A Deep Reinforcement Learning Enhanced Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search for Imaging Satellite Scheduling
-
摘要: 卫星调度问题(Satellite Scheduling Problem, SSP)是典型的NP-hard组合优化问题,其目标是在满足一系列复杂物理和运行约束的条件下,最大化观测收益或完成任务数量。自适应大邻域搜索(Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search, ALNS)是求解此类问题的有效元启发式算法,其性能高度依赖于破坏与修复算子的选择策略。传统ALNS算法通常采用基于历史表现的启发式计分机制来调整算子选择概率,这种机制受参数影响较大且无法动态适应搜索过程中的复杂状态变化。为解决此问题,该文提出了一种基于深度强化学习(Deep Reinforcement Learning, DRL)的自适应大邻域搜索算法(DR-ALNS)。该算法将算子选择过程建模为一个马尔可夫决策过程,智能体利用深度强化学习在每次迭代中根据当前解的状态动态选择最合适的破坏与修复算子。通过端到端的学习,DRL智能体能够学习到一种隐式的、高效的算子选择策略,从而更好地引导搜索方向,提升算法的全局探索与局部开发能力。通过在标准的卫星调度问题测试集上进行实验,可以看出DR-ALNS算法产生的解的质量优于传统ALNS及其他算法。Abstract:
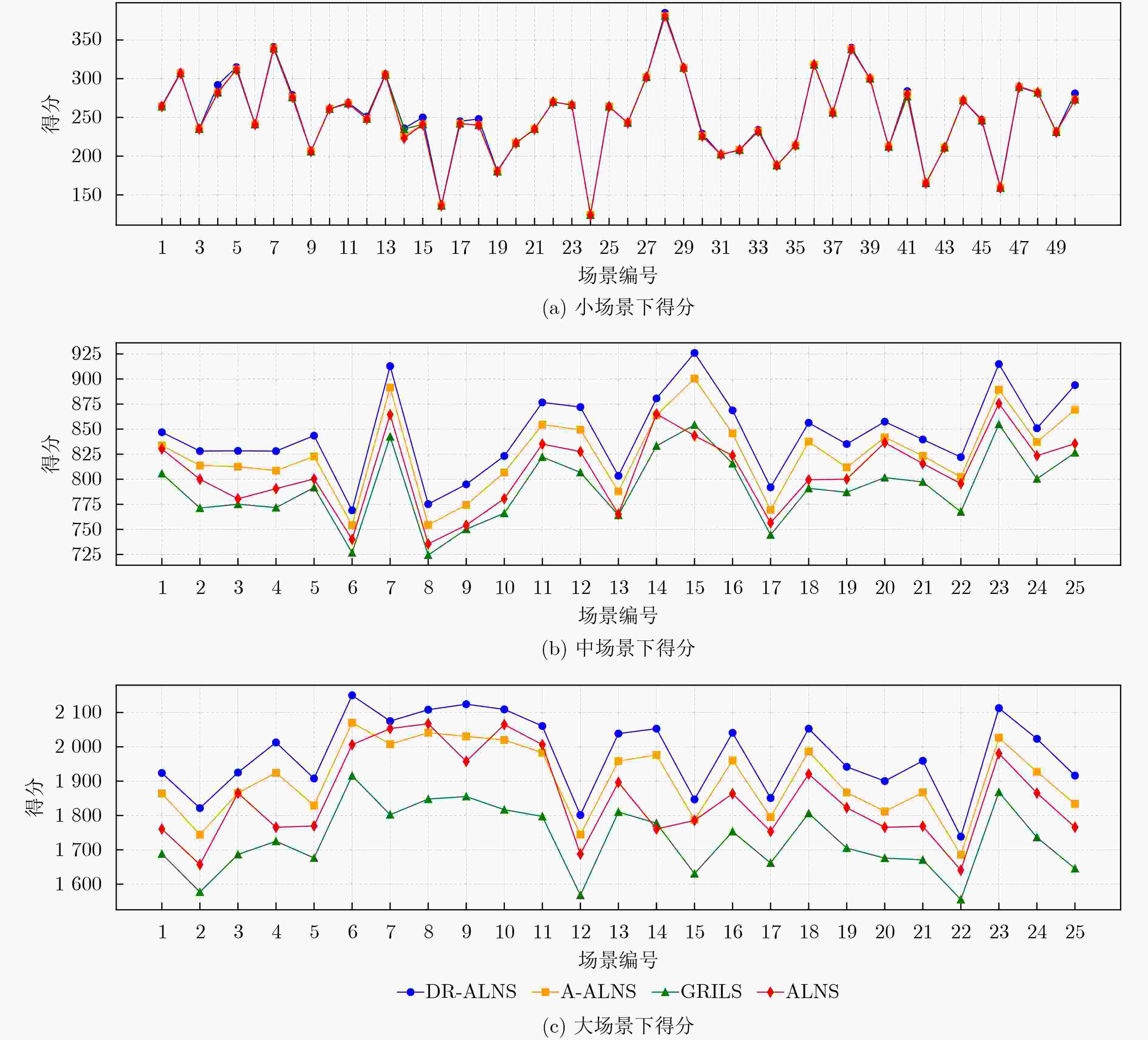
Objective The Satellite Scheduling Problem (SSP) is a typical NP-hard combinatorial optimization problem. The objective is to maximize observation benefits or the number of completed tasks under complex physical and operational constraints. Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search (ALNS) is an effective metaheuristic for this class of problems; however, its performance strongly depends on the selection of destroy and repair operators. Traditional ALNS methods usually employ heuristic scoring mechanisms based on historical performance to adjust operator selection probabilities. These mechanisms are sensitive to parameter settings and cannot adapt dynamically to complex state changes during the search process. This study aims to address this limitation and proposes an improved algorithm to enhance ALNS performance for SSP. Methods To achieve this objective, a Deep Reinforcement Learning based Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search algorithm (DR-ALNS) is proposed. The operator selection process is formulated as a Markov Decision Process (MDP). A Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) agent is employed to select destroy and repair operators dynamically according to the current solution state at each iteration. Through end-to-end learning, the DRL agent acquires an implicit and efficient operator selection strategy. This strategy guides the search process and improves both global exploration and local exploitation. Experiments are conducted on a standard satellite scheduling test suite, and the results indicate that DR-ALNS outperforms conventional ALNS and other comparison algorithms in solution quality and convergence speed. Results and Discussions To verify the effectiveness of DR-ALNS, experiments are conducted on 100 scenarios selected from the Tianzhi-Cup dataset. These scenarios are classified into small, medium, and large categories based on the number of task strips. The experimental results are summarized in Table 4, and detailed comparisons of average scores across scenario types are reported in Table 5. In small scenarios, the average score of DR-ALNS is 0.6% higher than that of the comparison algorithms. In medium scenarios, the average score exceeds that of the second-ranked algorithm by 2.3%. In large scenarios, DR-ALNS outperforms the second-ranked algorithm by 3.8%. Conclusions A DR-ALNS model for the SSP is proposed. By integrating DRL, destroy and repair operator selection and destruction coefficient settings in ALNS are dynamically guided through iterative learning of solution states. This strategy accelerates convergence toward high-quality solutions. Experiments on the Tianzhi-Cup dataset confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method, with clear advantages over A-ALNS and GRILS, particularly in large-scale satellite cluster scheduling. Future studies will evaluate the method in ultra-large-scale scenarios to assess stability and will explore adaptation to dynamic constraints to enhance practical applicability. -
表 1 符号说明
符号 描述 $ \text{sa{t}}_{j} $ 卫星集合中的第$ j $个卫星 $ {O}_{ij} $ 卫星$ \text{sa{t}}_{j} $可以观测到任务$ {m}_{i} $的窗口集合 $ {O}_{ijk} $ $ {O}_{ij} $中的第$ k $个时间窗 $ \text{s{t}}_{ijk} $ $ {O}_{ijk} $的开始时间 $ \text{e{t}}_{ijk} $ $ {O}_{ijk} $的结束时间 $ \text{du{r}}_{i} $ 任务$ {m}_{i} $的持续观测时间 $ \text{pri}_{i} $ 任务$ {m}_{i} $的收益值 $ \text{tran}{{\mathrm{s}}}_{i{{i}^{\prime}}} $ 卫星从一个任务$ {m}_{i} $转换到任务$ {m}_{{{i}^{\prime}}} $所需的转换时间 $ {x}_{ijk} $ 用来指示$ {m}_{i} $是否被执行,值为1时表示被执行,
为0时表示未被执行$ X $ 时间窗的决策空间 $ \text{s{t}}_{i} $ 执行任务$ {m}_{i} $的开始时间 $ \text{e{t}}_{i} $ 执行任务$ {m}_{i} $的结束时间 $ \text{SE} $ 计划执行任务集合 1 DR-ALNS
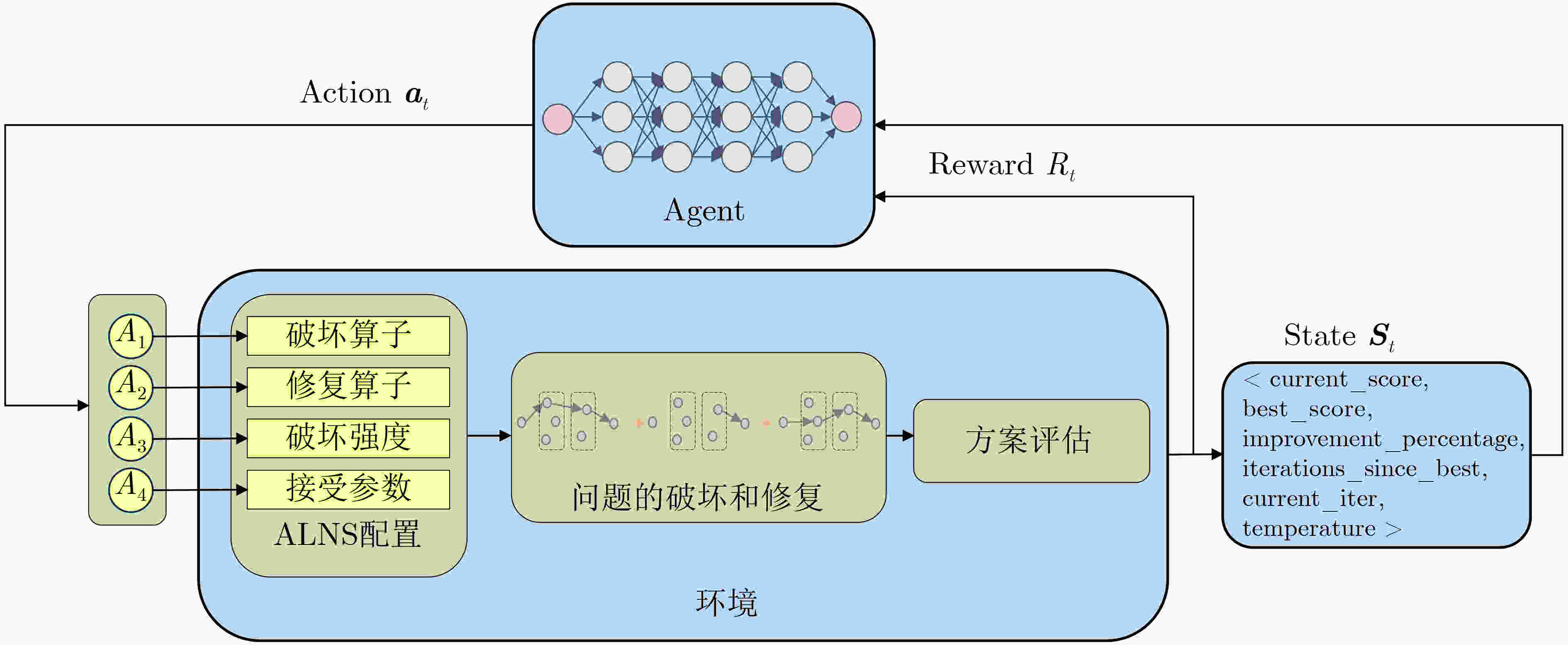
输入:步骤数M、策略、破坏算子集合、修复算子集合、问题实例 初始化:最优解$ {\boldsymbol{x}}\mathrm{_{best}} $=初始解$ {\boldsymbol{x}} $,初始状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}}_t=\text{initial} $$ \mathrm{state} $ (1) while 停止准则未满足 do (2) for t=0 to M–1 do (3) 基于当前状态$ {{\boldsymbol{s}}}_{t} $通过策略$ {\pi }_{\theta } $选择动作$ {{\boldsymbol{a}}}_{t} $ (4) 基于动作$ {{\boldsymbol{a}}}_{t} $,选择破坏算子$ d $和修复算子$ r $,并配置破
坏强度与接受准则(5) $ {{\boldsymbol{x}}}_{t}=r(d({\boldsymbol{x}})) $ (6) if $ \mathrm{\text{accept}}({\boldsymbol{x}}_t,{\boldsymbol{x}}) $then (7) $ {\boldsymbol{x}}={{\boldsymbol{x}}}_{t} $ (8) if 新解成本更低then (9) $ {\boldsymbol{x}}\mathrm{_\text{best}}={\boldsymbol{x}}_t $ (10) 更新状态$ {{\boldsymbol{s}}}_{t} $并获取奖励$ {R}_{t} $ (11) (训练模式下)更新策略$ {\pi }_{\theta } $ (12) return (部署模式下)$ {\boldsymbol{x}}\mathrm{_{best}} $ 表 2 DR-ALNS的状态空间特征
特征 描述 current_score 这是当前解的得分 best_score 算法从开始到目前为止找到的
历史最优解的得分improvement_percentage 表示当前解相对于历史最优解的
提升百分比iterations_since_best 自上一次找到新的最优解以来,
已经过去了多少次迭代current_iter 当前的迭代次数 temperature 模拟退火接受准则中当前的温度值 表 3 PPO参数设置
参数 取值 n_steps 2 048 batch_size 64 n_epochs 10 gamma 0.99 gae_lambda 0.95 clip_range 0.2 learning_rate 0.0003 vf_coef 0.5 max_grad_norm 0.5 表 4 得分分析
算法 小场景平均得分 中场景平均得分 大场景平均得分 DR-ALNS 252.18 845.59 1979.73 ALNS 250.62 820.76 1870.65 A-ALNS 250.54 826.25 1904.31 GRILS 250.66 791.68 1730.04 表 5 各场景中获得最优解迭代次数和运行时间
算法 小场景 中场景 大场景 迭代次数 运行时间(s) 迭代次数 运行时间(s) 迭代次数 运行时间(s) DR-ALNS 120.6 3.687 202.5 7.548 661.8 16.845 ALNS 158.6 4.405 461.5 12.365 1787 32.684 A-ALNS 142.8 4.318 350.5 10.625 1368.4 30.685 GRILS 128.1 4.139 384.9 10.983 1108.6 29.584 -
[1] KASLOW D. Planning and scheduling of earth observing satellites[C]. 2007 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2007: 1-12.DOI: 10.1109/AERO.2007.352824. [2] CHEN Ming, DU Yonghao, TANG Ke, et al. Learning to construct a solution for the agile satellite scheduling problem with time-dependent transition times[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(10): 5949–5963. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3411640. [3] LIU Quanyong, PENG Jiangtao, ZHANG Genwei, et al. Deep contrastive learning network for small-sample hyperspectral image classification[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 3: 0025. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0025. [4] HAN Zonghao, ZHANG Ziye, ZHANG Shun, et al. Aerial visible-to-infrared image translation: Dataset, evaluation, and baseline[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 3: 0096. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0096. [5] MEI Shaohui, LIAN Jiawei, WANG Xiaofei, et al. A comprehensive study on the robustness of deep learning-based image classification and object detection in remote sensing: Surveying and benchmarking[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0219. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0219. [6] KRIGMAN S, GRINSHPOUN T, and DERY L. Scheduling of Earth observing satellites using distributed constraint optimization[J]. Journal of Scheduling, 2024, 27(5): 507–524. doi: 10.1007/s10951-024-00816-x. [7] WU Jian, CHEN Yuning, HE Yongming, et al. Survey on autonomous task scheduling technology for Earth observation satellites[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 33(6): 1176–1189. doi: 10.23919/JSEE. 2022.000141. [8] FENG Xiaoen, LI Yuqing, and XU Minqiang.Multi-satellite cooperative scheduling method for large-scaletasks based on hybrid graph neural network andmetaheuristic algorithm[J]. Advanced EngineeringInformatics, 2024, 60: 102362. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2024.102362. [9] PISINGER D and ROPKE S. A general heuristic for vehicle routing problems[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2007, 34(8): 2403–2435. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2005.09.012. [10] DOERR C, DREO J, and KERSCHKE P. Making a case for (Hyper-)parameter tuning as benchmark problems[C]. The Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion, Prague, Czech Republic, 2019: 1755–1764. doi: 10.1145/3319619.3326857. [11] SANTINI A, ROPKE S, and HVATTUM L M. A comparison of acceptance criteria for the adaptive large neighbourhood search metaheuristic[J]. Journal of Heuristics, 2018, 24(5): 783–815. doi: 10.1007/s10732-018-9377-x. [12] WU Guohua, XIANG Zhiqing, WANG Yalin, et al. Improved adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm based on the two-stage framework for scheduling multiple super-agile satellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(5): 7185–7200. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3416427. [13] BENAVIDES-ROBLES M T, VALENCIA-RIVERA G H, CRUZ-DUARTE J M, et al. Robotic mobile fulfillment system: A systematic review[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 16767–16782. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3359434. [14] SHARIAT R and HUANG Kai. A large-scale neighborhood search algorithm for multi-activity tour scheduling problems[J]. Journal of Heuristics, 2024, 30(5): 225–267. doi: 10.1007/s10732-024-09527-0. [15] BOGYRBAYEVA A, MERALIYEV M, MUSTAKHOV T, et al. Machine learning to solve vehicle routing problems: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(6): 4754–4772. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3334976. [16] FENG Guosheng, WANG Hongzhi, and WANG Chunnan. Search for deep graph neural networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 649: 119617. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.119617. [17] WANG Chao, CAO Mingjiu, JIANG Hang, et al. A deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive large neighborhood search for capacitated electric vehicle routing problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2024, 8(5): 3907–3919. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3364966. [18] LAND A H and DOIG A G. An automatic method of solving discrete programming problems[J]. Econometrica, 1960, 28(3): 497–520. doi: 10.2307/1910129. [19] BELLMAN R and KALABA R. Dynamic Programming and Modern Control Theory[M]. New York, USA: Academic Press, 1965: 1–112. [20] ANTUORI V, WOJTOWICZ D T, and HEBRARD E. Solving the agile Earth observation satellite scheduling problem with CP and local search[C]. 31st International Conference on Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming, Glasgow, UK, 2025: 3: 1–3: 22. doi: 10.4230/LIPIcs.CP.2025.3. [21] 赵静, 赵卫虎, 李勇军, 等. 基于改进NSGA-Ⅱ算法的微波/光混合链路中继卫星多目标资源调度算法[J]. 中国激光, 2013, 40(12): 1205003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1205003.ZHAO Jing, ZHAO Weihu, LI Yongjun, et al. Multi-objective resources scheduling algorithm for microwave and laser hybrid links data relay satellite based on improved NSGA-Ⅱ algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2013, 40(12): 1205003. doi: 10.3788/CJL201340.1205003. [22] KANDEPI R, SAINI H, GEORGE R K, et al. Agile earth observation satellite constellations scheduling for large area target imaging using heuristic search[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2024, 219: 670–677. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2024.03.027. [23] WU Jian, SONG Bingyu, ZHANG Guoting, et al. A data-driven improved genetic algorithm for agile earth observation satellite scheduling with time-dependent transition time[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022, 174: 108823. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2022.108823. [24] HAN Chao, GU Yan, WU Guohua, et al. Simulated annealing-based heuristic for multiple agile satellites scheduling under cloud coverage uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 53(5): 2863-2874.DOI: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3218579. [25] HE Lei, LIU Xiaolu, LAPORTE G, et al. An improved adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm for multiple agile satellites scheduling[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2018, 100: 12–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2018.06.020. [26] YAO Feng, CHEN Yingguo, WANG Ling, et al. A bilevel evolutionary algorithm for large-scale multiobjective task scheduling in multiagile earth observation satellite systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(6): 3512–3524. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3359265. [27] CHEN Ming, LI Bohua, XING Lining, et al. DEEM: A differential evolution ensemble method for optimizing agile satellite scheduling[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 272: 126771. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.126771. [28] LIU Xiaolu, LAPORTE G, CHEN Yingwu, et al. An adaptive large neighborhood search metaheuristic for agile satellite scheduling with time-dependent transition time[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2017, 86: 41–53. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2017.04.006. [29] DA ROS F, SOPRANO M, DI GASPERO L, et al. Large language models for combinatorial optimization: A systematic review[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.03637, 2025. [30] LIU Zheng, XIONG WeI, HAN Chi, et al. A multi-pointer network for multiple agile optical satellite scheduling problem[J]. Aerospace, 2024, 11(10): 792. doi: 10.3390/aerospace11100792. [31] CHEN Ming, CHEN Yuning, CHEN Yingwu, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for agile satellite scheduling problem[C]. 2019 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, Xiamen, China, 2019: 126–132. doi: 10.1109/SSCI44817.2019.9002957. [32] CHUN Jie, YANG Wenyuan, LIU Xiaolu, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for the agile earth observation satellite scheduling problem[J]. Mathematics, 2023, 11(19): 4059. doi: 10.3390/math11194059. [33] MAZYAVKINA N, SVIRIDOV S, IVANOV S, et al. Reinforcement learning for combinatorial optimization: A survey[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2021, 134: 105400. doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2021.105400. [34] LONG Yaosong, SHAN Chengjun, SHANG Wei, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based approach with varying-scale generalization for the earth observation satellite scheduling problem considering resource consumptions and supplements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(3): 2572–2585. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3379169. [35] PENG Guansheng, SONG Guopeng, HE Yongming, et al. Solving the agile Earth observation satellite scheduling problem with time-dependent transition times[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(3): 1614–1625. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3031738. -





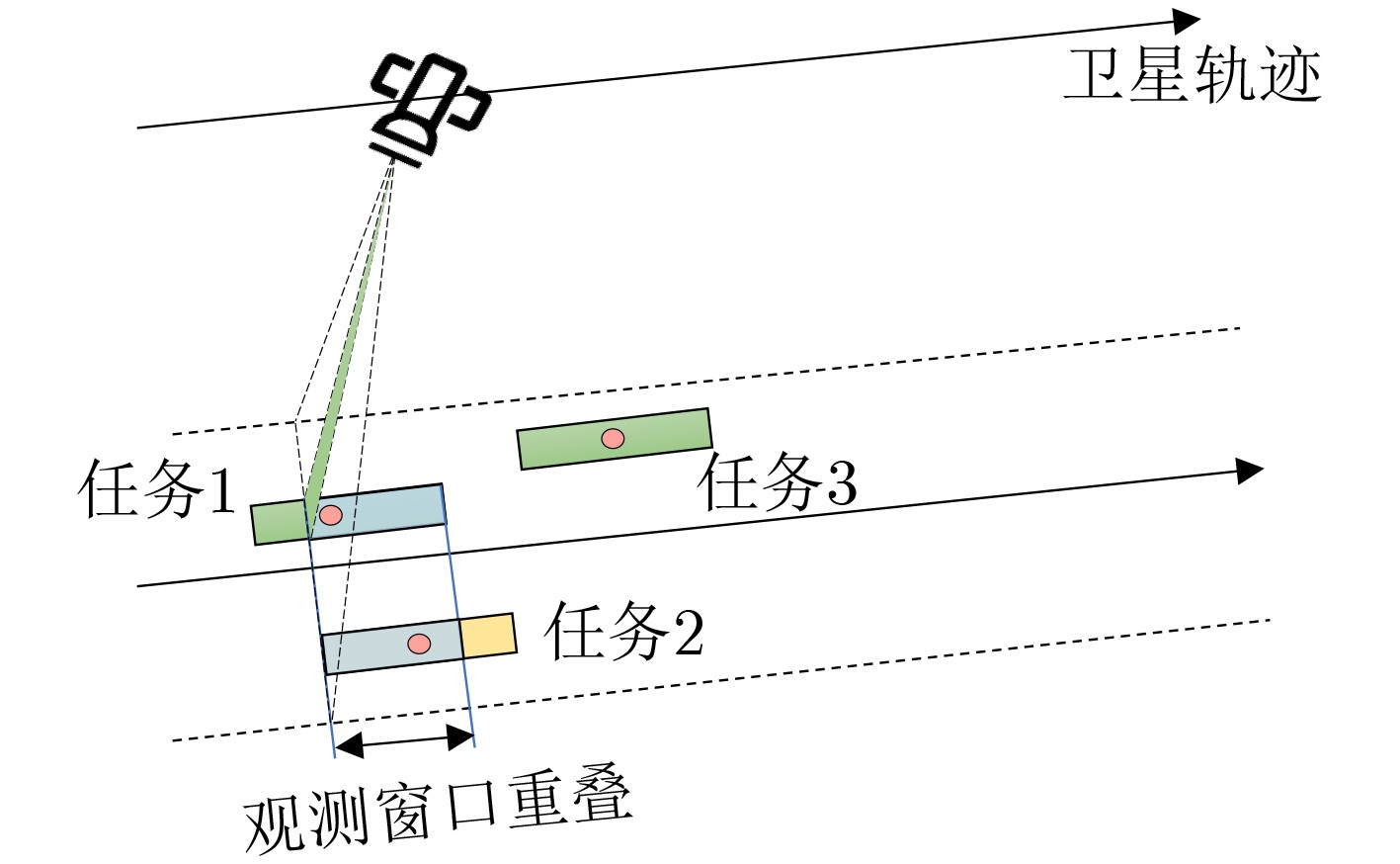
 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
