好 计算相对复杂,对快速变化的非平稳信号特征捕捉能力有限 铁芯、绕组松动等机械故障 中:适用于缓变工况,对剧烈动态适应性受限 LPCC 侧重刻画信号共振峰,对信号频谱的包络形状更敏感 对非平稳信号不敏感,性能受线性预测阶数影响大 分析机械故障的声学
共振特征中:依赖线性预测,动态适应性一般 时频域 STFT 方法直观易懂,能有效地分析信号的局部频谱特征 时间与频率分辨率固定且相互矛盾,难以同时兼顾 初步时频联合分析 中:固定窗长限制了其在动态过程中的表现 EMD 自适应分解,无需预设基函数,适合处理非平稳信号 模态混叠,端点效应,分解的稳定性和唯一性差 分析非平稳信号的固有模态 强:可揭示动态特征,适合
复杂工况下的隐含模式提取VMD 抗混叠,分解模态稳定,
噪声鲁棒性好需要预设模态数量,对中心频率参数敏感,计算复杂度高 重过载、直流偏磁、局部放电、短路冲击等电气故障 强:能清晰分离频带,有效追踪动态特征演化,是处理非平稳信号的有力工具 表 6 领域主流模型对比与适用性分析
模型类别 主流模型 优势 劣势 适用场景 动态工况适应性 机器学习 GMM 小样本友好、抗噪强、
计算快特征依赖人工、泛化弱 背景噪声大、样本量小 弱:依赖稳态特征假设,
难以建模动态过程SVM 小规模数据集上表现良好、
理论完备处理大规模和高维
数据性能下降故障类型少、需高精度 弱:对特征分布稳定性高度依赖,核函数需针对时序优化 RF 抗过拟合、特征重要性可解释 模型黑箱、调参复杂 需特征筛选、噪声中等 中:集成学习提供一定鲁棒性,
但难以捕捉连续时序动态BPNN 时频特征提取有效,结合
优化算法收敛速度快易陷入局部最优,
对初始权值敏感中小样本、特征工程明确 弱:静态网络结构,缺乏时序建模能力,难以处理时变信号 深度学习 CNN 自动特征提取、
适合图谱输入局部特征感知、时间序列
建模和计算效率局限数据量多、图谱输入 中:擅长从静态图谱中提取特征,但对时序演化规律捕捉不足 ResNet 深层稳定、精度高 结构复杂、部署难 高分辨率图谱、高精度 中:强特征提取能力,但受限于静态图像输入,对时序动态不敏感 RNN 擅长处理序列数据,能有效
捕捉长时序依赖关系训练速度慢,存在
梯度消失风险时序信息关键、数据为原始
波形或一维特征序列的场景强:专门为序列设计,能有效建模动态过程,学习特征演化模式 Transformer 长序列建模、并行计算 参数量大、训练慢,
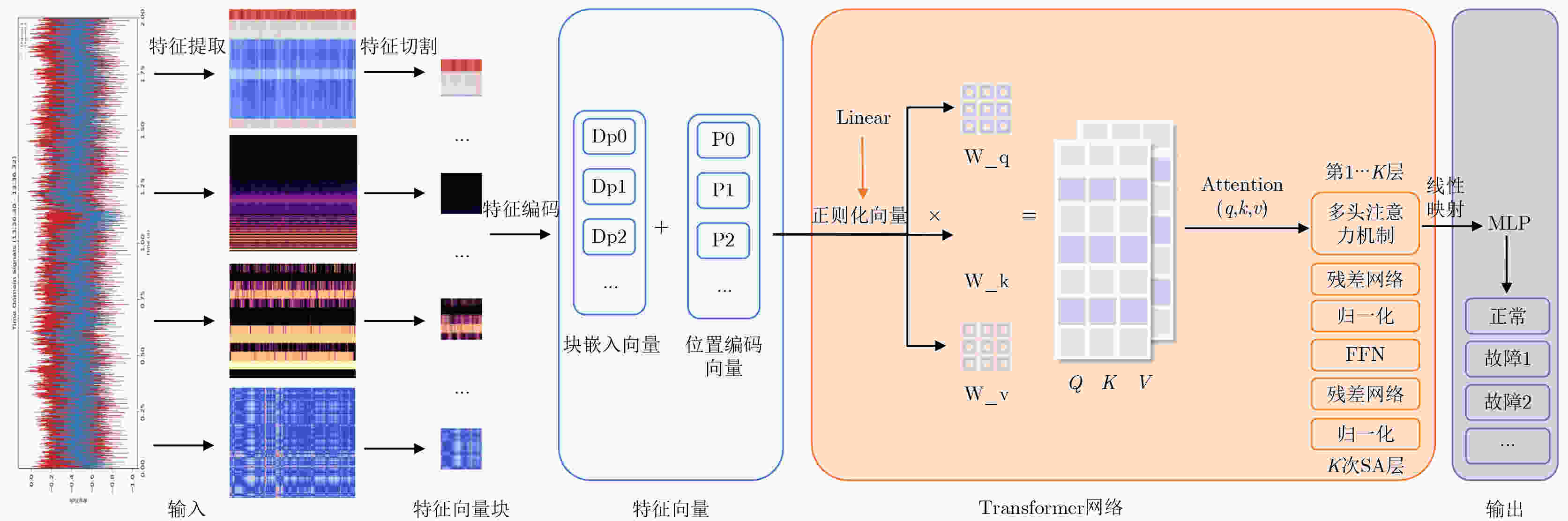
表征位置信息不足时序依赖强、计算资源充足、
周期性突发性故障识别强:自注意力机制能直接捕捉全过程的长程依赖与突发瞬态模式 -
[1] ZHU Yongcan, GUO Zhenyan, ZHAN Xiaoxuan, et al. Research on transformer fault diagnosis models with feature extraction[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2024, 95(11): 115109. doi: 10.1063/5.0225204. [2] 马宏忠, 李楠, 杨启帆, 等. 基于多特征声纹图谱的变压器绕组松动在线故障诊断方法[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2023, 27(5): 76–87. doi: 10.15938/j.emc.2023.05.009.MA Hongzhong, LI Nan, YANG Qifan, et al. On-line fault diagnosis method of transformer winding looseness based on multi-characteristic voiceprint maps[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2023, 27(5): 76–87. doi: 10.15938/j.emc.2023.05.009. [3] 周东旭, 王丰华, 党晓婧, 等. 基于压缩观测与判别字典学习的干式变压器声纹识别[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(19): 6380–6389. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.191577.ZHOU Dongxu, WANG Fenghua, DANG Xiaojing, et al. Dry type transformer voiceprint recognition based on compressed observation and discrimination dictionary learning[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(19): 6380–6389. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.191577. [4] 张重远, 罗世豪, 岳浩天, 等. 基于Mel时频谱-卷积神经网络的变压器铁芯声纹模式识别方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2020, 46(2): 413–422. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20200131005.ZHANG Zhongyuan, LUO Shihao, YUE Haotian, et al. Pattern recognition of acoustic signals of transformer core based on Mel-spectrum and CNN[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2020, 46(2): 413–422. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20200131005. [5] ELGOHARY A A, BADR M M, ELMALHY N A, et al. Transfer of learning in convolutional neural networks for thermal image classification in electrical transformer rooms[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2024, 105: 423–436. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2024.07.077. [6] NIU Ben, WEI Yangjie, YU Zhuoran, et al. Acoustic signal augmentation for fault diagnosis of power transformers based on improved cycle generative adversarial networks[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 288: 127997. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.127997. [7] 王玉伟, 余俊龙, 彭平, 等. 基于多模型融合的变压器故障在线检测方法[J]. 高电压技术, 2023, 49(8): 3415–3424. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20230646.WANG Yuwei, YU Junlong, PENG Ping, et al. Online detection method for transformer faults based on multi-model fusion[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2023, 49(8): 3415–3424. doi: 10.13336/j.1003-6520.hve.20230646. [8] 于达, 张玮, 王辉. 基于LSTM神经网络的油浸式变压器异常声纹诊断方法研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2023, 51(2): 45–52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2023.02.008.YU Da, ZHANG Wei, and WANG Hui. Abnormal voiceprint diagnosis method of oil-immersed transformer based on LSTM neural network[J]. Smart Power, 2023, 51(2): 45–52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2023.02.008. [9] 李楠, 马宏忠, 段大卫, 等. 基于多传感器融合声纹特征图谱的变压器铁芯松动故障诊断方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(15): 129–137,198. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.15.016.LI Nan, MA Hongzhong, DUAN Dawei, et al. Fault diagnosis method for transformer core looseness based on multi-sensor fusion voiceprint feature map[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(15): 129–137,198. doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.15.016. [10] PENG Jiaqi, MA Yulin, YE Haiping, et al. Voiceprint recognition method of transformer based on LBT-ODF and MVN[J]. Journal of Measurements in Engineering, 2025, 13(2): 387–404. doi: 10.21595/jme.2024.24496. [11] 柴斌, 韦鹏, 宁复茂, 等. 基于S变换时频谱和KHA-CNN的换流变故障声纹识别[J]. 电网与清洁能源, 2024, 40(2): 103–109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3814.2024.02.012.CHAI Bin, WEI Peng, NING Fumao, et al. Voiceprint recognition of converter transformer faults based on S transform time-frequency spectrum and KHA-CNN[J]. Power System and Clean Energy, 2024, 40(2): 103–109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3814.2024.02.012. [12] WANG Jianxin, ZHAO Zhishan, ZHU Jun, et al. Improved support vector machine for voiceprint diagnosis of typical faults in power transformers[J]. Machines, 2023, 11(5): 539. doi: 10.3390/machines11050539. [13] WANG Yuwei, DONG Wenjuan, AZAN D, et al. Voiceprint state identification of power transformers based on probabilistic neural network[C]. The 6th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications, Dalian, China, 2024: 154–158. doi: 10.1109/ICAICA63239.2024.10823067. [14] 梁广平, 彭昌, 王杰, 等. 基于图注意力网络的变压器声纹信号故障检测方法[J]. 华北电力大学学报: 自然科学版, 2024: 1–9. LIANG Guangping, PENG Chang, WANG Jie, et al. Fault detection method of graph attention network based on transformer acoustic signal[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University: Natural Science Edition, 2024: 1–9. [15] 万可力, 马宏忠, 崔佳嘉, 等. 基于Mel-GADF与ConvNeXt-T的变压器铁心松动故障诊断方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2024, 44(3): 217–224. doi: 10.16081/j.epae.202307003.WAN Keli, MA Hongzhong, CUI Jiajia, et al. Fault diagnosis method of transformer core loosening based on Mel-GADF and ConvNeXt-T[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2024, 44(3): 217–224. doi: 10.16081/j.epae.202307003. [16] WANG Shuchen, XU Qizhi, ZHU Shunpeng, et al. Making transformer hear better: Adaptive feature enhancement based multi-level supervised acoustic signal fault diagnosis[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 264: 125736. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125736. [17] 沈国堂, 郭振宇, 黄道均, 等. 基于特征提取和神经网络的电力变压器声纹诊断方法建立与应用[J]. 变压器, 2024, 61(6): 39–43. doi: 10.19487/j.cnki.1001-8425.2024.06.012.SHEN Guotang, GUO Zhenyu, HUANG Daojun, et al. Establishment and application of power transformer voiceprint diagnosis method based on feature fusion and neural network[J]. Transformer, 2024, 61(6): 39–43. doi: 10.19487/j.cnki.1001-8425.2024.06.012. [18] 吴晓文, 孙静玲, 曹浩, 等. 电力变压器典型声纹特征分布规律统计分析[J]. 武汉大学学报: 工学版, 2025, 58(1): 84–93. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2020.0172.WU Xiaowen, SUN Jingling, CAO Hao, et al. Statistical analysis of typical voiceprint feature distribution of power transformers[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2025, 58(1): 84–93. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8844.2020.0172. [19] YU Zhuoran, WEI Yangjie, NIU Ben, et al. Automatic condition monitoring and fault diagnosis system for power transformers based on voiceprint recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 9600411. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3384551. [20] 刘云鹏, 罗世豪, 王博闻, 等. 基于Mel时频谱-卷积神经网络的变压器铁芯夹件松动故障声纹模式识别[J]. 华北电力大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 47(6): 52–60,67. doi: 10.3969/j.ISSN.1007-2691.2020.06.06.LIU Yunpeng, LUO Shihao, WANG Bowen, et al. Voiceprint recognition of transformer core clamp looseness fault by Mel-spectrum and convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 47(6): 52–60,67. doi: 10.3969/j.ISSN.1007-2691.2020.06.06. [21] 冶海平, 彭家琦, 方保民, 等. 基于Mel时频谱的变压器铁心松动故障声纹识别[J]. 信息技术, 2025(9): 37–42. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2025.09.007.YE Haiping, PENG Jiaqi, FANG Baomin, et al. Voiceprint recognition of transformer core looseness fault based on Mel time-frequency spectrum[J]. Information Technology, 2025(9): 37–42. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2025.09.007. [22] 狄晓栋, 李震梅, 李宗哲, 等. 基于混合特征MGCC的干式变压器故障诊断[J]. 电子测量技术, 2021, 44(12): 57–62. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2106561.DI Xiaodong, LI Zhenmei, LI Zongzhe, et al. Fault diagnosis of dry-type transformer based on combination of MGCC feature parameters[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 44(12): 57–62. doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2106561. [23] PEI Xiping, HAN Songtao, BAO Yanyan, et al. Fault diagnosis of transformer winding short circuit based on WKPCA-WM and IPOA-CNN[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2023, 11: 1151612. doi: 10.3389/fenrg.2023.1151612. [24] 季坤, 张晨晨, 丁国成, 等. 粒子群优化算法在电力变压器声纹识别中的应用[J]. 沈阳工业大学学报, 2023, 45(6): 643–648. doi: 10.7688/j.issn.1000-1646.2023.06.08.JI Kun, ZHANG Chenchen, DING Guocheng, et al. Application of particle swarm optimization algorithm in power transformer voiceprint recognition[J]. Journal of Shenyang University of Technology, 2023, 45(6): 643–648. doi: 10.7688/j.issn.1000-1646.2023.06.08. [25] LI Hui, YAO Qi, and LI Xin. Voiceprint fault diagnosis of converter transformer under load influence based on multi-strategy improved Mel-Frequency spectrum coefficient and temporal convolutional network[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(3): 757. doi: 10.3390/s24030757. [26] 李明朗, 杨洋, 王凤雪, 等. 基于声纹信号的变压器故障检测技术分析[J]. 电子元器件与信息技术, 2025, 9(8): 58–60. doi: 10.19772/j.cnki.2096-4455.2025.08.018.LI Minglang, YANG Yang, WANG Fengxue, et al. Analysis of transformer fault detection technology based on acoustic signal[J]. Electronic Components and Information Technology, 2025, 9(8): 58–60. doi: 10.19772/j.cnki.2096-4455.2025.08.018. [27] 李波, 闫胜春. 基于深度学习的变压器声纹故障诊断方法研究[J]. 电工技术, 2025(17): 60–62,65. doi: 10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2025.17.015.LI Bo and YAN Shengchun. Research on deep learning based acoustic fault diagnosis method of transformer[J]. Electric Engineering, 2025(17): 60–62,65. doi: 10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2025.17.015. [28] SUN Yanfei, ZHAO Tao, GAO Li, et al. An attention-guided semi-supervised model for power transformer fault diagnosis via vibration-acoustic data fusion[J]. IET Electric Power Applications, 2025, 19(1): e70062. doi: 10.1049/elp2.70062. [29] 李腾, 樊培培, 廖军, 等. 基于奇异值能量标准谱和改进TVF-EMD的换流变压器局部放电去噪方法[J]. 高压电器, 2025, 61(11): 221–230. doi: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2025.11.021.LI Teng, FAN Peipei, LIAO Jun, et al. Partial discharge denoising method for converter transformer based on singular value energy standard spectrum and improved TVF-EMD[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2025, 61(11): 221–230. doi: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2025.11.021. [30] 魏才懿, 杨军, 马建桥. 参数优化VMD对变压器声音信号的故障诊断[J]. 兰州交通大学学报, 2021, 40(4): 49–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2021.04.008.WEI Caiyi, YANG Jun, and MA Jianqiao. Fault diagnosis of transformer sound signal by parameter optimization VMD[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2021, 40(4): 49–58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2021.04.008. [31] SHEN Xiang, XU Fei, XU Long, et al. Research on transformer voiceprint feature extraction oriented to complex noise environment[J]. International Journal of Acoustics and Vibration, 2023, 28(2): 193–199. doi: 10.20855/ijav.2023.28.21933. [32] 陆云才, 廖才波, 李群, 等. 基于声纹特征和集成学习的变压器缺陷诊断方法[J]. 电力工程技术, 2023, 42(5): 46–55. doi: 10.12158/j.2096-3203.2023.05.006.LU Yuncai, LIAO Caibo, LI Qun, et al. Transformer fault diagnosis method based on voiceprint feature and ensemble learning[J]. Electric Power Engineering Technology, 2023, 42(5): 46–55. doi: 10.12158/j.2096-3203.2023.05.006. [33] 段梵, 李先允, 单光瑞, 等. 基于融合特征和残差神经网络的10 kV高压断路器机械故障声纹识别方法[J]. 高压电器, 2025, 61(3): 205–213. doi: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2025.03.025.DUAN Fan, LI Xianyun, SHAN Guangrui, et al. Voiceprint recognition method for mechanical faults of 10 kV circuit breaker based on fusion feature residual neural network[J]. High Voltage Apparatus, 2025, 61(3): 205–213. doi: 10.13296/j.1001-1609.hva.2025.03.025. [34] CAI Rui, WANG Qian, HOU Yucheng, et al. Event monitoring of transformer discharge sounds based on voiceprint[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 2078(1): 012066. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2078/1/012066. [35] 王广真, 付德慧, 杜非, 等. 基于重复模式提取与高斯混合模型的变压器故障声纹识别[J]. 广东电力, 2023, 36(1): 126–134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-290X.2023.01.014.WANG Guangzhen, FU Dehui, DU Fei, et al. Transformer fault voiceprint recognition based on repeating pattern extraction and Gaussian mixture model[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023, 36(1): 126–134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-290X.2023.01.014. [36] 陈睿妍, 卢璐, 沈明威, 等. 基于线性SVM的变电站故障声纹检测算法[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2023, 18(11): 989–995. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2023.11.003.CHEN Ruiyan, LU Lu, SHEN Mingwei, et al. Faulty voiceprint detection algorithm based on linear SVM for substation[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2023, 18(11): 989–995. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2023.11.003. [37] 高家通, 康兵, 许志浩, 等. 基于FRCMDE与IBOA-LSSVM的变压器故障声纹诊断方法[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2025, 45(5): 123–130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2025.05.020.GAO Jiatong, KANG Bing, XU Zhihao, et al. Fault voiceprint diagnosis method for transformers based on FRCMDE and IBOA-LSSVM[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2025, 45(5): 123–130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1355.2025.05.020. [38] 熊威, 龚康, 张鑫, 等. 基于COA-SVM变压器铁芯松动识别模型[J]. 电工技术, 2025(5): 141–144. doi: 10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2025.05.036.XIONG Wei, GONG Kang, ZHANG Xin, et al. Based on the COA-SVM transformer core loosening identification model[J]. Electric Engineering, 2025(5): 141–144. doi: 10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2025.05.036. [39] 梁延昌. 基于机器学习的变压器声学异常检测方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华北电力大学(北京), 2021. doi: 10.27140/d.cnki.ghbbu.2021.001080.LIANG Yanchang. Research on machine learning based acoustic anomaly detection method for power transformers[D]. [Master dissertation], North China Electric Power University (Beijing), 2021. doi: 10.27140/d.cnki.ghbbu.2021.001080. [40] 耿琪深, 王丰华, 金霄. 基于Gammatone滤波器倒谱系数与鲸鱼算法优化随机森林的干式变压器机械故障声音诊断[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2020, 40(8): 191–196,224. doi: 10.16081/j.epae.202007022.GENG Qishen, WANG Fenghua, and JIN Xiao. Mechanical fault sound diagnosis based on GFCC and random forest optimized by whale algorithm for dry type transformer[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2020, 40(8): 191–196,224. doi: 10.16081/j.epae.202007022. [41] 陈静. 基于声音信号分析的牵引变压器故障诊断方法研究[J]. 电气应用, 2020, 39(2): 25–29.CHEN Jing. Research on traction transformer fault diagnosis method based on sound signal analysis[J]. Electrotechnical Application, 2020, 39(2): 25–29. [42] 吴国鑫, 詹花茂, 李敏. 声纹的变压器放电与机械故障诊断研究[J]. 应用声学, 2021, 40(4): 602–610. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2021.04.015.WU Guoxin, ZHAN Huamao, and LI Min. Research on transformer discharge and mechanical fault diagnosis based on voiceprint[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2021, 40(4): 602–610. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2021.04.015. [43] 黄锐, 吕学宾, 苏永智, 等. 基于“声音+BP神经网络”的变压器故障诊断[J]. 信息技术, 2022, 46(11): 71–76. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2022.11.013.HUANG Rui, LV Xuebin, SU Yongzhi, et al. Transformer fault diagnosis based on “sound + BP neural network”[J]. Information Technology, 2022, 46(11): 71–76. doi: 10.13274/j.cnki.hdzj.2022.11.013. [44] 余金龙. 电力变压器异常故障智能声纹监测与诊断系统研究及应用[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2024, 14(8): 149–152. doi: 10.19981/j.CN23-1581/G3.2024.08.034.YU Jinlong. Research and application of intelligent acoustic monitoring and diagnosis system for abnormal faults of power transformer[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2024, 14(8): 149–152. doi: 10.19981/j.CN23-1581/G3.2024.08.034. [45] 余长树. 基于声纹的变压器故障诊断算法及其应用研究[D]. [硕士论文], 华北电力大学(北京), 2023. doi: 10.27140/d.cnki.ghbbu.2023.001152.YU Changshu. Sound pattern based transformer fault diagnosis algorithm and application research[D]. [Master dissertation], North China Electric Power University (Beijing), 2023. doi: 10.27140/d.cnki.ghbbu.2023.001152. [46] 包艳艳, 杨广泽, 陈伟, 等. 基于SBSS与CNN的750 kV变压器和尖板的放电信号声纹识别[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2025, 60(3): 781–792. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230177.BAO Yanyan, YANG Guangze, CHEN Wei, et al. Voiceprint recognition of discharge aliasing signals from 750 kV transformer and pin-plate based on sparse representation theory and convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2025, 60(3): 781–792. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.20230177. [47] 崔佳嘉, 马宏忠. 基于改进MFCC和3D-CNN的变压器铁心松动故障声纹识别模型[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2022, 26(12): 150–160. doi: 10.15938/j.emc.2022.12.015.CUI Jiajia and MA Hongzhong. Voiceprint recognition model of transformer core looseness fault based on improved MFCC and 3D-CNN[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2022, 26(12): 150–160. doi: 10.15938/j.emc.2022.12.015. [48] 王欢, 王昕, 张峰, 等. 基于改进生成对抗网络的变压器声纹故障诊断[J]. 智慧电力, 2024, 52(4): 24–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2024.04.005.WANG Huan, WANG Xin, ZHANG Feng, et al. Transformer voiceprint fault diagnosis based on improved generative adversarial network[J]. Smart Power, 2024, 52(4): 24–31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7598.2024.04.005. [49] WAN Shuting, DONG Fan, ZHANG Xiong, et al. Fault voiceprint signal diagnosis method of power transformer based on mixup data enhancement[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(6): 3341. doi: 10.3390/s23063341. [50] 吴帆, 刘艳霞, 刘力铭, 等. 基于深度学习模型的电力变压器故障声音诊断方法研究[J]. 电声技术, 2020, 44(1): 76–80. doi: 10.16311/j.audioe.2020.01.020.WU Fan, LIU Yanxia, LIU Liming, et al. Study on the fault diagnosis method of power transformer by sound signals based on deep learning model[J]. Audio Engineering, 2020, 44(1): 76–80. doi: 10.16311/j.audioe.2020.01.020. [51] LI Min, ZHAN Huamao, and QIU Annan. Voiceprint recognition of transformer fault based on blind source separation and convolutional neural network[C]. 2021 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC), Denver, CO, USA, 2021: 618–621. doi: 10.1109/EIC49891.2021.9612322. [52] 刘鹏华, 段颖梨, 刘凯, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的换流变压器智能检测算法设计[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2025, 15(20): 142–145. doi: 10.19981/j.CN23-1581/G3.2025.20.033.LIU Penghua, DUAN Yingli, LIU Kai, et al. Design of intelligent detection algorithm for converter transformer based on convolutional neural network[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2025, 15(20): 142–145. doi: 10.19981/j.CN23-1581/G3.2025.20.033. [53] XU Zhendong, GAO Feng, JIA Yuebo, et al. Research on transformer fault diagnosis algorithm based on MFCC features and deep learning[C]. The 6th International Conference on Electrical, Electronic Information and Communication Engineering (EEICE), Shenzhen, China, 2025: 192–195. doi: 10.1109/EEICE65049.2025.11033961. [54] LONG Yujiang, WEI Wei, and WANG Ce. A lightweight sound diagnosis model for transformer discharge fault based on knowledge distillation with supercomputing[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Management Technology (ICCSMT), Shanghai, China, 2022: 408–412. doi: 10.1109/ICCSMT58129.2022.00093. [55] 宋诚, 夏翔, 王鑫一, 等. 基于MFCC和CNN的变压器声学特征提取及故障识别[J]. 电工电气, 2023(6): 49–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3175.2023.06.009.SONG Cheng, XIA Xiang, WANG Xinyi, et al. Transformer acoustic feature extraction and fault identification based on MFCC and CNN[J]. Electrotechnics Electric, 2023(6): 49–54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3175.2023.06.009. [56] 邹国春, 卢强, 鲁斌, 等. 复杂环境噪声条件下变压器故障声纹识别技术[J]. 电子制作, 2024, 32(24): 23–28. doi: 10.16589/j.cnki.cn11-3571/tn.2024.24.001.ZOU Guochun, LU Qiang, LU Bin, et al. Transformer fault acoustic recognition technology under complex environmental noise conditions[J]. Practical Electronics, 2024, 32(24): 23–28. doi: 10.16589/j.cnki.cn11-3571/tn.2024.24.001. [57] 吴宁, 王世旭, 杨宏宇, 等. 基于MDF-BSRNet的变压器声纹故障诊断方法研究[J/OL]. 自动化技术与应用, https://link.cnki.net/urlid/23.1474.TP.20241223.1335.076, 2024.WU Ning, WANG Shixu, YANG Hongyu, et al. Research on fault diagnosis method of transformer voicing based on MDF-BSRNet[J/OL]. Techniques of Automation and Applications, 2024: 1–8. [58] QIAN Qinglin, GAO Penglu, ZHAO Honglin, et al. Electrical voiceprint recognition algorithm based on SN-GAN-ResNet network[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Energy Internet (ICEI), Shenyang, China, 2023: 304–309. doi: 10.1109/icei60179.2023.00064. [59] 何萍, 李勇, 陈寿龙, 等. 基于变压器声纹Mel语谱图-ResNet的铁心松动故障诊断[J]. 电机与控制应用, 2022, 49(9): 75–80. doi: 10.12177/emca.2022.084.HE Ping, LI Yong, CHEN Shoulong, et al. Fault diagnosis of iron core looseness based on Mel spectrogram-ResNet with transformer voiceprint[J]. Electric Machines & Control Application, 2022, 49(9): 75–80. doi: 10.12177/emca.2022.084. [60] 张波, 黄英龄, 明志茂, 等. 基于同步压缩小波变换和ResNet的变压器放电故障诊断方法[J]. 现代电子技术, 2023, 46(10): 159–165. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2023.10.030.ZHANG Bo, HUANG Yingling, MING Zhimao, et al. Method of transformer discharge fault diagnosis based on synchrosqueezed wavelet transform and ResNet[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2023, 46(10): 159–165. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2023.10.030. [61] 李嘉宁, 李喆, 陈海威, 等. 基于数据增强的变压器机械故障声纹识别方法[J]. 电气自动化, 2024, 46(6): 106–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3886.2024.06.030.LI Jianing, LI Zhe, CHEN Haiwei, et al. Voiceprint recognition of mechanical faults in transformers based on data enhancement[J]. Electrical Automation, 2024, 46(6): 106–108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3886.2024.06.030. [62] 赵晋级, 戴云飞. 基于改进MFCC和RNN的变压器放电故障诊断方法[J]. 山东电力高等专科学校学报, 2024, 27(4): 1–4,8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3162.2024.04.001.ZHAO Jinji and DAI Yunfei. Transformer discharge fault diagnosis method based on improved MFCC and RNN[J]. Journal of Shandong Electric Power College, 2024, 27(4): 1–4,8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3162.2024.04.001. [63] XIA Yici, HE Yan, KANG Bing, et al. Research and application of MFCC-LSTM based on improved ZOA algorithm to optimize transformer voice-print diagnosis[C]. The 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Control Science (IC2ECS), Nanjing, China, 2024: 559–563. doi: 10.1109/IC2ECS64405.2024.10928641. [64] 侯文彪, 徐宁. 基于多特征提取分析的变压器声纹故障识别技术研究[J]. 江西电力, 2025, 49(1): 70–74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-348X.2025.01.016.HOU Wenbiao and XU Ning. Research on transformer acoustic fault identification technology based on multi-feature extraction and analysis[J]. Jiangxi Electric Power, 2025, 49(1): 70–74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-348X.2025.01.016. [65] 刘云鹏, 王博闻, 岳浩天, 等. 基于50Hz倍频倒谱系数与门控循环单元的变压器偏磁声纹识别[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(14): 4681–4694. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.191922.LIU Yunpeng, WANG Bowen, YUE Haotian, et al. Identification of transformer bias voiceprint based on 50Hz frequency multiplication cepstrum coefficients and gated recurrent unit[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(14): 4681–4694. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.191922. [66] ABULIZI J, CHEN Zhen, LIU Peng, et al. Research on voiceprint recognition of power transformer anomalies using gated recurrent unit[C]. 2021 Power System and Green Energy Conference (PSGEC), Shanghai, China, 2021: 743–747. doi: 10.1109/PSGEC51302.2021.9542338. [67] 齐子豪, 仝杰, 张中浩, 等. 基于多粒度知识特征和Transformer网络的电力变压器故障声纹辨识方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45(4): 1311–1322. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.231543.QI Zihao, TONG Jie, ZHANG Zhonghao, et al. A voiceprint classification method for power transformer fault identification based on multi-granularity knowledge features and transformer network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45(4): 1311–1322. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.231543. [68] 张寒, 熊云, 唐信, 等. 声纹信号-图形差分场增强和多头自注意力机制的变压器工作状态辨识方法[J]. 应用声学, 2024, 43(1): 119–130. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2024.01.015.ZHANG Han, XIONG Yun, TANG Xin, et al. Transformer working state identification method based on voiceprint signal-motif difference field enhancement and multi-head self-attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2024, 43(1): 119–130. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2024.01.015. [69] ZHANG Kai, LU Hongming, HAN Shuai, et al. A novel fault diagnosis method for power transformers based on voiceprint recognition considering multitype noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2025, 74: 3541311. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2025.3573012. [70] XUE Zichun, WANG Bo, MA Hengrui, et al. Research on transformer fault diagnosis and maintenance strategy generation based on TransQwen model[J]. Processes, 2025, 13(7): 1977. doi: 10.3390/pr13071977. [71] LU Hongming, ZHANG Kai, and HAN Shuai. A comparison of CNN-based transformer fault diagnosis methods based on voiceprint signal[C]. 2024 IEEE 13th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference (DDCLS), Kaifeng, China, 2024: 819–824. doi: 10.1109/ddcls61622.2024.10606641. [72] 辛全金, 李晓华, 杨义, 等. 基于冗余卷积编解码器的变压器噪声抑制[J]. 中国电力, 2023, 56(4): 112–118. doi: 10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.202203065.XIN Quanjin, LI Xiaohua, YANG Yi, et al. Research on transformer noise suppression based on redundant convolutional encoder decoder[J]. Electric Power, 2023, 56(4): 112–118. doi: 10.11930/j.issn.1004-9649.202203065. [73] 廖才波, 杨金鑫, 邱志斌, 等. 一种基于夏普利值及油中溶解气体分析的可解释变压器故障诊断方法[J]. 电网技术, 2024, 48(4): 1752–1761. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2023.0727.LIAO Caibo, YANG Jinxin, QIU Zhibin, et al. Interpretable transformer fault diagnosis based on SHAP value and dissolved gas analysis of transformer oil[J]. Power System Technology, 2024, 48(4): 1752–1762. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2023.0727. [74] TANG Pengfei, ZHANG Zhonghao, TONG Jie, et al. Predicting transformer temperature field based on physics-informed neural networks[J]. High Voltage, 2024, 9(4): 839–852. doi: 10.1049/hve2.12435. [75] 林春清, 周颖, 杨超, 等. 面向电力变压器的声纹智能诊断装置设计与应用[J]. 传感技术学报, 2021, 34(10): 1412–1420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2021.10.021.LIN Chunqing, ZHOU Ying, YANG Chao, et al. Design and application of intelligent voiceprint diagnosis device for power transformer[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2021, 34(10): 1412–1420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2021.10.021. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
