Research on the Architecture of Dual-Field Reconfigurable Polynomial Multiplication Unit for Lattice-Based Post-Quantum Cryptography
-
摘要: 多项式乘法作为格密码算法的核心运算,通过快速数论变换(NTT)/快速傅里叶变换(FFT)设计成多项式乘法架构能够降低计算复杂度,提升格密码算法的运算速度。为支持多参数的多项式乘法运算,并提升多项式乘法的运算速度,该文提出一种双域可重构多项式乘法运算单元架构。该文首先基于Kyber、Dilithium和Falcon算法中的参数特征,提取多项式乘法的运算网络,并对内部双域乘法运算在算法层进行优化设计。其次,基于多项式乘法运算网络设计出双域可重构多项式乘法运算单元架构,并对双域可重构乘法单元进行优化设计以提升运算速度。最后,为提高运算单元架构的资源利用率,该文对多项式乘法运算单元架构进行并行度分析,当支持1路64 bit、2路32 bit或4路16 bit的运算时,多项式乘法运算架构的面积效率最高。该文在Xilinx FPGA xc7v2000tflg1925上进行实验验证,能够支持Kyber、Dilithium和Falcon算法中所有多项式乘法运算,工作频率达到169 MHz,面积时间积降低了50%以上。Abstract:
Objective Polynomial multiplication accounts for over 80% of computational time in lattice cryptography algorithms. Utilizing the Nhanh Transform (NTT) and Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) can reduce the computational complexity of polynomial multiplication from exponential to logarithmic. However, current mainstream lattice cryptography algorithms such as Kyber, Dilithium, and Falcon exhibit significant differences in their parameter sets and polynomial multiplication implementations. To support multi-parameter polynomial multiplication operations and enhance resource utilization for polynomial multiplication, this paper proposes a dual-field reconfigurable polynomial multiplication unit architecture. Methods This paper first extracts the computational network for polynomial multiplication based on the parameter characteristics of the Kyber, Dilithium, and Falcon algorithms, and optimizes the internal dual-field multiplication operations at the algorithmic level. Secondly, it designs a dual-field reconfigurable polynomial multiplication unit architecture for the polynomial multiplication network and further optimizes the dual-field reconfigurable multiplication unit to enhance computational speed. Finally, to improve resource utilization of the computational unit architecture, the paper conducts a parallelism analysis. The polynomial multiplication architecture achieves the highest area efficiency when supporting 1-lane 64-bit, 2-lane 32-bit, or 4-lane 16-bit operations. Results and Discussions The paper was experimentally verified on the Xilinx FPGA XC7V2000TFLG1925. It simultaneously supports one channel of complex-form floating-point operations or two channels of 17- to 32-bit and four channels of 16-bit internal NTT operations. Operating at a frequency of 169 MHz, it achieves a reduction of over 50% in area-time product. Conclusions The dual-field reconfigurable processing unit architecture proposed in this paper offers advantages in scalability, area efficiency, and core unit performance. Its bit width configuration is more easily adaptable to traditional cryptographic processors, providing a recommended approach for transitioning traditional public-key cryptosystems to post-quantum cryptography. -
表 1 格基后量子密码多项式乘法参数分析
算法 系数类型 位宽(bit) 项数n 模数q Kyber 整数 12 256 3329 ≡1mod nDilithium 整数 23 256 8380417 ≡1mod 2nFalcon 整数 14 512/ 1024 12289 ≡1mod 2n浮点数形式的复数 64 512/ 1024 - 表 2 多项式乘法运算提取
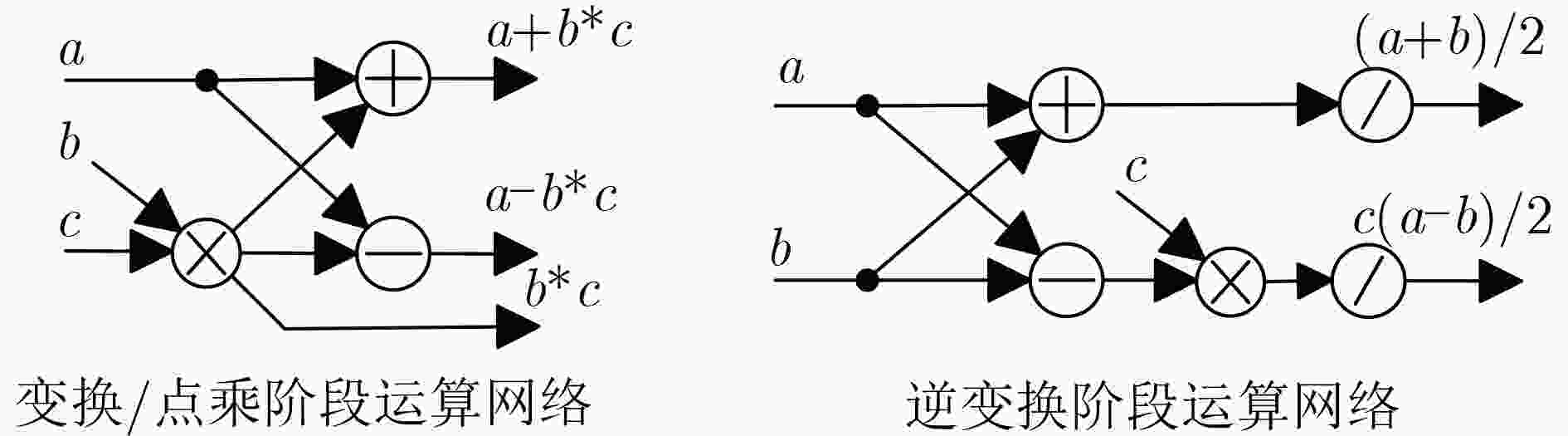
Kyber Dilithium/Falcon 变换 $ \left.\begin{array}{c}{a}^{\prime}=a+b\cdot \omega \\{b}^{\prime}=a-b\cdot \omega \end{array}\right\}\Rightarrow \begin{array}{c}a+b\cdot c\\a-b\cdot c\end{array} $ $ \left.\begin{array}{c}{a}^{\prime}=a+b\cdot \omega \\{b}^{\prime}=a-b\cdot \omega \end{array}\right\}\Rightarrow \begin{array}{c}a+b\cdot c\\a-b\cdot c\end{array} $ 点乘 $ \left.\begin{array}{c}{\hat{c}}_{2i}=({\hat{a}}_{2i}\cdot {\hat{b}}_{2i})+({\hat{a}}_{2i+1}\cdot {\hat{b}}_{2i+1})\cdot \omega \\{\hat{c}}_{2i+1}=({\hat{a}}_{2i}\cdot {\hat{b}}_{2i+1})+{\hat{a}}_{2i+1}\cdot {\hat{b}}_{2i}\end{array}\right\}\Rightarrow \begin{array}{c}b\cdot c\\a+d\cdot e\end{array} $ $ {c}_{i}={a}_{i}\cdot {b}_{i}\Rightarrow b\cdot c $ 逆变换 $ \left.\begin{array}{c}{a}^{\prime}=(a+b)/2\\{b}^{\prime}=\omega \cdot (a-b)/2\end{array}\right\}\Rightarrow \begin{array}{c}(a+b)/2\\\omega \cdot (a-b)/2\end{array} $ $ \left.\begin{array}{c}{a}^{\prime}=(a+b)/2\\{b}^{\prime}=\omega \cdot (a-b)/2\end{array}\right\}\Rightarrow \begin{array}{c}(a+b)/2\\\omega \cdot (a-b)/2\end{array} $ 算法1:Montgomery模乘 算法2:Barrett模乘 算法3:K-RED模乘 输入:$ A,B,R,P,{P}^{\prime} $ 输入:$ a,b,m=\left\lfloor {2}^{k}/q\right\rfloor ;k\approx 2\left\lceil \log q\right\rceil $ 输入:$ a,b,q=k\times {2}^{m}+1 $ 输出:$ u=A\times B\times {R}^{-1}(\mathrm{mod}P) $ 输出:$ O=a\times b(\mathrm{mod}q) $ 输出:$ {C}^{\prime}=k\times a\times b\mathrm{mod}q $ 1: $ t=A\times B $ 1: $ O=a\times b $ 1: $ C=a\times b $ 2: $ s=(t+(t\times {P}^{\prime}(\mathrm{mod}R)\times P)))/R $ 2: $ t=(O\times m)\gg k $ 2: $ {C}_{l}=C\mathrm{mod}{2}^{m} $ 3: $ if(s \gt P) $ 3: $ O=O-(t\times q) $ 3: $ {C}_{h}=C\gg m $ 4: $ s=s-P $ 4: $ if(O\geq q) $ 4: $ {C}^{\prime}=k{C}_{l}-{C}_{h} $ 5: $ returns $ 5: $ O=O-q $ 5: $ return{C}^{\prime} $ 6: $ returnO $ 4 双域可重构乘法单元
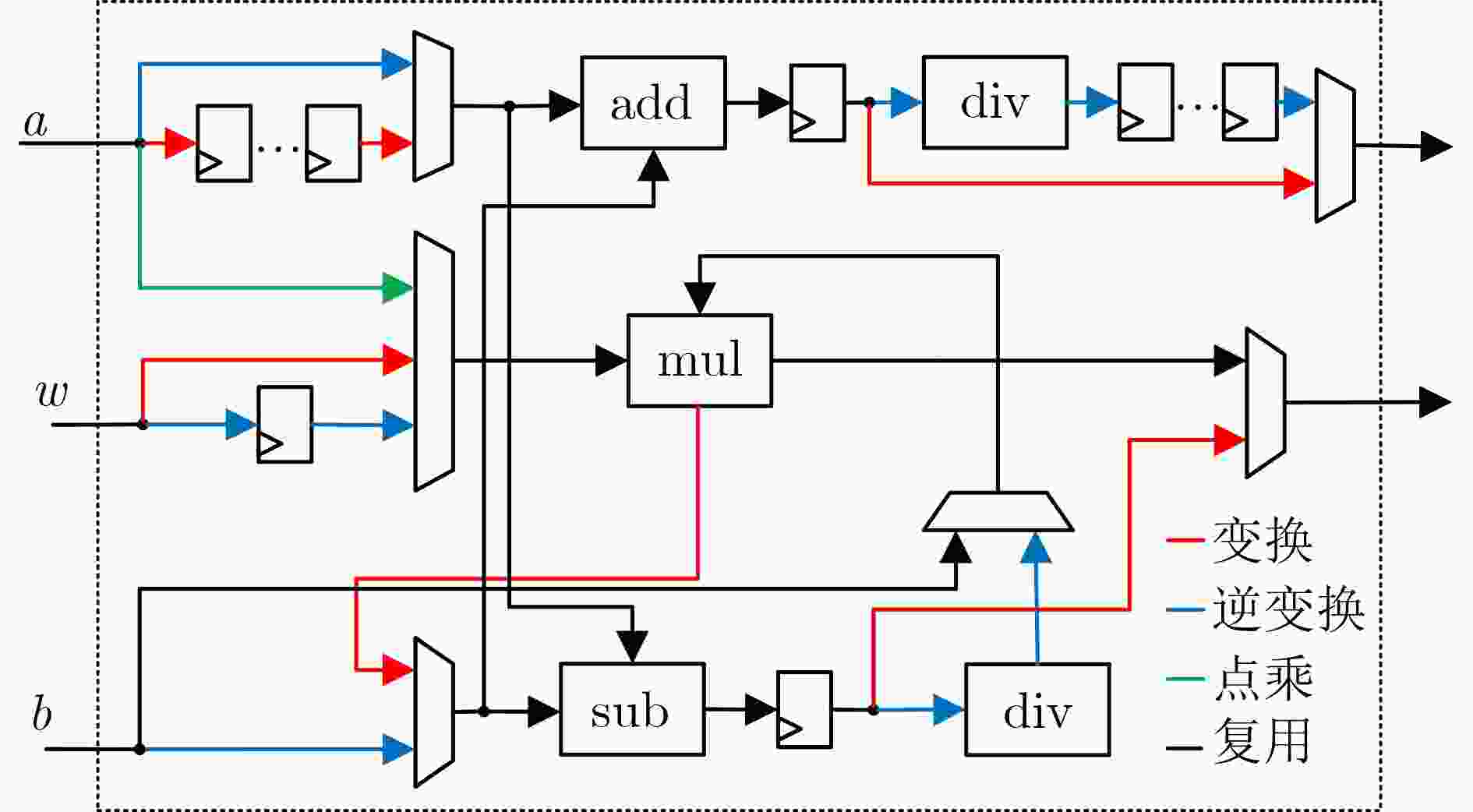
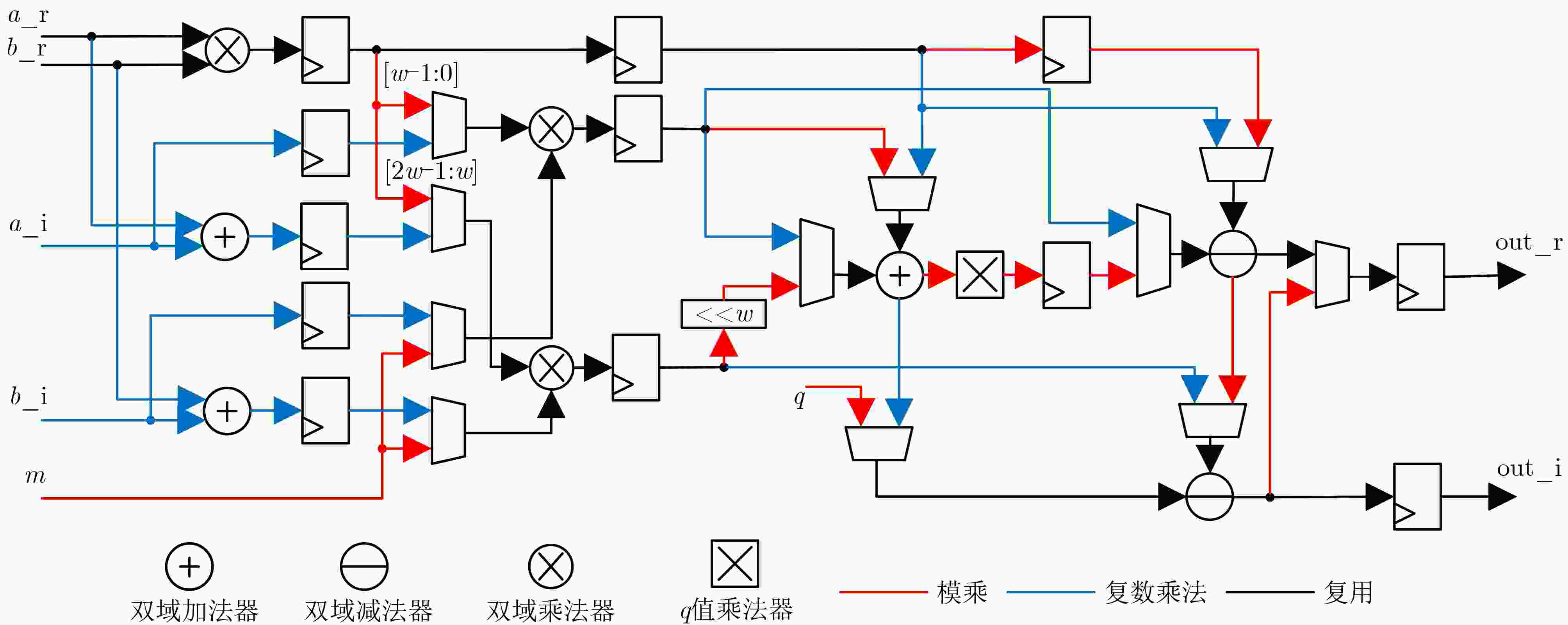
输入:$ \mathrm{a}\_ \mathrm{r},\mathrm{a}\_ \mathrm{i},\mathrm{b}\_ \mathrm{r},\mathrm{b}\_ \mathrm{i},\mathrm{q},\mathrm{m},\mathrm{k},\mathrm{sel} $ 输出:$ \mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{r},\mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{i} $ 1: $ \mathrm{mul}\_ 1=\mathrm{mul}(\mathrm{a}\_ \mathrm{r},\mathrm{b}\_ \mathrm{r}) $ 2: $ \mathrm{add}\_ 1=\mathrm{add}(\mathrm{a}\_ \mathrm{r},\mathrm{a}\_ \mathrm{i}) $ 3: $ \mathrm{add}\_ 2=\mathrm{add}(\mathrm{b}\_ \mathrm{r},\mathrm{b}\_ \mathrm{i}) $ /////////////sel=1,完成模乘运算;sel=0,完成复数乘法
//////////////////4: $ \mathrm{if}(\mathrm{sel}=1) $ 5: $ \mathrm{mul}\_ 2=\mathrm{mul}(\mathrm{mul}\_ 1[\mathrm{w}-1\colon 0],\mathrm{m}) $ 6: $ \mathrm{mul}\_ 3=\mathrm{mul}(\mathrm{mul}\_ 1[2\mathrm{w}-1\colon \mathrm{w}],\mathrm{m}) $ 7: $ \mathrm{else} $ 8: $ \mathrm{mul}\_ 2=\mathrm{mul}(\mathrm{a}\_ \mathrm{i},\mathrm{b}\_ \mathrm{i}) $ 9: $ \mathrm{mul}\_ 3=\mathrm{mul}(\mathrm{add}\_ 1,\mathrm{add}\_ 2) $ 10: $ \mathrm{if}(\mathrm{sel}=1) $ 11: $ \mathrm{add}\_ 3=\mathrm{add}(\mathrm{mul}\_ 2,\mathrm{mul}\_ 3) $ 12: $ \mathrm{add}\_ {3}^{\prime}=\mathrm{add}\_ 3 \gt > \mathrm{k} $ 13: $ \mathrm{add}\_ {3}^{\prime\prime}=\mathrm{mul}\_ \mathrm{q}(\mathrm{add}\_ {3}^{\prime}) $ 14: $ \mathrm{else} $ 15: $ \mathrm{add}\_ 3=\mathrm{add}(\mathrm{mul}\_ 1,\mathrm{mul}\_ 2) $ 16: $ \mathrm{if}(\mathrm{sel}=1) $ 17: $ \mathrm{sub}\_ 1=\mathrm{sub}(\mathrm{mul}\_ 1,\mathrm{add}\_ {3}^{\prime\prime}) $ 18: $ \mathrm{sub}\_ 2=\mathrm{sub}(\mathrm{sub}\_ 1,\mathrm{q}) $ 19: $ \mathrm{if}(\mathrm{sub}\_ 1 \lt \mathrm{q}) $ 20: $ \mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{r}=\mathrm{sub}\_ 1;\mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{i}=0 $ 21: $ \mathrm{else} $ 22: $ \mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{r}=\mathrm{sub}\_ 2;\mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{i}=0 $ 23: $ \mathrm{else} $ 24: $ \mathrm{sub}\_ 1=\mathrm{sub}(\mathrm{mul}\_ 1,\mathrm{mul}\_ 2) $ 25: $ \mathrm{sub}\_ 2=\mathrm{sub}(\mathrm{mul}\_ 3,\mathrm{add}\_ 3) $ 26: $ \mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{r}=\mathrm{sub}\_ 1;\mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{i}=\mathrm{sub}\_ 2 $ 27:$ \mathrm{return}\mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{r},\mathrm{c}\_ \mathrm{i} $ 表 3 运算单元架构子模块FPGA资源对比
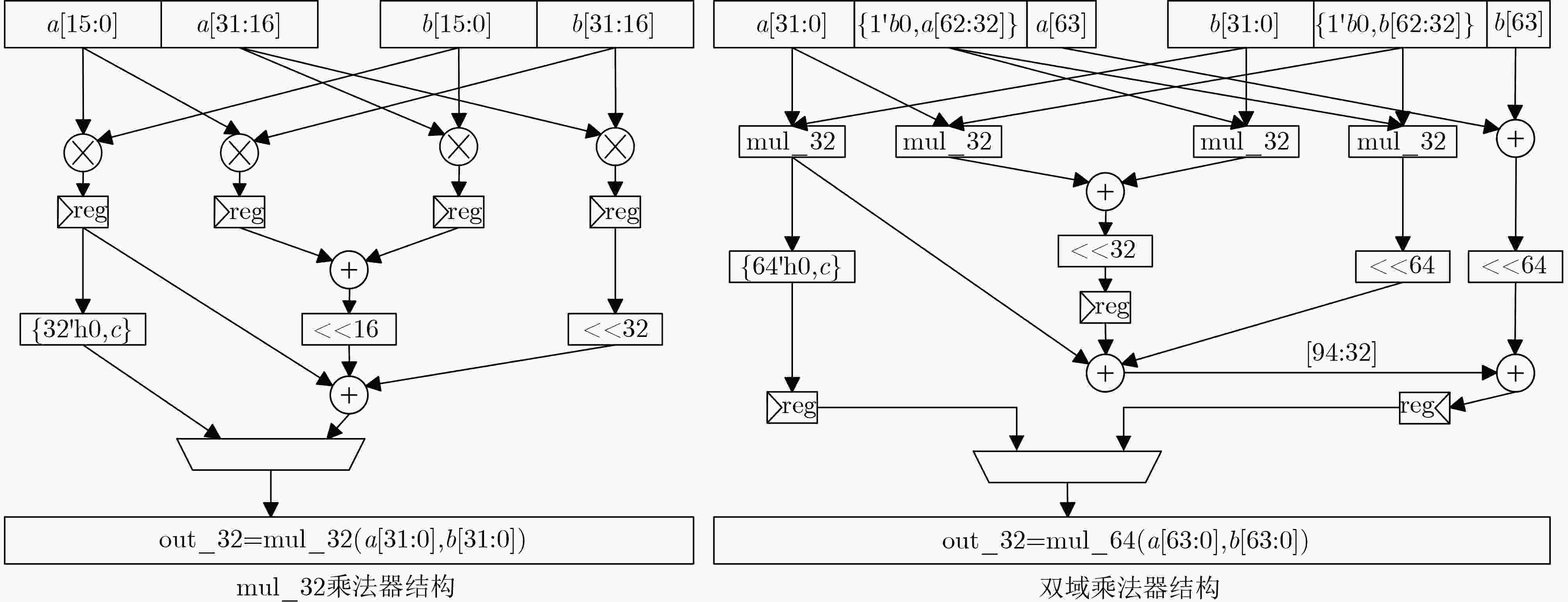
硬件单元 LUT FF DSP add 590 0 0 sub 475 0 0 div 143 0 0 add_64 64 0 0 add_96 288 0 0 mul_q 371 128 0 sub_64 256 0 0 表 4 多项式乘法单元性能对比
文献 频率
(MHz)时钟
周期时延
(us)器件 n 系数位宽 资源消耗
(LUT/FF/DSP/BRAM)ATP 算法 电子学报2025[15] 169 204** 0.4 V7 256 16bit 18120 /4000 /64/134.79 Kyber 444** 1.56 512 14bit 75.72 Falcon TCAS-I 2022[19] 224 192 8.571 A7 256 13bit 25674 /3137 /64/6317.22 Kyber
DilithiumTCAS-I
2024[4]334 638 1.91 A7 256 13bit 1052 /1058 /0/13.511.77 Kyber TCAD
2023[20]154 1470 9.55 V7 512 14bit 28616 /4211 /24/48473.94 Falcon TCAS-I
2023[7]140 867 6.19 A7 256 23bit 11100 /8700 /32/4149.80 Dilithium TCAS-II
2025[13]362 - - US+ 1024 64bit 11408 /11634 /60/20.50.097* FFT 本文 169 859 5.08 V7 256 <16bit 6522 /3018 /48/580.47 Kyber 1883 11.15 512 <16bit 176.62 Falcon 1691 10.01 256 <32bit 158.56 Dilithium 7451 44.11 1024 64bit 698.70
(0.094*)FFT 注:1.在上述FPGA型号中,US+为Zynq UltraScale+,V7为Virtex-7,A7为Artix-7;
2.*表示处理单次运算的ATP值;
3.**表示由于未查询到整个多项式乘法流程消耗的资源,因此将NTT消耗的时钟进行3倍处理; -
[1] BOS J, DUCAS L, KILTZ E, et al. CRYSTALS - Kyber: A CCA-secure module-lattice-based KEM[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy, London, UK, 2018: 353–367. doi: 10.1109/EuroSP.2018.00032. [2] DUCAS L, KILTZ E, LEPOINT T, et al. CRYSTALS-Dilithium: A lattice-based digital signature scheme[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2018, 2018(1): 238–268. doi: 10.13154/tches.v2018.i1.238-268. [3] FOUQUE P A, HOFFSTEIN J, KIRCHNER P, et al. Falcon: Fast-Fourier lattice-based compact signatures over NTRU[R]. Submission to the NIST’s Post-Quantum Cryptogr. Standardization Process, 2020. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版信息, 请确认). [4] ALHASSANI A and BENAISSA M. High-speed polynomials multiplication HW accelerator for CRYSTALS-Kyber[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2024, 71(12): 6105–6113. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2024.3427011. [5] LI Aobo, LU Jiahao, LIU Dongsheng, et al. A 40nm 2.76μJ/Op energy-efficient secure post-quantum crypto-processor for crystals-Kyber on module-LWE[C]. Proceedings of 2023 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), Haikou, China, 2023: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/A-SSCC58667.2023.10347915. [6] LI Xiang, LU Jiahao, LIU Dongsheng, et al. A high speed post-quantum crypto-processor for crystals-dilithium[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(1): 435–439. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2023.3304416. [7] HU Xiao, TIAN Jing, LI Minghao, et al. AC-PM: An area-efficient and configurable polynomial multiplier for lattice based cryptography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2023, 70(2): 719–732. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3218192. [8] 陈韬, 李慧琴, 吴艾青, 等. 基于2KNTT的多项式乘法单元设计[J]. 电子学报, 2024, 52(2): 455–467. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220629.CHEN Tao, LI Huiqin, WU Aiqing, et al. A polynomial multiplier design based on 2KNTT[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2024, 52(2): 455–467. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220629. [9] XU Tianyu, CUI Yijun, LIU Dongsheng, et al. Lightweight and efficient hardware implementation for saber using NTT multiplication[C]. Proceedings of 2022 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), Shenzhen, China, 2022: 601–605. doi: 10.1109/APCCAS55924.2022.10090310. [10] AIKATA A, MERT A C, IMRAN M, et al. KaLi: A crystal for post-quantum security using Kyber and dilithium[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2023, 70(2): 747–758. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3219555. [11] LU Jiahao, ZHANG Jiaming, LUO Zhixiang, et al. An efficient and configurable hardware architecture of polynomial modular operation for CRYSTALS-Kyber and dilithium[C]. Proceedings of 2024 IEEE 67th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Springfield, USA, 2024: 29–32. doi: 10.1109/MWSCAS60917.2024.10658892. [12] ZHU Yihong, ZHU Wenping, OUYANG Yi, et al. 16.2 A 28nm 69.4kOPS 4.4μJ/Op versatile post-quantum crypto-processor across multiple mathematical problems[C]. Proceedings of 2024 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2024: 298–300. doi: 10.1109/ISSCC49657.2024.10454332. [13] WANG Jianfei, YANG Chen, HOU Jia, et al. A compact and efficient hardware accelerator for RNS-CKKS En/decoding and En/decryption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2025, 72(1): 243–247. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2024.3454024. [14] 陈韬, 李慧琴, 李伟, 等. 面向格基后量子密码算法的可重构多项式乘法架构[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(9): 3380–3392. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230284.CHEN Tao, LI Huiqin, LI Wei, et al. Reconfigurable polynomial multiplication architecture for lattice-based post-quantum cryptography algorithms[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(9): 3380–3392. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230284. [15] 付秋兴, 李伟, 别梦妮, 等. 格基后量子密码的可重构NTT运算单元与高效调度算法研究[J]. 电子学报, 2025, 53(4): 1182–1191. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20240788.FU Qiuxing, LI Wei, BIE Mengni, et al. Research on reconfigurable NTT arithmetic unit and efficient scheduling algorithm for lattice post-quantum cryptography[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2025, 53(4): 1182–1191. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20240788. [16] LYUBASHEVSKY V, MICCIANCIO D, PEIKERT C, et al. SWIFFT: A modest proposal for FFT hashing[C]. Proceedings of the 15th International Workshop on Fast Software Encryption, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2008: 54–72. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-71039-4_4. [17] COOLEY J W and TUKEY J W. An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex Fourier series[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1965, 19(90): 297–301. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1965-0178586-1. [18] GENTLEMAN W M and SANDE G. Fast Fourier transforms: For fun and profit[C]. Proceedings of the November 7-10, 1966, Fall Joint Computer Conference, San Francisco, USA, 1966: 563–578. doi: 10.1145/1464291.1464352. [19] ZHAO Yifan, XIE Ruiqi, XIN Guozhu, et al. A high-performance domain-specific processor with matrix extension of RISC-V for module-LWE applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(7): 2871–2884. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3162593. [20] MU Jianan, REN Yi, WANG Wen, et al. Scalable and conflict-free NTT hardware accelerator design: Methodology, proof, and implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2023, 42(5): 1504–1517. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2022.3205552. [21] LIAO Junhao, CHO K T, and SHIEH M D. A unified FFT/NTT design for efficient NTRU equation solving in FALCON cryptography[C]. Proceedings of 2025 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), London, United Kingdom, 2025: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS56072.2025.11043318. [22] PORNIN T. Improved key pair generation for falcon, BAT and hawk[J]. IACR Cryptol ePrint Arch, 2023, 2023: 290. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献刊名和卷期页码信息, 请确认). -





 下载:
下载:
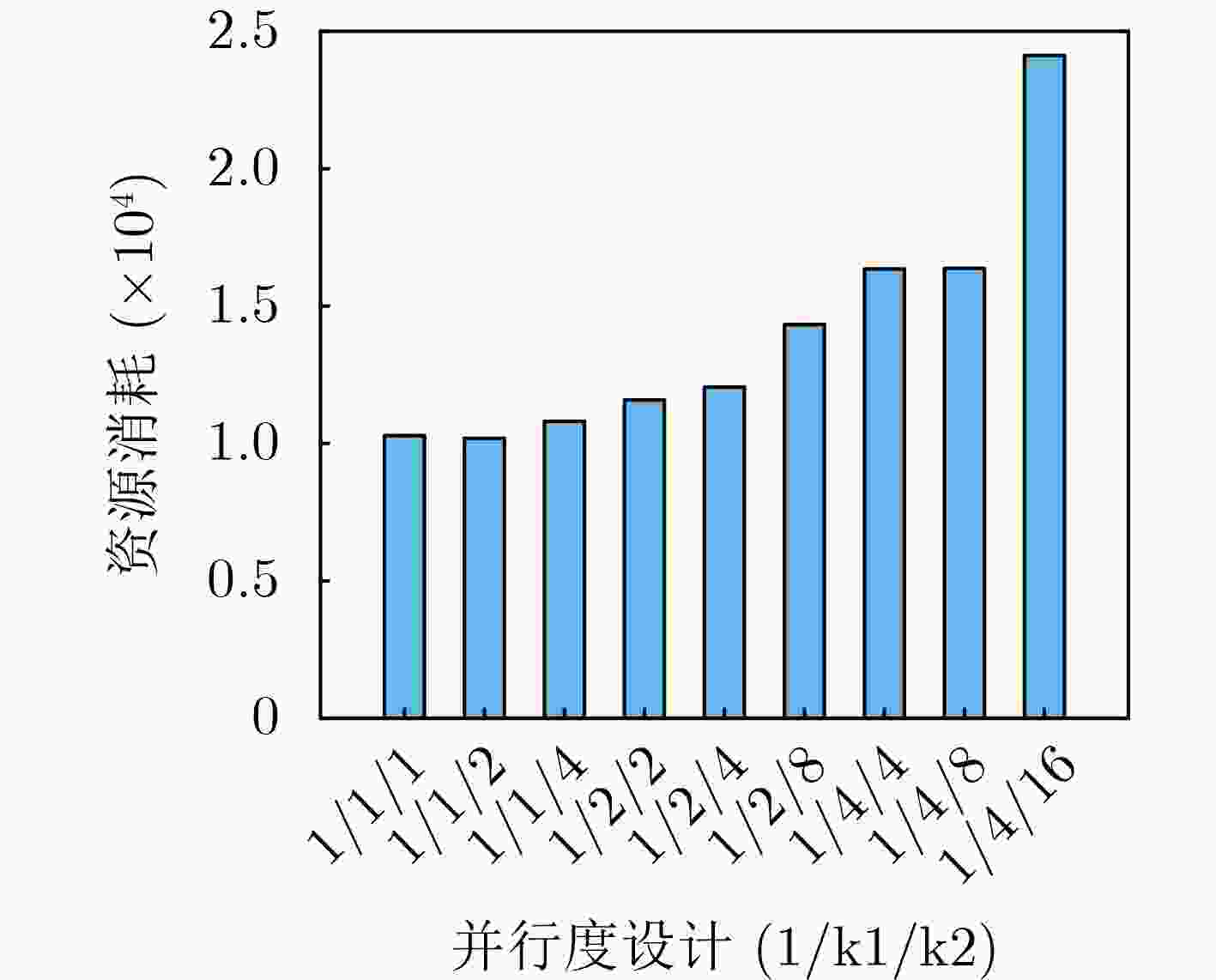
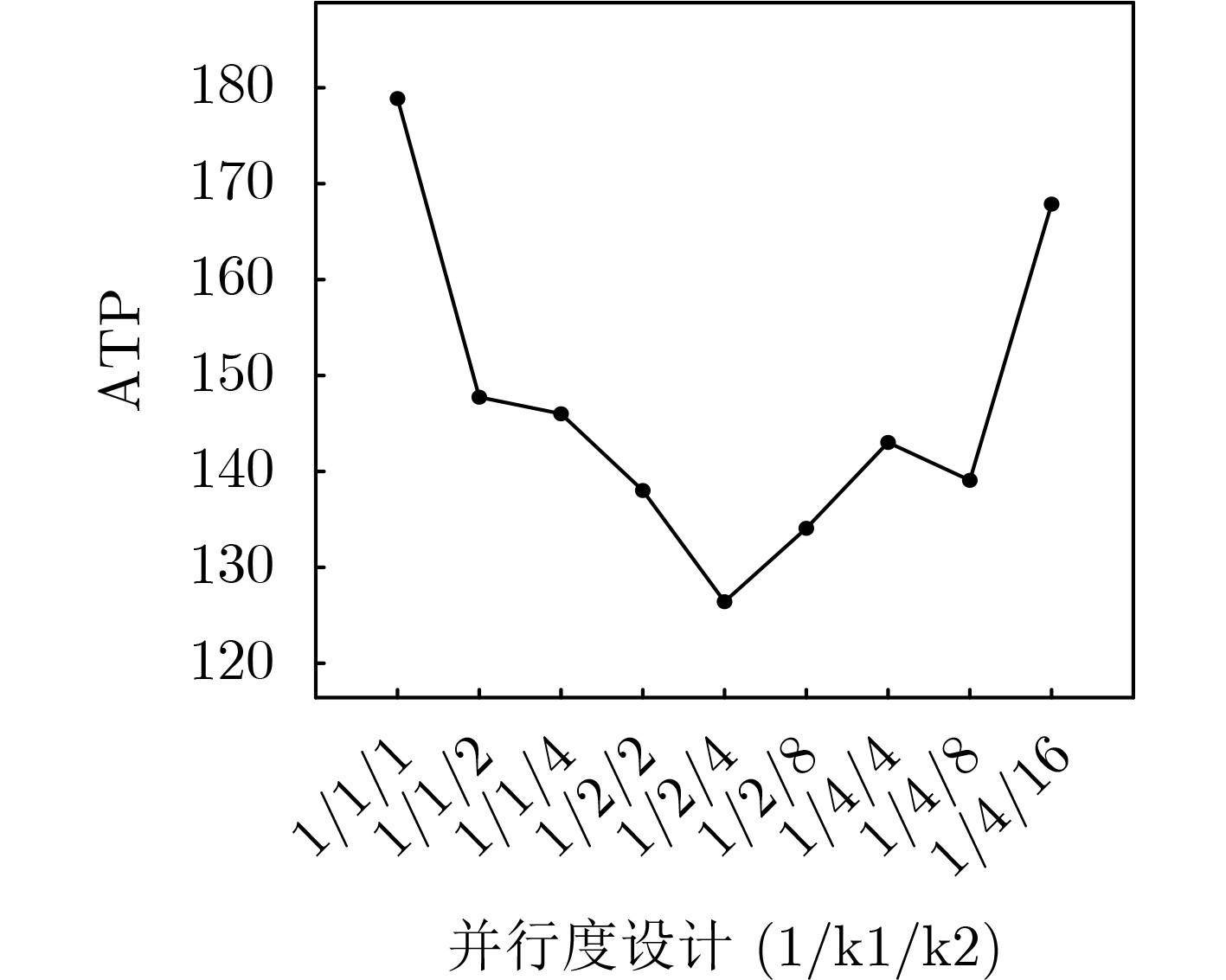
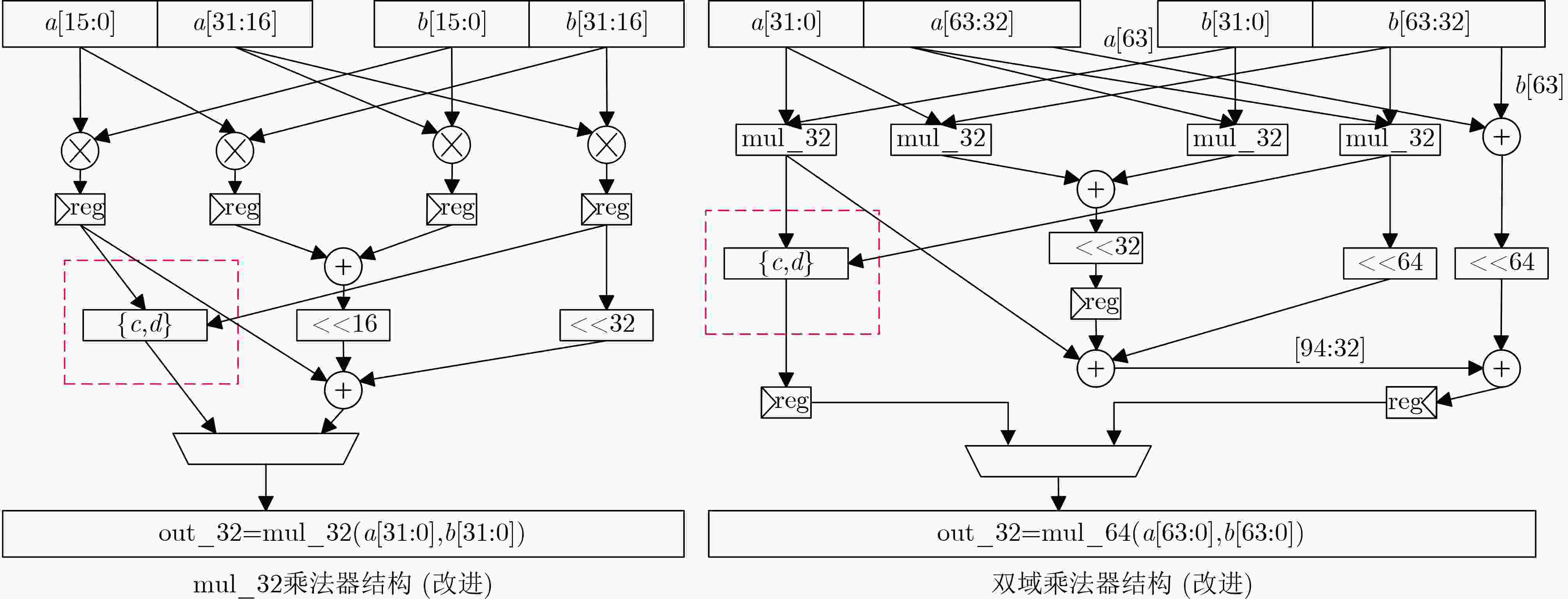


 下载:
下载:
