Towards Privacy-Preserving and Lightweight Modulation Recognition for Short-Wave Signals under Channel Shifts
-
摘要: 现有基于监督学习范式的短波信号调制识别方法通常假设训练数据(源域)与测试数据(目标域)服从同一分布。然而,短波信道易受电离层变化影响,导致域间分布差异显著,进而引发模型性能退化。此外,无人平台边缘侧部署还面临设备资源受限、标注样本稀缺以及数据隐私保护等多重挑战。针对上述问题,本文提出一种基于源模型迁移的轻量化识别方法,能够在不访问源域数据的条件下实现隐私安全的模型迁移。该方法的优势主要体现在三个方面:首先,具备良好的轻量化特性,仅需在无标签目标域上进行单轮训练即可快速收敛,显著降低了计算开销;其次,具备优异的小样本适应能力,在目标域样本极少的场景下仍能保持较高的识别精度;最后,通过融合涵盖同相/正交分量、幅度/相位信息及频谱特征的多模态信号特征,充分利用特征互补性增强了模型鲁棒性。仿真实验结果表明,该方法在大幅降低资源消耗的同时,在小样本条件下仍能保持稳定的识别性能,验证了其兼具快速收敛、低资源需求和良好泛化能力的特性。Abstract:
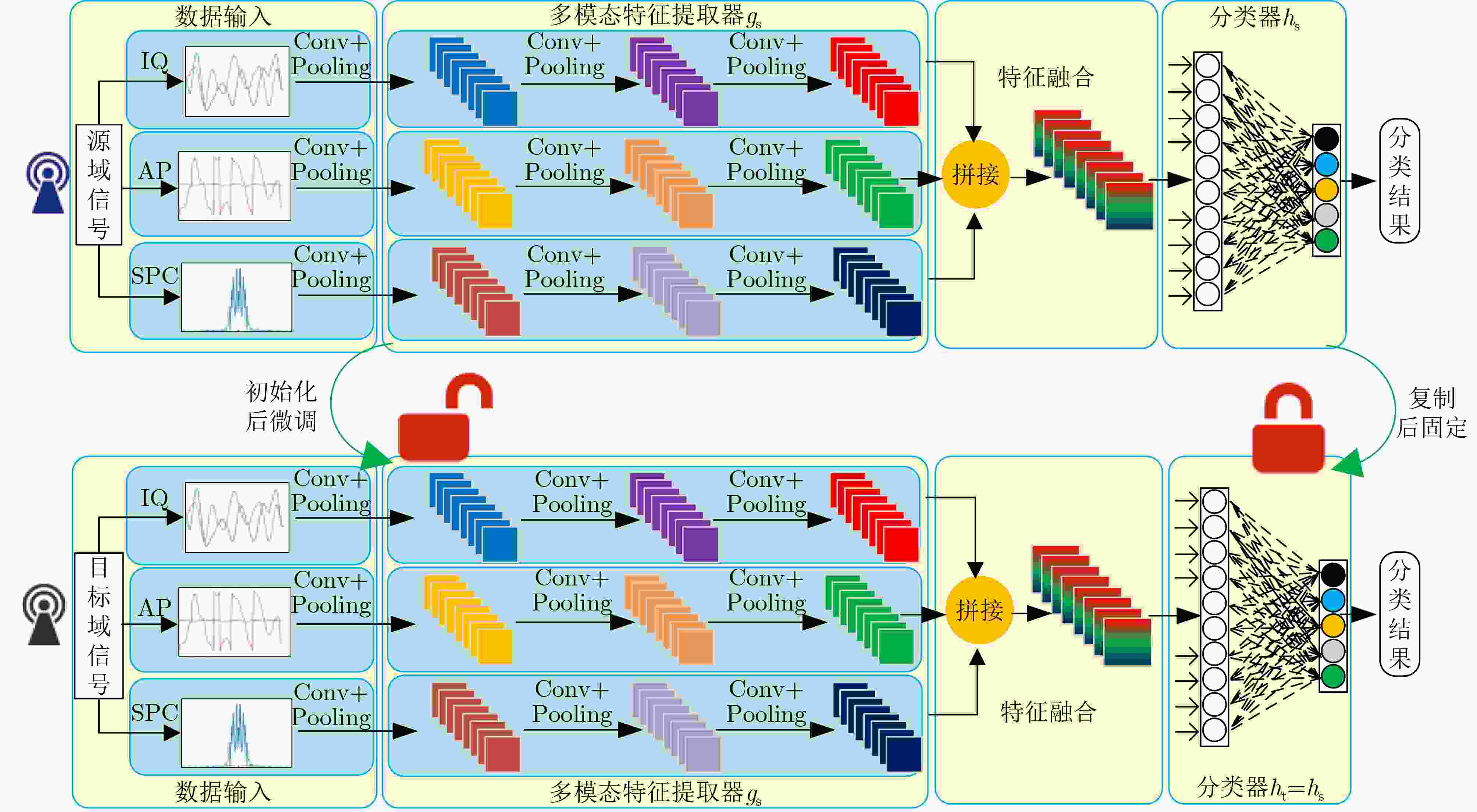
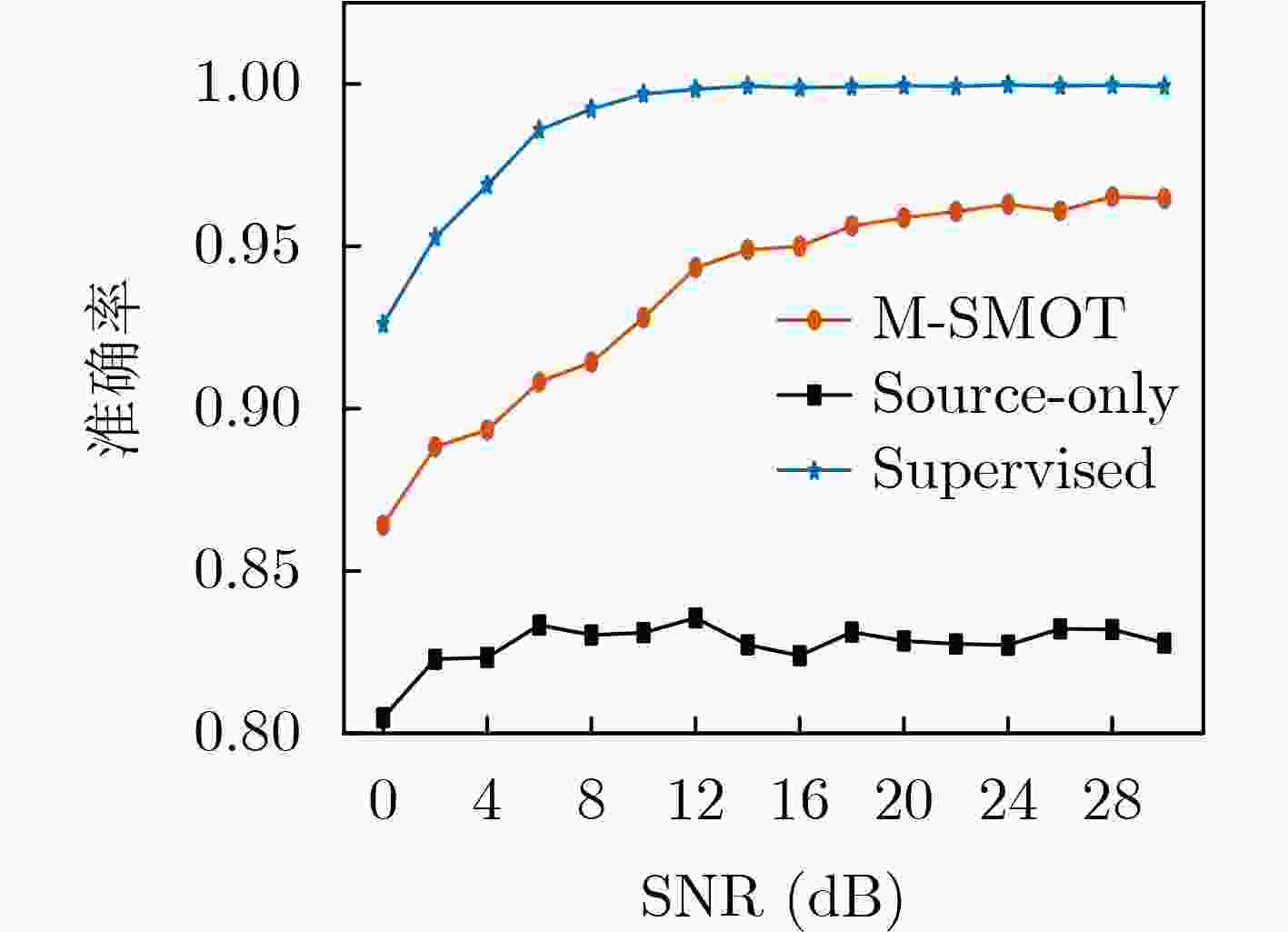
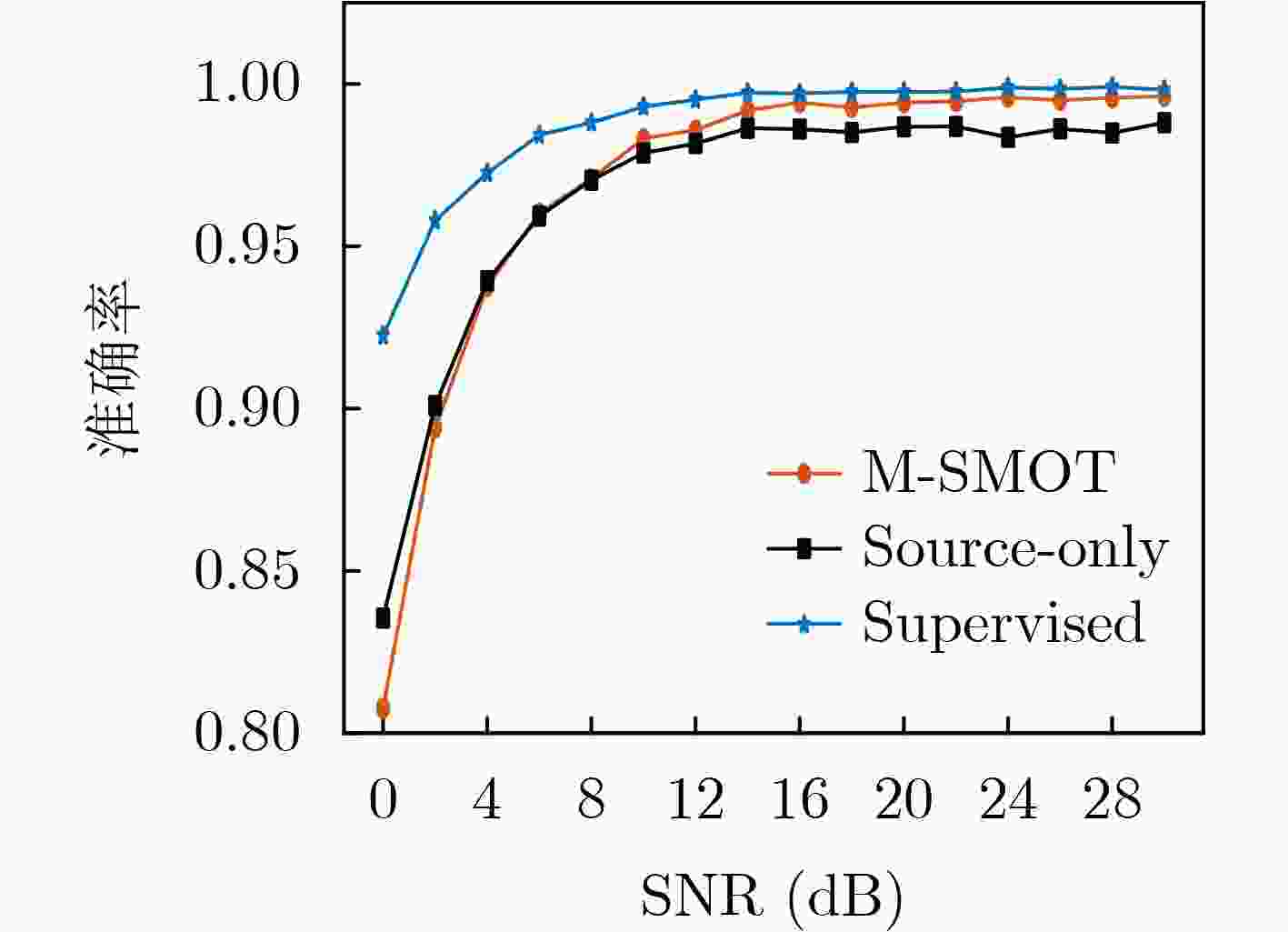
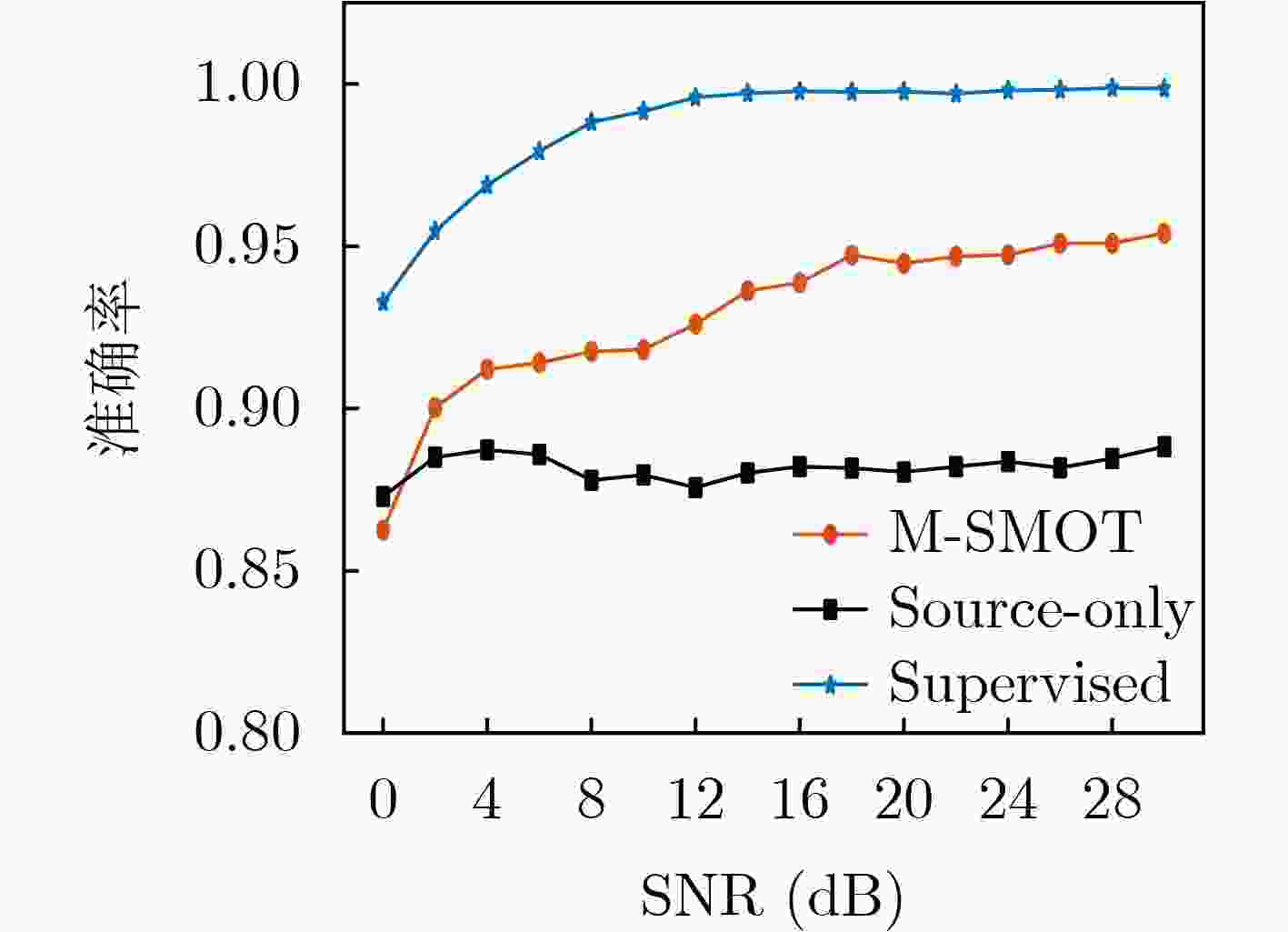
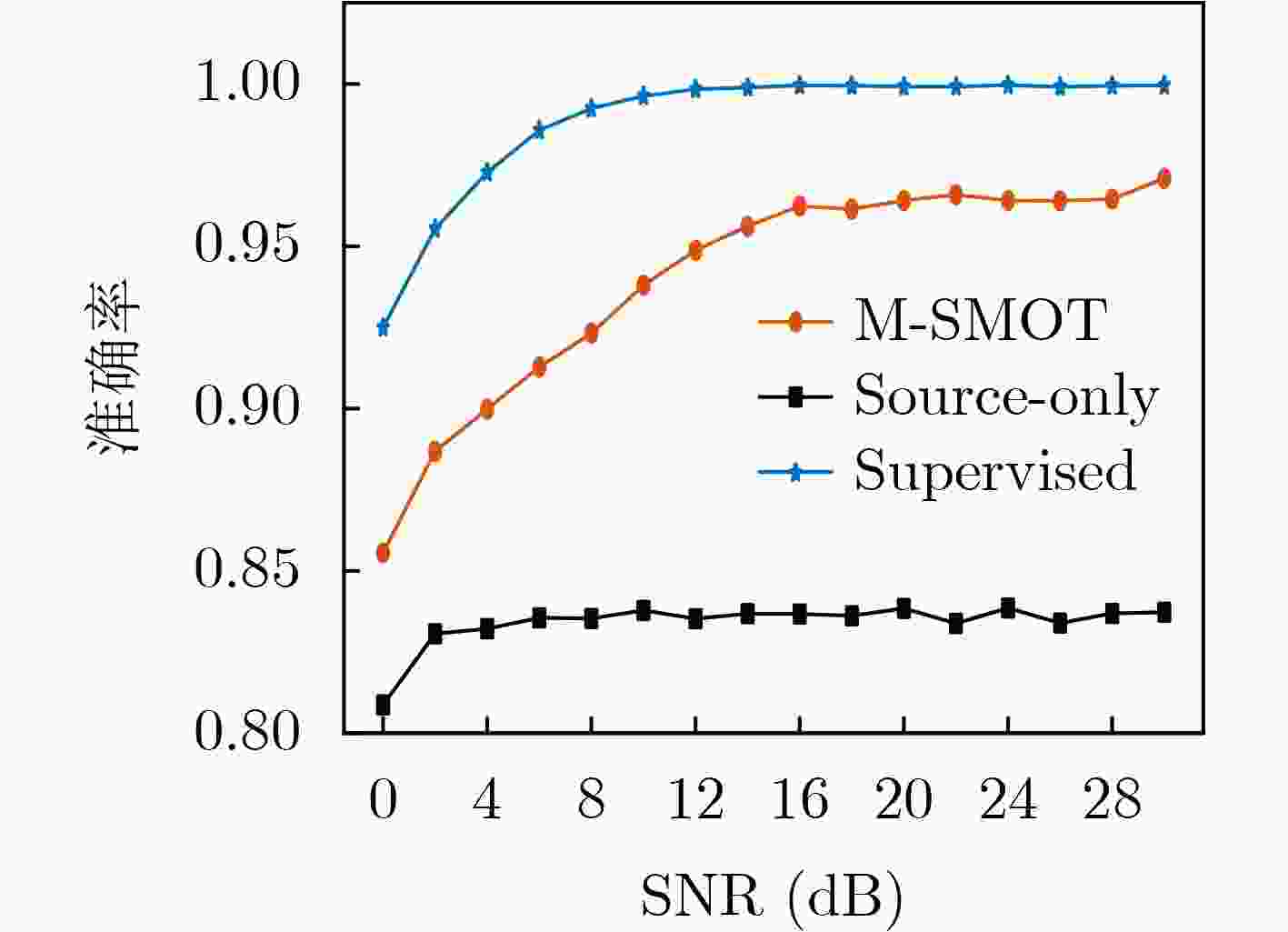
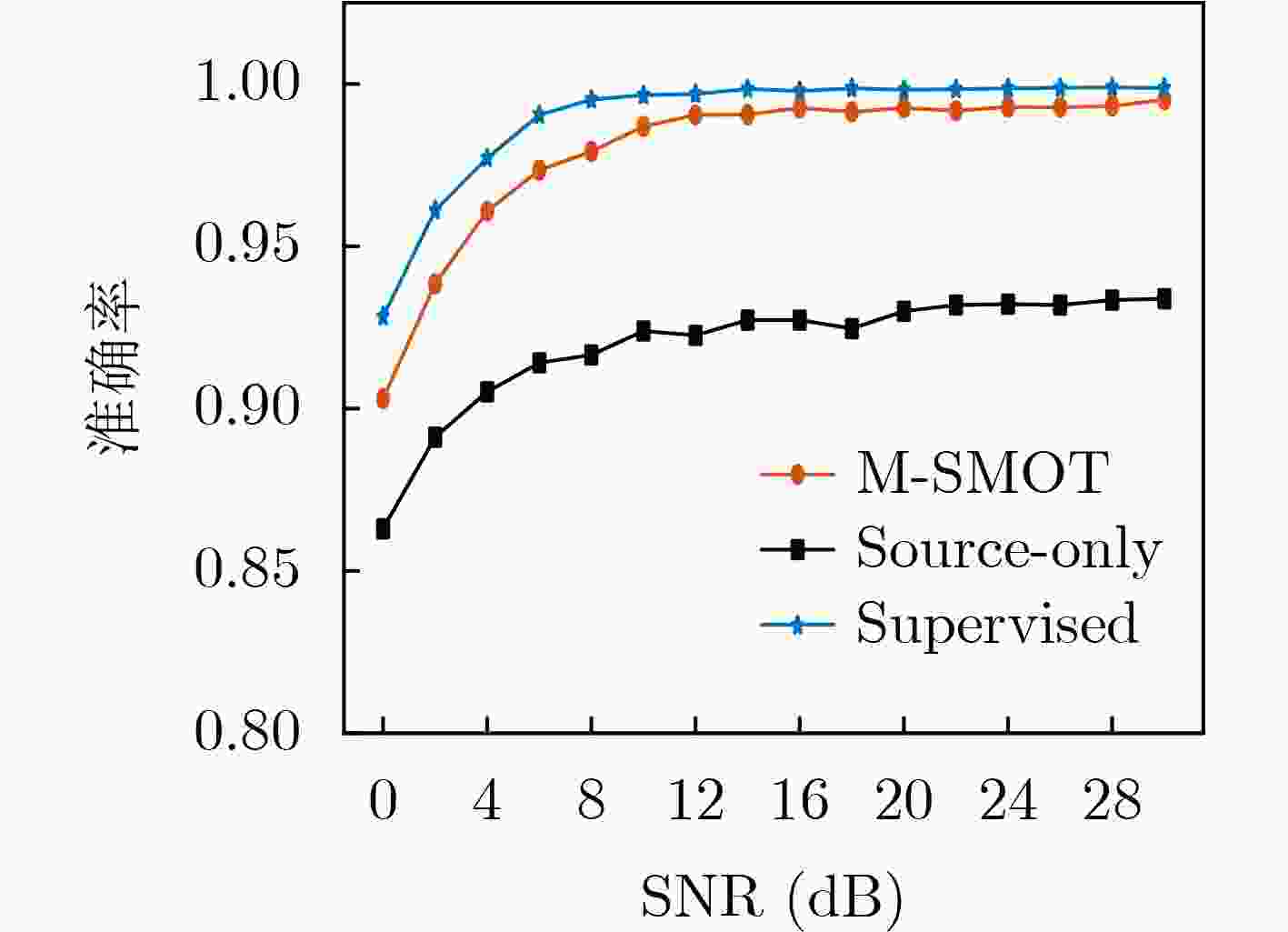
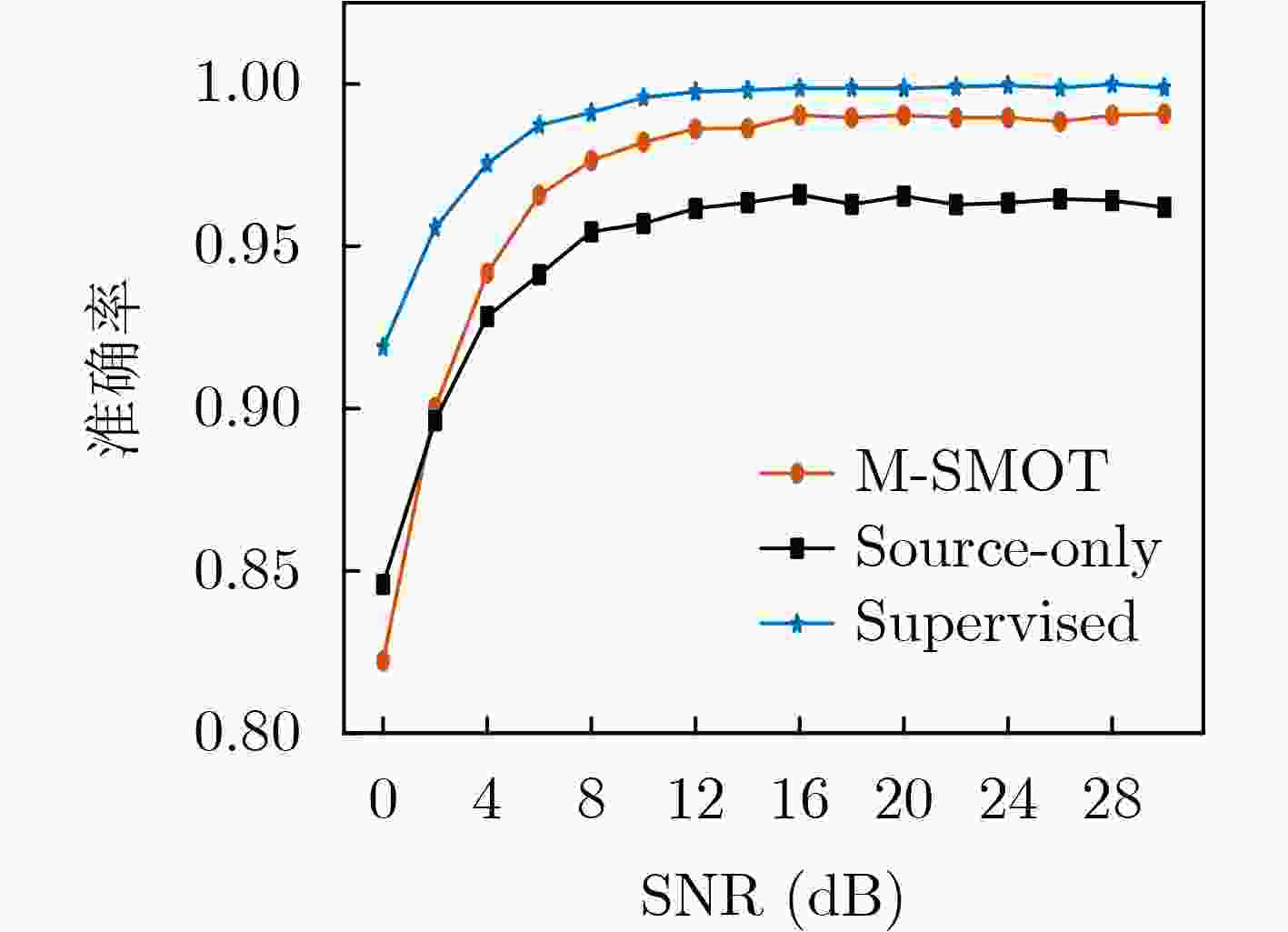
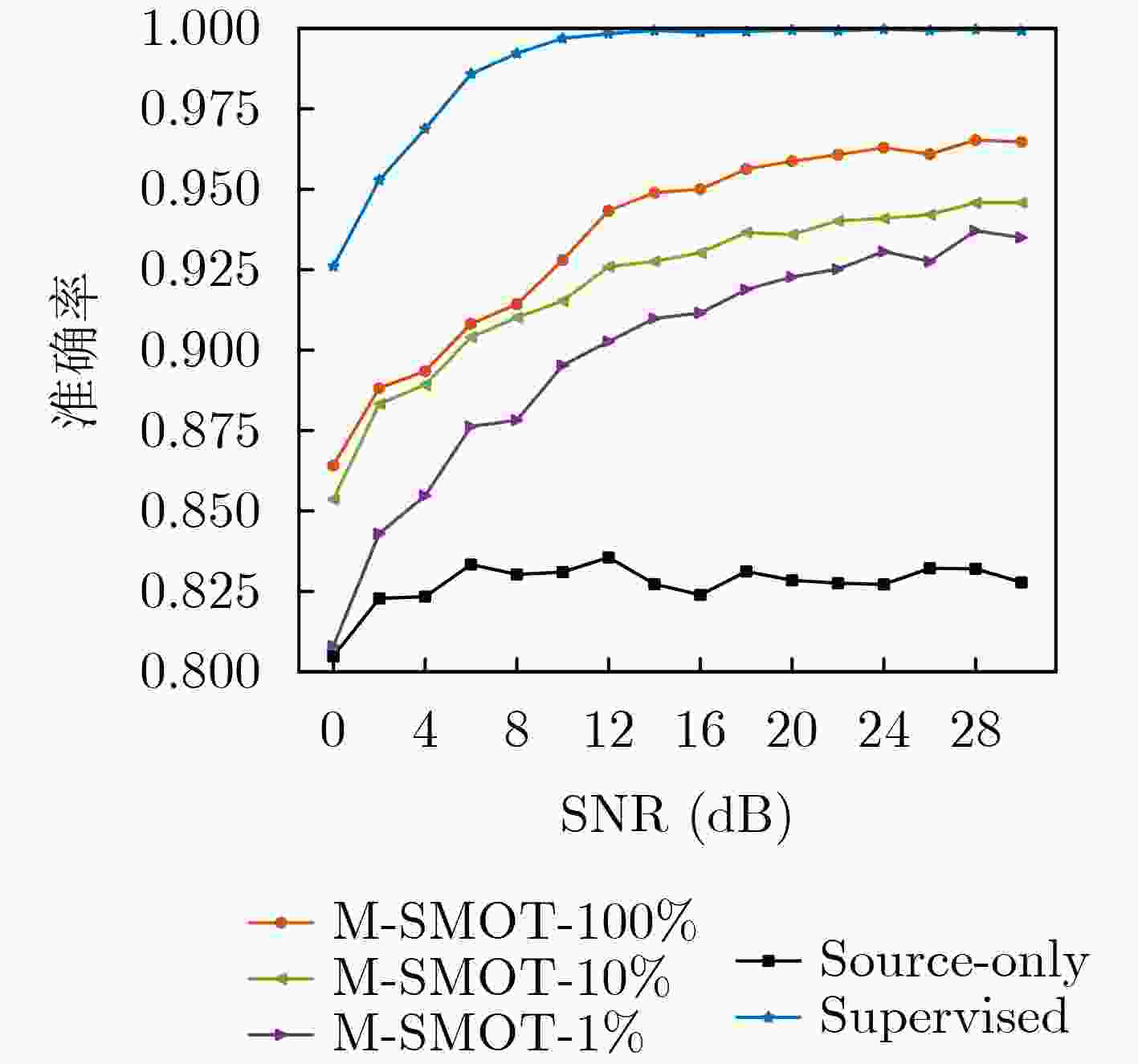
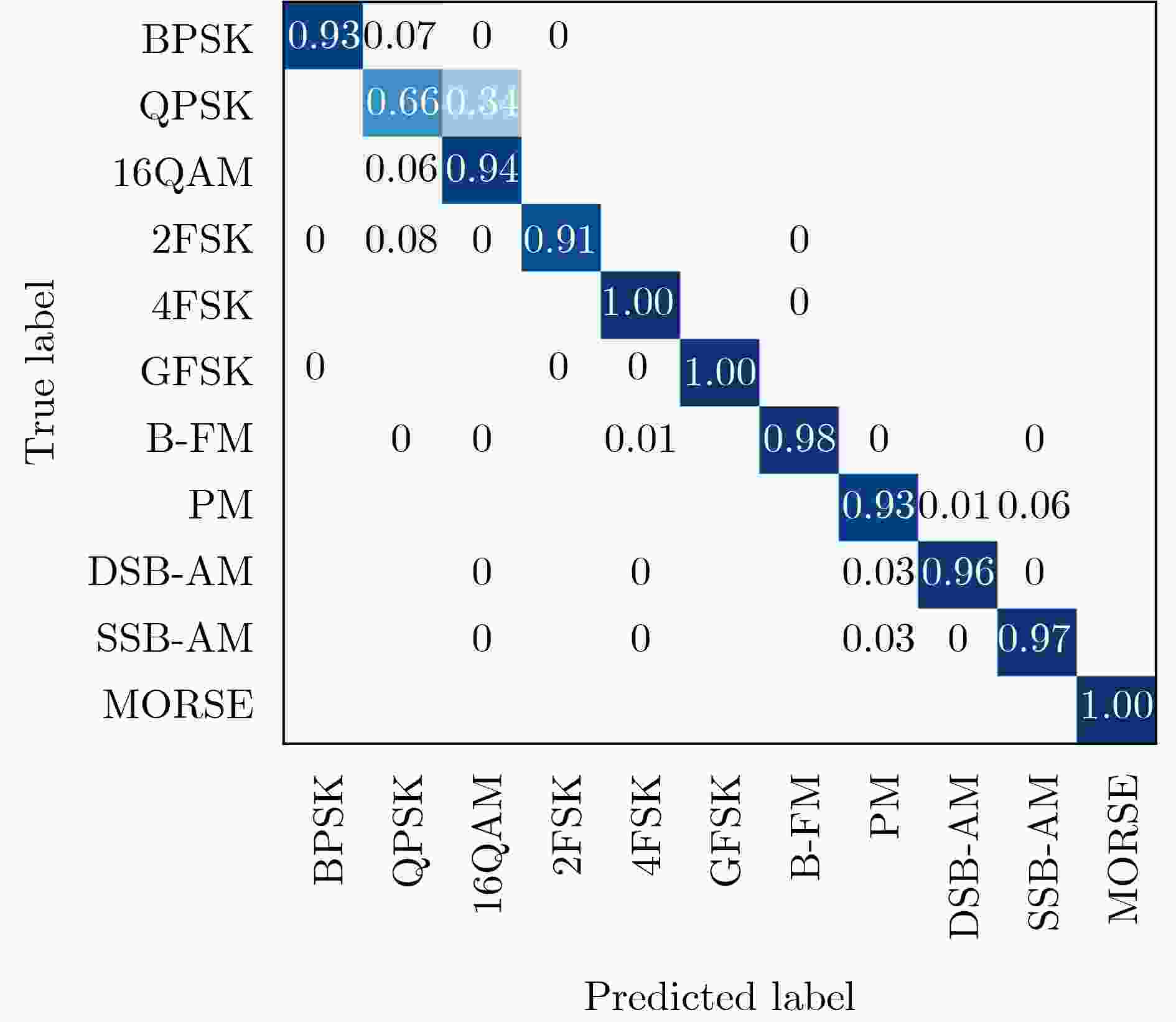
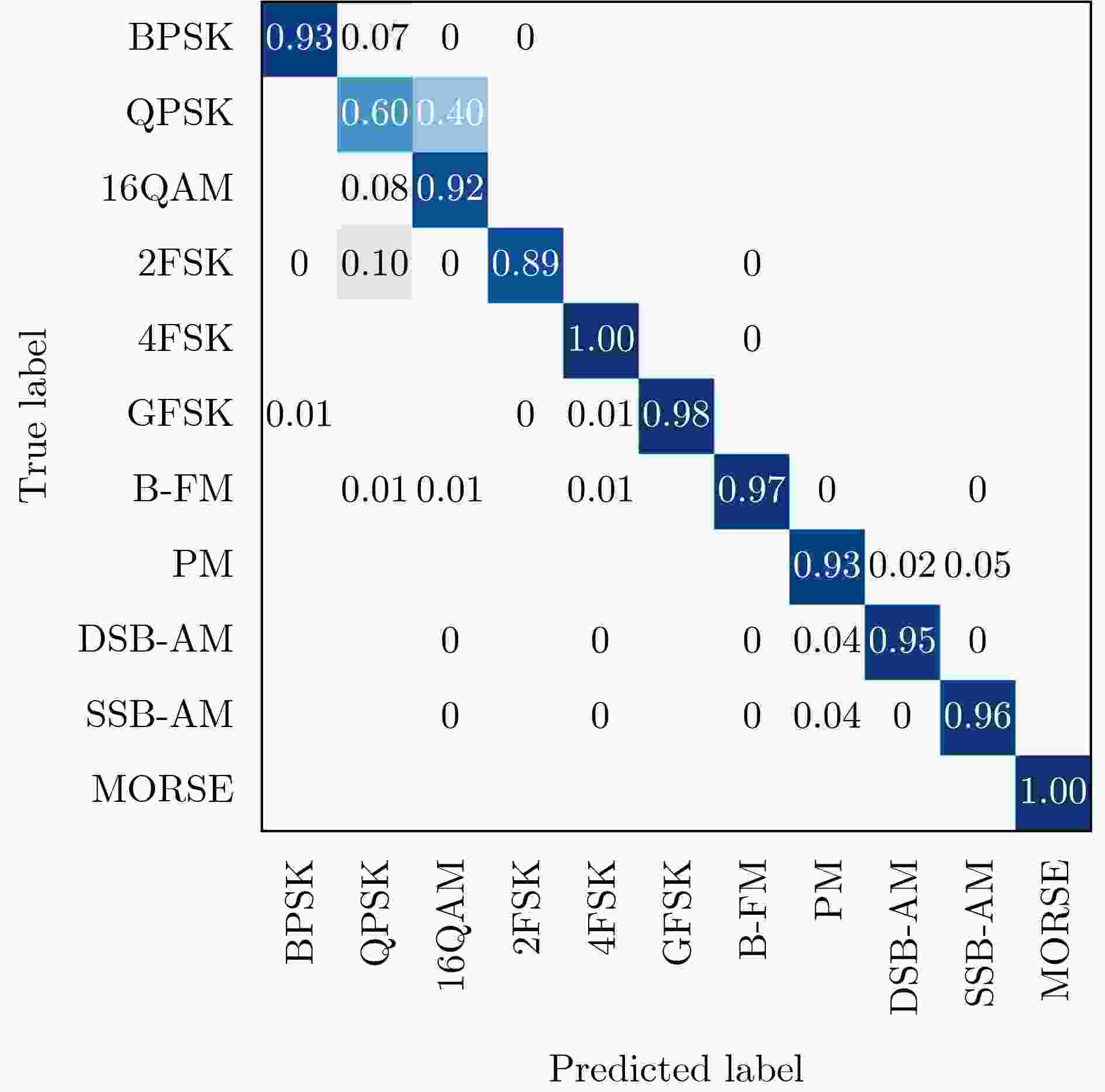
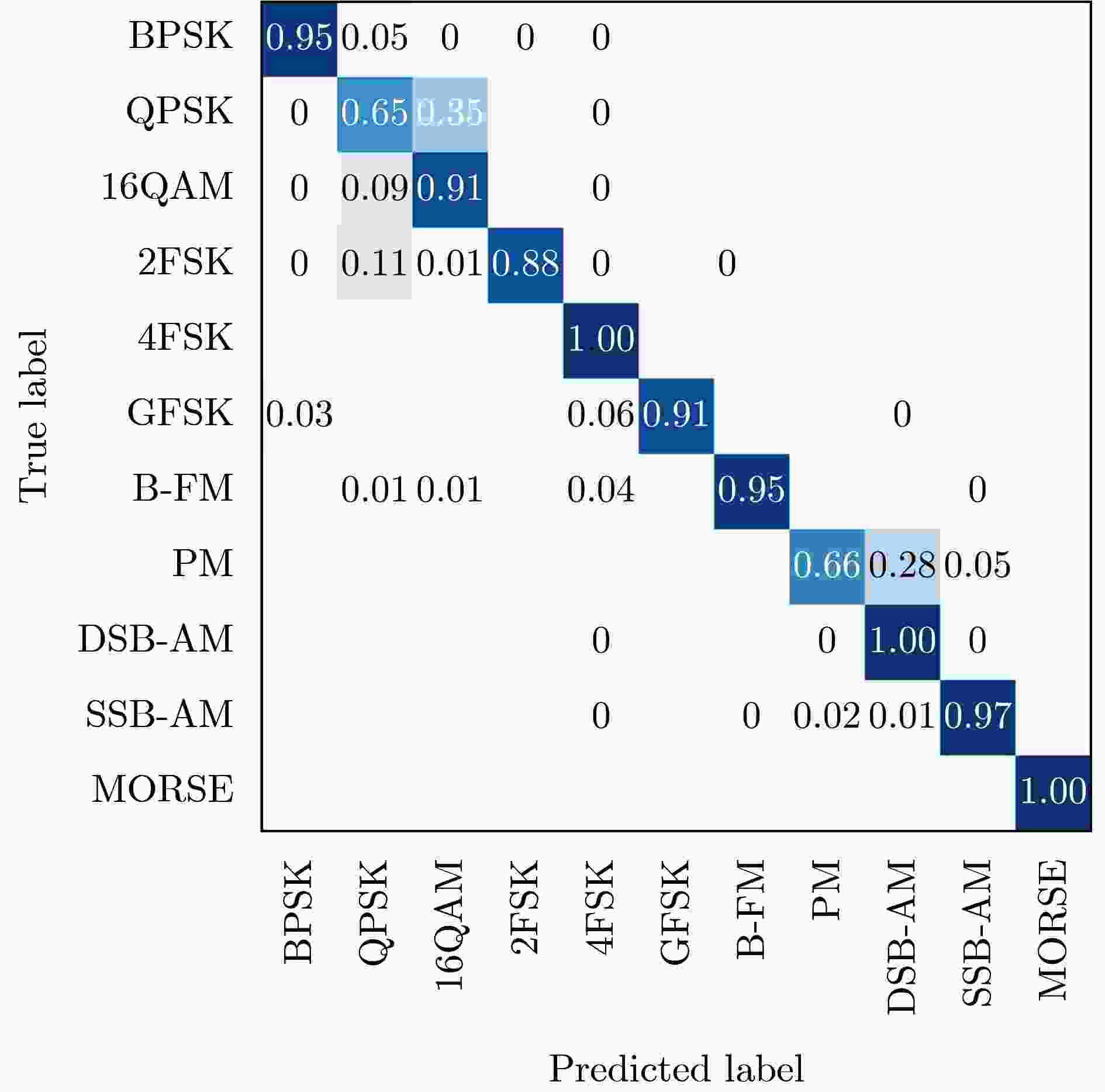
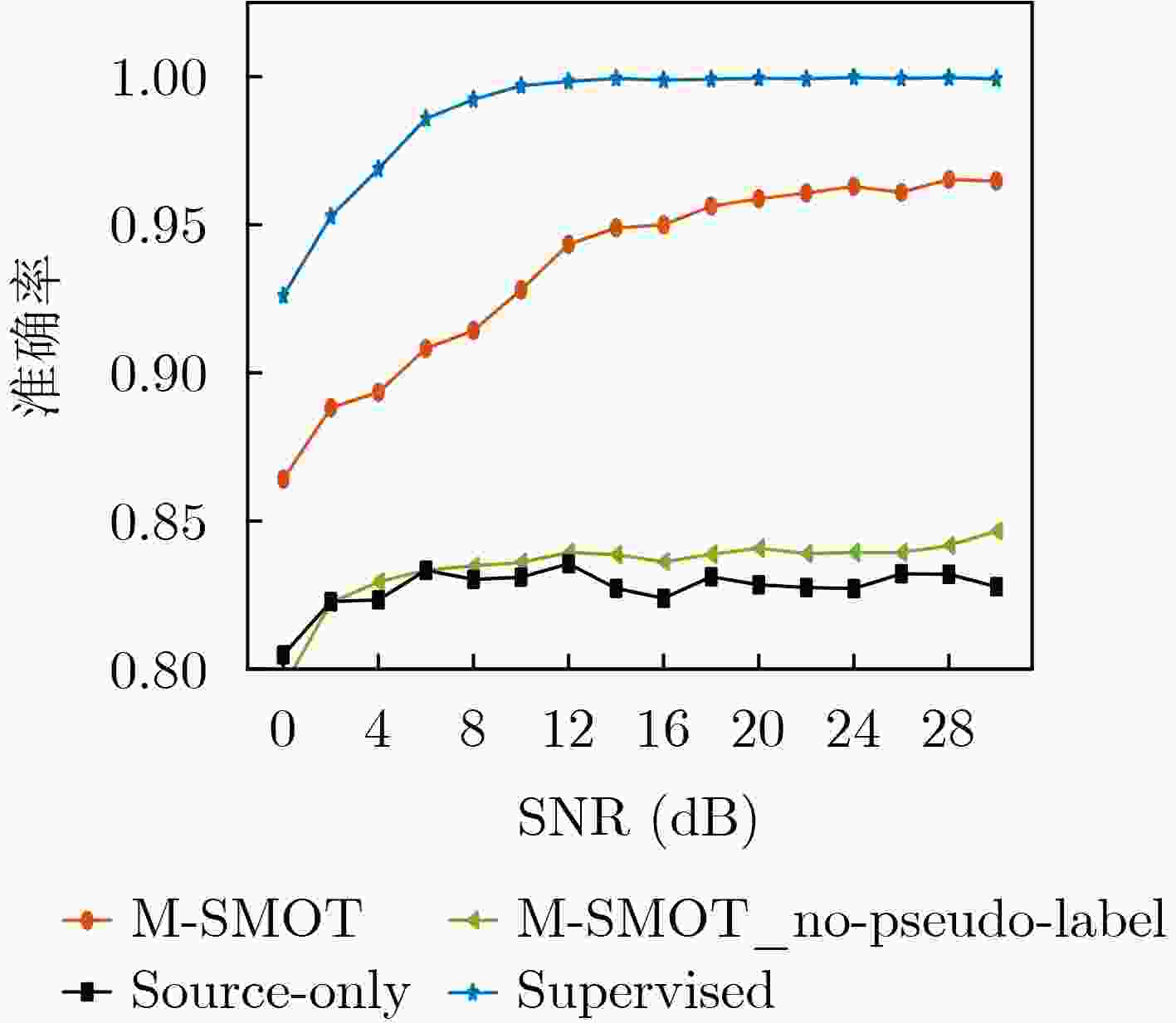
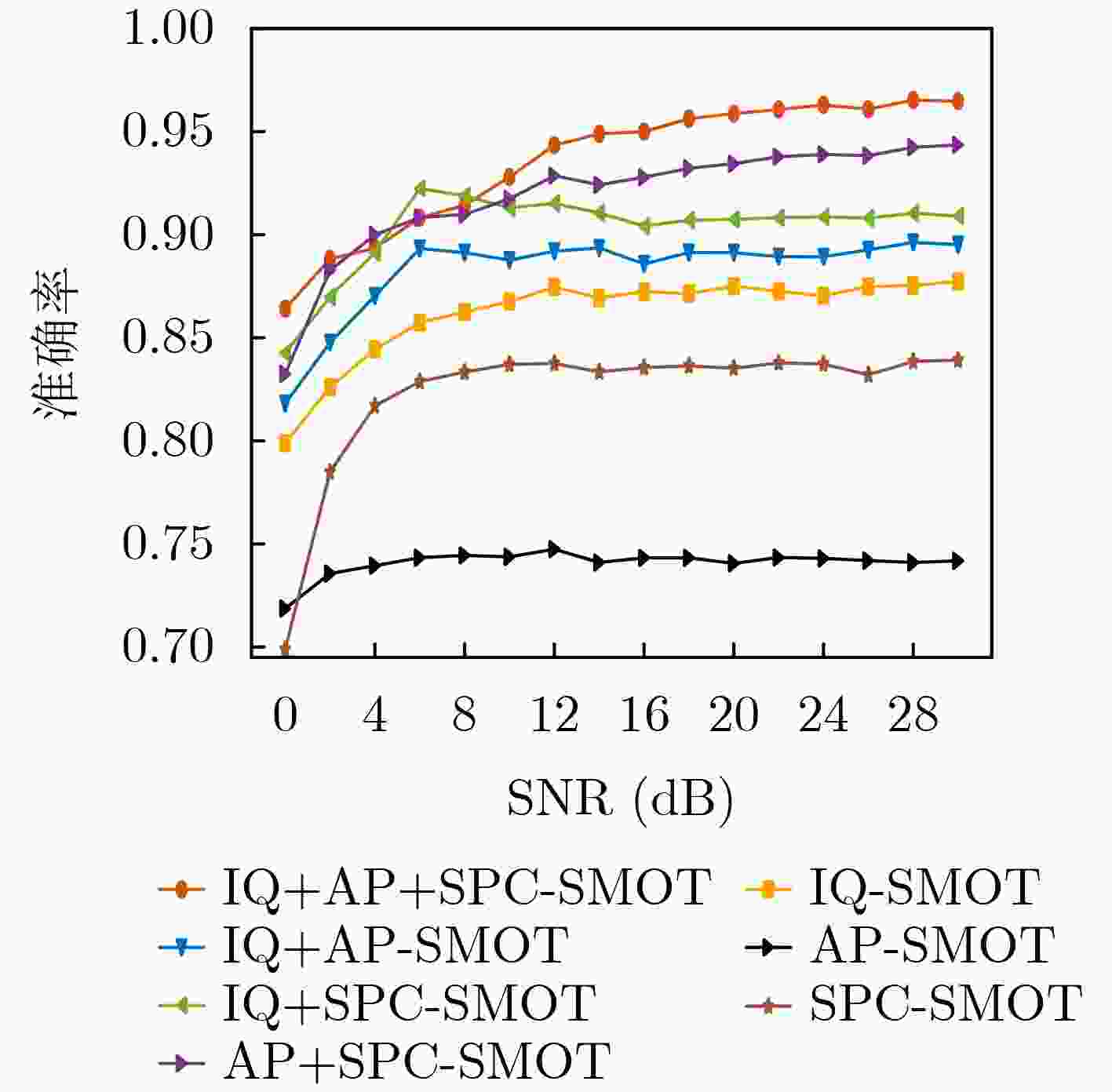
Objective Existing short-wave signal modulation recognition methods based on the supervised learning paradigm typically assume that training data (source domain) and test data (target domain) follow identical distributions. However, short-wave channels are susceptible to ionospheric variations, leading to significant distribution discrepancies across domains, which consequently causes model performance degradation. Furthermore, deployment on the edge side of unmanned platforms is constrained by limited device resources, scarce labeled samples, and data privacy requirements. To address these challenges, a lightweight recognition method based on source-model transfer is proposed in this paper, enabling privacy-preserving model adaptation without the need to access source domain data. Methods A multi-modal source-model transfer framework (M-SMOT) is developed, which utilizes information maximization loss and self-supervised pseudo-labeling techniques to facilitate model adaptation without revisiting source domain data. This approach achieves effective cross-channel recognition of short-wave modulation signals while reducing computational resource consumption and preserving data privacy. Additionally, multi-modal information—comprising in-phase/quadrature (I/Q) components, amplitude-phase (AP) characteristics, and spectral features—is fused to leverage complementary feature representations, thereby enhancing the robustness of the recognition network against complex channel variations. Results and Discussions Experimental results demonstrate that the recognition performance of the proposed method consistently surpasses that of the Source-Only baseline across six cross-channel scenarios, with improvements ranging from 0.31% to 10.81% ( Table 1 ). In terms of few-shot adaptation, average recognition accuracies are maintained at 98.3% and 96% relative to the full-sample baseline, even when target domain training samples are reduced to 10% and 1%, respectively (Fig. 12 ). Ablation studies verify the necessity and effectiveness of the self-supervised pseudo-labeling module (Fig. 16 ) and the multi-modal fusion strategy (Fig. 17 ), confirming that both components contribute to the overall performance. Furthermore, the lightweight advantages are quantified: the method requires zero storage for source data, exhibits a peak memory consumption of only 6.00 MB, and achieves convergence within a single fine-tuning epoch (Table 2 ). These findings validate the capability of the proposed mechanism to mitigate domain discrepancies and protect privacy under resource-constrained conditions.Conclusions The M-SMOT method successfully integrates data privacy protection, source model adaptation, few-shot generalization, and low resource consumption. Consequently, it provides a practical solution for cross-channel modulation recognition in short-wave communications, demonstrating significant potential for deployment on resource-limited edge devices. -
Key words:
- Short-wave communication /
- Modulation recognition /
- Source-model transfer /
- Lightweight /
- Multi-modal fusion /
- Few-shot
-
表 1 不同跨信道场景下各方法的平均识别准确率(%)
纬度 源域信道状态 目标域信道状态 有监督学习 Source-Only M-SMOT 低纬度 静态环境 中等环境 98.0 82.7 93.6 恶劣环境 98.7 96.5 96.8 中纬度 静态环境 中等环境 98.7 88.2 92.9 恶劣环境 98.9 83.4 94.0 高纬度 静态环境 中等环境 98.7 91.9 97.9 恶劣环境 98.8 94.8 96.8 -
[1] 郑庆河, 李秉霖, 于治国, 等. 深度学习使能的自动调制分类技术研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(11): 4096–4111. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250674.ZHENG Qinghe, LI Binglin, YU Zhiguo, et al. Research progress of deep learning enabled automatic modulation classification technology[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(11): 4096–4111. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250674. [2] O’SHEA T J, CORGAN J, and CLANCY T C. Convolutional radio modulation recognition networks[C]. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Engineering Applications of Neural Networks, Aberdeen, UK, 2016: 213–226. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-44188-7_16. [3] O’SHEA T J, ROY T, and CLANCY T C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(1): 168–179. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2797022. [4] SUN Xiaochuan, WU Changcheng, LI Yingqi, et al. Toward interference-tolerant automatic modulation recognition via multi-stage feature extraction network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(8): 12629–12640. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3555769. [5] 郑庆河, 刘方霖, 余礼苏, 等. 基于改进Kolmogorov-Arnold混合卷积神经网络的调制识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(8): 2584–2597. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250161.ZHENG Qinghe, LIU Fanglin, YU Lisu, et al. An improved modulation recognition method based on hybrid Kolmogorov-Arnold convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(8): 2584–2597. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250161. [6] LAI Fan, WANG Chengxiang, HUANG Jie, et al. A novel 3D non-stationary massive MIMO channel model for shortwave communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2023, 71(9): 5473–5486. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3281875. [7] 李国军, 马欢, 叶昌荣, 等. 基于Watterson模型的短波航空移动信道建模与仿真[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 332–338. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200890.LI Guojun, MA Huan, YE Changrong, et al. Modeling and simulation of HF aeronautical mobile channel based on Watterson model[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 332–338. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200890. [8] ZHUANG Fuzhen, QI Zhiyuan, DUAN Keyu, et al. A comprehensive survey on transfer learning[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(1): 43–76. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2020.3004555. [9] LONG Mingsheng, CAO Yue, WANG Jianmin, et al. Learning transferable features with deep adaptation networks[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 97–105. [10] TZENG E, HOFFMAN J, SAENKO K, et al. Adversarial discriminative domain adaptation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2962–2971. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.316. [11] ZHOU Quan, ZHANG Ronghui, MU Junsheng, et al. AMCRN: Few-shot learning for automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26(3): 542–546. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3135688. [12] 许华, 苟泽中, 蒋磊, 等. 适用于样本分布差异的迁移学习调制识别算法[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 49(4): 127–132. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.210422.XU Hua, GOU Zezhong, JIANG Lei, et al. Transfer learning modulation recognition algorithm for differences in sample distribution[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science & Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2021, 49(4): 127–132. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.210422. [13] 史蕴豪, 许华, 单俊杰. 基于域适应神经网络的调制方式分类方法[J]. 空军工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 21(5): 69–75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2020.05.011.SHI Yunhao, XU Hua, and SHAN Junjie. A modulation recognition method based on domain adaptive neural network[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 21(5): 69–75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2020.05.011. [14] BU Ke, HE Yuan, JING Xiaojun, et al. Adversarial transfer learning for deep learning based automatic modulation classification[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 880–884. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2991875. [15] DENG Wen, WANG Xiang, HUANG Zhitao, et al. Modulation classifier: A few-shot learning semi-supervised method based on multimodal information and domain adversarial network[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(2): 576–580. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3225566. [16] 王祯, 刘伟, 卢万杰, 等. 面向低信噪比序列的多模态联合自动调制方式识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(12): 5082–5093. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250594.WANG Zhen, LIU Wei, LU Wanjie, et al. Multi-modal joint automatic modulation recognition method towards low SNR sequences[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(12): 5082–5093. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250594. [17] 王华华, 张睿哲, 黄永洪. 基于生成式对抗网络和多模态注意力机制的扩频与常规调制信号识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(4): 1212–1221. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230518.WANG Huahua, ZHANG Ruizhe, and HUANG Yonghong. Spread spectrum and conventional modulation signal recognition method based on generative adversarial network and multi-modal attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(4): 1212–1221. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230518. [18] WU Xueyu, TYRRELL A M, and KO Y. Federated K-means clustering for adaptive OFDM-IM[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2023, 27(10): 2648–2651. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2023.3308334. -





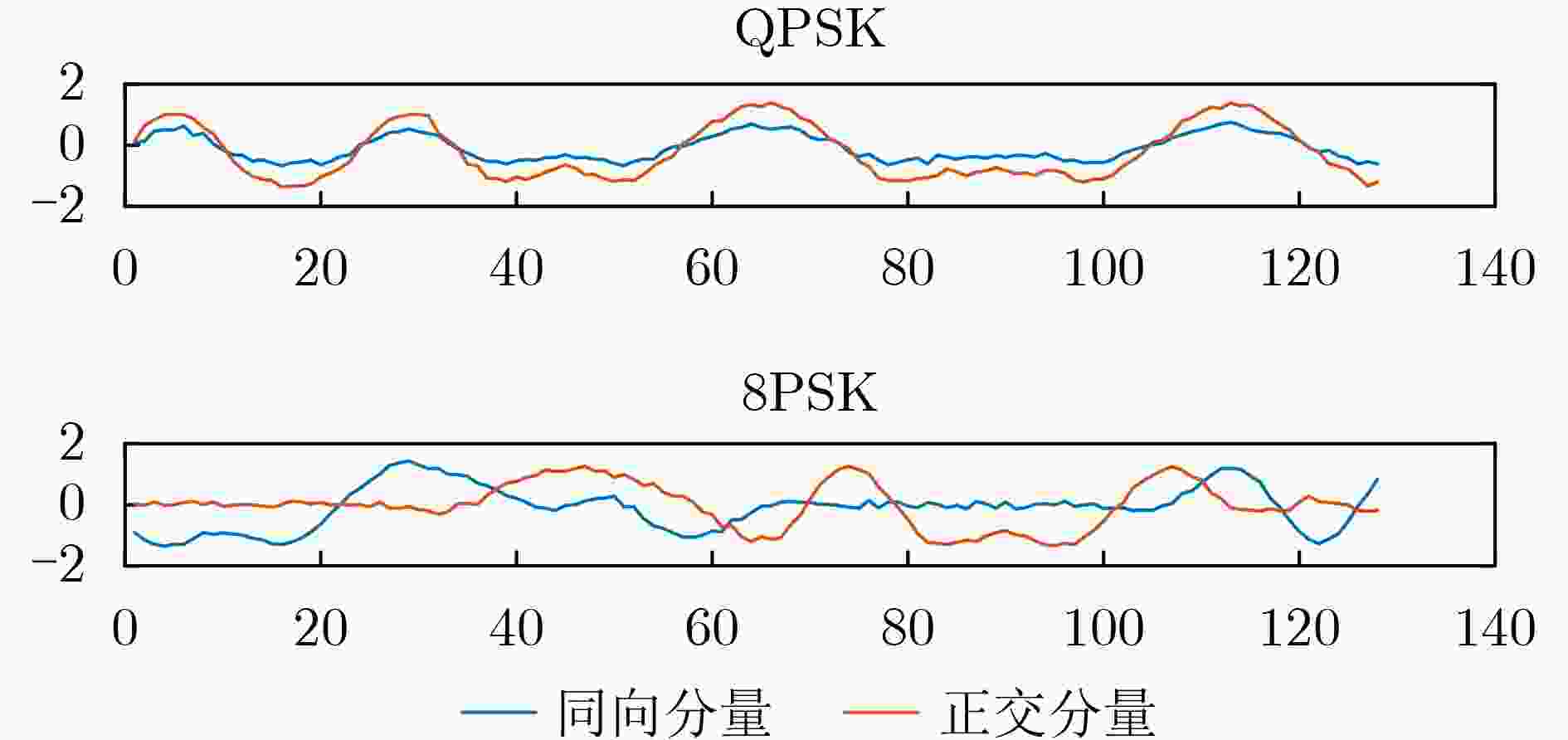
 下载:
下载:
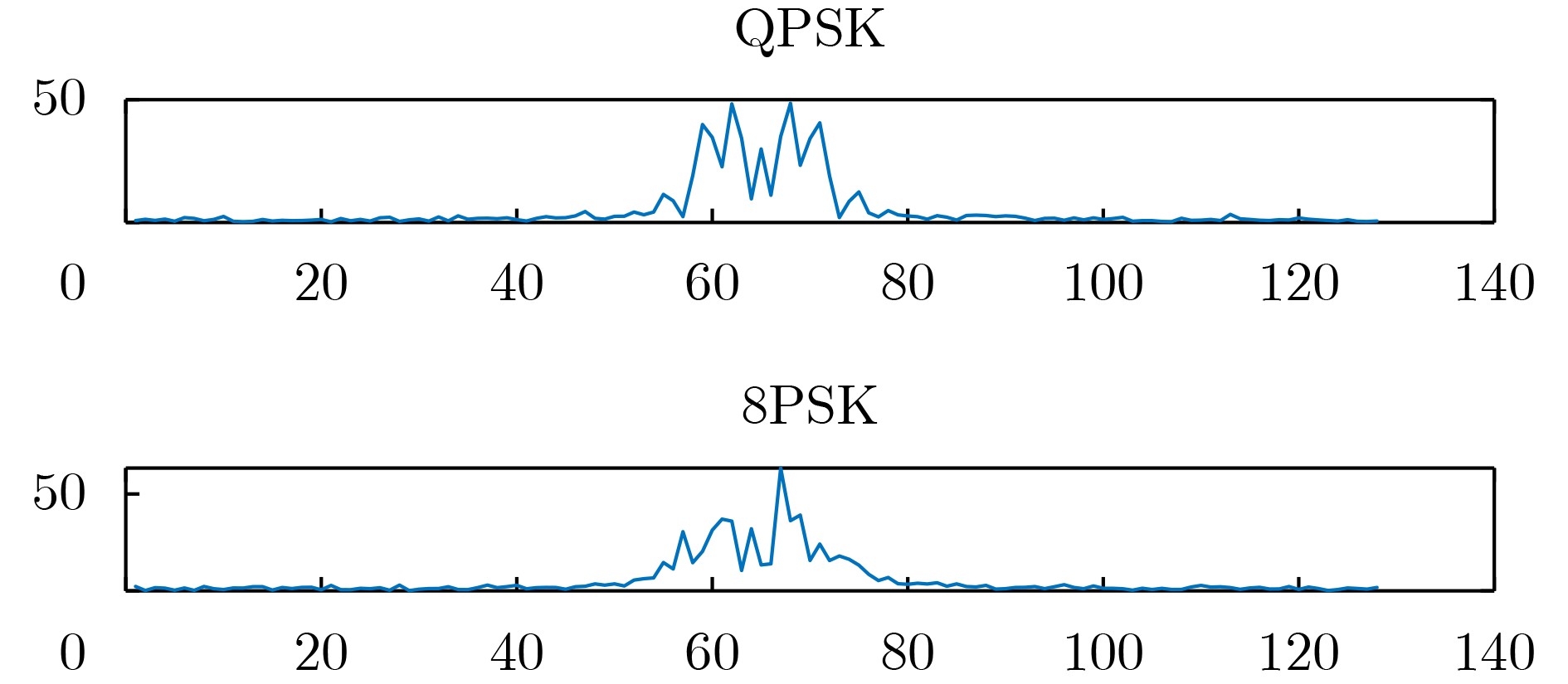
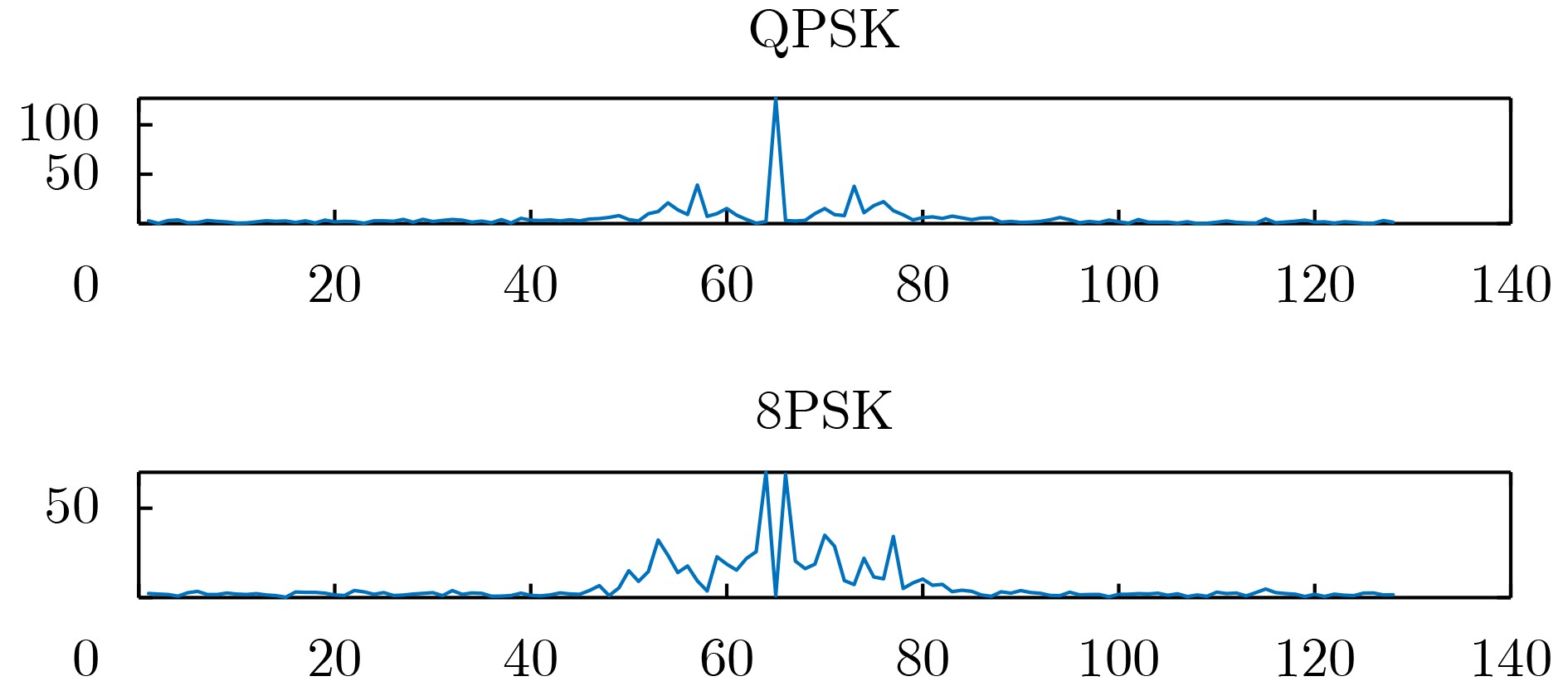
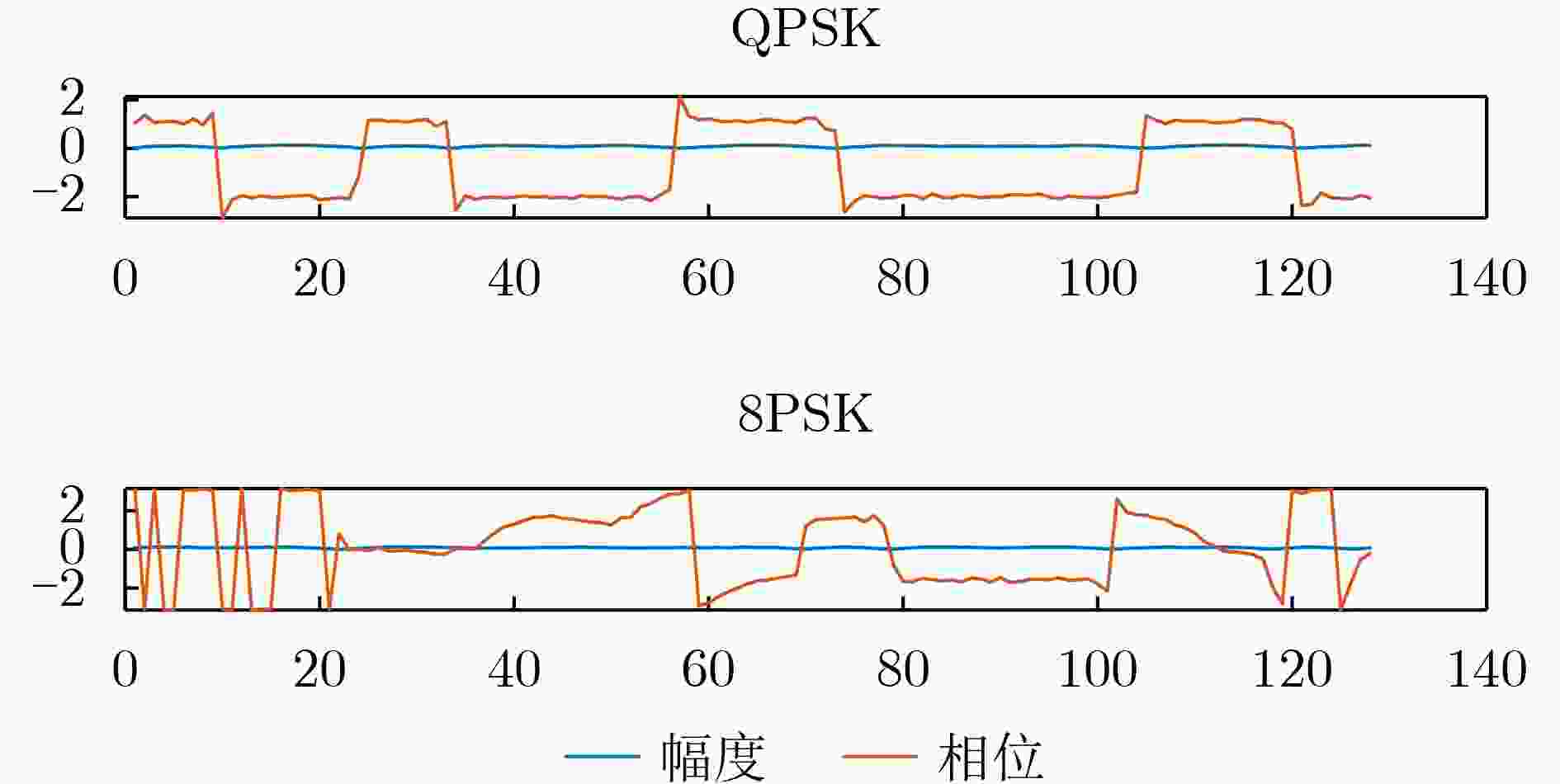


 下载:
下载:
