A Study on Lightweight Method of TCM Structured Large Model Based on Memory-Constrained Pruning
-
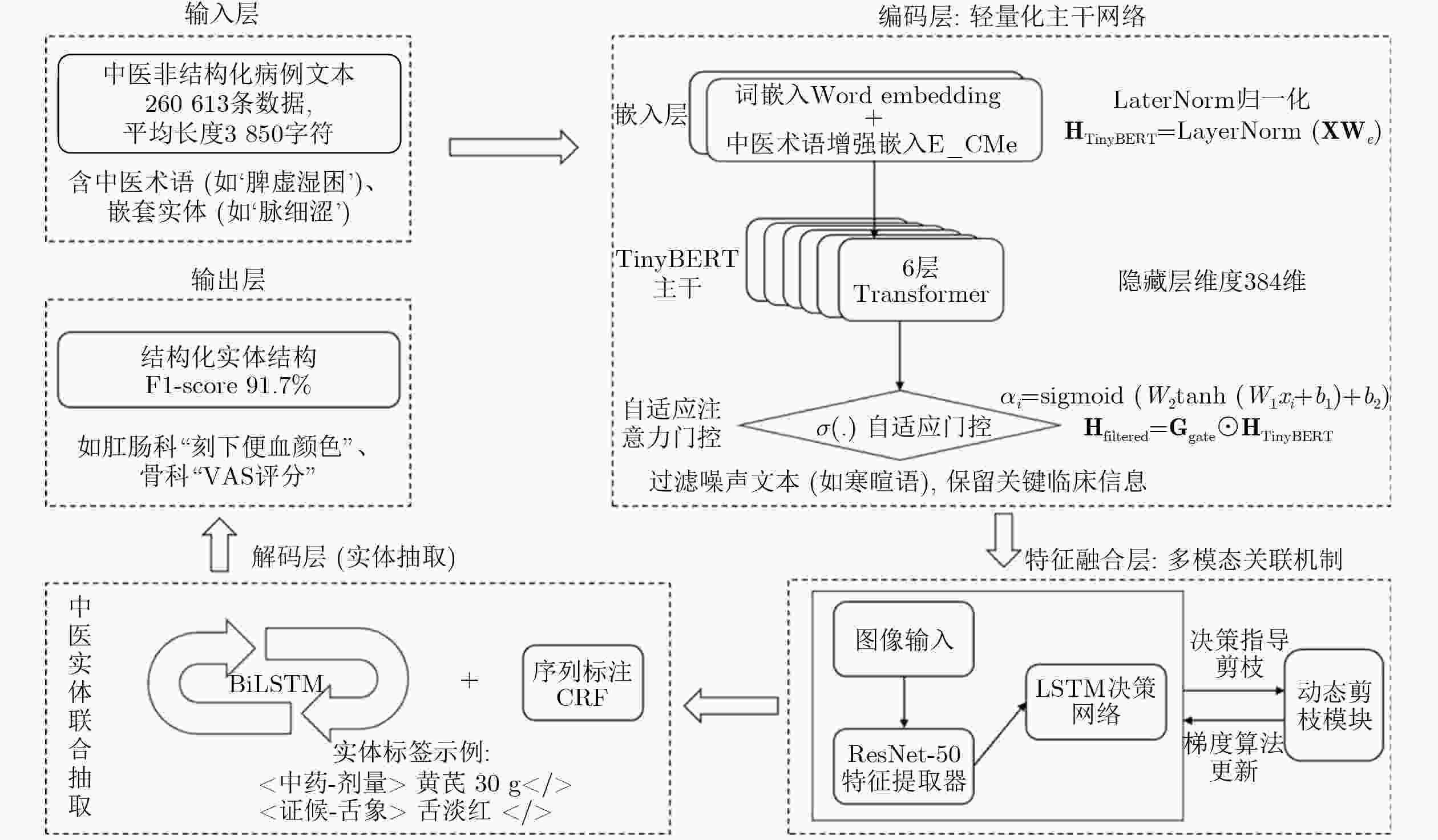
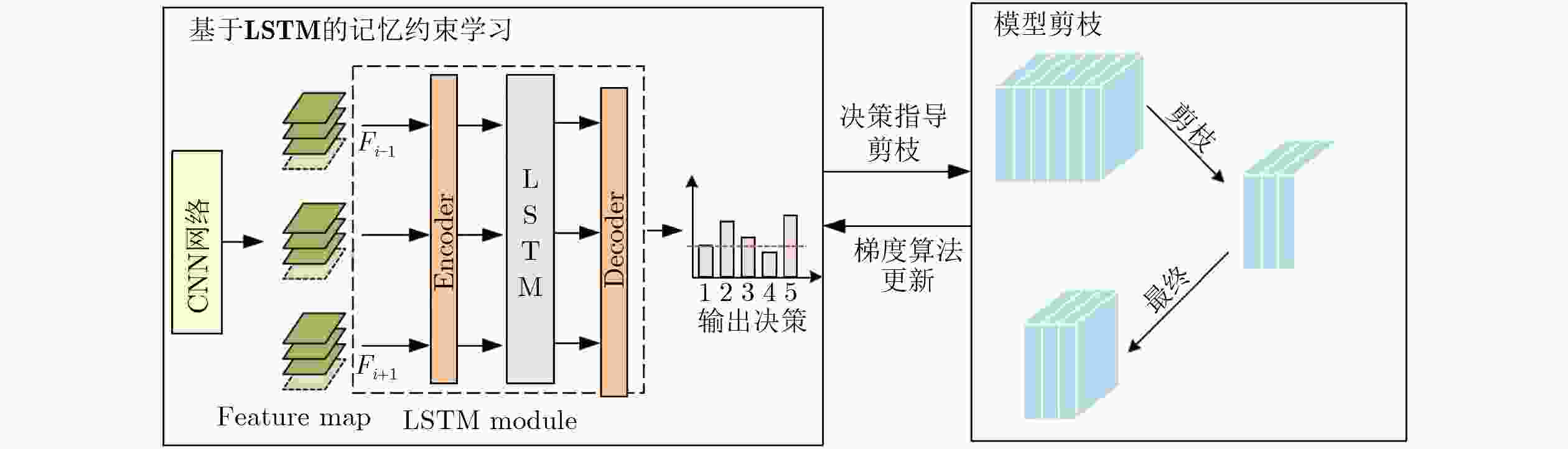
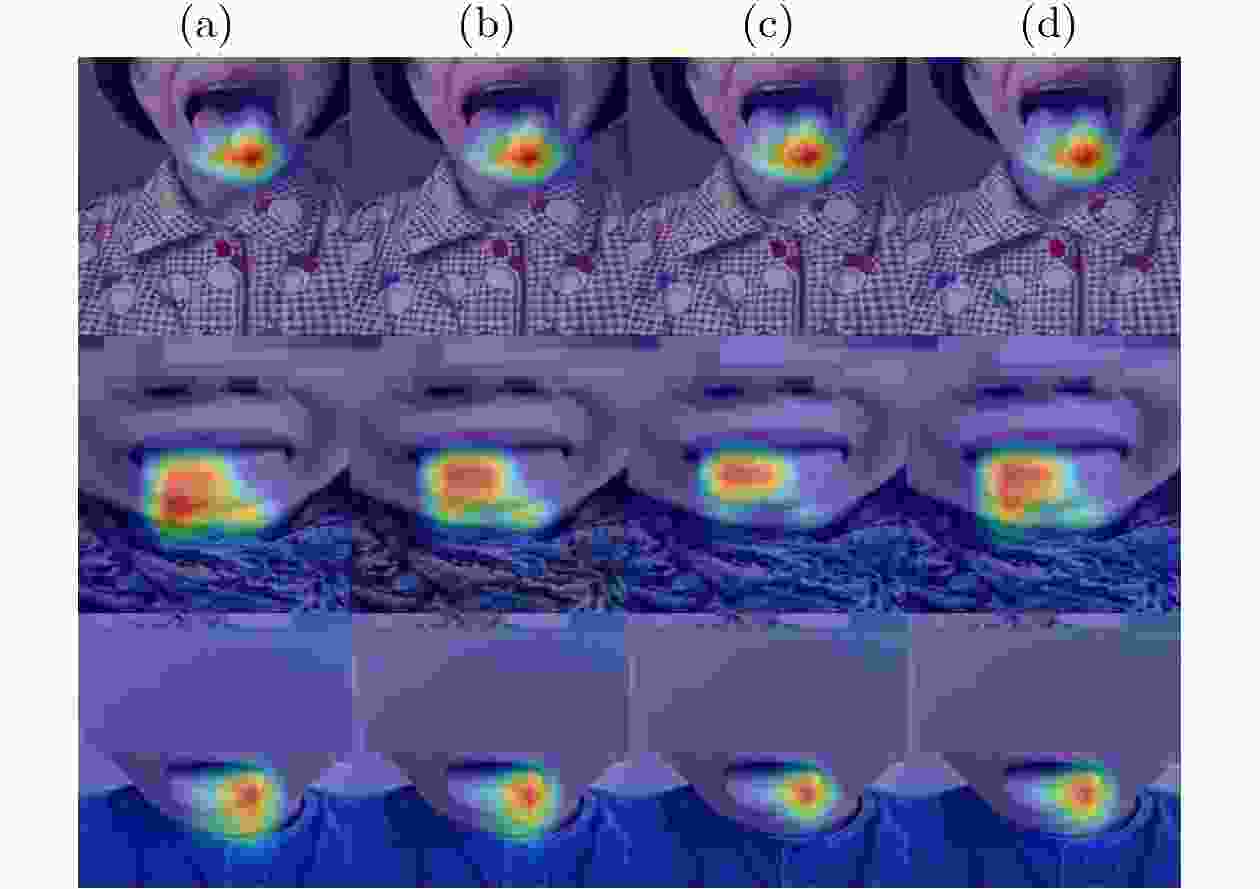
摘要: 随着人工智能技术的快速发展,大语言模型正在中医医疗领域广泛试点应用。但基层中医医院部署大模型面临GPU资源受限、中医非结构化病历利用率低的双重痛点。为此,本论文提出一种轻量化的中医病历智能结构化模型。所提模型不仅借助知识蒸馏实现文本编码器轻量化,更为重要是在传统文本编码其中引入多模态融合模块,实现轻量化舌诊图像表征。具体而言,提出了一种基于记忆约束的多模态表征轻量化方法。所提方法将长短时记忆网络作为剪枝决策器,分析历史信息中长时依赖关系,以此来学习并量化多模态表征中特征连接的重要性。在此基础上,引入增强学习方法对舌诊特征提取模型参数进行反向更新,进一步提升剪枝决策的准确性。实验采用多中心21家三甲医院的
10500 份脱敏中医电子病历及舌像图像关联文本进行训练与验证。所提模型F1-score达91.7%,显存占用3.8GB,推理速度22rec/s,较BERT-Large提升27.2%效率且显存降低75%。消融实验表明,动态批次裁剪对显存节省贡献75%(较BERT-Large基准),在模型自身消融对比中节省62%显存,中医术语增强词表使罕见实体F1提升6.2%。Abstract:Objective The structuring of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) electronic medical records (EMRs) is essential for enabling knowledge discovery, clinical decision support, and intelligent diagnosis. However, two significant barriers exist: (1) TCM EMRs are primarily unstructured free text and often paired with tongue images, which complicates automated processing; and (2) grassroots hospitals typically face limited GPU resources, preventing deployment of large-scale pretrained models. This study aims to resolve these challenges by proposing a lightweight multimodal model based on memory-constrained pruning. The approach is designed to retain near–state-of-the-art accuracy while dramatically reducing memory consumption and computation cost, thereby ensuring practical applicability in resource-limited healthcare settings. Methods A three-stage architecture is established, consisting of an encoder, a multimodal fusion module, and a decoder. For textual inputs, a distilled TinyBERT encoder is combined with a BiLSTM-CRF decoder to extract 23 categories of TCM clinical entities, including symptoms, syndromes, prescriptions, and herbs. For visual inputs, a ResNet-50 encoder processes tongue diagnosis images. A novel memory-constrained pruning strategy is introduced: an LSTM decision network observes convolutional feature maps and adaptively prunes redundant channels while retaining crucial diagnostic features. To expand pruning flexibility, gradient re-parameterization and dynamic channel grouping are employed, with stability ensured through a reinforcement-learning controller. In parallel, INT8 mixed-precision quantization, gradient accumulation, and dynamic batch pruning (DBP) are adopted to reduce memory usage. Finally, a TCM terminology–enhanced lexicon is incorporated into the encoder embeddings to address recognition of rare entities. The entire system is trained end-to-end on paired EMR–tongue datasets ( Fig. 1 ), ensuring joint optimization of multimodal information flow.Results and Discussions Experiments are conducted on 10,500 de-identified EMRs paired with tongue images, collected from 21 tertiary hospitals. On an RTX 3060 GPU, the proposed model achieves an F1-score of 91.7%, with peak GPU memory reduced to 3.8 GB and inference speed improved to 22 records per second (Table 1 ). Compared with BERT-Large, memory consumption decreases by 75% and throughput increases 2.7×, while accuracy remains comparable. Ablation studies confirm the contributions of each module: the adaptive attention gating mechanism raises overall F1 by 2.8% (Table 2 ); DBP reduces memory usage by 40–62% with minimal accuracy loss and significantly improves performance on EMRs exceeding 5,000 characters (Fig. 2 ); and the terminology-enhanced lexicon boosts recognition of rare entities such as “blood stasis” by 6.2%. Moreover, structured EMR fields enable association rule mining, where the confidence of syndrome–symptom relationships increases by 18% (Algorithm 1). These findings highlight three main insights: (1) multimodal fusion with lightweight design yields clinical benefits beyond unimodal models; (2) memory-constrained pruning offers stable channel reduction under strict hardware limits, outperforming traditional magnitude-based pruning; and (3) pruning, quantization, and dynamic batching exhibit strong synergy when co-designed, rather than used independently. Collectively, these results demonstrate the feasibility of deploying high-performing TCM EMR structuring systems in real-world environments with limited computational capacity.Conclusions This work proposes and validates a lightweight multimodal framework for structuring TCM EMRs. By introducing memory-constrained pruning combined with quantization and dynamic batch pruning, the method significantly compresses the visual encoder while maintaining fusion accuracy between text and images. The approach delivers near–state-of-the-art performance with drastically reduced hardware requirements, enabling deployment in regional hospitals and clinics. Beyond immediate efficiency gains, the structured multimodal outputs enrich TCM knowledge graphs and improve the reliability of downstream tasks such as syndrome classification and treatment recommendation. The study thus provides both theoretical and practical contributions: it bridges the gap between powerful pretrained models and the limited hardware of grassroots medical institutions, and establishes a scalable paradigm for lightweight multimodal NLP in medical informatics. Future directions include incorporating additional modalities such as pulse-wave signals, extending pruning strategies with graph neural networks, and exploring adaptive cross-modal attention mechanisms to further enhance clinical applicability. -
表 1 不同模型的性能对比
表 2 按实体类别细分的F1-score(测试集)
实体类别 具体实体名称 F1-score(%) 数据说明 肛肠科 刻下便血颜色 94.2 枚举型实体(淡红/鲜红/暗红),标签明确 刻下便后肛内肿物是否脱出 93.8 二元枚举(是/否),关键词规则清晰 骨科 患处VAS评分 95.6 数值型实体(整数),格式固定 健侧腕关节周径(cm) 95.1 decimal型数值,单位明确 呼吸内科 痰色 92.5 枚举型(黄/白/绿等),存在模糊描述(如“黄白相间”) 有无发热 93.3 二元枚举(有/无),时间范围明确 消化内科 刻下腹泻频次 91.8 范围枚举(每日<4次等),需处理模糊表述(如“5~8次”) 刻下有无黏液脓血便 92.1 三元枚举(有/无/未提及),文本表述直接 证候类 舌象(如“舌淡红”) 88.7 描述性文本,存在模糊性(如“淡红偏暗”) 脉象(如“脉细涩”) 87.5 术语嵌套(脉象+病机),表述抽象 注:数据来源于 2100 份测试集(来自总数据集10500 份),各类实体标注参照《中医诊断学术语》表 3 各模块对性能的影响
模块 F1-score 变化 显存变化 长文本处理稳定性 自适应注意力门控 +2.8% ±0% 无影响 动态批次裁剪 ±0.2% -62% 提升至99.6% 术语增强词表 +6.2% ±0% 无影响 注:显存节省率计算公式:$ \Delta _{mem}=\frac{{M}_{base}-{M}_{\text{o}pt}}{{M}_{base}}\text{×}100\text{%} $
其中:$ {M}_{base} $未使用优化策略时的显存(如无DBP时为6.2 GB)-$ {M}_{opt} $使用优化后的显存(3.8 GB)。表 4 剪枝策略对比
剪枝策略 F1-score(%) 显存占用(GB) 推理速度(rec/s) CNN-BiLSTM+无剪枝 91.7 6.2 18 CNN-BiLSTM+L1范数剪枝 91.2 4.8 20 CNN-BiLSTM+记忆约束剪枝 91.5 3.8 22 表 5 不同剪枝比例下的模型性能
剪枝比例 F1-score(%) 显存占用(GB) 推理速度(rec/s) 30% 91.2 4.5 19 40% 90.9 4.0 21 50% 90.1 3.5 24 60% 89.5 3.1 27 70% 87.1 2.7 30 表 6 不同LSTM隐藏层大小下的模型性能
LSTM隐藏层大小 F1-score(%) 模型参数量(M) 64 89.2 58.2 128 89.5 59.1 192 89.5 60.3 256 89.4 61.8 表 7 不同跨模态注意力头数下的模型性能
注意力头数 F1-score(%) 证候类实体F1-score(%) 4 89.1 86.5 8 89.5 87.4 12 89.6 87.5 -
[1] 国家卫生健康委, 国家发展改革委, 教育部, 等. 2023年度全国三级公立中医医院绩效监测分析情况通报[EB/OL]. http://www.natcm.gov.cn/yizhengsi/zhengcewenjian/2025-03-28/36079.html, 2025. (查阅网上资料,未找到本条文献英文翻译,请确认并补充). [2] 张敏, 李军, 王芳, 等. 基于CNN-BiLSTM的电子病历实体识别研究[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(5): 1567–1573. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认).ZHANG Min, LI Jun, WANG Fang, et al. Entity recognition in electronic medical records based on CNN-BiLSTM[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2023, 43(5): 1567–1573. [3] WANG J, LI Y, and ZHANG Q. Lightweight BERT for TCM entity recognition in primary hospitals[C]. International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), 2023: 1–5. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). [4] 王建国, 刘敏, 张强. 中医电子病历结构化方法研究进展[J]. 北京中医药大学学报, 2022, 45(8): 789–795. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认).WANG Jianguo, LIU Min, and ZHANG Qiang. Progress in structured methods of TCM electronic medical records[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 45(8): 789–795. [5] DEVLIN J, CHANG Mingwei, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, USA, 2019: 4171–4186. doi: 10.18653/v1/N19-1423. [6] 李华, 王磊, 张明, 等. 基于轻量化和极化自注意力的中医望诊异常形态分类[J]. 数字中医药, 2024, 3(4): 25–33. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). [7] JIAO Xiaoqi, YIN Yichun, SHANG Lifeng, et al. TinyBERT: Distilling BERT for natural language understanding[C]. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP, Hong Kong, China, 2020: 4163–4174. doi: 10.18653/v1/2020.findings-emnlp.372. (查阅网上资料,未找到本条文献出版地信息,请确认). [8] 李明, 张华, 王红. 基于注意力机制的中医实体识别轻量化研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(2): 312–318. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认).LI Ming, ZHANG Hua, and WANG Hong. TCM entity recognition based on attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(2): 312–318. [9] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention - MICCAI, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28. [10] 中国中医药信息学会. T/CIATCM 013-2019 中医电子病历基本数据集[S]. 2019. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版信息, 请确认并补充).China Information Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine. T/CIATCM 013-2019 Basic datasets for electronic medical records of traditional Chinese medicine[S]. 2019. [11] 国家中医药管理局. 中医诊断学术语[S]. 北京: 国家中医药管理局, 2021. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). [12] 国家中医药管理局. 中药处方规范[S]. 北京: 国家中医药管理局, 2010. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). [13] 范骁辉, 张俊华, 等. TCMChat: 基于LoRA的中医药生成式大模型[J]. 药理研究, 2025, 112: 105986. (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献信息, 请确认). [14] LI Hao, KADAV A, DURDANOVIC I, et al. Pruning filters for efficient ConvNets[C]. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. [15] LIU Zhuang, SUN Mingjie, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Rethinking the value of network pruning[C]. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, USA, 2019. [16] KUNDU S, NAZEMI M, BEEREL P A, et al. DNR: A tunable robust pruning framework through dynamic network rewiring of DNNs[C]. Proceedings of the 26th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 2021: 344–350. doi: 10.1145/3394885.3431542. [17] JACOB B, KLIGYS S, CHEN Bo, et al. Quantization and training of neural networks for efficient integer-arithmetic-only inference[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2704–2713. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00286. [18] HAN Song, MAO Huizi, and DALLY W J. Deep compression: Compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and Huffman coding[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1510.00149, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1510.00149. (查阅网上资料,请作者核对文献类型及格式是否正确). [19] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [20] ZHAO Xiongjun, WANG Xiang, YU Fenglei, et al. UniMed: Multimodal multitask learning for medical predictions[C]. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). Las Vegas, USA, 2022: 1399–1404. doi: 10.1109/BIBM55620.2022.9995044. [21] MA Xinyin, FANG Gongfan, and WANG Xinchao. LLM-pruner: On the structural pruning of large language models[C]. Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2023: 950. [22] POUDEL P, CHHETRI A, GYAWALI P, et al. Multimodal federated learning with missing modalities through feature imputation network[C]. 29th Annual Conference on Medical Image Understanding and Analysis, Leeds, UK, 2026: 289–299. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-98688-8_20. [23] BACK J, AHN N, and KIM J. Magnitude attention-based dynamic pruning[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 276: 126957. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.126957. [24] LIU Jiaxin, LIU Wei, LI Yongming, et al. Attention-based adaptive structured continuous sparse network pruning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2024, 590: 127698. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.127698. [25] TAN Mingxing and LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6105–6114. [26] WU Qinzhuo, XU Weikai, LIU Wei, et al. MobileVLM: A vision-language model for better intra- and inter-UI understanding[C]. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024, Miami, USA, 2024: 10231–10251. doi: 10.18653/v1/2024.findings-emnlp.599. [27] FU Zheren, ZHANG Lei, XIA Hou, et al. Linguistic-aware patch slimming framework for fine-grained cross-modal alignment[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 26297–26306. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.02485. [28] PAN Zhengxin, WU Fangyu, and ZHANG Bailing. Fine-grained image-text matching by cross-modal hard aligning network[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 19275–19284. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01847. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
