A Review of Compressed Sensing Technology for Efficient Receiving and Processing of Communication Signal
-
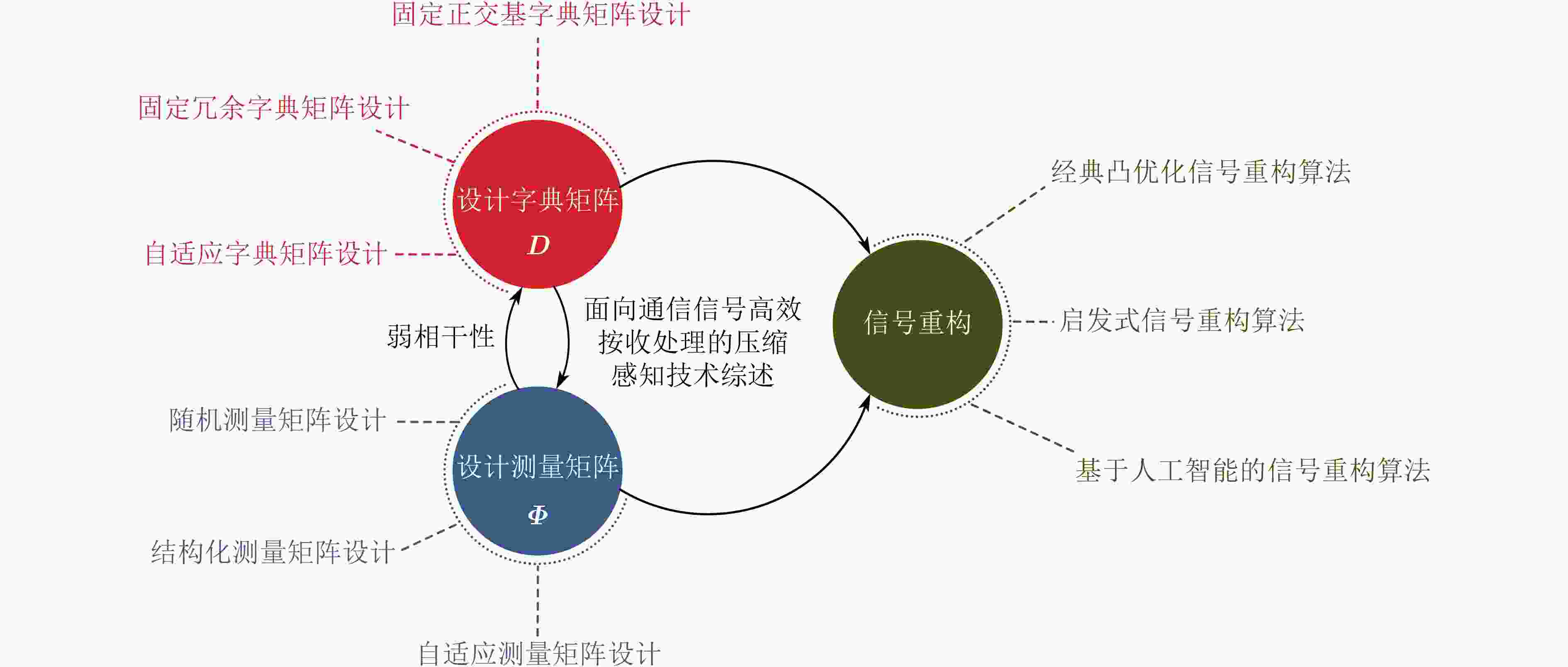
摘要: 压缩感知凭借其突破奈奎斯特采样定理限制、实现超低采样率的高质量信号处理与重构的优势,成为通信信号高效接收处理的研究热点。该文依据压缩感知原理,按照字典矩阵设计、测量矩阵设计和信号重构3个主要研究方向对技术发展脉络进行了梳理,提出了当前压缩感知技术研究面临的挑战。基于现阶段工程应用面临的问题,对压缩感知技术发展趋势进行展望。Abstract:
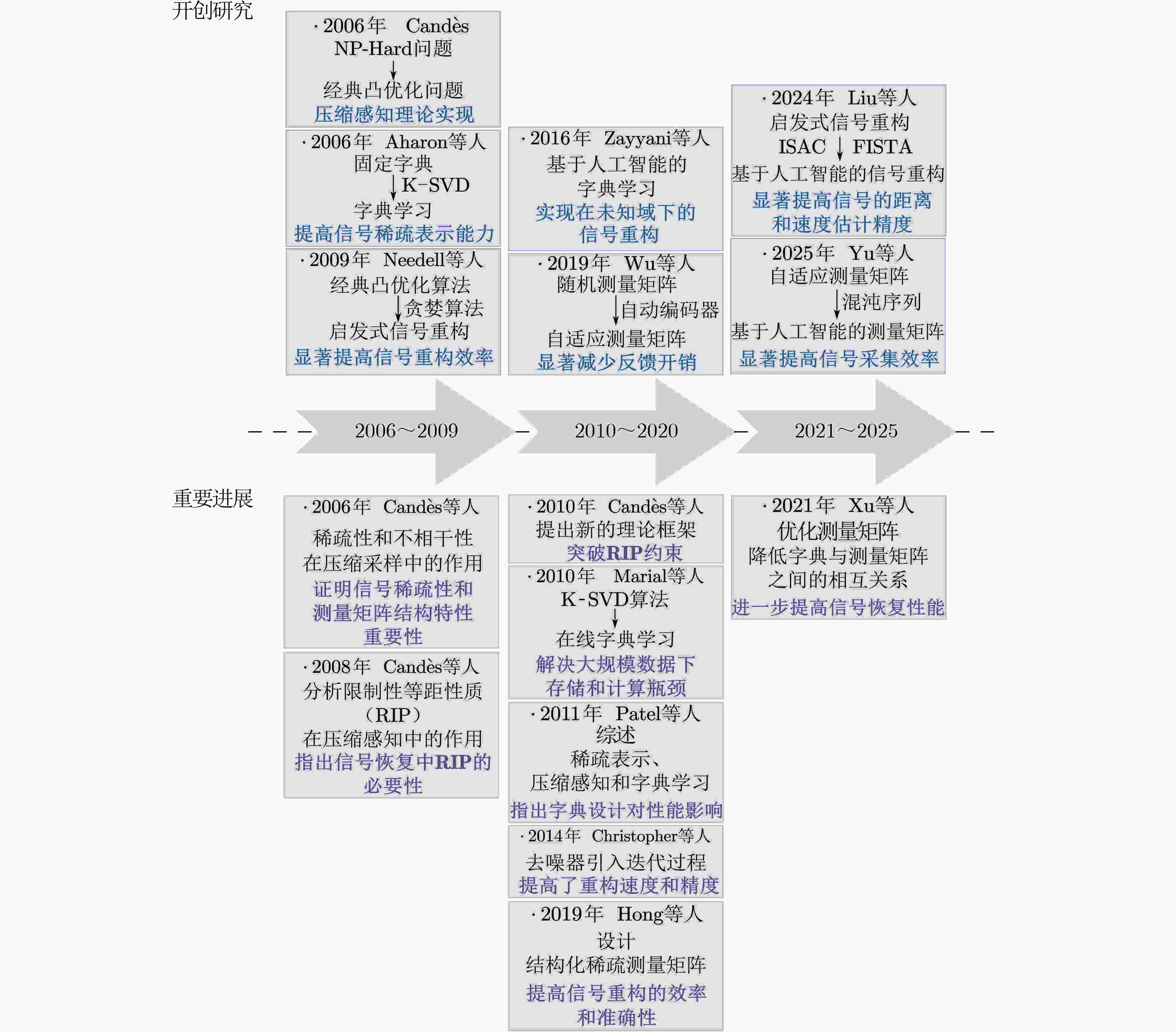
Significance (1)Lower data acquisition and storage costs: By exploiting signal sparsity and designing effective dictionary and measurement matrices, compressed sensing enables reconstruction below the Nyquist sampling rate, making it suitable for resource-constrained environments; (2)Smaller pilot overhead: With sparse prior information and optimized observation design, compressed sensing reduces pilot overhead compared with traditional schemes. This saving releases spectrum resources and improves transmission efficiency; (3)Higher signal processing efficiency: Compressed sensing enhances channel estimation performance by approximately 3$ \sim $5 dB under the same data volume and achieves linear computational complexity, which is markedly lower than that of conventional super-linear approaches. Progress Between 2006 and 2009, compressed sensing progressed rapidly. Candès established the theoretical basis by converting zero-norm sparsity into a convex one-norm formulation under the Restricted Isometry Property (RIP). Aharon et al. then introduced dictionary matrices to strengthen sparse representation, and Needell et al. applied greedy algorithms to speed up reconstruction. From 2010 to 2020, research shifted toward engineering application and algorithm refinement. Wu et al. proposed more robust recovery strategies to improve adaptability, and Zayyani et al. later advanced AI-based dictionary learning. Since 2020, compressed sensing has integrated with deep learning for data-driven sparse modelling and reconstruction. Liu’s work in Integrated Sensing-And-Communication (ISAC) systems demonstrates this trend and supports deployment in next-generation communication networks. Conclusion This paper reviews compressed sensing for efficient receiving and processing of communication signal across three dimensions: current progress, key technical challenges, and future directions. It highlights three main research pathways, including dictionary matrix design, measurement matrix development, and reconstruction strategies. The review also shows that compressed sensing is moving toward greater adaptiveness, lightweight design, and intelligence. Current challenges are also summarized, including high computational cost, limited adaptability, and reduced performance under non-ideal conditions. These observations provide guidance for further study. Prospects (1)Research on relaxed sparse condition: Existing sparsity assumptions remain strict and constrain the use of compressed sensing in high-dimensional or non-stationary scenarios where ideal sparse representations are difficult to obtain. Loosening sparse requirements is therefore essential. Present work explores adaptive dictionary learning, structured sparse priors, and neural-network-driven relaxation, yet issues persist, such as dependence on prior assumptions, insufficient interpretability, and lack of theoretical convergence. Future work may refine optimization objectives, develop neural models with clear mathematical interpretation, and establish sparse representation methods that do not rely on rigid sparsity priors. (2)Research on algorithm complexity: Further complexity reduction is required in non-stationary time-varying channels, high-dimensional processing, and long-sequence reconstruction. Promising directions include pre-trained dictionary models, deep-learning-based structured measurement matrices, and robust deep reconstruction networks. (3)Research on algorithm adaptability: Practical systems face noise, spectrum fragmentation, fading, and multipath propagation, with stronger effects in cognitive radio and integrated sensing applications. Adaptive strategies should therefore be prioritized. Possible solutions include dynamic sliding-window modelling or optimized regularization for adaptive dictionaries, structured measurement matrices with tunable parameters, and semi-supervised reconstruction algorithms. (4)Research on non-cooperative user detection: Spectrum scarcity heightens the need for efficient sensing to manage uncoordinated users and prevent high-frequency occupancy. Future research may integrate deep learning with statistical models or embed time-frequency information in online dictionary learning to enhance generalization. Multi-objective design of adaptive measurement matrices may further support reliable detection of non-cooperative users. -
Key words:
- Compressed sensing /
- Dictionary learning /
- Measurement matrix /
- Signal reconstruction
-
表 1 文献涉及符号阐释表
符号 解释 ${\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} $ 测量矩阵 X 目标原始信号 x 目标原始信号样本 Y 接收端测得的测量数据 y 接收端测得的测量数据样本 P 样本数 N 目标原始信号长度 M 测量数据长度 D 字典矩阵 A 目标原始信号X对应的稀疏向量 a 每一目标原始信号样本x对应的稀疏向量 K 字典原子数 s 稀疏度 $ {\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} $ $ {\boldsymbol{\varTheta}} = {\boldsymbol{\varPhi}}{\boldsymbol{D}} $感知矩阵 λ 正则化参数 i, j 矩阵索引号 表 2 主流固定字典类型及特性表述
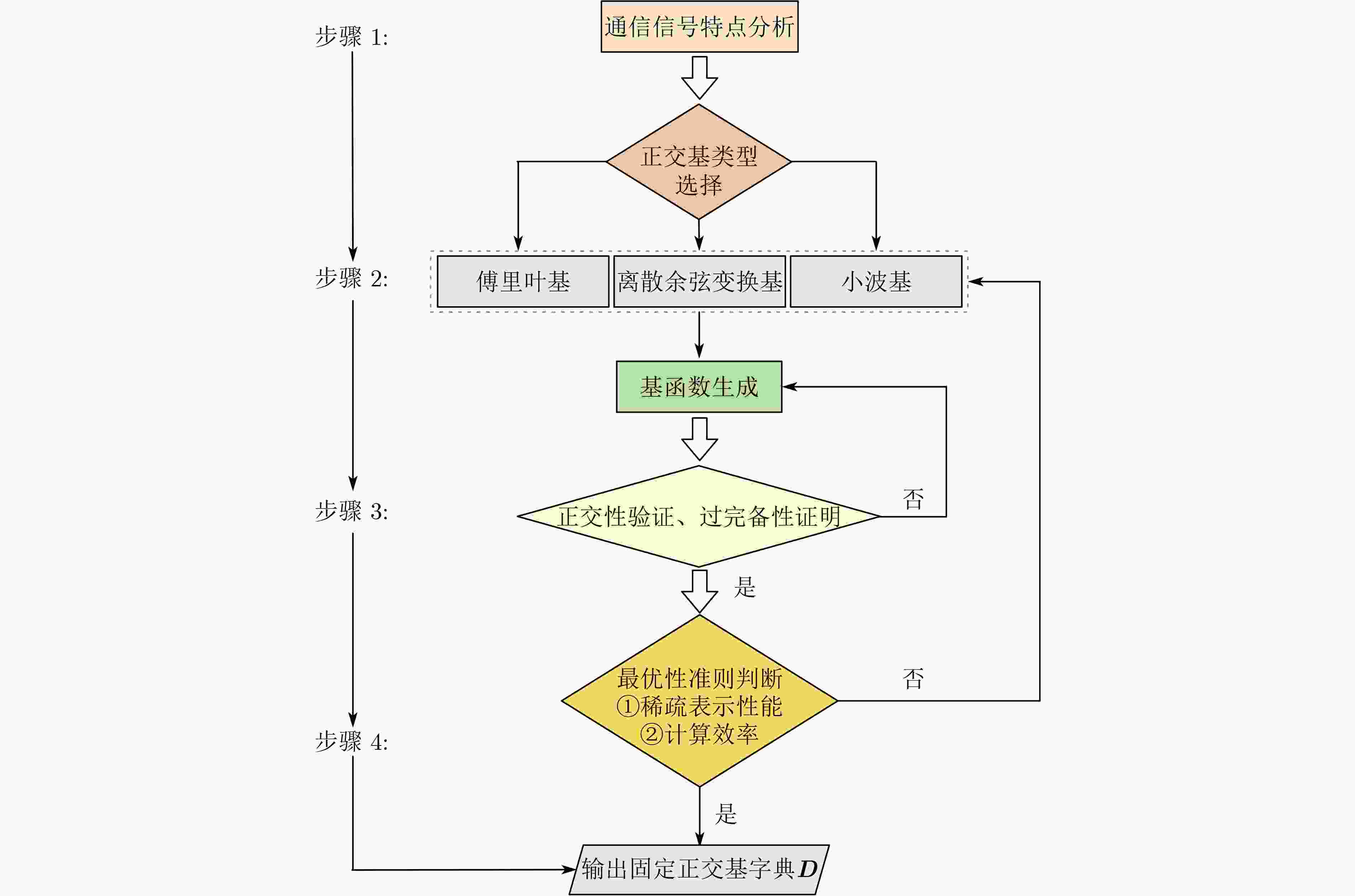
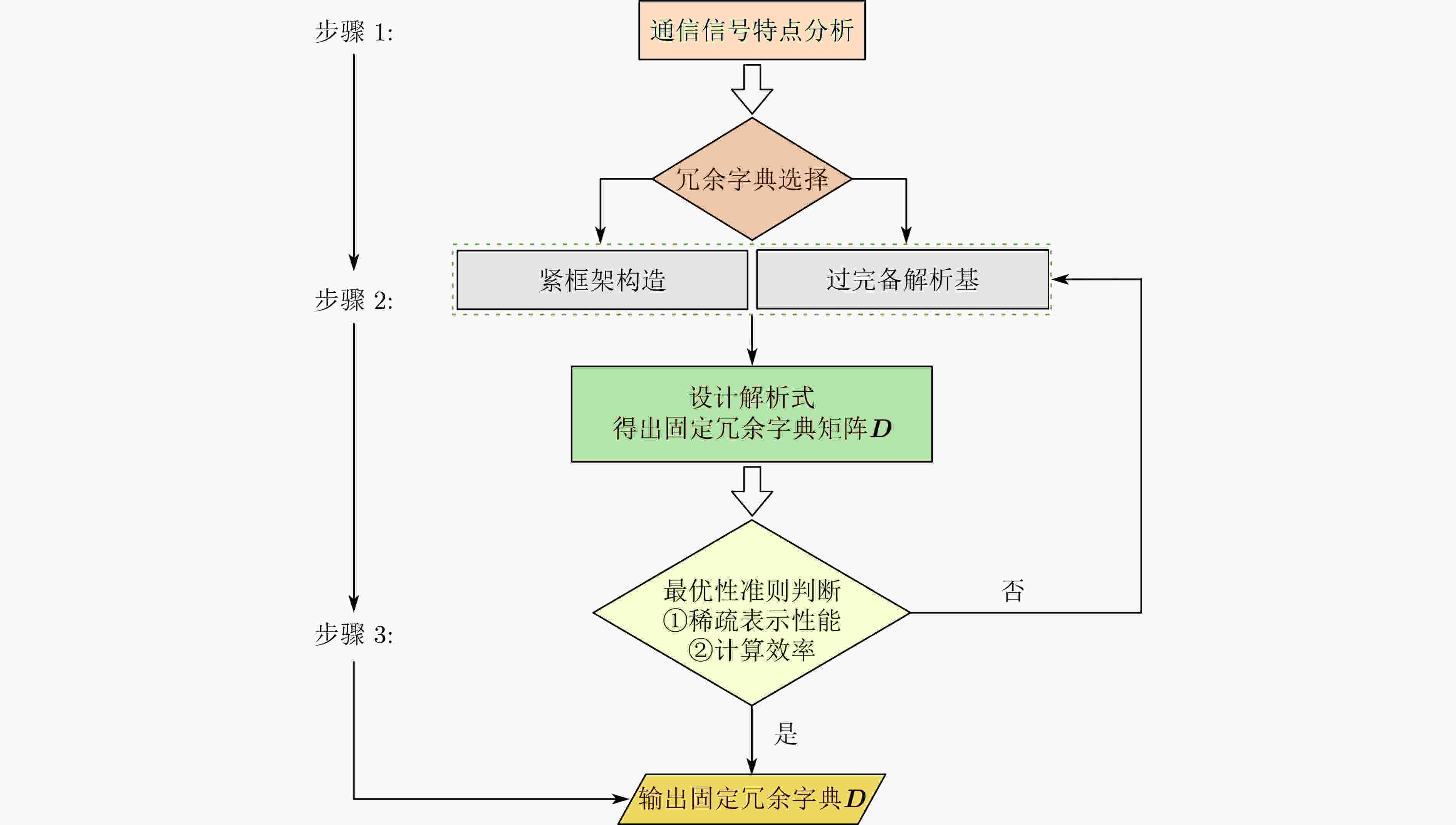
字典类型 表述 傅里叶基 由正弦和余弦函数组成,适用于平稳信号 离散余弦变换基 傅里叶基的实数对称形式,
适用于具有平滑区域的信号小波基 通过母小波的缩放和平移生成,适用于非平稳信号 表 3 不同测量矩阵的计算复杂度与应用场景说明
测量矩阵类型 计算复杂度 应用场景 随机测量矩阵 O(MN) 适用于对信号先验信息了解较少,且计算资源相对充足的场景 结构化测量矩阵 O(N)~O(N2) 对于计算资源有限制,且信号稀疏结构有一定的预测性场景中应用广泛 自适应测量矩阵 >O(N2) 信号特征复杂多变时,对重构精度要求高的场景中表现出色 -
[1] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582. [2] CANDÈS E J. Compressive sampling[C]. The International Congress of Mathematicians, Madrid, Spain, 2006, 3: 1433–1452. doi: 10.4171/022-3/69. [3] LAURANO C, TOSCANI S, PEGORARO P A, et al. Compressive sensing-based pruning of frequency-domain Volterra models[C]. 2025 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Chemnitz, Germany, 2025: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/I2MTC62753.2025.11079214. [4] BOUFOUNOS P T and BARANIUK R G. 1-Bit compressive sensing[C]. IEEE 42nd Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems, Princeton, USA, 2008: 16–21. doi: 10.1109/CISS.2008.4558487. [5] AHARON M, ELAD M, and BRUCKSTEIN A. K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4311–4322. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881199. [6] NEEDELL D and TROPP J A. CoSaMP: Iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2009, 26(3): 301–321. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2008.07.002. [7] WU Pengxia, LIU Zichuan, and CHENG Julian. Compressed CSI feedback with learned measurement matrix for mmWave massive MIMO[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.02127, 2019. [8] ZAYYANI H, KORKI M, and MARVASTI F. Dictionary learning for blind one bit compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(2): 187–191. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2503804. [9] YU Huimin and ZHANG Xuanwei. Compressed sensing measurement matrix construction method based on uniform chaotic sequence and matrix factorization[J]. Measurement, 2025, 242: 115913. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.115913. [10] LIU Haotian, WEI Zhiqing, LI Fengyun, et al. Integrated sensing and communication signal processing based on compressed sensing over unlicensed spectrum bands[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2024, 10(5): 1801–1816. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2024.3391307. [11] CANDÈS E J. The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing[J]. Comptes Rendus. Mathématique, 2008, 346(9/10): 589–592. doi: 10.1016/j.crma.2008.03.014. [12] CANDÈS E J and PLAN Y. A probabilistic and RIPless theory of compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2011, 57(11): 7235–7254. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2011.2161794. [13] KRAHMER F, NEEDELL D, and WARD R. Compressive sensing with redundant dictionaries and structured measurements[J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 2015, 47(6): 4606–4629. doi: 10.1137/151005245. [14] MAIRAL J, BACH F, PONCE J, et al. Online dictionary learning for sparse coding[C]. The 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, Montreal, Canada, 2009: 689–696. doi: 10.1145/1553374.1553463. [15] HUANG Yuang, MENG Xuedong, ZHANG Shuang, et al. Adaptive detection of frequency-hopping spread spectrum signals based on compressed measurements and artificial neural networks[C]. 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 2021: 271–277. doi: 10.1109/IAEAC50856.2021.9390887. [16] PAN Lu, MARCELLIN M W, RYAN W E, et al. Viterbi detection for compressively sampled FHSS-GFSK signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(22): 5965–5975. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2461518. [17] HUANG Sai, CHAI Yuqing, YING Shanchuan, et al. Compressed sensing-based genetic Markov localization for mobile transmitters[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(1): 56. doi: 10.3390/drones7010056. [18] TIBSHIRANI R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 1996, 58(1): 267–288. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1996.tb02080.x. [19] XU Jianping, PI Yiming, and CAO Zongjie. Optimized projection matrix for compressive sensing[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2010, 2010(1): 560349. doi: 10.1155/2010/560349. [20] XU Qiangrong, SHENG Zhichao, FANG Yong, et al. Measurement matrix optimization for compressed sensing system with constructed dictionary via Takenaka-Malmquist functions[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(4): 1229. doi: 10.3390/s21041229. [21] ZHANG Yidong, YANG Wenge, and CHENG Yanhe. Sparsity analysis of FH-BPSK signals via K-SVD dictionary learning[C]. 2016 First IEEE International Conference on Computer Communication and the Internet (ICCCI), Wuhan, China, 2016: 310–315. doi: 10.1109/CCI.2016.7778932. [22] WU Jun, LIU Naian, ZHANG Yanfei, et al. Blind detection of frequency hopping signal based on compressive sensing[C]. 2012 2nd International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Communications and Networks (CECNet), Yichang, China, 2012: 1691–1694. doi: 10.1109/CECNet.2012.6201767. [23] WANG Huabei, WANG Lizheng, WANG Zhichao, et al. Deep learning based channel estimation for massive MIMO: A sparsity adaptive compressive sensing method and FPGA implementation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2025. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2025.3586863. [24] JEON Y S, AMIRI M M, LI Jun, et al. A compressive sensing approach for federated learning over massive MIMO communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(3): 1990–2004. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3038407. [25] LIU Shengheng, ZHANG Y D, SHAN Tao, et al. Structure-aware Bayesian compressive sensing for frequency-hopping spectrum estimation with missing observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(8): 2153–2166. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2806351. [26] LIU Feng, KIM Y, GOODMAN N A, et al. Compressive sensing of frequency-hopping spread spectrum signals[C]. SPIE 8365, Compressive Sensing, Baltimore, USA, 2012: 168–174. doi: 10.1117/12.919561. [27] RAUHUT H. Compressive sensing and structured random matrices[M]. FORNASIER M. Theoretical Foundations and Numerical Methods for Sparse Recovery. Berlin: de Gruyter, 2010: 1–92. doi: 10.1515/9783110226157.1. [28] OSEI-WUSU F, AHENE E, and MUNTAKA S A. An enhanced subsampling technique in compressive sensing using linear interpolation and random measurement matrix[J]. 2024. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4117361/v1. [29] LEBLANC O, WIAUX Y, and JACQUES L. Compressive radio-interferometric sensing with random beamforming as rank-one signal covariance projections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2025, 11: 1229–1242. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2025.3587449. [30] WANG Chao and SONG Ling. An image encryption scheme based on chaotic system and compressed sensing for multiple application scenarios[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 642: 119166. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2023.119166. [31] MESNARD P, ENDERLI C, and LECUÉ G. Periodic patterns frequency hopping waveforms: From conventional matched filtering to an improved compressed sensing approach[C]. 2018 19th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Bonn, Germany, 2018: 1–10. doi: 10.23919/IRS.2018.8448046. [32] CORMODE G and MUTHUKRISHNAN S. Combinatorial algorithms for compressed sensing[C]. 13th International Colloquium on Structural Information and Communication Complexity, Chester, UK, 2006: 280–294. doi: 10.1007/11780823_22. [33] WANG J H, WU J M, and CHENNAKESAVULA P. Attenuated-RMMP: A compressed sensing estimation over OTFS modulation for high Doppler shift communications[C]. 2024 33rd Wireless and Optical Communications Conference (WOCC), Hsinchu, China, 2024: 70–74. doi: 10.1109/WOCC61718.2024.10786084. [34] ARIF M H, DAWOD F S, NEGRA R, et al. Direction of arrival estimation using compressive sensing and green's function interpretation for a frequency-diverse metasurface[C]. 2025 14th International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies (MOCAST), Dresden, Germany, 2025: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/MOCAST65744.2025.11083936. [35] HONG Tao, LI Xiao, ZHU Zhihui, et al. Optimized structured sparse sensing matrices for compressive sensing[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 159: 119–129. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.02.004. [36] WANG Xingyuan, LIU Cheng, and JIANG Donghua. A novel triple-image encryption and hiding algorithm based on chaos, compressive sensing and 3D DCT[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 574: 505–527. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.06.032. [37] CHAI Xiuli, WU Haiyang, GAN Zhihua, et al. An efficient visually meaningful image compression and encryption scheme based on compressive sensing and dynamic LSB embedding[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 124: 105837. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.105837. [38] YE Guodong, PAN Chen, DONG Youxia, et al. Image encryption and hiding algorithm based on compressive sensing and random numbers insertion[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 172: 107563. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107563. [39] JIANG Donghua, LIU Lidong, ZHU Liya, et al. Adaptive embedding: A novel meaningful image encryption scheme based on parallel compressive sensing and slant transform[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 188: 108220. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2021.108220. [40] MAZAIDEH M A and LEVENDOVSZKY J. A multi-hop routing algorithm for WSNs based on compressive sensing and multiple objective genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Communications and Networks, 2021, 23(2): 138–147. doi: 10.23919/JCN.2021.000003. [41] SHEN Liyue, PAULY J, and XING Lei. NeRP: Implicit neural representation learning with prior embedding for sparsely sampled image reconstruction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(1): 770–782. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3177134. [42] MATSUMOTO N and MAZUMDAR A. Binary iterative hard thresholding converges with optimal number of measurements for 1-bit compressed sensing[J]. Journal of the ACM, 2024, 71(5): 35. doi: 10.1145/3680542. [43] SONG Zihang, SHE Yiyuan, YANG Jian, et al. Nonuniform sampling pattern design for compressed spectrum sensing in mobile cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(9): 8680–8693. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3353591. [44] GUO Muran, LUO Kaixi, CHEN Hua, et al. Direction finding for compressed massive MIMO systems exploiting mixed circular and non-circular sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2025, 73: 4027–4042. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2025.3620259. [45] TAN Guoping, YUAN Hui, HU Hexuan, et al. A framework of decentralized federated learning with soft clustering and 1-bit compressed sensing for vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(13): 23617–23629. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3385913. [46] CANDÈS E J and TAO T. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(12): 5406–5425. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.885507. [47] RAUHUT H and WARD R. Sparse Legendre expansions via ℓ1-minimization[J]. Journal of Approximation Theory, 2012, 164(5): 517–533. doi: 10.1016/j.jat.2012.01.008. [48] TROPP J A. Just relax: Convex programming methods for identifying sparse signals in noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(3): 1030–1051. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2005.864420. [49] BACH F, JENATTON R, MAIRAL J, et al. Optimization with sparsity-inducing penalties[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2012, 4(1): 1–106. doi: 10.1561/2200000015. [50] METZLER C A, MALEKI A, and BARANIUK R G. From denoising to compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2016, 62(9): 5117–5144. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2556683. [51] BERTSIMAS D and JOHNSON N A G. Compressed sensing: A discrete optimization approach[J]. Machine Learning, 2024, 113(9): 6725–6764. doi: 10.1007/s10994-024-06577-0. [52] LI Dandan, WANG Songhua, LI Yong, et al. A convergence analysis of hybrid gradient projection algorithm for constrained nonlinear equations with applications in compressed sensing[J]. Numerical Algorithms, 2024, 95(3): 1325–1345. doi: 10.1007/s11075-023-01610-0. [53] TROPP J A. Greed is good: Algorithmic results for sparse approximation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2004, 50(10): 2231–2242. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2004.834793. [54] TROPP J A and GILBERT A C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655–4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108. [55] WANG Shuai, AN Jianping, REN Yanyang, et al. Compressed receiver for multipath DSSS signals[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(8): 1359–1362. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2332493. [56] KNILL C, SCHWEIZER B, SPARRER S, et al. High range and doppler resolution by application of compressed sensing using low baseband bandwidth OFDM radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2018, 66(7): 3535–3546. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2018.2830389. [57] DIAO Xinyu, SUN Zhongfeng, TANG Jingyong, et al. Accelerated over-relaxation heavy-ball hard thresholding pursuit for compressive sensing[J]. AIMS Mathematics, 2025, 10(8): 18603–18626. doi: 10.3934/math.2025831. [58] BERINDE R, GILBERT A C, INDYK P, et al. Combining geometry and combinatorics: A unified approach to sparse signal recovery[C]. 46th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Monticello, USA, 2008: 798–805. doi: 10.1109/ALLERTON.2008.4797639. [59] GILBERT A C, GUHA S, INDYK P, et al. Near-optimal sparse Fourier representations via sampling[C]. The 34th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Montreal, Canada, 2002: 152–161. doi: 10.1145/509907.509933. [60] WANG Mou, WEI Shunjun, SHI Jun, et al. CSR-Net: A novel complex-valued network for fast and precise 3-D microwave sparse reconstruction[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 4476–4492. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3014696. [61] CHEN Bin, ZHANG Xuanyu, LIU Shuai, et al. Self-supervised scalable deep compressed sensing[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2025, 133(2): 688–723. doi: 10.1007/s11263-024-02209-1. [62] JI Xingyu, CHENG Lei, and ZHAO Hangfang. Multipath time-delay estimation with impulsive noise via Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2023, 30: 937–941. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2023.3295750. [63] PATEL V M and CHELLAPPA R. Sparse representations, compressive sensing and dictionaries for pattern recognition[C]. The First Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 2011: 325–329. doi: 10.1109/ACPR.2011.6166711. -





 下载:
下载:
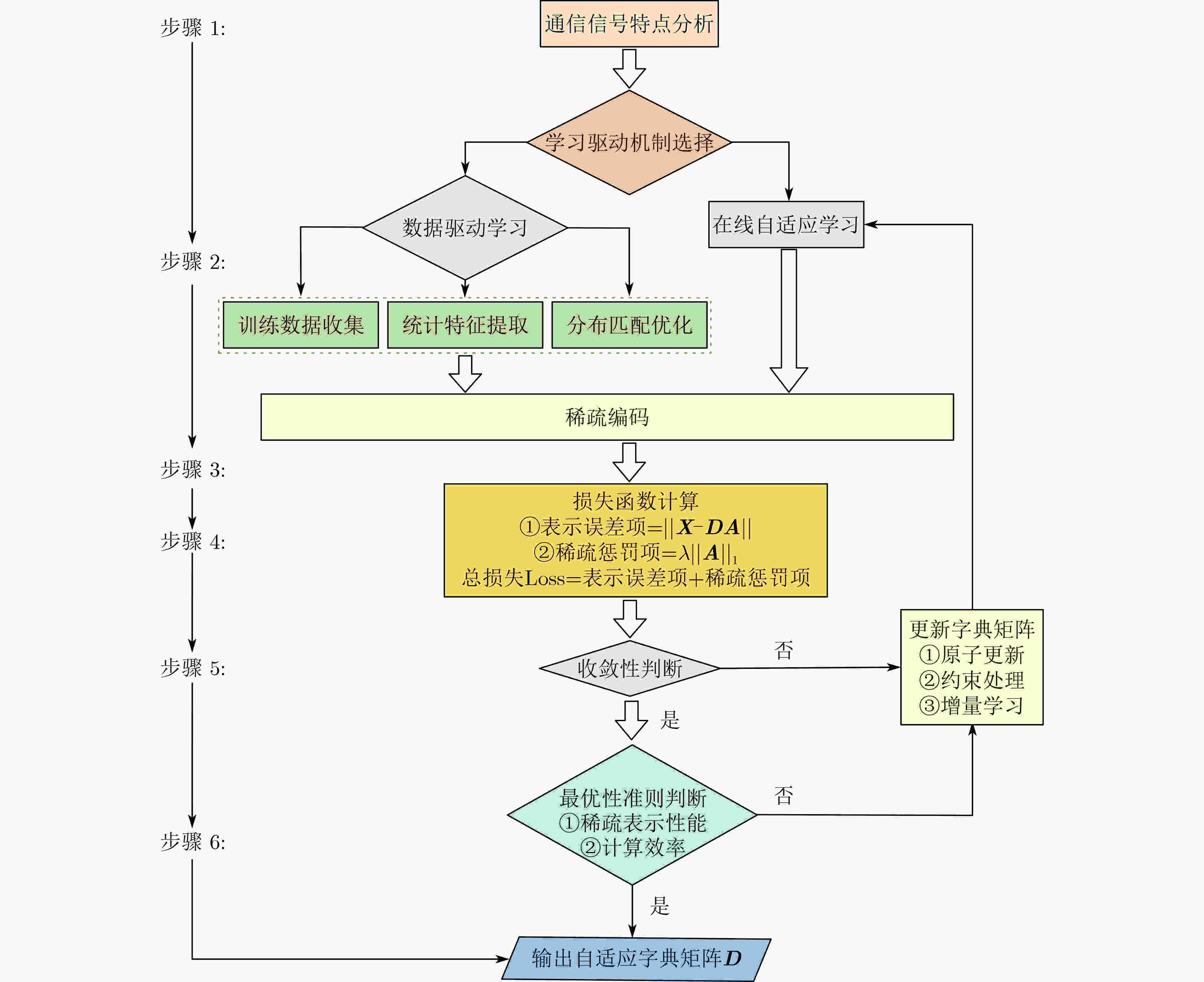
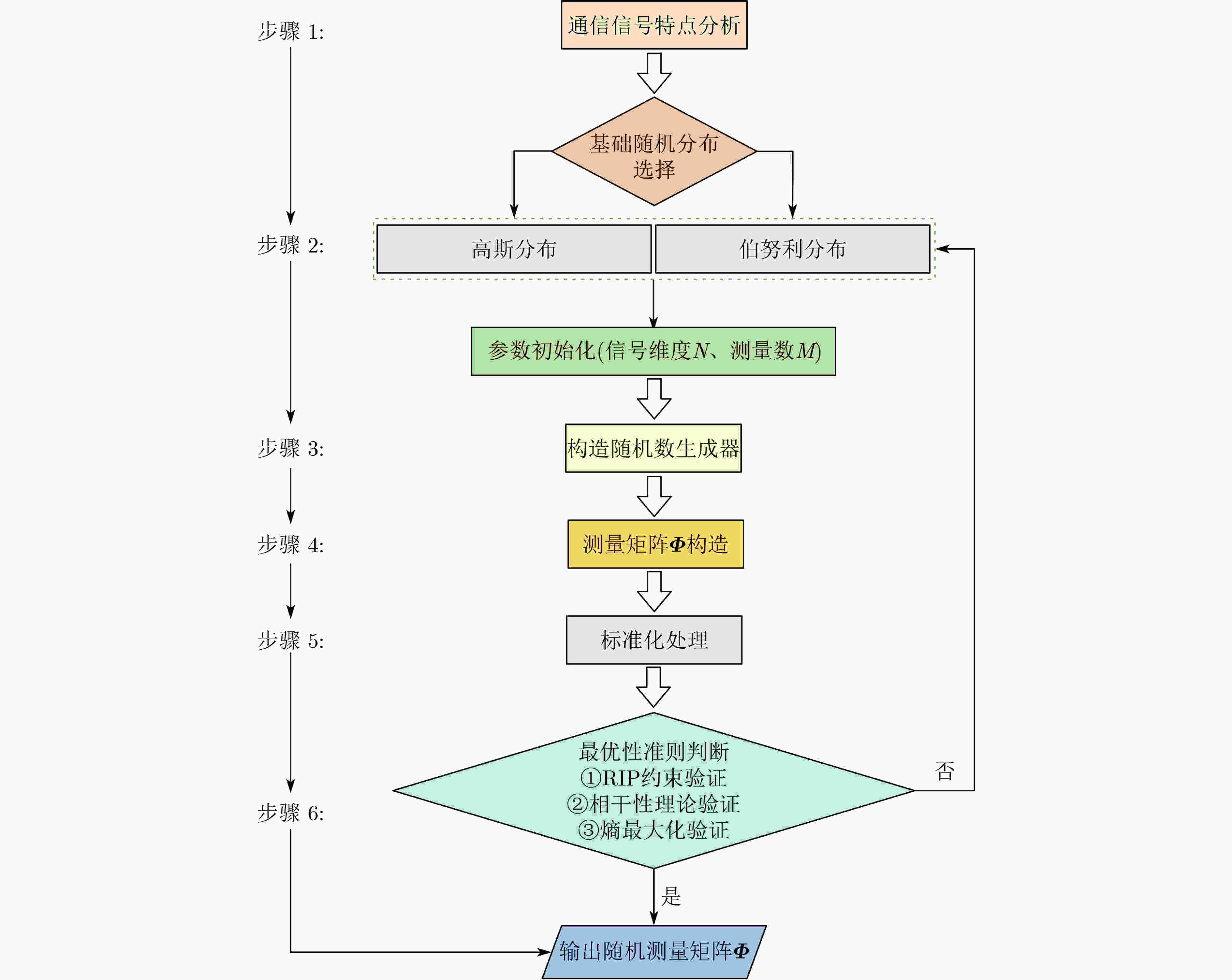
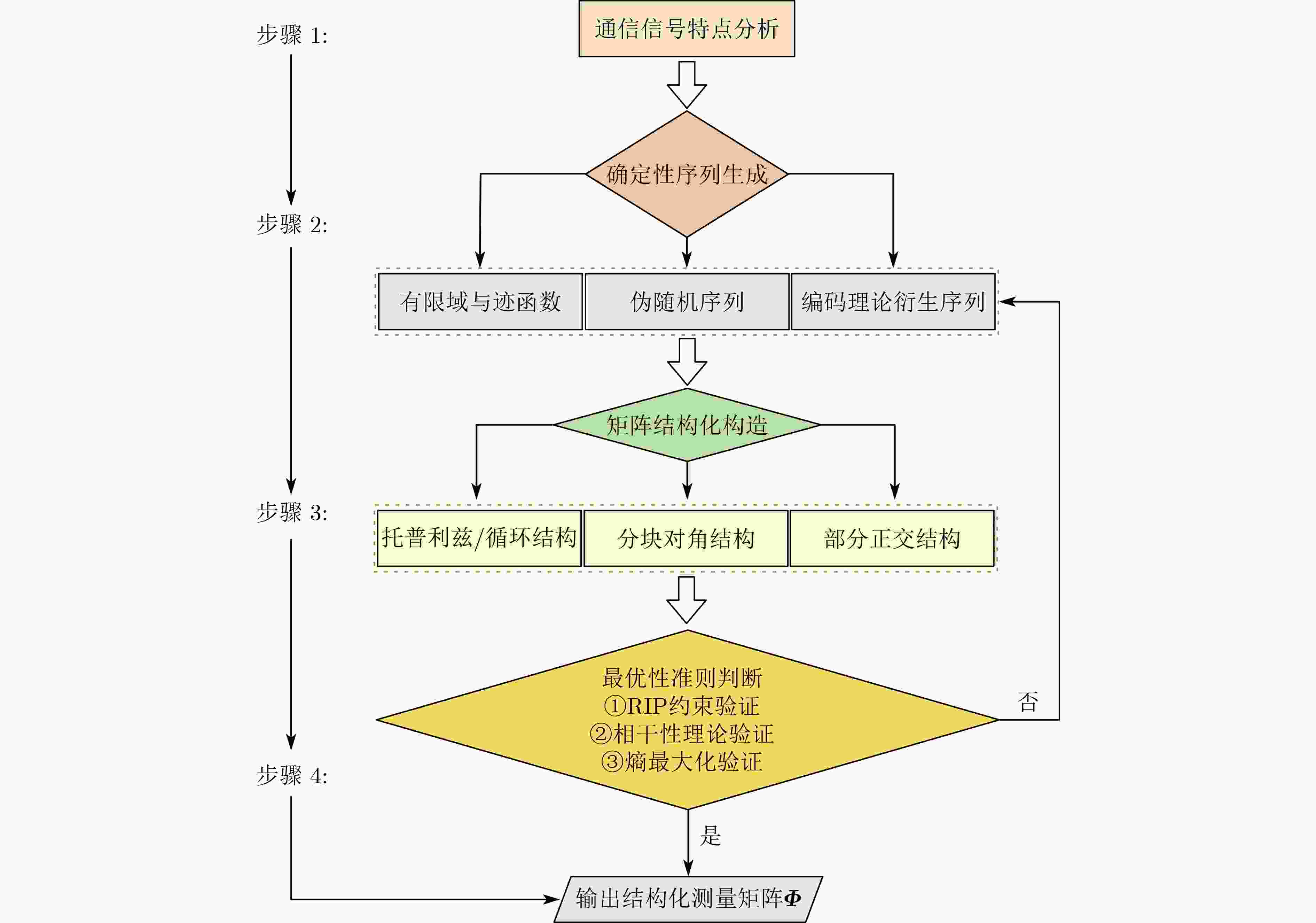
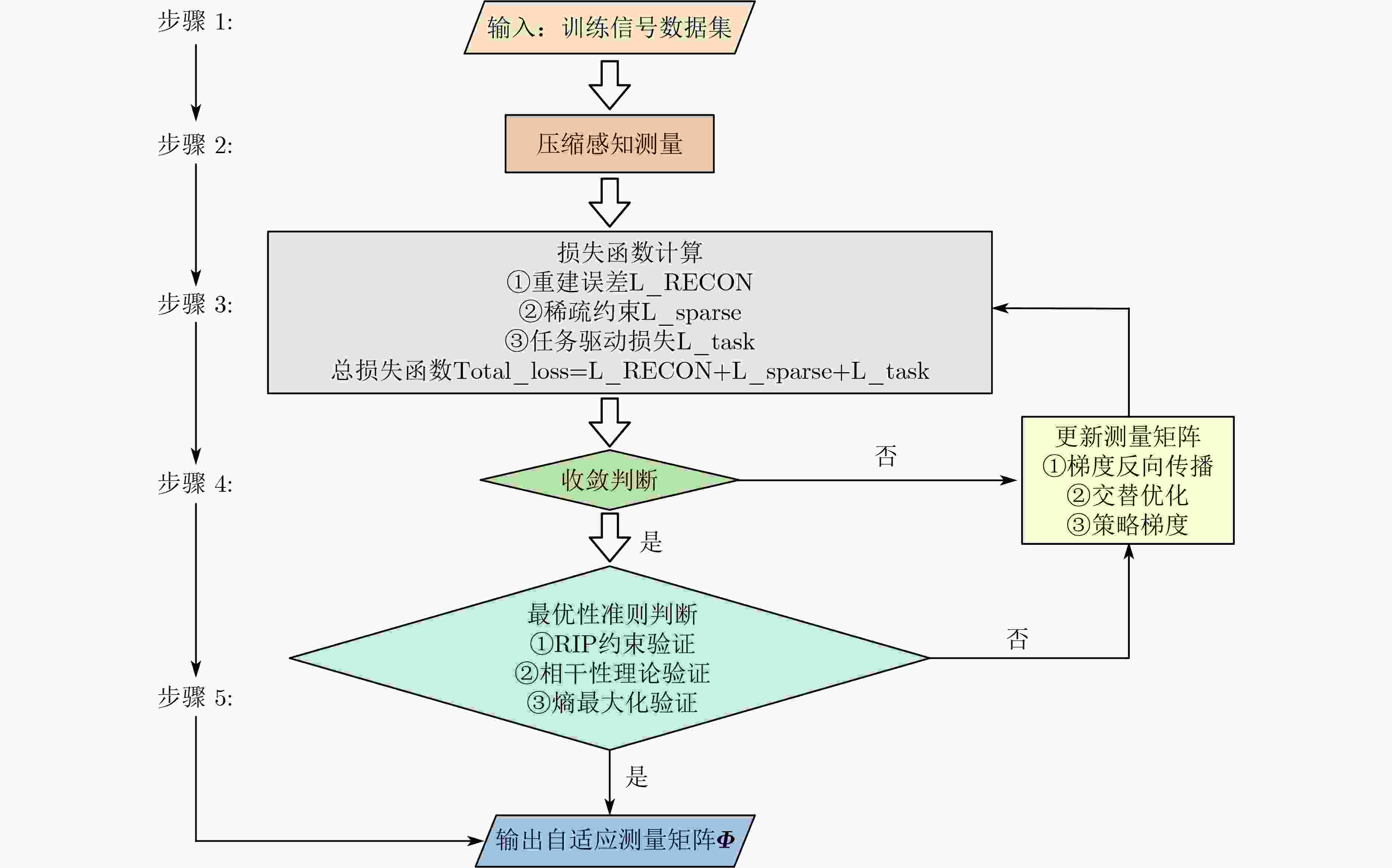


 下载:
下载:
