AutoPenGPT: Drift-Resistant Penetration Testing Driven by Search-Space Convergence and Dependency Modeling
-
摘要: 随着工业互联网的发展,Web管理平台与工业路由器等边界组件被广泛配置为可达生产内网,显著扩大了工业控制系统的攻击面。针对这一风险,渗透测试已成为保障工控系统安全的重要手段。近年来,部分研究尝试引入大语言模型(LLMs)以实现智能化渗透测试,进而降低人力消耗。然而,工控安全测试任务空间庞大且利用链条复杂,同时测试过程容错空间有限、语义约束严格,现有系统在此类场景下易出现“策略漂移”和“意图漂移”问题,导致无法有效完成测试任务。为此,该文提出了一种智能化 Web 漏洞测试与利用系统 AutoPenGPT。该系统通过引入与测试目标一致的上下文约束,引导LLMs收敛测试空间,以缓解复杂任务场景下的策略漂移问题;同时,AutoPenGPT 基于语义分析从反馈数据中提取并组织关键信息,对多步骤漏洞利用过程进行依赖建模,从而降低意图漂移对测试连贯性的影响。针对工控系统测试任务参数复杂且上下文动态变化的特点,系统进一步设计了高灵活性的半结构化提示词框架,以支持不同测试场景下的语义对齐与任务适配,最终实现与用户需求一致的自动化漏洞检测与利用。实验结果显示,AutoPenGPT在CTF测试集中漏洞类型探测准确率达97.62%,需求完成率为80.95%;在多个工控、通用Web平台的脆弱性测试中达到约70%的需求完成率,并成功发现7个未披露漏洞,其中已有两个漏洞获得CVE和CNVD编号,验证了其在真实场景下的实用性。Abstract:
Objective Industrial Control Systems (ICS) are widely deployed in critical sectors and often contain long-standing vulnerabilities due to strict availability requirements and limited patching opportunities. The increasing exposure of external management and access infrastructure has expanded the attack surface and allows adversaries to pivot from boundary components into fragile production networks. Continuous penetration testing of these components is essential but remains costly and difficult to scale when carried out manually. Recent work examines Large Language Models (LLMs) for automated penetration testing; however, existing systems often experience strategy drift and intention drift, which produce incoherent testing behaviors and ineffective exploitation chains. Methods This study proposes AutoPenGPT, a multi-agent framework for automated Web security testing. AutoPenGPT uses an adaptive exploration-space convergence mechanism that predicts likely vulnerability types from target semantics and constrains LLM-driven testing through a dynamically updated payload knowledge base. To reduce intention drift in multi-step exploitation, a dependency-driven strategy module rewrites historical feedback, models step dependencies, and generates coherent, executable strategies in a closed-loop workflow. A semi-structured prompt embedding scheme is also developed to support heterogeneous penetration testing tasks while preserving semantic integrity. Results and Discussions AutoPenGPT is evaluated on Capture-the-Flag (CTF) benchmarks and real-world ICS and Web platforms. On CTF datasets, it achieves 97.62% vulnerability-type detection accuracy and an 80.95% requirement completion rate, exceeding state-of-the-art tools by a wide margin. In real-world deployments, it reaches approximately 70% requirement completion and identifies six previously undisclosed vulnerabilities, demonstrating practical effectiveness. Conclusions The contributions are threefold. (1) Strategy drift and intention drift in LLM-driven penetration testing are examined and addressed through adaptive exploration and dependency-aware strategy mechanisms that stabilize long-horizon testing behaviors. (2) AutoPenGPT is designed and implemented as a multi-agent penetration testing system that integrates semantic vulnerability prediction, closed-loop strategy generation, and semi-structured prompt embedding. (3) Extensive evaluation on CTF and real-world ICS and Web platforms confirms the effectiveness and practicality of the system, including the discovery of previously unknown vulnerabilities. -
表 1 各方法在不同模型下的CTF测试集漏洞探测能力(%)
模型 方法 注入 权限 文件处理 信息泄露 全部类型 VTP VTD RCR VTP VTD RCR VTP VTD RCR VTP VTD RCR VTP VTD RCR DV-3 ① 100.0 100.0 76.5 100.0 90.0 70.0 80.0 100.0 91.7 50.0 100.0 100.0 90.0 97.6 81.0 ② 100.0 94.1 23.5 60.00 40.0 20.0 80.0 100.0 33.3 50.0 100.0 0.0 80.0 83.3 23.8 ③ 100.0 94.1 17.7 100.0 90.0 40.0 80.0 83.3 25.0 50.0 66.7 33.3 90.0 88.1 26.2 ④ 28.6 11.8 - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4o-m ① 100.0 88.2 41.2 100.0 90.0 50.0 80.0 100.0 58.3 25.0 66.7 33.3 85.0 90.5 47.6 ② 100.0 88.2 11.8 100.0 40.0 20.0 80.0 100.0 25.0 25.0 66.7 66.7 85.0 78.6 21.4 ③ 85.7 82.4 5.9 40.0 20.0 0.0 80.0 75.0 0.0 25.0 33.3 0.0 65.0 61.9 2.4 ④ 28.6 11.8 - - - - - - - - - - - - - 注:其中①代表AutoPenGPT、②代表PentestGPT③代表VulnBot、④代表YuraScan。DV-3代表DeepSeek-V3、4o-m代表GPT-4o-mini。 表 2 消融实验结果(%)
模型 方法 整体性能 VTP VTD RCR DeepSeek-V3 Variant-1 75.00 76.19 71.43 Variant-2 90.00 92.86 64.29 Variant-3 80.00 83.33 66.67 AutoPenGPT 90.00 97.62 80.95 GPT-4o-mini Variant-1 50.00 59.52 42.86 Variant-2 70.00 83.33 38.10 Variant-3 60.00 78.57 40.48 AutoPenGPT 85.00 90.48 47.62 表 3 平台脆弱性探测-已知漏洞的测试与利用(%)
CVE编号 无外部知识库信息 有外部知识库信息 AutoPenGPT VulnBot AutoPenGPT VulnBot VTD RCR VTD RCR VTD RCR VTD RCR CVE-2021- 44228 √ × √ × √ √ √ √ CVE-2024- 36401 × × × × √ √ × × CVE-2025- 8127 × × × × √ √ √ × CVE-2024- 39722 × × × × √ √ √ × CVE-2021- 43798 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ CVE-2024- 23897 √ √ √ × √ √ √ √ CVE-2017- 16720 × × × × × × × × CVE-2020- 10644 √ √ √ × √ √ √ × CVE-2022- 30694 √ × √ × √ × √ × CVE-2021- 42013 √ × √ × √ × √ × 整体准确率 60.00 30.00 60.00 10.00 90.00 70.00 80.00 30.00 表 4 平台脆弱性探测-未知漏洞的挖掘
系统名称 AutoPenGPT VulnBot PentestGPT YuraScanner Moodle 文件上传 \ \ XSS XSS \ \ \ Tpshop SQL注入 SQL注入 SQL注入 \ SQL注入 SQL注入 SQL注入 \ EmlogCMS XSS \ \ XSS SURF CNVD-2025- 28965 \ \ \ WS7204 CVE-2025- 9424 \ \ \ 总共挖掘数量 7 2 2 2 -
[1] PAN Xiaojun, WANG Zhuoran, and SUN Yanbin. Review of PLC security issues in industrial control system[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2020, 2(2): 69–83. doi: 10.32604/jcs.2020.010045. [2] ASLAM M M, TUFAIL A, APONG R A A H M, et al. Scrutinizing security in industrial control systems: An architectural vulnerabilities and communication network perspective[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 67537–67573. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3394848. [3] LIU Chenyang, ALROWAILI Y, SAXENA N, et al. Cyber risks to critical smart grid assets of industrial control systems[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(17): 5501. doi: 10.3390/en14175501. [4] KASNECI E, SESSLER K, KÜCHEMANN S, et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education[J]. Learning and Individual Differences, 2023, 103: 102274. doi: 10.1016/j.lindif.2023.102274. [5] GE Yingqiang, HUA Wenyue, MEI Kai, et al. OpenAGI: When LLM meets domain experts[C]. The 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2023: 242. [6] DENG Gelei, LIU Yang, MAYORAL-VILCHES V, et al. PENTESTGPT: Evaluating and harnessing large language models for automated penetration testing[C]. The 33rd USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Philadelphia, USA, 2024: 48. [7] KONG He, HU Die, GE Jingguo, et al. VulnBot: Autonomous penetration testing for a multi-agent collaborative framework[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2501.13411, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2501.13411. (查阅网上资料,不确定本文献类型是否正确,请确认). [8] ZHUO Jingming, ZHANG Songyang, FANG Xinyu, et al. ProSA: Assessing and understanding the prompt sensitivity of LLMs[C]. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024, Miami, USA, 2024: 1950–1976. doi: 10.18653/v1/2024.findings-emnlp.108. [9] CLAROTY. Getting from 5 to 0 - VPN security flaws pose cyber risk to organizations with remote OT personnel[EB/OL]. https://www.globalsecuritymag.com/Getting-from-5-to-0-VPN-Security,20200729,101254.html, 2020. [10] Censys Research Team. Over 145, 000 exposed ICS services worldwide[EB/OL]. https://industrialcyber.co/industrial-cyber-attacks/censys-data-reports-over-145000-exposed-ics-services-worldwide-highlights-us-vulnerabilities, 2024. (查阅网上资料,未找到本条文献信息,请确认). [11] CLAROTY. OT operators slow to update vulnerable Secomea remote access devices[EB/OL]. https://claroty.com/team82/research/ot-operators-slow-to-update-vulnerable-secomea-remote-access-devices, 2020. [12] Acunetix. Acunetix web vulnerability scanner overview[EB/OL]. https://www.acunetix.com/support/docs/wvs/overview/, 2025. (查阅网上资料,未找到本条文献出版年信息,请确认). [13] OWASP. Zed attack proxy (ZAP)[EB/OL]. https://www.zaproxy.org/, 2025. (查阅网上资料,未找到本条文献作者和出版年信息,请确认). [14] JFrog. Xray. Software composition analysis (SCA) tool[EB/OL]. https://jfrog.com/xray/, 2025. (查阅网上资料,未找到本条文献信息,请确认). [15] Sqlmap. Automatic SQL injection and database takeover tool[EB/OL]. https://sqlmap.org/, 2025. [16] HUANG Dong, DAI Jianbo, WENG Han, et al. EffiLearner: Enhancing efficiency of generated code via self-optimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2405.15189, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2405.15189. (查阅网上资料,不确定本文献类型是否正确,请确认). [17] LIU Zihan, ZENG Ruinan, WANG Dongxia, et al. Agents4PLC: Automating closed-loop PLC code generation and verification in industrial control systems using LLM-based agents[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2410.14209, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2410.14209. (查阅网上资料,不确定本文献类型是否正确,请确认). [18] LIU Peiyu, LIU Junming, FU Lirong, et al. Exploring ChatGPT’s capabilities on vulnerability management[C]. The 33rd USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Philadelphia, USA, 2024: 46. [19] WANG Che, ZHANG Jiashuo, GAO Jianbo, et al. ContractTinker: LLM-empowered vulnerability repair for real-world smart contracts[C]. The 39th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, Sacramento, USA, 2024: 2350–2353. [20] LIU Zijun, ZHANG Yanzhe, LI Peng, et al. A dynamic LLM-powered agent network for task-oriented agent collaboration[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2310.02170, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2310.02170. (查阅网上资料,不确定本文献类型是否正确,请确认). [21] HAPPE A, KAPLAN A, and CITO J. LLMs as hackers: Autonomous Linux privilege escalation attacks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2310.11409, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2310.11409. (查阅网上资料,不确定本文献类型是否正确,请确认). [22] HUANG Junjie and ZHU Quanyan. PenHeal: A two-stage LLM framework for automated pentesting and optimal remediation[C]. The Workshop on Autonomous Cybersecurity, Salt Lake City, USA, 2024: 11–22. doi: 10.1145/3689933.3690831. [23] WEI J, WANG Xuezhi, SCHUURMANS D, et al. Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models[C]. Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 1800. [24] SAHOO P, SINGH A K, SAHA S, et al. A systematic survey of prompt engineering in large language models: Techniques and applications[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2402.07927, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2402.07927. (查阅网上资料,不确定本文献类型是否正确,请确认). [25] GIOACCHINI L, MELLIA M, DRAGO I, et al. AutoPenBench: Benchmarking generative agents for penetration testing[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2410.03225, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2410.03225. (查阅网上资料,不确定本文献类型是否正确,请确认). [26] STAFEEV A, RECKTENWALD T, DE STEFANO G, et al. YuraScanner: Leveraging LLMs for task-driven web app scanning[C]. The Network and Distributed System Security (NDSS) Symposium 2025, San Diego, USA, 2025: 11–22. [27] VAN DER MAATEN L and HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9: 2579–2605. [28] DEVLIN J, CHANG Mingwei, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1810.04805, 2018. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1810.04805. (查阅网上资料,不确定本文献类型是否正确,请确认). -





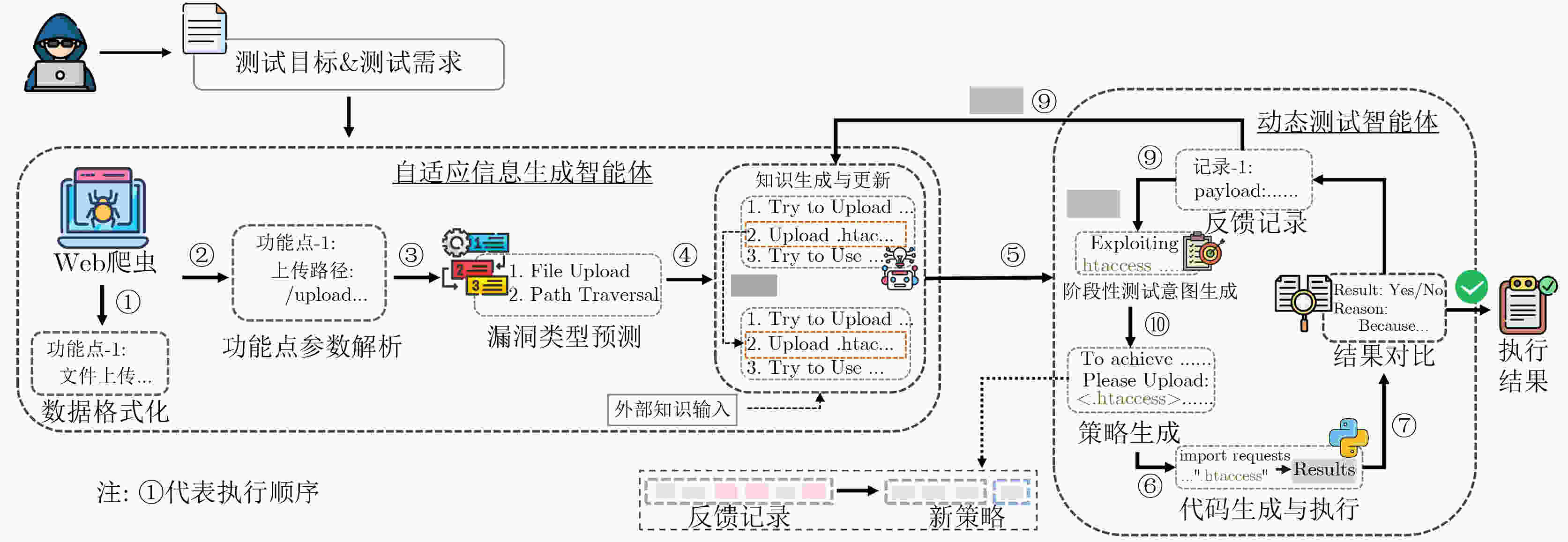
 下载:
下载:
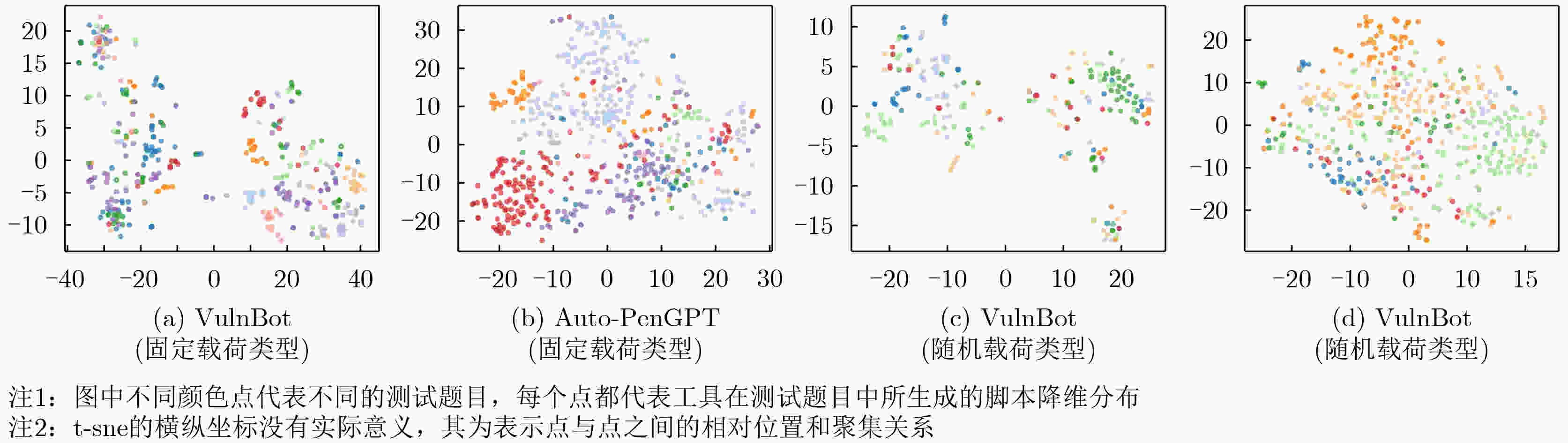
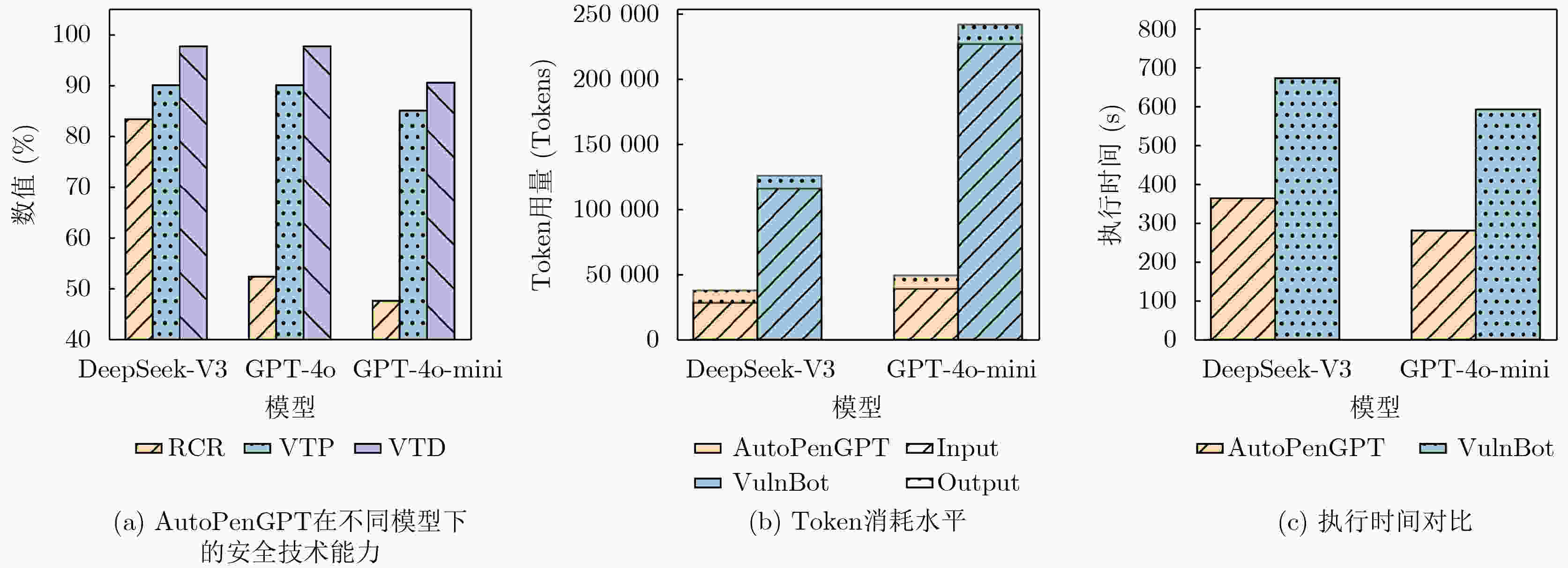


 下载:
下载:
