High-Efficiency Side-Channel Analysis: From Collaborative Denoising to Adaptive B-Spline Dimension Reduction
-
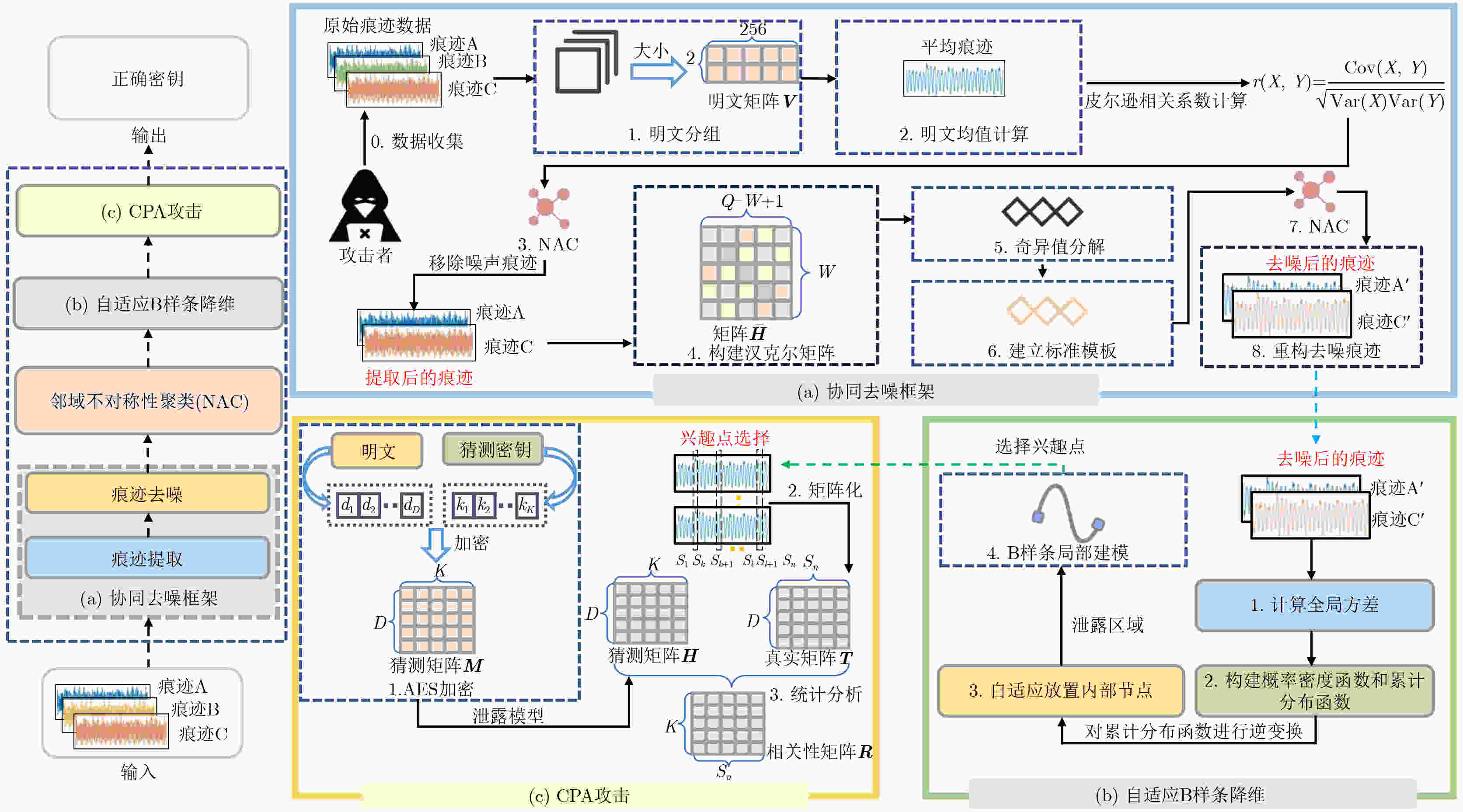
摘要: 侧信道分析(SCA)是一种强大的密码分析技术,但其攻击效率受到原始功耗轨迹信噪比低、冗余高维数据掩盖局部泄露以及关键参数设定依赖经验等挑战的严重制约。针对上述问题,该文提出自适应B样条降维与协同去噪的侧信道分析方法,以实现高效且鲁棒的侧信道攻击。该框架包含3个核心步骤。首先,构建协同去噪框架(CDF),通过整合基于皮尔逊相关系数的轨迹筛选机制和基于奇异值模板的去噪方法,有效提升了功耗轨迹的信噪比。其次,设计一种新颖的基于邻域不对称性聚类(NAC)的方法,用于自适应地确定CDF中的关键阈值,从而增强方法的鲁棒性。最后,首次将B样条技术引入功耗轨迹的降维处理,并提出基于自适应B样条降维(ABDR)的高效局部建模降维方法,在大幅度压缩数据量的同时,最大限度地保留了关键泄漏信息,显著降低后续侧信道分析的计算开销。实验结果表明,在数据集OSR2560上,信噪比提升了60%,密钥恢复所需的痕迹数量从
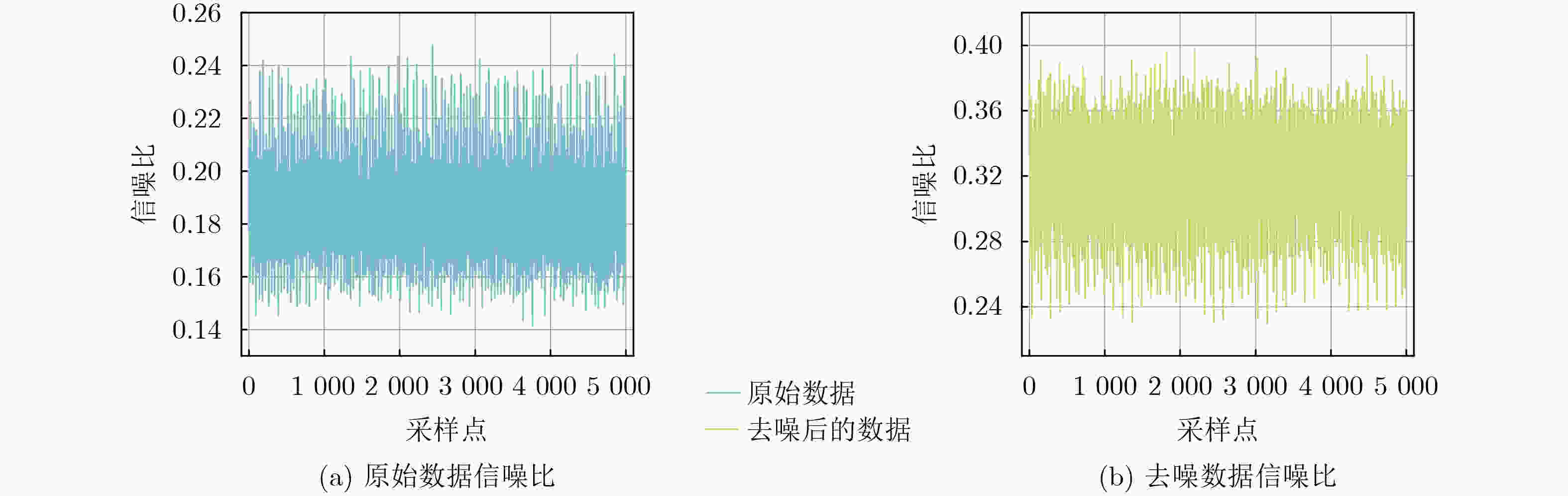
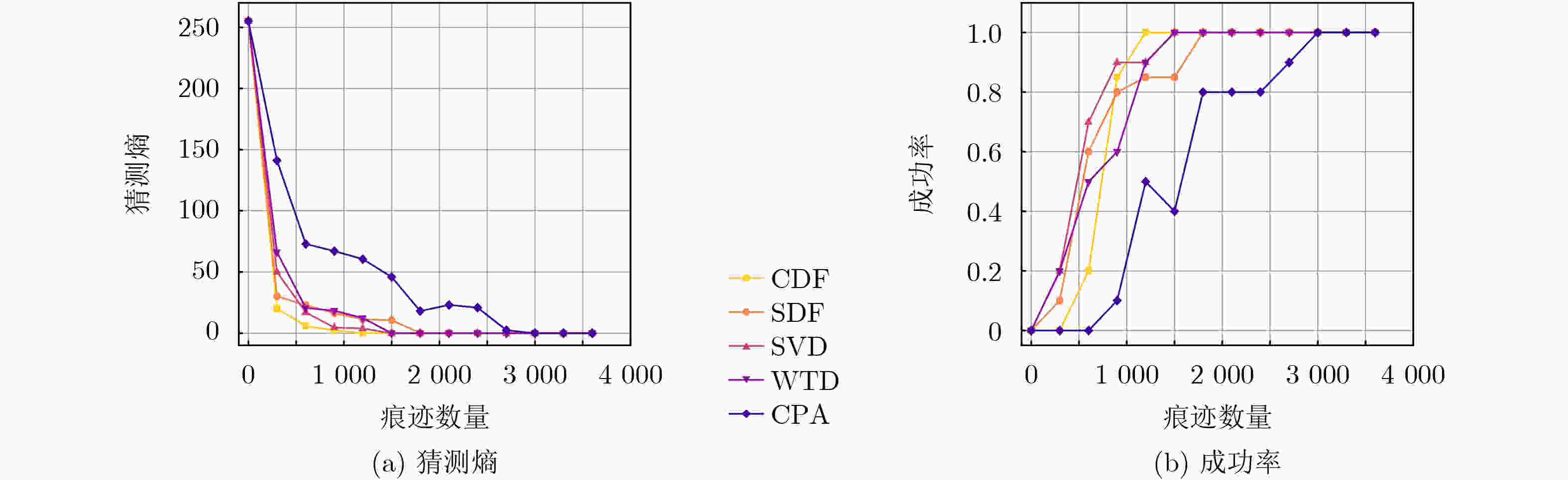
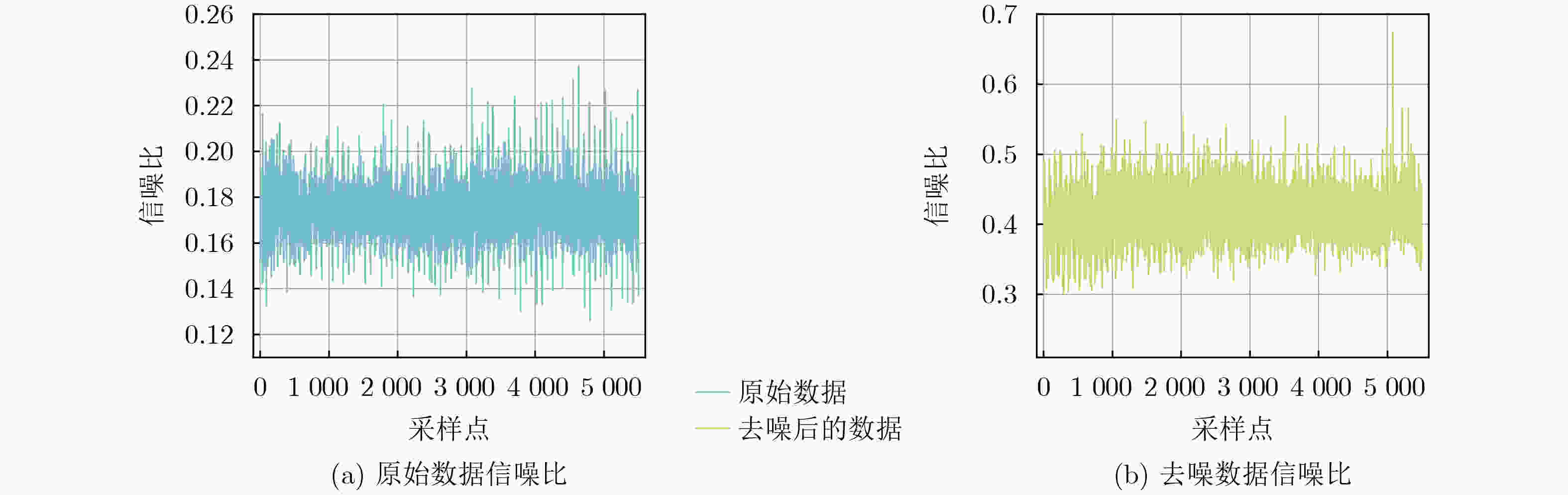
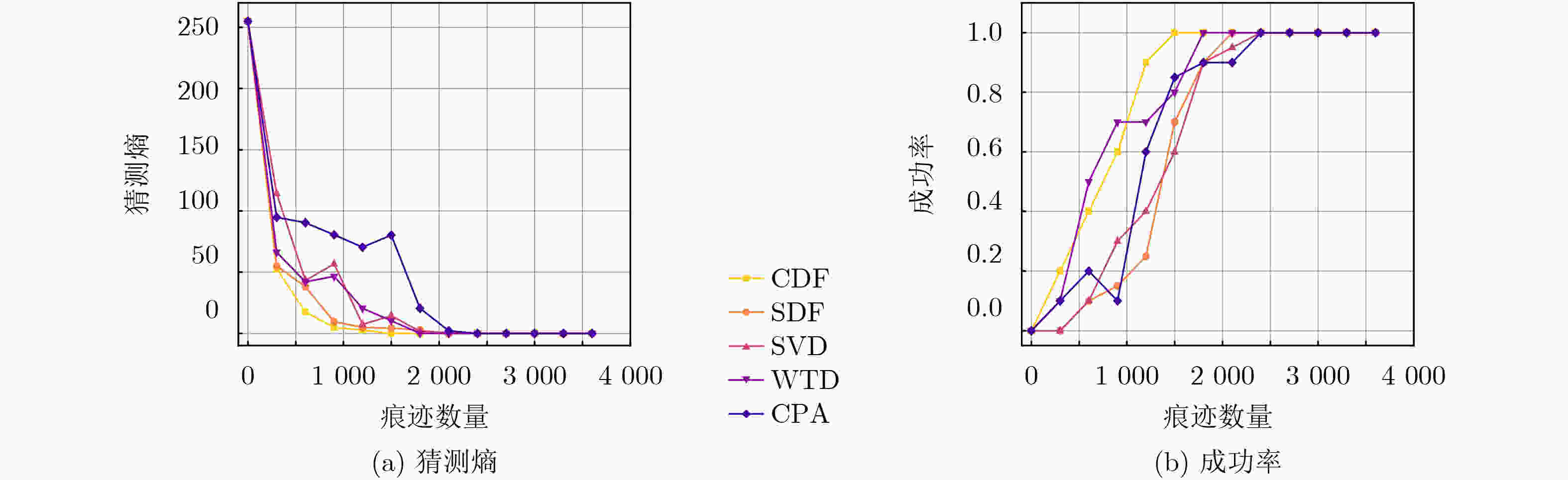
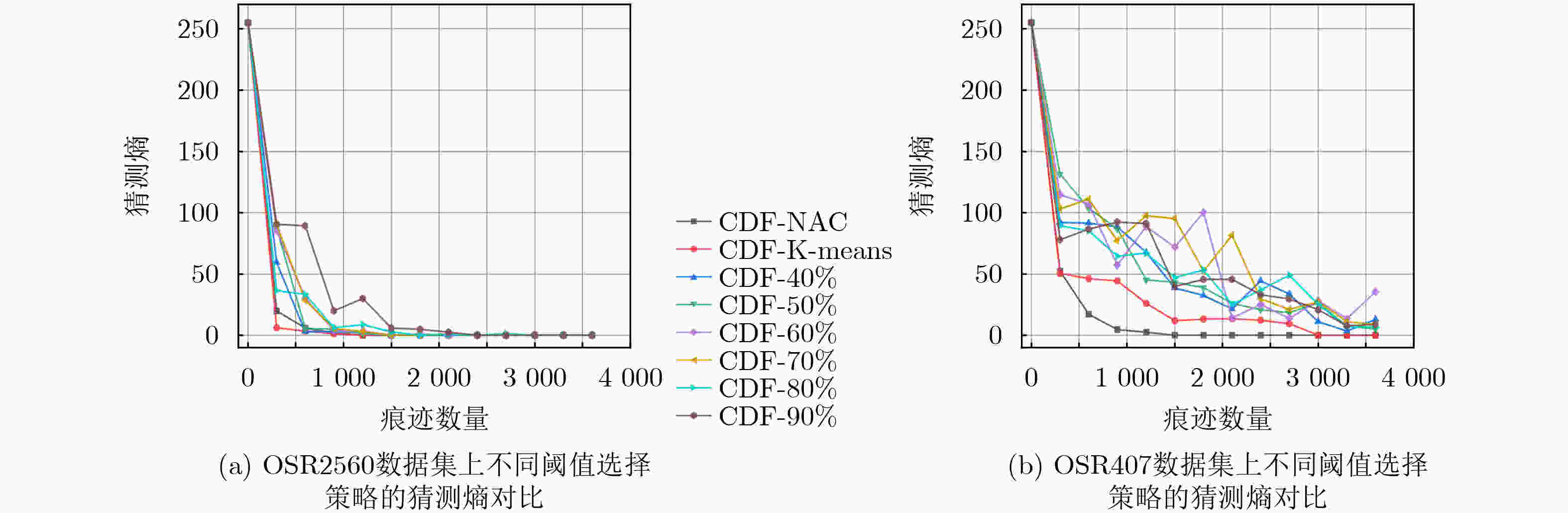
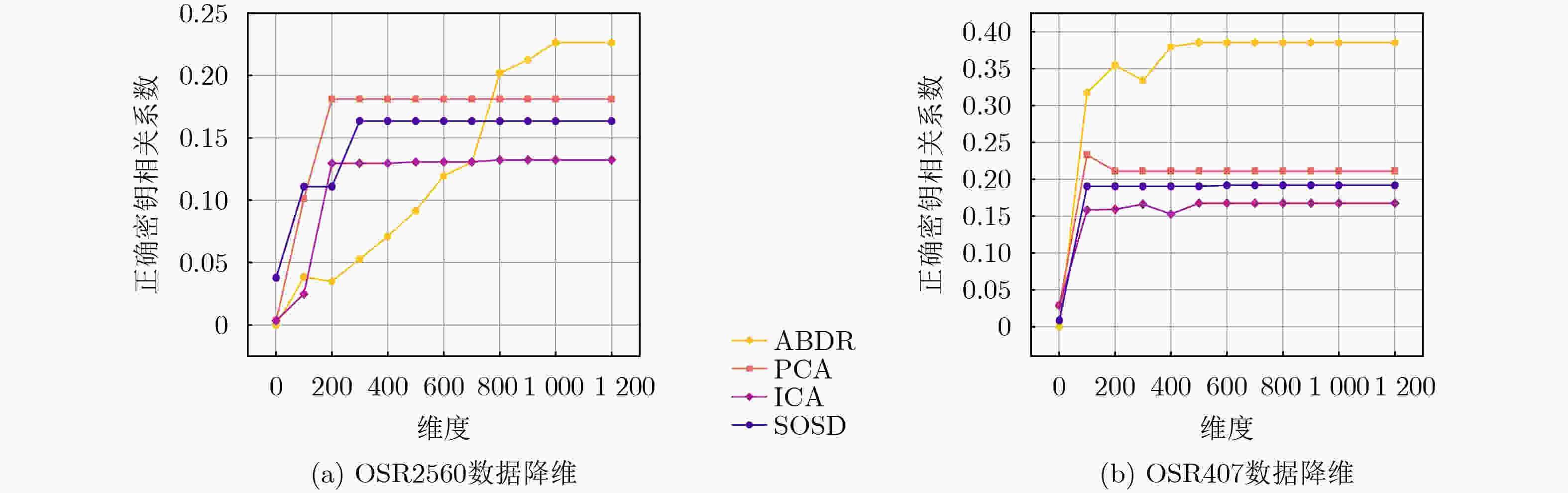
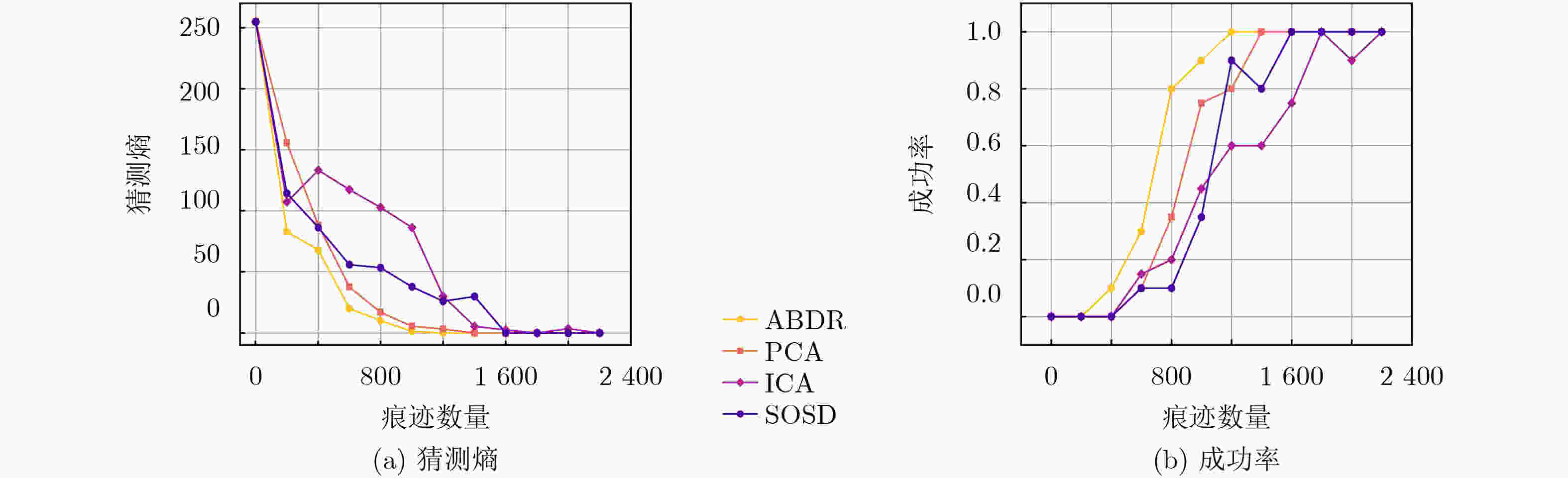
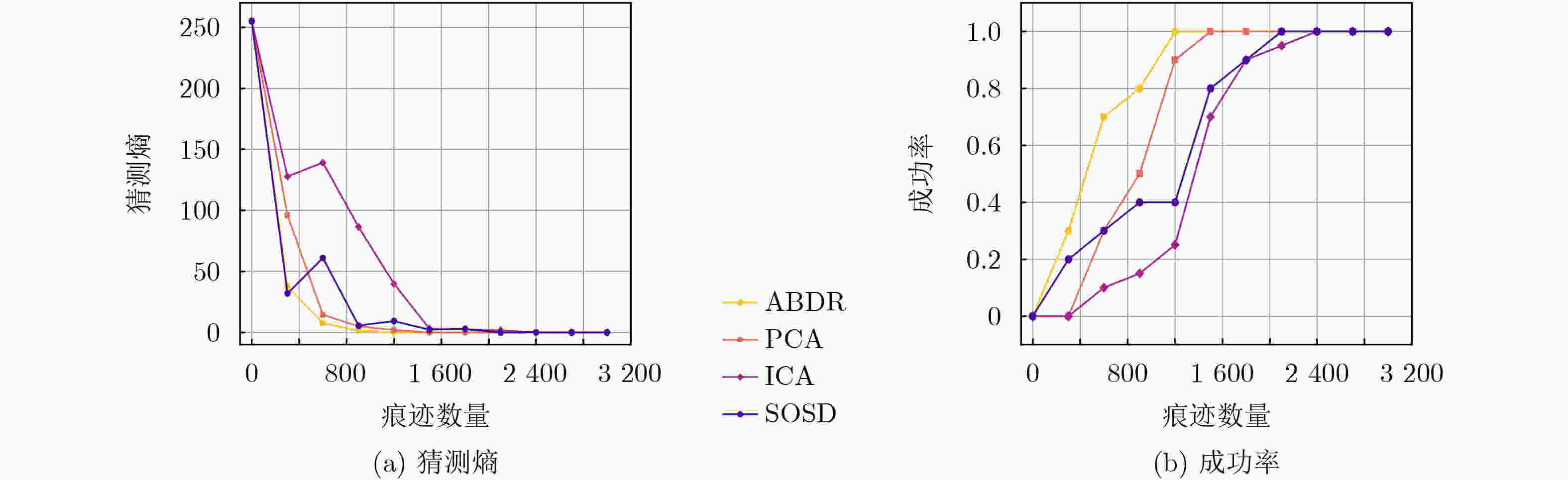
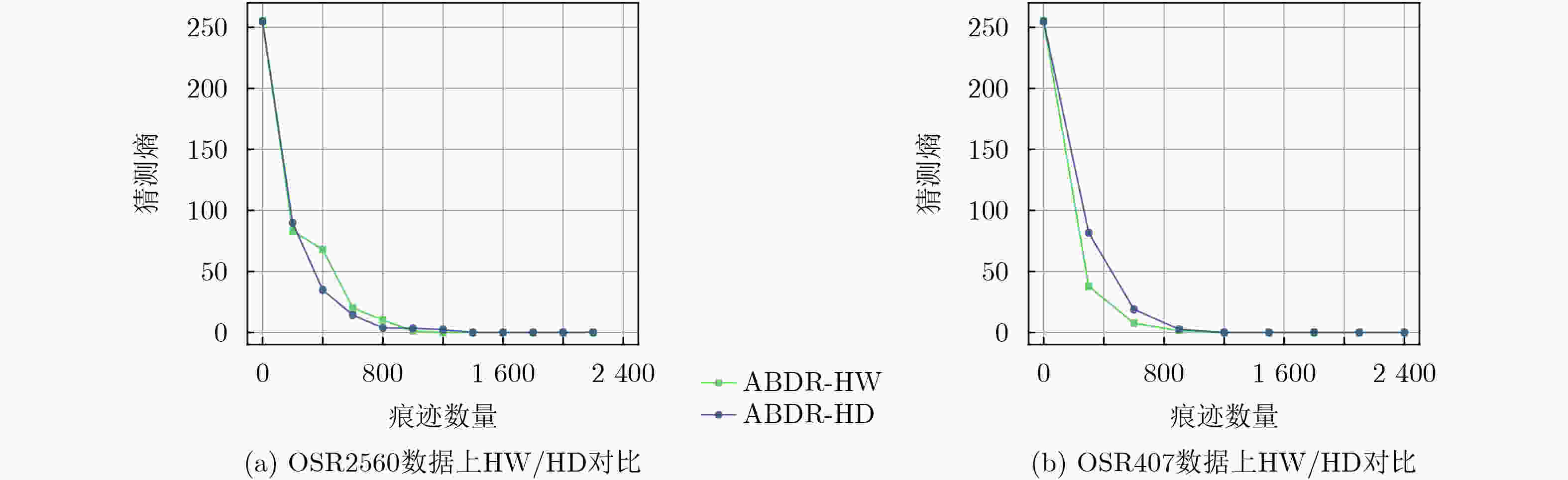
3 000 条减少至1 200 条。在数据集OSR407上,信噪比提升了150%,将痕迹数量从2 400 条减少至1 500 条,在显著降低数据维度的基础上,有效增强了正确密钥与错误猜测密钥的区分度,进而提高了攻击效率。Abstract:Objective The performance of side-channel attacks is often constrained by the low signal-to-noise ratio of raw power traces, the masking of local leakage by redundant high-dimensional data, and the reliance on empirically chosen preprocessing parameters. Existing studies typically optimize individual stages, such as denoising or dimensionality reduction, in isolation, lack a unified framework, and fail to balance signal-to-noise ratio enhancement with the preservation of local leakage features. A unified analysis framework is therefore proposed to integrate denoising, adaptive parameter selection, and dimensionality reduction while preserving local leakage characteristics. Through coordinated optimization of these components, both the efficiency and robustness of side-channel attacks are improved. Methods Based on the similarity of power traces corresponding to identical plaintexts and the local approximation properties of B-splines, a side-channel analysis method combining collaborative denoising and Adaptive B-Spline Dimension Reduction (ABDR) is presented. First, a Collaborative Denoising Framework (CDF) is constructed, in which high-quality traces are selected using a plaintext-mean template, and targeted denoising is performed via singular value decomposition guided by a singular-value template. Second, a Neighbourhood Asymmetry Clustering (NAC) method is applied to adaptively determine key thresholds within the CDF. Finally, an ABDR algorithm is proposed, which allocates knots non-uniformly according to the variance distribution of power traces, thereby enabling efficient data compression while preserving critical local leakage features. Results and Discussions Experiments conducted on two datasets based on 8-bit AVR (OSR2560) and 32-bit ARM Cortex-M4 (OSR407) architectures demonstrate that the CDF significantly enhances the signal-to-noise ratio, with improvements of 60% on OSR2560 ( Fig. 2 ) and 150% on OSR407 (Fig. 4 ). The number of power traces required for successful key recovery is reduced from 3 000/2 400 to 1 200/1 500 for the two datasets, respectively (Figs. 3 and5 ). Through adaptive threshold selection in the CDF, NAC achieves faster and more stable guessing-entropy convergence than fixed-threshold and K-means-based strategies, which enhances overall robustness (Fig. 6 ). The ABDR algorithm places knots densely in high-variance leakage regions and sparsely in low-variance regions. While maintaining a high attack success rate, it reduces the data dimensionality from 5 000 and 5 500 to 1 000 and 500, respectively, corresponding to a compression rate of approximately 80%. At the optimal dimensionality (Fig. 7 ), the correlation coefficients of the correct key reach 0.186 0 on OSR2560 and 0.360 5 on OSR407, both exceeding those obtained using other dimensionality reduction methods. These results indicate superior local information retention and attack efficiency (Tables 3 and4 ).Conclusions The results confirm that the proposed CDF substantially improves the signal-to-noise ratio of power traces, while NAC enables adaptive parameter selection and enhances robustness. Through accurate local modeling, ABDR effectively alleviates the trade-off between high-dimensional data reduction and the preservation of critical leakage information. Comprehensive experimental validation shows that the integrated framework addresses key challenges in side-channel analysis, including low signal-to-noise ratio, redundancy-induced information masking, and dependence on empirical parameters, and provides a practical and scalable solution for real-world attack scenarios. -
1 协同去噪框架
输入:原始功耗轨迹$ \boldsymbol{L}=\left\{{l}_{i}\right\}_{i=\text{1}}^{n} $,明文$ \boldsymbol{P}=\left\{{p}_{i}\right\}_{i=1}^{n} $。 输出:去噪后的功耗轨迹$ {{\boldsymbol{L}}^{\prime\prime}} $,对应明文$ {{\boldsymbol{P}}^{\prime\prime}} $。 (1) 遍历轨迹获取$ {M}_{\text{group}}\left[p\right] $, $ {C}_{\text{count}} $ (2) $ {M}^{p}\left(\tau \right)={M}_{\text{group}}\left[p\right]/{C}_{\text{count}} $//计算明文均值模板 (3) 循环$ i $从$ 1\sim n $执行 (4) 由式(3)计算相关系数 (5) 结束循环 (6) NAC聚类筛选 (7)由 $ \boldsymbol{u}_{r}^{p}\leftarrow {\boldsymbol{U}}^{p} $构建奇异值向量模板 (8) 循环$ r $从$ 1\sim W $执行 (9) 由式(6)计算相关系数 (10)结束循环 (11)NAC聚类筛选 2 基于邻域不对称性聚类
输入:皮尔逊相关系数$ \rho \left({\boldsymbol{l}}_{i},{\boldsymbol{M}}^{{{P}_{i}}}\right) $, $ \rho \left({\boldsymbol{u}}_{r},\boldsymbol{u}_{r}^{p}\right) $,不对称性阈
值$ {T}_{A} $,Z值百分数$ {Z}_{\text{h}},{Z}_{\text{l}} $。输出:聚类后的系数$ {\rho }^{\prime}\left({\boldsymbol{l}}_{i},{\boldsymbol{M}}^{{{P}_{i}}}\right) $和$ {\rho }^{\prime}\left({\boldsymbol{u}}_{r},\boldsymbol{u}_{r}^{p}\right) $。 (1) 循环$ i $从$ 1\sim N $执行 (2)由式(7), (8)计算不对称性分数 (3) 结束循环 (4) 循环$ i $从$ 1\sim N $执行 (5) $ A\left({Z}_{i}\right) < {T}_{A} $ (6) 根据$ Z_i > Z_{\text{h}},\ Z_i < Z_{\text{l}} $划分高/低值核心区 (7) 分配边界点 (8) 结束循环 3 自适应B样条降维
输入:去噪轨迹T, B样条次数$ {k}_{d} $,B样条内部节点数量$ m $。 输出:提取的B样条系数集合 (1) 循环$ j $从$ 1\sim N_{\mathrm{s}} $执行 (2) 由式(12)计算方差剖面 (3) 结束循环 (4) 由式(13)、式(14)计算累计分布函数 (5) 自适应放置节点 (6) 最小二乘法获取B样条系数 表 1 不同去噪方法在OSR2560数据集上的相关系数对比(痕迹数量:
1200 条,正确密钥0x0a)表 2 不同去噪方法在OSR407数据集上的相关系数对比(痕迹数量:
1500 条,正确密钥0x0a)表 3 不同降维方法在OSR2560数据集上的相关系数对比(维度:
1000 ,痕迹数量:1200 条)方法 正确密钥相关系数 错误密钥最高相关系数 相关系数差值 猜测密钥 攻击结果 CDF+PCA 0.0509 0.1225 0.0716 0x39 失败 CDF+ICA 0.1420 0.1539 0.0119 0x16 失败 CDF+SOSD 0.0913 0.1226 0.0313 0xd3 失败 CDF+ABDR 0.1860 0.1854 0.0006 0x0a 成功 表 4 不同降维方法在OSR407数据集上的相关系数对比(维度:500,痕迹数量:
1200 条)方法 正确密钥相关系数 错误密钥最高相关系数 相关系数差值 猜测密钥 攻击结果 CDF+PCA 0.0891 0.1759 0.0868 0x8d 失败 CDF+ICA 0.1064 0.1773 0.0709 0xfe 失败 CDF+SOSD 0.0652 0.1539 0.0887 0xc1 失败 CDF+ABDR 0.3605 0.1636 0.1969 0x0a 成功 -
[1] ARPAIA P, CAPUTO F, CIOFFI A, et al. Uncertainty analysis in cryptographic key recovery for machine learning-based power measurements attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 1006108. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3284933. [2] PANTOJA J J, BUCHELI V A, and DONALDSON R. Electromagnetic side-channel attack risk assessment on a practical quantum-key-distribution receiver based on multi-class classification[J]. EPJ Quantum Technology, 2024, 11(1): 78. doi: 10.1140/epjqt/s40507-024-00290-6. [3] MAJI S, BANERJEE U, and CHANDRAKASAN A P. Leaky nets: Recovering embedded neural network models and inputs through simple power and timing side-channels—Attacks and defenses[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(15): 12079–12092. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3061314. [4] RAEKER-JORDAN N, CHUNG J, KONG Zhenyu, et al. Ensuring additive manufacturing quality and cyber–physical security via side-channel measurements and transmissions[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2024, 73: 275–286. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2024.02.005. [5] LIU A, WANG An, SUN Shaofei, et al. CL-SCA: A contrastive learning approach for profiled side-channel analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2025, 20: 5109–5122. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2025.3570123. [6] KOCHER P, JAFFE J and JUN B. Differential power analysis[C]. The 19th Annual International Cryptology Conference (CRYPTO 1999), Santa Barbara, USA, 1999: 388–397. doi: 10.1007/3-540-48405-1_25. [7] WU Lichao, PERIN G, and PICEK S. Weakly profiling side-channel analysis[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2024, 2024(3): 707–730. doi: 10.46586/tches.v2024.i3.707-730. [8] YOU Chunheng, CHIANG C H, CHAO P C P, et al. New adaptive template attacks against Montgomery-ladder-based ECCs in IoT devices[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(12): 22716–22725. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3384076. [9] WU Lichao, WEISSBART L, KRČEK M, et al. Label correlation in deep learning-based side-channel analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18: 3849–3861. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2023.3287728. [10] GAO Pengfei, SONG Fu, and CHEN Taolue. Compositional verification of first-order masking countermeasures against power side-channel attacks[J]. ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology, 2024, 33(3): 79. doi: 10.1145/3635707. [11] DUCHARME G R and MAURINE P. Estimating the Signal-to-Noise ratio under repeated sampling of the same centered signal: Applications to side-channel attacks on a cryptoprocessor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2018, 64(9): 6333–6339. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2018.2851217. [12] MOZIPO A T and ACKEN J M. Analysis of countermeasures against remote and local power side channel attacks using correlation power analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2024, 21(6): 5128–5142. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2024.3370711. [13] OU Changhai, LAM S K, SUN Degang, et al. SNR-centric power trace extractors for side-channel attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2021, 40(4): 620–632. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2020.3003849. [14] DEL POZO S M and STANDAERT F X. Blind source separation from single measurements using singular spectrum analysis[C]. The 17th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES 2015), Saint-Malo, France, 2015: 42–59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-48324-4_3. [15] ZHANG Fan, DONG Xiaofei, YANG Bolin, et al. A systematic evaluation of wavelet-based attack framework on random delay countermeasures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 1407–1422. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2941774. [16] WANG Yuanzhen, ZHANG Hongxin, FANG Xing, et al. Hybrid threshold denoising framework using singular value decomposition for side-channel analysis preprocessing[J]. Entropy, 2023, 25(8): 1133. doi: 10.3390/e25081133. [17] LIU Songran and YI Wang. Task parameters analysis in schedule-based timing side-channel attack[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 157103–157115. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3019323. [18] PENG Dehua, GUI Zhipeng, WANG Dehe, et al. Clustering by measuring local direction centrality for data with heterogeneous density and weak connectivity[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 5455. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33136-9. [19] PAGUADA S, BATINA L, and ARMENDARIZ I. Toward practical autoencoder-based side-channel analysis evaluations[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 196: 108230. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108230. [20] KONG Yinan and SAEEDI E. The investigation of neural networks performance in side-channel attacks[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2019, 52(1): 607–623. doi: 10.1007/s10462-018-9640-4. [21] MAGHREBI H and PROUFF E. On the use of independent component analysis to denoise side-channel measurements[C]. The 9th International Workshop on Constructive Side-Channel Analysis and Secure Design (COSADE 2018), Singapore, Singapore, 2018: 61–81. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-89641-0_4. [22] RIOJA U, BATINA L, FLORES J L, et al. Auto-tune POIs: Estimation of distribution algorithms for efficient side-channel analysis[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 198: 108405. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108405. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
