Research on Collaborative Reasoning Framework and Algorithms of Cloud-Edge Large Models for Intelligent Auxiliary Diagnosis Systems
-
摘要: 大模型在辅助诊断方面潜力大,但本地算力限制和云端医疗数据隐私风险制约其落地。针对此现状,该文提出一种云边大模型协同推理框架与算法,核心为云边协同推理智能体,集成智能路由与动态语义脱敏能力,实现边缘侧(医院端)与云端(区域云)推理任务的动态分配。智能路由机制基于问题语义特征与历史决策数据优化路径,平衡模型使用成本与诊断精度;动态语义脱敏技术通过识别与分级脱敏策略,在保证隐私安全的同时实现数据安全传输与有效推理。实验表明,该框架在医学实体理解等任务中表现优异,诊断准确率与云端大模型相当,且显著降低模型使用成本,为医疗人工智能系统提供技术范式。未来将聚焦算网资源智能调度、属地化大模型结合检索增强生成(RAG)优化,以及医疗诊断评估指标扩展。Abstract:
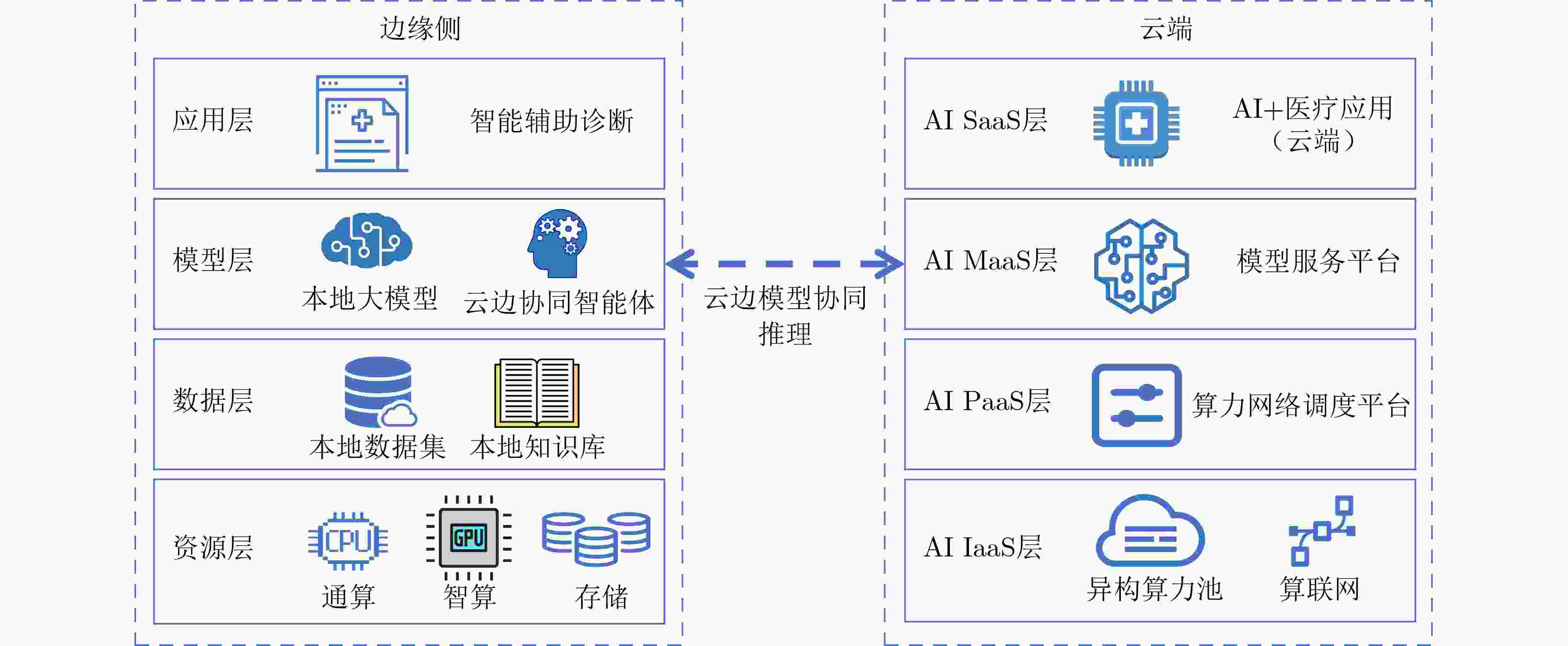
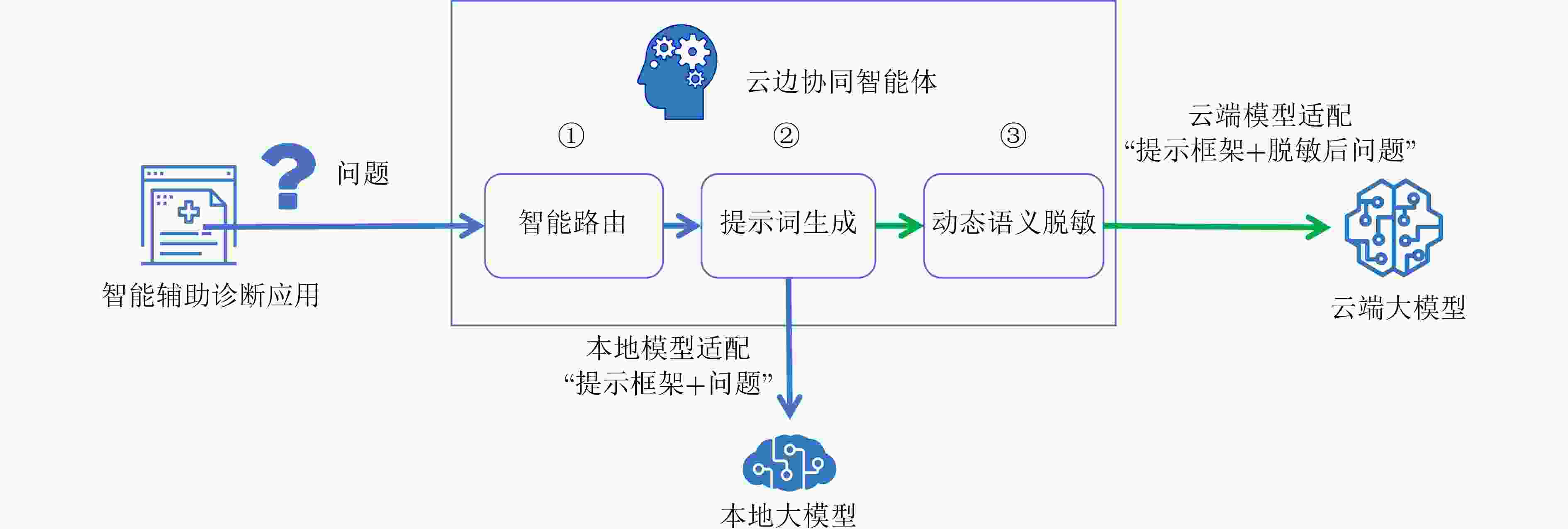
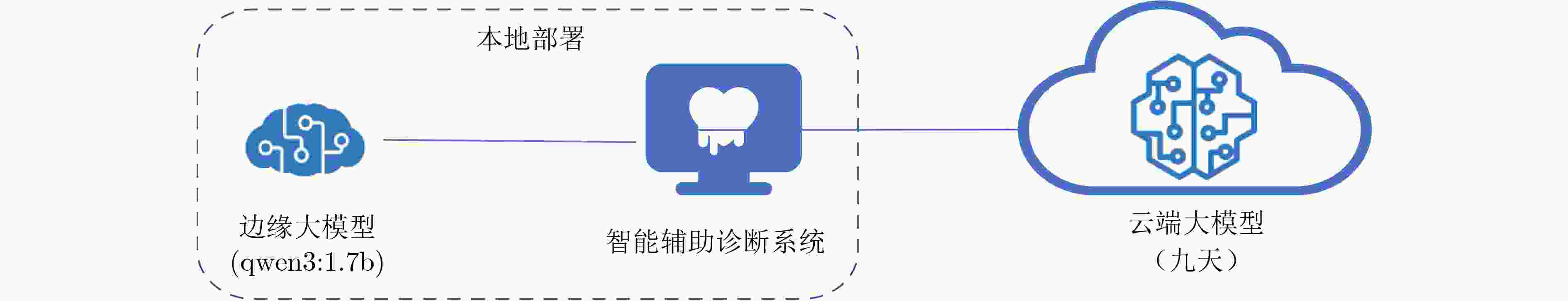
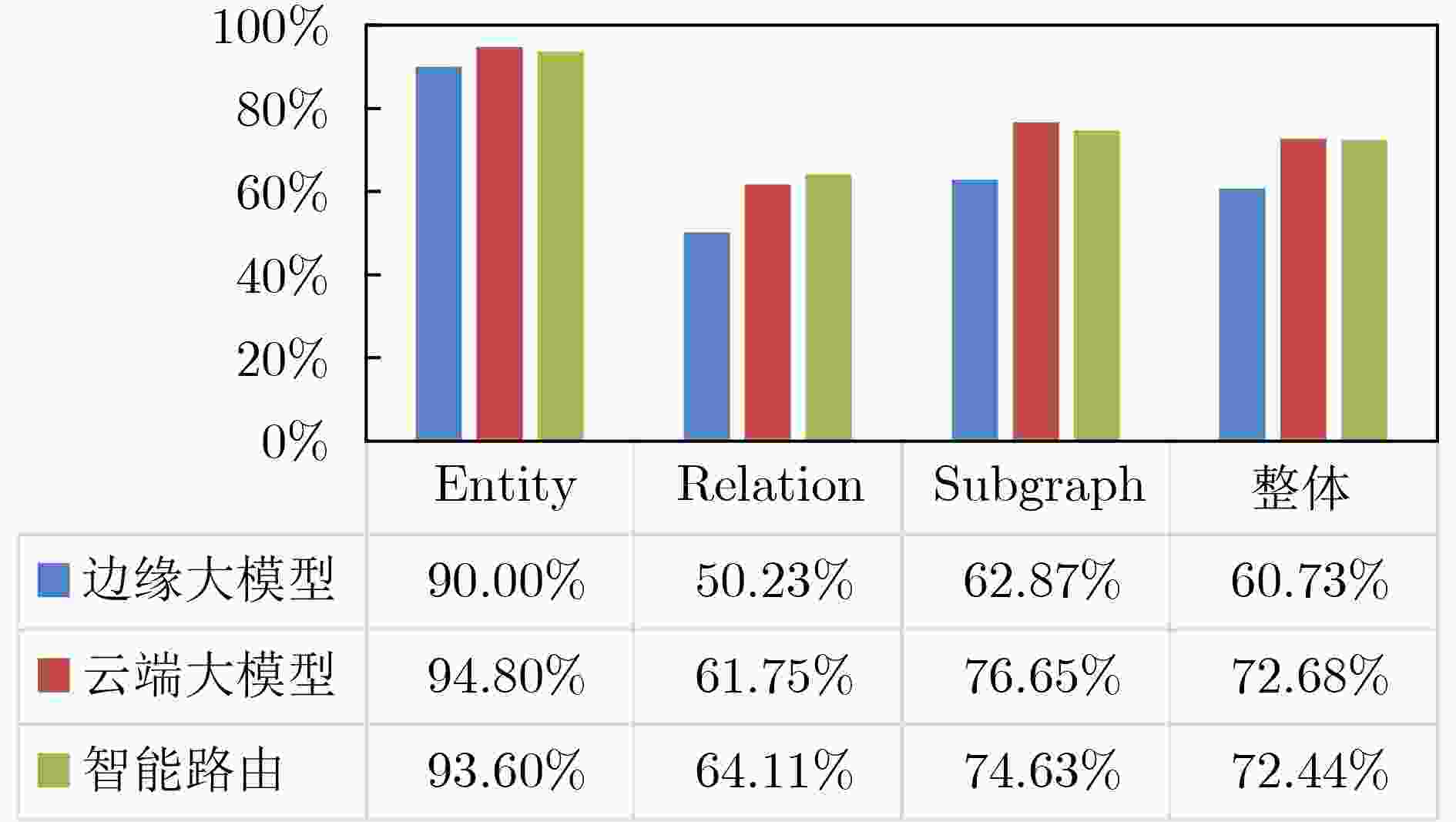
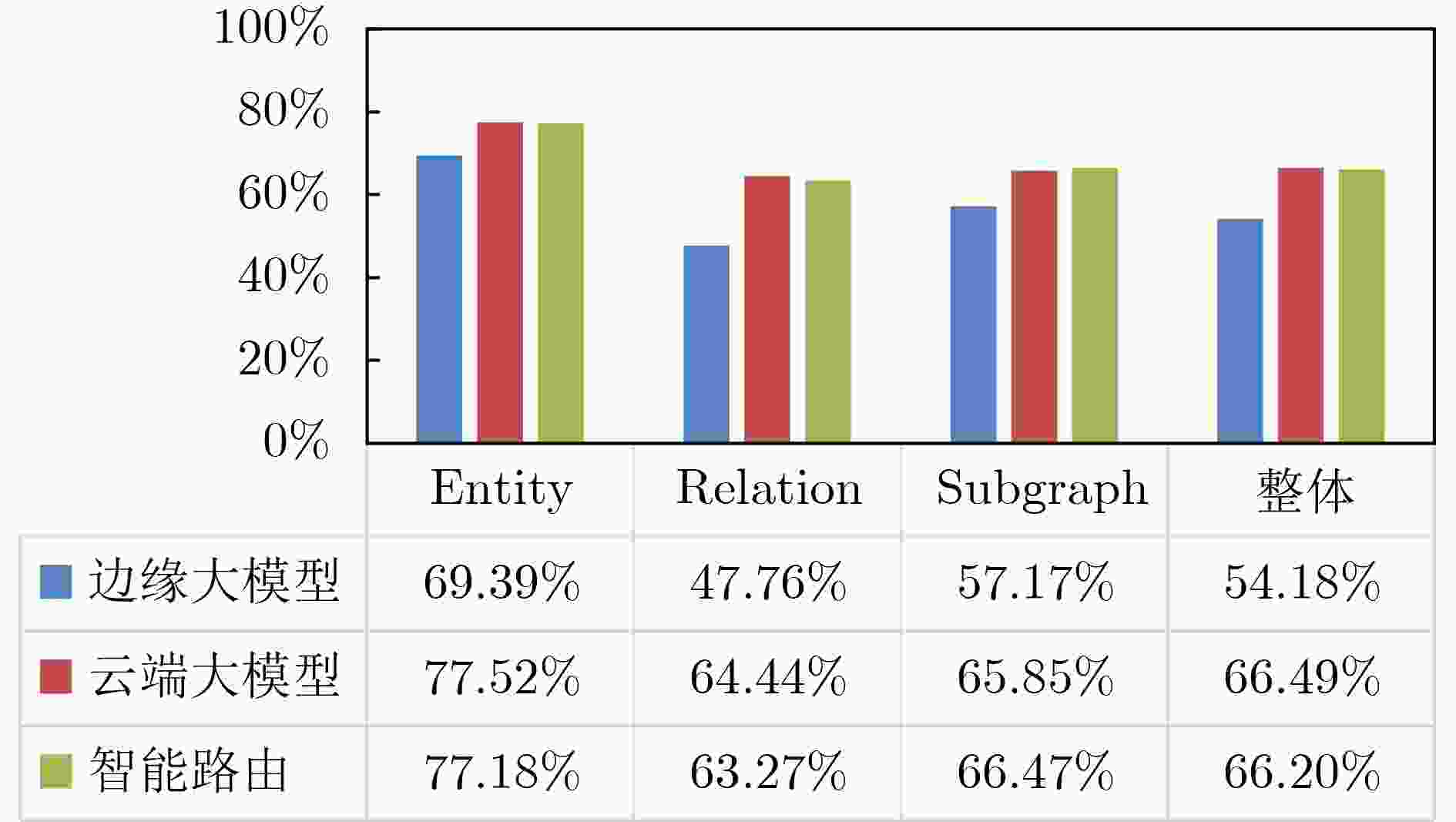
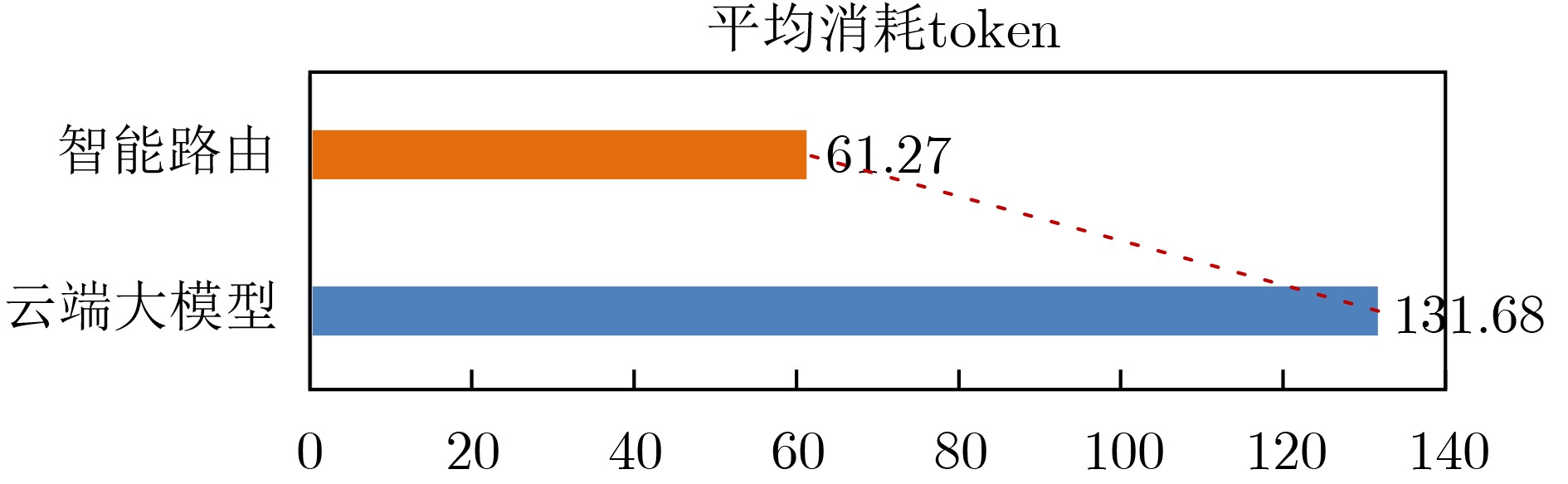
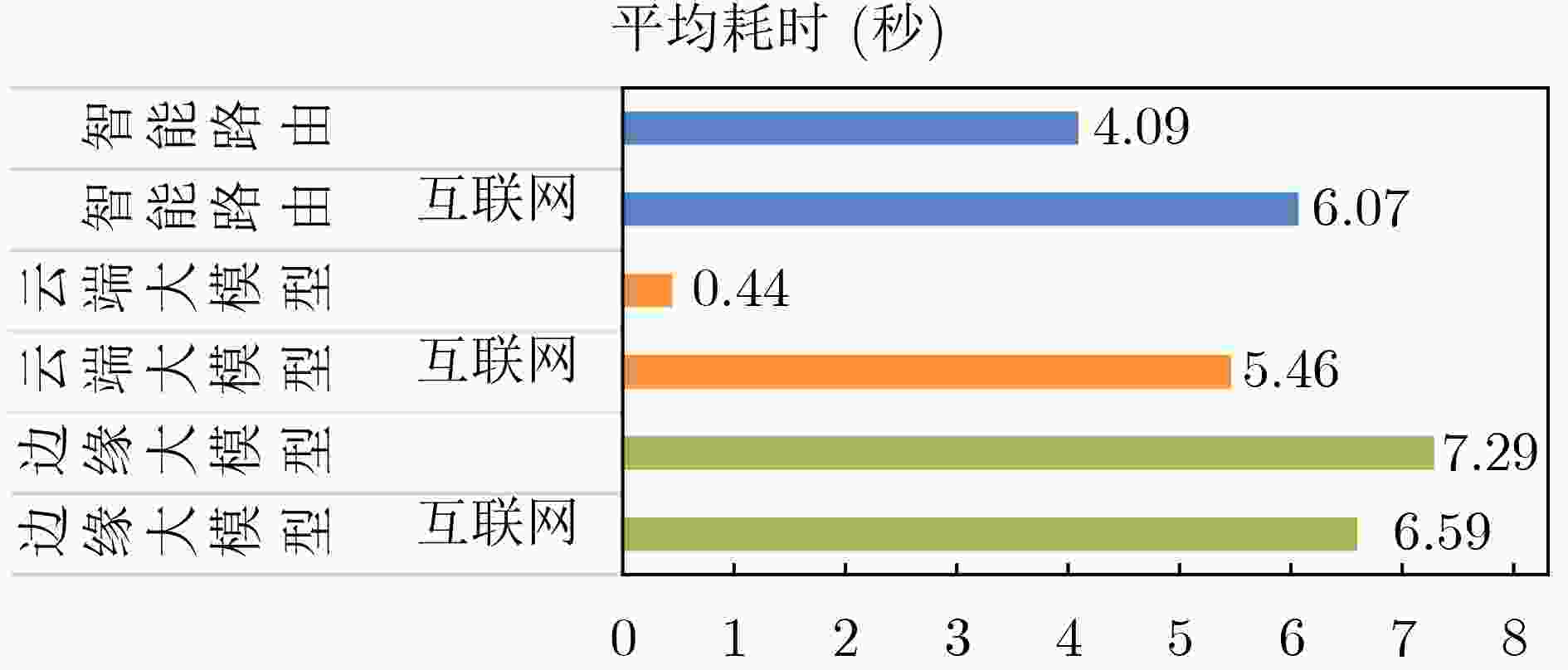
Objective The deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) in intelligent auxiliary diagnosis is constrained by limited computing resources for local hospital deployment and by privacy risks related to the transmission and storage of medical data in cloud environments. Low-parameter local LLMs show 20%–30% lower accuracy in medical knowledge question answering and 15%–25% reduced medical knowledge coverage compared with full-parameter cloud LLMs, whereas cloud-based systems face inherent data security concerns. To address these issues, a cloud-edge LLM collaborative reasoning framework and related algorithms are proposed for intelligent auxiliary diagnosis systems. The objective is to design a cloud-edge collaborative reasoning agent equipped with intelligent routing and dynamic semantic desensitization to enable adaptive task allocation between the edge (hospital side) and cloud (regional cloud). The framework is intended to achieve a balanced result across diagnostic accuracy, data privacy protection, and resource use efficiency, providing a practical technical path for the development of medical artificial intelligence systems. Methods The proposed framework adopts a layered architectural design composed of a four-tier progressive architecture on the edge side and a four-tier service-oriented architecture on the cloud side ( Fig. 1 ). The edge side consists of resource, data, model, and application layers, with the model layer hosting lightweight medical LLMs and the cloud-edge collaborative agent. The cloud side comprises AI IaaS, AI PaaS, AI MaaS, and AI SaaS layers, functioning as a center for computing power and advanced models. The collaborative reasoning process follows a structured workflow (Fig. 2 ), beginning with user input parsed by the agent to extract key clinical features, followed by reasoning node decision-making. Two core technologies support the agent: 1) Intelligent routing: This mechanism defaults to edge-side processing and dynamically selects the reasoning path (edge or cloud) through a dual-driven weight update strategy. It integrates semantic feature similarity computed through Chinese word segmentation and pre-trained medical language models and incorporates historical decision data, with an exponential moving average used to update feature libraries for adaptive optimization. 2) Dynamic semantic desensitization: Employing a three-stage architecture (sensitive entity recognition, semantic correlation analysis, and hierarchical desensitization decision-making), this technology identifies sensitive entities through a domain-enhanced Named Entity Recognition (NER) model, calculates entity sensitivity and desensitization priority, and applies a semantic similarity constraint to prevent excessive desensitization. Three desensitization strategies (complete deletion, general replacement, partial masking) are used based on entity sensitivity. Experimental validation is conducted with two open-source Chinese medical knowledge graphs (CMeKG and CPubMedKG) containing more than 2.7 million medical entities. The experimental environment (Fig. 3 ) deploys a qwen3:1.7b model on the edge and the Jiutian LLM on the cloud, with a 5,000-sample evaluation dataset divided into entity-level, relation-level, and subgraph-level questions. Performance is assessed with three metrics: answer accuracy, average token consumption, and average response time.Results and Discussions Experimental results show that the proposed framework achieves strong performance across the main evaluation dimensions. For answer accuracy, the intelligent routing mechanism attains 72.44% on CMeKG ( Fig. 4 ) and 66.20% on CPubMedKG (Fig. 5 ), which are higher than the edge-side LLM alone (60.73% and 54.18%) and close to the cloud LLM (72.68% and 66.49%). These results indicate that the framework maintains diagnostic consistency with cloud-based systems while taking advantage of edge-side capabilities. For resource use, the intelligent routing model reduces average token consumption to 61.27, representing 45.63% of the cloud LLM’s token usage (131.68) (Fig. 6 ), which supports substantial cost reduction. For response time, the edge-side LLM shows latency greater than 6 s because of limited computing power, whereas the cloud LLM reaches 0.44 s latency through dedicated line access (8% of the 5.46 s latency under internet access). The intelligent routing model produces average latency values between those of the edge and cloud LLMs under both access modes (Fig. 7 ), consistent with expected trade-offs. The framework also shows applicability across common medical scenarios (Table 1 ), including outpatient triage, chronic disease management, medical image analysis, intensive care, and health consultation, by combining local real-time processing with cloud-based deep reasoning. Limitations appear in emergency rescue settings with weak network conditions because of latency constraints and in rare disease diagnosis because of limited edge-side training samples and potential loss of specific features during desensitization. Overall, the results verify that the cloud-edge collaborative reasoning mechanism reduces computing resource overhead while preserving consistency in diagnostic results.Conclusions This study constructs a cloud-edge LLM collaborative reasoning framework for intelligent auxiliary diagnosis systems, addressing the challenges of limited local computing power and cloud data privacy risks. Through the integration of intelligent routing, prompt engineering adaptation, and dynamic semantic desensitization, the framework achieves balanced optimization of diagnostic accuracy, data security, and resource economy. Experimental validation shows that its accuracy is comparable to cloud-only LLMs while resource consumption is substantially reduced, providing a feasible technical path for medical intelligence development. Future work focuses on three directions: intelligent on-demand scheduling of computing and network resources to mitigate latency caused by edge-side computing constraints; collaborative deployment of localized LLMs with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to raise edge-side standalone accuracy above 90%; and expansion of diagnostic evaluation indicators to form a three-dimensional scenario–node–indicator system incorporating sensitivity, specificity, and AUC for clinical-oriented assessment. -
表 1 智能辅助诊断系统云边大模型协同推理框架适用的典型场景
适用场景 边缘侧任务 云端任务 框架优势 门诊分诊 症状初步分析,数据预处理,
高频问答复杂症状深度研判,多维度信息整合
(病史、区域疾病谱)提高分诊效率,结合本地与全局知识,
提升准确性慢病管理 生理数据实时采集,实时风险预警,
患者互动长期健康趋势分析,个性化健康
计划生成,多中心数据聚合实现全程个性化管理,减轻医护负担,
优化资源分配医学影像分析 影像质控,快速初筛,
关键区域定位,影像预处理复杂影像的精细分析、多模态数据
融合诊断,历史影像对比保障质控,提升诊断效率,优化专家资源 重症监护 实时生命体征监测,异常预警,
数据预处理多模态数据整合分析,复杂病情研判 实时响应,主动预警,减轻医护负担 健康咨询与导诊 基于本地知识库回答常见问题,
引导患者就医流程处理复杂查询,提供基于大规模知识的建议,
更新知识库快速响应常见需求,云端补充深度信息,
提升服务质量 -
[1] GUO Daya, YANG Dejian, ZHANG Haowei, et al. DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing reasoning capability in LLMs via reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.12948, 2025. [2] LIU Aixin, FENG Bei, XUE Bing, et al. DeepSeek-V3 technical report[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.19437, 2025. [3] ZHANG Ziheng, LIN Zhenxi, ZHENG Yefeng, et al. How much medical knowledge do LLMs have? An evaluation of medical knowledge coverage for LLMs[C]. The ACM on Web Conference 2025, Sydney, Australia, 2025: 5330–5341. doi: 10.1145/3696410.3714535. [4] VINEELA A, KASIVISWANATH N, and BINDU C S. Data integrity auditing scheme for preserving security in cloud based big data[C]. 2022 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 2022: 609–613. doi: 10.1109/ICICCS53718.2022.9788365. [5] ZHANG Sainan and SONG J. A chatbot based question and answer system for the auxiliary diagnosis of chronic diseases based on large language model[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 17118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67429-4. [6] MAO Yuqiang, XU Nan, WU Yanan, et al. Assessments of lung nodules by an artificial intelligence chatbot using longitudinal CT images[J]. Cell Reports Medicine, 2025, 6(3): 101988. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.101988. [7] PANAGOULIAS D P, PALAMIDAS F A, VIRVOU M, et al. Rule-augmented artificial intelligence-empowered systems for medical diagnosis using large language models[C]. 2023 IEEE 35th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Atlanta, USA, 2023: 70–77. doi: 10.1109/ICTAI59109.2023.00018. [8] YU Han, GUO Peikun, and SANO A. Zero-shot ECG diagnosis with large language models and retrieval-augmented generation[C]. Machine Learning Research, New Orleans, USA, 2023: 650–663. [9] 陈玉平, 刘波, 林伟伟, 等. 云边协同综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(3): 259–268. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.201000109.CHEN Yuping, LIU Bo, LIN Weiwei, et al. Survey of cloud-edge collaboration[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(3): 259–268. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.201000109. [10] LUO Zeliang, DING Xiaoxuan, HOU Ning, et al. A deep-learning-based collaborative edge-cloud telemedicine system for retinopathy of prematurity[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(1): 276. doi: 10.3390/s23010276. [11] LIU Yehui, XU Aobo, ZENG Hui, et al. Edge computing-based cloud platform for snakebite assisted diagnosis[C]. The 2023 8th International Conference on Biomedical Signal and Image Processing, Chengdu, China, 2023: 18–22. doi: 10.1145/3613307.3613311. [12] 王继彬, 张虎, 陈静, 等. 算力网络场景下的超算互联网建设探索与实践[J]. 邮电设计技术, 2024(2): 14–21. doi: 10.12045/j.issn.1007-3043.2024.02.003.WANG Jibin, ZHANG Hu, CHEN Jing, et al. Exploration and practice of supercomputing internet construction in computing power network scenarios[J]. Designing Techniques of Posts and Telecommunications, 2024(2): 14–21. doi: 10.12045/j.issn.1007-3043.2024.02.003. [13] 李逸博, 李小平, 王爽, 等. 面向算力网络的智慧调度综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(6): 1086–1103. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230196.LI Yibo, LI Xiaoping, WANG Shuang, et al. Survey on wise scheduling in computing power network[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(6): 1086–1103. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230196. [14] GAN Wensheng, WAN Shicheng, and YU P S. Model-as-a-service (MaaS): A survey[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Sorrento, Italy, 2023: 4636–4645. doi: 10.1109/BigData59044.2023.10386351. [15] 赵婵婵, 吕飞, 石宝, 等. 面向边缘智能的协同推理方法研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2025, 61(3): 1–20. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2406-0040.ZHAO Chanchan, LYU Fei, SHI Bao, et al. Review of collaborative inference methods for edge intelligence[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2025, 61(3): 1–20. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2406-0040. [16] 庄严, 张军雁, 卢若谷, 等. 基于医学大模型的智能问诊助手构建研究[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2025, 46(2): 126–133. doi: 10.12435/j.issn.2095-5227.24070108.ZHUANG Yan, ZHANG Junyan, LU Ruogu, et al. Constructing an intelligent consultation assistant system based on medical large language models[J]. Academic Journal of Chinese PLA Medical School, 2025, 46(2): 126–133. doi: 10.12435/j.issn.2095-5227.24070108. [17] ZHANG Xianwei, WU Peng, CAI Jiuming, et al. A contrastive study of Chinese text segmentation tools in marketing notification texts[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2019, 1302(2): 022010. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1302/2/022010. [18] DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. The 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, USA, 2019: 4171–4186. doi: 10.18653/v1/N19-1423. [19] ROMEO J, ABBASS M, SHERIF A, et al. Privacy-preserving machine learning for E-health applications: A survey[C]. 2024 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Computing and Machine Intelligence (ICMI), Mt Pleasant, USA, 2024: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICMI60790.2024.10586115. [20] 奥德玛, 杨云飞, 穗志方, 等. 中文医学知识图谱CMeKG构建初探[J]. 中文信息学报, 2019, 33(10): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2019.10.001.AO Dema, YANG Yunfei, SUI Zhifang, et al. Preliminary study on the construction of Chinese medical knowledge graph[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2019, 33(10): 1–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2019.10.001. [21] LI Bin, SUN Bin, LI Shutao, et al. Distinct but correct: Generating diversified and entity-revised medical response[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2024, 67(3): 132106. doi: 10.1007/s11432-021-3534-9. [22] 赵鹏, 李金翼, 王琛, 等. 人工智能能力与算力网络智慧运营研究与应用[J]. 计算机应用, 2025, 45(S1): 295–301.ZHAO Peng, LI Jinyi, WANG Chen, et al. Research and application on intelligent operation of artificial intelligence capability and computing power network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2025, 45(S1): 295–301. [23] REZAEI M R, FARD R S, PARKER J L, et al. Agentic medical knowledge graphs enhance medical question answering: Bridging the gap between LLMs and evolving medical knowledge[C]. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Suzhou, China, 2025: 12682–12701. doi: 10.18653/v1/2025.findings-emnlp.679. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
