Survey on Intelligent Methods for Large-scale Remote Sensing Satellite Scheduling
-
摘要: 针对遥感卫星任务调度大规模、复杂化的发展趋势和星群协同、即时服务的常态要求,依据自顶向下的原则,该文相继综述了其任务调度框架、模型与算法的发展现状。首先,基于集中式调度框架、分布式调度框架和集中-分布式调度框架,阐明了各调度框架的典型流程和适用场景。其次, 按照发源时间与建模特点的不同,从经典运筹学模型、约束满足优化模型和基于神经网络的决策模型3个角度出发, 探讨了不同卫星任务调度模型的描述方式和适用性。在此基础上,介绍了精确求解、元启发式和机器学习类等3类卫星任务调度主流算法, 揭示了各算法运行原理与优劣势。最后, 指出了规模化、订单化改造调度框架,发展混合式调度模型以及机器学习、大模型交融背景下算法工程化等未来研究新方向。Abstract:
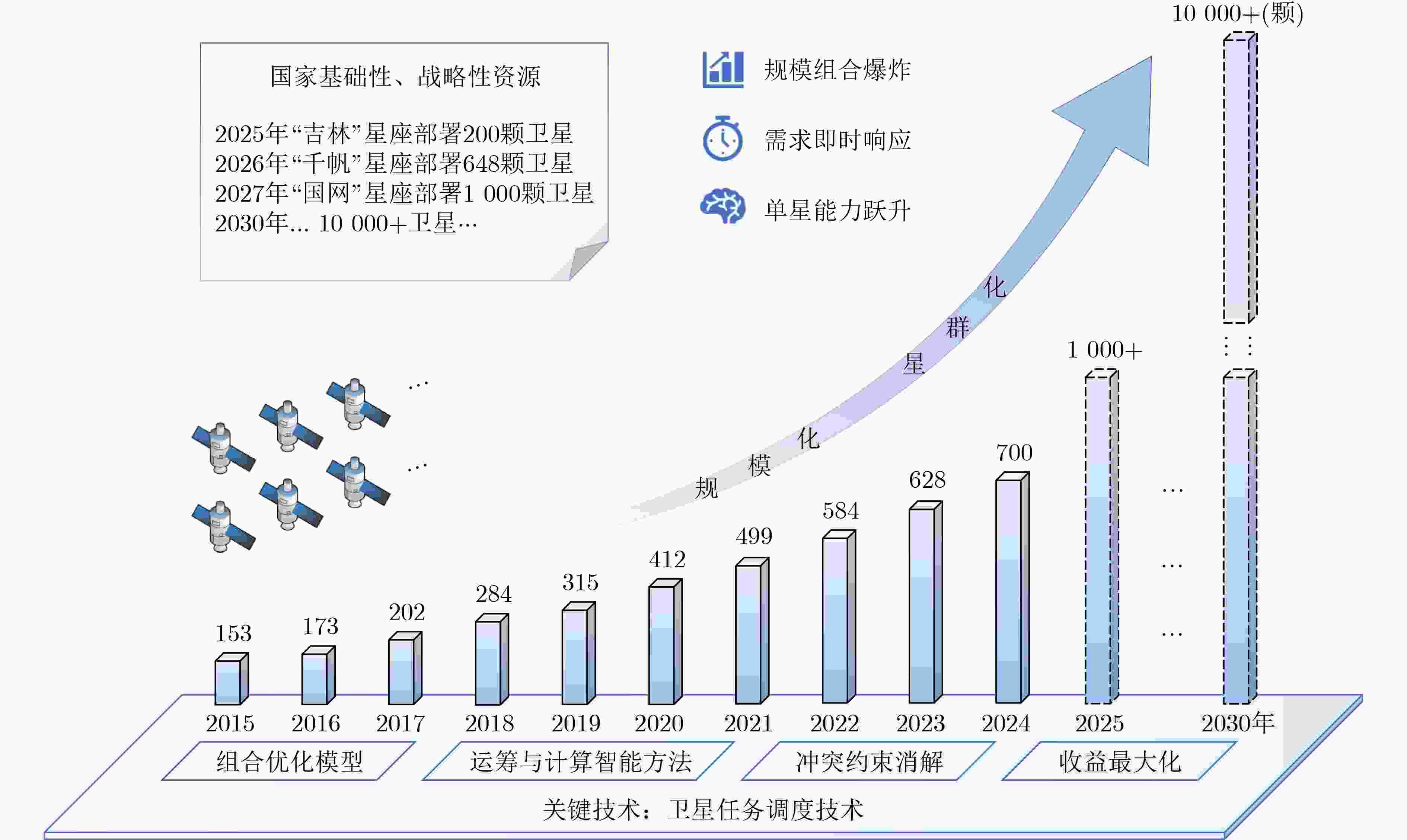
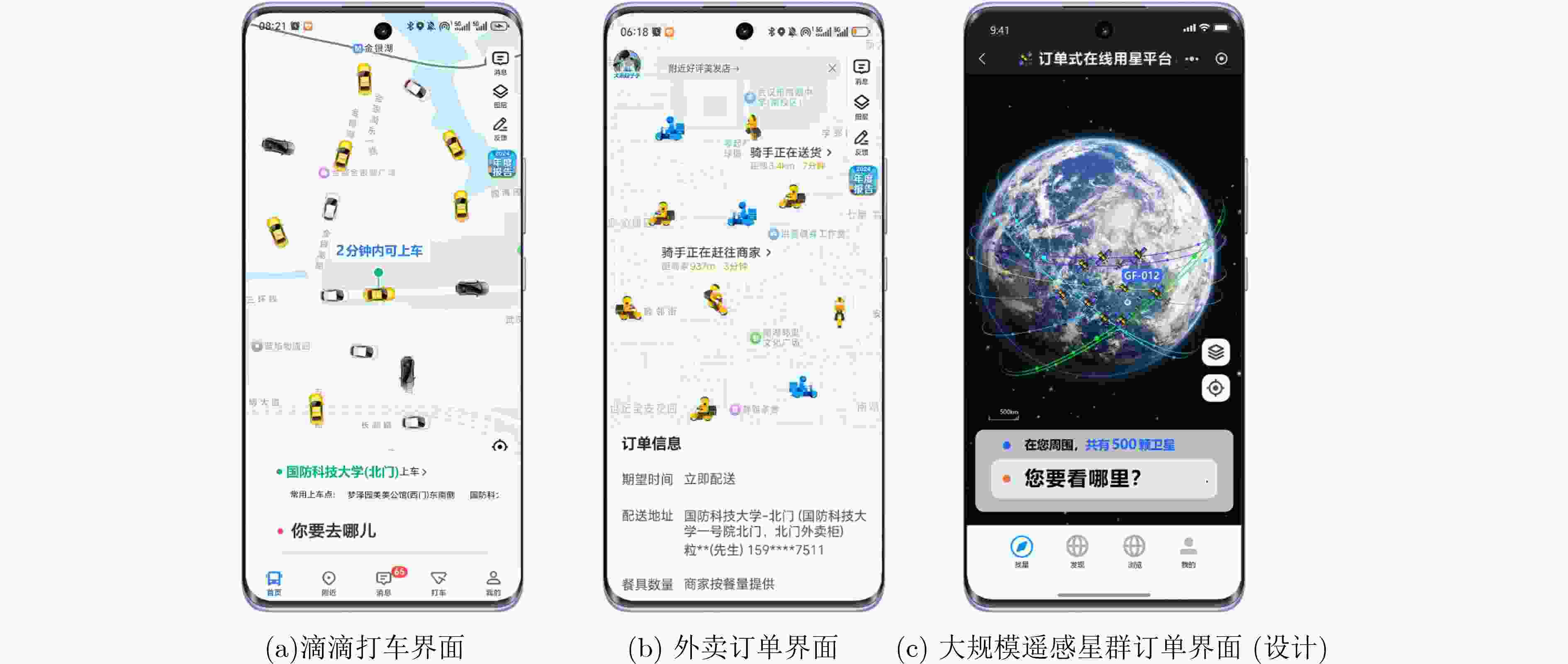
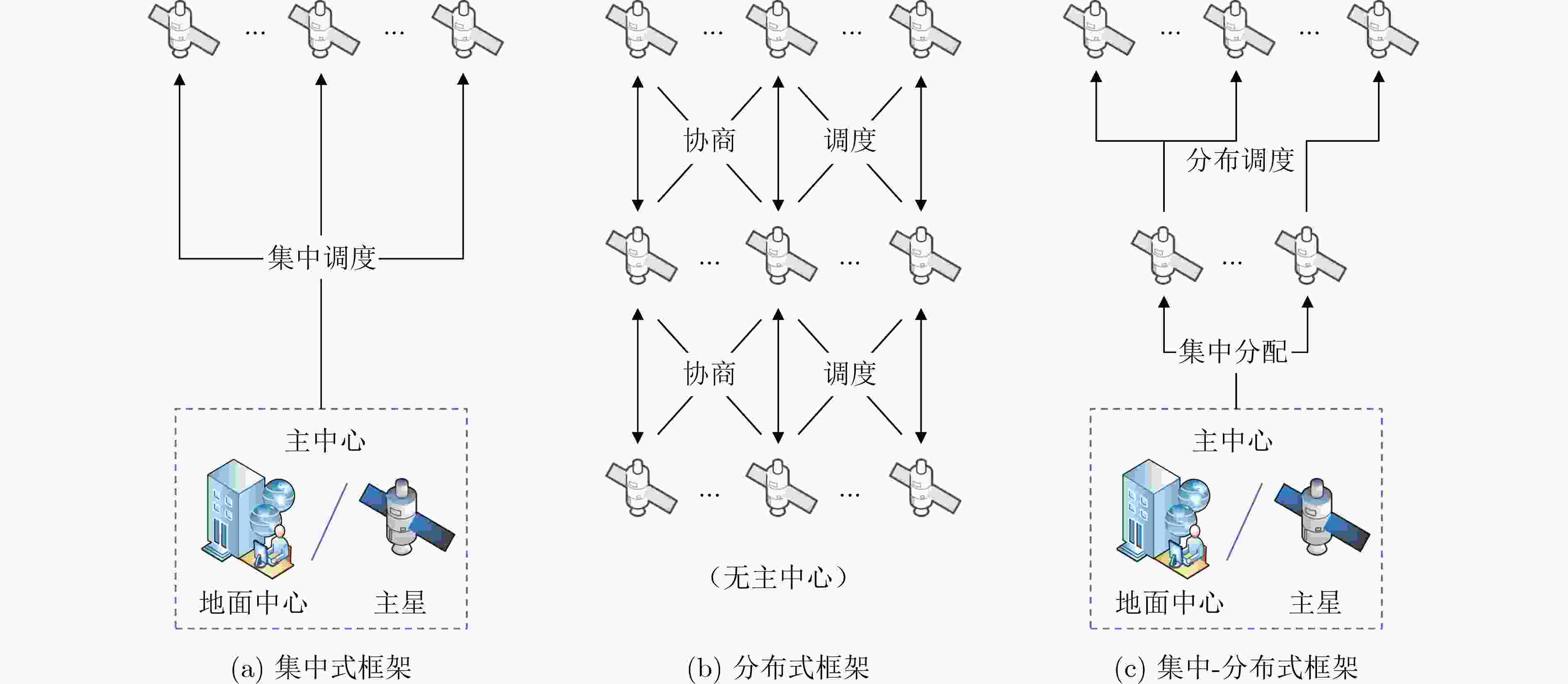
Significance Satellite task scheduling is an operational optimization technique. It constructs combinatorial optimization models for space-ground resources and applies operations research and computational intelligence methods to generate task plans, resolve task conflicts and constraints, and maximize satellite utilization efficiency. With the development of large-scale constellations, satellite task scheduling faces several new challenges. (1) The rapid increase in the number of satellites and tasks leads to a combinatorial explosion of the solution space. (2) Satellite applications are shifting from planned operations to on-demand services, which require response times to be reduced from hours to minutes or even seconds. (3) Advances in satellite payload capabilities enable onboard autonomous decision making and in-orbit collaboration, which support interactive and swarm-intelligence-based management of large-scale remote sensing constellations. Progress To address large-scale complexity, constellation collaboration, and on-demand service requirements in satellite task scheduling, recent research developments are reviewed from the perspectives of task scheduling frameworks, task scheduling models, and task scheduling algorithms, following a top-down approach. First, centralized scheduling frameworks, distributed scheduling frameworks, and hybrid centralized-distributed scheduling frameworks are described, and their control paradigms and application scenarios are clarified. Second, task scheduling models are examined according to their theoretical foundations and applicable solution methods, including classical operations research models, constraint satisfaction optimization models, and artificial neural network-based decision-making models. Their modeling approaches and application scopes are discussed in detail. Subsequently, three major classes of task scheduling algorithms are summarized, including exact algorithms, metaheuristic algorithms, and machine learning-based algorithms. Their decision-making mechanisms, advantages, and limitations are analyzed. Finally, future research directions are identified, including the reconstruction of large-scale and order-oriented task scheduling frameworks, the development of novel task scheduling models, and the innovative integration of different task scheduling algorithms. Conclusions and prospects At the framework level, task scheduling frameworks for constellations consisting of more than one thousand satellites have not yet been reported. Existing task scheduling frameworks mainly address problems with fewer than 100 satellites, which remains insufficient for large-scale remote sensing constellations with thousands or even tens of thousands of satellites. The hybrid centralized-distributed task scheduling framework combines the advantages of centralized scheduling frameworks and distributed scheduling frameworks and is consistent with the hierarchical construction and management characteristics of satellite constellations. It can further adapt to satellite scale expansion and order-based process mechanisms. At the model level, constraint satisfaction optimization models focus on detailed representations of optimization attributes and elements and are suitable for small-scale and medium-scale satellite task scheduling problems. In contrast, artificial neural network-based decision-making models emphasize classification and decision-making characteristics and support online and on-demand scheduling, which makes them suitable for large-scale satellite task scheduling scenarios. These two types of task scheduling models can therefore be coordinated to characterize different stages of large-scale constellation task scheduling. At the algorithm level, the integration of metaheuristic algorithms and machine learning-based algorithms has become an important technical approach for solving satellite task scheduling problems. This integrated approach supports hybrid centralized-distributed task scheduling frameworks and complements both constraint satisfaction optimization models and artificial neural network-based decision-making models. -

表 4 部分参考文献中所解决的卫星任务调度问题规模一览
-
[1] HU Fengming, XU Feng, WANG R, et al. Conceptual study and performance analysis of tandem multi-antenna spaceborne SAR interferometry[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0137. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0137. [2] Union of Concerned Scientists. UCS satellite database[DB/OL]. https://www.ucsusa.org/resources/satellite-database, 2025. [3] 李宗凌, 龙腾, 赵保军, 等. 巨型星座信息系统核心功能及发展研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2024, 45(11): 1685–1700. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.11.001.LI Zongling, LONG Teng, ZHAO Baojun, et al. Research on the key functions and development of mega-constellation information System[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2024, 45(11): 1685–1700. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.11.001. [4] 杜永浩, 黎磊, 徐世龙, 等. 基于智能优化算法引擎的可演进星群智能任务规划[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(6): 1645–1657. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240974.DU Yonghao, LI Lei, XU Shilong, et al. Evolutionary optimization for satellite constellation task scheduling based on intelligent optimization engine[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(6): 1645–1657. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240974. [5] 刘立祥, 孙楚雄. 分层智能体架构下的巨星座自适应管控研究[J]. 航天技术与工程学报, 2025, 2(1): 93–101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-4701.2025.01.012.LIU Lixiang and SUN Chuxiong. A hierarchical agent architecture for adaptive governance and control of mega-constellations[J]. Journal of Space Technology and Engineering, 2025, 2(1): 93–101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-4701.2025.01.012. [6] 贺仁杰, 高鹏, 白保存, 等. 成像卫星任务规划模型、算法及其应用[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2011, 31(3): 411–422. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2011)3-411.HE Renjie, GAO Peng, BAI Baocun, et al. Models, algorithms and applications to the mission planning system of imaging satellites[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2011, 31(3): 411–422. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2011)3-411. [7] VALICKA C G, GARCIA D, STAID A, et al. Mixed-integer programming models for optimal constellation scheduling given cloud cover uncertainty[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 275(2): 431–445. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2018.11.043. [8] TRUSZKOWSKI W, HALLOCK H, ROUFF C, et al. Autonomous and Autonomic Systems: With Applications to NASA Intelligent Spacecraft Operations and Exploration Systems[M]. London: Springer, 2010. doi: 10.1007/b105417. [9] WOLFE W J and SORENSEN S E. Three scheduling algorithms applied to the earth observing systems domain[J]. Management Science, 2000, 46(1): 148–166. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.46.1.148.15134. [10] WANG Haijiao, YANG Zhen, ZHOU Wugen, et al. Online scheduling of image satellites based on neural networks and deep reinforcement learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32(4): 1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2018.12.018. [11] CORDEAU J F, LAPORTE G, and MERCIER A. A unified tabu search heuristic for vehicle routing problems with time windows[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 2001, 52(8): 928–936. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601163. [12] CORDEAU J F and LAPORTE G. Maximizing the value of an earth observation satellite orbit[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 2005, 56(8): 962–968. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.jors.2601926. [13] 赵琳, 王硕, 郝勇, 等. 基于能量最优的敏捷遥感卫星在轨任务规划[J]. 航空学报, 2017, 38(6): 320654. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2016.0298.ZHAO Lin, WANG Shuo, HAO Yong, et al. Energy-optimal in orbit mission planning for agile remote sensing satellites[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(6): 320654. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2016.0298. [14] XIAO Yiyong, ZHANG Siyue, YANG Pei, et al. A two-stage flow-shop scheme for the multi-satellite observation and data-downlink scheduling problem considering weather uncertainties[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2019, 188: 263–275. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2019.03.016. [15] LIANG Jun, ZHU Yuehe, LUO Yazhong, et al. A precedence-rule-based heuristic for satellite onboard activity planning[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 178: 757–772. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.10.020. [16] 陈祥国, 武小悦. 基于解构造图的卫星数传调度ACO算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2010, 32(3): 592–597.CHEN Xiangguo and WU Xiaoyue. ACO algorithm of satellite data transmission scheduling based on solution construction graph[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(3): 592–597. [17] LIU Xiaolu, LAPORTE G, CHEN Yingwu, et al. An adaptive large neighborhood search metaheuristic for agile satellite scheduling with time-dependent transition time[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2017, 86: 41–53. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2017.04.006. [18] LIU Zhehan, LIU Jinming, LIU Xiaolu, et al. Knowledge-assisted adaptive large neighbourhood search algorithm for the satellite-ground link scheduling problem[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2024, 192: 110219. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2024.110219. [19] 李海, 李勇军, 刘元皓, 等. 基于ESWO的敏捷对地观测卫星任务调度算法[J]. 航空学报, 2024, 45(10): 329370. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.29370.LI Hai, LI Yongjun, LIU Yuanhao, et al. ESWO-based task-scheduling algorithm for agile earth observation satellites[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45(10): 329370. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.29370. [20] 杜永浩, 邢立宁, 陈盈果, 等. 卫星任务调度统一化建模与多策略协同求解方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(9): 1847–1856. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2019.0111.DU Yonghao, XING Lining, CHEN Yingguo, et al. Unified modeling and multi-strategy collaborative optimization for satellite task scheduling[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(9): 1847–1856. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2019.0111. [21] LI Lei, DU Yonghao, YAO Feng, et al. Learning memetic algorithm based on variable population and neighborhood for multi-complex target scheduling of large-scale imaging satellites[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2025, 92: 101789. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2024.101789. [22] 齐伟华, 刘晓路, 姚锋, 等. 面向智能敏捷卫星的自主任务规划与调度[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2024, 30(9): 3142–3153. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2022.0112.QI Weihua, LIU Xiaolu, YAO Feng, et al. Autonomous task planning and scheduling method for intelligent agile satellite[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2024, 30(9): 3142–3153. doi: 10.13196/j.cims.2022.0112. [23] SONG Bingyu, CHEN Yingwu, YANG Qing, et al. On-board decentralized observation planning for LEO satellite constellations[J]. Algorithms, 2023, 16(2): 114. doi: 10.3390/a16020114. [24] LIN Zhiyuan, NI Zuyao, KUANG Linling, et al. Satellite-terrestrial coordinated multi-satellite beam hopping scheduling based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(8): 10091–10103. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3368689. [25] YANG Weiyi, LIU Xiaolu, HE Lei, et al. Game-theoretic distributed approach for heterogeneous-cost task allocation with budget constraints[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 255: 124721. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124721. [26] 靳鹏, 李康. 基于改进合同网协议的分布式卫星资源调度[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(10): 3164–3173. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.10.20.JIN Peng and LI Kang. Distributed satellite resource scheduling based on improved contract network protocol[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3164–3173. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.10.20. [27] 杨唯一, 何磊, 刘晓路, 等. 面向批量应急任务的分布式卫星在线协同方法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2025, 45(1): 310–325. doi: 10.12011/SETP2023-0876.YANG Weiyi, HE Lei, LIU Xiaolu, et al. A distributed satellite online collaboration method for batch emergency tasks[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2025, 45(1): 310–325. doi: 10.12011/SETP2023-0876. [28] DU Yonghao, WANG Tao, XIN Bin, et al. A data-driven parallel scheduling approach for multiple agile earth observation satellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2020, 24(4): 679–693. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2934148. [29] WU Jian, YAO Feng, SONG Yanjie, et al. Frequent pattern-based parallel search approach for time-dependent agile earth observation satellite scheduling[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 636: 118924. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.04.003. [30] CHEN Jiawei, WANG Feiran, CHEN Yingguo, et al. A generalized bilevel optimization model for large-scale task scheduling in multiple agile earth observation satellites[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2025, 309: 112809. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2024.112809. [31] YANG Weiyi, HE Lei, LIU Xiaolu, et al. Onboard coordination and scheduling of multiple autonomous satellites in an uncertain environment[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 68(11): 4505–4524. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.09.003. [32] YANG Wenyuan, TANG Jun, HE Renjie, et al. A medium-term conflict detection and resolution method for open low-altitude city airspace based on temporally and spatially integrated strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2020, 28(5): 1817–1830. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2925579. [33] WEN Jun, LIU Xiaolu, and HE Lei. Real-time online rescheduling for multiple agile satellites with emergent tasks[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32(6): 1407–1420. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000120. [34] 杜永浩, 邢立宁, 姚锋, 等. 航天器任务调度模型、算法与通用求解技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(12): 2715–2741. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190656.DU Yonghao, XING Lining, YAO Feng, et al. Survey on models, algorithms and general techniques for spacecraft mission scheduling[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(12): 2715–2741. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190656. [35] WU Jian, CHEN Yuning, HE Yongming, et al. Survey on autonomous task scheduling technology for Earth observation satellites[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 33(6): 1176–1189. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2022.000141. [36] HE Lei, LIU Xiaolu, LAPORTE G, et al. An improved adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm for multiple agile satellites scheduling[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2018, 100: 12–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2018.06.020. [37] DU Yonghao, XING Lining, and CHEN Yingguo. Satellite scheduling engine: The intelligent solver for future multi-satellite management[J]. Frontiers of Engineering Management, 2022, 9(4): 683–688. doi: 10.1007/s42524-022-0222-4. [38] YAO Feng, DU Yonghao, LI Lei, et al. General modeling and optimization technique for real-world earth observation satellite scheduling[J]. Frontiers of Engineering Management, 2023, 10(4): 695–709. doi: 10.1007/s42524-023-0263-3. [39] HE Yongming, XING Lining, CHEN Yingwu, et al. A generic Markov decision process model and reinforcement learning method for scheduling agile earth observation satellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(3): 1463–1474. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3020732. [40] 吴健, 姚锋, 杜永浩, 等. 基于数据驱动的自适应并行搜索算法求解多星协同调度问题[J]. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(12): 4064–4072. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2023.0946.WU Jian, YAO Feng, DU Yonghao, et al. A data-driven adaptive parallel search algorithm for multiple agile satellites cooperative scheduling problem[J]. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(12): 4064–4072. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2023.0946. [41] WEI Luona, CHEN Yuning, CHEN Ming, et al. Deep reinforcement learning and parameter transfer based approach for the multi-objective agile earth observation satellite scheduling problem[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 110: 107607. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107607. [42] 马一凡, 赵凡宇, 王鑫, 等. 密集观测场景下的敏捷成像卫星任务规划方法[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 55(6): 1215–1224. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2021.06.023.MA Yifan, ZHAO Fanyu, WANG Xin, et al. Agile imaging satellite task planning method for intensive observation[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Engineering Science, 2021, 55(6): 1215–1224. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2021.06.023. [43] CHUN Jie, YANG Wenyuan, LIU Xiaolu, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for the agile earth observation satellite scheduling problem[J]. Mathematics, 2023, 11(19): 4059. doi: 10.3390/math11194059. [44] HERRMANN A and SCHAUB H. Reinforcement learning for the agile earth-observing satellite scheduling problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(5): 5235–5247. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3251307. [45] CHEN Ming, DU Yonghao, TANG Ke, et al. Learning to construct a solution for the agile satellite scheduling problem with time-dependent transition times[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(10): 5949–5963. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3411640. [46] 王沛, 谭跃进. 多星联合对地观测调度问题的列生成算法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2011, 31(10): 1932–1939. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2011)10-1932.WANG Pei and TAN Yuejin. Column generation for the earth observation satellites scheduling problem[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2011, 31(10): 1932–1939. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2011)10-1932. [47] CHU Xiaogeng, CHEN Yuning, and TAN Yuejin. An anytime branch and bound algorithm for agile earth observation satellite onboard scheduling[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2017, 60(9): 2077–2090. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2017.07.026. [48] PENG Guansheng, SONG Guopeng, XING Lining, et al. An exact algorithm for agile earth observation satellite scheduling with time-dependent profits[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2020, 120: 104946. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2020.104946. [49] CHEN Ming, CHEN Yuning, DU Yonghao, et al. Heuristic algorithms based on deep reinforcement learning for quadratic unconstrained binary optimization[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 207: 106366. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106366. [50] PENG Guansheng, SONG Guopeng, HE Yongming, et al. Solving the agile earth observation satellite scheduling problem with time-dependent transition times[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(3): 1614–1625. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3031738. [51] CHEN Xiaoyu, REINELT G, DAI Guangming, et al. A mixed integer linear programming model for multi-satellite scheduling[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 275(2): 694–707. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2018.11.058. [52] 白保存, 贺仁杰, 李菊芳, 等. 卫星单轨任务合成观测问题及其动态规划算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2009, 31(7): 1738–1742. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.07.046.BAI Baocun, HE Renjie, LI Jufang, et al. Satellite orbit task merging problem and its dynamic programming algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(7): 1738–1742. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.07.046. [53] WU Guohua, LUO Qizhang, DU Xiao, et al. Ensemble of metaheuristic and exact algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer framework for multisatellite observation scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(5): 4396–4408. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3160993. [54] WANG Pei, REINELT G, GAO Peng, et al. A model, a heuristic and a decision support system to solve the scheduling problem of an earth observing satellite constellation[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2011, 61(2): 322–335. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2011.02.015. [55] 靳肖闪, 李军, 王钧, 等. 基于随机搜索与松弛方法的多卫星联合成像优化调度研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2009, 30(1): 49–55. [56] RIBEIRO G M, CONSTANTINO M F, and LORENA L A N. Strong formulation for the spot 5 daily photograph scheduling problem[J]. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 2010, 20(4): 385–398. doi: 10.1007/s10878-009-9215-z. [57] LIN Weicheng, LIAO Dayin, LIU Chungyang, et al. Daily imaging scheduling of an earth observation satellite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 2005, 35(2): 213–223. doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2005.843380. [58] MARINELLI F, NOCELLA S, ROSSI F, et al. A Lagrangian heuristic for satellite range scheduling with resource constraints[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2011, 38(11): 1572–1583. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2011.01.016. [59] 石鑫, 邢孟道, 张金松, 等. 基于改进遗传算法的SAR多星协同复杂区域观测规划[J]. 遥感学报, 2024, 28(7): 1822–1834. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20243258.SHI Xin, XING Mengdao, ZHANG Jinsong, et al. SAR multi-satellite collaborative complex area observation planning based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2024, 28(7): 1822–1834. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20243258. [60] ZHIBO E, SHI Renhe, GAN Lan, et al. Multi-satellites imaging scheduling using individual reconfiguration based integer coding genetic algorithm[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 178: 645–657. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.08.041. [61] SONG Yanjie, OU Junwei, SUGANTHAN P N, et al. Learning adaptive genetic algorithm for earth electromagnetic satellite scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 9010–9025. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3312626. [62] SONG Yanjie, OU Junwei, PEDRYCZ W, et al. Generalized model and deep reinforcement learning-based evolutionary method for multitype satellite observation scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(4): 2576–2589. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3345928. [63] SONG Yanjie, WEI Luona, YANG Qing, et al. RL-GA: A reinforcement learning-based genetic algorithm for electromagnetic detection satellite scheduling problem[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2023, 77: 101236. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2023.101236. [64] 耿远卓, 郭延宁, 李传江, 等. 敏捷凝视卫星密集点目标聚类与最优观测规划[J]. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(3): 613–621. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0800.GENG Yuanzhuo, GUO Yanning, LI Chuanjiang, et al. Optimal mission planning with task clustering for intensive point targets observation of staring mode agile satellite[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(3): 613–621. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2018.0800. [65] WANG He, HUANG Weiquan, MAGNÚSSON S, et al. A strategy fusion-based multiobjective optimization approach for agile earth observation satellite scheduling problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5930214. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3472749. [66] HILTON S, THANGAVEL K, GARDI A, et al. Intelligent mission planning for autonomous distributed satellite systems[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2024, 225: 857–869. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2024.08.050. [67] 陈旺, 邵庆龙, 周晓, 等. 海洋一号卫星观测任务规划算法设计及系统应用[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2024, 44(2): 145–153. doi: 10.16708/j.cnki.1000-758X.2024.0031.CHEN Wang, SHAO Qinglong, ZHOU Xiao, et al. Algorithm design and system application of HY-1 satellite observation mission planning[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2024, 44(2): 145–153. doi: 10.16708/j.cnki.1000-758X.2024.0031. [68] GU Yi, HAN Chao, CHEN Yuhan, et al. Large region targets observation scheduling by multiple satellites using resampling particle swarm optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(2): 1800–1815. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3205565. [69] WU Xiande, YANG Yuheng, SUN Yuqi, et al. Dynamic regional splitting planning of remote sensing satellite swarm using parallel genetic PSO algorithm[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2023, 204: 531–551. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2022.09.020. [70] LONG Xi, CAI Weiwei, YANG Leping, et al. Improved particle swarm optimization with reverse learning and neighbor adjustment for space surveillance network task scheduling[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2024, 85: 101482. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2024.101482. [71] 张佳唯, 邢立宁, 张玮, 等. 基于统一资源编码的成像卫星联合任务规划算法框架[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(6): 1497–1504. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1718.ZHANG Jiawei, XING Lining, ZHANG Wei, et al. A united mission planning algorithm framework based on uniform resource encoding for imaging satellites[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(6): 1497–1504. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.1718. [72] WU Jian, LU Fang, ZHANG Jiawei, et al. Design of task priority model and algorithm for imaging observation problem[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 31(2): 321–334. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2020.000010. [73] 周毅荣, 陈浩, 李龙梅, 等. 一种基于免疫遗传的卫星数传调度方法[J]. 小型微型计算机系统, 2015, 36(12): 2725–2729. doi: 10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/tp.2015.12.020.ZHOU Yirong, CHEN Hao, LI Longmei, et al. Immune genetic algorithm for satellite data transmission scheduling[J]. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2015, 36(12): 2725–2729. doi: 10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/tp.2015.12.020. [74] KIM H and CHANG Y K. Mission scheduling optimization of SAR satellite constellation for minimizing system response time[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2015, 40: 17–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2014.10.006. [75] LI Jun, LI Jun, CHEN Hao, et al. A data transmission scheduling algorithm for rapid-response earth-observing operations[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2014, 27(2): 349–364. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2014.02.014. [76] NIU Xiaonan, TANG Hong, and WU Lixin. Satellite scheduling of large areal tasks for rapid response to natural disaster using a multi-objective genetic algorithm[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2018, 28: 813–825. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2018.02.013. [77] XHAFA F, SUN Junzi, BAROLLI A, et al. Genetic algorithms for satellite scheduling problems[J]. Mobile Information Systems, 2012, 8(4): 351–377. doi: 10.1109/bwcca.2013.58. [78] XHAFA F, HERRERO X, BAROLLI A, et al. Evaluation of struggle strategy in Genetic Algorithms for ground stations scheduling problem[J]. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 2013, 79(7): 1086–1100. doi: 10.1016/j.jcss.2013.01.023. [79] TANG Yinyin, WANG Yueke, CHEN Jianyun, et al. Uplink scheduling of navigation constellation based on genetic algorithm[C]. 2016 IEEE 13th International Conference on Signal Processing, Chengdu, China, 2017: 1124–1129. doi: 10.1109/ICSP.2016.7878003. [80] DU Yonghao, XING Lining, ZHANG Jiawei, et al. MOEA based memetic algorithms for multi-objective satellite range scheduling problem[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 50: 100576. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2019.100576. [81] 邱涤珊, 郭浩, 贺川, 等. 敏捷成像卫星多星密集任务调度方法[J]. 航空学报, 2013, 34(4): 882–889. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2013.0149.QIU Dishan, GUO Hao, HE Chuan, et al. Intensive task scheduling method for multi-agile imaging satellites[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(4): 882–889. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2013.0149. [82] 严珍珍, 陈英武, 邢立宁. 基于改进蚁群算法设计的敏捷卫星调度方法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2014, 34(3): 793–801. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2014)3-793.YAN Zhenzhen, CHEN Yingwu, and XING Lining. Agile satellite scheduling based on improved ant colony algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2014, 34(3): 793–801. doi: 10.12011/1000-6788(2014)3-793. [83] 陈宇宁, 邢立宁, 陈英武. 基于蚁群算法的灵巧卫星调度[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2011, 11(3): 484–489,502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2011.03.012.CHEN Yuning, XING Lining, and CHEN Yingwu. Scheduling of agile satellites based on ant colony algorithm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2011, 11(3): 484–489,502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2011.03.012. [84] 何磊, 刘晓路, 陈英武, 等. 面向敏捷卫星任务规划的云层建模及处理方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2016, 38(4): 852–858. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.04.19.HE Lei, LIU Xiaolu, CHEN Yingwu, et al. Cloud modeling and processing method for agile observing satellite mission planning[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(4): 852–858. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2016.04.19. [85] HE Lei, DE WEERDT M, and YORKE-SMITH N. Time/sequence-dependent scheduling: The design and evaluation of a general purpose tabu-based adaptive large neighbourhood search algorithm[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020, 31(4): 1051–1078. doi: 10.1007/s10845-019-01518-4. [86] YANG Weiyi, HE Lei, LIU Xiaolu, et al. A fast insertion tabu search with conflict-avoidance heuristic for the multisatellite multimode crosslink scheduling problem[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2024, 29(3): 843–862. doi: 10.26599/TST.2023.9010064. [87] WU Guohua, WANG Huilin, PEDRYCZ W, et al. Satellite observation scheduling with a novel adaptive simulated annealing algorithm and a dynamic task clustering strategy[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2017, 113: 576–588. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2017.09.050. [88] WU Xiande, YANG Yuheng, XIE Yaen, et al. Multiregion mission planning by satellite swarm using simulated annealing and neighborhood search[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(2): 1416–1439. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3337066. [89] 贺仁杰, 谭跃进. 具有时间窗口约束的并行机床调度问题研究[J]. 系统工程, 2004, 22(5): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4098.2004.05.004.HE Renjie and TAN Yuejin. On parallel machine scheduling problem with time windows[J]. Systems Engineering, 2004, 22(5): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4098.2004.05.004. [90] 郑起存, 岳海霞, 刘大成, 等. 基于区域目标网格化的多星协同观测方法[J]. 中国科学院大学学报(中英文), 2024, 41(6): 803–809. doi: 10.7523/j.ucas.2023.019.ZHENG Qicun, YUE Haixia, LIU Dacheng, et al. Multi-satellite cooperative observation method based on area target gridding[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2024, 41(6): 803–809. doi: 10.7523/j.ucas.2023.019. [91] 丁祎男, 田科丰, 王淑一. 基于遗传禁忌混合算法的敏捷卫星任务规划[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2019, 45(6): 27–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2019.06.004.DING Yinan, TIAN Kefeng, and WANG Shuyi. Mission scheduling for agile earth observation satellites based on genetic-tabu hybrid algorithm[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2019, 45(6): 27–32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2019.06.004. [92] 李君, 邢立宁, 彭观胜, 等. 考虑多类型时间依赖资源约束的敏捷卫星调度优化[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2024, 41(6): 1038–1046. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2023.20914.LI Jun, XING Lining, PENG Guansheng, et al. The agile earth observation satellite scheduling with multiple resource constraints[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2024, 41(6): 1038–1046. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2023.20914. [93] WU Jian, SONG Bingyu, ZHANG Guoting, et al. A data-driven improved genetic algorithm for agile earth observation satellite scheduling with time-dependent transition time[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022, 174: 108823. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2022.108823. [94] XIANG S, WANG L, XING L, et al. Knowledge-based memetic algorithm for joint task planning of multi-platform earth observation system[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 160: 107559 [95] 刘建银, 王忠伟. 面向森林资源观测的成像卫星任务规划算法设计[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2018, 38(10): 41–46. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2018.10.007.LIU Jianyin and WANG Zhongwei. Research on the tasks scheduling algorithm for imaging satellite observing forest area[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2018, 38(10): 41–46. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2018.10.007. [96] 李庥甜, 王凌, 陈英武, 等. 基于自适应大邻域搜索的多场景多卫星任务规划方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2025, 37(7): 1836–1847. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.25-0095.LI Xiutian, WANG Ling, CHEN Yingwu, et al. Multi-scenario multi-satellite mission planning method based on adaptive large neighborhood search[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2025, 37(7): 1836–1847. doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.25-0095. [97] DU Yonghao, WANG Ling, XING Lining, et al. Data-driven heuristic assisted memetic algorithm for efficient inter-satellite link scheduling in the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2021, 8(11): 1800–1816. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2021.1004174. [98] SONG Yanjie, SUGANTHAN P N, PEDRYCZ W, et al. Energy-efficient satellite range scheduling using a reinforcement learning-based memetic algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 4073–4087. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3371964. [99] 陈珂昕, 刘晓路, 淳洁, 等. 考虑多类型任务的成像卫星群调度模型与算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2025, 40(6): 1913–1921. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2024.0897.CHEN Kexin, LIU Xiaolu, CHUN Jie, et al. Model and algorithm for scheduling imaging satellite constellations based on multi-type tasks[J]. Control and Decision, 2025, 40(6): 1913–1921. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2024.0897. [100] 刘正, 熊伟, 简平, 等. 基于Transformer的成像卫星星群调度方法研究[C]. 第六届体系工程学术会议论文集—体系工程与高质量发展. 昆明, 2024. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2024.028403.LIU Zheng, XIONG Wei, JIAN Ping, et al. Study on imaging satellite swarm scheduling method based on Transformer[C]. Kunming, China, 2024. doi: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2024.028403. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
