DetDiffRS: A Detail-Enhanced Diffusion Model for Remote Sensing Image Super-Resolution
-
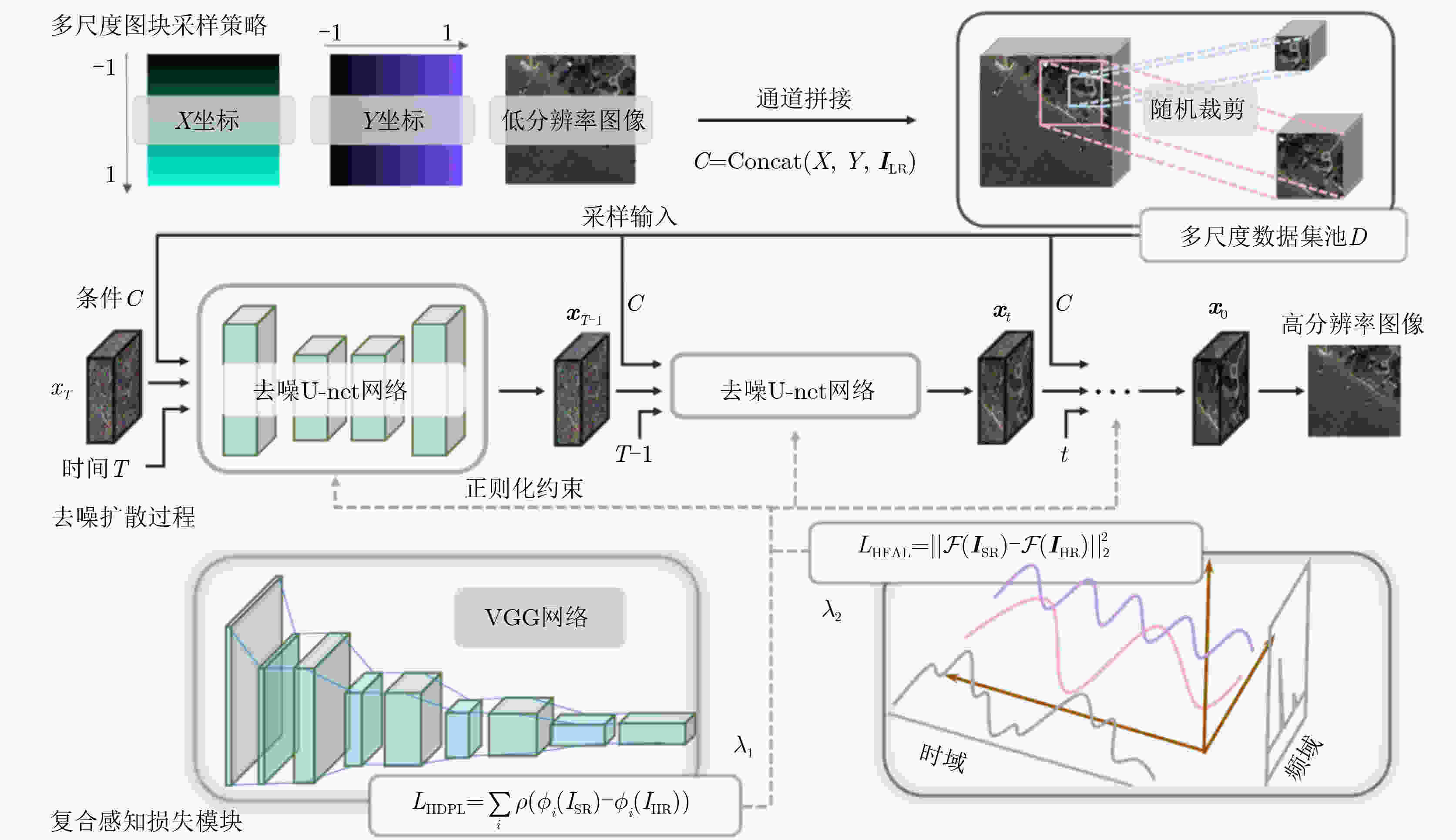
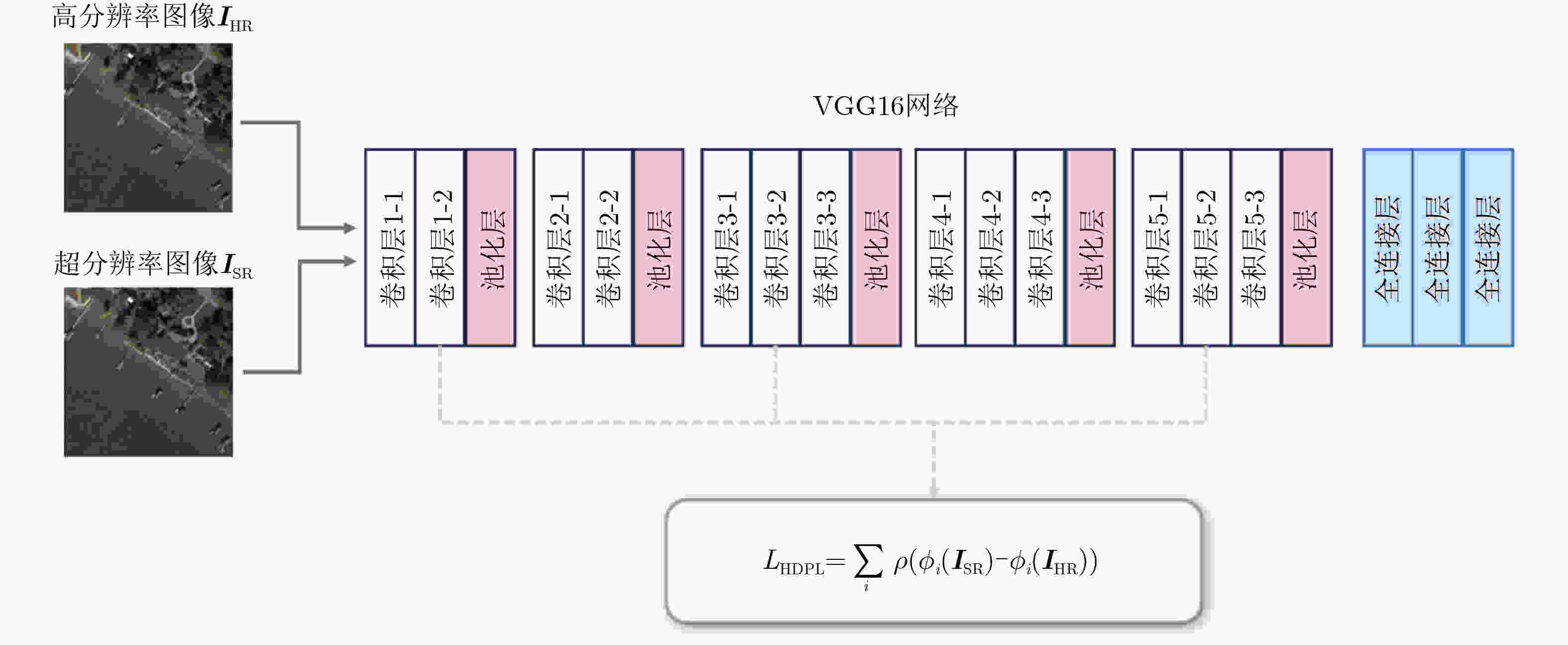
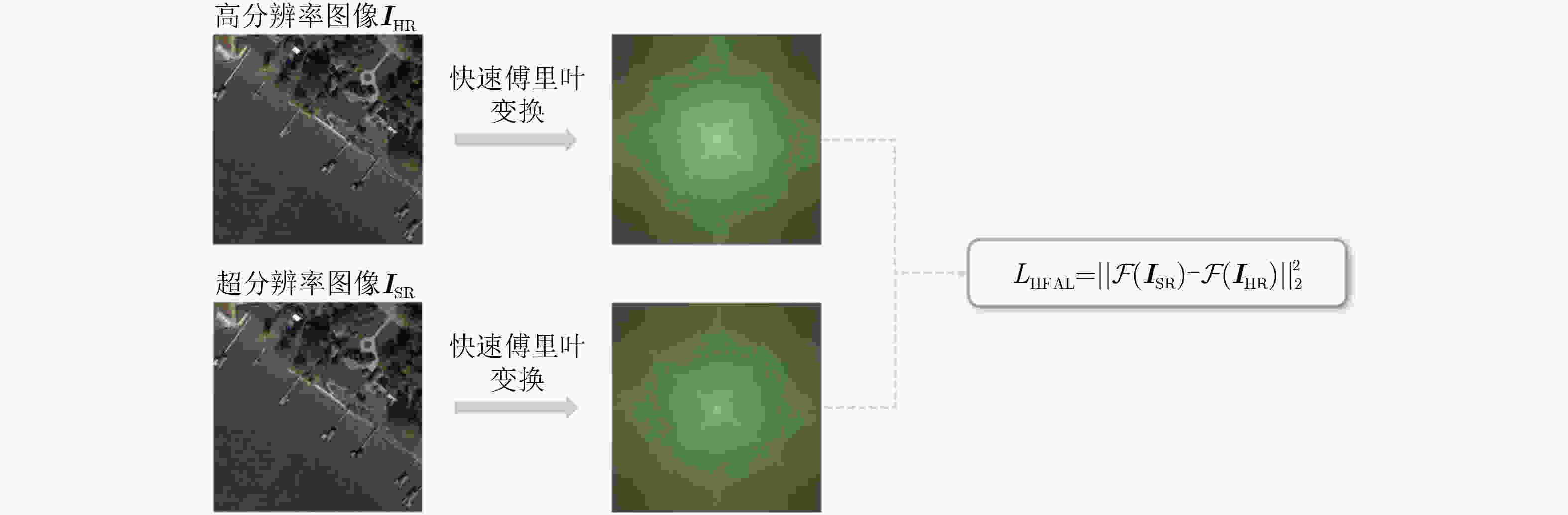
摘要: 遥感图像超分辨率技术对精确解析地物、支持城市规划与环境监测等下游应用具有至关重要的价值。近期基于扩散模型的方法在自然图像超分辨率任务中展现了卓越的性能,其强大的生成能力使其能够恢复精细的纹理。然而,当直接应用于遥感领域时,模型会面临由遥感影像特有的数据高低频信息分布不均衡所带来的挑战。影像中大面积、纹理单一的低频区域在训练中占据主导地位,导致模型对承载着关键信息的稀疏高频细节学习不足,最终的重建结果往往呈现全局平滑、细节模糊的特征。 因此,为解决这一问题,该文提出一种能够显著增强高频细节重建能力的遥感图像超分辨率扩散模型(DetDiffRS)。首先在数据输入端提出多尺度图块采样策略以应对低频区域在训练过程中占主导问题,该策略通过对多尺度图块进行加权采样,提升了富含高频信息图块的采样频率,从而引导模型更充分地学习这些关键细节。其次在优化端设计了一种复合感知损失函数,该损失函数在深度特征空间中约束高维感知损失,并且在傅里叶频域中对高频分量进行高频感知损失。这一设计从空间域和频率域两个维度增强了模型对高频细节的精确恢复能力。大量的实验结果表明,在AID, DOTA和DIOR等多个公开数据集上,DetDiffRS在客观量化指标(Fréchet Inception距离(FID)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数(SSIM))与视觉真实感方面均超越了现有的先进方法,尤其在细节恢复的清晰度上优势显著。Abstract:
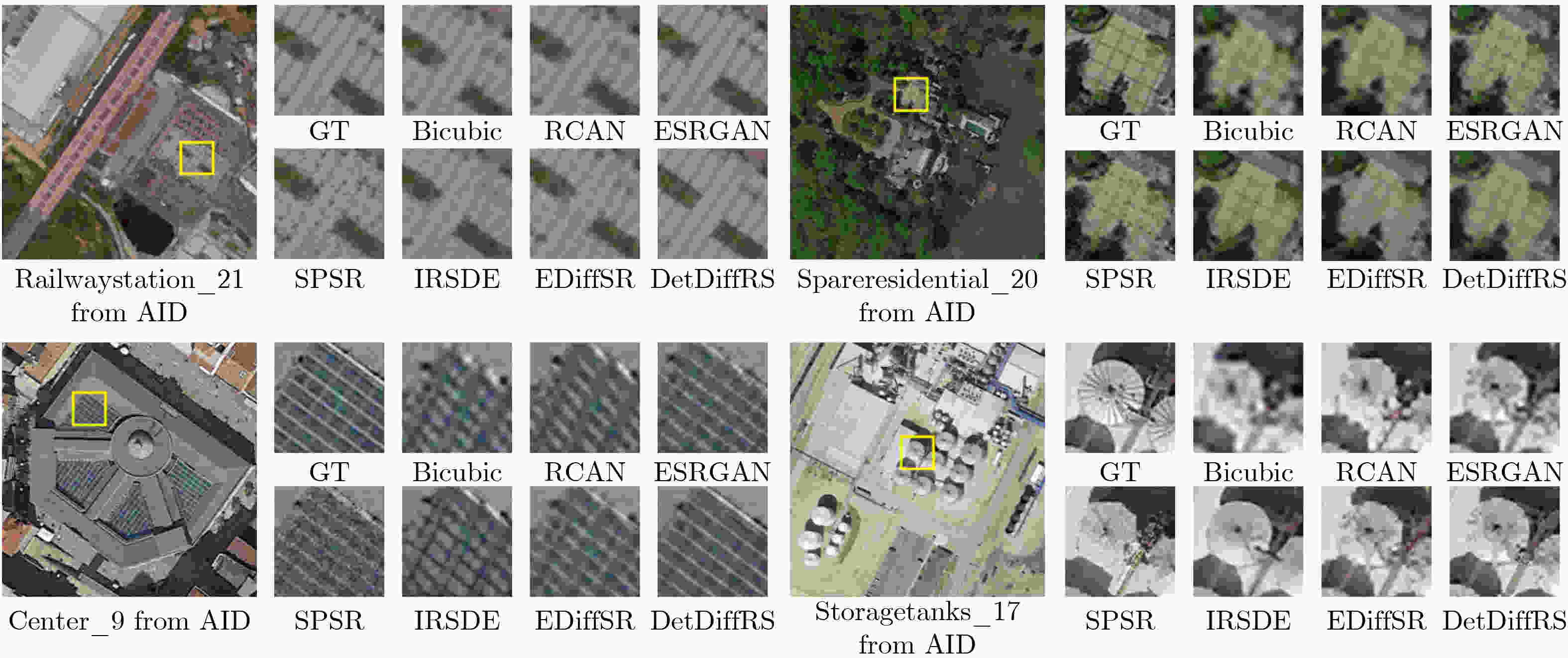
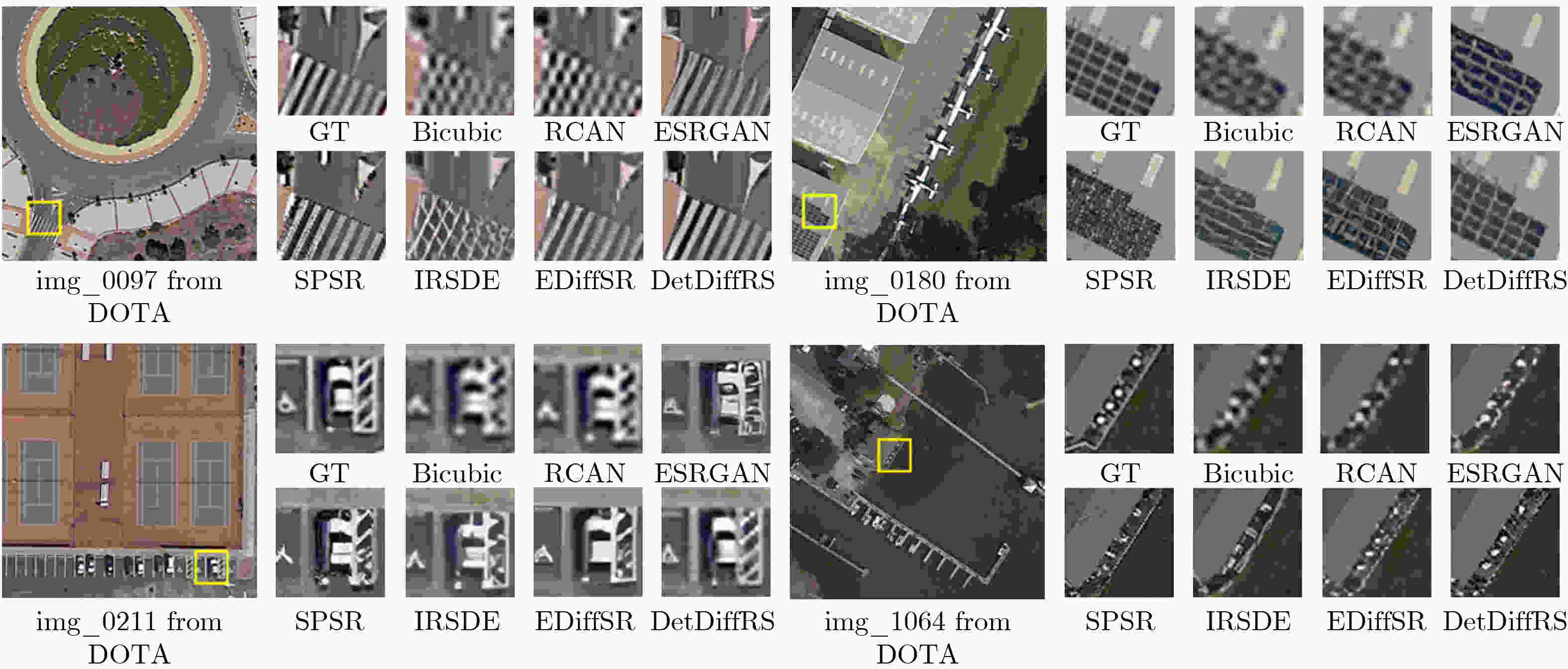
Objective This study aims to enhance the reconstruction of fine structural details in High-Resolution (HR) Remote Sensing image Super-Resolution (RSSR) by leveraging Diffusion Models (DM). Although diffusion-based approaches achieve strong performance in natural image restoration, their direct application to remote sensing imagery remains suboptimal because of the pronounced imbalance between extensive low-frequency homogeneous regions, such as water bodies and farmland, and localized high-frequency regions with complex structures, such as buildings, ports, and aircraft. This imbalance leads to insufficient learning of critical high-frequency details, resulting in reconstructions that appear globally smooth but lack sharpness and realism. To address this limitation, DetDiffRS, a detail-enhanced diffusion-based framework, is proposed to explicitly increase sensitivity to high-frequency information during data sampling and optimization, thereby improving perceptual quality and structural fidelity. Methods The DetDiffRS framework introduces improvements at both the data input and loss-function levels to mitigate the high-low frequency imbalance in remote sensing imagery. First, a Multi-Scale Patch Sampling (MSPS) strategy is proposed to increase the probability of selecting patches containing high-frequency structures during training. This is achieved by constructing a multi-scale patch pool and applying weighted sampling to prioritize structurally complex regions. Second, a composite perceptual loss is designed to provide supervision beyond conventional denoising objectives. This loss integrates a High-Dimensional Perceptual Loss (HDPL) to enforce structural consistency in deep feature space and a High-Frequency-Aware Loss (HFAL) to constrain high-frequency components in the frequency domain. The combination of MSPS and the composite perceptual loss enables the DM to capture and reconstruct fine details more effectively, improving both objective quality metrics and visual realism. Results and Discussions Extensive experiments are conducted on three publicly available remote sensing datasets, AID, DOTA, and DIOR, and comparisons are performed against representative state-of-the-art super-resolution methods, including CNN-based approaches (EDSR and RCAN), Transformer-based approaches (HAT-L and TTST), GAN-based approaches (MSRGAN, ESRGAN, and SPSR), and diffusion-based approaches (SR3 and IRSDE). Quantitative evaluation using Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) on the AID dataset shows that DetDiffRS achieves the best performance in 21 of 30 scene categories, with an average FID of 48.37, exceeding the second-best method by 1.14. The improvements are most evident in texture-rich and structurally complex categories such as Dense Residential, Meadow, and River, where FID reductions exceed 3.0 relative to competing diffusion-based methods ( Table 1 ). Although PSNR-oriented methods such as RCAN achieve the highest PSNR and SSIM values in some cases, they generate overly smooth reconstructions with limited fine detail. In contrast, DetDiffRS, supported by HDPL and HFAL, achieves a balanced improvement in objective metrics and perceptual quality, improving PSNR by 1.178 9 dB over SR3 on AID and SSIM by 0.064 4 on DOTA (Table 2 ). Visual comparisons further indicate that DetDiffRS consistently produces sharper edges, clearer structures, and more realistic textures, reducing over-smoothing in PSNR-focused methods and artifacts commonly observed in GAN-based approaches (Fig. 5 andFig. 6 ).Conclusions This study presents DetDiffRS, a detail-enhanced diffusion-based super-resolution framework tailored to the frequency distribution characteristics of remote sensing imagery. Through integration of the MSPS strategy and a composite perceptual loss that combines HDPL and HFAL, the proposed method addresses the underrepresentation of high-frequency regions during training and achieves substantial improvements in detail preservation and perceptual fidelity. Experimental results across multiple datasets and scene types demonstrate that DetDiffRS outperforms existing CNN-, Transformer-, GAN-, and diffusion-based methods in FID while maintaining a competitive balance between PSNR, SSIM, and visual realism. These results indicate that DetDiffRS provides a robust and generalizable solution for high-quality RSSR in applications requiring structural accuracy and fine detail reconstruction. -
表 1 AID遥感图像分类数据集FID指标
类别 Bicubic EDSR[33] RCAN[34] HAT-L[41] TTST[59] MSRGAN[44] ESRGAN[12] SPSR[45] SR3[16] IRSDE[48] EDiffSR[51] 本文 Airport 126.84 86.77 88.27 87.46 86.47 54.23 55.23 57.55 56.93 54.47 53.33 50.83 Bare Land 112.58 91.31 93.86 90.81 90.12 66.66 61.83 70.93 77.75 80.25 66.38 67.13 Baseball Field 130.83 88.67 92.01 90.85 90.91 50.48 46.39 56.85 71.56 57.95 52.58 51.53 Beach 122.18 105.67 104.97 101.97 102.06 50.07 48.45 52.34 51.38 42.39 43.49 40.55 Bridge 138.11 80.77 81.96 81.63 80.84 48.34 50.85 49.93 74.43 45.64 50.45 46.02 Center 139.63 71.68 73.32 70.99 72.19 49.88 55.44 48.15 53.27 44.93 42.73 44.09 Church 122.35 86.47 88.44 88.57 87.67 52.38 51.59 54.86 62.99 49.66 50.12 50.85 Commercial 111.69 110.98 110.77 103.94 105.05 54.75 56.53 60.38 70.82 51.92 55.44 54.69 Dense Residential 126.94 112.81 126.07 125.57 122.28 51.21 58.55 55.76 64.04 39.87 40.59 37.57 Desert 114.92 77.88 77.49 76.88 75.41 55.61 54.88 63.27 59.86 60.11 53.79 53.02 Farmland 144.04 91.86 94.38 95.59 95.03 67.17 55.39 57.49 78.23 61.11 50.94 51.68 Forest 103.82 88.32 94.51 95.85 95.64 59.53 64.44 62.13 72.79 48.49 46.28 43.26 Industrial 106.64 78.49 81.02 75.68 72.80 38.94 37.65 45.88 45.09 36.92 42.26 37.69 Meadow 134.26 108.74 105.79 102.09 101.07 96.61 69.71 65.49 86.11 69.64 65.95 68.78 Medium Residential 116.72 99.53 104.77 101.10 102.32 46.65 50.76 48.85 74.12 42.18 40.58 39.43 Mountain 103.45 106.11 106.29 103.11 101.10 58.24 54.94 70.40 71.89 58.55 51.93 52.48 Park 137.36 110.36 112.83 110.82 103.57 60.05 61.47 73.19 81.58 63.76 63.28 60.35 Parking 134.26 60.09 67.81 63.55 65.14 42.25 42.43 44.32 55.42 36.74 35.69 35.77 Playground 113.08 58.52 62.03 59.91 58.72 41.34 39.49 40.78 54.89 38.47 36.26 33.88 Pond 162.09 123.54 124.05 127.08 126.09 61.91 54.44 63.54 103.73 55.69 56.77 55.42 Port 134.49 77.28 79.89 80.11 82.35 46.27 46.94 51.13 58.19 47.90 47.62 47.54 Railway Station 113.93 92.81 94.43 88.41 87.88 49.58 53.01 57.65 56.99 49.01 51.57 50.06 Resort 131.65 100.04 104.77 105.61 105.13 59.20 61.23 68.16 68.03 59.86 57.76 57.43 River 150.87 105.66 108.52 108.43 107.60 54.18 59.81 64.47 83.71 59.55 57.15 58.21 School 109.36 85.29 89.02 81.65 82.24 50.59 49.66 53.26 59.63 48.28 46.63 46.39 Sparse Residential 148.27 134.92 141.27 133.06 132.01 72.99 75.88 76.72 84.86 69.16 71.89 69.32 Square 109.76 71.02 75.39 72.66 72.68 43.70 45.55 45.85 53.65 44.67 42.95 42.38 Stadium 121.39 55.55 59.47 59.77 56.22 37.02 35.74 37.65 38.71 33.05 33.94 32.49 Storage Tanks 162.28 90.12 92.94 88.55 90.39 46.16 50.93 50.82 52.71 45.45 43.74 41.16 Viaduct 109.63 67.43 68.73 66.48 65.54 35.84 33.86 38.17 45.65 33.84 33.26 31.02 平均值 126.48 90.62 93.50 91.27 90.55 53.39 52.77 56.20 65.63 50.98 49.51 48.37 表 2 AID, DOTA和DIOR数据集上PSNR/SSIM对比结果
模型 AID DOTA DIOR 参数量(M) PSNR↑ SSIM↑ FID↓ PSNR↑ SSIM↑ FID↓ PSNR↑ SSIM↑ FID↓ EDSR[33] 30.5987 0.8034 90.6217 33.6742 0.8571 56.3559 30.6519 0.8085 41.1396 43.096 RCAN[34] 30.8543 0.8126 93.5024 33.8764 0.8622 51.6321 30.8684 0.8157 44.1177 15.673 HAT-L[41] 30.8732 0.8133 91.2743 33.9388 0.8745 43.2568 30.8892 0.8283 40.9004 40.396 TTST[59] 30.9274 0.8169 90.5602 34.1066 0.8742 40.8301 30.9246 0.8296 39.2227 37.573 MSRGAN[44] 28.8027 0.7481 53.3889 29.4572 0.7859 27.8021 28.8469 0.7596 23.2691 1.510 ESRGAN[12] 28.3994 0.7248 52.7719 28.9591 0.7793 24.9884 28.1226 0.7015 23.2864 16.706 SPSR[45] 27.6995 0.7098 56.2035 28.0487 0.7792 25.9249 27.4461 0.7169 24.2751 24.872 SR3[16] 26.2583 0.6695 65.6274 27.5896 0.6781 34.8752 26.2508 0.6691 31.9048 92.654 IRSDE[48] 27.2186 0.6647 50.9811 27.9721 0.7093 24.3797 27.0014 0.6482 22.8679 137.255 EDiffSR[51] 27.3817 0.6752 50.5063 28.2049 0.7294 22.3208 27.5169 0.6792 22.7289 26.790 DDIM[15] 27.1338 0.6519 51.4447 28.0186 0.6914 26.0746 27.1224 0.6523 26.6102 26.166 本文 27.4372 0.7093 48.3711 28.4218 0.7425 21.1314 27.6715 0.6987 22.1396 26.532 表 3 多尺度图块采样策略消融实验结果
方法 多尺度 加权采样策略 位置编码 N PSNR↑ SSIM↑ Baseline × × × - 27.1596 0.6660 MS-uniform-noPos √ × × 4 27.2645 0.6899 MS-weighted-noPos √ √ × 4 27.2990 0.6954 MS-weighted-noPos(本文) √ √ √ 4 27.4372 0.7093 表 4 不同尺度数量 N的性能对比
N PSNR↑ SSIM↑ 2 27.1997 0.6705 3 27.2659 0.6914 4 27.4372 0.7093 5 27.3027 0.6988 表 5 复合感知损失消融实验结果
方法 $ {L}_{\text{denoise}} $ HDPL HFAL PSNR↑ SSIM↑ Baseline √ × × 27.2823 0.6899 +HDPL √ √ × 27.3054 0.6912 +HFAL √ × √ 27.3155 0.6954 +HDPL +HFAL √ √ √ 27.4372 0.7093 表 6 不同 $ {\lambda }_{1} $与$ {\lambda }_{2} $设置对性能的影响
$ {\lambda }_{1} $ $ {\lambda }_{2} $ PSNR↑ SSIM↑ $ 1\times {10}^{-2} $ 0 27.3054 0.6912 $ 6\times {10}^{-3} $ $ 4\times {10}^{-3} $ 27.3366 0.7002 $ 4\times {10}^{-3} $ $ 6\times {10}^{-3} $ 27.4372 0.7093 $ 2\times {10}^{-3} $ $ 8\times {10}^{-3} $ 27.3298 0.6958 0 $ 1\times {10}^{-2} $ 27.3155 0.6954 -
[1] 张永生, 巩丹超, 刘军, 等. 高分辨率遥感卫星应用: 成像模型、处理算法及应用技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.ZHANG Yongsheng, GONG Danchao, LIU Jun, et al. Applications of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Satellites[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004. [2] LI Songnian, DRAGICEVIC S, CASTRO F A, et al. Geospatial big data handling theory and methods: A review and research challenges[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2016, 115: 119–133. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.10.012. [3] 童旭东. 中国高分辨率对地观测系统重大专项建设进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2016, 20(5): 775–780. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20166302.TONG Xudong. Development of China high-resolution earth observation system[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(5): 775–780. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20166302. [4] ZHU Xiaoxiang, TUIA D, MOU Lichao, et al. Deep learning in remote sensing: A comprehensive review and list of resources[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2017, 5(4): 8–36. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2017.2762307. [5] FARSIU S, ROBINSON M D, ELAD M, et al. Fast and robust multiframe super resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(10): 1327–1344. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2004.834669. [6] WANG Qi, LI Qiang, and LI Xuelong. Spatial-spectral residual network for hyperspectral image super-resolution[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2001.04609, 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2001.04609. [7] 成科扬, 荣兰, 蒋森林, 等. 基于深度学习的遥感图像超分辨率重建方法综述[J]. 郑州大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 43(5): 8–16. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6833.2022.05.013.CHENG Keyang, RONG Lan, JIANG Senlin, et al. Overview of methods for remote sensing image super-resolution reconstruction based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University: Engineering Science, 2022, 43(5): 8–16. doi: 10.13705/j.issn.1671-6833.2022.05.013. [8] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 295–307. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2439281. [9] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, and FEI-FEI L. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 694–711. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_43. [10] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680. [11] TIAN Chunwei, ZHANG Xuanyu, ZHU Qi, et al. Generative adversarial networks for image super-resolution: A survey[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2204.13620, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2204.13620. [12] WANG Xintao, YU Ke, WU Shixiang, et al. ESRGAN: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks[C]. The European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Munich, Germany, 2019: 63–79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11021-5_5. [13] 彭晏飞, 高艺, 杜婷婷, 等. 生成对抗网络的单图像超分辨率重建方法[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2020, 14(9): 1612–1620. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.1910067.PENG Yanfei, GAO Yi, DU Tingting, et al. Single image super-resolution reconstruction method for generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2020, 14(9): 1612–1620. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.1910067. [14] HO J, JAIN A, and ABBEEL P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 574. [15] SONG Jiaming, MENG Chenlin, and ERMON S. Denoising diffusion implicit models[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. [16] SAHARIA C, HO J, CHAN W, et al. Image super-resolution via iterative refinement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(4): 4713–4726. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3204461. [17] ROMBACH R, BLATTMANN A, LORENZ D, et al. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 10674–10685. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01042. [18] 韩阳, 朱军鹏, 郭春雨, 等. 基于扩散模型的流场超分辨率重建方法[J]. 力学学报, 2023, 55(10): 2309–2320. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-167.HAN Yang, ZHU Junpeng, GUO Chunyu, et al. A flow field super-resolution reconstruction method based on diffusion model[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2023, 55(10): 2309–2320. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-167. [19] XIA Guisong, BAI Xiang, DING Jian, et al. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3974–3983. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00418. [20] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848. [21] JUSTICE C O, VERMOTE E, TOWNSHEND J R G, et al. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS): Land remote sensing for global change research[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(4): 1228–1249. doi: 10.1109/36.701075. [22] 甘甫平, 王润生, 王永江, 等. 基于遥感技术的土地利用与土地覆盖的分类方法[J]. 国土资源遥感, 1999, 11(4): 40–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-070X.1999.04.008.GAN Fuping, WANG Runsheng, WANG Yongjiang, et al. The classification method based on remote sensing techniques for land use and cover[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 1999, 11(4): 40–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-070X.1999.04.008. [23] 张秀再, 沈涛, 许岱. 基于改进YOLOv8算法的遥感图像目标检测[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61(10): 1028001. doi: 10.3788/LOP231803.ZHANG Xiuzai, SHEN Tao, and XU Dai. Remote-sensing image object detection based on improved YOLOv8 algorithm[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(10): 1028001. doi: 10.3788/LOP231803. [24] SHAO Zhenfeng, WANG Lei, WANG Zhongyuan, et al. Remote sensing image super-resolution using sparse representation and coupled sparse autoencoder[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(8): 2663–2674. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2925456. [25] ZHOU Weixun, GUAN Haiyan, LI Ziyu, et al. Remote sensing image retrieval in the past decade: Achievements, challenges, and future directions[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 1447–1473. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3236662. [26] 王海波, 马明国. 基于遥感的湖泊水域动态变化监测研究进展[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2009, 24(5): 674–684. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2009.5.674.WANG Haibo and MA Mingguo. A review of monitoring change in lake water areas based on remote sensing[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2009, 24(5): 674–684. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2009.5.674. [27] BILJECKI F, STOTER J, LEDOUX H, et al. Applications of 3D city models: State of the art review[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2015, 4(4): 2842–2889. doi: 10.3390/ijgi4042842. [28] PARK S C, PARK M K, and KANG M G. Super-resolution image reconstruction: A technical overview[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2003, 20(3): 21–36. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2003.1203207. [29] KEYS R. Cubic convolution interpolation for digital image processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1981, 29(6): 1153–1160. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1981.1163711. [30] KIM J, LEE J K, and LEE K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1646–1654. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.182. [31] KIM J, LEE J K, and LEE K M. Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1637–1645. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.181. [32] DONG Chao, LOY C C, and TANG Xiao’ou. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 391–407. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_25. [33] LIM B, SON S, KIM H, et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1132–1140. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2017.151. [34] ZHANG Yulun, LI Kunpeng, LI Kai, et al. Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 294–310. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_18. [35] MEI Yiqun, FAN Yuchen, and ZHOU Yuqian. Image super-resolution with non-local sparse attention[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 3516–3525. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00352. [36] NIU Ben, WEN Weilei, REN Wenqi, et al. Single image super-resolution via a holistic attention network[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 191–207. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58610-2_12. [37] HAUT J M, FERNANDEZ-BELTRAN R, PAOLETTI M E, et al. Remote sensing image superresolution using deep residual channel attention[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9277–9289. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2924818. [38] KONG Dezhi, GU Lingjia, LI Xiaofeng, et al. Multiscale residual dense network for the super-resolution of remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5612612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3370826. [39] WANG Hongyuan, CHENG Shuli, LI Yongming, et al. Lightweight remote-sensing image super-resolution via attention-based multilevel feature fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 2005715. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3336524. [40] XIAO Huanling, CHEN Xintong, LUO Liuhui, et al. A dual-path feature reuse multi-scale network for remote sensing image super-resolution[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2025, 81(1): 17. doi: 10.1007/s11227-024-06569-w. [41] CHEN Xiangyu, WANG Xintao, ZHOU Jiantao, et al. Activating more pixels in image super-resolution transformer[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 22367–22377. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.02142. [42] LIU Jingyi and YANG Xiaomin. Multi-stage remote sensing super-resolution network with deep fusion and structure enhancement based on CNN and transformer[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2025, 19(5): 407. doi: 10.1007/s11760-025-03988-x. [43] LUGMAYR A, DANELLJAN M, VAN GOOL L, et al. SRFlow: Learning the super-resolution space with normalizing flow[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 715–732. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58558-7_42. [44] LEDIG C, THEIS L, HUSZÁR F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 105–114. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.19. [45] MA Cheng, RAO Yongming, LU Jiwen, et al. Structure-preserving image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(11): 7898–7911. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3114428. [46] SONG Yang and ERMON S. Generative modeling by estimating gradients of the data distribution[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 1067. [47] LI Haoying, YANG Yifan, CHANG Meng, et al. SRDiff: Single image super-resolution with diffusion probabilistic models[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 479: 47–59. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.01.029. [48] LUO Ziwei, GUSTAFSSON F K, ZHAO Zheng, et al. Image restoration with mean-reverting stochastic differential equations[C]. The 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, USA, 2023: 23045–23066. [49] LIU Jinzhe, YUAN Zhiqiang, PAN Zhaoying, et al. Diffusion model with detail complement for super-resolution of remote sensing[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(19): 4834. doi: 10.3390/rs14194834. [50] HAN Lintao, ZHAO Yuchen, LV Hengyi, et al. Enhancing remote sensing image super-resolution with efficient hybrid conditional diffusion model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(13): 3452. doi: 10.3390/rs15133452. [51] XIAO Yi, YUAN Qiangqiang, JIANG Kui, et al. EDiffSR: An efficient diffusion probabilistic model for remote sensing image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5601514. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3341437. [52] 张文雪, 罗一涵, 刘雅卿, 等. 基于主动位移成像的图像超分辨率重建[J]. 光电工程, 2024, 51(1): 230290. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.230290.ZHANG Wenxue, LUO Yihan, LIU Yaqing, et al. Image super-resolution reconstruction based on active displacement imaging[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2024, 51(1): 230290. doi: 10.12086/oee.2024.230290. [53] 房垚鑫, 郭宝峰, 马超. 基于改进点扩散函数的遥感图像超分辨率重建[J]. 激光技术, 2019, 43(5): 713–718. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2019.05.024.FANG Yaoxin, GUO Baofeng, and MA Chao. Super-resolution reconstruction of remote sensing images based on the improved point spread function[J]. Laser Technology, 2019, 43(5): 713–718. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2019.05.024. [54] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. [55] XIA Guisong, HU Jingwen, HU Fan, et al. AID: A benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3965–3981. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2685945. [56] LI Ke, WAN Gang, CHENG Gong, et al. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 159: 296–307. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.11.023. [57] HEUSEL M, RAMSAUER H, UNTERTHINER T, et al. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6629–6640. [58] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861. [59] XIAO Yi, YUAN Qiangqiang, JIANG Kui, et al. TTST: A top-k token selective transformer for remote sensing image super-resolution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2024, 33: 738–752. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3349004. [60] LIU Quanyong, PENG Jiangtao, ZHANG Genwei, et al. Deep contrastive learning network for small-sample hyperspectral image classification[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 3: 0025. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0025. [61] SHI Qian, ZHU Jiajun, LIU Zhengyu, et al. The last puzzle of global building footprints—Mapping 280 million buildings in East Asia based on VHR images[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0138. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0138. [62] LIU Shuaijun, LIU Jia, TAN Xiaoyue, et al. A hybrid spatiotemporal fusion method for high spatial resolution imagery: Fusion of Gaofen-1 and Sentinel-2 over agricultural landscapes[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0159. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0159. [63] MEI Shaohui, LIAN Jiawei, WANG Xiaofei, et al. A comprehensive study on the robustness of deep learning-based image classification and object detection in remote sensing: Surveying and benchmarking[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0219. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0219. -






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
