An Expert Chain Construction and Optimization Method for Satellite Mission Planning
-
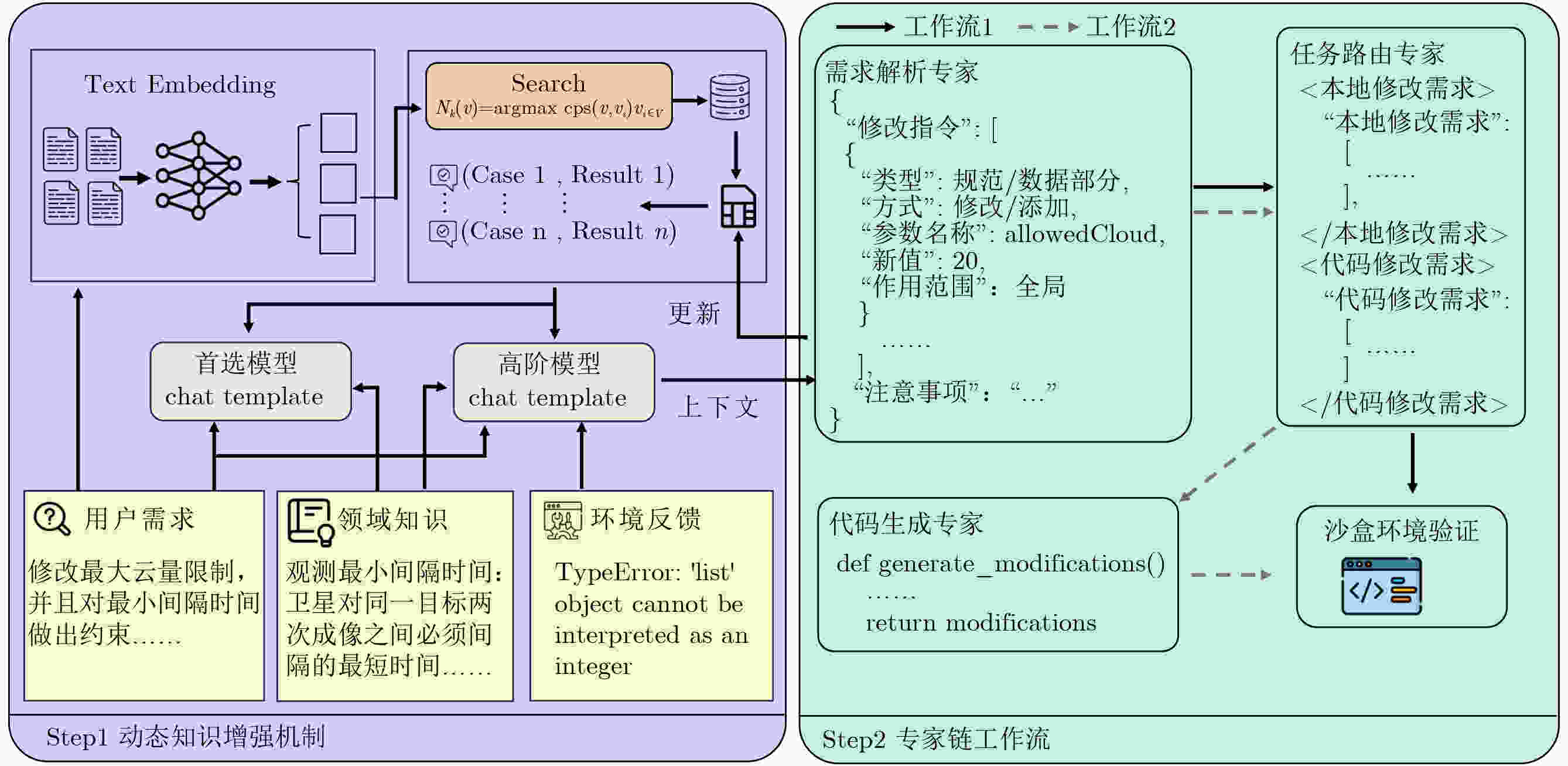
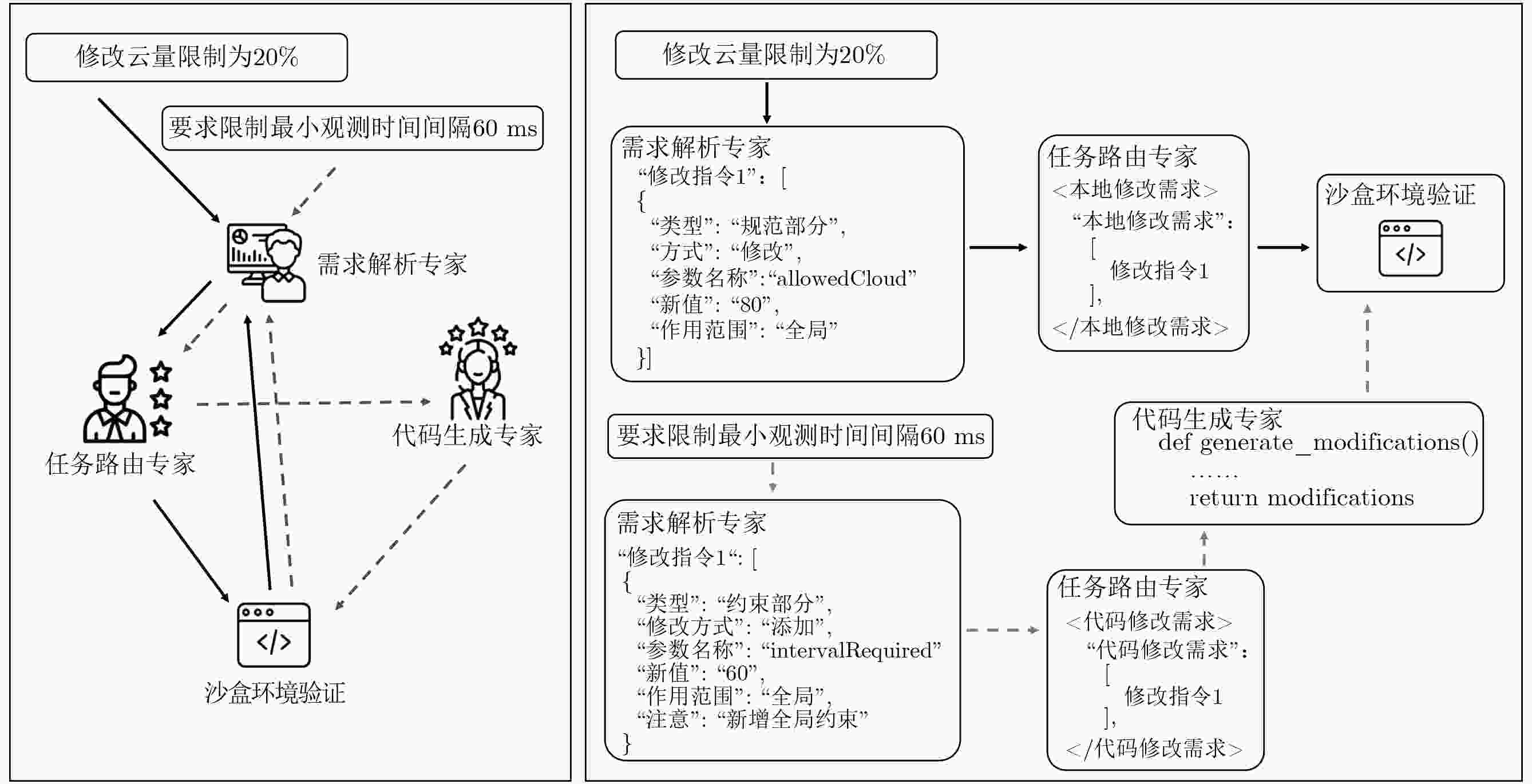
摘要: 卫星任务规划是航天资源调度领域的关键优化问题,在面对动态需求时,传统方法因其复杂的建模流程,常面临响应滞后、灵活性不足等挑战,且业务语言与数学模型间存在语义断层。为此,该文提出一种基于专家链(CoE)与动态知识增强机制(DKE)的大语言模型(LLM)推理框架。该框架聚焦于模型动态修改,通过设计一个需求解析、指令路由和代码生成的专家协同工作流,实现从自然语言指令到数学模型的精确映射。此外,该框架借助动态知识库与Few-Shot学习策略,使系统在不依赖梯度更新情况下具备持续优化能力。实验结果表明,相较于标准提示词方法(SP)、思维链技术(CoT)以及基于GPT4-o的标准提示词方法,准确率达到82%,平均响应时间81.28 s,显著优于所有对比基线,实验结果验证了该方法能够有效提升LLM在卫星任务规划模型动态修改任务中的处理能力。Abstract:
Objective Satellite mission planning is a core optimization problem in space resource scheduling. Existing workflows exhibit a semantic gap between business-level natural language requirements and the mathematical models used for planning. In dynamic operational scenarios, model updates, such as constraint modification, parameter recalculation, or task attribute adjustment, rely heavily on human experts. This dependence leads to slow responses, limited adaptability, and high operational costs. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a Large Language Model (LLM)-driven inference framework based on a Chain of Experts (CoE) and a Dynamic Knowledge Enhancement (DKE) mechanism. The framework enables accurate, efficient, and robust modification of satellite mission planning models from natural language instructions. Methods The proposed framework decomposes natural language-driven model modification into a collaborative workflow comprising requirement parsing, task routing, and code generation experts. The requirement parsing expert converts natural language requests into structured modification instructions. The task routing expert assesses task difficulty and dispatches instructions accordingly. The code generation expert produces executable modification scripts for complex, large-scale, or batch operations. To improve accuracy and reduce reliance on manual expert intervention, a DKE mechanism is incorporated. This mechanism adopts a tiered LLM strategy, using a lightweight general model for rapid processing and a stronger reasoning model for complex cases, and constructs a dynamic knowledge base of validated modification cases. Through retrieval-augmented few-shot prompting, historical successful cases are integrated into the reasoning process, enabling continuous self-improvement without model fine-tuning. A sandbox environment performs mathematical consistency checks, including constraint completeness, parameter validity, and solution feasibility, before final acceptance of model updates. Results and Discussions Experiments are conducted on a simulated satellite mission planning dataset comprising 100 heterogeneous satellites and 1,000 point targets with different payload types, resolution requirements, and operational constraints. A test set of 100 natural language modification requests with varying complexity is constructed to represent dynamic real-world adjustment scenarios ( Table 1 ). The proposed CoE with DKE framework is evaluated against three baselines: standard prompting with DeepSeek R1, Chain-of-Thought prompting with DeepSeek R1, and standard prompting with GPT-4o. The proposed method achieves an accuracy of 82% with an average response time of 81.28 s, outperforming all baselines in both correctness and efficiency (Table 2 ). Accuracy increases by 35 percentage points relative to the best-performing baseline, whereas response time decreases by 53.3% (Table 2 ). Scalability experiments show that the CoE with DKE framework maintains stable response times across small, medium, and large problem instances, whereas baseline methods exhibit significant delays as problem size increases (Table 3 ). Ablation studies indicate that DKE substantially reduces reliance on high-cost reasoning models, improves the general model’s ability to resolve complex modifications independently, and increases accuracy without sacrificing efficiency (Table 5 ).Conclusions This paper presents an LLM-powered reasoning framework that integrates a Chain of Experts workflow with a DKE mechanism to bridge the semantic gap between natural language requirements and formal optimization models in satellite mission planning. Through layered model collaboration, retrieval-augmented prompting, and sandbox-based mathematical verification, the proposed method achieves high accuracy, fast processing, and strong adaptability to dynamic and complex planning scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate its effectiveness in supporting precise model modification and improving operational intelligence. Future work will extend the framework to multimodal inputs and real-world mission environments to further improve robustness and engineering applicability. -
1 基于大语言模型的卫星任务规划模型动态修改算法
输入 修改请求q,卫星任务规划模型建模$ \mathrm{V}{\mathrm{M}}_{\mathrm{user}} $,动态知识库K 输出 符合用户需求进行修改并且成功验证的卫星任务规划模型
$ \mathrm{V}{\mathrm{M}}_{\mathrm{target}} $(1) initialize parameters //参数初始化 (2) $ \boldsymbol{v}=\sigma (q) $ //用户修改需求文本向量化 (3) $ {\boldsymbol{N}}_{\mathrm{k}}(\boldsymbol{v})=\mathrm{argmaxcos}(\boldsymbol{v},{\boldsymbol{v}}_{{i}})_{{\boldsymbol{v}}_{{i}}\in \boldsymbol{V}}^{\mathrm{k}} $ //检索相似向量 (4) $ \{{E}_{i}\}_{i=1}^{\mathrm{k}}=\{\varphi_{i=1}^{\mathrm{k}} ({\boldsymbol{v}}_{{i}})|{\boldsymbol{v}}_{{i}}\in {\boldsymbol{N}}_{\mathrm{k}}(\boldsymbol{v})\} $ //根据向量检索经验3
元组(5) $ P=\mathrm{Template}_{i=1}^{\mathrm{k}}({E}_{i})\oplus q $ //在上下文中嵌入经验3元组 (6) IF $ \varPhi ({M}_{1}(q))==0 $ THEN (7) RETURN (8) ELSE THEN (9) activate$ {M}_{2}(q) $ //激活高阶模型专家链 (10) RETURN $ \mathrm{V}{\mathrm{M}}_{\mathrm{target}} $ 表 1 难度等级
难度等级 说明 简单 无大规模批量操作,且修改点数量少(<8个)。 中等 满足以下条件之一:①修改点数量较多(≥8个);
②包含大规模批量操作困难 修改点数量较多(≥8个)且包含大规模批量操作 表 2 COE with DKE 与其他实验方法的Accuracy与ART对比
方法 模型 Accuracy(%) ART(s) Standard Prompt DeepSeek R1 35 307.23 COT DeepSeek R1 42 350.19 Standard Prompt GPT-4o 47 173.99 COE with DKE - 82 81.28 表 3 CoE with DKE与其他实验方法在不同实例规模下平均响应时间对比(s)
方法 模型 n=0~100 n=101~500 n=501~ 1000 ART ART ART Standard Prompt DeepSeek R1 83.72 254.53 458.21 CoT DeepSeek R1 92.36 301.37 450.52 Standard Prompt GPT-4o 37.82 168.91 331.26 CoE with DKE - 69.72 82.48 86.58 表 4 COE with DKE与其他实验方法在不同难度等级需求下的结果对比
方法 模型 简单 中等 困难 Accuracy (%) ART(s) Accuracy (%) ART(s) Accuracy(%) ART(s) Standard Prompt DeepSeek R1 47.91 265.41 26.83 326.25 18.18 213.83 CoT DeepSeek R1 54.17 275.47 31.71 361.78 27.30 275.47 Standard Prompt GPT-4o 62.50 74.05 39.02 100.84 18.18 87.42 COE with DKE - 93.75 40.43 82.92 86.03 54.54 116.13 表 5 消融实验结果对比
方法 模型 Accuracy(%) ART(s) 首选模型 高阶模型 CoE DeepSeek R1 - 74 123.49 CoE with DKE DeepSeek R1 DeepSeek R1 83 126.78 CoE DeepSeek V3 - 59 78.32 CoE with DKE DeepSeek V3 DeepSeek V3 70 80.43 CoE DeepSeek V3 DeepSeek R1 73 134.74 CoE with DKE DeepSeek V3 DeepSeek R1 82 81.28 表 6 不同配置下高阶模型调用次数对比
方法 模型 高阶模型调用次数 首选模型 高阶模型 CoE DeepSeek V3 DeepSeek R1 58 CoE with DKE DeepSeek R1 DeepSeek R1 33 CoE with DKE DeepSeek V3 DeepSeek V3 42 CoE with DKE DeepSeek V3 DeepSeek R1 36 -
[1] LI Peiyan, CUI Peixing, and WANG Huiquan. Mission sequence model and deep reinforcement learning-based replanning method for multi-satellite observation[J]. Sensors, 2025, 25(6): 1707. doi: 10.3390/s25061707. [2] ZHENG Qingbiao, CAI Yuanwen, and WANG Peng. A modified genetic algorithm for large-scale and joint satellite mission planning[J]. Egyptian Informatics Journal, 2025, 31: 100713. doi: 10.1016/j.eij.2025.100713. [3] YAO Wei, SHEN Xin, ZHANG Guo, et al. A spiking neural network based proximal policy optimization method for multi-point imaging mission scheduling of earth observation satellite[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2025, 94: 101867. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2025.101867. [4] LI Shuo, WANG Gang, and CHEN Jinyong. AEM-D3QN: A graph-based deep reinforcement learning framework for dynamic earth observation satellite mission planning[J]. Aerospace, 2025, 12(5): 420. doi: 10.3390/aerospace12050420. [5] LI Xinyi, WANG Sai, ZENG Siqi, et al. A survey on LLM-based multi-agent systems: Workflow, infrastructure, and challenges[J]. Vicinagearth, 2024, 1(1): 9. doi: 10.1007/s44336-024-00009-2. [6] FOURATI F and ALOUINI M S. Artificial intelligence for satellite communication: A review[J]. Intelligent and Converged Networks, 2021, 2(3): 213–243. doi: 10.23919/ICN.2021.0015. [7] SUN Chuanneng, HUANG Songjun, and POMPILI D. LLM-based multi-agent decision-making: Challenges and future directions[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2025, 10(6): 5681–5688. doi: 10.1109/lra.2025.3562371. [8] SHI Qian, HE Da, LIU Zhengyu, et al. Globe230k: A benchmark dense-pixel annotation dataset for global land cover mapping[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 3: 0078. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0078. [9] HU Fengming, XU Feng, WANG R, et al. Conceptual study and performance analysis of tandem multi-antenna spaceborne SAR interferometry[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0137. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0137. [10] JIANG Liguang, NIELSEN K, and ANDERSEN O B. Beyond exact repeat missions: Embracing geodetic altimetry for inland water monitoring and modeling[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0269. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0269. [11] JI H R and HUANG Dianyuan. A mission planning method for multi-satellite wide area observation[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2019, 16(6): 1729881419890715. doi: 10.1177/1729881419890715. [12] SONG Yanjie, ZHOU Ziyu, ZHANG Zhongshan, et al. A framework involving MEC: Imaging satellites mission planning[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(19): 15329–15340. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04047-6. [13] ZHANG Guohui, LI Xinhong, WANG Xun, et al. Research on the prediction problem of satellite mission schedulability based on Bi-LSTM model[J]. Aerospace, 2022, 9(11): 676. doi: 10.3390/aerospace9110676. [14] LI Zhouxiao and LIU Yuan. Onboard autonomous mission generation method based on user preference[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2024, 74(1): 437–453. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2024.03.055. [15] CARRASCO A, RODRIGUEZ-FERNANDEZ V, and LINARES R. Large language models as autonomous spacecraft operators in Kerbal Space Program[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2025, 76(6): 3480–3497. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2025.06.034. [16] WU Di, ZHANG R, ZUCCHELLI E M, et al. APBench and benchmarking large language model performance in fundamental astrodynamics problems for space engineering[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 7944. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91150-5. [17] RAMAMONJISON R, YU T T L, LI R, et al. NL4Opt competition: Formulating optimization problems based on their natural language descriptions[C]. The NeurIPS 2022 Competitions Track, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 189–203. [18] XIAO Ziyang, ZHANG Dongxiang, WU Yangjun, et al. Chain-of-experts: When LLMs meet complex operations research problems[C]. The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 2024. [19] ASTORGA N, LIU T, XIAO Yuanzhang, et al. Autoformulation of mathematical optimization models using LLMs[C]. The 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Vancouver, Canada, 2025. [20] JIANG Caigao, SHU Xiang, QIAN Hong, et al. LLMOPT: Learning to define and solve general optimization problems from scratch[C]. The 13th International Conference on Learning Representations, Singapore, Singapore, 2025. [21] HUANG Chenyu, TANG Zhengyang, HU Shixi, et al. ORLM: A customizable framework in training large models for automated optimization modeling[J]. Operations Research, 2025, 73(6): 2986–3009. doi: 10.1287/opre.2024.1233. [22] AHMADITESHNIZI A, GAO Wenzhi, and UDELL M. OptiMUS: Optimization modeling using MIP solvers and large language models[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.06116, 2023. [23] YE Haoran, WANG Jiarui, CAO Zhiguang, et al. ReEvo: Large language models as hyper-heuristics with reflective evolution[C]. The 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2024. [24] YAO Shunyu, LIU Fei, LIN Xi, et al. Multi-objective evolution of heuristic using large language model[C]. The 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, USA, 2025: 27144–27152. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v39i25.34922. [25] DAT P V T, DOAN L, and BINH H T T. HSEvo: Elevating automatic heuristic design with diversity-driven harmony search and genetic algorithm using LLMs[C]. The 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, USA, 2025: 26931–26938. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v39i25.34898. [26] SURINA A, MANSOURI A, QUAEDVLIEG L, et al. Algorithm discovery with LLMs: Evolutionary search meets reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2504.05108, 2025. [27] LI Zhanxian, YE Nan, and HE Yifeng. Meteorological data transmission management system based on multi-source satellite data[C]. 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Big Data and Algorithms, Changchun, China, 2023: 1343–1346. doi: 10.1109/EEBDA56825.2023.10090642. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
