A Fake Attention Map-Driven Multi-Task Deepfake Video Detection Model
-
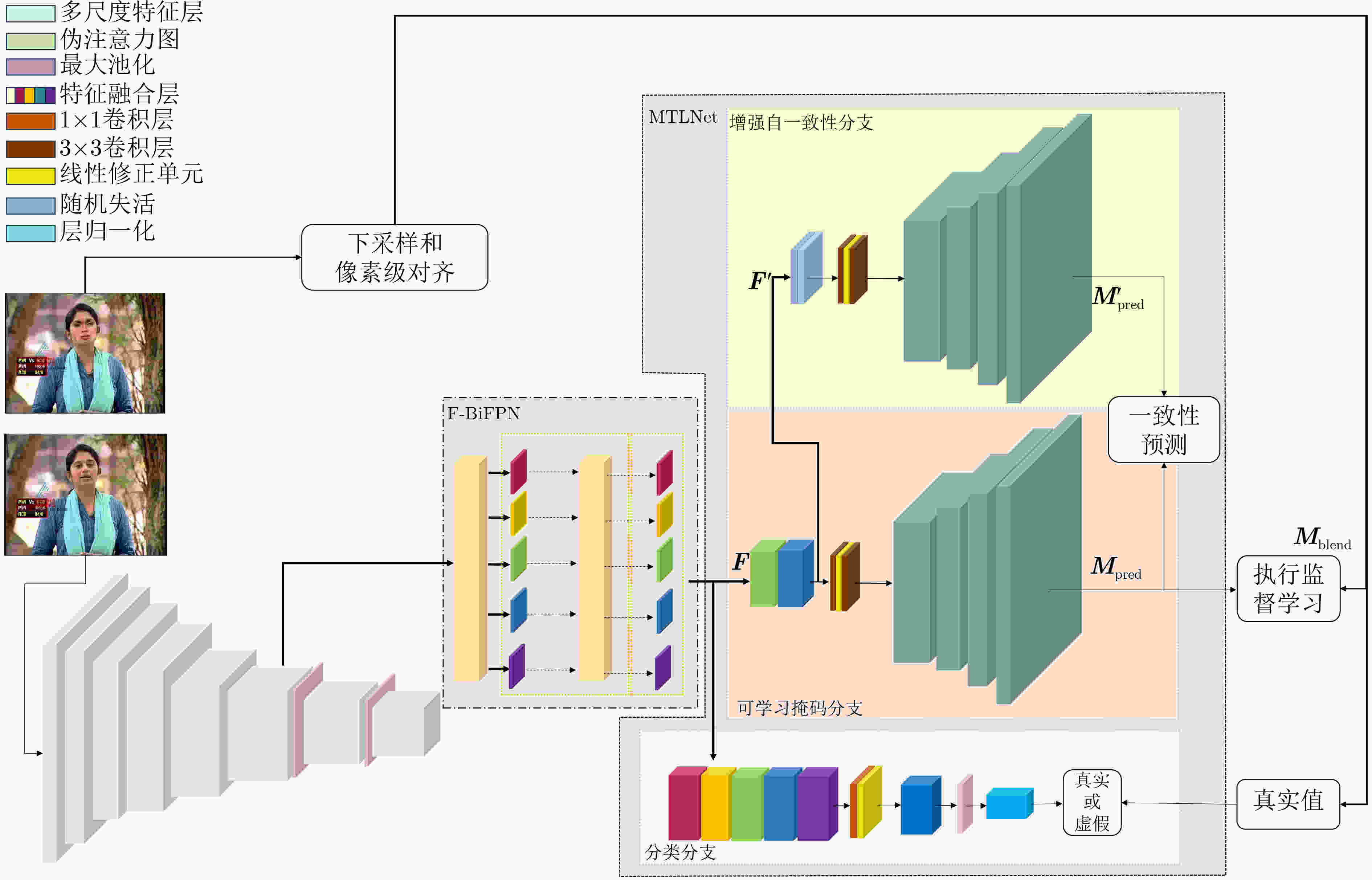
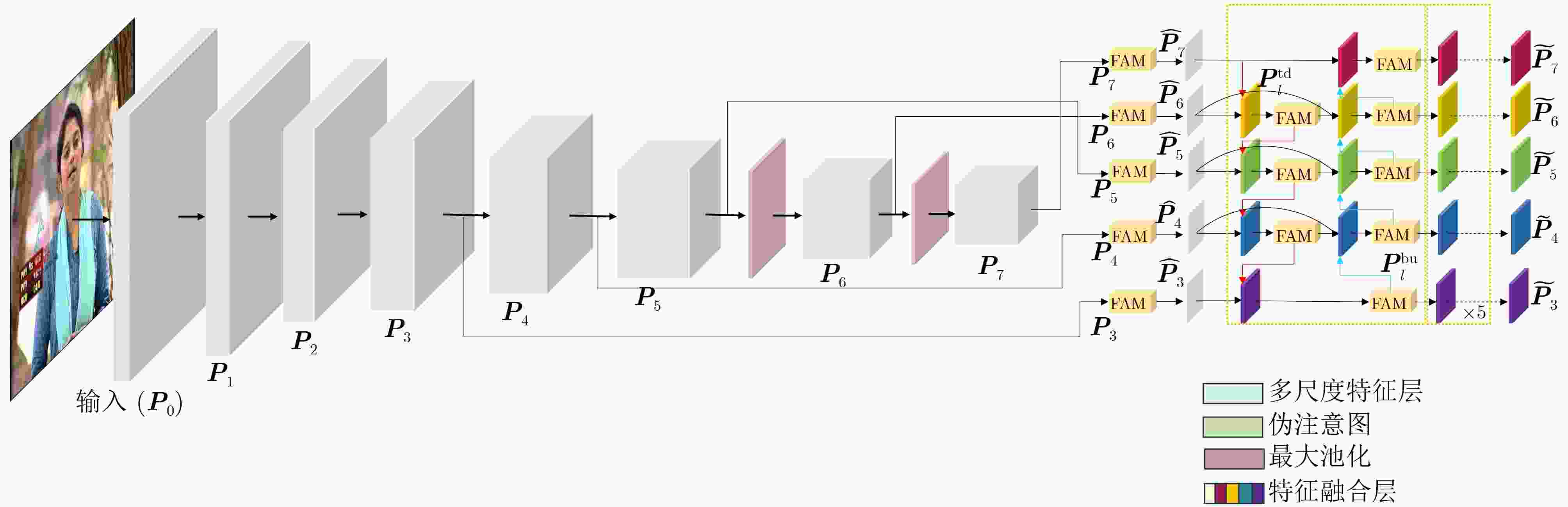
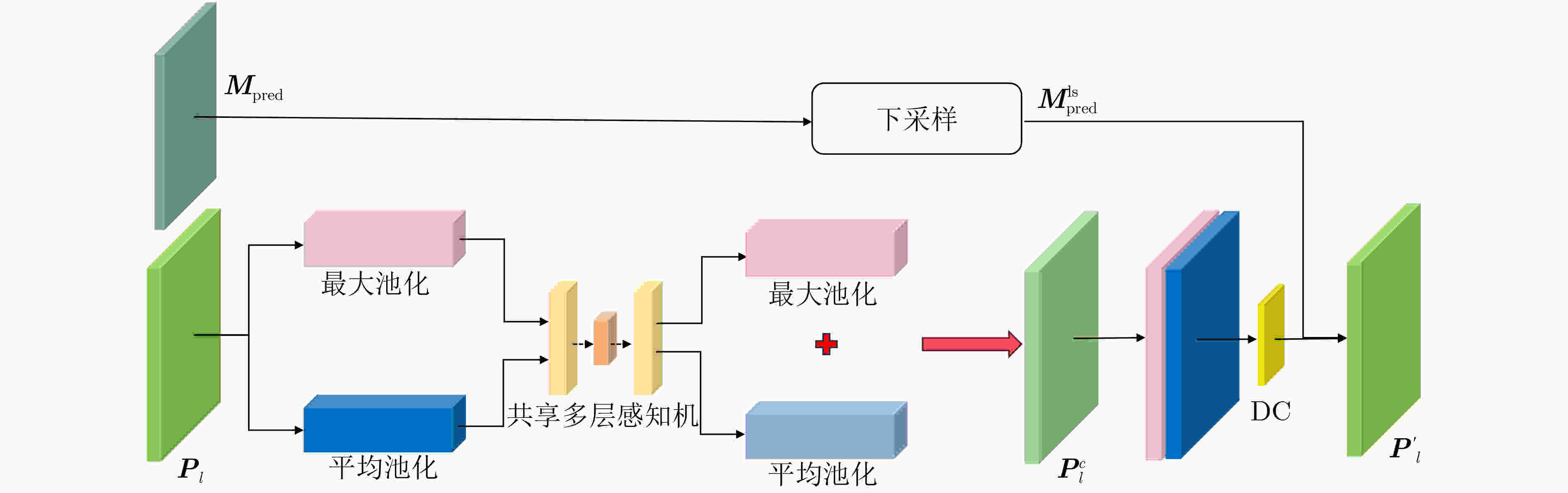
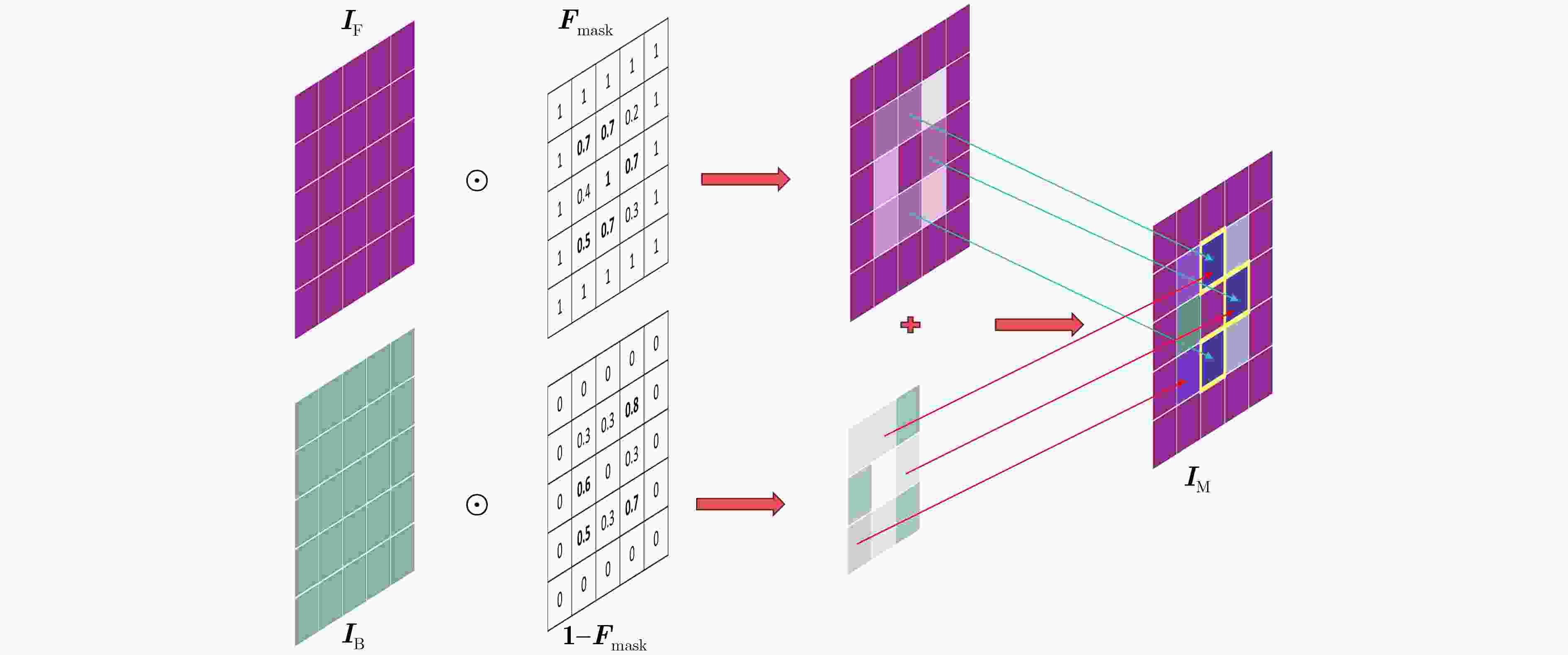
摘要: 目前高质量深度伪造视频检测方法大多基于隐式注意力机制的监督二分类模型。虽然该类模型能够通过自学习,判别伪造痕迹,鉴别异常区域,但在面对未经学习的伪造技术时,对伪造区域的敏感性降低,泛化性不足。基于此,该文提出一种伪造注意图驱动的多任务深伪视频检测模型(F-BiFPN-MTLNet)。首先,设计了一种融合伪造注意图的新型加权双向特征金字塔网络(F-BiFPN),通过伪造注意图监督低层和高层特征图的融合过程,在减少信息冗余的同时,增强模型对高质量伪造区域的敏感性。然后,定义了一种基于显式注意力机制的多任务学习网络(MTLNet)。一方面,该网络在原有基于监督二分类器的单任务模型的基础上,结合基于可学习掩码的注意策略与增强自一致性的注意策略,实现多任务加权判别,提高模型检测的可靠性;另一方面,引入显式注意力机制,通过生成的伪造位置标签对特征图进行监督,显式地指导模型聚焦于容易产生伪影的敏感区域,提高模型的泛化能力。实验结果表明,该文构建的F-BiFPN-MTLNet模型在多个基准测试中均表现出了较好性能,在曲线下面积(AUC)和平均精度(AP)等指标上取得了显著的提升。Abstract:
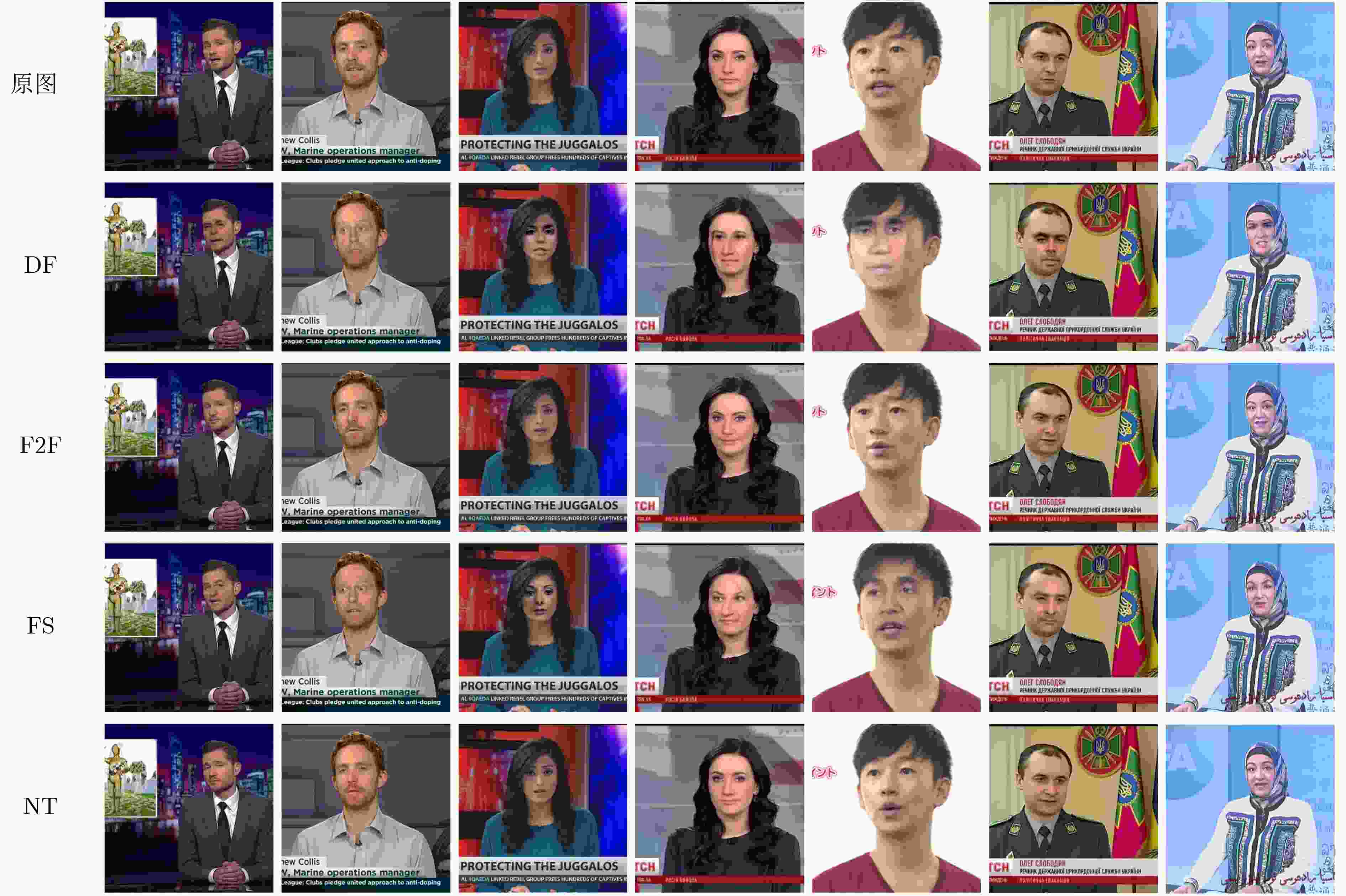
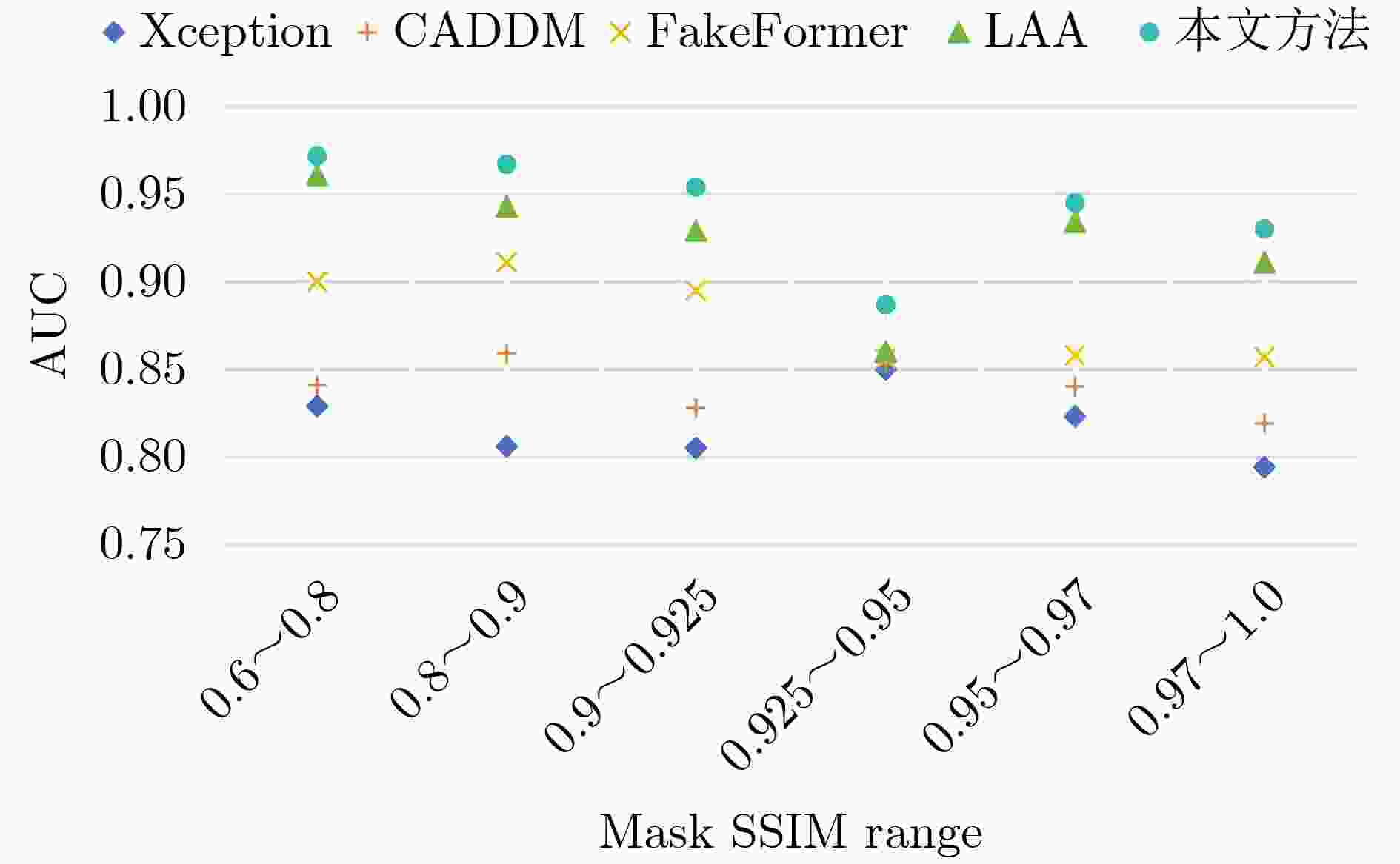
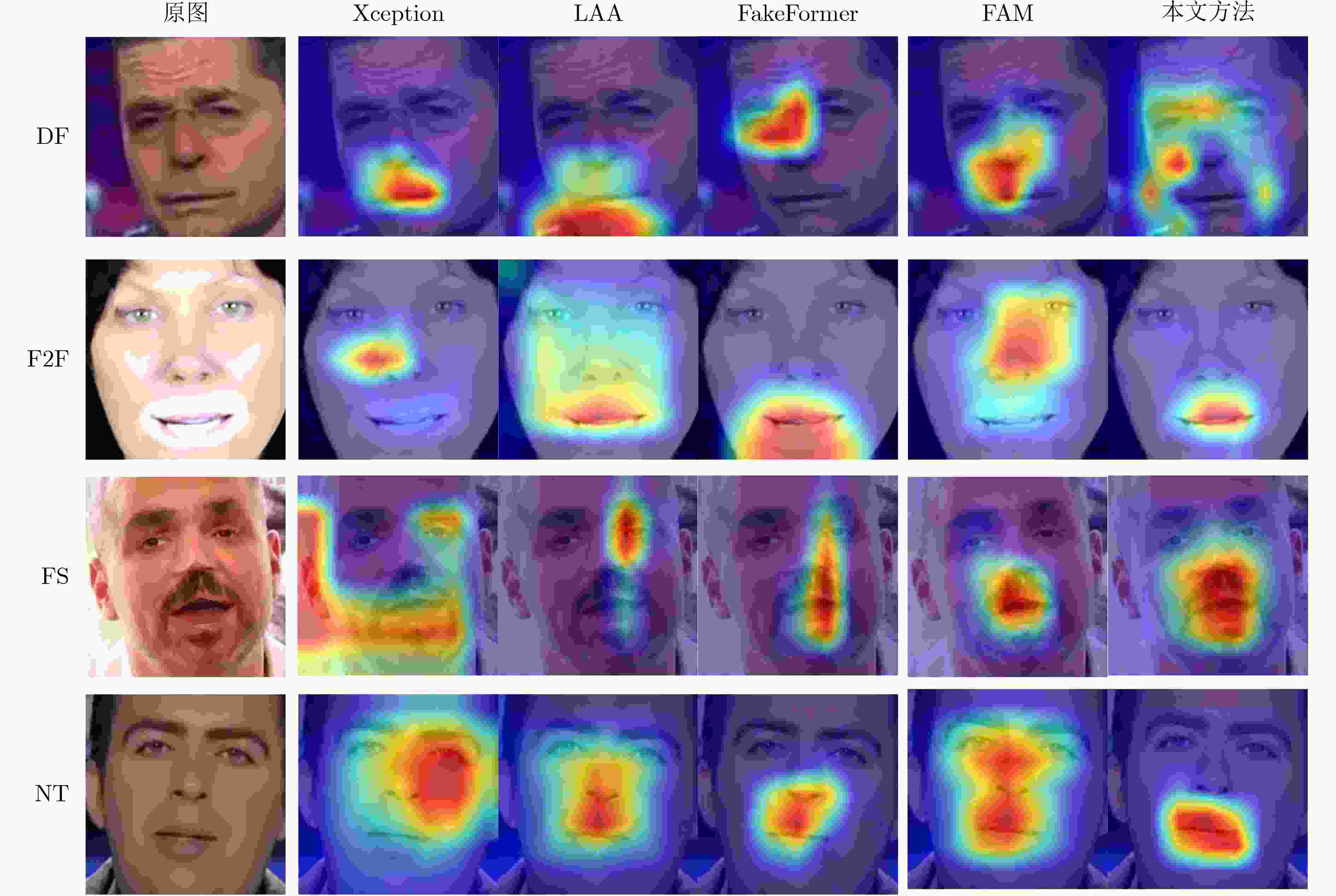
Objective Deepfake detection is a major challenge in multimedia forensics and information security as synthetic media generation advances. Most high-quality detection methods rely on supervised binary classification models with implicit attention mechanisms. Although these models learn discriminative features and reveal manipulation traces, their performance decreases when confronted with unseen forgery techniques. The absence of explicit guidance during feature fusion reduces sensitivity to subtle artifacts and weakens cross-domain generalization. To address these issues, a detection framework named F-BiFPN-MTLNet is proposed. The framework is designed to achieve high detection accuracy and strong generalization by introducing an explicit forgery-attention-guided multi-scale feature fusion mechanism and a multi-task learning strategy. This research strengthens the interpretability and robustness of deepfake detection models, particularly in real-world settings where forgery methods are diverse and continuously changing. Methods The proposed F-BiFPN-MTLNet contains two components: a Forgery-attention-guided Bidirectional Feature Pyramid Network (F-BiFPN) and a Multi-Task Learning Network (MTLNet). The F-BiFPN ( Fig. 1 ) is designed to provide explicit guidance for fusing multi-scale feature representations from different backbone layers. Instead of using simple top-down and bottom-up fusion, a forgery-attention map is applied to supervise the fusion process. This map highlights potential manipulation regions and assigns adaptive weights to each feature level, ensuring that both semantic and spatial details are retained and redundant information is reduced. This attention-guided fusion strengthens the sensitivity of the network to fine-grained forged traces and improves the quality of the resulting representations.Results and Discussions Experiments are conducted on multiple benchmark datasets, including FaceForensics++, DFDC, and Celeb-DF ( Table 1 ). The proposed F-BiFPN-MTLNet shows consistent gains over state-of-the-art methods in both Area Under the Curve (AUC) and Average Precision (AP) metrics (Table 1 ). The findings show that attention-guided fusion strengthens the detection of subtle manipulations, and the multi-task learning structure stabilizes performance across different forgery types. Ablation analyses (Table 2 ) confirm the complementary effects of the two modules. Removing F-BiFPN reduces sensitivity to local artifacts, whereas omitting the self-consistency branch reduces robustness under cross-dataset evaluation. Visualization results (Fig. 8 ) show that F-BiFPN-MTLNet consistently focuses on forged regions and produces interpretable attention maps that align with actual manipulation areas. The framework achieves a balanced improvement in accuracy, generalization, and transparency, while maintaining computational efficiency suitable for practical forensic applications.Conclusions In this study, a forgery-attention-guided weighted bidirectional feature pyramid network combined with a multi-task learning framework is proposed for robust and interpretable deepfake detection. The F-BiFPN provides explicit supervision for multi-scale feature fusion through forgery-attention maps, reducing redundancy and emphasizing informative regions. The MTLNet introduces a learnable mask branch and a self-consistency branch, jointly strengthening localization accuracy and cross-domain robustness. Experimental results show that the proposed model exceeds existing baselines in AUC and AP metrics while retaining strong interpretability through visualized attention maps. Overall, F-BiFPN-MTLNet achieves a balanced improvement in fine-grained localization, detection reliability, and generalization ability. Its explicit attention and multi-task strategies offer a new direction for developing interpretable and resilient deepfake detection systems. Future work will examine the extension of the framework to weakly supervised and unsupervised settings, reduce dependence on pixel-level annotations, and explore adversarial training strategies to strengthen adaptability against evolving forgery methods. -
Key words:
- Deepfake /
- Deep learning /
- Explicit attention /
- Multi-task learning
-
表 1 基于单数据集的算法性能对比(%)
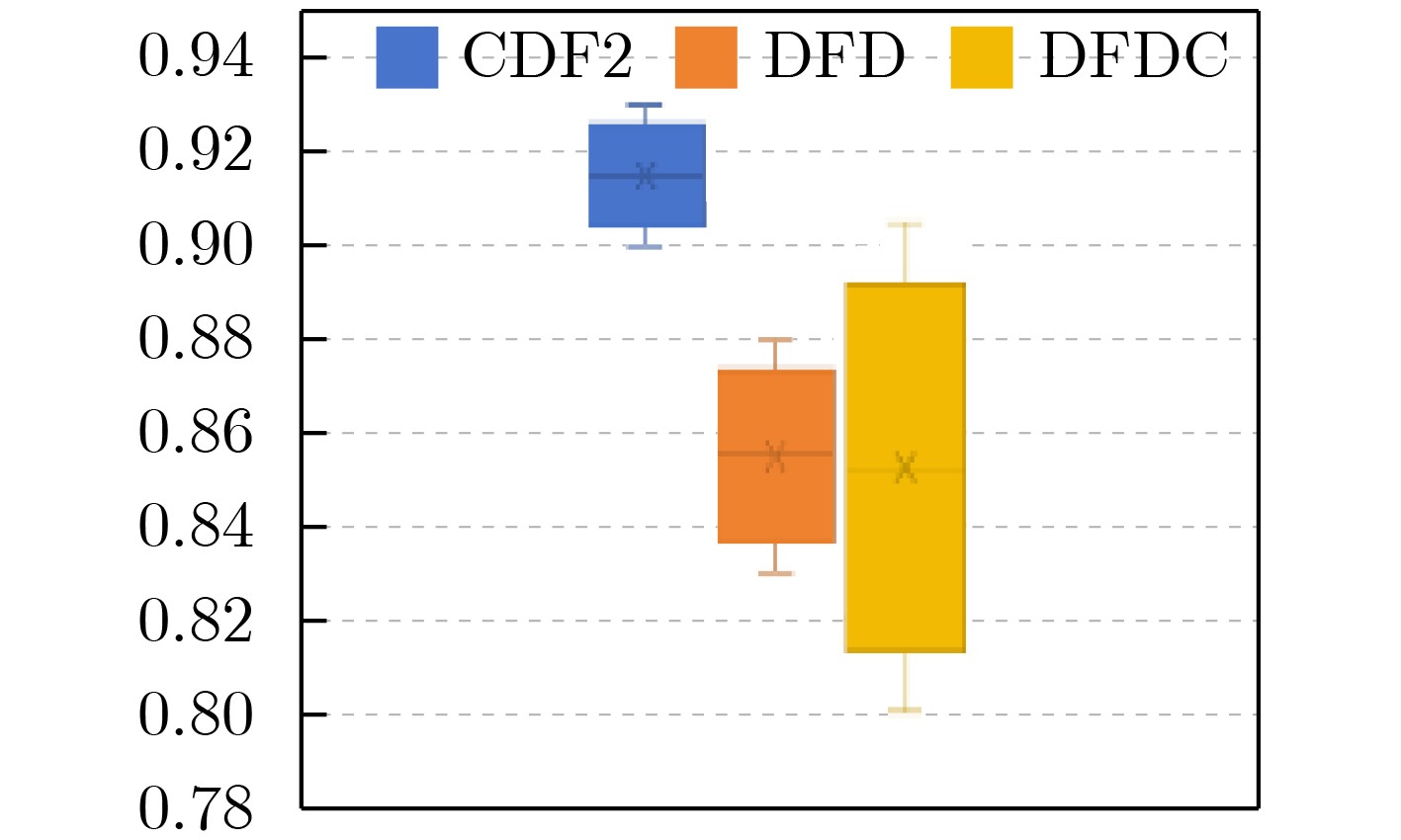
方法 FF++ CDF2 DFW DFD DFDC AUC AUC AP AUC AP AUC AP AUC AP Xception[11] 99.09 61.08 66.39 65.20 55.37 89.77 85.48 69.90 91.89 EfficientNet[12] 95.01 74.54 - 67.12 - 94.53 - 77.93 - Face x-ray[34] 99.20 79.51 - - - 95.40 93.51 65.50 - RECCE[30] - 68.71 70.35 68.16 54.41 - - 91.33 - Multi-attentional[13] - 67.02 75.30 59.74 73.80 92.95 96.51 68.01 - CADDM[41] 99.69 93.88 91.12 74.48 75.23 99.03 99.59 - - TBX[55] 96.88 74.31 - - - 82.37 - - - UCF[56] - 82.41 - - - 94.47 - 80.51 - ViT[57] 97.45 92.62 - - - 95.72 - 77.35 - FakeFormer[58] 97.67 94.45 97.15 81.74 83.72 96.12 98.31 78.91 - SBI[38] 99.64 93.18 85.16 67.45 55.79 97.58 92.83 86.15 94.24 AUNet[59] 99.46 92.77 - - - 99.22 - 86.16 - LAA-Net[40] 99.46 95.40 97.64 80.03 81.08 98.95 99.40 86.94 97.70 本文方法 99.71 96.04 94.27 82.11 81.47 99.51 98.76 88.27 96.47 注:粗体表示最优值,下划线表示次优值。 表 2 屏蔽各个部件后的多数据集AUC值(%)
F-BiFPN L E AUC测试结果 CDF2 DFW DFD DFDC 平均值 √ √ √ 96.04 82.11 99.51 88.27 91.48(+13.19) √ √ × 95.97 80.24 97.74 88.50 90.61(+12.32) √ × √ 92.14 79.72 96.43 84.31 88.15(+9.86) √ × × 92.32 79.46 97.38 81.57 87.68(+9.39) × √ √ 90.61 73.23 97.04 76.74 84.41(+6.12) × √ × 85.79 70.77 96.80 75.37 82.18(+3.89) × × × 77.42 68.01 95.57 72.16 78.29 注:粗体表示最优值,下划线表示次优值。 表 3 选取不同特征层进行融合检测(%)
EfficientNetV2-S AUC测试结果 CDF2 DFW DFD DFDC $ {\mathrm{P}}_{7} $ $ {\mathrm{P}}_{6} $ $ {\mathrm{P}}_{5} $ $ {\mathrm{P}}_{4} $ $ {\mathrm{P}}_{3} $ FAC F-Bi- E- FPN F-Bi- E- FPN F-Bi- E- FPN F-Bi- E- FPN √ × × × × √ 89.03 91.56 91.56 90.25 98.27 98.27 70.47 73.02 73.02 78.55 78.35 78.35 √ √ × × × √ 89.97 91.79 93.42 71.30 71.39 73.78 96.27 97.12 98.59 77.89 75.80 78.40 √ √ √ × × √ 90.99 92.86 88.72 73.21 74.93 69.40 96.94 98.95 97.96 80.11 83.97 71.91 √ √ √ √ × √ 93.71 95.40 88.35 80.11 80.03 70.94 97.52 98.43 98.89 87.04 86.94 79.02 √ √ √ √ √ √ 92.32 94.22 92.16 79.46 72.54 65.17 97.38 97.31 96.58 81.57 82.90 74.31 √ √ √ √ √ × 92.29 94.22 92.16 76.75 72.54 65.17 97.35 97.31 96.58 81.47 82.90 74.31 平均值 91.20 93.16 90.84 78.86 74.38 76.40 91.72 98.02 98.06 81.03 81.59 76.40 表 4 不同权重系数模型检测效果(%)
$ {\lambda }_{1} $ $ {\lambda }_{2} $ $ {\lambda }_{3} $ $ {\lambda }_{s} $ AUC测试结果 CDF2 DFW DFDC Avg 1 1 0.01~1 0.4 0.3 0.15 0.1 0.05 91.10 77.14 73.47 80.57 10 1 0.01~1 0.4 0.3 0.15 0.1 0.05 94.55 79.94 86.27 86.92 100 10 0.5~10 0.4 0.3 0.15 0.1 0.05 97.27 81.17 76.26 84.90 10 10 0.5~1 0.4 0.3 0.15 0.1 0.05 91.65 82.58 81.94 85.39 10 5 0.01~1 0.4 0.3 0.15 0.1 0.05 96.04 82.11 88.27 88.81 10 5 0.01~1 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.1 0.05 95.54 83.98 77.41 85.64 注:粗体表示最优值。 -
[1] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139–144. doi: 10.1145/3422622. [2] TORA M. Deepfakes[EB/OL]. https://github.com/deepfakes/faceswap, 2018. [3] LIU Kunlin, PEROV I, GAO Daiheng, et al. Deepfacelab: Integrated, flexible and extensible face-swapping framework[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 141: 109628. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109628. [4] MarekKowalski. Faceswap[EB/OL]. https://github.com/MarekKowalski/FaceSwap, 2019. [5] CAHLAN S. How misinformation helped spark an attempted coup in Gabon[EB/OL]. https://wapo.st/3KZARDF, 2020. [6] WAKEFIELD J. Deepfake presidents used in Russia-Ukraine war[EB/OL]. https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-60780142, 2022. [7] 陈宇飞, 沈超, 王骞, 等. 人工智能系统安全与隐私风险[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2019, 56(10): 2135–2150. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190415.CHEN Yufei, SHEN Chao, WANG Qian, et al. Security and privacy risks in artificial intelligence systems[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2019, 56(10): 2135–2150. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2019.20190415. [8] YANG Rui, YOU Kang, PANG Cheng, et al. CSTAN: A deepfake detection network with CST attention for superior generalization[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(22): 7101. doi: 10.3390/s24227101. [9] JHA A K, YADAV A K, DUBEY A K, et al. Deep learning based deepfake video detection system[C]. 2025 3rd International Conference on Disruptive Technologies (ICDT), Greater Noida, India, 2025: 408–412. doi: 10.1109/ICDT63985.2025.10986738. [10] MISHRA S, SHARMA A, DWIVEDI P D, et al. TransDFD: A deepfake detection system of mesoscopic level deepfake-guard-AI[C]. 2025 IEEE International Conference on Interdisciplinary Approaches in Technology and Management for Social Innovation (IATMSI), Gwalior, India, 2025: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/IATMSI64286.2025.10984648. [11] CHOLLET F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1800–1807. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.195. [12] TAN Mingxing and LE Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6105–6114. doi: 10.1109/ICML.2019.00615. [13] ZHAO Hanqing, WEI Tianyi, ZHOU Wenbo, et al. Multi-attentional deepfake detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2185–2194. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00222. [14] LE B M and WOO S S. Quality-agnostic deepfake detection with intra-model collaborative learning[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 22321–22332. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.02045. [15] 孙磊, 张洪蒙, 毛秀青, 等. 基于超分辨率重建的强压缩深度伪造视频检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 2967–2975. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200531.SUN Lei, ZHANG Hongmeng, MAO Xiuqing, et al. Super-resolution reconstruction detection method for DeepFake hard compressed videos[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 2967–2975. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200531. [16] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.106. [17] ZAFAR F, KHAN T A, AKBAR S, et al. A hybrid deep learning framework for deepfake detection using temporal and spatial features[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 79560–79570. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3566008. [18] XIANG Sheng, MA Junhao, SHANG Qunli, et al. Two-layer attention feature pyramid network for small object detection[J]. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 2024, 141(1): 713–731. doi: 10.32604/cmes.2024.052759. [19] DANG Jin, TANG Xiaofen, and LI Shuai. HA-FPN: Hierarchical attention feature pyramid network for object detection[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(9): 4508. doi: 10.3390/s23094508. [20] TAN Mingxing, PANG Ruoming, and LE Q V. EfficientDet: Scalable and efficient object detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10778–10787. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01079. [21] CHEN Yuqi, ZHU Xiangbin, LI Yonggang, et al. Enhanced semantic feature pyramid network for small object detection[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2023, 113: 116919. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2023.116919. [22] AYINDE B O, INANC T, and ZURADA J M. Regularizing deep neural networks by enhancing diversity in feature extraction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(9): 2650–2661. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2885972. [23] HESSE R, SCHAUB-MEYER S, and ROTH S. Content-adaptive downsampling in convolutional neural networks[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 4544–4553. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW59228.2023.00478. [24] WANG Shuai, ZHU Donghui, CHEN Jian, et al. Deepfake face discrimination based on self-attention mechanism[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2024, 183: 92–97. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2024.02.019. [25] 赖志茂, 章云, 李东. 基于Transformer的人脸深度伪造检测技术综述[J]. 广东工业大学学报, 2023, 40(6): 155–167. doi: 10.12052/gdutxb.230130.LAI Zhimao, ZHANG Yun, and LI Dong. A survey of deepfake detection techniques based on Transformer[J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Technology, 2023, 40(6): 155–167. doi: 10.12052/gdutxb.230130. [26] KINGRA S, AGGARWAL N, and KAUR N. SFormer: An end-to-end spatio-temporal transformer architecture for deepfake detection[J]. Forensic Science International: Digital Investigation, 2024, 51: 301817. doi: 10.1016/j.fsidi.2024.301817. [27] KHORMALI A and YUAN J S. Self-supervised graph transformer for deepfake detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 58114–58127. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3392512. [28] COCCOMINI D A, MESSINA N, GENNARO C, et al. Combining EfficientNet and vision transformers for video deepfake detection[C]. 21st International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Lecce, Italy, 2022: 219–229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-06433-3_19. [29] CAI Zhixi, GHOSH S, STEFANOV K, et al. MARLIN: Masked autoencoder for facial video representation LearnINg[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 1493–1504. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00150. [30] CAO Junyi, MA Chao, YAO Taiping, et al. End-to-end reconstruction-classification learning for face forgery detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Orleans, USA, 2022: 4103–4112. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00408. [31] MEJRI N, GHORBEL E, and AOUADA D. UNTAG: Learning generic features for unsupervised type-agnostic deepfake detection[C]. ICASSP 2023–2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 2023: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP49357.2023.10095983. [32] ZHENG Junshuai, ZHOU Yichao, HU Xiyuan, et al. DT-TransUNet: A dual-task model for deepfake detection and segmentation[C]. 6th Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), Xiamen, China, 2023: 244–255. doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-8540-1_20. [33] ZOU Mian, YU Baosheng, ZHAN Yibing, et al. Semantics-oriented multitask learning for DeepFake detection: A joint embedding approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2025, 35(10): 9950–9963. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2025.3572508. [34] LI Lingzhi, BAO Jianmin, ZHANG Ting, et al. Face X-ray for more general face forgery detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 5000–5009. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00505. [35] YANG Yang, IDRIS N B, LIU Chang, et al. A destructive active defense algorithm for deepfake face images[J]. PeerJ Computer Science, 2024, 10: e2356. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2356. [36] GONG Liangyu and LI Xuejun. A contemporary survey on deepfake detection: Datasets, algorithms, and challenges[J]. Electronics, 2024, 13(3): 585. doi: 10.3390/electronics13030585. [37] NGUYEN H H, FANG Fuming, YAMAGISHI J, et al. Multi-task learning for detecting and segmenting manipulated facial images and videos[C]. 2019 IEEE 10th International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Tampa, USA, 2019: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/BTAS46853.2019.9185974. [38] SHIOHARA K and YAMASAKI T. Detecting deepfakes with self-blended images[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 18699–18708. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01816. [39] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. [40] NGUYEN D, MEJRI N, SINGH I P, et al. LAA-Net: Localized artifact attention network for quality-agnostic and generalizable deepfake detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 17395–17405. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01647. [41] DONG Shichao, WANG Jin, JI Renhe, et al. Implicit identity leakage: The stumbling block to improving deepfake detection generalization[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 3994–4004. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.00389. [42] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.324. [43] ZHAO Tianchen, XU Xiang, XU Mingze, et al. Learning self-consistency for deepfake detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 15003–15013. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01475. [44] RÖSSLER A, COZZOLINO D, VERDOLIVA L, et al. FaceForensics++: Learning to detect manipulated facial images[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00009. [45] THIES J, ZOLLHÖFER M, STAMMINGER M, et al. Face2Face: Real-time face capture and reenactment of RGB videos[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016, 2387–2395. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.262. [46] THIES J, ZOLLHÖFER M, and NIEßNER M. Deferred neural rendering: Image synthesis using neural textures[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2019, 38(4): 66. doi: 10.1145/3306346.3323035. [47] LI Yuezun, YANG Xin, SUN Pu, et al. Celeb-DF: A large-scale challenging dataset for DeepFake forensics[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 3204–3213. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00327. [48] DUFOUR N and GULLY A. Contributing data to deepfake detection research[EB/OL]. https://research.google/blog/contributing-data-to-deepfake-detection-research/, 2019. [49] DOLHANSKY B, HOWES R, PFLAUM B, et al. The deepfake detection challenge (DFDC) preview dataset[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1910.08854, 2019. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1910.08854. [50] ZI Bojia, CHANG Minghao, CHEN Jingjing, et al. WildDeepfake: A challenging real-world dataset for deepfake detection[C]. The 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, USA, 2020: 2382–2390. doi: 10.1145/3394171.3413769. [51] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848. [52] TAN Mingxing and LE Q. EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 10096–10106. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2104.00298. [53] FORET P, KLEINER A, MOBAHI H, et al. Sharpness-aware minimization for efficiently improving generalization[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 2021. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2010.01412. [54] MÜLLER R, KORNBLITH S, and HINTON G. When does label smoothing help?[C]. The 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 422. doi: 10.5555/3454287.3454709. [55] ZHANG Rui, JIANG Zixuan, and SUN Changxu. Two-branch deepfake detection network based on improved Xception[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Automation and Computer Engineering (ICEACE), Changchun, China, 2023: 227–231. doi: 10.1109/ICEACE60673.2023.10442716. [56] YAN Zhiyuan, ZHANG Yong, FAN Yanbo, et al. UCF: Uncovering common features for generalizable deepfake detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2023: 22355–22366. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.02048. [57] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 2021. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2010.11929. [58] NGUYEN D, ASTRID M, GHORBEL E, et al. FakeFormer: Efficient vulnerability-driven transformers for generalisable deepfake detection[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2410.21964, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2410.21964. [59] BAI Weiming, LIU Yufan, ZHANG Zhipeng, et al. AUNet: Learning relations between action units for face forgery detection[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 24709–24719. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.02367. [60] SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 618–626. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.74. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
