Unsupervised 3D Medical Image Segmentation With Sparse Radiation Measurement
-
摘要: 神经衰减场是一种具有前景的三维医学图像重建方法,此方法利用稀疏辐射测量实现与完整观察相接近的重构精度。该文提出一种无监督三维医学影像分割方法,将无监督分割与神经衰减场集成为一个端到端的网络架构。具体而言,所提网络架构包括两个阶段:稀疏测量重建和交互式三维图像分割。两个阶段可通过联合学习自适应实现互惠优化。为解决类似肛肠等复杂病灶中边界模糊和区域过度扩展的难题,所提三维分割网络的交互式三维分割阶段设计了密度引导模块,有效利用衰减系数的先验知识,调节密度感知的注意力机制,提升三维分割泛化性能。通过与南京市中医院合作构建的结直肠癌数据集以及两个公开数据集上的大量实验证明所提方法的优越性,例如与基于全辐射观测的SAM-MED3D算法相比,所提网络仅使用14%稀疏观测值,在3个数据集的平均 Dice 系数提升 2.0%。Abstract:
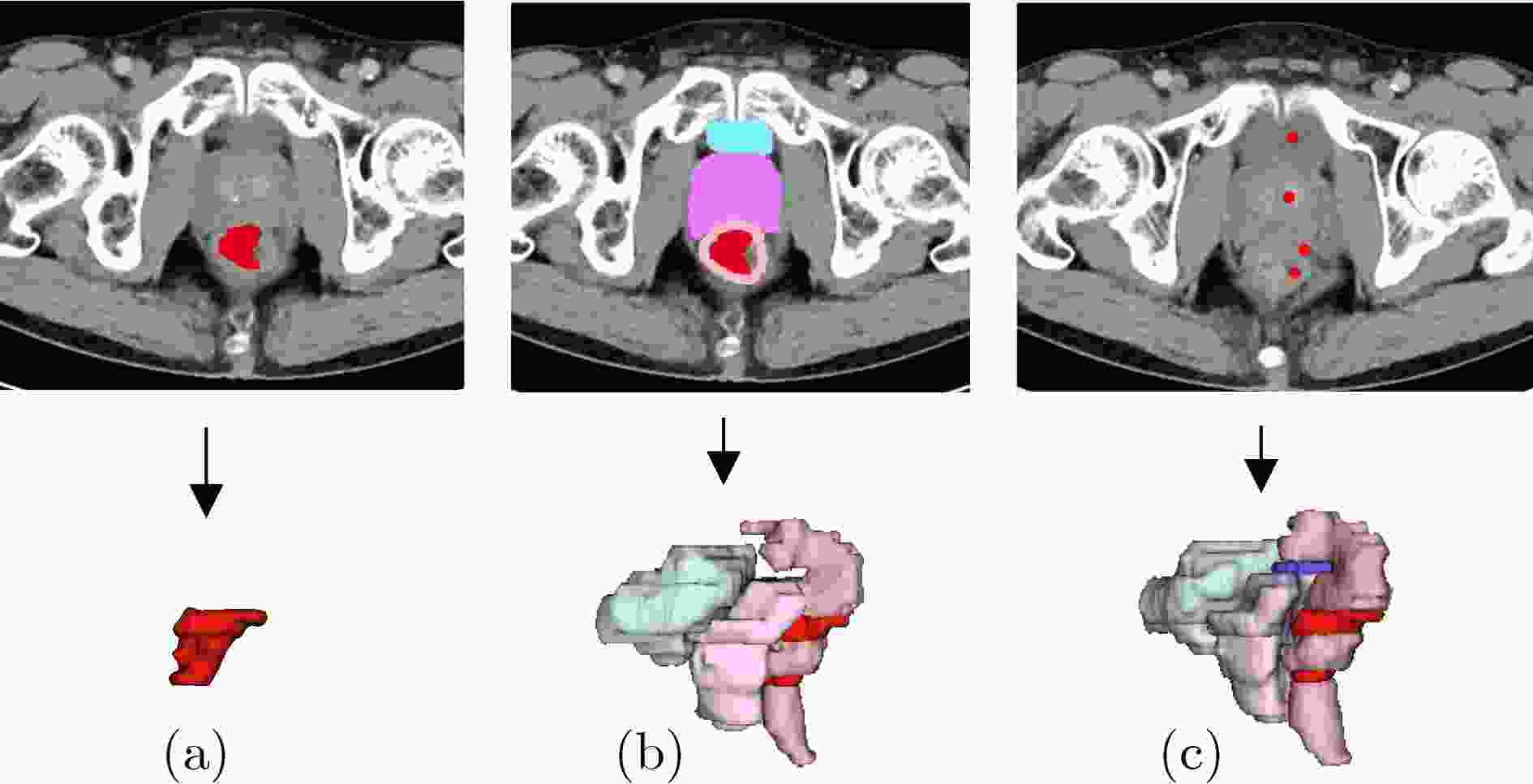
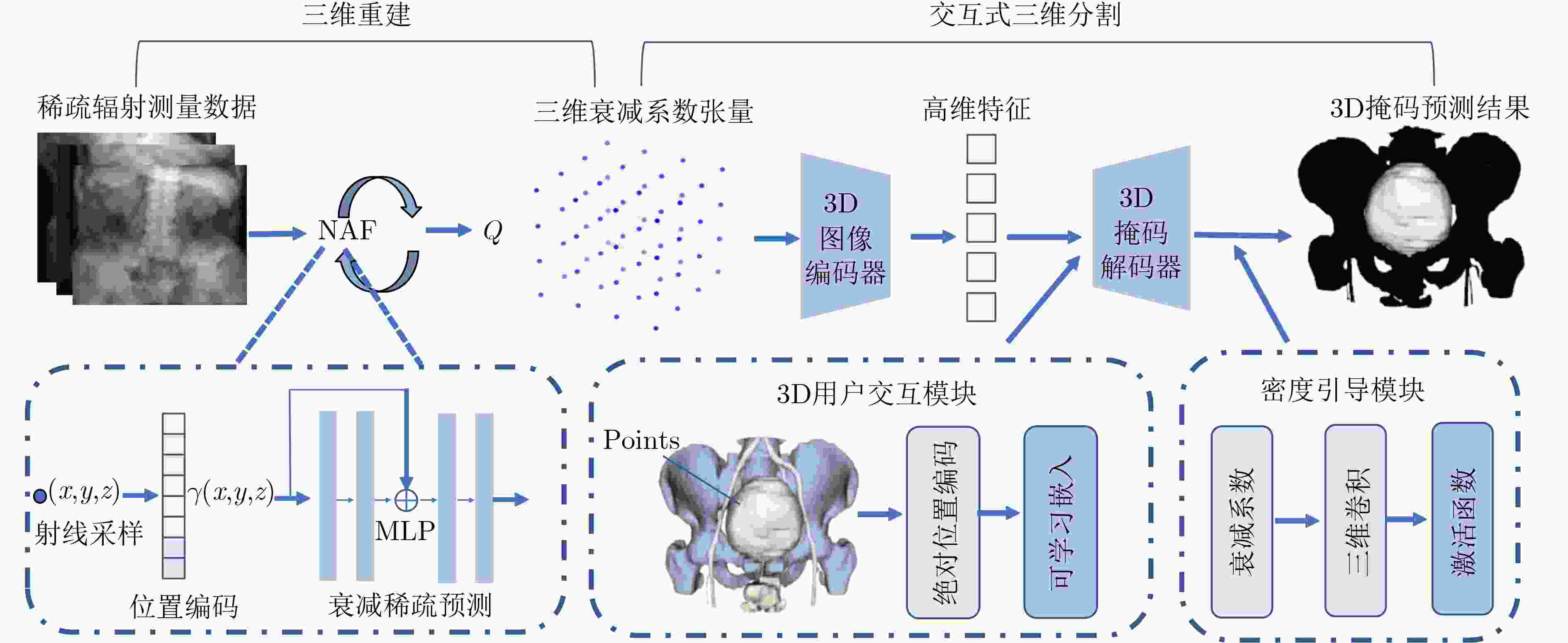
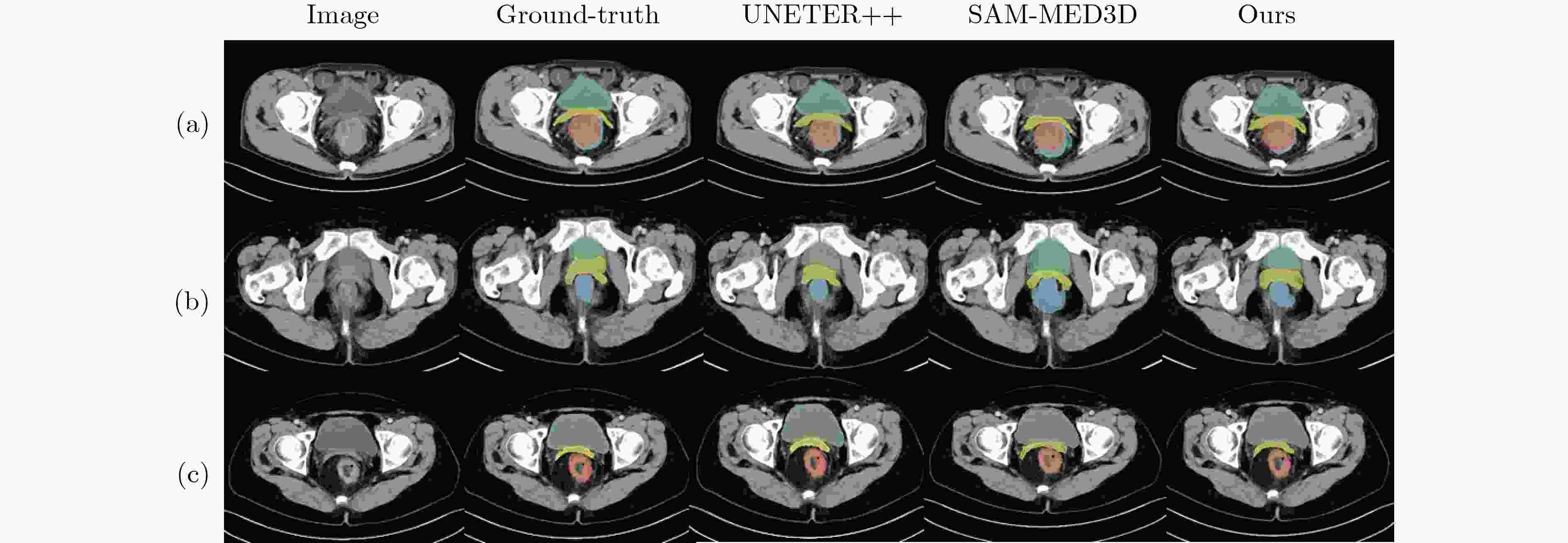
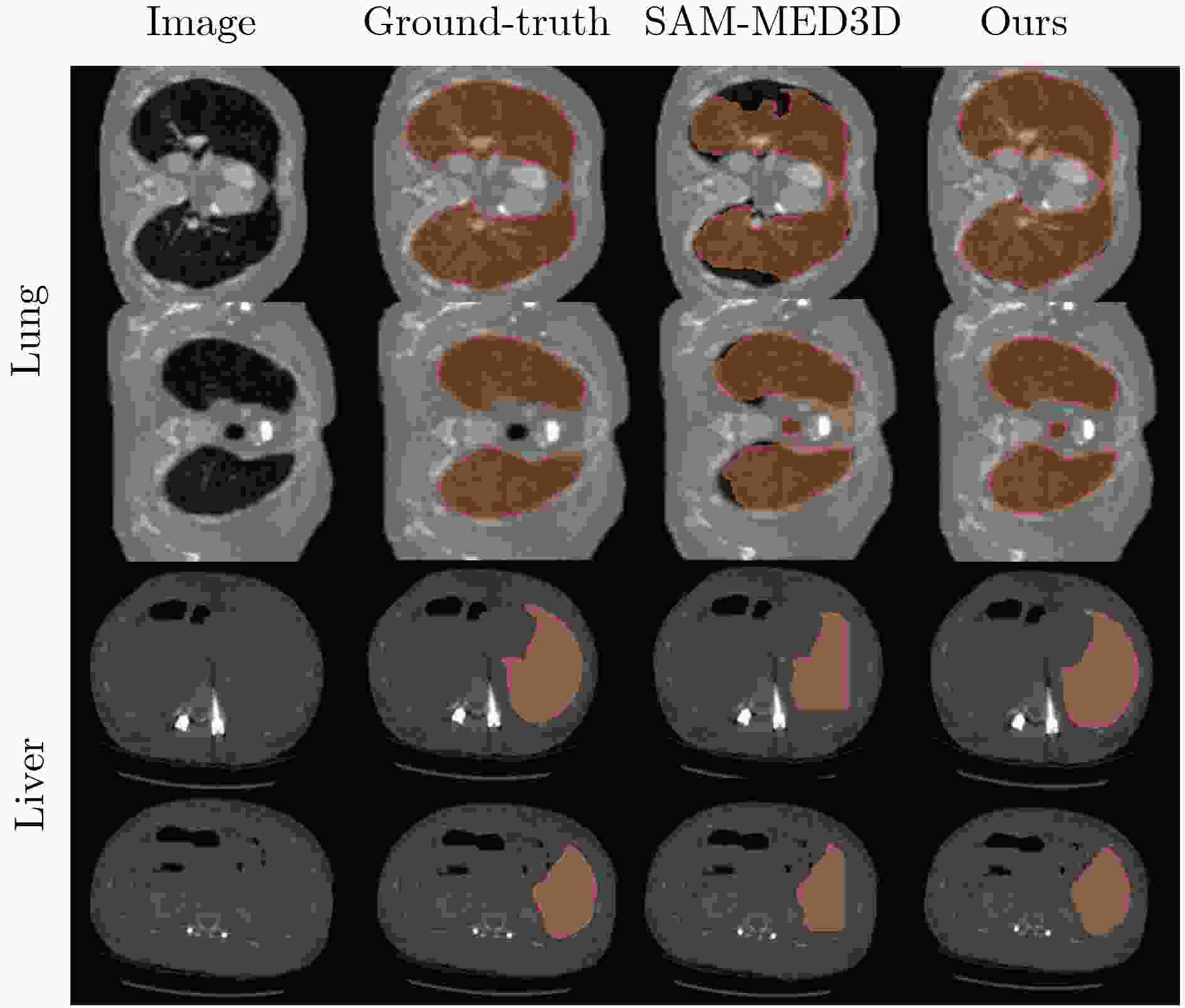
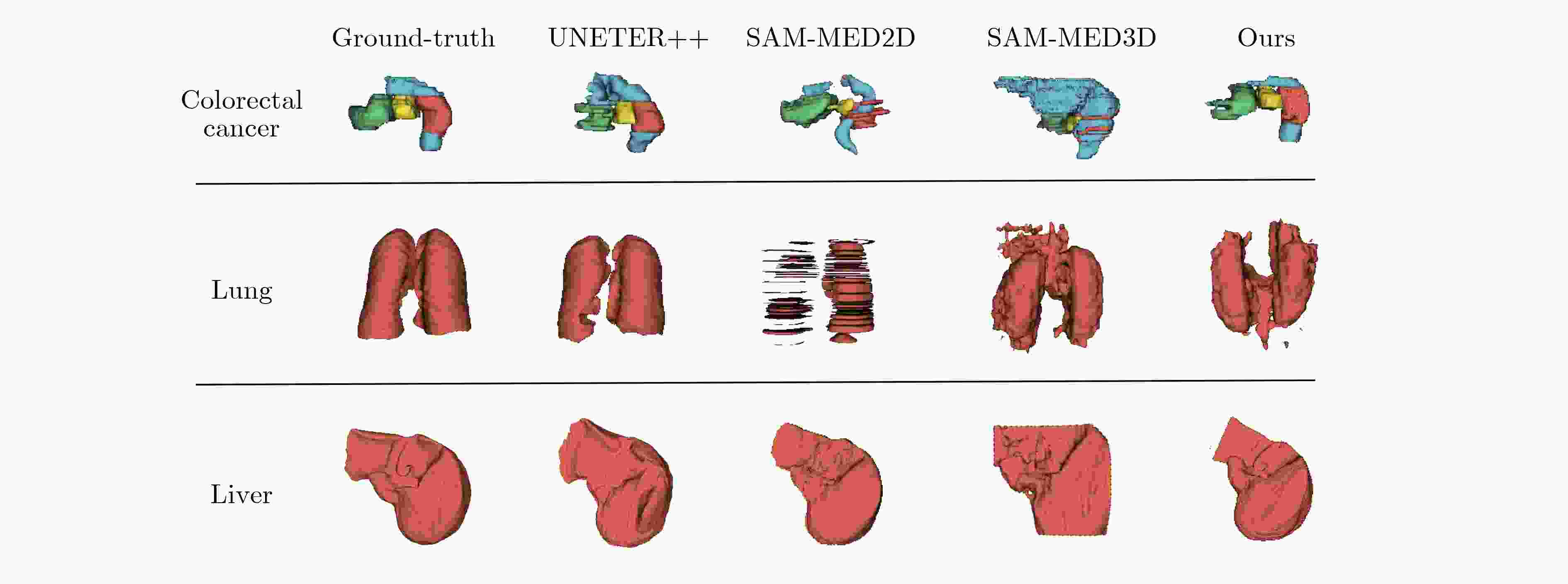
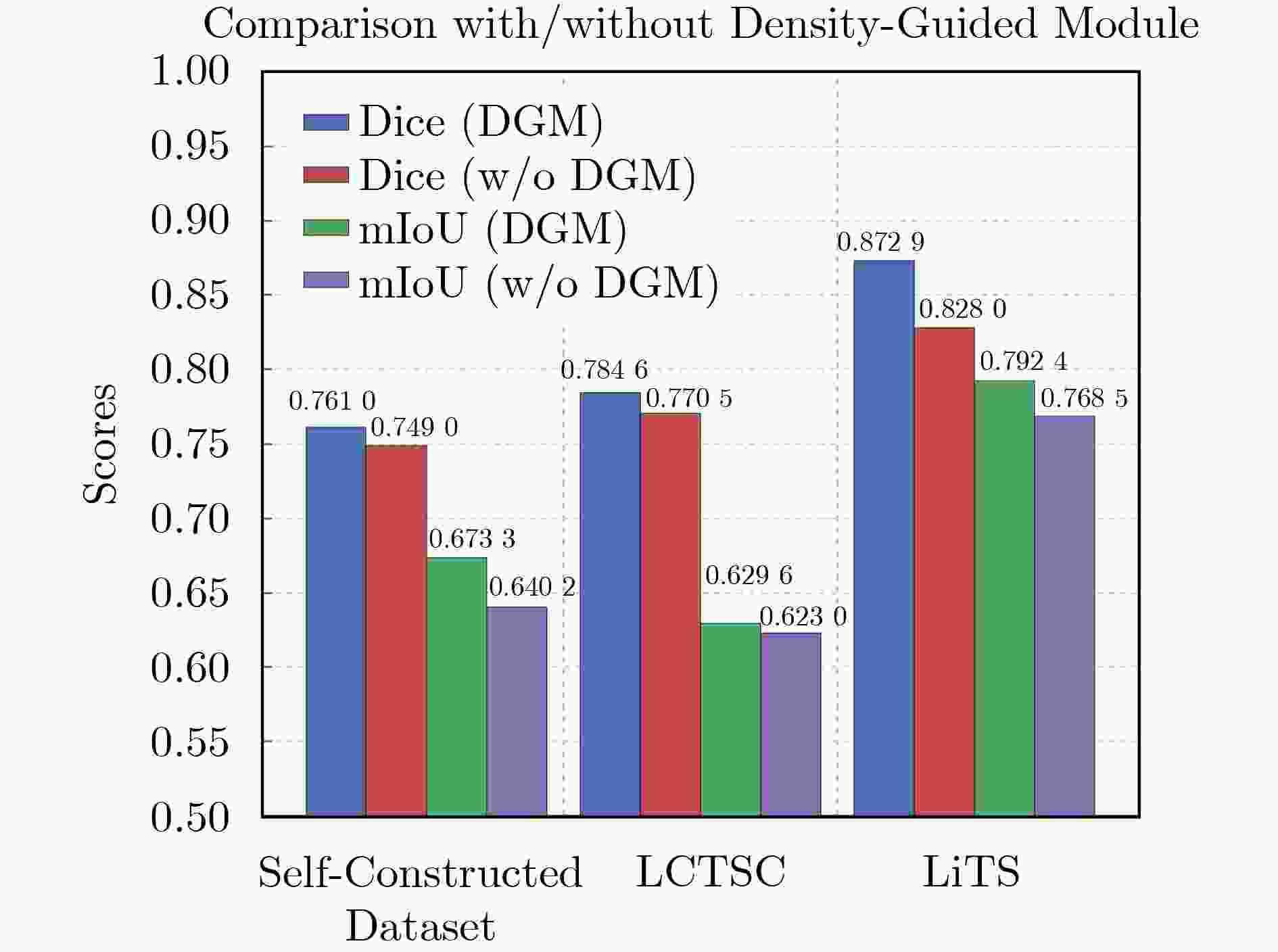
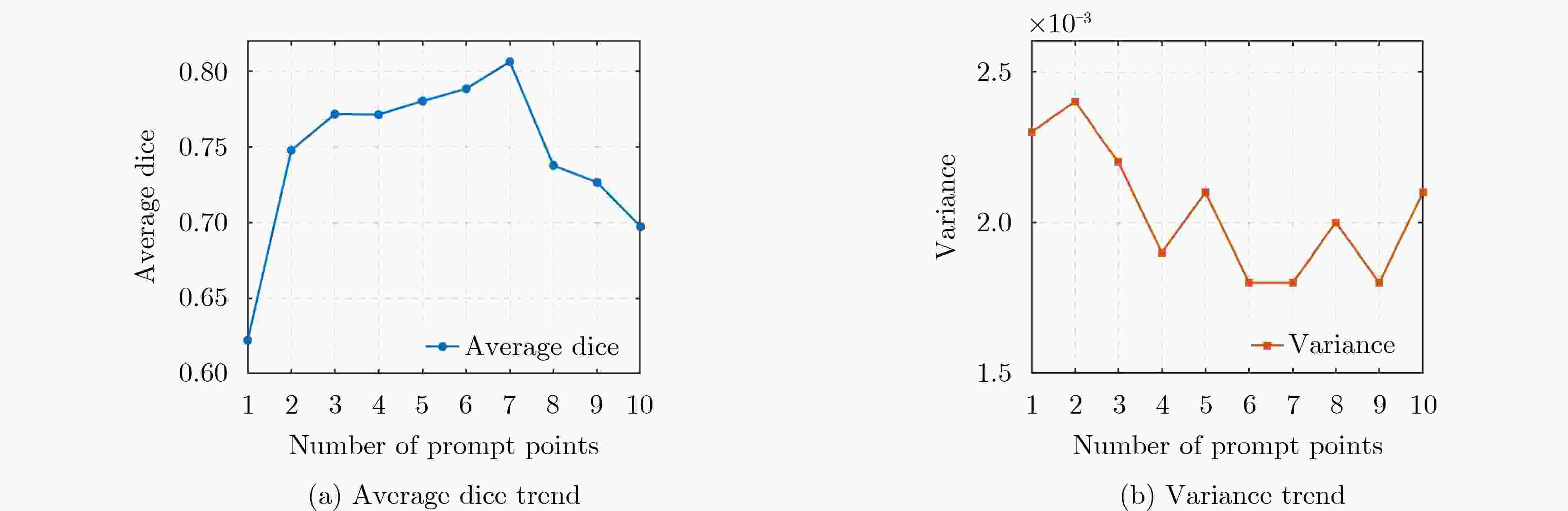
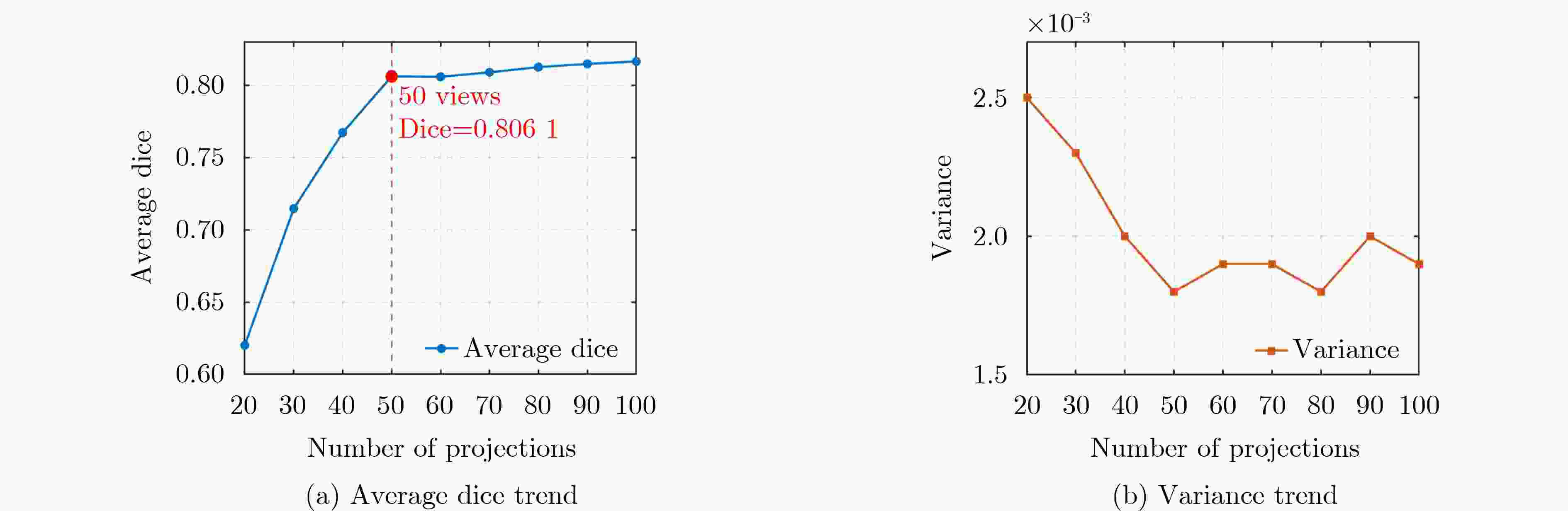
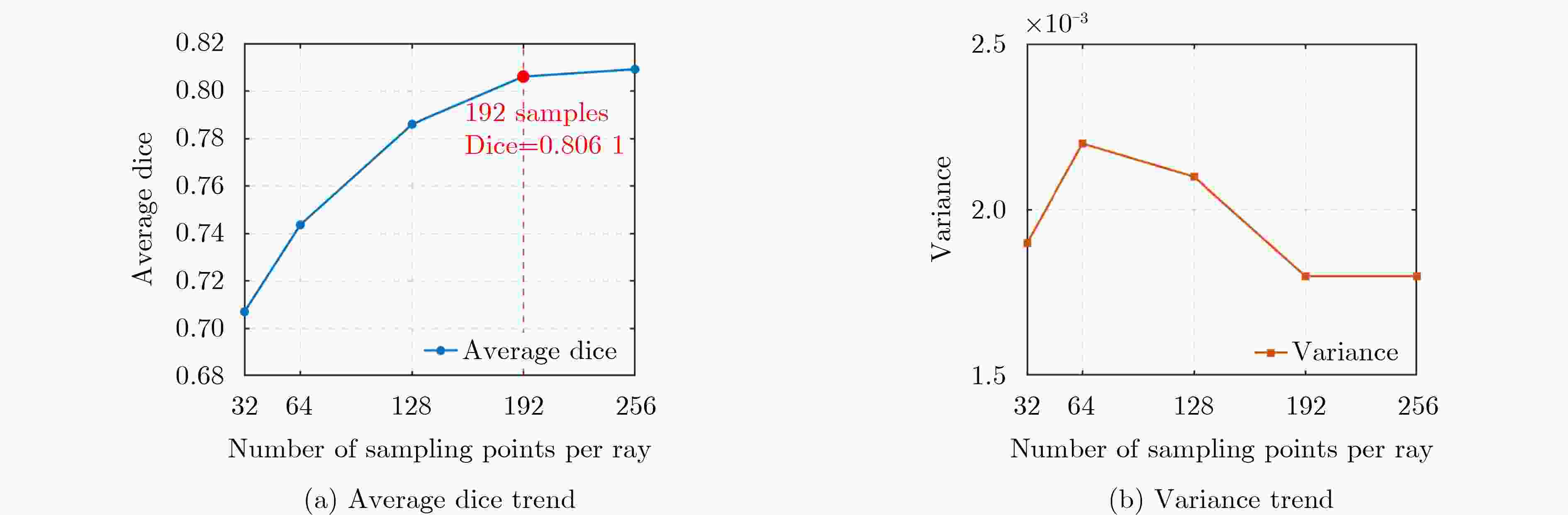
Objective Three-dimensional medical image segmentation is a central task in medical image analysis. Compared with two-dimensional imaging, it captures organ and lesion morphology more completely and provides detailed structural information, supporting early disease screening, personalized surgical planning, and treatment assessment. With advances in artificial intelligence, three-dimensional segmentation is viewed as a key technique for diagnostic support, precision therapy, and intraoperative navigation. However, methods such as SwinUNETR-v2 and UNETR++ depend on extensive voxel-level annotations, which create high annotation costs and restrict clinical use. High-quality segmentation also often requires multi-view projections to recover full volumetric information, increasing radiation exposure and patient burden. Segmentation under sparse radiation measurements is therefore an important challenge. Neural Attenuation Fields (NAF) have recently been introduced for low-dose reconstruction by recovering linear attenuation coefficient fields from sparse views, yet their suitability for three-dimensional segmentation remains insufficiently examined. To address this limitation, a unified framework termed NA-SAM3D is proposed, integrating NAF-based reconstruction with interactive segmentation to enable unsupervised three-dimensional segmentation under sparse-view conditions, reduce annotation dependence, and improve boundary perception. Methods The framework is designed in two stages. In the first stage, sparse-view reconstruction is performed with NAF to generate a continuous three-dimensional attenuation coefficient tensor from sparse X-ray projections. Ray sampling and positional encoding are applied to arbitrary three-dimensional points, and the encoded features are forwarded to a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) to predict linear attenuation coefficients that serve as input for segmentation. In the second stage, interactive segmentation is performed. A three-dimensional image encoder extracts high-dimensional features from the attenuation coefficient tensor, and clinician-provided point prompts specify regions of interest. These prompts are embedded into semantic features by an interactive user module and fused with image features to guide the mask decoder in producing initial masks. Because point prompts provide only local positional cues, boundary ambiguity and mask expansion may occur. To address these issues, a Density-Guided Module (DGM) is introduced at the decoder output stage. NAF-derived attenuation coefficients are transformed into a density-aware attention map, which is fused with the initial masks to strengthen tissue-boundary perception and improve segmentation accuracy in complex anatomical regions. Results and Discussions NA-SAM3D is evaluated on a self-constructed colorectal cancer dataset comprising 299 patient cases (collected in collaboration with Nanjing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine) and on two public benchmarks: the Lung CT Segmentation Challenge (LCTSC) and the Liver Tumor Segmentation Challenge (LiTS). The results show that NA-SAM3D achieves overall better performance than mainstream unsupervised three-dimensional segmentation methods based on full radiation observation (SAM-MED series) and reaches accuracy comparable to, or in some cases higher than, the fully supervised SwinUNETR-v2. Compared with SAM-MED3D, NA-SAM3D increases the Dice on the LCTSC dataset by more than 3%, while HD95 and ASD decrease by 5.29 mm and 1.32 mm, respectively, indicating improved boundary localization and surface consistency. Compared with the sparse-field-based method SA3D, NA-SAM3D achieves higher Dice scores on all three datasets ( Table 1 ). Compared with the fully supervised SwinUNETR-v2, NA-SAM3D reduces HD95 by 1.28 mm, and the average Dice is only 0.3% lower. Compared with SA3D, NA-SAM3D increases the average Dice by about 6.6% and reduces HD95 by about 11 mm, further confirming its capacity to restore structural details and boundary information under sparse-view conditions (Table 2 ). Although the overall performance remains slightly lower than that of the fully supervised UNETR++ model, NA-SAM3D still shows strong competitiveness and good generalization under label-free inference. Qualitative analysis shows that in complex pelvic and intestinal regions, NA-SAM3D produces clearer boundaries and higher contour consistency (Fig. 3 ). On public datasets, segmentation of the lung and liver also shows superior boundary localization and contour integrity (Fig. 4 ). Three-dimensional visualization further confirms that in colorectal, lung, and liver regions, NA-SAM3D achieves stronger structural continuity and boundary preservation than SAM-MED2D and SAM-MED3D (Fig. 5 ). The DGM further enhances boundary sensitivity, increasing Dice and mIoU by 1.20% and 3.31% on the self-constructed dataset, and by 4.49 and 2.39 percentage points on the LiTS dataset (Fig. 6 ).Conclusions An unsupervised three-dimensional medical image segmentation framework, NA-SAM3D, is presented, integrating NAF-based reconstruction with interactive segmentation to achieve high-precision segmentation under sparse radiation measurements. The DGM effectively uses attenuation coefficient priors to enhance boundary recognition in complex lesion regions. Experimental results show that the framework approaches the performance of fully supervised methods under unsupervised inference and yields an average Dice improvement of 2.0%, indicating strong practical value and clinical potential for low-dose imaging and complex anatomical segmentation. Future work will refine the model for additional anatomical regions and assess its practical use in preoperative planning. -
表 1 不同数据集的定量结果对比,(表中加粗值表示该列指标的最优结果,HD95 与 ASD 的单位均为 mm)
方法 LCTSC LiTS 自建数据集 DICE mIoU HD95 ASD DICE mIoU HD95 ASD DICE mIoU HD95 ASD Swinunetr-v2[5] 0.7812 0.6285 18.54 3.66 0.8865 0.8033 10.36 3.27 0.7598 0.6721 17.28 3.71 UNETR++[6] 0.8171 0.7003 11.20 3.04 0.9126 0.8312 10.08 3.23 0.7835 0.6894 9.70 2.75 SAM-MED2D[18] 0.5805 0.4090 24.89 5.13 0.8623 0.7577 12.94 3.86 0.7196 0.6361 26.88 5.40 SA3D[21] 0.6931 0.5389 23.48 4.91 0.8027 0.7123 26.81 5.92 0.7235 0.6108 25.14 5.73 SAM-MED3D[22] 0.7623 0.6257 21.21 4.69 0.8511 0.7741 17.00 4.22 0.7448 0.6426 18.25 4.05 本文 0.7946 0.6296 15.92 3.37 0.8629 0.7924 12.79 3.31 0.7610 0.6733 13.61 3.05 表 2 不同模型的均值与方差比较(表中加粗值表示该列指标的最优结果)
方法 平均值 方差 DICE mIoU HD95 ASD DICE mIoU HD95 ASD Swinunetr-v2[5] 0.8092 0.7013 15.39 3.55 0.0031 0.0055 12.93 0.04 UNETR++[6] 0.8377 0.7403 10.33 2.94 0.0030 0.0042 0.41 0.02 SAM-MED2D[18] 0.7208 0.6009 21.57 4.80 0.0132 0.0209 37.90 0.45 SA3D[21] 0.7398 0.6207 25.14 5.52 0.0021 0.0051 1.84 0.19 SAM-MED3D[22] 0.7861 0.6808 18.82 4.32 0.0022 0.0044 3.11 0.07 本文 0.8061 0.6984 14.11 3.24 0.0018 0.0047 1.76 0.02 表 3 基于自建数据集微调下的交叉域评估结果,(表中加粗值表示该列指标的最优结果)
-
[1] EMRE T, CHAKRAVARTY A, RIVAIL A, et al. 3DTINC: Time-equivariant non-contrastive learning for predicting disease progression from longitudinal OCTs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2024, 43(9): 3200–3210. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3391215. [2] ZHU Pengfei, WANG Tingmin, YANG Fan, et al. A transformer-based multi-scale deep learning model for lung cancer surgery optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 70044–70054. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3561948. [3] WU Junde, ZHANG Yu, FANG Huihui, et al. Calibrate the inter-observer segmentation uncertainty via diagnosis-first principle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2024, 43(9): 3331–3342. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3394045. [4] MA Yuxi, WANG Jiacheng, YANG Jing, et al. Model-heterogeneous semi-supervised federated learning for medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2024, 43(5): 1804–1815. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2023.3348982. [5] HE Yufan, NATH V, YANG Dong, et al. SwinUNETR-V2: Stronger swin transformers with stagewise convolutions for 3D medical image segmentation[C]. The 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 416–426. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-43901-8_40. [6] SHAKER A, MAAZ M, RASHEED H, et al. UNETR++: Delving into efficient and accurate 3D medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2024, 43(9): 3377–3390. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3398728. [7] PERERA S, NAVARD P, YILMAZ A, et al. SegFormer3D: An efficient transformer for 3D medical image segmentation[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, USA, 2024: 4981–4988. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW63382.2024.00503. [8] TOWLE B, CHEN Xin, and ZHOU Ke. SimSAM: Zero-shot medical image segmentation via simulated interaction[C]. The 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Athens, Greece, 2024: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ISBI56570.2024.10635227. [9] BUI N T, HOANG D H, TRAN M T, et al. SAM3D: Segment anything model in volumetric medical images[C]. 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Athens, Greece, 2024: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ISBI56570.2024.10635844. [10] YAMAGISHI Y, HANAOKA S, KIKUCHI T, et al. Using segment anything model 2 for zero-shot 3D segmentation of abdominal organs in computed tomography scans to adapt video tracking capabilities for 3D medical imaging: Algorithm development and validation[J]. JMIR AI, 2025, 4(1): e72109. doi: 10.2196/72109. [11] MILDENHALL B, SRINIVASAN P P, TANCIK M, et al. NeRF: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2021, 65(1): 99–106. doi: 10.1145/3503250. [12] ZHA Ruyi, ZHANG Yanhao, LI Hongdong, et al. NAF: Neural attenuation fields for sparse-view CBCT reconstruction[C]. The 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 2022: 442–452. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-16446-0_42. [13] TAN Pinhuang, GENG Mengxiao, LU Jingya, et al. MSDiff: Multi-scale diffusion model for ultra-sparse view CT reconstruction[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2405.05814, 2024. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2405.05814. [14] SONG Bowen, HU J, LUO Zhaoxu, et al. DiffusionBlend: Learning 3D image prior through position-aware diffusion score blending for 3D computed tomography reconstruction[C]. The 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 2844. [15] ZHAO Xuzhi, DU Yi, YUE Haizhen, et al. Deep learning-based projection synthesis for low-dose cone-beam computed tomography imaging in image-guided radiotherapy[J]. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery, 2024, 14(1): 23150–23250. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-759. [16] YANG Liutao, HUANG Jiahao, YANG Guang, et al. CT-SDM: A sampling diffusion model for sparse-view CT reconstruction across various sampling rates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2025, 44(6): 2581–2593. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2025.3541491. [17] KANG E, CHANG W, YOO J, et al. Deep convolutional framelet denosing for low-dose CT via wavelet residual network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1358–1369. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2823756. [18] CHENG Junlong, YE Jin, DENG Zhongying, et al. SAM-Med2D[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2308.16184, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2308.16184. [19] LEI Wenhui, XU Wei, LI Kang, et al. MedLSAM: Localize and segment anything model for 3D CT images[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2025, 99: 103370. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2024.103370. [20] GONG Shizhan, ZHONG Yuan, MA Wenao, et al. 3DSAM-Adapter: Holistic adaptation of SAM from 2D to 3D for promptable tumor segmentation[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2024, 98: 103324. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2024.103324. [21] CEN Jiazhong, FANG Jiemin, ZHOU Zanwei, et al. Segment anything in 3D with radiance fields[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2025, 133(8): 5138–5160. doi: 10.1007/s11263-025-02421-7. [22] WANG Haoyu, GUO Sizheng, YE Jin, et al. SAM-Med3D: Towards general-purpose segmentation models for volumetric medical images[C]. The European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 2024: 51–67. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-91721-9_4. [23] YANG J, SHARP G, VEERARAGHAVAN H, et al. Data from Lung CT Segmentation Challenge (LCTSC) (Version 3)[M]. The Cancer Imaging Archive, 2017. [24] BILIC P, CHRIST P, LI H B, et al. The Liver Tumor Segmentation benchmark (LiTS)[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2023, 84: 102680. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102680. [25] FELDKAMP L A, DAVIS L C, and KRESS J W. Practical cone-beam algorithm[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1984, 1(6): 612–619. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.1.000612. [26] ANDERSEN A H and KAK A C. Simultaneous Algebraic Reconstruction Technique (SART): A superior implementation of the ART algorithm[J]. Ultrasonic Imaging, 1984, 6(1): 81–94. doi: 10.1177/016173468400600107. [27] CAI Yuanhao, WANG Jiahao, YUILLE A, et al. Structure-aware sparse-view X-ray 3D reconstruction[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 11174–11183. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01062. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
