Coalition Formation Game based User and Networking Method for Status Update Satellite Internet of Things
-
摘要: 状态更新是卫星物联网(S-IoT)的重要场景。该文研究了状态更新S-IoT中基于基站辅助的用户组网问题。首先,建立了地面用户经基站向卫星网络传输的双层正交接入状态更新模型,并分析推导了地面用户的平均信息年龄(aAoI)的闭合表达式和高信噪比下的渐进表达式。其次,基于联盟形成博弈(CFG),提出一种双层CFG用户-基站-卫星组网算法。接着,利用精确势能博弈,证明了所提博弈算法具有纳什均衡解,能够形成稳定的基站-用户-卫星网络。最后,仿真结果表明,aAoI的理论分析的正确性以及所提算法的较传统算法的性能提升。Abstract:
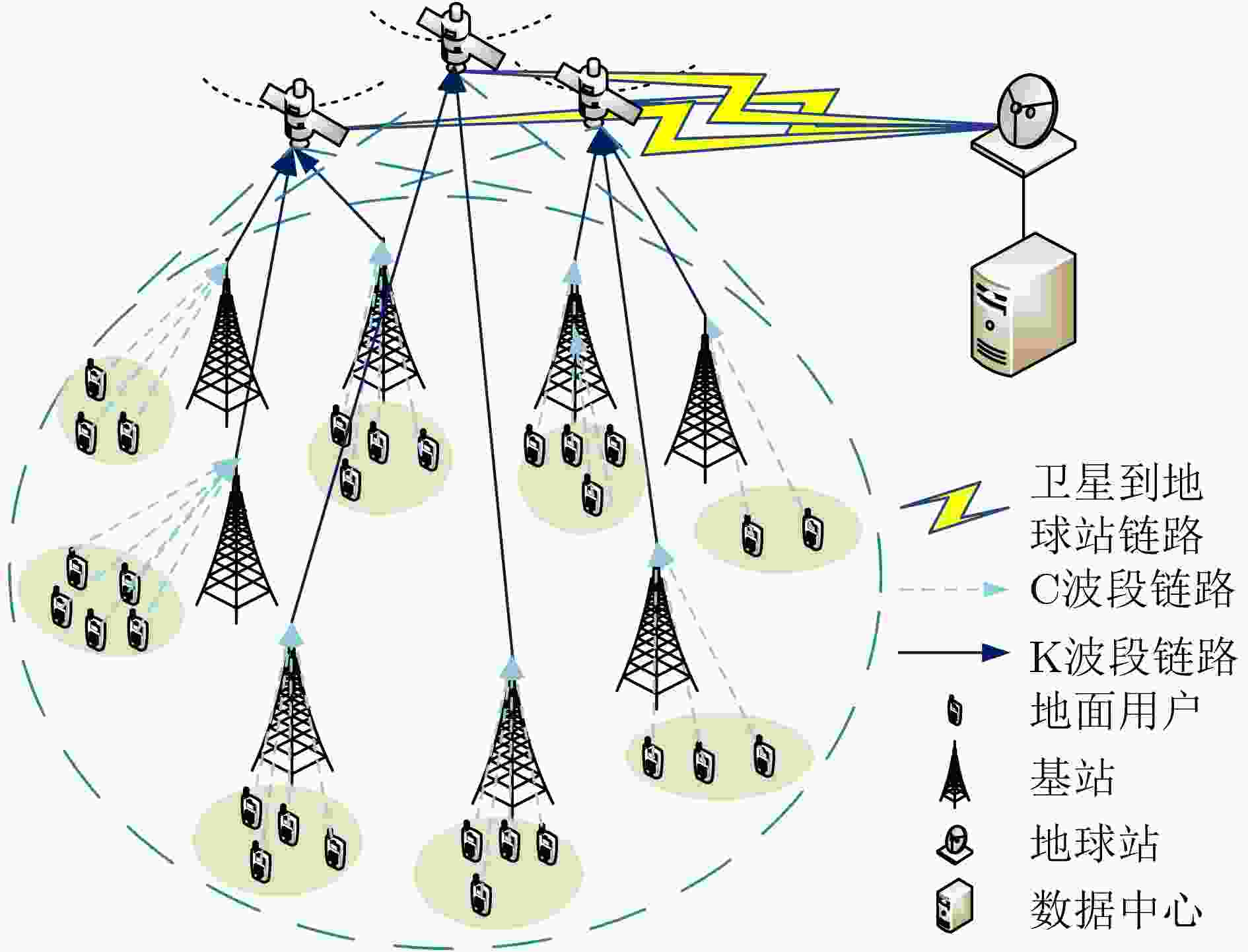
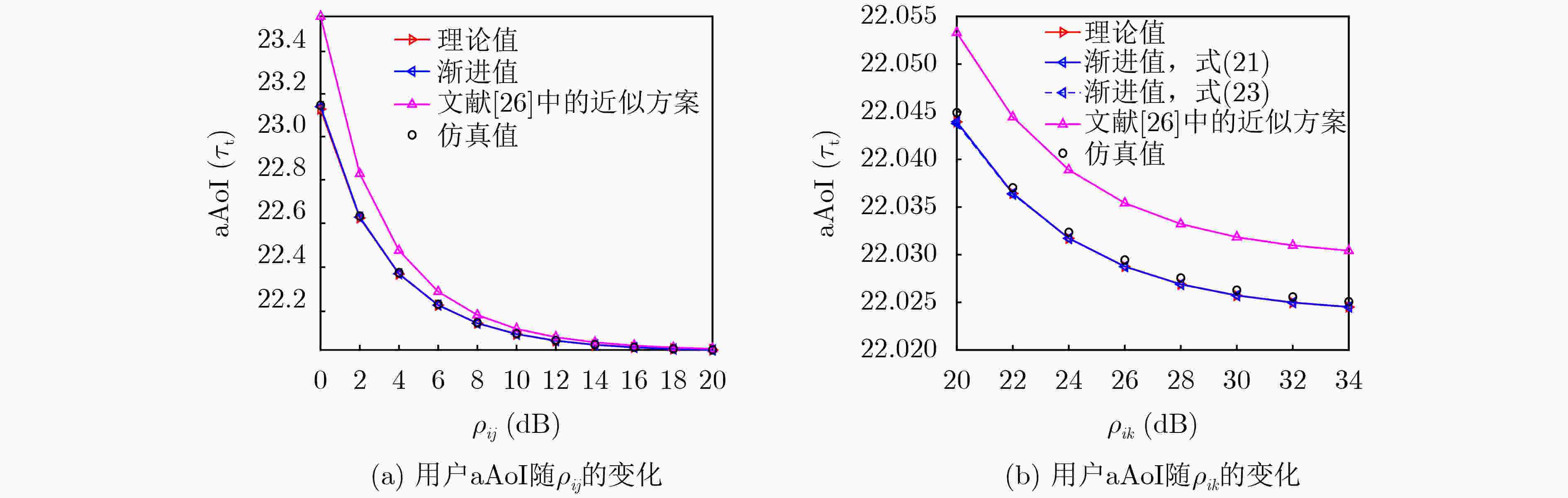
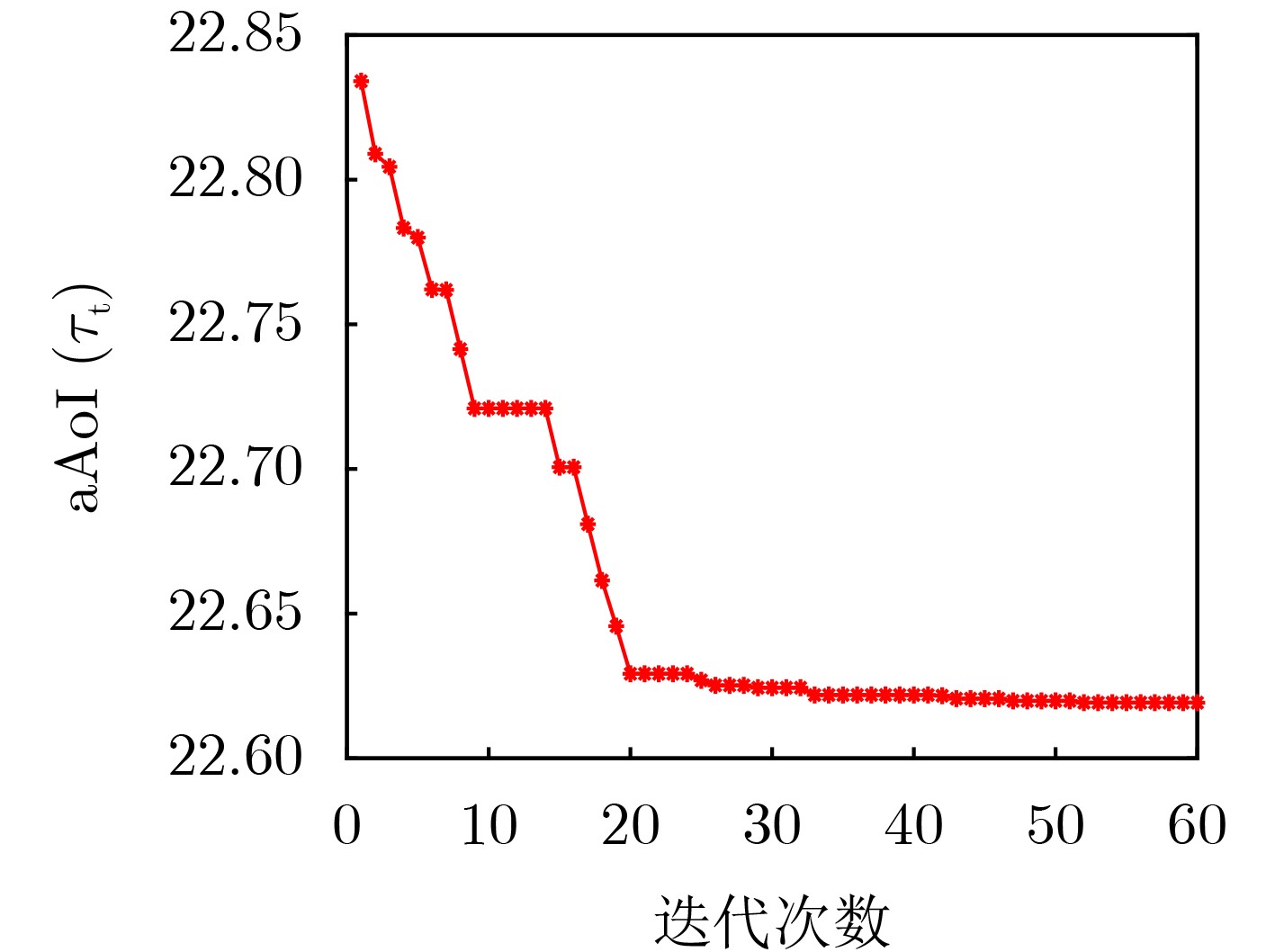
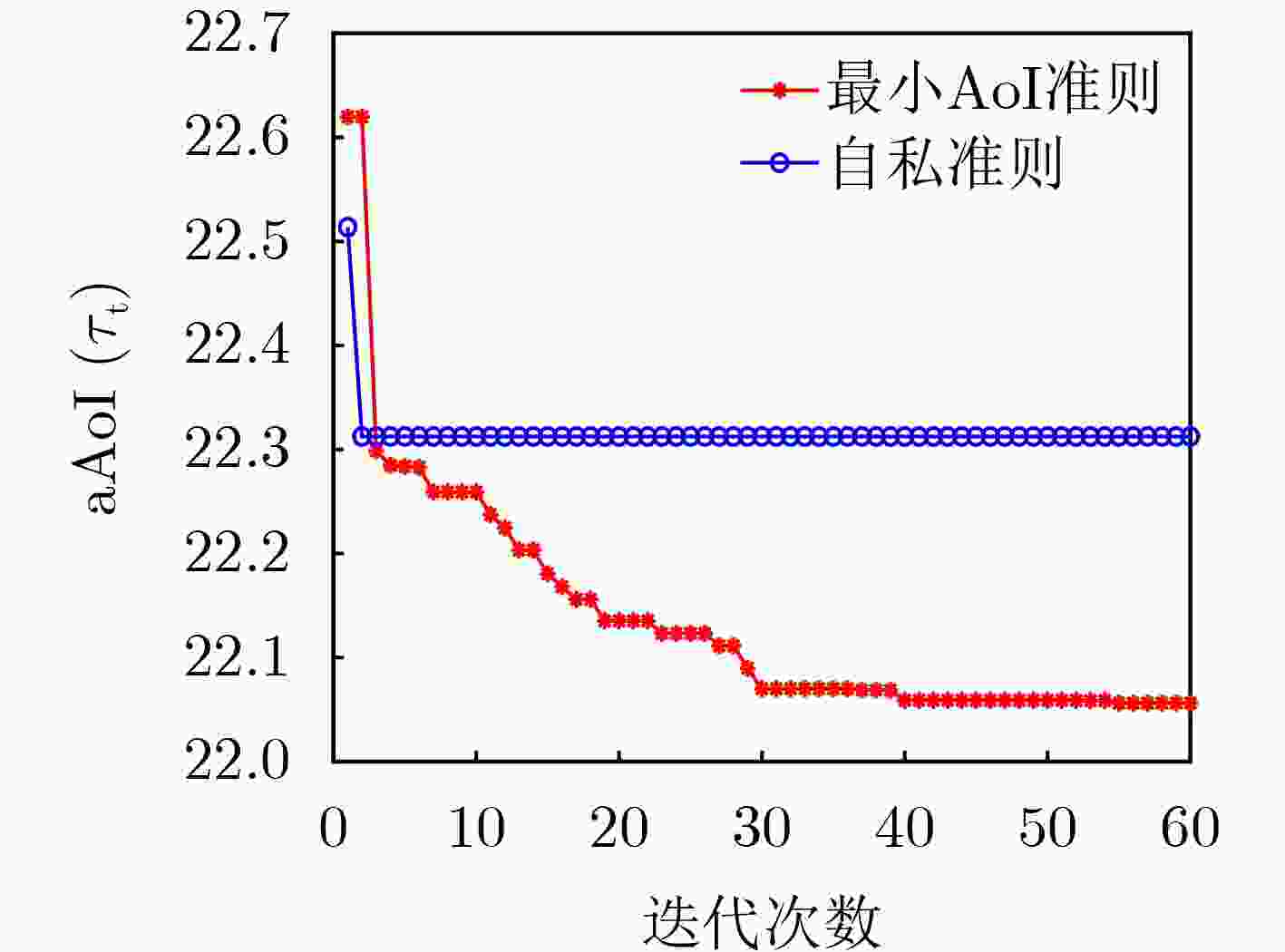
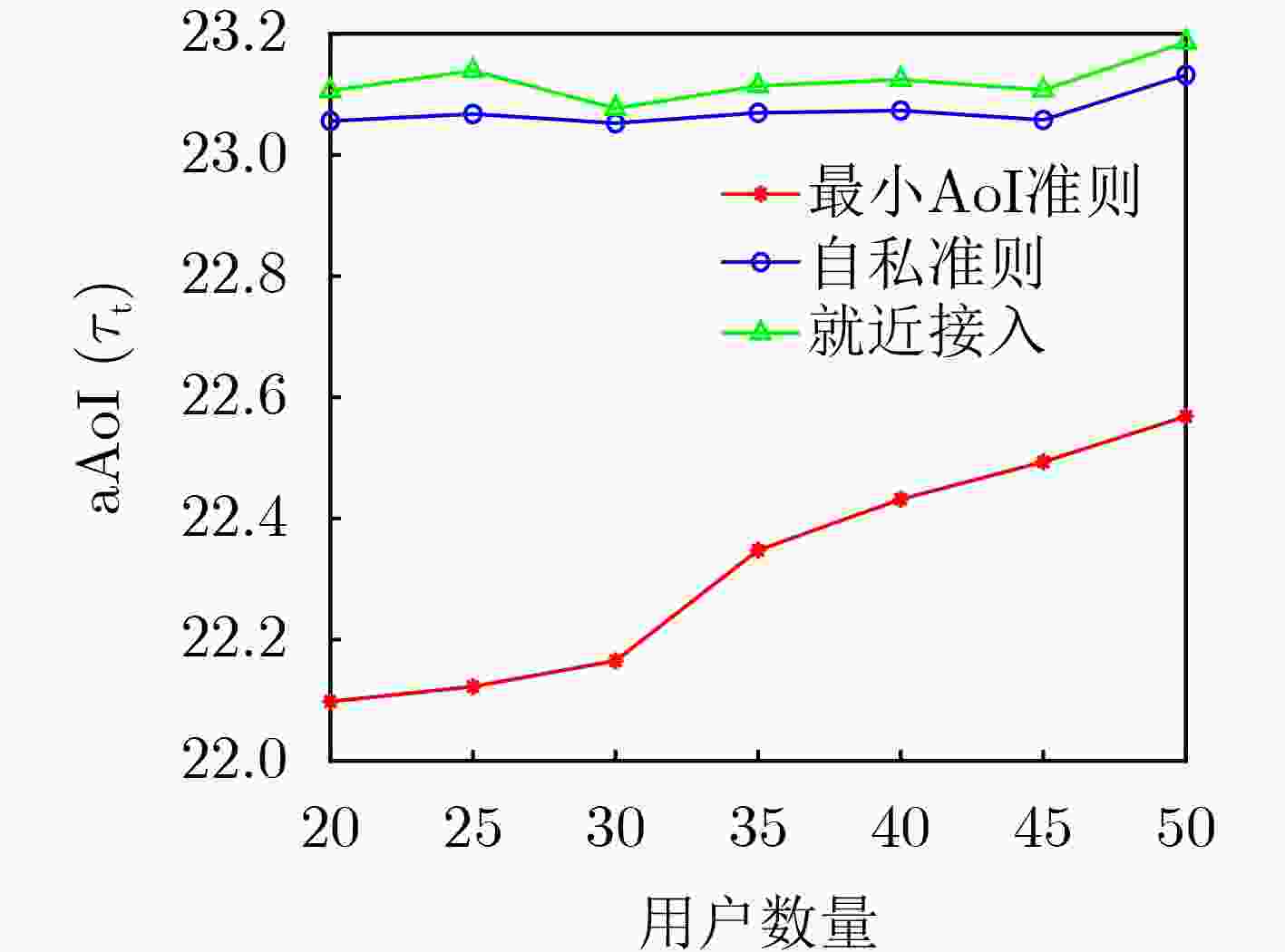
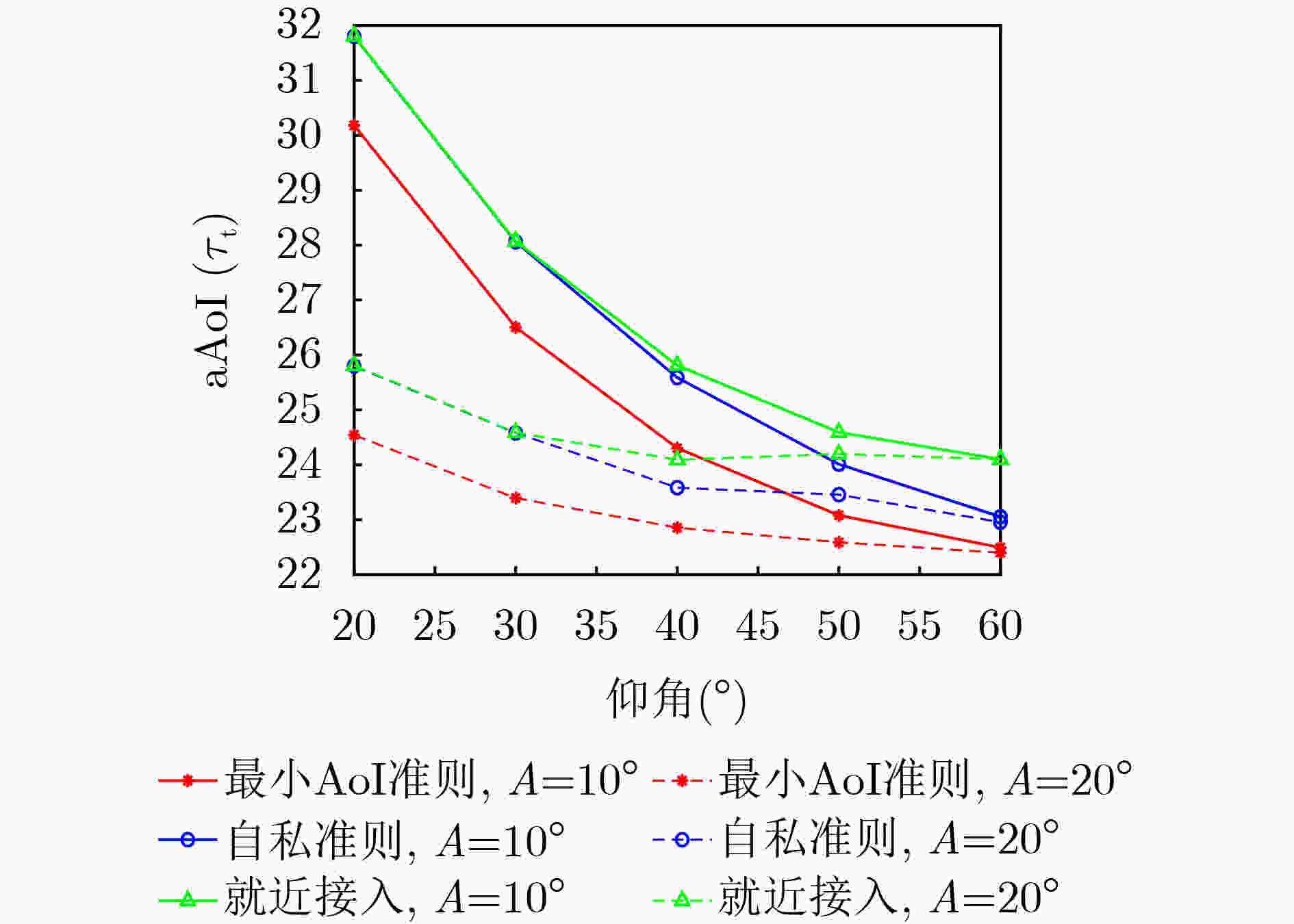
Objective Satellite communication has become a major focus in the development of next-generation wireless networks due to its advantages of wide coverage, long communication distance, and high flexibility in networking. Short-packet communication represents a critical scenario in the Satellite Internet of Things (S-IoT). However, research on the status update problem for massive users remains limited. It is necessary to design reasonable user-networking schemes to address the contradiction between massive user access demands and limited communication resources. In addition, under the condition of large-scale user access, the design of user-networking schemes with low complexity remains a key research challenge. This study presents a solution for status updates in S-IoT based on dynamic orthogonal access for massive users. Methods In the S-IoT, a state update model for user orthogonal dual-layer access is established. A dual-layer networking scheme is proposed in which users dynamically allocate bandwidth to access the base station, and the base station adopts time-slot polling to access the satellite. The closed-form expression of the average Age of Information (aAoI) for users is derived based on short-packet communication theory, and a simplified approximate expression is further obtained under high signal-to-noise ratio conditions. Subsequently, a distributed Dual-layer Coalition Formation Game User-base Station-Satellite Networking (DCFGUSSN) algorithm is proposed based on the coalition formation game framework. Results and Discussions The approximate aAoI expression effectively reduces computational complexity. The exact potential game is used to demonstrate that the proposed DCFGUSSN algorithm achieves stable networking formation. Simulation results verify the correctness of the theoretical analysis of user aAoI in the proposed state update model ( Fig. 5 ). The results further indicate that with an increasing number of iterations, the user’s aAoI gradually decreases and eventually converges (Fig. 6 ). Compared with other access schemes, the proposed dual-layer access scheme achieves a lower aAoI (Figs. 7 $ \sim $9 ).Conclusions This study investigates the networking problem of massive users assisted by base stations in the status update S-IoT. A dynamic dual-layer user access framework and the corresponding status update model are first established. Based on this framework, the DCFGUSSN algorithm is proposed to reduce user’s aAoI. Theoretical and simulation results show strong consistency, and the proposed algorithm demonstrates significant performance improvement compared with traditional algorithms. -
表 1 主要系统参数
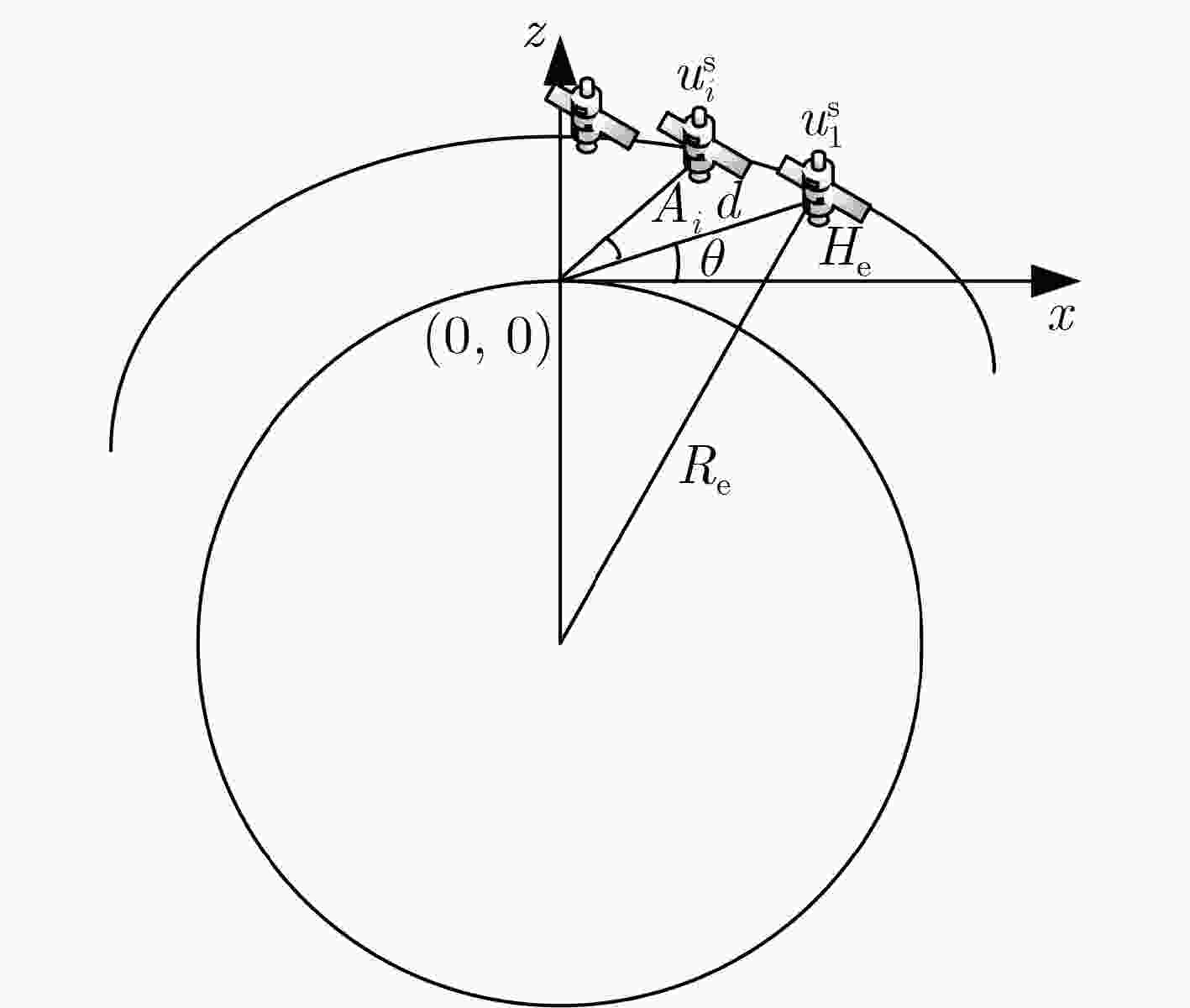
参数 含义 参数 含义 $ H_{\mathrm{\mathrm{s}}} $ LEO卫星高度 $ N_{\mathrm{s}} $ 卫星数量 $ N\mathrm{_{\mathrm{t}}} $ 基站数量 $ N_{\mathrm{u}} $ 用户数量 $ B_{\mathrm{s}} $ 卫星带宽 $ B_{\mathrm{t}} $ 地面带宽 $ u_i^{\mathrm{u}} $ 第i个用户 $ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $ 第j个基站 $ u_k^{\mathrm{s}} $ 第k个卫星 $ \tau $ 时隙长度 $ {N_j^{\mathrm{t}}} $ 接入基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{\mathrm{\mathrm{v}}}} $的用户数量 $ D $ 数据包大小 $ {h_{ij}} $ 用户$ u_i^{\mathrm{u}} $和基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $间的信道增益 $ {{\mathbf{g}}_{jk}} $ 基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $和卫星$ u_k^{\mathrm{s}} $间的信道增益 $ {p_i} $ 用户功率 $ {P_{jk}} $ 基站功率 $ {L_k} $ 接入卫星$ u_k^{\mathrm{s}} $的基站数 $ {\bar \varDelta _{ijk}} $ 用户$ u_i^{\mathrm{u}} $经基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $到卫星$ u_k^{\mathrm{s}} $的aAoI $ \bar{\varXi}(\gamma_{jk}^{\mathrm{s}},l_{\mathrm{s}},R_{\mathrm{s}}) $ 基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $解调用户$ u_i^{\mathrm{u}} $的数据包的平均误块率 $ \bar{\varXi}(\gamma_{ij}^{\mathrm{t}},l_j^{\mathrm{t}},R_{\mathrm{t}}) $ 卫星$ u_k^{\mathrm{s}} $侧解调基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $的平均误块率 $ \gamma_{ij}^{\mathrm{t}} $ 用户$ u_i^{\mathrm{u}} $在基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $处的信干噪比 $ \gamma_{jk}^{\mathrm{s}} $ 基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $在卫星$ u_k^{\mathrm{s}} $处的信干噪比 $ l_j^{\mathrm{t}} $ 接入基站$ u_j^{\mathrm{v}} $信道的数据包块长 $ l_{\mathrm{s}} $ 卫星信道的数据包块长 $ R_{\mathrm{s}} $ 星地传输速率 $ R_{\mathrm{t}} $ 地面传输速率 1 双层CFG用户-基站-卫星组网算法
输入:用户位置、基站位置、卫星位置 输出:用户-基站连接关系,基站-卫星连接关系 (1) 初始化分组,每个用户只接入1个基站、每个基站只接入1个卫星 (2) 循环 (3) 随机选择1个用户,根据式(28)计算用户的原有效用函数 (4) 该用户计划接入其他基站,根据式(28)计算用户接入依次所有其他基站的效用函数,若用户最小的新的效用函数小于用户原有效用函
数,则用户接入对应的新的基站,反之不改变接入关系(5) 随机选择一个基站,根据式(32)计算基站的原有效用函数 (6) 该基站计划接入其他卫星,根据式(32)计算基站依次接入所有其他卫星的效用函数,若基站最小的新的效用函数小于用户原有效用函
数,则该基站接入对应的新的卫星,反之不改变接入关系(7) 循环结束:所有用户的aAoI不再改变 表 2 主要仿真参数
参数 值 参数 值 LEO卫星高度$ H_{\mathrm{s}} $ 600/700 km 中心频率$ f_{\mathrm{{c}}} $ 20 GHz 卫星带宽$ B_{\mathrm{s}} $ 10 MHz 地面带宽$ B_{\mathrm{t}} $ 4 MHz 卫星天线增益 43.3 dB 用户天线增益 3 dBi 地面噪声密度 –174 dBm/Hz 卫星噪声密度 –203 dBm/Hz 路径损耗指数$ \chi $ 2 距离$ D_{\mathrm{th}} $ 100 km 数据包大小 80 bit 时隙长度$ \tau $ 0.1 ms 用户功率$ {p_i} $ 25 mW 基站功率$ {P_{jk}} $ 4 W -
[1] 李平, 王璐, 聂欣, 等. “北斗”短报文通信现状与发展[J]. 中国航天, 2024(5): 44–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7742.2024.05.008.LI Ping, WANG Lu, NIE Xin, et al. The current situation and development of “Beidou” short message communication[J]. Aerospace China, 2024(5): 44–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7742.2024.05.008. [2] ZUO Yong, YUE Mingyang, YANG Huiyuan, et al. Integrating communication, sensing and computing in satellite internet of things: Challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2024, 31(3): 332–338. doi: 10.1109/MWC.019.2200574. [3] KAUL S, YATES R, and GRUTESER M. Real-time status: How often should one update?[C]. 2012 Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, Orlando, USA, 2012: 2731–2735. doi: 10.1109/INFCOM.2012.6195689. [4] YU Baoquan, CHEN Xiaoming, and CAI Yuemin. Age of information for the cellular internet of things: Challenges, key techniques, and future trends[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2022, 60(12): 20–26. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.008.2200148. [5] 于宝泉, 杨炜伟, 王权, 等. 无人机辅助通感一体化系统中的信息年龄分析优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 1996–2003. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231175.YU Baoquan, YANG Weiwei, WANG Quan, et al. Age of information analysis and optimization in unmanned aerial vehicles-assisted integrated sensing and communication systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 1996–2003. doi: 10.11999/JEIT231175. [6] 陈泳, 蔡跃明, 王萌. 认知物联网短包通信中双向中继系统的信息年龄分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(12): 4254–4261. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221377.CHEN Yong, CAI Yueming, and WANG Meng. Age of information for short-packet two-way relay system in cognitive IoT network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(12): 4254–4261. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221377. [7] 张洋译, 管新荣, 王权, 等. 智能反射面辅助短包通信中时效与能效间的折衷[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(2): 315–323. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240666.ZHANG Yangyi, GUAN Xinrong, WANG Quan, et al. Tradeoff between age of information and energy efficiency for intelligent reflecting surface assisted short packet communications[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(2): 315–323. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240666. [8] ZHU Zeyuan, GUAN Xinrong, YU Baoquan, et al. Adaptive NOMA/OMA in short packet-based sensor status update systems with imperfect CSI[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(3): 2923–2933. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3343420. [9] 李凯, 李峰, 杨伟铭, 等. 天基物联网概念辨析、能力目标及应用[J]. 无线电工程, 2024, 54(12): 2933–2941. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2024.12.021.LI Kai, LI Feng, YANG Weiming, et al. Concept discrimination, capability goals and applications of space-based internet of things[J]. Radio Engineering, 2024, 54(12): 2933–2941. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3106.2024.12.021. [10] CHEN Ying, ZHAO Jie, WU Yuan, et al. Multi-user task offloading in UAV-assisted LEO satellite edge computing: A game-theoretic approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2025, 24(1): 363–378. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3465591. [11] DING Xiaojin, REN Yumen, XIE Xuxu, et al. Improving user capacity of satellite internet of things via joint user grouping and multi-beam processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2024, 72(7): 3957–3969. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2024.3370445. [12] DAI Cuiqin, LI Shipeng, WU Jinsong, et al. Distributed user association with grouping in satellite–terrestrial integrated networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(12): 10244–10256. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3122939. [13] 吉用华, 张晨, 张更新. 面向高吞吐量的NB-IoT低轨卫星物联网资源调度[J]. 太赫兹科学与电子信息学报, 2024, 22(9): 933–943,951. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2024112.JI Yonghua, ZHANG Chen, and ZHANG Gengxin. NB-IoT low-orbit satellite IoT resource scheduling for high throughput[J]. Journal of Terahertz Science and Electronic Information Technology, 2024, 22(9): 933–943,951. doi: 10.11805/TKYDA2024112. [14] ZHEN Li, ZHANG Yukun, YU Keping, et al. Early collision detection for massive random access in satellite-based internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(5): 5184–5189. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3076015. [15] 赵海涛, 刘颖, 王琴, 等. 无人机-卫星辅助去蜂窝大规模MIMO系统中无人机部署和功率优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(5): 1282–1290. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240058.ZHAO Haitao, LIU Ying, WANG Qin, et al. Jointly optimized deployment and power for unmanned aerial vehicle - satellite assisted cell-free massive MIMO systems[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(5): 1282–1290. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240058. [16] WANG Qingming, LIANG Xiao, ZHANG Hua, et al. AoI-aware energy efficiency resource allocation for integrated satellite-terrestrial IOT networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2025, 9(1): 125–139. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2024.3425848. [17] GAO Zhixiang, LIU Aijun, HAN Chen, et al. Non-orthogonal multiple access-based average age of information minimization in LEO satellite-terrestrial integrated networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2022, 6(3): 1793–1805. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2022.3159559. [18] YANG Tao, JIAO Jian, WANG Ye, et al. Unequal timeliness protection random access scheme for satellite internet of things[C]. ICC 2023-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 2023: 4798–4803. doi: 10.1109/ICC45041.2023.10278831. [19] WEI Qing, SHI Jia, LI Zan, et al. AoI and Energy minimization for LEO satellite-terrestrial networks: A constrained multi-objective optimization approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(8): 12436–12448. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3553499. [20] GAO Zhixiang, LIU Aijun, XU Xin, et al. Sum data minimization in LEO satellite-UAV integrated multi-tier computing networks: A game-theoretic multiple access approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2024, 72(3): 1701–1715. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3332932. [21] LIN Xin, LIU Aijun, HAN Chen, et al. Intelligent adaptive MIMO transmission for nonstationary communication environment: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2025, 73(8): 5965–5979. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2025.3529263. [22] GAO Zhixiang, LIU Aijun, XU Xin, et al. Rate splitting-based nonorthogonal multiple access transmission in satellite–terrestrial relay networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 8859–8872. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3314002. [23] AN Kang, LIN Min, LIANG Tao, et al. Performance analysis of multi-antenna hybrid satellite-terrestrial relay networks in the presence of interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2015, 63(11): 4390–4404. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2015.2474865. [24] YATES R D and KAUL S K. The age of information: Real-time status updating by multiple sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2019, 65(3): 1807–1827. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2018.2871079. [25] ZWILLINGER D and JEFFREY A. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products[M]. 7th ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2007. [26] YU Baoquan, CAI Yueming, WU Dan, et al. Average age of information in short packet based machine type communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 10306–10319. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3004828. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
