A Focused Attention and Feature Compact Fusion Transformer for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Remote Sensing Images
-
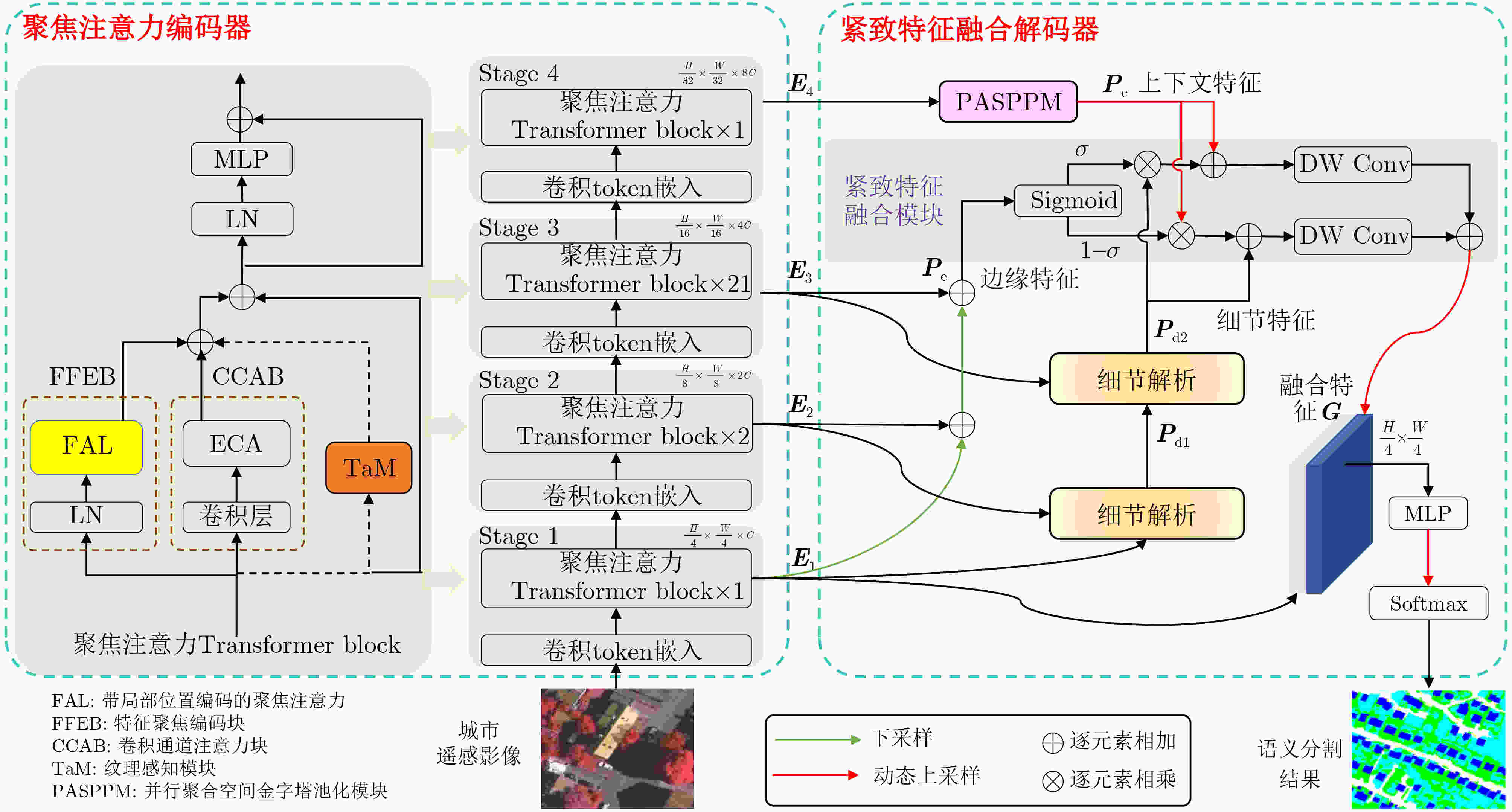
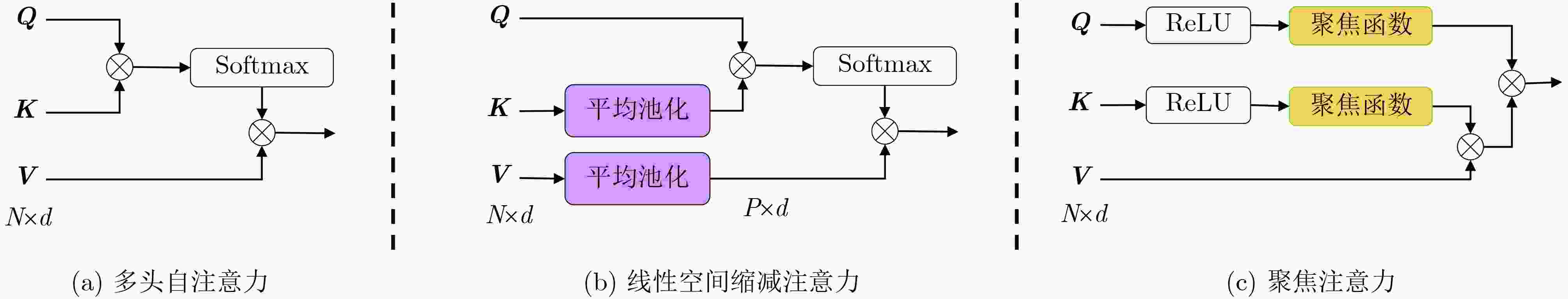
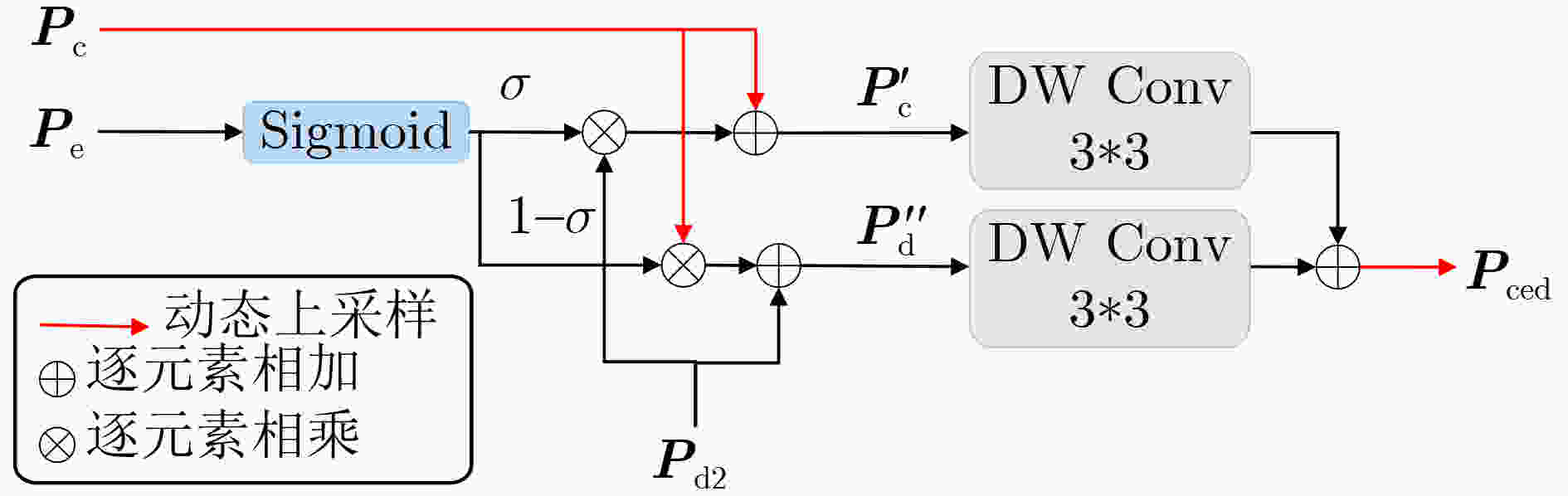
摘要: 在空天信息智能处理深度融合遥感数据获取与智能解译技术的推动下,城市遥感影像(URSI)语义分割逐渐发展成为连接空天信息与城市计算的关键研究方向。然而,与通用遥感影像相比,URSI中地物目标具有高度多样性和复杂性,表现为同类地物内部细节有差异、不同类地物之间特征相似易混淆,同时地物边界往往模糊且形态不规则,这些因素共同构成了其精细化分割面临的挑战。尽管基于Transformer的遥感影像语义分割方法取得了显著进展,但将其用于URSI时,不仅要考虑其对细节和边缘的提取能力,还需应对自注意力机制带来的计算复杂度等问题。为此,该文在编码器端引入聚焦注意力,以高效捕捉类内和类间关键特征;同时在解码器端对边缘特征进行紧致融合。针对URSI的独特特性,该文提出一种聚焦注意力与紧致特征融合Transformer语义分割模型(F3Former)。首先,在编码器端引入特征聚焦编码块(FFEB),通过建模Query-Key特征对的方向性,在保持较低线性复杂度的同时提升类内特征聚合与类间判别能力;在解码器端设计紧致特征融合模块(CFFM),结合深度卷积降低跨通道冗余计算,增强URSI边缘区域的细粒度分割表现。实验结果表明,该文提出的F3Former在Potsdam, Vaihingen和LoveDA数据集上的mIoU分别为88.33%, 81.32%和53.16%,计算成本减少到35.42 M Params, 48.02 GFLOPs和0.09 s测试时间,相较基线计算成本下降了28.91 M Params和194.86 GFLOPs,显著平衡了URSI语义分割的精度和速度。
-
关键词:
- 城市遥感影像 /
- 语义分割 /
- Transformer /
- 聚焦注意力 /
- 紧致特征融合
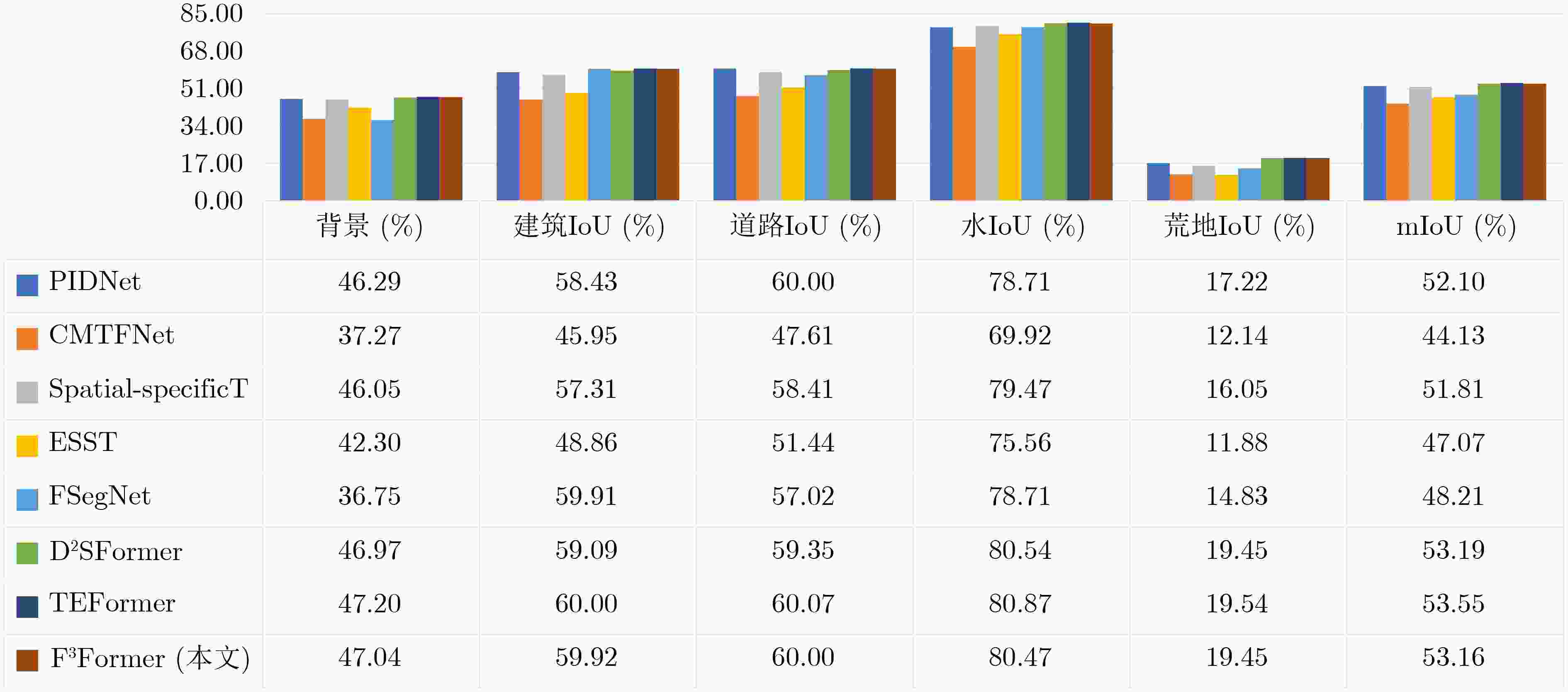
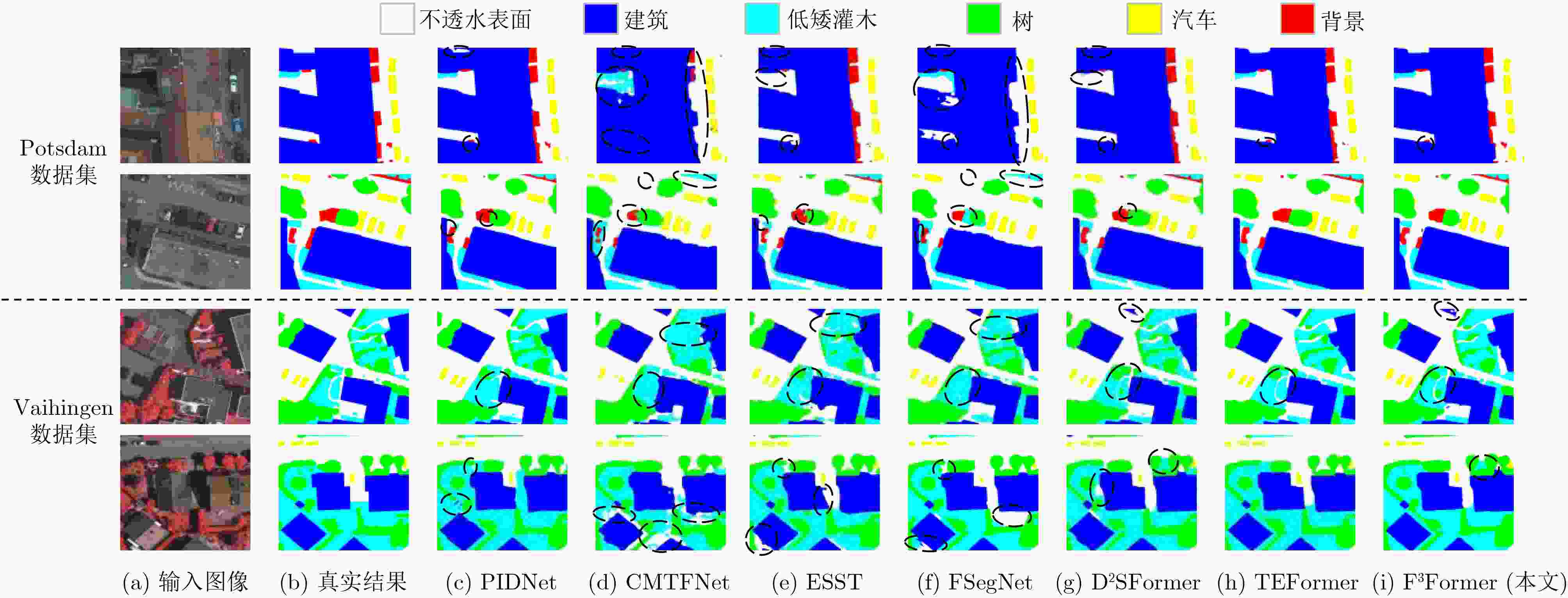
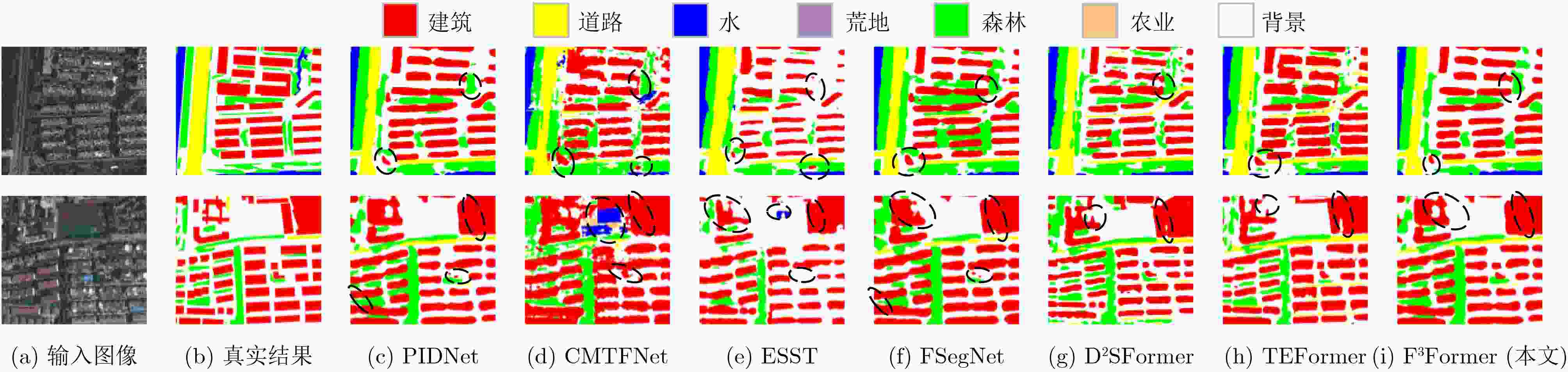
Abstract:Objective Driven by the growing integration of remote sensing data acquisition and intelligent interpretation technologies within aerospace information intelligent processing, semantic segmentation of Urban Remote Sensing Image (URSI) has emerged as a key research area connecting aerospace information and urban computing. However, compared to general Remote Sensing Image (RSI), URSI exhibits a high diversity and complex of geo-objects, characterized by fine-grained intra-class variations, inter-class similarities that cause confusion, as well as blurred and irregular object boundaries. These factors present difficulties for fine-grained segmentation. Despite their success in RSI semantic segmentation, applying Transformer-based methods to URSI requires a balance between capturing detailed features and boundaries, and managing the computational cost of self-attention. To address these issues, this paper introduces a focused attention mechanism in the encoder to efficiently capture discriminative intra- and inter-class features, while performing compact edge feature fusion in the decoder. Methods This paper proposes a Focused attention and Feature compact Fusion Transformer (F3Former). The encoder incorporates a dedicated Feature-Focused Encoding Block (FFEB). By leveraging the focused attention mechanism, it adjusts the directions of Query and Key features such that the features of the same class are pulled closer while those of different classes are repelled, thereby enhancing intra-class consistency and inter-class separability during feature representation. This process yields a compact and highly discriminative attention distribution, which amplifies semantically critical features while curbing computational overhead. To complement this design, the decoder employs a Compact Feature Fusion Module (CFFM), where Depth-Wise Convolution (DW Conv) is utilized to minimize redundant cross-channel computations. This design strengths the discriminative power of edge representations, improvs inference efficiency and deployment adaptability, and maintains segmentation accuracy. Results and Discussions F3Former demonstrates favorable performance on several benchmark datasets, alongside a lower computational complexity. On the Potsdam and Vaihingen benchmarks, it attained mIoU scores of 88.33%/81.32%, respectively, ranking second only to TEFormer with marginal differences in accuracy ( Table 1 ). Compared to other lightweight models including CMTFNet, ESST, and FSegNet, F3Former consistently delivered superior results in mIoU, mF1, and PA, demonstrating the efficacy of the proposed FFEB and CFFM modules in capturing complex URSI features. On the LoveDA dataset, it reached 53.16% mIoU and outperformed D2SFormer in several critical categories (Fig. 4 ). Moreover, F3Former strikes a favorable balance between accuracy and efficiency, reducing parameter count and FLOPs by over 30% compared to TEFormer, with only negligible degradation in accuracy (Table 2 ). Qualitative results further indicate clearer boundary delineation and improved recognition of small or occluded objects relative to other lightweight approaches (Fig. 5 andFig. 6 ). Ablation studies validate the critical role of both the Focused Attention (FA) mechanism and the Compact Feature Fusion Head (CFFHead) in achieving accuracy and efficiency gains (Tables 3 &Tables 4 ).Conclusions This work tackles key challenges in URSI semantic segmentation—including intra-class variability, inter-class ambiguity, and complex boundaries—by proposing F3Former. In the encoder, the FFEB improves intra-class aggregation and inter-class discrimination through directional feature modeling. In the decoder, the CFFM employs DW Conv to minimize redundancy and enhance boundary representations. With linear complexity, F3Former attains higher accuracy and stronger representational capacity while remaining efficient and deployment-friendly. Extensive experiments across multiple URSI benchmarks confirm its superior performance, highlighting its practicality for large-scale URSI applications. However, compared to existing State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) lightweight methods, the computational efficiency of the FFEB still has room for improvement. Future work is directed towards replacing Softmax with a more efficient operator to accelerate attention computation, maintaining accuracy while advancing efficient URSI semantic segmentation. Additionally, as the decoder’s channel interaction mechanism remains relatively limited, we plan to incorporate lightweight attention or pointwise convolution designs to further strengthen feature fusion. -
表 1 基于ISPRS 数据集与主流方法的精度对比(%)
方法 Potsdam数据集 Vaihingen数据集 mIoU mF1 PA mIoU mF1 PA PIDNet[26] 86.74 93.17 93.55 80.21 88.34 89.70 RingNet[33] 76.30 86.20 86.70 76.90 86.50 91.60 TAGNet[34] 82.54 90.31 88.99 80.02 88.72 90.16 CMTFNet[7] 83.57 90.93 90.77 77.95 87.42 89.24 Spatial-specificT[12] 87.61 93.26 93.97 80.08 88.74 90.36 ESST[23] 87.81 93.43 93.94 79.36 88.27 90.06 FSegNet[8] 80.52 88.21 91.57 75.15 84.46 90.90 D2SFormer[13] 87.84 94.02 94.63 81.24 88.99 90.55 TEFormer[14] 88.57 94.37 94.98 81.46 89.24 90.64 F3Former(本文) 88.33 94.25 94.86 81.32 89.20 90.57 注:粗体代表最优,下划线代表次优。 表 2 在3个数据集上的平均mIoU和计算成本对比
方法 mIoU (%) Params (M) FLOPs (G) 测试时间 (s) PIDNet[26] 73.02 (↓1.51) 37.31 (↑9.30) 34.46 (↑1.61) 0.09 (↑0.02) CMTFNet[7] 68.55 (↓5.98) 30.07 (↑2.06) 32.85 (-) 0.08 (-) Spatial-specificT[12] 73.17 (↓1.36) 58.96 (↑30.95) 81.91 (↑49.06) 0.20 (↑0.12) ESST[23] 71.41 (↓3.12) 28.01 (-) 60.67 (↑27.82) 0.09 (↑0.01) FSegNet[8] 67.96 (↓6.57) 33.28 (↑5.27) 56.04 (↑23.19) 0.09 (↑0.01) D2SFormer[13] 74.09 (↓0.44) 52.10 (↑24.09) 51.42 (↑18.57) 0.09 (↑0.02) TEFormer[14] 74.53 (-) 52.67 (↑24.66) 72.25 (↑42.40) 0.10 (↑0.03) F3Former(本文) 74.27 (↓0.26) 35.42 (↑7.41) 48.02 (↑15.17) 0.09 (↑0.02) 注:粗体代表最优。 表 3 聚焦函数中参数a的有效性(%)
a mIoU mF1 2 88.02 93.55 3 88.33 94.25 4 87.94 93.51 6 87.82 93.44 表 4 聚焦注意力的有效性
FAL 缩减block数 CFFM mIoU (%) mF1 (%) Params (M) FLOPs (G) - - - 88.74 94.45 52.67 72.25 - - √ 88.63 94.34 52.53 68.87 - √ - 88.15 93.63 34.70 54.26 - √ √ 87.55 93.28 34.34 48.82 √ - √ 88.57 94.38 47.73 68.18 √ √ - 88.11 93.61 36.56 53.54 √ √ √ 88.33 94.25 35.42 48.02 表 5 紧致特征融合解码器的有效性
编码器 解码器 mIoU (%) mF1 (%) Params (M) FLOPs (G) CSwinT UperHead 87.38 (↓1.36) 93.80 (↓0.65) 64.33 (↑28.91) 242.88 (↑194.86) CFFHead 87.57 (↓1.17) 93.94 (↓0.51) 36.23 (↑0.81) 50.96 (↑2.94) 双重注意力Transformer
编码器(D2SFormer)DBFAHead 87.84 (↓0.90) 94.02 (↓0.43) 52.10 (↑16.68) 51.42 (↑3.40) CFFHead 88.09 (↓0.65) 93.98 (↓0.47) 52.34 (↑16.92) 66.98 (↑18.96) 纹理感知Transformer
编码器(TEFormer)Eg3Head 88.74 (-) 94.45 (-) 52.67 (↑17.25) 72.25 (↑24.23) CFFHead 88.63 (↓0.11) 94.34 (↓0.11) 52.53 (↑17.11) 68.87 (↑20.85) 聚焦注意力编码器 CFFHead 88.33 (↓0.41) 94.25 (↓0.20) 35.42 (-) 48.02 (-) -
[1] 北京市大数据工作推进小组. 北京市“十四五”时期智慧城市发展行动纲要[EB/OL]. https://www.beijing.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengcefagui/202103/t20210323_2317136.html, 2021.Beijing Municipal Leading Group for Big Data. Action plan for the development of smart cities in beijing during the 14th five-year plan period[EB/OL]. https://www.beijing.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengcefagui/202103/t20210323_2317136.html, 2021. [2] KHAND K and SENAY G B. A web-based application for exploring potential changes in design peak flow of US urban areas driven by land cover change[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 3: 0037. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0037. [3] 李彦胜, 武康, 欧阳松, 等. 地学知识图谱引导的遥感影像语义分割[J]. 遥感学报, 2024, 28(2): 455–469. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20231110.LI Yansheng, WU Kang, OUYANG Song, et al. Geographic knowledge graph-guided remote sensing image semantic segmentation[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2024, 28(2): 455–469. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20231110. [4] TIAN Jiaqi, ZHU Xiaolin, SHEN Miaogen, et al. Effectiveness of spatiotemporal data fusion in fine-scale land surface phenology monitoring: A simulation study[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0118. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0118. [5] WANG Haoyu and LI Xiaofeng. Expanding horizons: U-Net enhancements for semantic segmentation, forecasting, and super-resolution in ocean remote sensing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 4: 0196. doi: 10.34133/remotesensing.0196. [6] HAN Kai, WANG Yunhe, CHEN Hanting, et al. A survey on vision transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(1): 87–110. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3152247. [7] WU Honglin, HUANG Peng, ZHANG Min, et al. CMTFNet: CNN and multiscale transformer fusion network for remote-sensing image semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 2004612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3314641. [8] LUO Wen, DENG Fei, JIANG Peifan, et al. FSegNet: A semantic segmentation network for high-resolution remote sensing images that balances efficiency and performance[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4501005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3398804. [9] HATAMIZADEH A, HEINRICH G, YIN Hongxu, et al. FasterViT: Fast vision transformers with hierarchical attention[C]. The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 2024. [10] FAN Lili, ZHOU Yu, LIU Hongmei, et al. Combining swin transformer with UNet for remote sensing image semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5530111. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3329152. [11] LI Xin, XU Feng, LI Linyang, et al. AAFormer: Attention-attended Transformer for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 5002805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3397851. [12] WU Xinjia, ZHANG Jing, LI Wensheng, et al. Spatial-specific transformer with involution for semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2023, 44(4): 1280–1307. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2023.2179897. [13] YAN Yi, LI Jiafeng, ZHANG Jing, et al. D2SFormer: Dual attention-dynamic bidirectional transformer for semantic segmentation of urban remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 12248–12262. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3566159. [14] ZHOU Guoyu, ZHANG Jing, YAN Yi, et al. TEFormer: Texture-aware and edge-guided Transformer for semantic segmentation of urban remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2026, 23: 8000605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2025.3639147. [15] PAN Zizheng, ZHUANG Bohan, HE Haoyu, et al. Less is more: Pay less attention in vision transformers[C]. The 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022: 2035–2043. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i2.20099. [16] FENG Zhanzhou and ZHANG Shiliang. Efficient vision transformer via token merger[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 4156–4169. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2023.3293763. [17] 金极栋, 卢宛萱, 孙显, 等. 分布采样对齐的遥感半监督要素提取框架及轻量化方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(5): 2187–2197. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240220.JIN Jidong, LU Wanxuan, SUN Xian, et al. Remote sensing semi-supervised feature extraction framework and lightweight method integrated with distribution-aligned sampling[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(5): 2187–2197. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240220. [18] YU Weihao, LUO Mi, ZHOU Pan, et al. MetaFormer is actually what you need for vision[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 10819–10829. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01055. [19] HAN Dongchen, YE Tianzhu, HAN Yizeng, et al. Agent attention: On the integration of softmax and linear attention[C]. 18th European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 2024: 124–140. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-72973-7_8. [20] YUN Seokju and RO Y. SHViT: Single-head vision transformer with memory efficient macro design[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2024: 5756–5767. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00550. [21] LIANG Youwei, GE Chongjian, TONG Zhan, et al. Not all patches are what you need: Expediting vision transformers via token reorganizations[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.07800, 2022. [22] WU Xinjian, ZENG Fanhu, WANG Xiudong, et al. PPT: Token pruning and pooling for efficient vision transformers[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2310.01812, 2023. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2310.01812. [23] YAN Yi, ZHANG Jing, WU Xinjia, et al. When zero-padding position encoding encounters linear space reduction attention: An efficient semantic segmentation transformer of remote sensing images[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 45(2): 609–633. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2023.2299276. [24] HAN Dongchen, PAN Xuran, HAN Yizeng, et al. FLatten transformer: Vision transformer using focused linear attention[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2023: 5938–5948. doi: 10.1109/ICCV51070.2023.00548. [25] HOU Jianlong, GUO Zhi, WU Youming, et al. BSNet: Dynamic hybrid gradient convolution based boundary-sensitive network for remote sensing image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5624022. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3176028. [26] XU Jiacong, XIONG Zixiang, and BHATTACHARYYA S P. PIDNet: A real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by PID controllers[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 19529–19539. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01871. [27] WANG Chi, ZHANG Yunke, CUI Miaomiao, et al. Active boundary loss for semantic segmentation[C]. The 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022: 2397–2405. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v36i2.20139. [28] MA Xiaohu, WANG Wuli, LI Wei, et al. An ultralightweight hybrid CNN based on redundancy removal for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5506212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3356524. [29] XU Guoan, LI Juncheng, GAO Guangwei, et al. Lightweight real-time semantic segmentation network with efficient transformer and CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(12): 15897–15906. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3248089. [30] HOSSEINPOUR H, SAMADZADEGAN F, and JAVAN F D. CMGFNet: A deep cross-modal gated fusion network for building extraction from very high-resolution remote sensing images[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 184: 96–115. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.12.007. [31] ROTTENSTEINER F, SOHN G, GERKE M, et al. ISPRS semantic labeling contest[J]. ISPRS: Leopoldshöhe, Germany, 2014, 1(4): 4. [32] WANG Junjue, ZHENG Zhuo, MA Ailong, et al. LoveDA: A remote sensing land-cover dataset for domain adaptation semantic segmentation[C]. The 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021. [33] 徐睿, 韩斌, 陈飞, 等. 基于环形卷积的遥感影像语义分割方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2025, 42(12): 3793–3798. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2025.03.0099.XU Rui, HAN Bin, CHEN Fei, et al. RingNet: Semantic segmentation of remote sensing images based on ring convolution[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2025, 42(12): 3793–3798. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2025.03.0099. [34] 王诗瑞, 杜康宁, 田澍, 等. 门限注意力引导的遥感图像语义分割网络[J]. 遥感信息, 2025, 40(3): 164–171. doi: 10.20091/j.cnki.1000-3177.2025.03.019.WANG Shirui, DU Kangning, TIAN Shu, et al. Threshold attention guided network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2025, 40(3): 164–171. doi: 10.20091/j.cnki.1000-3177.2025.03.019. [35] DONG Xiaoyi, BAO Jianmin, CHEN Dongdong, et al. CSWin transformer: A general vision transformer backbone with cross-shaped windows[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, USA, 2022: 12114–12124. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01181. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
