Satellite Test Tasks Autonomous Orchestration Based on Task-Coupling Constraints and Time-Bounded Windows
-
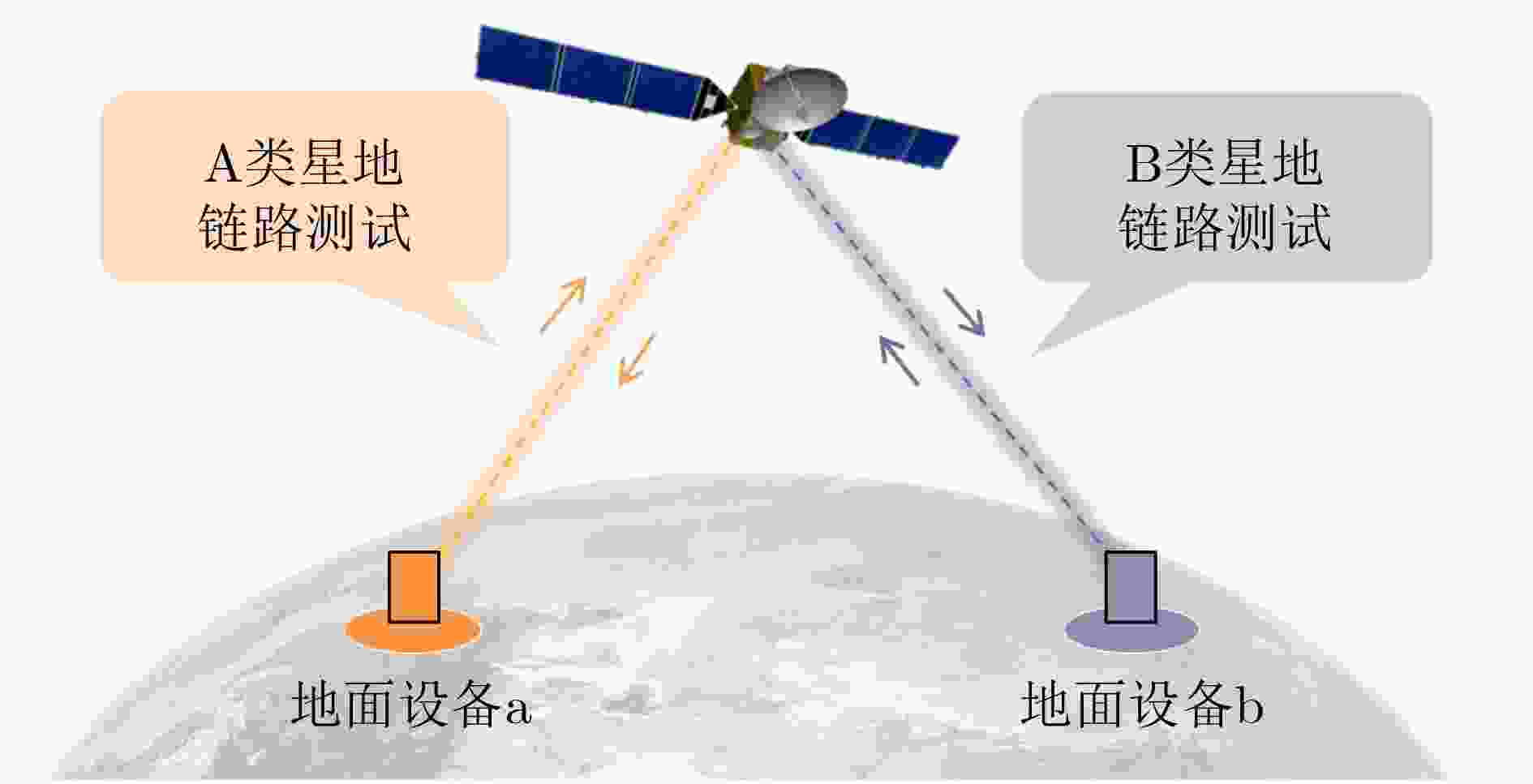
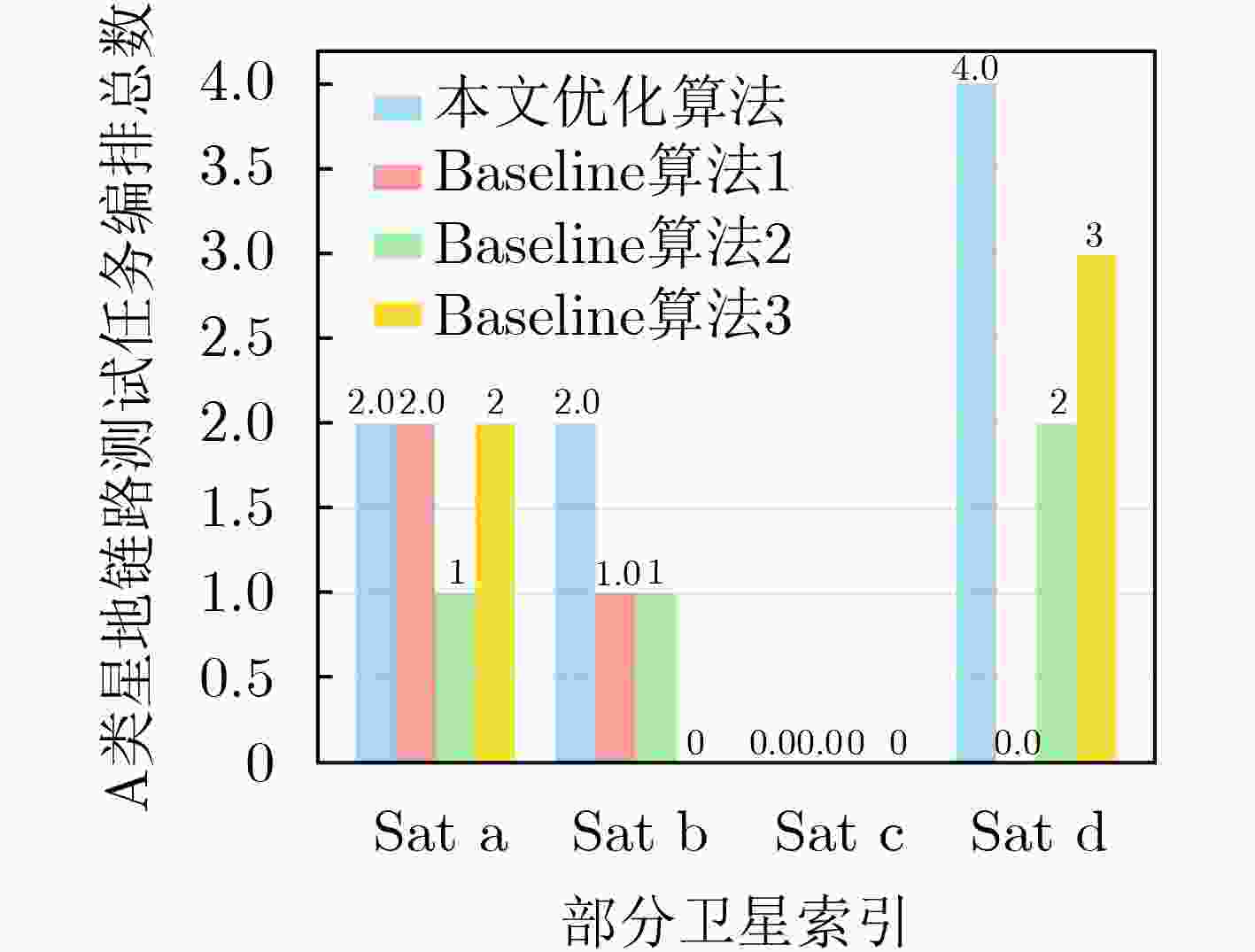
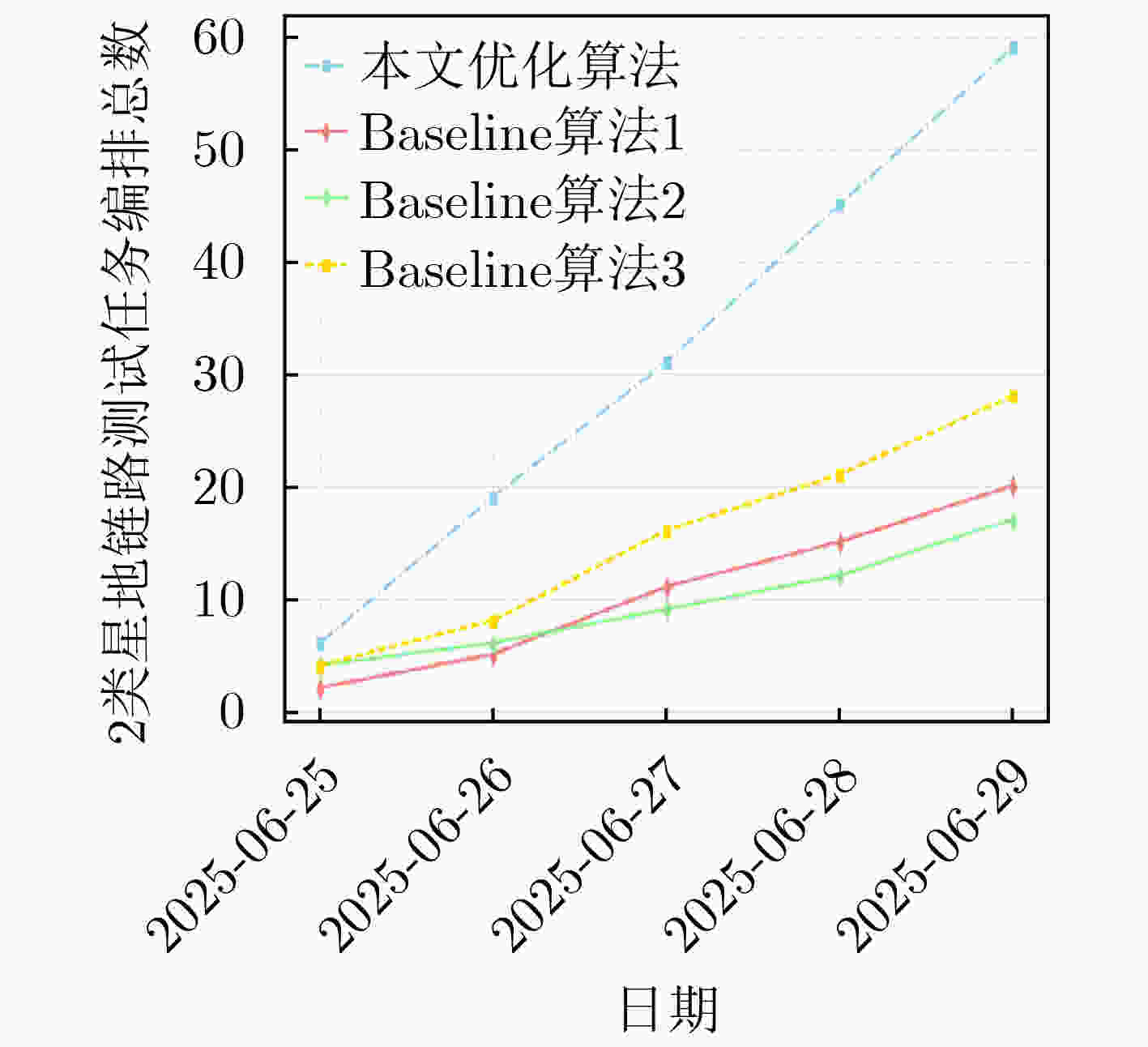
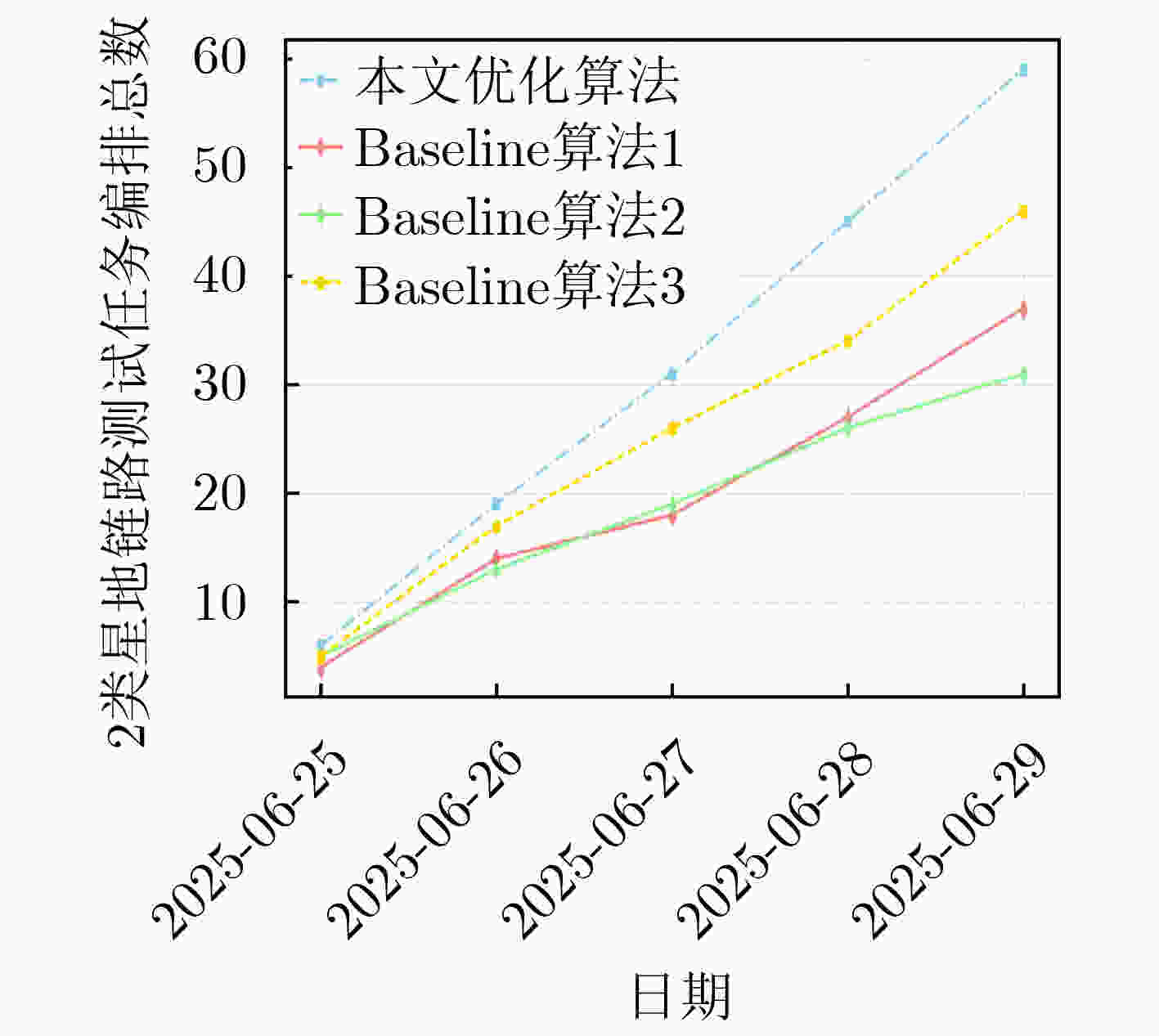
摘要: 近年来,空间在轨资产规模持续扩张,卫星星座建设步伐显著加快,卫星发射数量快速攀升,在轨测试需求急剧增加,而受限于地面站数量和可见弧段资源,测试机会高度稀缺,“星多站少、弧段稀缺”的矛盾日益突出。传统以人工预编排为主的卫星任务规划方式,因决策周期长、规划效率低、调度易出错等缺点,难以适应大规模、多任务和高耦合的复杂测试场景,亟需发展高效的在轨测试任务自动化规划技术,提升星地可见弧段的测试利用效率。为解决上述问题,该文提出卫星任务自动化规划技术,以支撑未来星地一体化系统在建设与运维全生命周期中的高效性与可靠性。首先,建立任务滑块模型及时间窗口模型,通过设计基础任务编排约束以及专有任务编排约束,构建卫星任务通用约束范式,提出非凸约束转换方案;其次,选取星地链路测试为典型应用场景,在可见弧段极度受限的星地链路中,以可编排的任务数量为优化目标,提出基于任务耦合约束及时间受限窗口的卫星任务自动化编排模型,实现测试任务自动化编排的同时,进一步提高星地可见弧段的利用效率;最后,以星地链路测试作为典型的在轨测试场景,该文通过涉及多个低地球轨道卫星和有限可见弧段的仿真实验,对所自主编排框架进行了评估。仿真结果表明,所提方法能够有效地调度测试任务,同时严格满足所有运行约束。与包括遗传算法、禁忌搜索和粒子群优化在内的传统启发式算法相比,该方法性能显著提升,使调度的星地链路测试任务总数增加了约1.9~2.3倍。结果进一步表明,在高度受限的可见窗口条件下,所提模型能够充分利用可用弧段并避免资源冲突,从而显著提高星地链路的利用效率。Abstract:
Objective In recent years, the scale of on-orbit space assets has continued to expand, satellite constellation deployment has accelerated significantly, and the number of satellite launches has increased rapidly. As a result, the demand for on-orbit testing has grown sharply. However, limited ground station availability and scarce visibility arcs severely constrain testing opportunities, giving rise to an increasingly prominent contradiction between “many satellites and few ground stations” under highly limited visibility resources. Traditional satellite mission planning approaches, which rely primarily on manual pre-scheduling, suffer from long decision cycles, low planning efficiency, and high susceptibility to scheduling errors. These limitations make them inadequate for large-scale, multi-task, and highly coupled testing scenarios. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop efficient automated on-orbit test mission planning technologies to improve the utilization efficiency of satellite-ground visibility arcs. Methods To address these limitations, this thesis proposes an automated satellite task orchestration framework to ensure effectiveness and reliability in integrated space-ground systems throughout their lifecycle of construction and operation. A task slider model and a time window model are established, and both general and task-specific orchestration constraints are designed to form a unified constraint paradigm for satellite tasks. A non-convex constraint transformation scheme is further proposed. Using satellite-to-ground link testing as a representative application scenario, an automated task orchestration model is constructed to maximize the number of schedulable tasks under stringent visibility arc constraints while improving the efficiency of visibility arc utilization. Results and Discussions Using satellite-to-ground link testing as a representative on-orbit testing scenario, the proposed autonomous orchestration framework is evaluated through simulations with multiple low Earth orbit satellites and limited visibility arcs. The results show that the proposed method schedules testing tasks effectively while strictly satisfying all operational constraints. Compared with traditional heuristic-based algorithms, including genetic algorithms, tabu search, and particle swarm optimization, the proposed approach achieves a significant performance improvement, increasing the total number of scheduled satellite-ground link testing tasks by approximately 1.9 to 2.3 times. The results also indicate that, under highly constrained time windows, the proposed model fully exploits available visibility arcs and avoids resource conflicts, which substantially improves the utilization efficiency of satellite-ground links. Conclusions This paper proposes an autonomous orchestration framework for satellite on-orbit testing tasks under complex coupling constraints and time-bounded visibility windows. By modeling testing subtasks and visibility arcs using task slider and time window abstractions, and by integrating general and task-specific constraints into a unified mixed-integer programming formulation, the proposed method provides an effective solution for large-scale testing task scheduling. Simulation results confirm that the framework outperforms traditional heuristic-based methods in terms of the number of executable testing tasks and visibility arc utilization. The proposed approach provides a practical and extensible scheduling paradigm for future large-scale satellite constellation testing scenarios. Future work will consider additional resource-layer constraints and uncertainty factors to further improve robustness in real-world testing environments. -
1 卫星测试任务自动化编排算法
输入:任务信息集$ \{\mathcal{K},{\left\{{\mathcal{I}}_{k}\right\}}_{k\in \mathcal{K}},{\left\{{{\varDelta }}^{k}\right\}}_{k\in \mathcal{K}},\left\{\mathcal{G}_{i}^{k}{\}}_{k\in \mathcal{K},i\in {{\mathcal{I}}_{k}}}\right\} $以
及窗口信息集$ \left\{\mathcal{S},\mathcal{O},{\left\{{\mathcal{J}}_{s}\right\}}_{s\in \mathcal{S}},{\left\{{\mathcal{B}}^{s}\right\}}_{s\in \mathcal{S}},{\left\{{\mathcal{E}}^{s}\right\}}_{s\in \mathcal{S}},\right. $
$\left.{{\{\mathcal{H}_{j}^{s}}\}}_{s\in \mathcal{S},j\in {{\mathcal{I}}_{k}}}\right\} $输出:决策变量$ {\left\{{\left\{x_{ij}^{ks}\right\}}_{j\in {{\mathcal{J}}_{s}}},y_{i}^{k}\right\}}_{k\in \mathcal{K},i\in {{\mathcal{I}}_{k}},s\in \mathcal{S},} $,辅助变量
$ {\left\{\gamma _{i}^{k}\right\}}_{k\in \mathcal{K},i\in {{\mathcal{I}}_{k}}} $1: 初始化:$ {\boldsymbol{K}}^{\rm{r}\rm{e}\rm{s}\rm{u}\rm{l}\rm{t}}=\left\{{K}_{1},{K}_{2},\cdots ,{K}_{S}\right\} $, $ {\bf{S}\bf{o}\bf{l}}^{\rm{r}\rm{e}\rm{s}\rm{u}\rm{l}\rm{t}} $ $ =\left\{{\mathrm{Sol}}_{1},{\mathrm{Sol}}_{2},\cdots ,{\mathrm{Sol}}_{S}\right\} $ 2: for $ s=1{,}2,\cdots ,S $ 3: $ {{\mathrm{Sol}}}_{s}=\text{Null} $ 4: 对于任意的$ {K}_{s}\in {\boldsymbol{K}}^{\rm{r}\rm{e}\rm{s}\rm{u}\rm{l}\rm{t}} $,令$ {K}_{s}=J_{s}^{\varPhi_2} $ 5: while $ {K}_{s}\geq 1 $ 6: $ \mathrm{Sol}_s\leftarrow $调用CPLEX找到一组满足约束
$ {{\mathrm{C}}}{1},{\mathrm{C}}{2}^{'},{{\mathrm{C}}}{3},{\mathrm{C}}{4}^{'},{\mathrm{C}}{5}^{'},{{\mathrm{C}}}{5}{\text{~}}{{\mathrm{C}}}{11} $的可行解。7: if 找到可行解$ {{\mathrm{Sol}}}_{s} $ then 8: return $ {K}_{s} $和$ {{\mathrm{Sol}}}_{s} $ 9: else 10: $ {K}_{s}\leftarrow {K}_{s}-1 $ 11: end if 12: end while 13: if $ {K}_{s}=0 $ then 14: return $ {K}_{s}=0 $和$ {{\rm{Sol}}}_{s}=\text{Null} $ 15: end if 16: end for 17: return $ {\boldsymbol{K}}^{\rm{r}\rm{e}\rm{s}\rm{u}\rm{l}\rm{t}} $, $ {\bf{S}\bf{o}\bf{l}}^{\rm{r}\rm{e}\rm{s}\rm{u}\rm{l}\rm{t}} $ 表 1 星地链路弧段信息样例
卫星 信关站 天线 跟踪模式 跟踪开始时间(北斗时) 跟踪结束时间(北斗时) 最大仰角(°) d A 837 Φ1 2025-06-29 08:49:45 2025-06-29 08:51:35 5.536425 c A 837 Φ1 2025-06-29 09:10:08 2025-06-29 09:16:02 12.90948 d B 826 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:15:11 2025-06-29 10:19:38 78.57337 a B 825 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:16:44 2025-06-29 10:23:52 74.55824 d C 824 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:20:41 2025-06-29 10:26:43 25.79927 a D 836 Φ1 2025-06-29 10:19:51 2025-06-29 10:27:12 19.11916 b C 822 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:23:44 2025-06-29 10:29:54 27.59913 d E1 834 Φ1 2025-06-29 10:22:58 2025-06-29 10:31:27 39.66145 a E3 842 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:24:31 2025-06-29 10:33:01 40.83499 d E2 841 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:26:53 2025-06-29 10:31:27 39.66145 c D 836 Φ1 2025-06-29 10:39:48 2025-06-29 10:44:45 46.63377 c A 837 Φ1 2025-06-29 10:44:55 2025-06-29 10:53:10 81.14615 a F 829 Φ1 2025-06-29 11:11:36 2025-06-29 11:19:21 13.99255 c F 829 Φ1 2025-06-29 11:30:58 2025-06-29 11:39:27 22.97701 d C 824 Φ2 2025-06-29 11:57:39 2025-06-29 12:04:06 31.18105 b D 836 Φ1 2025-06-29 11:58:03 2025-06-29 12:06:19 30.98595 b C 822 Φ2 2025-06-29 12:00:51 2025-06-29 12:07:12 29.4712 a E3 842 Φ2 2025-06-29 12:01:48 2025-06-29 12:10:19 38.24031 a E1 834 Φ1 2025-06-29 12:01:48 2025-06-29 12:10:19 38.24031 d E2 841 Φ2 2025-06-29 12:04:16 2025-06-29 12:08:46 38.9376 b A 837 Φ1 2025-06-29 12:06:29 2025-06-29 12:11:48 31.67761 表 2 两类星地链路测试任务编排结果表
卫星 信关站 天线 跟踪模式 跟踪开始时间(北斗时) 跟踪结束时间(北斗时) 最大仰角(°) 编排结果 d A 837 Φ1 2025-06-29 08:49:45 2025-06-29 08:51:35 5.536425 c A 837 Φ1 2025-06-29 09:10:08 2025-06-29 09:16:02 12.90948 d B 826 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:15:11 2025-06-29 10:19:38 78.57337 不发令:A类链路测试 a B 825 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:16:44 2025-06-29 10:23:52 74.55824 不发令:A类链路测试 d C 824 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:20:41 2025-06-29 10:26:43 25.79927 a D 836 Φ1 2025-06-29 10:19:51 2025-06-29 10:27:12 19.11916 发令:载荷关机 b C 822 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:23:44 2025-06-29 10:29:54 27.59913 d E1 834 Φ1 2025-06-29 10:22:58 2025-06-29 10:31:27 39.66145 发令:载荷关机 a E3 842 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:24:31 2025-06-29 10:33:01 40.83499 d E2 841 Φ2 2025-06-29 10:26:53 2025-06-29 10:31:27 39.66145 c D 836 Φ1 2025-06-29 10:39:48 2025-06-29 10:44:45 46.63377 c A 837 Φ1 2025-06-29 10:44:55 2025-06-29 10:53:10 81.14615 a F 829 Φ1 2025-06-29 11:11:36 2025-06-29 11:19:21 13.99255 c F 829 Φ1 2025-06-29 11:30:58 2025-06-29 11:39:27 22.97701 d C 824 Φ2 2025-06-29 11:57:39 2025-06-29 12:04:06 31.18105 b D 836 Φ1 2025-06-29 11:58:03 2025-06-29 12:06:19 30.98595 b C 822 Φ2 2025-06-29 12:00:51 2025-06-29 12:07:12 29.4712 不发令:B类链路测试 a E3 842 Φ2 2025-06-29 12:01:48 2025-06-29 12:10:19 38.24031 不发令:B类链路测试 a E1 834 Φ1 2025-06-29 12:01:48 2025-06-29 12:10:19 38.24031 发令:载荷关机 d E2 841 Φ2 2025-06-29 12:04:16 2025-06-29 12:08:46 38.9376 b A 837 Φ1 2025-06-29 12:06:29 2025-06-29 12:11:48 31.67761 发令:载荷关机 -
[1] Wikipedia Contributors. 2025 in spaceflight[EB/OL]. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=2025_in_spaceflight&oldid=1308788930.2025.9, 2025. [2] LIU Bingkun, KUANG Linling, and LU Jianhua. Performance analysis of NGSO satellite communication systems with flexible beams[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(14): 24726–24738. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3379586. [3] 虞志刚, 冯旭, 戴天, 等. 空间边缘计算: 需求、架构及关键技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(12): 4416–4425. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211157.YU Zhigang, FENG Xu, DAI Tian, et al. Space edge computing: Requirement, architecture and key technique[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(12): 4416–4425. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211157. [4] LI Zhen, JIANG Chunxiao, SUN Jiachen, et al. Resource collaboration between satellite and wide-area mobile base stations in integrated satellite-terrestrial network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2025, 24(2): 875–889. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3472081. [5] 杜永浩, 邢立宁, 姚锋, 等. 航天器任务调度模型、算法与通用求解技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(12): 2715–2741. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190656.DU Yonghao, XING Lining, YAO Feng, et al. Survey on models, algorithms and general techniques for spacecraft mission scheduling[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(12): 2715–2741. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190656. [6] XIE Jiaxuan, KUANG Linling, and MU Honglei. A bilevel edge computing architecture and collaborative offloading mechanism for offshore buoys network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2026, 73(1): 1164–1173. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2025.3567704. [7] XIE Haoran, ZHAN Yafeng, and LU Jianhua. Mega-constellations based TT&C resource sharing: Keep reliable aeronautical communication in an emergency[J]. China Communications, 2024, 21(2): 1–16. doi: 10.23919/jcc.fa.2023-0313.202402. [8] SUN Jiachen, CHEN Xu, JIANG Chunxiao, et al. Distributionally robust optimization of on-orbit resource scheduling for remote sensing in space-air-ground integrated 6g networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2025, 43(1): 382–395. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2024.3460057. [9] LIN Zhiyuan, NI Zuyao, KUANG Linling, et al. Satellite-terrestrial coordinated multi-satellite beam hopping scheduling based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(8): 10091–10103. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3368689. [10] 刘晔伟, 周庆瑞, 黄昊. 分布式卫星系统动态任务协同规划算法研究[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2022, 48(4): 46–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2022.04.006.LIU Yewei, ZHOU Qingrui, and HUANG Hao. Distributed satellite system dynamic task collaborative assignment algorithm[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2022, 48(4): 46–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2022.04.006. [11] 雷永刚, 张若禹, 马佳楠. 人工智能技术在卫星任务管控领域的应用[J]. 电讯技术, 2022, 62(9): 1377–1382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2022.09.026.LEI Yonggang, ZHANG Ruoyu, and MA Jianan. Application of artificial intelligence technology in satellite control system[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2022, 62(9): 1377–1382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2022.09.026. [12] 蔡德荣. 基于蚁群算法的多星联合成像任务规划问题研究[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2012. doi: 10.7666/d.D770918.CAI Derong. Research-based the “Ant Colony” algorithm multi-satellite mission planning joint imaging problems[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and technology, 2012. doi: 10.7666/d.D770918. [13] 岳群彬, 尚希杰, 林晓勇, 等. 分段分策略调度的遥感卫星任务规划架构[J]. 天地一体化信息网络, 2024, 5(2): 63–69. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-8930.2024017.YUE Qunbin, SHANG Xijie, LIN Xiaoyong, et al. Task scheduling framework of multi-stage and multi-strategy for remote sensing satellites[J]. Space-Integrated-Ground Information Networks, 2024, 5(2): 63–69. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-8930.2024017. [14] 贺仁杰, 李菊芳, 姚锋, 等. 成像卫星任务规划技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 20–41.HE Renjie, LI Jufang, YAO Feng, et al. Imaging Satellite Mission Planning Technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 20–41. [15] 杨志玺, 伍国华, 叶淦华, 等. 基于星间链路的天基遥感中继联合调度方法[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 56(6): 1104–1113. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2024.06.014.YANG Zhixi, WU Guohua, YE Ganhua, et al. A joint scheduling method of space based remote sensing and relay through inter satellite link[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2024, 56(6): 1104–1113. doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2024.06.014. [16] 赵博, 周锋, 苏天祥. 基于ILOG OPL的导航卫星地面站任务规划问题研究[C]. 第四届中国卫星导航学术年会论文集-S8卫星导航模型与方法, 武汉, 中国, 2013: 59–61.ZHAO Bo, ZHOU Feng, and SU Tianxiang. The mission planning of navigation satellites tracking station based on ILOG OPL[C]. The 4th China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC), Session S8: Satellite Navigation Models and Methods, Wuhan, China, 2013: 59–61. [17] VOIGT S. A review and ranking of operators in adaptive large neighborhood search for vehicle routing problems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2025, 322(2): 357–375. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2024.05.033. [18] GAO Qinglin, LIU Jianhua, LIU Shimin, et al. From human-related to human-centric: A review of shop floor scheduling problem under Industry 5.0[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2025, 82: 531–546. doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2025.07.003. [19] DIESTEL R. Graph Theory[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2025: 34–69. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-70107-2. [20] 王海燕, 赵剑, 史丽娟. 自适应约束满足问题求解方法的研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021: 12–54.WANG Haiyan, ZHAO Jian, and SHI Lijuan. Research on the Solving Methods of Adaptive Constraint Satisfaction Problem[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021: 12–54. [21] BIANCHESSI N, CORDEAU J F, DESROSIERS J, et al. A heuristic for the multi-satellite, multi-orbit and multi-user management of Earth observation satellites[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, 177(2): 750–762. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2005.12.026. [22] HALL N G and MAGAZINE M J. Maximizing the value of a space mission[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1994, 78(2): 224–241. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(94)90385-9. [23] ZHAO Hang, ZHANG Yamin, JIANG Qiangqiang, et al. Software-defined satellite observation: A fast method based on virtual resource pools[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(22): 5388. doi: 10.3390/rs15225388. [24] 王钧. 成像卫星综合任务调度模型与优化方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2007.WANG Jun. Research on modeling and optimization techniques in united mission scheduling of imaging satellites[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2007. [25] 方炎申, 陈英武, 邹凯, 等. 基于约束满足问题的中继卫星调度问题研究[J]. 运筹与管理, 2005, 14(4): 74–79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2005.04.017.FANG Yanshen, CHEN Yingwu, ZOU Kai, et al. Research on relay satellite scheduling problem with CSP[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2005, 14(4): 74–79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2005.04.017. [26] ZHU Waiming, HU Xiaoxuan, XIA Wei, et al. A two-phase genetic annealing method for integrated Earth observation satellite scheduling problems[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(1): 181–196. doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2889-8. [27] CHEN Xiaoyu, REINELT G, DAI Guangming, et al. A mixed integer linear programming model for multi-satellite scheduling[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 275(2): 694–707. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2018.11.058. [28] MOK S H, JO S, BANG H, et al. Heuristic-based mission planning for an agile earth observation satellite[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Sciences, 2019, 20(3): 781–791. doi: 10.1007/s42405-018-0105-4. [29] ZHANG Ziyong, DONG Tao, YIN Jie, et al. A particle swarm optimization-based queue scheduling and optimization mechanism for large-scale low-earth-orbit satellite communication networks[J]. Sensors, 2025, 25(4): 1069. doi: 10.3390/s25041069. -





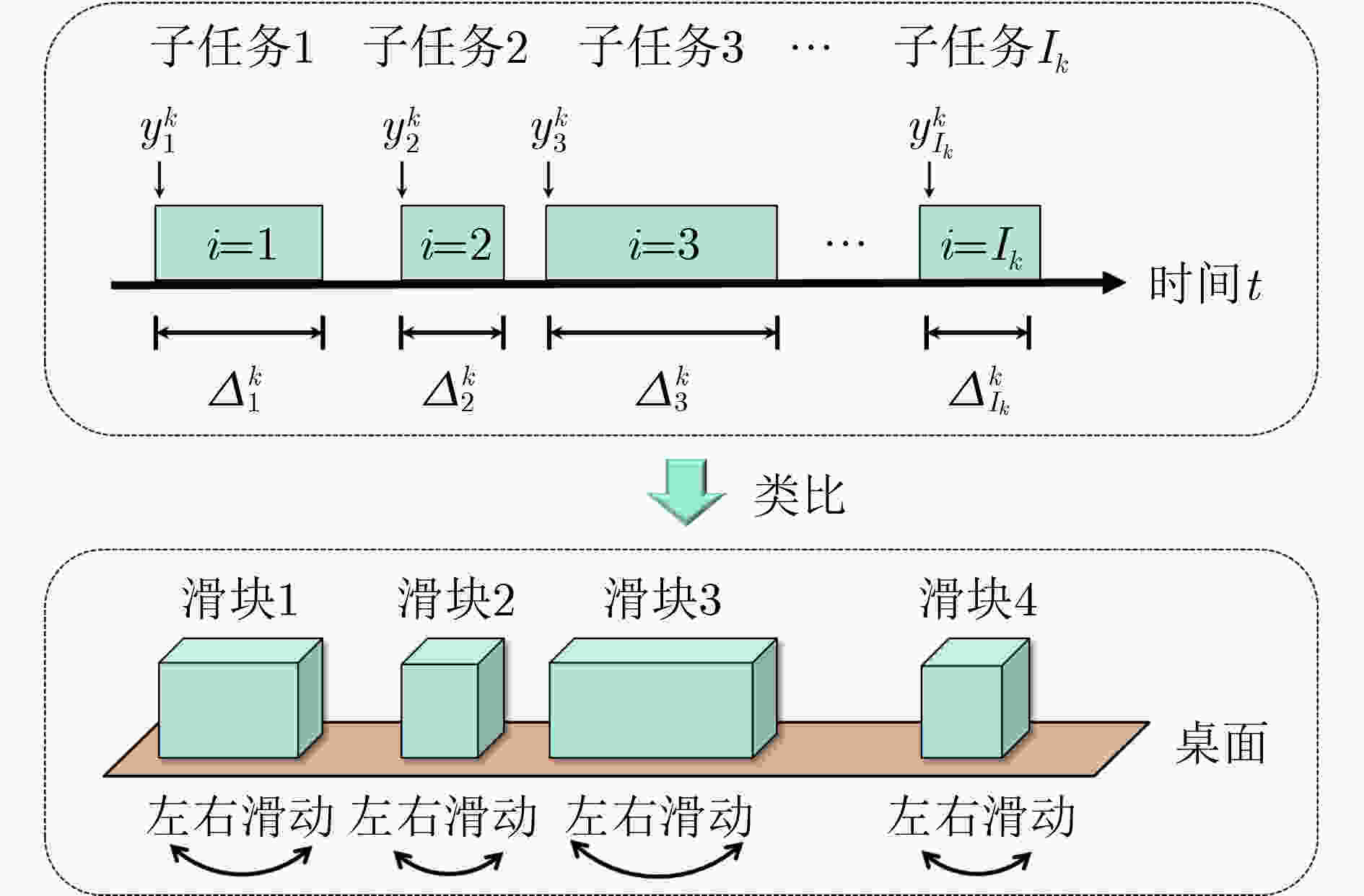
 下载:
下载:
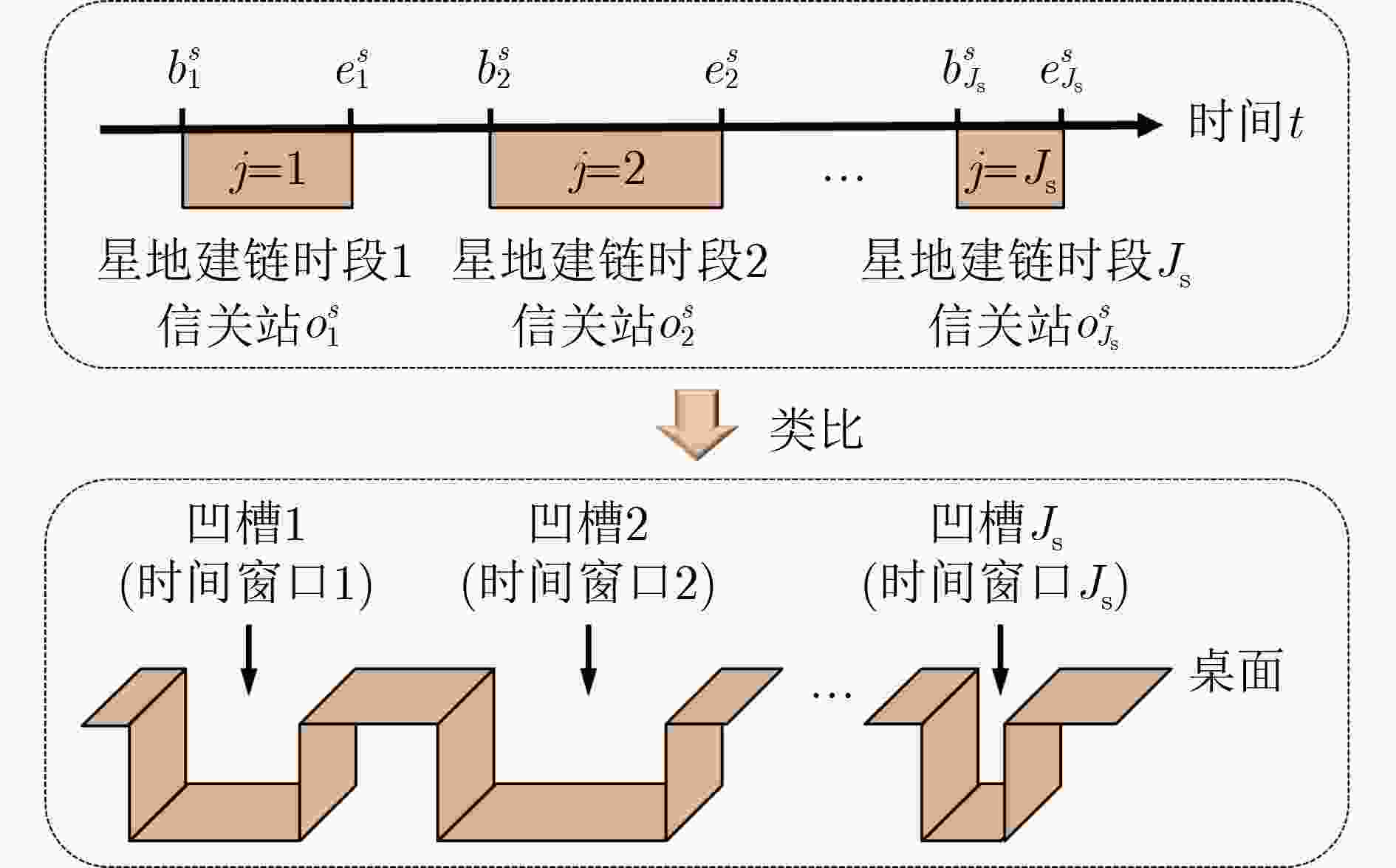
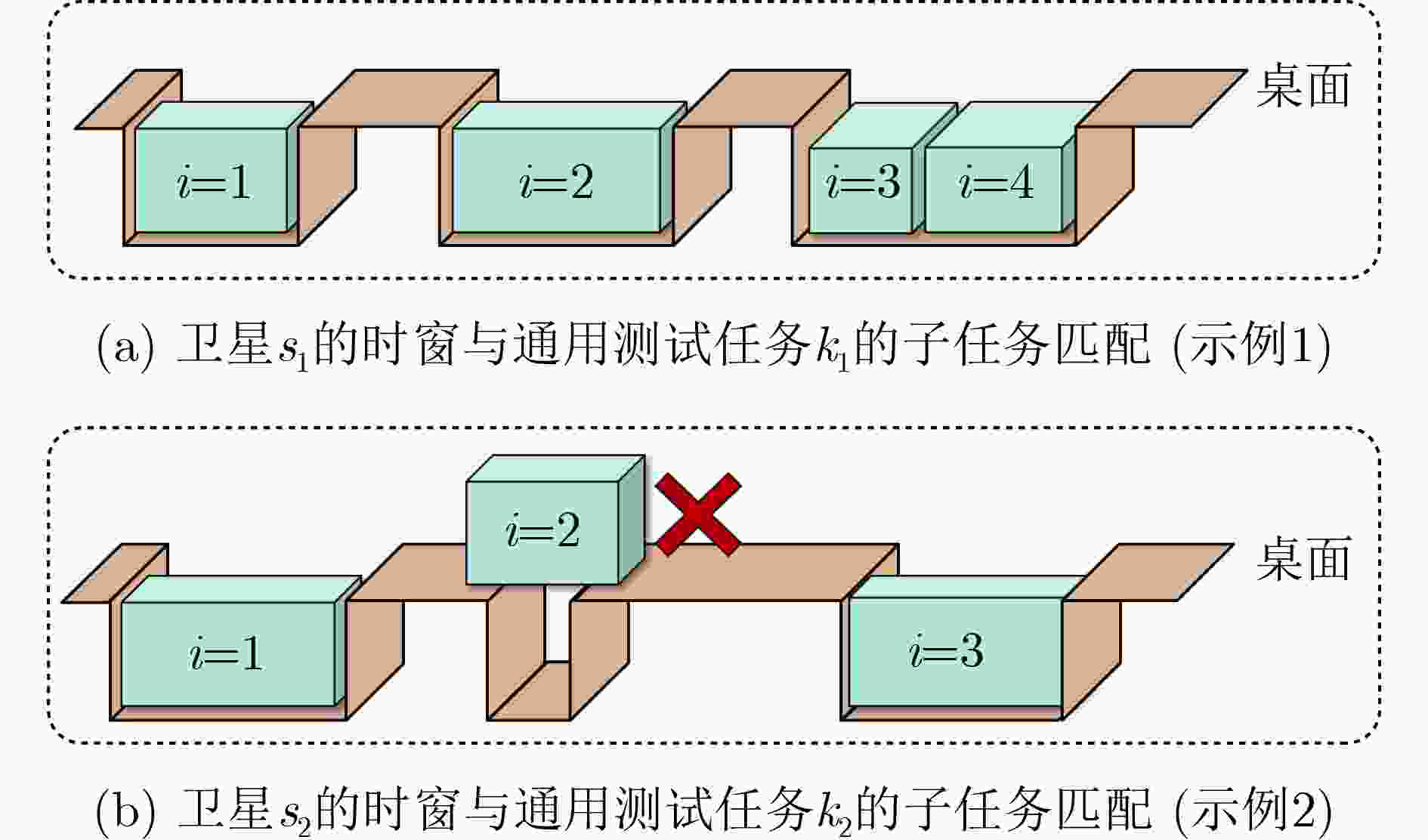
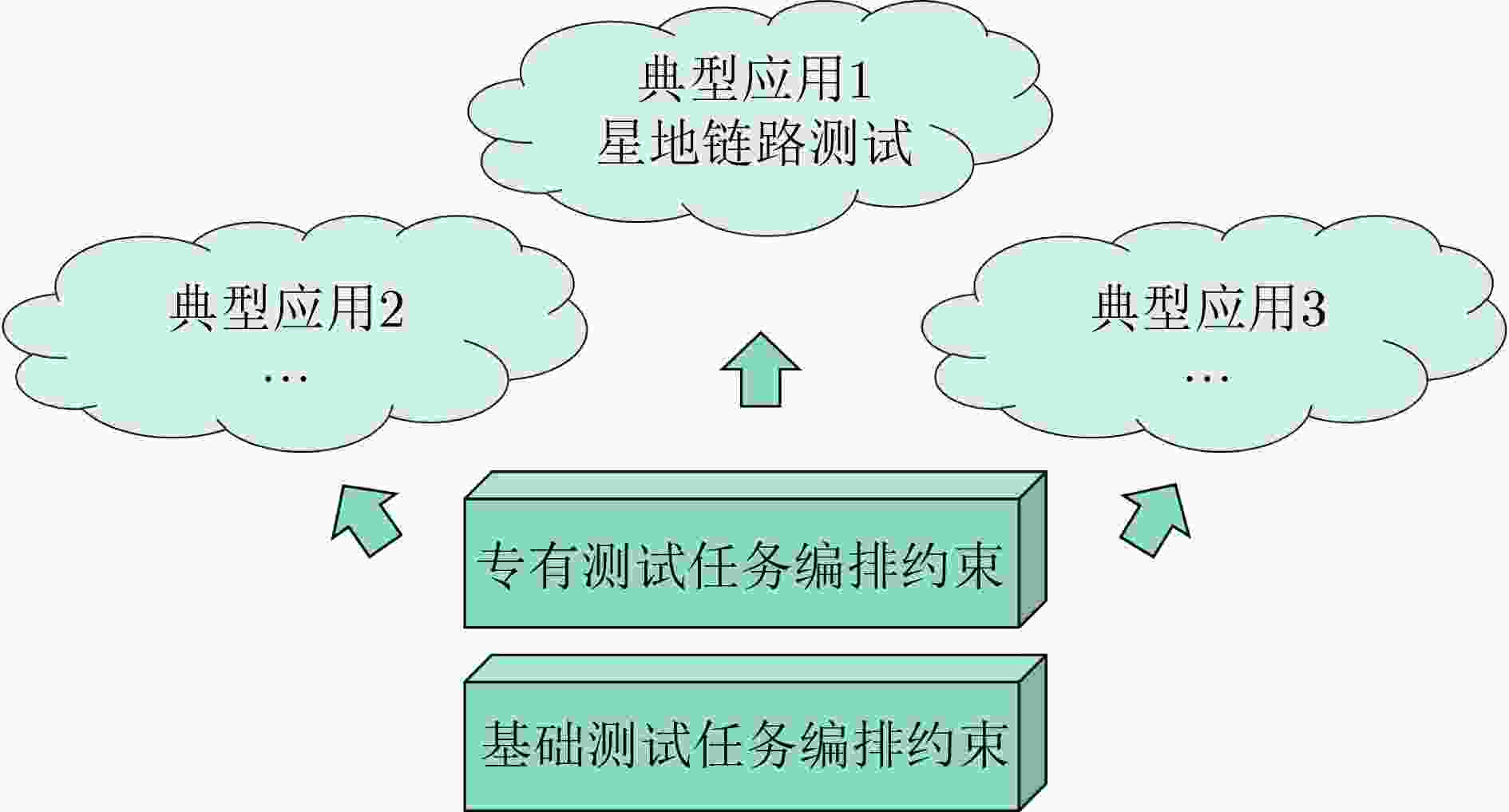


 下载:
下载:
