Automating Algorithm Design for Agile Satellite Task Assignment with Large Language Models and Reinforcement Learning
-
摘要: 多敏捷对地观测卫星任务调度(MAEOSMSP)是一个复杂的NP-难问题,其求解算法的设计长期受限于对专家经验的依赖和场景适应性差的瓶颈。为突破这一局限,该文提出一种创新的自适应算法设计(AAD)框架,通过深度融合大语言模型(LLM)与强化学习(RL),实现调度算法的自动化生成与智能应用。框架的核心是一个离线进化-在线决策架构:离线阶段,利用LLM驱动的进化计算自动生成超越人类范式的分配算法,构建强大算法库;在线阶段,通过RL智能体根据实时求解状态,从算法库中动态选择最优算子,实现对新场景的强大泛化能力。在多个标准算例上的实验表明,AAD框架生成的任务分配算法在性能上全面超越了传统专家设计算法,尤其在复杂场景下性能提升高达9.8%。该研究证实了LLM与RL协同在自动化算法设计上的巨大潜力,为MAEOSMSP提供了一种高效、自适应的求解新范式。Abstract:
Objective The Multi-Agile Earth Observation Satellite Mission Scheduling Problem (MAEOSMSP) is an NP-hard problem. Algorithm design for this problem has long been constrained by reliance on expert experience and limited adaptability across diverse scenarios. To address this limitation, an Adaptive Algorithm Design (AAD) framework is proposed. The framework integrates a Large Language Model (LLM) and Reinforcement Learning (RL) to enable automated generation and intelligent application of scheduling algorithms. It is built on a novel offline evolution-online decision-making architecture. The objective is to discover heuristic algorithms that outperform human-designed methods and to provide an efficient and adaptive solution methodology for the MAEOSMSP. Methods The AAD framework adopts a two-stage mechanism. In the offline evolution stage, LLM-driven evolutionary computation is used to automatically generate a diverse and high-quality library of task assignment algorithms, thereby alleviating the limitations of manual design. In the online decision-making stage, an RL agent is trained to dynamically select the most suitable algorithm from the library based on the real-time solving state (e.g., solution improvement and stagnation). This process is formulated as a Markov decision process, which allows the agent to learn a policy that adapts to problem-solving dynamics. Results and Discussions The effectiveness of the AAD framework is evaluated through comprehensive experiments on 15 standard test scenarios. The framework is compared with several state-of-the-art methods, including expert-designed heuristics, an advanced deep learning approach, and ablation variants of the proposed framework. The results show that the dynamic strategies generated by AAD consistently outperform the baselines, with performance improvements of up to 9.8% in complex scenarios. Statistical analysis further indicates that AAD achieves superior solution quality and demonstrates strong robustness across different problem instances. Conclusions A novel AAD framework is presented to automate algorithm design for the MAEOSMSP by decoupling algorithm generation from algorithm application. The combination of LLM-based generation and RL-based decision making is validated empirically. Compared with traditional hyper-heuristics and existing LLM-based methods, the proposed architecture enables both the creation of new algorithms and their dynamic application. The framework provides a new paradigm for solving complex combinatorial optimization problems and shows potential for extension to other domains. -
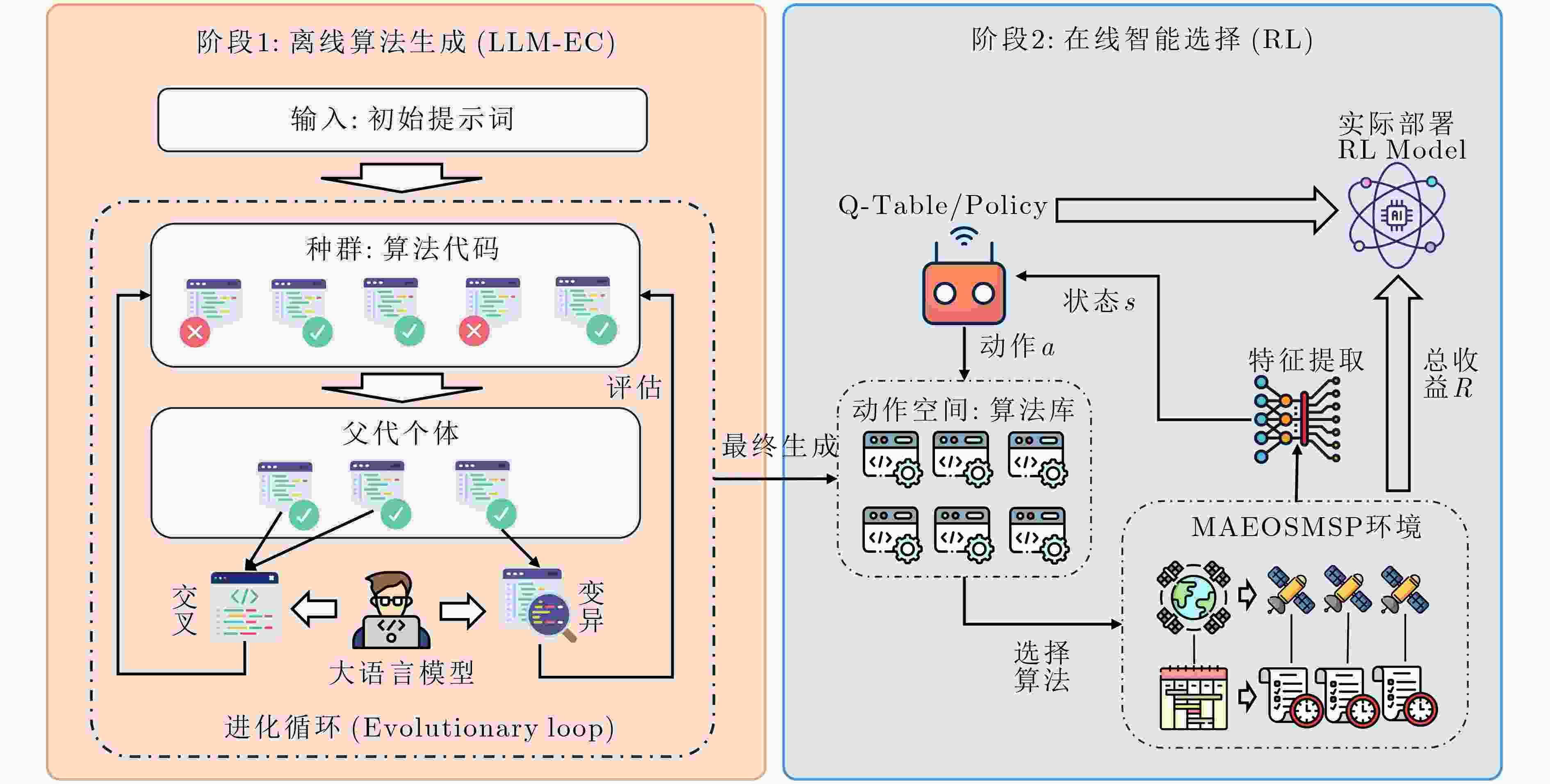
1 自适应分配算法设计(AAD)框架
输入:MAEOSMSP训练场景$ \mathcal{S}_{\mathrm{train}} $,LLM-EC进化代数
$ G\mathrm{_{EC}} $,种群大小$ N\mathrm{_{pop}} $,交叉概率$ p\mathrm{_c\mathrm{ }} $,变异概率$ p\mathrm{_m} $,子代规模
$ N\mathrm{_o} $,学习率$ \alpha $,折扣因子$ \gamma $,训练迭代次数$ E\mathrm{_{max}} $输出:最优任务分配算法库$ \mathcal{A} $,训练好的RL策略$ {Q}^{\mathrm{*}} $ /* 第一阶段:基于多场景进化的离线算法库构建 */ 1 初始化算法库$ \mathcal{A}\leftarrow \mathcal{\varnothing } $ 2 for 每个场景$ S\mathit{\mathrm{_{\mathit{\mathrm{\mathrm{k\mathrm{ }}}}}}}\in\mathcal{S}_{\mathrm{train}} $ do: 3 初始化:使用LLM生成针对场景$ S{_{{{k}}}} $的初始种群$ \mathrm{Pop} $ 4 for $ g=1 $ to $ G\mathrm{_{EC}} $ do 5 评估$ \mathrm{Pop} $中所有个体的适应度(在场景$ S{_k} $下的收益) 6 通过轮盘赌方法选择父代个体 7 交叉与变异: 8 for 每一对父代 do 9 if $ \text{Random} < p\mathrm{_c} $ then 10 通过LLM对父代代码进行交叉,生成子代 11 else 12 直接保留父代 13 end if 14 end for 15 for 每个子代 do 16 if $ \text{Random} < p\mathrm{_c} $ then 17 通过LLM变异提示对代码进行变异 18 end if 19 end for 20 更新种群$ \mathrm{\mathrm{Pop}\mathrm{ }} $,保留最优个体 21 end for 22 $ \pi_{\mathrm{\mathit{k}}}^{\mathrm{*}}\leftarrow $从$ \mathrm{Pop} $中选取的最优算法 23 $ \mathcal{A}\leftarrow \mathcal{A}\cup \{\pi _{k}^{\mathrm{*}}\} $ 24 end for /* 第二阶段:基于求解状态的RL策略训练 */ 25 初始化Q表$ Q(\boldsymbol{s},a)\leftarrow 0 $ 26 for episode $ e=1 $ to $ E\mathrm{_{max}} $ do 27 随机选择场景$ S\in\mathcal{S}\mathrm{_{train}} $,初始化解$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{0} $ 28 初始化求解状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}}_{0} $ 29 while 未满足终止条件 do 30 动作选择:基于当前状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}}_{t} $,使用$\varepsilon $-greedy策略从库
$ \mathcal{A} $中选择算法$ a\mathit{\mathrm{_{\mathit{\mathit{t\mathit{\mathit{ }}}}}}\mathit{\mathit{ }}} $31 执行:将算法$ a\mathrm{_{\mathit{t}}} $应用于当前解$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{t} $,通过单星调度得到
新解$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{t+1} $32 奖励计算:计算收益$ {r}_{t}=f({\boldsymbol{x}}_{t+1})-f({\boldsymbol{x}}_{t}) $及额外激励 33 状态观测:观测新的求解状态$ {\boldsymbol{s}}_{t+1} $ 34 Q值更新:$Q({\boldsymbol{s}}_{t},{a}_{t})\leftarrow Q({\boldsymbol{s}}_{t},{a}_{t})+ $
$ \alpha [{r}_{t}+\gamma \underset{a\mathrm{'}}{\max }Q({\boldsymbol{s}}_{t+1},a\mathrm{'})-Q({\boldsymbol{s}}_{t},{a}_{t})] $35 更新当前解与状态:$ {\boldsymbol{x}}_{t}\leftarrow {\boldsymbol{x}}_{t+1},{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t}\leftarrow {\boldsymbol{s}}_{t+1} $ 36 end while 37 end for 38 return $ \mathcal{A},{Q}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 表 1 对比算法在求解MAEOSMSP上的收益结果对比
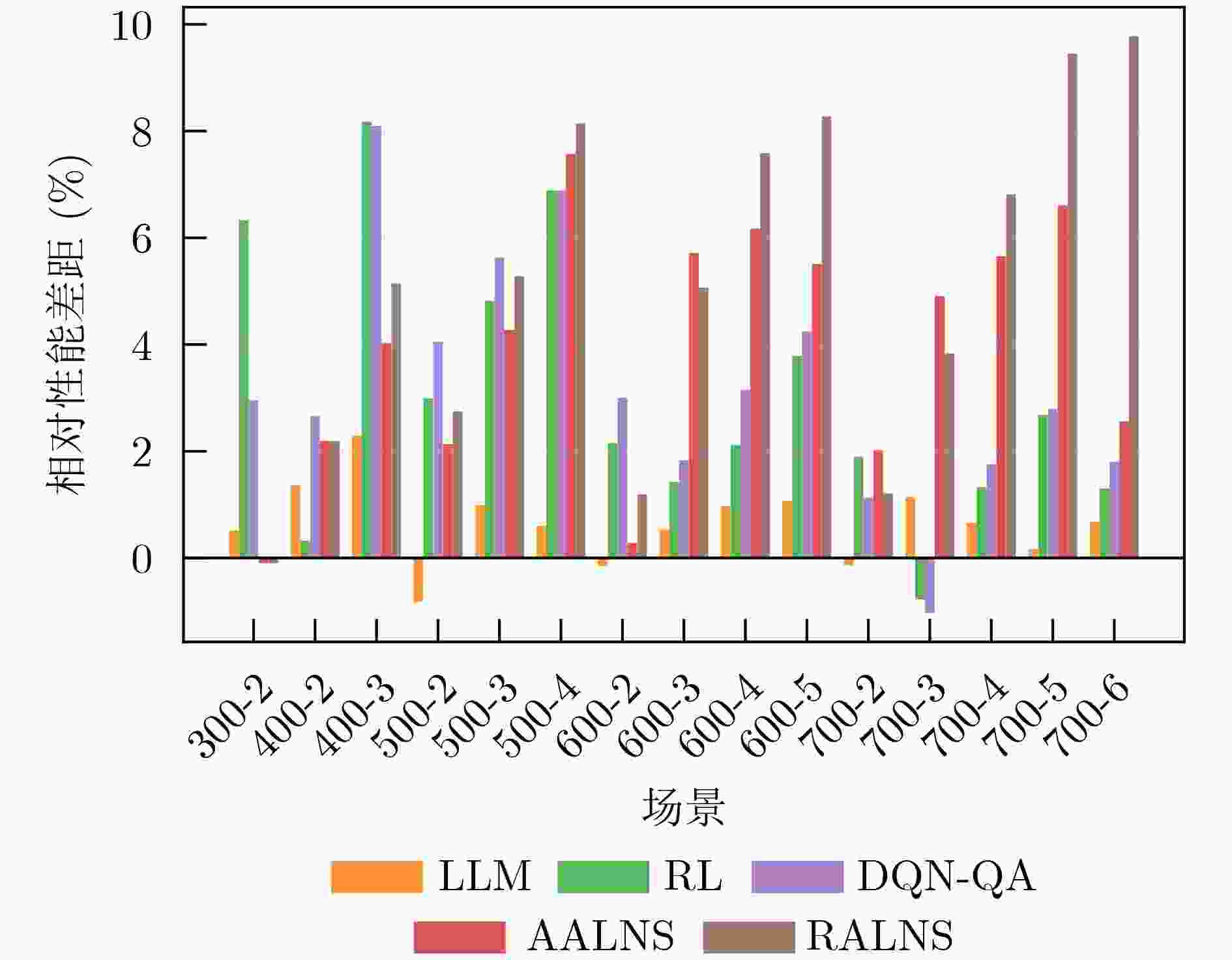
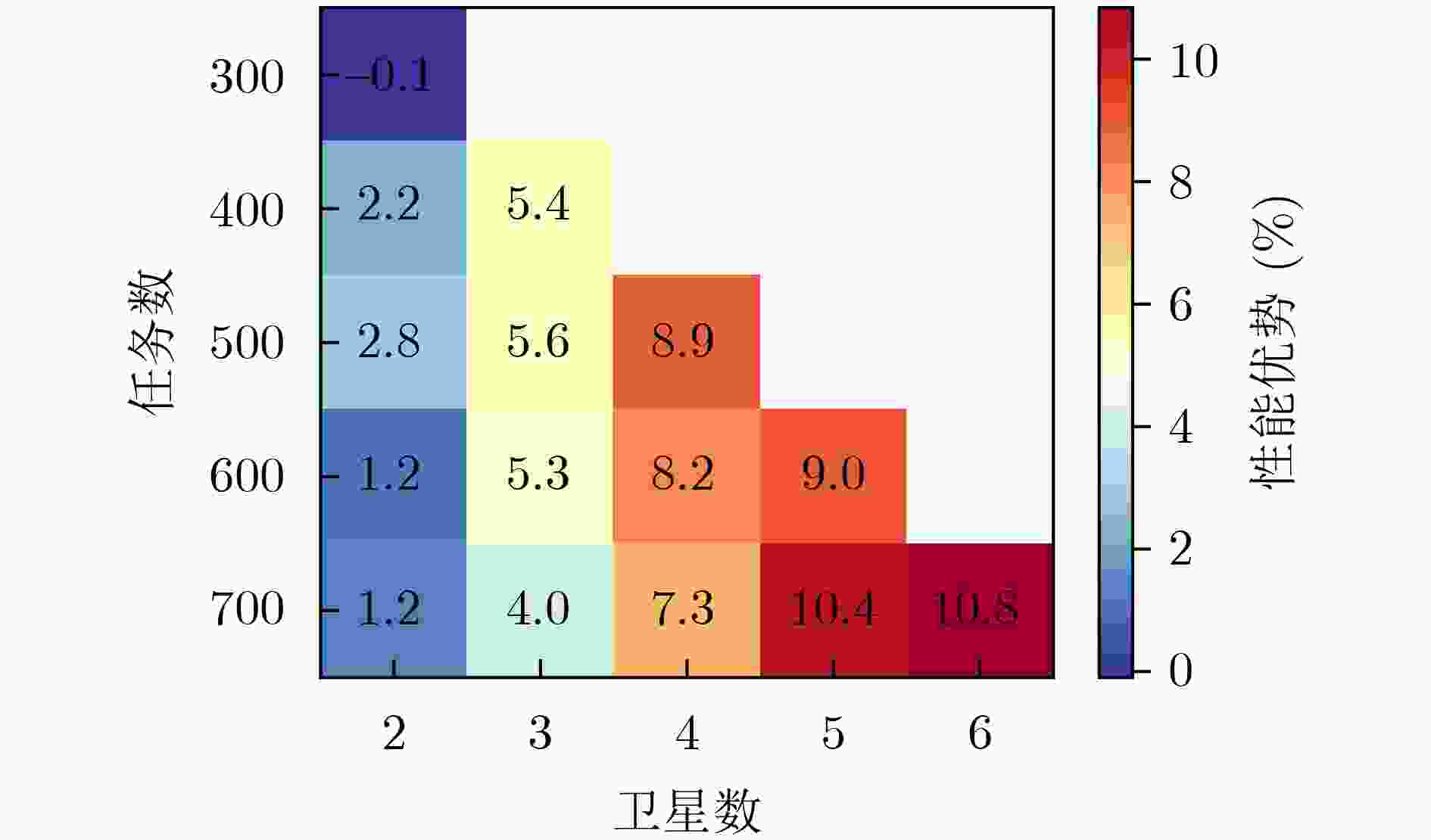
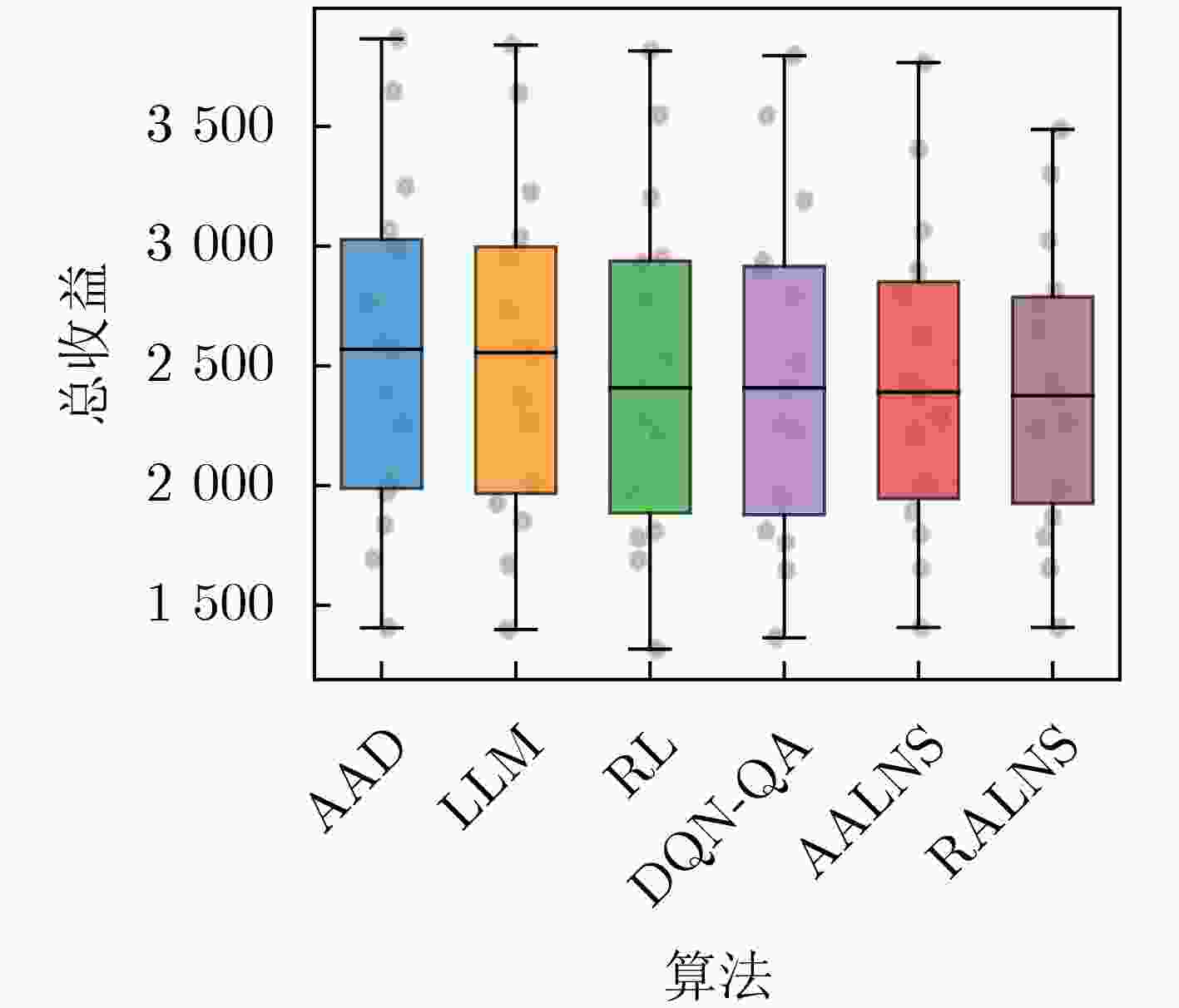
Scen. AAD LLM-Only RL-Only DQN-QA A-ALNS R-ALNS Profit Profit Gap Profit Gap Profit Gap Profit Gap Profit Gap 300-2 1405.8 1398.5 0.5 1316.8 6.3 1364.2 3.0 1407.2 –0.1 1407.2 –0.1 400-2 1693 1669.8 1.4 1687.5 0.3 1647.9 2.7 1655.9 2.2 1655.9 2.2 400-3 1969.9 1924.8 2.3 1808.8 8.2 1810.4 8.1 1890.5 4.0 1868.5 5.1 500-2 1836.9 1852.1 –0.8 1782 3.0 1762.4 4.1 1797.7 2.1 1786.4 2.8 500-3 2388.2 2364.5 1.0 2273.1 4.8 2253.8 5.6 2286.1 4.3 2262 5.3 500-4 2586.2 2570.6 0.6 2408 6.9 2408 6.9 2390.2 7.6 2375.6 8.1 600-2 2004.7 2007.8 –0.2 1961.5 2.2 1944.5 3.0 1999 0.3 1980.7 1.2 600-3 2569.4 2555.5 0.5 2532.8 1.4 2522.3 1.8 2422.4 5.7 2439.1 5.1 600-4 2989.4 2960.1 1.0 2926.1 2.1 2895.1 3.2 2804.8 6.2 2762.6 7.6 600-5 3067.2 3034.2 1.1 2951.1 3.8 2936.7 4.3 2898.2 5.5 2813.4 8.3 700-2 2260 2263.2 –0.1 2217.1 1.9 2234.3 1.1 2214.3 2.0 2232.6 1.2 700-3 2762.4 2730.7 1.1 2783.9 –0.8 2790.9 –1.0 2626.7 4.9 2656.4 3.8 700-4 3246.3 3225 0.7 3203.1 1.3 3189.3 1.8 3062.8 5.7 3025.1 6.8 700-5 3646.3 3640.1 0.2 3548.6 2.7 3544.5 2.8 3405.1 6.6 3301.6 9.5 700-6 3865.6 3839.5 0.7 3815.2 1.3 3795.6 1.8 3766.5 2.6 3487.5 9.8 表 2 AAD框架在不同规模场景下的离线训练时间开销(h)
场景规模 算法库构建 策略训练 总离线训练时间 300-2 ~ 1.5 ~ 0.3 ~ 1.8 500-3 ~ 2.5 ~ 0.5 ~ 3.0 700-6 ~ 4.0 ~ 1.0 ~ 5.0 表 3 演化分配算子的多标准评估方法概述
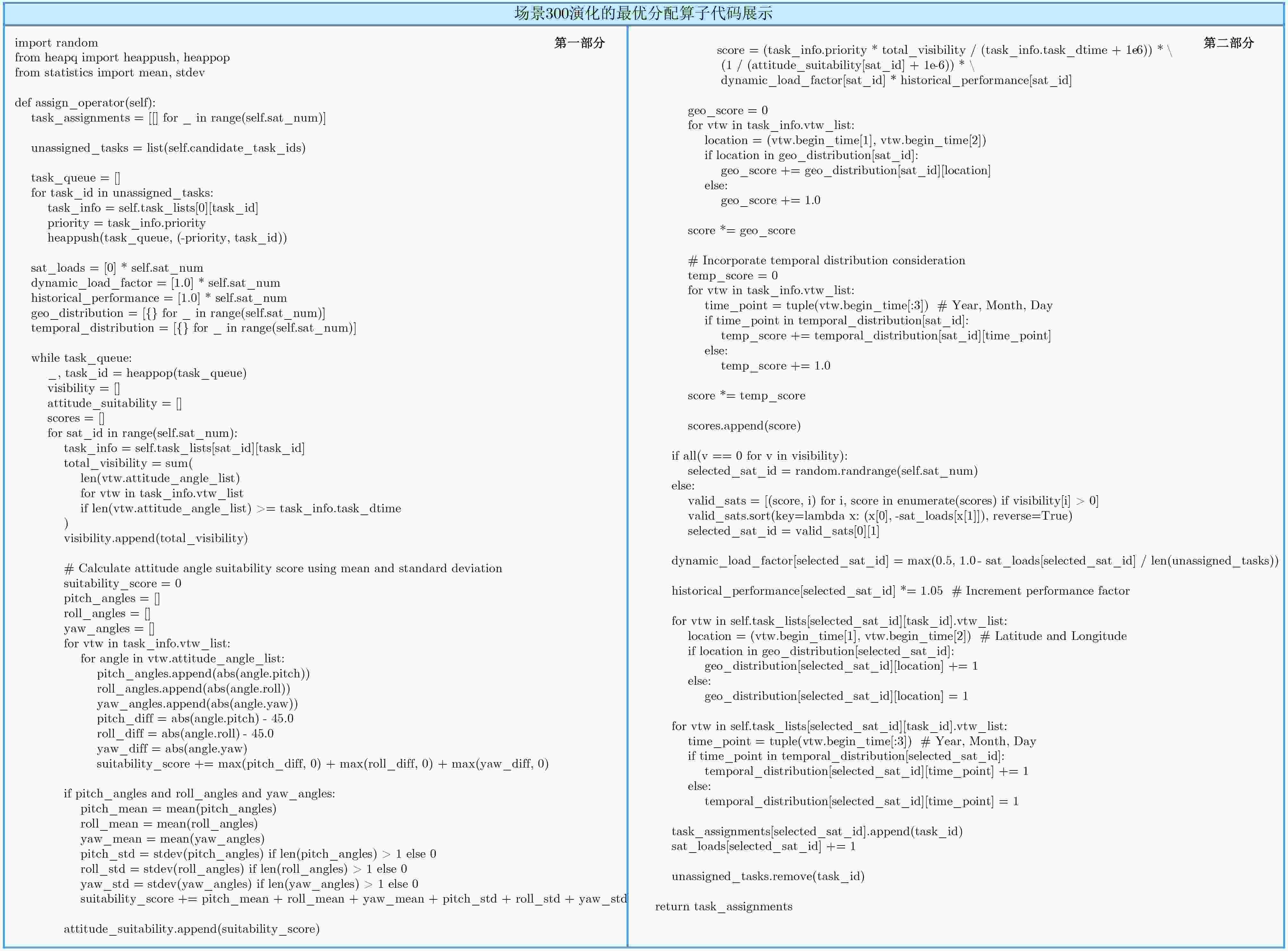
评估标准 具体描述 关注领域 专家对比 优先级与可见性综合评分 结合任务的内在优先级、对特定卫星的总有效可见时长,并根据任务执行时长进行归一化,形成基础价值分数:$ {S}_{\text{base}}(i,j)=\dfrac{{P}_{i}\cdot {V}_{ij}}{{D}_{i}+\epsilon } $ 任务价值与机会 融合多种单一规则,
实现综合量化评估姿态适宜性
评分引入复杂的姿态成本函数,惩罚超出理想范围的姿态角,并结合姿态剖面的统计特性(均值与标准差)来量化姿态控制的稳定性与综合成本。该评分为成本的倒数:$ {S}_{\text{att}}(i,j)=\dfrac{1}{{C}_{\text{att}}(i,j)+\epsilon } $ 卫星姿态动力学 新颖概念:超越了硬约束检查,引入统计指标来评估姿态剖面的整体质量 动态负载
均衡因子根据卫星当前的负载情况,动态调整其被分配任务的可能性。负载越高,该因子越低,从而在系统层面促进任务的均衡分配:$ {F}_{\text{load}}(j)=\mathrm{max}(0.5,1-\dfrac{{L}_{j}}{{N}_{\text{rem}}}) $ 系统资源均衡 在每次决策中实现动态均衡,而非静态或后置调整 历史性能激励 为被成功分配任务的卫星累积一个性能因子,模拟一种“优胜劣汰”的自适应机制,使其在后续分配中更具竞争力:$ H_{j}^{(t+1)}=(1+\beta )\cdot H_{j}^{(t)} $ 卫星性能演化 新颖概念:引入自适应学习机制,打破了卫星能力固定的传统假设 地理/时间分布均衡度 评估将任务分配给某卫星后,是否有助于该卫星任务集的时空聚集性,鼓励其对已覆盖区域或已安排任务的日期进行强化观测:$ {S}_{\mathrm{geo}/\text{temp}}(i,j)\propto \sum (\text{History}+1) $ 时空覆盖策略 新颖概念:从微观的任务满足,转向宏观的系统级时空布局优化 表 4 数学符号定义
符号 定义 $ i,j $ 分别代表任务索引和卫星索引 $ {S}_{\text{base}}(i,j) $ 将任务$ i $分配给卫星$ j $的基础价值分数 $ {S}_{\text{att}}(i,j) $ 将任务$ i $分配给卫星$ j $的姿态适宜性分数 $ {S}_{\text{final}}(i,j) $ 将任务$ i $分配给卫星$ j $的最终综合得分 $ {P}_{i} $ 任务$ i $的优先级 $ {V}_{ij} $ $ j $对任务$ i $的总有效可见时长 $ {D}_{i} $ 任务$ i $所需的执行时长 $ {C}_{\text{att}}(i,j) $ 卫星$ j $执行任务$ i $的综合姿态成本 $ {F}_{\text{load}}(j) $ 卫星$ j $的动态负载均衡因子 $ {L}_{j} $ 卫星$ j $的当前负载(已分配任务数) $ {N}_{\text{rem}} $ 系统中剩余未分配的任务总数 $ H_{j}^{(t)} $ 卫星$ j $在决策轮次$ t $的历史性能因子 $ \beta $ 历史性能因子的增长率(常数) $ {S}_{\mathrm{geo}/\text{temp}}(i,j) $ 分配任务$ i $给卫星$ j $的时空分布均衡度分数 $ \epsilon $ 一个极小的正数,用于防止分母为零 -
[1] ZHAO Qiang, YU Le, DU Zhenrong, et al . An overview of the applications of Earth observation satellite data: Impacts and future trends[J]. Remote Sensing,2022 ,14 (8 ):1863 . doi: 10.3390/rs14081863[2] HE Lei, DE WEERDT M, and YORKE-SMITH N . Time/sequence-dependent scheduling: The design and evaluation of a general purpose tabu-based adaptive large neighbourhood search algorithm[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,2020 ,31 (4 ):1051 –1078 . doi: 10.1007/s10845-019-01518-4[3] WANG Xinwei, WU Guohua, XING Lining, et al . Agile Earth observation satellite scheduling over 20 years: Formulations, methods, and future directions[J]. IEEE Systems Journal,2021 ,15 (3 ):3881 –3892 . doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2997050[4] PENG Guansheng, SONG Guopeng, HE Yongming, et al . Solving the agile Earth observation satellite scheduling problem with time-dependent transition times[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems,2022 ,52 (3 ):1614 –1625 . doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3031738[5] CHO D H, KIM J H, CHOI H L, et al . Optimization-based scheduling method for agile Earth-observing satellite constellation[J]. Journal of Aerospace Information Systems,2018 ,15 (11 ):611 –626 . doi: 10.2514/1.I010620[6] WU Jian, YAO Feng, SONG Yanjie, et al . Frequent pattern-based parallel search approach for time-dependent agile earth observation satellite scheduling[J]. Information Sciences,2023 ,636 :118924 . doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.04.003[7] WEI Luona, CUI Yongqiang, CHEN Ming, et al . Multi-objective neural policy approach for agile earth satellite scheduling problem considering image quality[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation,2025 ,94 :101857 . doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2025.101857[8] LI Lei, DU Yonghao, YAO Feng, et al . Learning memetic algorithm based on variable population and neighborhood for multi-complex target scheduling of large-scale imaging satellites[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation,2025 ,92 :101789 . doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2024.101789[9] 彭观胜, 宋国鹏, 刘晓路, 等 . 考虑时间依赖收益特性的敏捷卫星调度问题[J]. 运筹与管理,2024 ,33 (8 ):1 –7 . doi: 10.12005/orms.2024.0243PENG Guansheng, SONG Guopeng, LIU Xiaolu, et al . Agile earth observation satellite scheduling with time-dependent profits[J]. Operations Research and Management Science,2024 ,33 (8 ):1 –7 . doi: 10.12005/orms.2024.0243[10] DU Yonghao, WANG Tao, XIN Bin, et al . A data-driven parallel scheduling approach for multiple agile earth observation satellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation,2020 ,24 (4 ):679 –693 . doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2934148[11] WANG Xinwei, GU Yi, WU Guohua, et al . Robust scheduling for multiple agile Earth observation satellites under cloud coverage uncertainty[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering,2021 ,156 :107292 . doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107292[12] SUN Haiquan, XIA Wei, WANG Zhilong, et al . Agile earth observation satellite scheduling algorithm for emergency tasks based on multiple strategies[J]. Journal of Systems Science and Systems Engineering,2021 ,30 (5 ):626 –646 . doi: 10.1007/s11518-021-5506-4[13] YAO Feng, CHEN Yingguo, WANG Ling, et al . A bilevel evolutionary algorithm for large-scale multiobjective task scheduling in multiagile earth observation satellite systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems,2024 ,54 (6 ):3512 –3524 . doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3359265[14] CHEN Jiawei, WANG Feiran, CHEN Yingguo, et al . A generalized bilevel optimization model for large-scale task scheduling in multiple agile earth observation satellites[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems,2025 ,309 :112809 . doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2024.112809[15] HE Yongming, WU Guohua, CHEN Yingwu, et al. A two-stage framework and reinforcement learning-based optimization algorithms for complex scheduling problems[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2103.05847, 2021. [16] FENG Xiaoen, LI Yuqing, and XU Minqiang . Multi-satellite cooperative scheduling method for large-scale tasks based on hybrid graph neural network and metaheuristic algorithm[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics,2024 ,60 :102362 . doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2024.102362[17] LI Rui, WANG Ling, SANG Hongyan, et al. LLM-assisted automatic memetic algorithm for lot-streaming hybrid job shop scheduling with variable sublots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2025, Early Access. [18] LIU Fei, TONG Xialiang, YUAN Mingxuan, et al. Algorithm evolution using large language model[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2311.15249, 2023. [19] LIU Fei, TONG Xialiang, YUAN Mingxuan, et al. Evolution of heuristics: Towards efficient automatic algorithm design using large language model[C]. Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2024. [20] YE Haoran, WANG Jiarui, CAO Zhiguang, et al. ReEvo: Large language models as hyper-heuristics with reflective evolution[C]. The 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 1381. doi: 10.5555/3737916.3739297. [21] LI Hanxiao, GAO Kaizhou, DUAN Peiyong, et al . An improved artificial bee colony algorithm with Q-learning for solving permutation flow-shop scheduling problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems,2023 ,53 (5 ):2684 –2693 . doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3219380[22] QI Rui, LI Junqing, WANG Juan, et al . QMOEA: A Q-learning-based multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for solving time-dependent green vehicle routing problems with time windows[J]. Information Sciences,2022 ,608 :178 –201 . doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.06.056[23] CHEN Ming, DU Yonghao, TANG Ke, et al . Learning to construct a solution for the agile satellite scheduling problem with time-dependent transition times[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems,2024 ,54 (10 ):5949 –5963 . doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3411640[24] GONG Yupeng, LI Anshou, and PENG Xuan . Geometrical design method of Walker constellation in non-terrestrial network[J]. Acta Astronautica,2024 ,219 :618 –626 . doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2024.03.069[25] KOLAEE M H, JABBARZADEH A, and AL-E-HASHEM S M J M . Sustainable group tourist trip planning: An adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications,2024 ,237 :121375 . doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121375[26] JIA Shengyang, DENG Lei, ZHAO Quanwu, et al . An adaptive large neighborhood search heuristic for multi-commodity two-echelon vehicle routing problem with satellite synchronization[J]. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization,2023 ,19 (2 ):1187 –1210 . doi: 10.3934/jimo.2021225[27] WU Guohua, XIANG Zhiqing, WANG Yalin, et al . Improved adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm based on the two-stage framework for scheduling multiple super-agile satellites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems,2024 ,60 (5 ):7185 –7200 . doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3416427[28] HE Lei, LIU Xiaolu, LAPORTE G, et al . An improved adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm for multiple agile satellites scheduling[J]. Computers & Operations Research,2018 ,100 :12 –25 . doi: 10.1016/j.cor.2018.06.020 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
