Few-Shot Remote Sensing Image Classification Based on Parameter-Efficient Vision Transformer and Multimodal Guidance
-
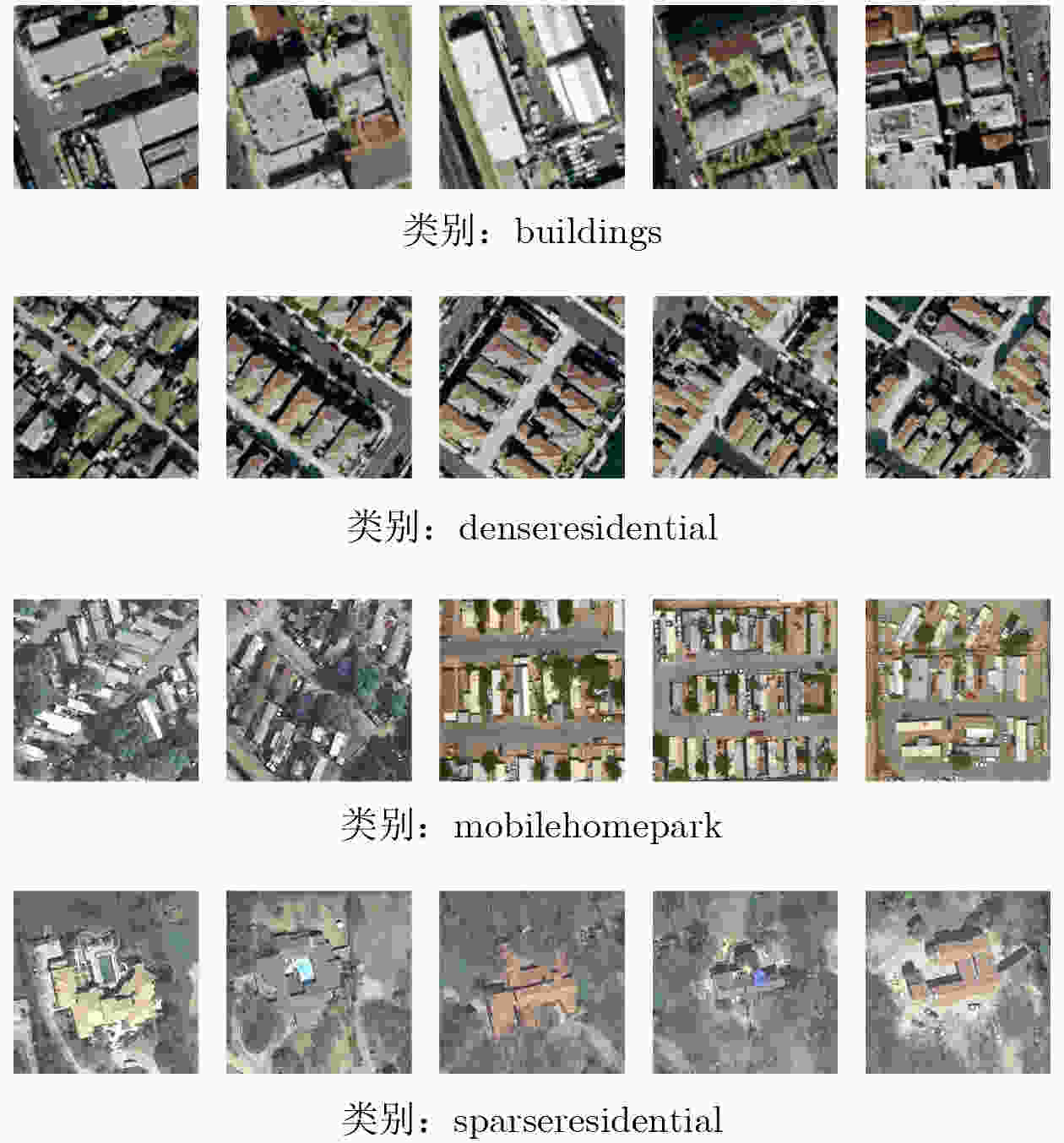
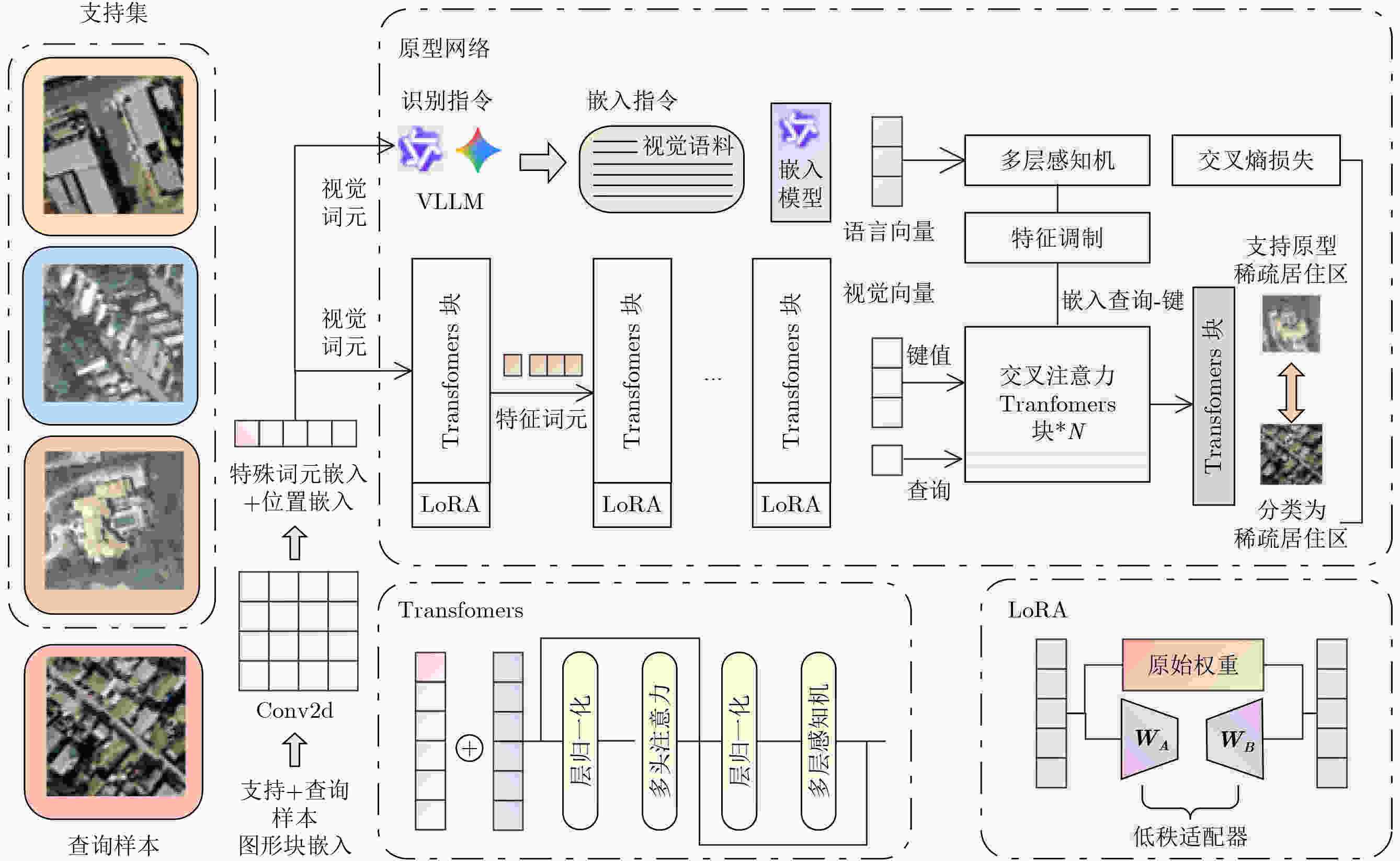
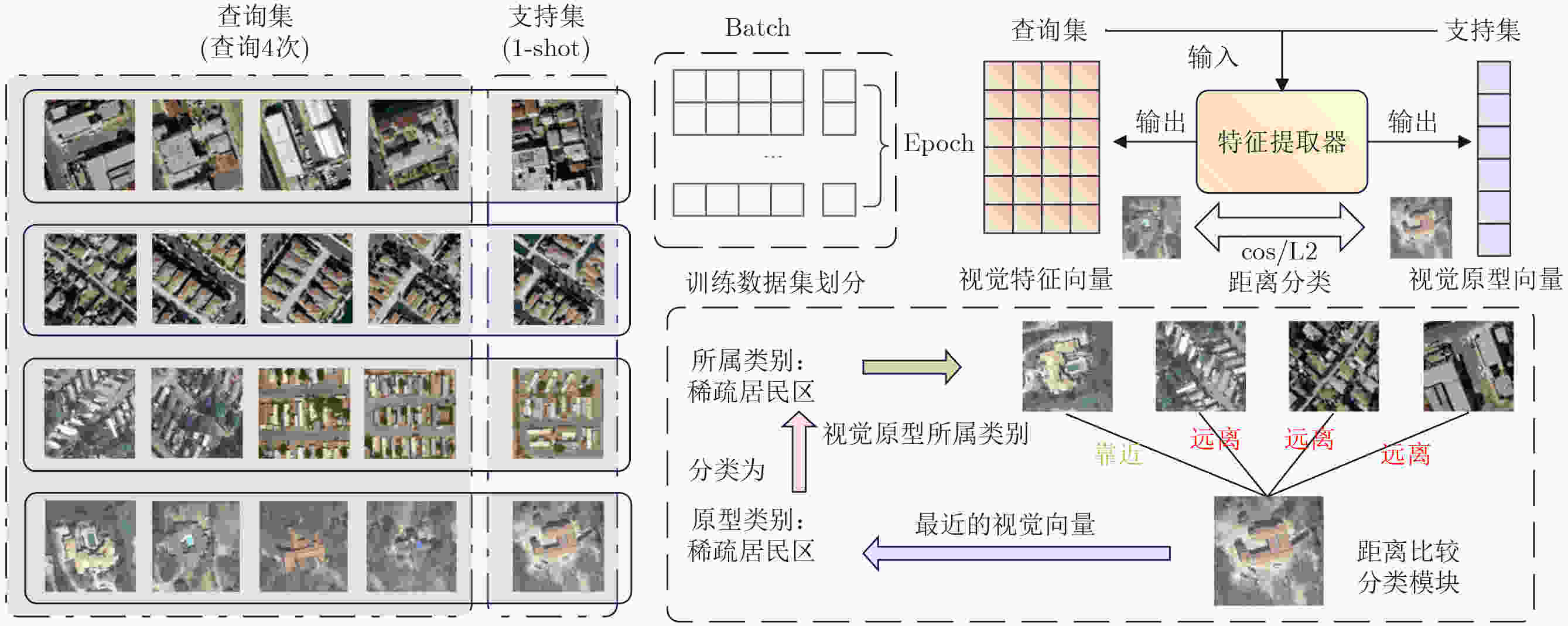
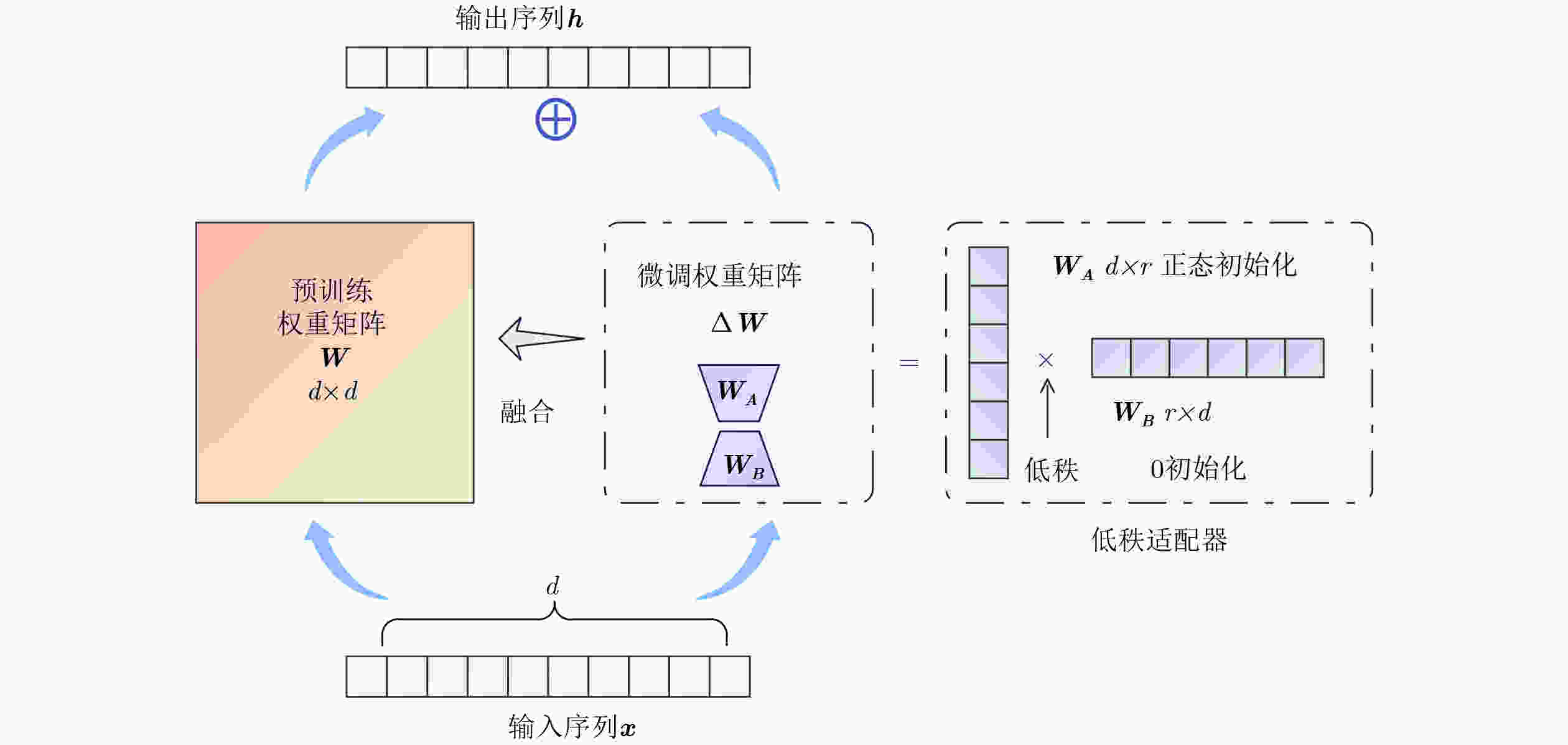
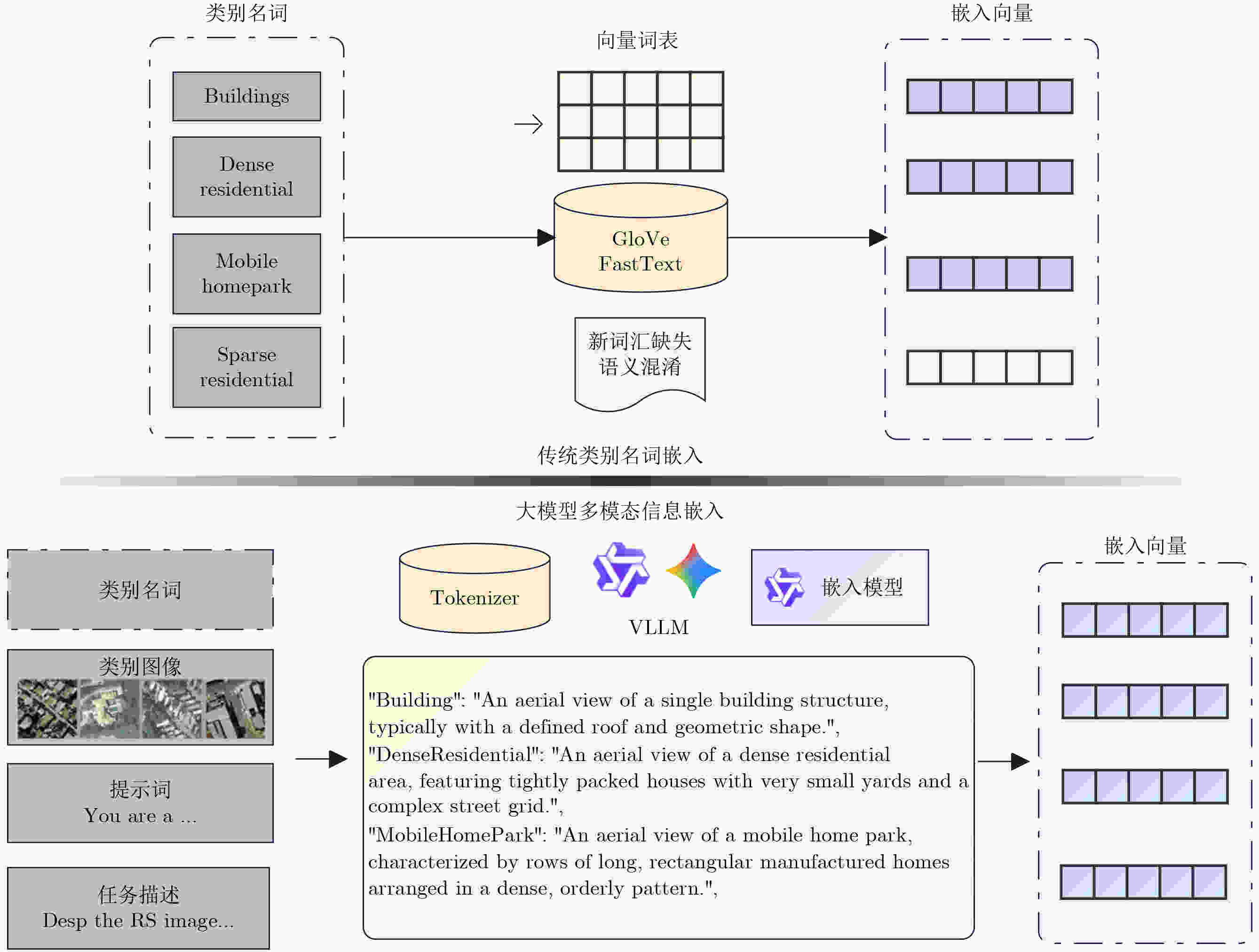
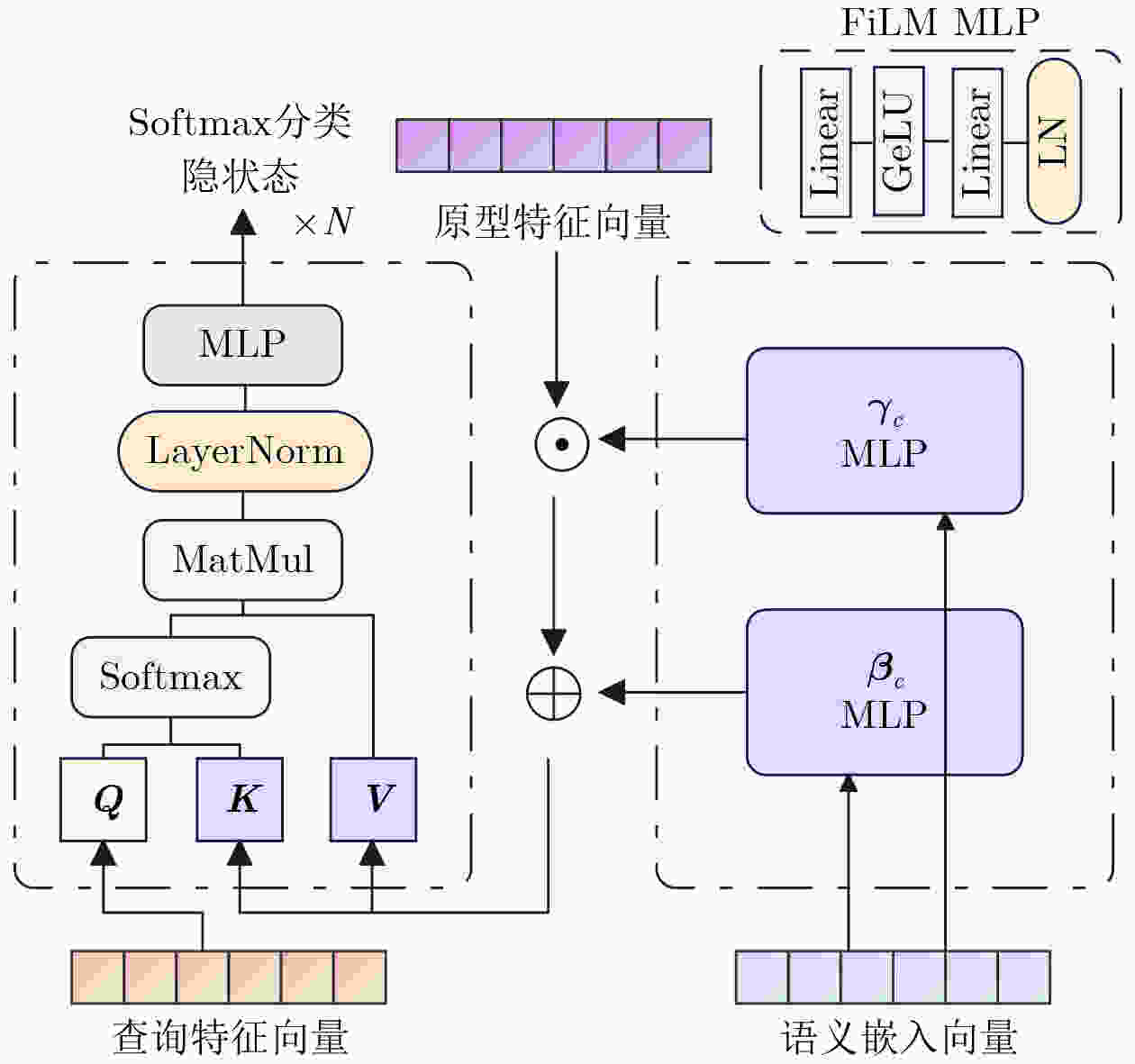
摘要: 针对传统少样本遥感图像分类方法在特征提取能力、模型泛化性及计算资源消耗等方面存在的不足,该文提出一种基于参数高效微调预训练视觉变换器(ViT)与多模态交叉度量的少样本遥感图像分类方法(EFS-ViT-MM)。该方法首先构建一个低秩高效视觉特征提取器(ELR-ViT),采用前沿预训练Transformers作为骨干网络,并引入低秩参数高效微调策略,以利用其强大的视觉特征提取能力,在大幅降低训练参数量的同时有效抑制了过拟合且提升了其泛化性。其次,为了引入更丰富的语义信息以指导分类,该方法利用多模态大语言模型为支持集样本生成描述性文本,并通过先进的文本嵌入模型将其转换为语义向量,进而通过特征级线性调制(FiLM)将语义向量融入视觉特征中,实现对视觉表征的动态调整。最后,该文设计了一种新颖的交叉注意力度量模块,以替代传统的人工设计距离函数。该模块能够自适应地学习查询图像与多模态增强后的支持集样本之间的相关性,实现更精准的相似度匹配。在NWPU-RESISC45, WHU-RS19, UC-Merced和AID等多个公开遥感数据集上的实验结果表明,相较于基线模型,所提方法在5 way-1shot和5 way-5shot任务上的分类准确率分别提升了4.7%和7.0%,同时可训练参数量显著减少。研究表明,该方法有效融合了预训练大模型的强大能力与参数高效微调技术,并通过多模态信息与交叉注意力机制显著提升了少样本分类性能,为解决遥感领域数据稀缺场景下的图像分类问题提供了一个高效、泛化的新范式。Abstract:
Objective Remote sensing image classification is a core task in Earth observation. Its development is limited by the scarcity of high-quality labeled data. Few-shot learning provides a feasible solution. However, existing methods often suffer from limited feature representation, weak generalization to unseen classes, and high computational cost when adapting large models. These issues restrict their application in time-sensitive and resource-constrained scenarios. To address these challenges, this study proposes an Efficient Few-Shot Vision Transformer with Multimodal Guidance (EFS-ViT-MM). The objective is to construct an efficient and accurate classification framework by combining the strong representation capability of a pre-trained Vision Transformer with parameter-efficient fine-tuning. Discriminative capability is further enhanced by incorporating semantic information from textual descriptions to guide prediction. Methods The proposed EFS-ViT-MM framework is formulated as a metric-based learning system composed of three coordinated components. First, an Efficient Low-Rank Vision Transformer (ELR-ViT) is adopted as the visual backbone. A pre-trained Vision Transformer is used for feature extraction, whereas a low-rank adaptation strategy is applied for fine-tuning. The pre-trained parameters are frozen, and only a small number of injected low-rank matrices are optimized. This design reduces the number of trainable parameters and mitigates overfitting while preserving generalization capability. Second, a multimodal guidance mechanism is introduced to enrich visual features with semantic context. A Multimodal Large Language Model generates descriptive text for each support image. The text is embedded into a semantic vector and injected into the visual features through Feature-wise Linear Modulation, which adaptively recalibrates visual representations. Third, a cross-attention metric module is designed to replace fixed distance functions. The module learns similarity between query images and multimodally enhanced support samples by adaptively weighting feature correlations, leading to more precise matching in complex remote sensing scenes. Results and Discussions The proposed method is evaluated on multiple public remote sensing datasets, including NWPU-RESISC45, WHU-RS19, UC-Merced, and AID. The results demonstrate consistent performance gains over baseline methods. Under the 5 way-1shot and 5 way-5 shot settings, classification accuracy increases by 4.7% and 7.0%, respectively. These improvements are achieved with a substantially reduced number of trainable parameters, indicating high computational efficiency. The results confirm that combining large pre-trained models with parameter-efficient fine-tuning is effective for few-shot classification. Performance gains are primarily attributed to multimodal guidance and the cross-attention-based metric, which improve feature discrimination and similarity measurement. Conclusions The EFS-ViT-MM framework effectively addresses limited feature representation, poor generalization, and high computational cost in few-shot remote sensing image classification. The integration of a pre-trained Vision Transformer with parameter-efficient fine-tuning enables effective utilization of large models with reduced computational burden. Multimodal guidance introduces semantic context that enhances visual understanding, whereas the cross-attention metric provides adaptive and accurate similarity estimation. Extensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across multiple datasets. The proposed framework offers an efficient and generalizable solution for data-scarce remote sensing applications and provides a foundation for future research on multimodal and efficient deep learning methods for Earth observation. -
表 1 各方法模型在NWPU-RESISC45数据集上训令显存与收敛速度对比
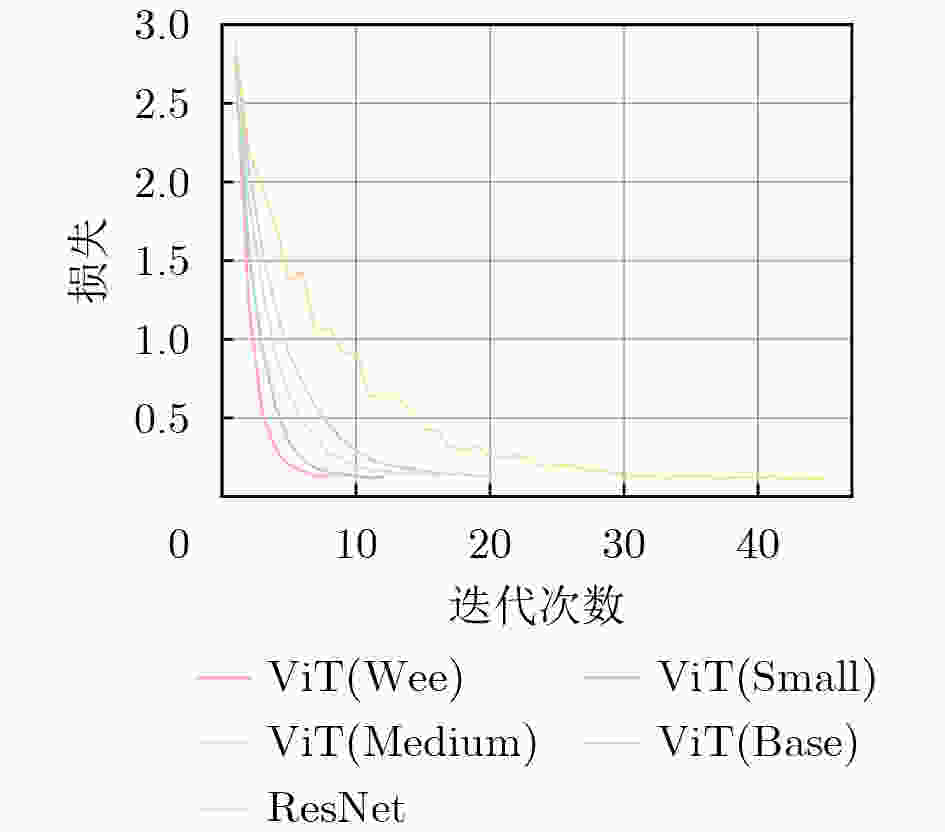
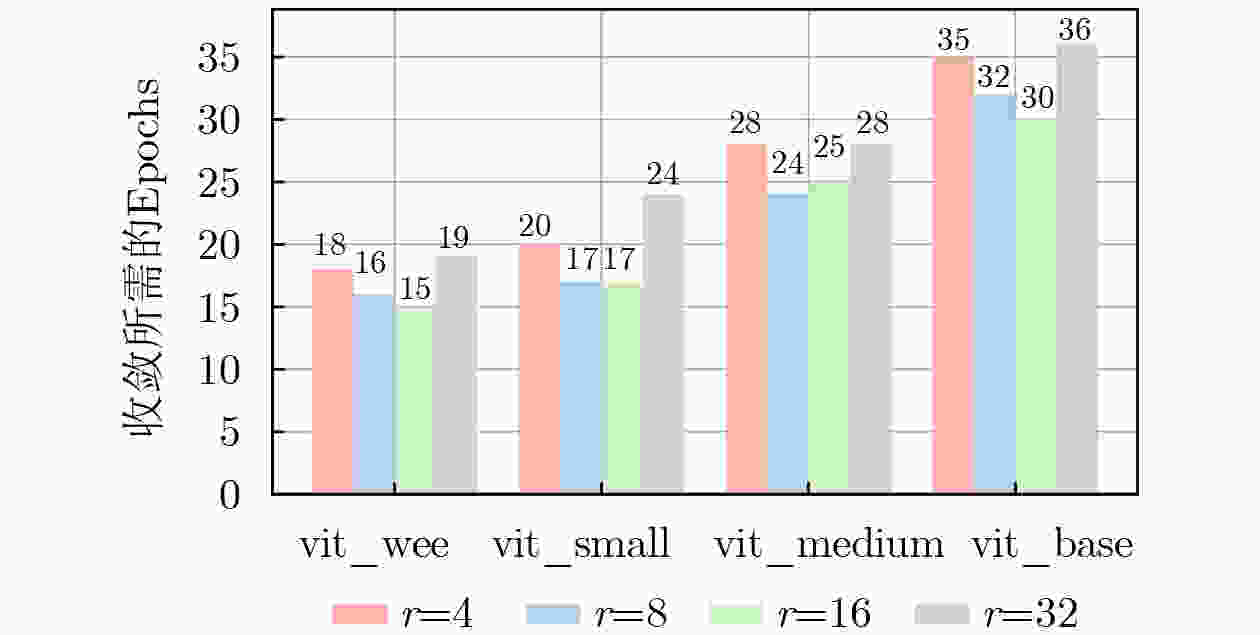
模型名称 训练方法 秩 (Rank) 显存占用 (GB) 总收敛耗时 (s) resnet18 全量微调 - 2.45 201 vit_wee_patch16 全量微调 - 3.10 311 EFS-ViT-MM (wee) LoRA 8 2.85 53 EFS-ViT-MM (wee) LoRA 32 2.86 58 vit_small_patch16 全量微调 - 4.80 475 EFS-ViT-MM (small) LoRA 8 4.52 79 EFS-ViT-MM (small) LoRA 32 4.53 87 vit_medium_patch16 全量微调 - 7.50 750 EFS-ViT-MM (medium) LoRA 8 7.15 128 EFS-ViT-MM (medium) LoRA 32 7.16 145 表 2 不同规模和架构预训练模型的对比
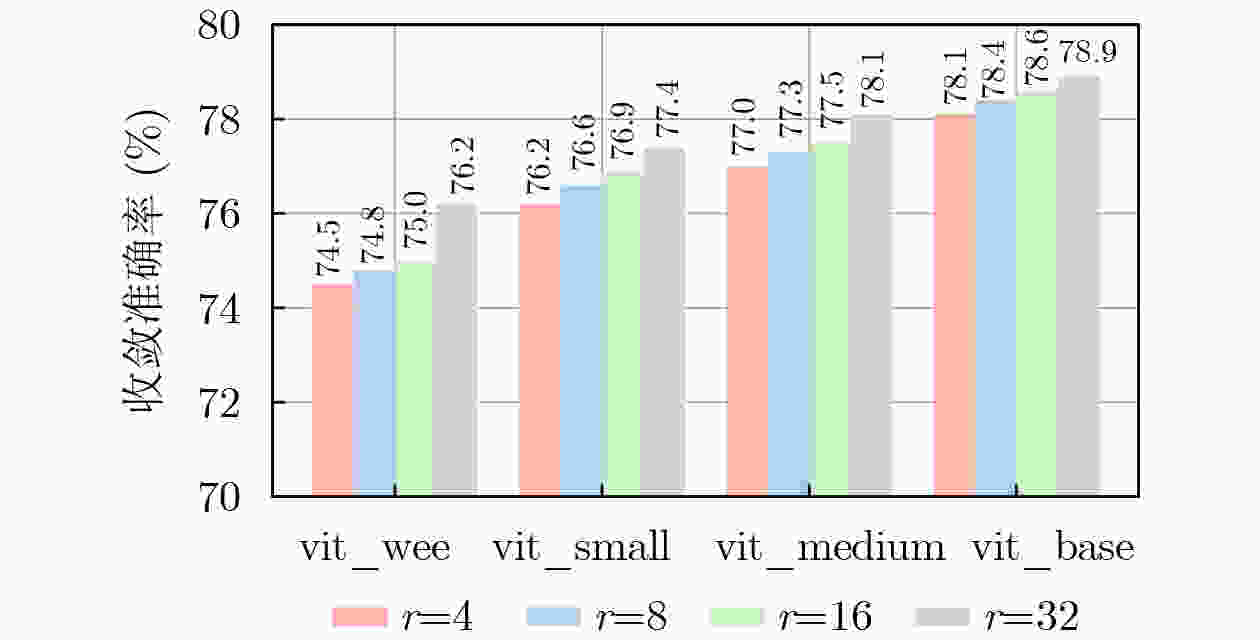
基础模型 低秩 测试集精度±方差 参数量(M) 数据集 resnet18 全量 73.9±0.086 11.7 NWPU vit_base_patch16 16 78.6±0.098 86.6(6.26) NWPU vit_medium_patch16 16 77.5±0.109 38.9(4.71) NWPU vit_small_patch16 16 76.9±0.099 22.1(2.93) NWPU vit_wee_patch16 16 75.0±0.101 13.4(2.50) NWPU resnet18 全量 68.9±0.109 11.7 WHU-RS19 vit_base_patch16 16 75.9±0.097 86.6(6.26) WHU-RS19 vit_medium_patch16 16 74.4±0.109 38.9(4.71) WHU-RS19 vit_small_patch16 16 73.6±0.105 22.1(2.93) WHU-RS19 vit_wee_patch16 16 72.7±0.109 13.4(2.50) WHU-RS19 注:括号内表示可学习参数量,其他表格同理。 表 3 NWPU-RESISC45数据集上各方法表现对比
方法 1-shot精度±
方差(%)5-shot精度±
方差(%)参数量(M) MatchingNet [54] 40.31 ± 0.13 47.27 ± 0.38 10.72 ProtoNet[47] 41.38 ± 0.26 62.77 ± 0.14 11.19 RelationNet[55] 66.21 ± 0.28 78.37 ± 0.28 27.07 DLA-MatchNet[20] 68.80 ± 0.70 81.63 ± 0.46 50.91 SPNet[41] 67.84 ± 0.87 83.94 ± 0.50 - SCL-MLNet[56] 62.21 ± 1.12 80.86 ± 0.76 191.59 TAE-Net[57] 69.13 ± 0.83 82.37 ± 0.52 - MKN[58] 65.84 ± 0.89 82.67 ± 0.55 - MPCL-Net[59] 55.94 ± 0.04 76.24 ± 0.12 45.01 TDNET[60] 65.85 ± 0.53 82.16 ± 0.32 8.33 HiReNet[61] 70.43 ± 0.90 81.24 ± 0.58 13.94 CNSPN-Conv4[28] 66.10 ± 0.75 - 3.83 CNSPN-ResNet18[28] 70.35 ± 0.78 - 13.96 PA-SRM[17] 72.65 ± 0.43 83.64 ± 0.61 14.53 EFS-ViT-MM(wee) 75.01±0.10 88.61 ± 0.04 13.40(2.50) EFS-ViT-MM(base) 78.64±0.09 90.04 ± 0.04 86.60(6.26) 表 4 WHU-RS19数据集上各方法表现对比
方法 1-shot精度±
方差(%)5-shot精度±
方差(%)参数量(M) MatchingNet 51.25 ± 0.61 54.36 ± 0.38 10.72 ProtoNet 58.17 ± 0.56 80.54 ± 0.42 11.19 RelationNet 61.74 ± 0.51 79.15 ± 0.35 27.07 DLA-MatchNet 68.27 ± 1.83 79.89 ± 0.33 50.91 SPNet 81.06 ± 0.60 88.04 ± 0.28 - SCL-MLNet 63.36 ± 0.88 77.62 ± 0.81 191.59 TAE-Net 73.67 ± 0.74 88.95 ± 0.52 - MPCL-Net 61.84 ± 0.12 80.34 ± 0.54 45.01 TDNET 64.24 ± 0.51 84.15 ± 0.32 8.33 CNSPN-Conv4[28] 57.39 ± 0.87 - 3.83 CNSPN-ResNet18[28] 59.73 ± 0.81 - 13.96 EFS-ViT-MM(wee) 72.71 ± 0.10 87.10 ± 0.05 13.40(2.50) EFS-ViT-MM(base) 75.92 ± 0.10 89.24 ± 0.06 86.60(6.26) 表 5 UC-Merced数据集上各方法表现对比
方法 1-shot精度±
方差(%)5-shot精度±
方差(%)参数量(M) MatchingNet 34.68 ± 0.91 53.34 ± 0.17 10.72 ProtoNet 52.34 ± 0.19 41.38 ± 0.26 11.19 RelationNet 48.48 ± 0.75 62.17 ± 0.33 27.07 DLA-MatchNet 53.76 ± 0.62 68.80 ± 0.70 50.91 SPNet 57.64 ± 0.73 73.52 ± 0.51 - SCL-MLNet 51.37 ± 0.79 68.09 ± 0.92 191.59 TAE-Net 60.21 ± 0.72 77.44 ± 0.51 - MKN 58.45 ± 0.54 77.92 ± 0.23 - MPCL-Net 56.41 ± 0.21 76.57 ± 0.07 45.01 HiReNet 58.60 ± 0.80 76.84 ± 0.56 13.94 PA-SRM 60.79 ± 0.28 78.64 ± 0.42 14.53 EFS-ViT-MM(wee) 71.80 ± 0.08 84.20 ± 0.08 13.40(2.50) EFS-ViT-MM(base) 73.34 ± 0.03 87.10 ± 0.04 86.60(6.26) 表 6 AID数据集上各方法表现对比
方法 1-shot精度±
方差(%)5-shot精度±
方差(%)参数量(M) MatchingNet 42.17 ± 0.78 52.34 ± 0.89 10.72 ProtoNet 49.91 ± 0.47 70.48 ± 0.21 11.19 RelationNet 53.51 ± 0.68 68.65 ± 0.95 27.07 DLA-MatchNet 68.27 ± 1.83 63.01 ± 0.51 50.91 SCL-MLNet 59.46 ± 0.96 76.31 ± 0.68 191.59 MKN 57.29 ± 0.59 75.42 ± 0.31 - MPCL-Net 60.61 ± 0.43 76.78 ± 0.08 45.01 TDNET 67.48 ± 0.51 80.56 ± 0.36 8.33 HiReNet 59.43 ± 0.66 74.12 ± 0.43 13.94 PA-SRM 68.75 ± 0.36 81.47 ± 0.65 14.53 EFS-ViT-MM(wee) 67.36 ± 0.10 81.42 ± 0.07 13.40(2.50) EFS-ViT-MM(base) 69.14 ± 0.12 83.17 ± 0.04 86.60(6.26) 表 7 融合方法对模型精度的影响
方法 1-shot 精度±方差 (%) 5-shot 精度±方差(%) avg 72.86±0.24 85.97± 0.12 cat 72.84±0.11 86.11 ± 0.10 gate 74.21±0.21 87.83 ± 0.29 mfb 74.39±0.16 88.77± 0.12 FiLM 75.01±0.10 88.61 ± 0.04 表 8 词嵌入模式对模型精度的影响
嵌入模型 嵌入方式 1-shot 精度±方差(%) 5-shot 精度±方差(%) glove 词嵌入 71.91±0.21 83.12 ± 0.16 bert 词嵌入 72.38±0.24 83.44 ± 0.14 bert 语料嵌入 73.56±0.09 84.61 ± 0.08 qwen3 语料嵌入 75.01±0.10 88.61 ± 0.04 -
[1] HU Qiong, WU Wenbin, XIA Tian, et al. Exploring the use of google earth imagery and object-based methods in land use/cover mapping[J]. Remote Sensing, 2013, 5(11): 6026–6042. doi: 10.3390/rs5116026. [2] PHAM H M, YAMAGUCHI Y, and BUI T Q. A case study on the relation between city planning and urban growth using remote sensing and spatial metrics[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 2011, 100(3): 223–230. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.12.009. [3] CHENG Gong, GUO Lei, ZHAO Tianyun, et al. Automatic landslide detection from remote-sensing imagery using a scene classification method based on BoVW and pLSA[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 34(1): 45–59. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2012.705443. [4] ZHU Qiqi, ZHONG Yanfei, ZHAO Bei, et al. Bag-of-visual-words scene classifier with local and global features for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(6): 747–751. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2513443. [5] SHI Qian, HE Da, LIU Zhengyu, et al. Globe230k: A benchmark dense-pixel annotation dataset for global land cover mapping[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 3: 0078. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0078. [6] TIAN Jiaqi, ZHU Xiaolin, SHEN Miaogen, et al. Effectiveness of spatiotemporal data fusion in fine-scale land surface phenology monitoring: A simulation study[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0118. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0118. [7] LI Xiaoxiao and SHAO Guofan. Object-based urban vegetation mapping with high-resolution aerial photography as a single data source[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 34(3): 771–789. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2012.714508. [8] MANFREDA S, MCCABE M F, MILLER P E, et al. On the use of unmanned aerial systems for environmental monitoring[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(4): 641. doi: 10.3390/rs10040641. [9] LI Ying, ZHANG Haokui, XUE Xizhe, et al. Deep learning for remote sensing image classification: A survey[J]. WIREs Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2018, 8(6): e1264. doi: 10.1002/widm.1264. [10] HAN Wei, ZHANG Xiaohan, WANG Yi, et al. A survey of machine learning and deep learning in remote sensing of geological environment: Challenges, advances, and opportunities[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 202: 87–113. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.05.032. [11] XU Feng, HU Cheng, LI Jun, et al. Special focus on deep learning in remote sensing image processing[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2020, 63(4): 140300. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-2810-x. [12] MEI Shaohui, LIAN Jiawei, WANG Xiaofei, et al. A comprehensive study on the robustness of deep learning-based image classification and object detection in remote sensing: Surveying and benchmarking[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0219. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0219. [13] RAVI S and LAROCHELLE H. Optimization as a model for few-shot learning[C]. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. [14] JI Zhong, HOU Liyuan, WANG Xuan, et al. Dual contrastive network for few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5605312. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3260121. [15] ZHANG Pei, BAI Yunpeng, WANG Dong, et al. Few-shot classification of aerial scene images via meta-learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(1): 108. doi: 10.3390/rs13010108. [16] QIU Chunping, ZHANG Xiaoyu, TONG Xiaochong, et al. Few-shot remote sensing image scene classification: Recent advances, new baselines, and future trends[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2024, 209: 368–382. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2024.02.005. [17] JIA Yuyu, SUN Chenchen, GAO Junyu, et al. Few-shot remote sensing scene classification via parameter-free attention and region matching[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2025, 227: 265–275. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2025.05.026. [18] ZHANG Linna, ZHENG Le, WEN Yuxin, et al. Effective SAR image despeckling using noise-guided transformer and multi-scale feature fusion[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(23): 3863. doi: 10.3390/rs17233863. [19] BO Fuyu, MA Xiaole, HU Shaohai, et al. Speckle-driven unsupervised despeckling for SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 13023–13034. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3568854. [20] LI Lingjun, HAN Junwei, YAO Xiwen, et al. DLA-MatchNet for few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7844–7853. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3033336. [21] XU Yulong, BI Hanbo, YU Hongfeng, et al. Attention-based contrastive learning for few-shot remote sensing image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5620317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3385655. [22] LIU Shuaijun, LIU Jia, TAN Xiaoyue, et al. A hybrid spatiotemporal fusion method for high spatial resolution imagery: Fusion of Gaofen-1 and Sentinel-2 over agricultural landscapes[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0159. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0159. [23] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Austria, 2021. [24] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [25] TOUVRON H, CORD M, DOUZE M, et al. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 10347–10357. [26] OQUAB M, DARCET T, MOUTAKANNI T, et al. DINOv2: Learning robust visual features without supervision[Z]. arXiv: 2304.07193, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2304.07193. [27] HU E J, SHEN Yelong, WALLIS P, et al. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models[C]. 10th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022. [28] CHEN Jie, GUO Ya, ZHU Jingru, et al. Improving few-shot remote sensing scene classification with class name semantics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5633712. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3219726. [29] CHENG Kaihui, YANG Chule, FAN Zunlin, et al. TeAw: Text-aware few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10095523. [30] COMANICI G, BIEBER E, SCHAEKERMANN M, et al. Gemini 2.5: Pushing the frontier with advanced reasoning, multimodality, long context, and next generation agentic capabilities[Z]. arXiv: 2507.06261, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2507.06261. [31] BAI Shuai, CHEN Keqin, LIU Xuejing, et al. Qwen2.5-VL technical report[Z]. arXiv: 2502.13923, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2502.13923. [32] ZHANG Yanzhao, LI Mingxin, LONG Dingkun, et al. Qwen3 embedding: Advancing text embedding and reranking through foundation models[Z]. arXiv: 2506.05176, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2506.05176. [33] PEREZ E, STRUB F, DE VRIES H, et al. FiLM: Visual reasoning with a general conditioning layer[C]. The 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 3942–3951. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v32i1.11671. [34] ROSTAMI M, KOLOURI S, EATON E, et al. Deep transfer learning for few-shot SAR image classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(11): 1374. doi: 10.3390/rs11111374. [35] SUN Xian, WANG Bing, WANG Zhirui, et al. Research progress on few-shot learning for remote sensing image interpretation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 2387–2402. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3052869. [36] YU Xingrui, WU Xiaomin, LUO Chunbo, et al. Deep learning in remote sensing scene classification: A data augmentation enhanced convolutional neural network framework[J]. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 2017, 54(5): 741–758. doi: 10.1080/15481603.2017.1323377. [37] MA Dongao, TANG Ping, and ZHAO Lijun. SiftingGAN: Generating and sifting labeled samples to improve the remote sensing image scene classification baseline in vitro[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(7): 1046–1050. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2890413. [38] YAN Yiming, TAN Zhichao, and SU Nan. A data augmentation strategy based on simulated samples for ship detection in RGB remote sensing images[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2019, 8(6): 276. doi: 10.3390/ijgi8060276. [39] LI Haifeng, CUI Zhenqi, ZHU Zhiqiang, et al. RS-MetaNet: Deep metametric learning for few-shot remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6983–6994. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3027387. [40] SHI Jiawei, JIANG Zhiguo, and ZHANG Haopeng. Few-shot ship classification in optical remote sensing images using nearest neighbor prototype representation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 3581–3590. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3066539. [41] CHENG Gong, CAI Liming, LANG Chunbo, et al. SPNet: Siamese-prototype network for few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5608011. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3099033. [42] ALAJAJI D A and ALHICHRI H. Few shot scene classification in remote sensing using meta-agnostic machine[C]. 2020 6th Conference on Data Science and Machine Learning Applications (CDMA), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2020: 77–80. doi: 10.1109/CDMA47397.2020.00019. [43] LOBRY S, MARCOS D, MURRAY J, et al. RSVQA: Visual question answering for remote sensing data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(12): 8555–8566. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2988782. [44] HOXHA G, MELGANI F, and DEMIR B. Retrieving images with generated textual descriptions[C]. 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 5812–5815. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8899321. [45] SUMBUL G, CINBIS R G, and AKSOY S. Fine-grained object recognition and zero-shot learning in remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 770–779. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2754648. [46] LI Aoxue, LU Zhiwu, WANG Liwei, et al. Zero-shot scene classification for high spatial resolution remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 4157–4167. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2689071. [47] SNELL J, SWERSKY K, and ZEMEL R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4080–4090. [48] ZHANG Xiang, WEI Tianyu, LIU Wenchao, et al. Cosine margin prototypical networks for remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8017805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3098515. [49] CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, and LU Xiaoqiang. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(10): 1865–1883. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2675998. [50] XIA Guisong, YANG Wen, DELON J, et al. Structural high-resolution satellite image indexing[C]. ISPRS Technical Commission VII Symposium on Advancing Remote Sensing Science, Vienna, Austria, 2010. [51] NEUMANN M, PINTO A S, ZHAI Xiaohua, et al. In-domain representation learning for remote sensing[Z]. arXiv: 1911.06721, 2019. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1911.06721. [52] XIA Guisong, HU Jingwen, HU Fan, et al. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3965–3981. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2685945. [53] WIGHTMAN R. PyTorch image models[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4414861, 2019. [54] VINYALS O, BLUNDELL C, LILLICRAP T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 3637–3645. [55] SUNG F, YANG Yongxin, ZHANG Li, et al. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1199–1208. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00131. [56] LI Xiaomin, SHI Daqian, DIAO Xiaolei, et al. SCL-MLNet: Boosting few-shot remote sensing scene classification via self-supervised contrastive learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5801112. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3109268. [57] HUANG Wendong, YUAN Zhengwu, YANG Aixia, et al. TAE-Net: Task-adaptive embedding network for few-shot remote sensing scene classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(1): 111. doi: 10.3390/rs14010111. [58] CUI Zhenqi, YANG Wang, CHEN Li, et al. MKN: Metakernel networks for few shot remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4705611. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3153679. [59] MA Jingjing, LIN Weiquan, TANG Xu, et al. Multipretext-task prototypes guided dynamic contrastive learning network for few-shot remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5614216. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3291357. [60] WANG Bing, WANG Zhirui, SUN Xian, et al. TDNet: A novel transductive learning framework with conditional metric embedding for few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 4591–4606. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3263149. [61] TIAN Feng, LEI Sen, ZHOU Yingbo, et al. HiReNet: Hierarchical-relation network for few-shot remote sensing image scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5603710. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3348464. -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
