UMM-Det: A Unified Object Detection Framework for Heterogeneous Multimodal Remote Sensing Imagery
-
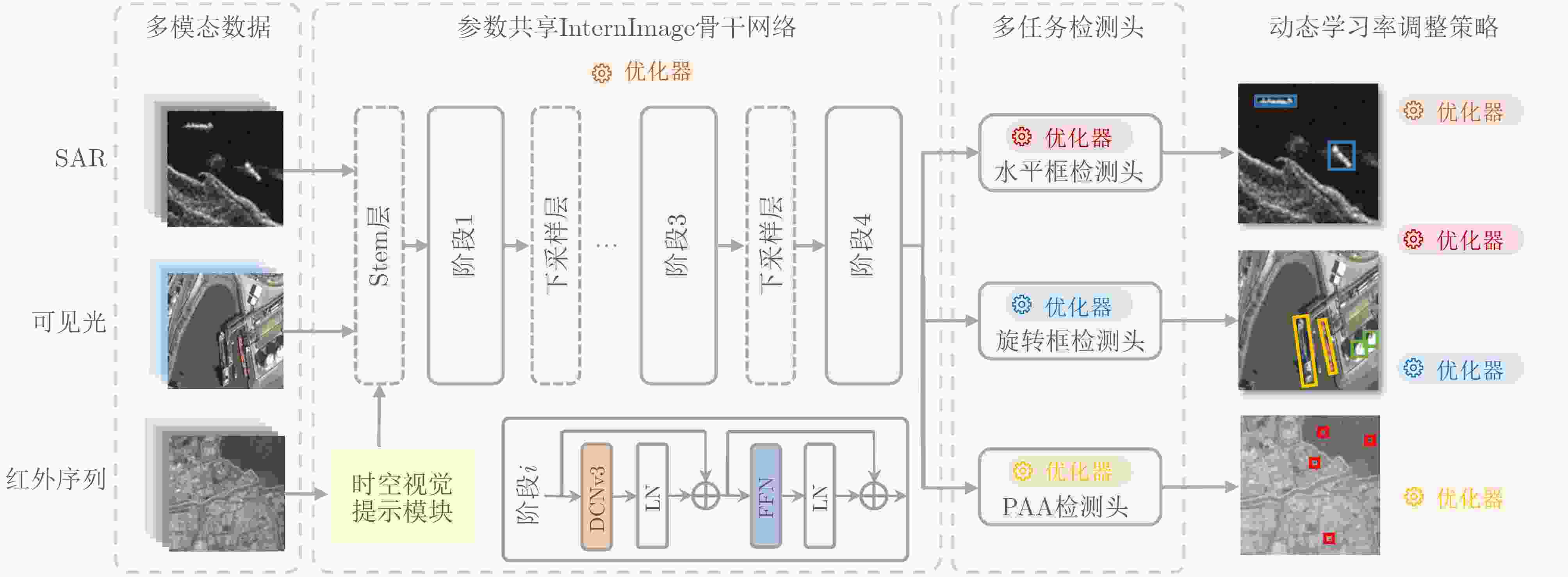
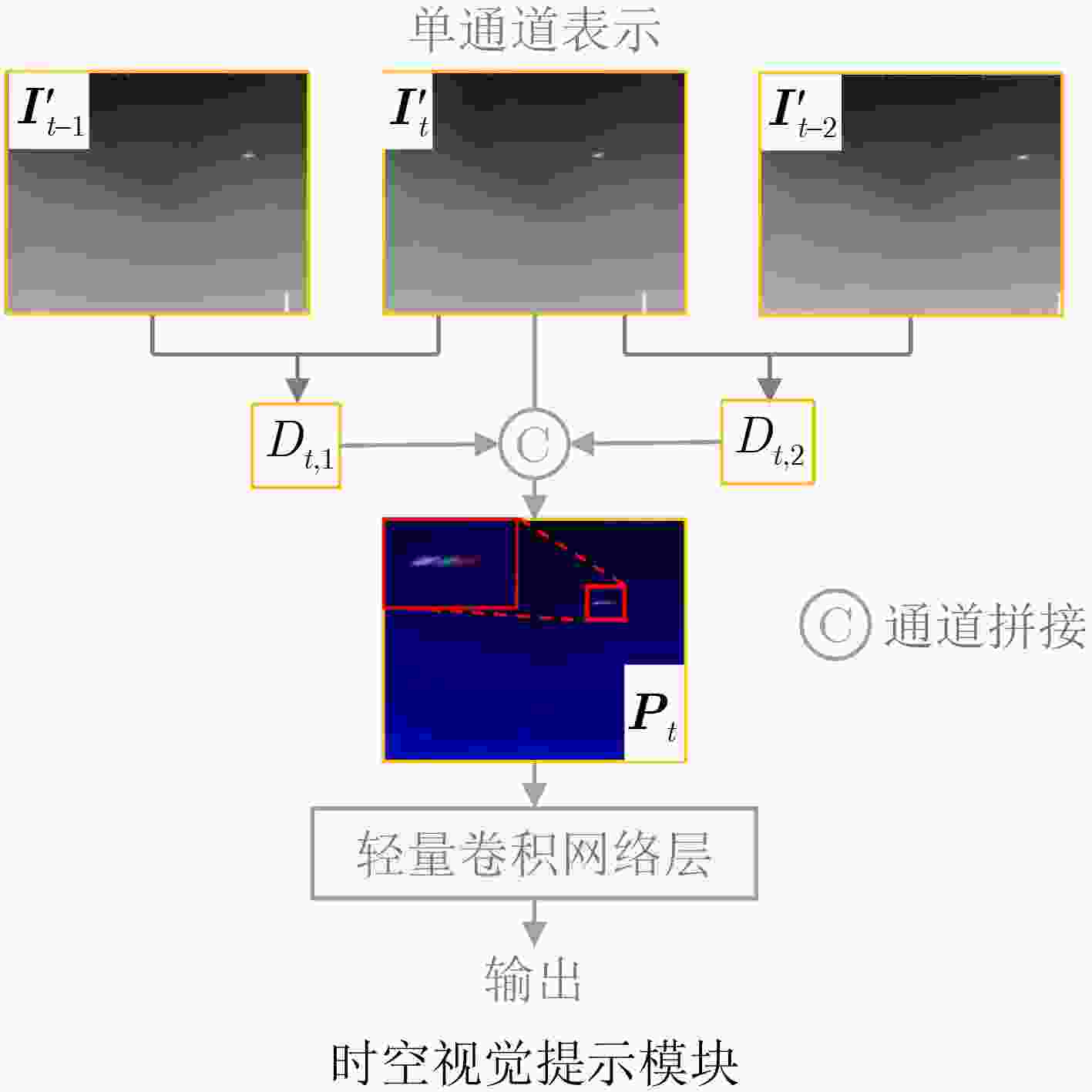
摘要: 当前天基遥感目标检测任务面临着如何构建一个统一模型以有效处理合成孔径雷达(SAR)、可见光、红外等多模态异构数据的挑战。针对此,该文提出一种异构多模态遥感影像一体化目标检测框架UMM-Det,致力于通过单一架构实现对多源数据的高性能目标检测。该框架采用单一共享架构,旨在实现对多源遥感数据的高效、统一检测。UMM-Det在基线模型SM3Det的基础上进行3点关键改进:首先,以具备动态采样与大感受野建模能力的InternImage替换原有ConvNeXt主干,旨在提升对多尺度、低对比度目标的特征提取精度;其次,针对红外分支设计了基于时序信息的时空视觉提示模块,通过精细化的帧差增强策略生成高对比度的运动特征,以此作为先验知识辅助网络区分动态弱小目标;最后,针对红外序列中普遍存在的弱小目标正负样本极度不均衡问题,引入概率性锚框分配策略(PAA)优化检测头,显著提升了目标采样的精确性与检测性能。在SARDet-50K、DOTA与SatVideoIRSTD 3个公开数据集上的实验表明,UMM-Det在SAR与可见光检测任务中mAP@0.5:0.95分别提升2.40%和1.77%,并且在红外序列弱小目标检测任务中较基线模型SM3Det检测率提升了2.54%。同时,该模型在保证精度提升的前提下将参数量减少50%以上,展现出精度、效率与轻量化的综合优势,为新一代高性能天基遥感态统一检测框架的构建提供了有效路径。
-
关键词:
- 天基多模态统一检测框架 /
- 多模态遥感检测 /
- 红外序列感知 /
- 弱小目标检测
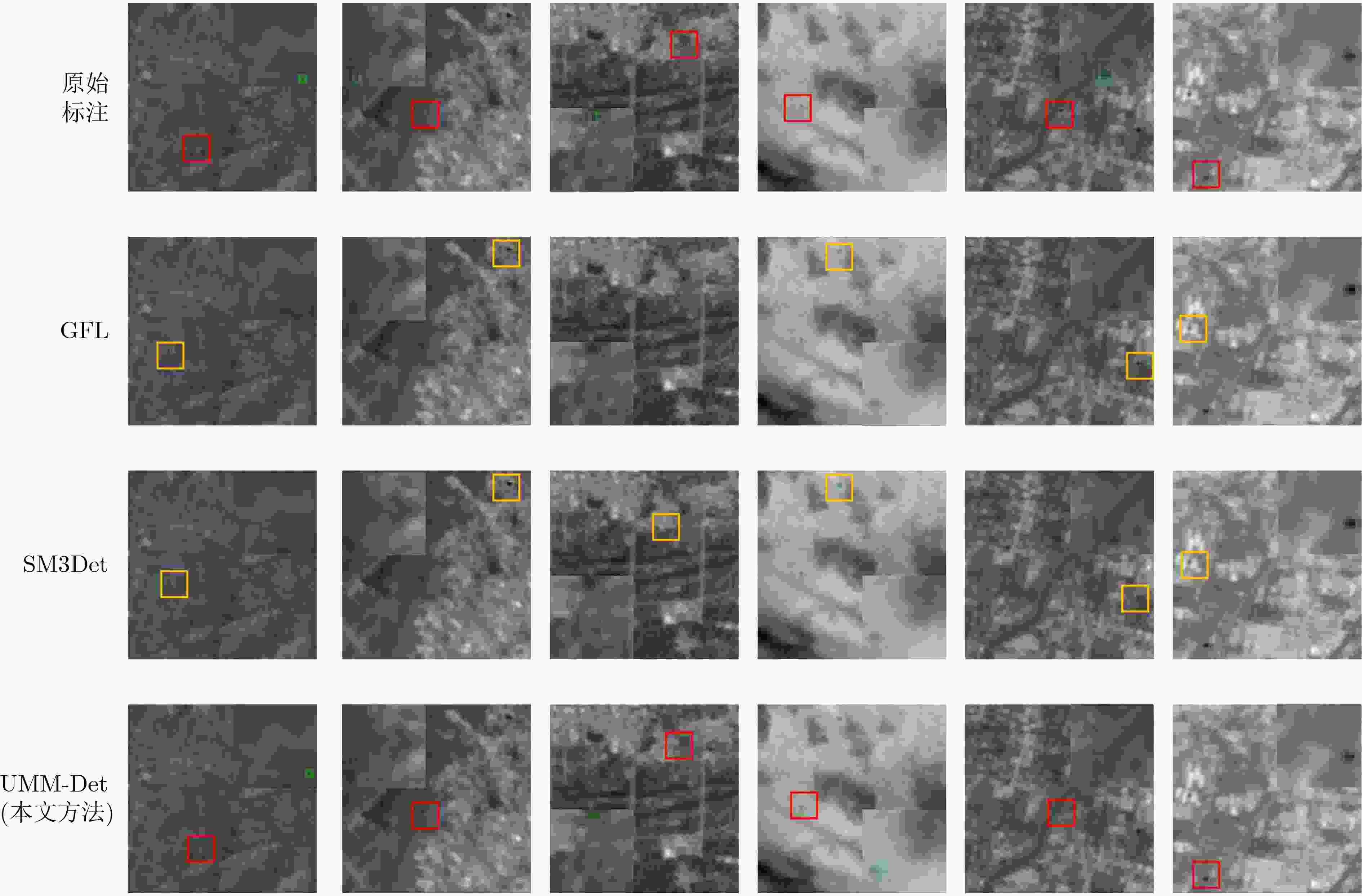
Abstract:Objective With the increasing demand for space-based situational awareness, object detection across multiple modalities has become a fundamental yet challenging task. Existing large-scale multimodal detection models for space-based remote sensing mainly operate on single-frame images from visible light, Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), and infrared modalities. Although these models achieve acceptable performance in conventional detection tasks, they largely neglect the critical role of infrared video sequences in improving weak and small target detection. Temporal information in sequential infrared data provides discriminative cues for separating dynamic targets from complex clutter, which cannot be captured by single-frame detectors. To address this limitation, this study proposes UMM-Det, a unified detection model designed for infrared sequences. The proposed model extends existing space-based multimodal frameworks to sequential data and demonstrates that exploiting temporal dynamics is essential for next-generation high-precision space-based sensing systems. Methods UMM-Det is developed based on the unified multimodal detection framework SM3Det and introduces three key innovations. First, the ConvNeXt backbone is replaced with InternImage, a state-of-the-art architecture with dynamic sampling and large receptive field modeling. This replacement improves feature extraction robustness under multi-scale variations and low-contrast conditions that are typical of weak and small targets. Second, a spatiotemporal visual prompting module is designed for the infrared branch. This module generates high-contrast motion features using a refined frame-difference enhancement strategy. The resulting temporal priors guide the backbone to focus on dynamic target regions, thereby reducing interference from static background clutter. Third, to address the imbalance between positive and negative samples during training, Probabilistic Anchor Assignment (PAA) is incorporated into the infrared detection head. This strategy improves anchor selection reliability and enhances small target detection under highly skewed data distributions. The overall pipeline is shown in Fig. 1 , and the structure of the spatiotemporal visual prompting module is illustrated inFig. 2 .Results and Discussions Extensive experiments are conducted on three public benchmarks: SatVideoIRSTD for infrared sequence detection, SARDet-50K for SAR target detection, and DOTA for visible light remote sensing detection. The results in Table 2 show that UMM-Det consistently outperforms the baseline SM3Det across all modalities while significantly improving efficiency. For infrared sequence small target detection, UMM-Det improves detection accuracy by 2.54% compared with SM3Det, confirming the effectiveness of temporal priors. In SAR target detection, the model achieves a 2.40% improvement in mAP@0.5:0.95. In visible light detection, an improvement of 1.77% is observed. These results demonstrate the strong generalization capability of the proposed framework across heterogeneous modalities. In addition, UMM-Det reduces the number of parameters by more than 50% relative to SM3Det, which supports efficient and lightweight deployment in space-based systems. Qualitative results inFig. 3 show that UMM-Det detects low-contrast and dynamic weak targets that are missed by the baseline model. The analysis highlights three main findings. First, the spatiotemporal visual prompting strategy effectively converts frame-to-frame variations into salient motion-aware cues, which are critical for distinguishing small dynamic targets from clutter in complex infrared scenes. Second, the use of InternImage substantially strengthens multi-scale representation capability, improving robustness to variations in target size and contrast. Third, PAA alleviates training imbalance, leading to more stable optimization and higher detection reliability. Together, these components produce a synergistic effect, resulting in superior performance on both sequential infrared data and static SAR and visible light imagery.Conclusions This study proposes UMM-Det, a space-based multimodal detection model that explicitly integrates infrared sequence information into a unified detection framework. By adopting InternImage for feature extraction, a spatiotemporal visual prompting module for motion-aware enhancement, and PAA for balanced training, UMM-Det achieves notable improvements in detection accuracy while reducing computational cost by more than 50%. Experimental results on SatVideoIRSTD, SARDet-50K, and DOTA demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across infrared, SAR, and visible light modalities, with accuracy gains of 2.54%, 2.40%, and 1.77%, respectively. The proposed framework provides a practical solution for future high-performance space-based situational awareness systems, where accuracy, efficiency, and lightweight design are all required. Future work may extend this framework to multi-satellite cooperative sensing and real-time onboard deployment. -
表 1 不同模块的消融实验结果
InternImage骨干 PAA检测头 时空视觉
提示模块Pd(%) Fa 77.13 3.24×10–4 √ 77.93 5.34×10–4 √ √ 78.44 8.24×10–4 √ √ √ 79.67 6.61×10–4 表 2 不同基线网络在3个模态数据集上的实验结果
SARDet-50K DOTA SatVideoIRSTD 计算量 参数量 mAP@0.5:0.95 mAP@0.5 mAP@0.5:0.95 mAP@0.5 Pd Fa RetinaNet[27] 53.04 83.99 - - 66.55 1.19×10–4 520.74G 206.69M Faster RCNN[28] 54.56 85.62 - - 45.05 7.99×10–5 435.69G 173.55M Cascade RCNN[29] 56.30 85.39 - - 58.06 8.44×10–5 463.44G 201.30M GFL[30] 59.01 88.77 - - 72.51 3.51×10–4 733.85G 274.95M RoI Transformer[31] - - 45.43 76.79 - - 520.74G 206.69M S2ANet[32] - - 39.92 76.20 - - 463.44G 201.30M VAN-T[24] 49.28 80.85 43.60 74.73 70.52 3.05×10–4 270.47G 45.32M VAN-S[24] 57.98 88.36 45.50 76.66 74.84 4.94×10–4 366.56G 64.87M LSKNet-T[25] 49.95 81.76 43.56 75.44 70.81 3.51×10–4 269.38G 45.03M LSKNet-S[25] 58.41 88.48 44.80 76.69 74.51 6.13×10–4 369.67G 65.37M PVT-v2-T[26] 48.58 80.71 42.72 75.39 71.94 3.88×10–4 236.92G 40.20M PVT-v2-S[26] 54.53 85.48 44.37 77.53 75.19 6.83×10–4 293.87G 51.45M SM3Det[15] 60.64 89.94 46.47 77.88 77.13 3.24×10–4 741.29G 164.29M UMM-Det(本文方法) 63.04 91.55 48.24 80.91 79.67 6.61×10–4 977.31G 76.64M 注:粗体表示最优值。 -
[1] 安成锦, 杨俊刚, 梁政宇, 等. 阵列相机图像邻近目标超分辨方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(11): 4050–4059. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230810.AN Chengjin, YANG Jungang, LIANG Zhengyu, et al. Closely spaced objects super-resolution method using array camera images[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(11): 4050–4059. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230810. [2] 杨俊刚, 刘婷, 刘永贤, 等. 基于非凸低秩塔克分解的红外小目标检测方法[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2025, 44(2): 311–325. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2025.02.018.YANG Jungang, LIU Ting, LIU Yongxian, et al. Infrared small target detection method based on nonconvex low-rank Tuck decomposition[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2025, 44(2): 311–325. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2025.02.018. [3] 林再平, 罗伊杭, 李博扬, 等. 基于梯度可感知通道注意力模块的红外小目标检测前去噪网络[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2024, 43(2): 254–260. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2024.02.015.LIN Zaiping, LUO Yihang, LI Boyang, et al. Gradient-aware channel attention network for infrared small target image denoising before detection[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2024, 43(2): 254–260. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2024.02.015. [4] SHI Qian, HE Da, LIU Zhengyu, et al. Globe230k: A benchmark dense-pixel annotation dataset for global land cover mapping[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 3: 0078. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0078. [5] TIAN Jiaqi, ZHU Xiaolin, SHEN Miaogen, et al. Effectiveness of spatiotemporal data fusion in fine-scale land surface phenology monitoring: A simulation study[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0118. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0118. [6] LIU Shuaijun, LIU Jia, TAN Xiaoyue, et al. A hybrid spatiotemporal fusion method for high spatial resolution imagery: Fusion of gaofen-1 and sentinel-2 over agricultural landscapes[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0159. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0159. [7] MEI Shaohui, LIAN Jiawei, WANG Xiaofei, et al. A comprehensive study on the robustness of deep learning-based image classification and object detection in remote sensing: Surveying and benchmarking[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0219. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0219. [8] GUO Xin, LAO Jiangwei, DANG Bo, et al. SkySense: A multi-modal remote sensing foundation model towards universal interpretation for earth observation imagery[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2024: 27662–27673. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.02613. [9] ZHANG Yingying, RU Lixiang, Wu Kang, et al. SkySense V2: A unified foundation model for multi-modal remote sensing[C]. International Conference on Computer Vision, Honolulu, Hawaii, 2025: 9136-9146. [10] BI Hanbo, FENG Yingchao, TONG Boyuan, et al. RingMoE: Mixture-of-modality-experts multi-modal foundation models for universal remote sensing image interpretation[J]. arXiv: 2504.03166, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2504.03166. [11] LI Xuyang, LI Chenyu, GHAMISI P, et al. FlexiMo: A flexible remote sensing foundation model[J]. arXiv: 2503.23844, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.23844. [12] YAO Kelu, XU Nuo, YANG Rong, et al. Falcon: A remote sensing vision-language foundation model (Technical Report)[J]. arXiv: 2503.11070, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2503.11070. [13] QIN Xiaolei, WANG Di, ZHANG Jing, et al. TiMo: Spatiotemporal foundation model for satellite image time series[J]. arXiv: 2505.08723, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2505.08723. [14] YAO Liang, LIU Fan, CHEN Delong, et al. RemoteSAM: Towards segment anything for earth observation[C]. The 33rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Dublin, Ireland, 2025: 3027–3036. doi: 10.1145/3746027.3754950. [15] LI Yuxuan, LI Xiang, LI Yunheng, et al. SM3Det: A unified model for multi-modal remote sensing object detection[J]. arXiv: 2412.20665, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2412.20665. [16] WANG Wenhai, DAI Jifeng, CHEN Zhe, et al. InternImage: Exploring large-scale vision foundation models with deformable convolutions[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 14408–14419. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01385. [17] LIU Zhuang, MAO Hanzi, WU Chaoyuan, et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 11966–11976. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01167. [18] KIM K and LEE H S. Probabilistic anchor assignment with IoU prediction for object detection[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision – ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 355–371. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58595-2_22. [19] LI Yuxuan, LI Xiang, LI Weijie, et al. SARDet-100K: Towards open-source benchmark and toolkit for large-scale SAR object detection[C]. The 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 4079. [20] XIA Guisong, BAI Xiang, DING Jian, et al. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3974–3983. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00418. [21] LI Ruojing, AN Wei, YING Xinyi, et al. Probing deep into temporal profile makes the infrared small target detector much better[J]. arXiv: 2506.12766, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2506.12766. [22] 李朝旭, 徐清宇, 安玮, 等. 红外图像暗弱目标轻量级检测网络[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2025, 44(2): 299–310. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2025.02.017.LI Zhaoxu, XU Qingyu, AN Wei, et al. A lightweight dark object detection network for infrared images[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2025, 44(2): 299–310. doi: 10.11972/j.issn.1001-9014.2025.02.017. [23] YING Xinyi, LIU Li, LIN Zaipin, et al. Infrared small target detection in satellite videos: A new dataset and a novel recurrent feature refinement framework[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5002818. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3542368. [24] GUO Menghao, LU Chengze, LIU Zhengning, et al. Visual attention network[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2023, 9(4): 733–752. doi: 10.1007/s41095-023-0364-2. [25] LI Yuxuan, HOU Qibin, ZHENG Zhaohui, et al. Large selective kernel network for remote sensing object detection[C]. 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2023: 16748–16759. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.01540. [26] WANG Wenhai, XIE Enze, LI Xiang, et al. PVT v2: Improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2022, 8(3): 415–424. doi: 10.1007/s41095-022-0274-8. [27] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.324. [28] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031. [29] CAI Zhaowei, VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6154–6162. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00644. [30] LI Xiang, WANG Wenhai, WU Lijun, et al. Generalized focal loss: Learning qualified and distributed bounding boxes for dense object detection[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 1763. [31] DING Jian, XUE Nan, LONG Yang, et al. Learning RoI transformer for oriented object detection in aerial images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2844–2853. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00296. [32] LIU Yujie, SUN Xiaorui, SHAO Wenbin, et al. S2ANet: Combining local spectral and spatial point grouping for point cloud processing[J]. Virtual Reality & Intelligent Hardware, 2024, 6(4): 267–279. doi: 10.1016/j.vrih.2023.06.005. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
