A Multi-scale Spatiotemporal Correlation Attention and State Space Modeling-based Approach for Precipitation Nowcasting
-
摘要: 降水临近预报,作为气象预测领域最具代表性的任务之一,通过利用雷达回波或降水序列来预测未来0-2小时的降水情况。当前的主流方法普遍存在局部细节丢失、条件信息挖掘不充分、对复杂地区适配性不足等问题。因此,该文提出一种基于扩散网络模型的PredUMamba模型。在该模型中,一方面,引入一种基于自适应蛇形扫描机制的Mamba块,不仅充分挖掘到关键的局部细节信息,且有效降低了计算复杂度;另一方面,设计一种多尺度时空相关注意力模型,在增强时空层次化特征交互能力的同时实现了条件信息的全面表示。更重要地,构建一个针对复杂地区降水临近预报任务的雷达回波数据集,即皖南山区雷达数据集,以验证模型对复杂地区突发性极端强降水的精准预报能力。此外,在领域内一些公开数据集上进一步开展了对比实验。实验结果表明,PredUMamba模型在上海雷达数据集和皖南山区雷达数据集上取得了最好的结果。同时,在SEVIR数据集上也取得了非常有竞争力的结果。Abstract:
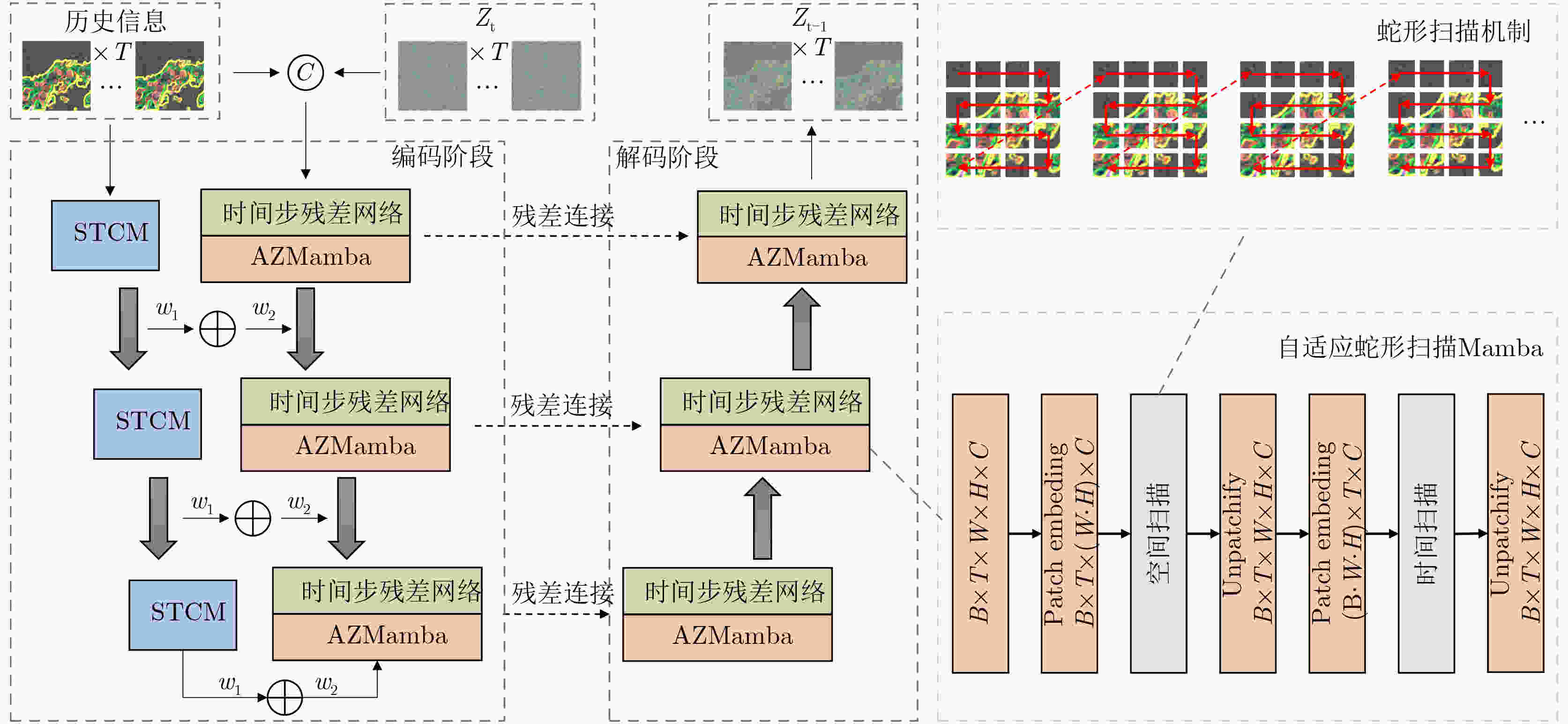
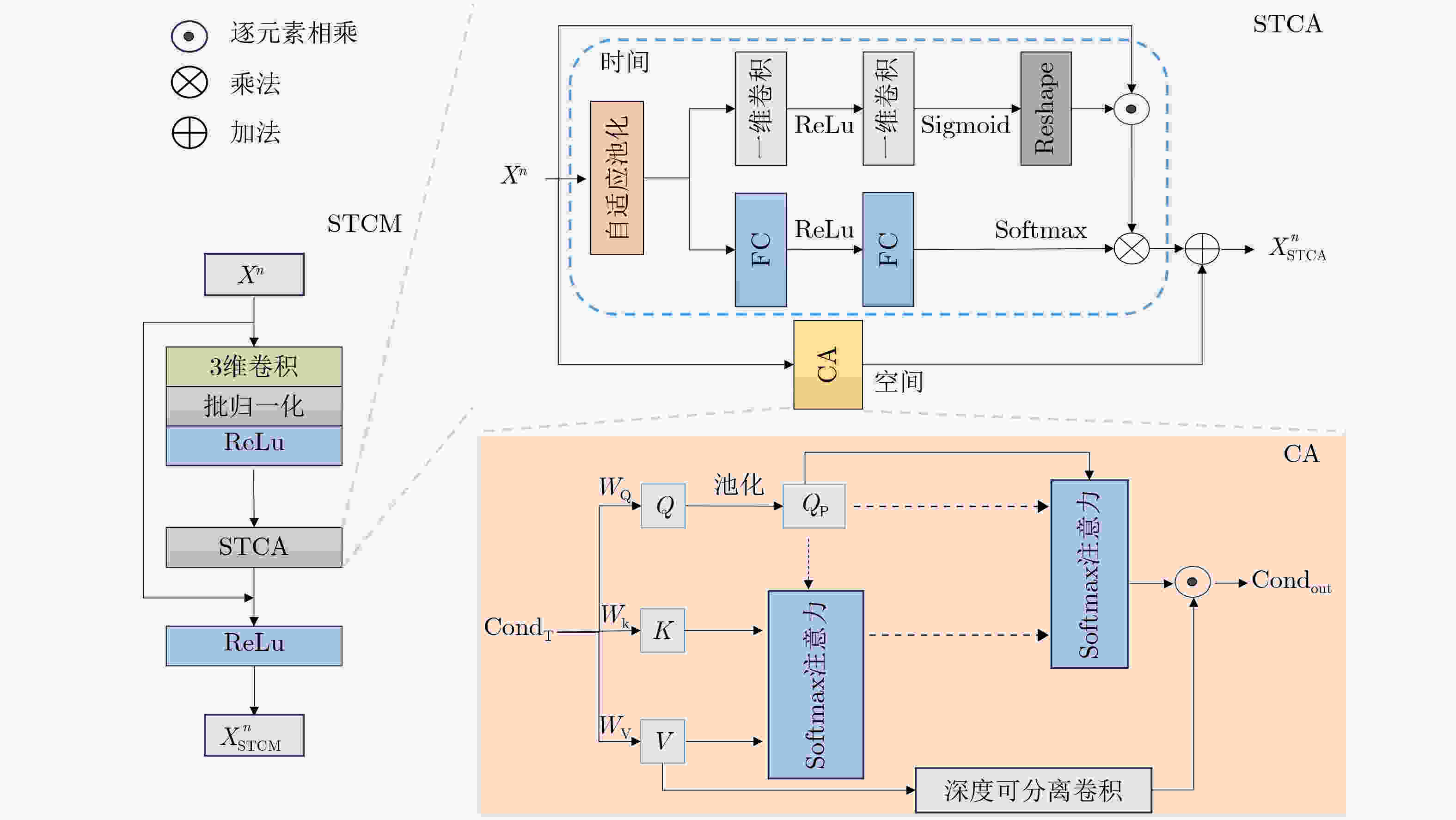
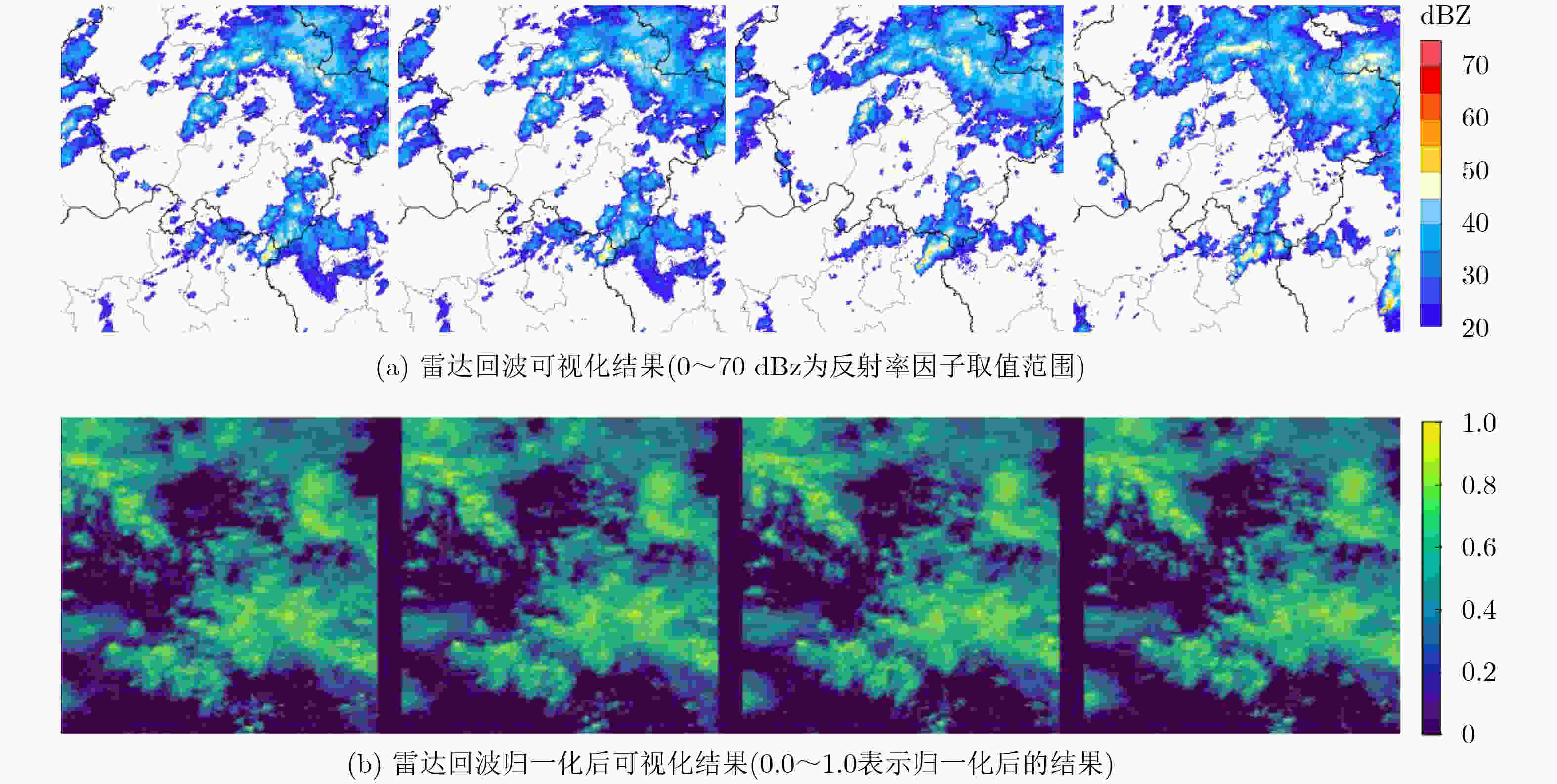
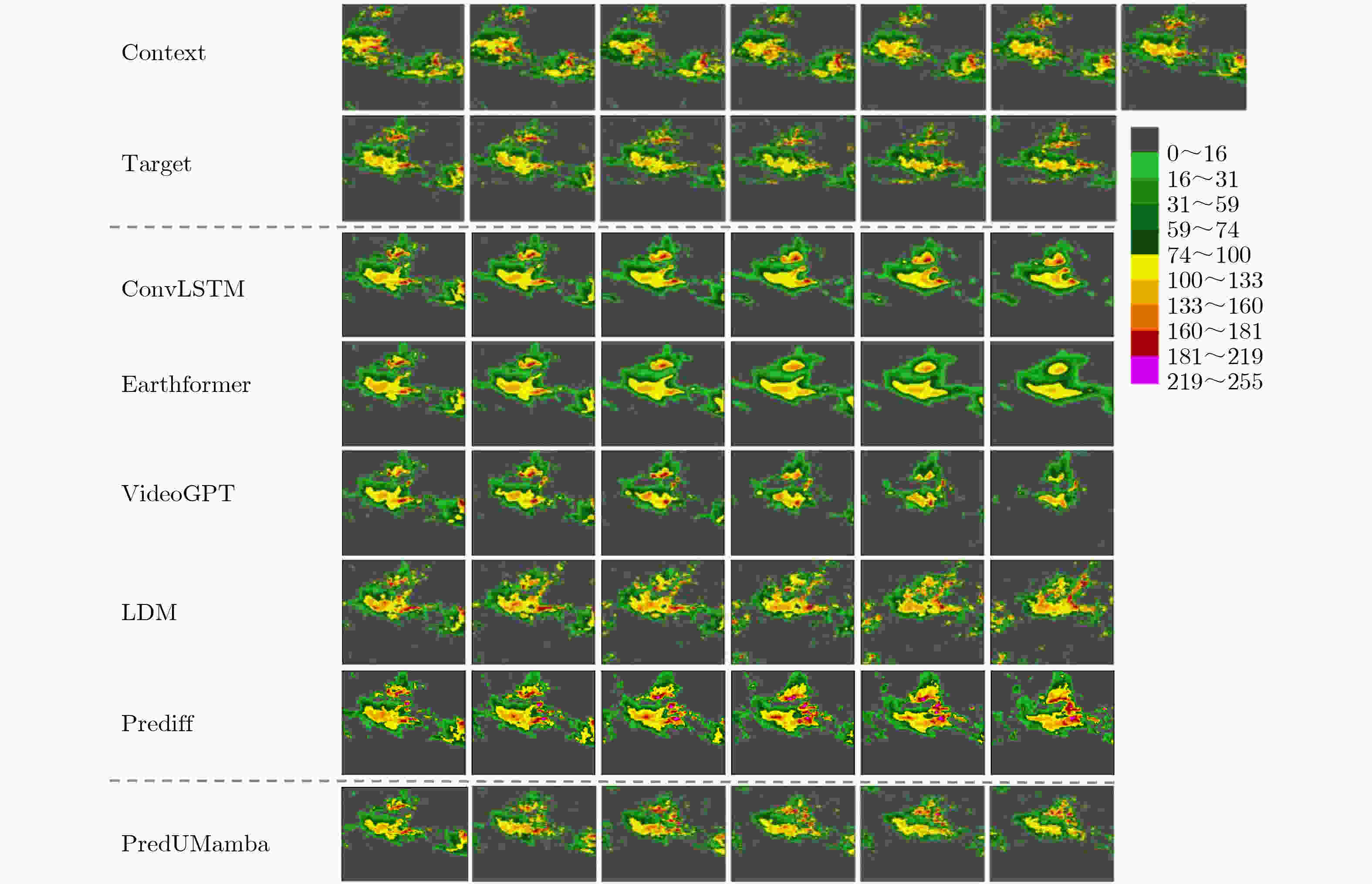
Objective Precipitation nowcasting is a representative task in meteorological forecasting. It uses radar echoes or precipitation sequences to predict precipitation distribution in the next 0–2 hours. It supports disaster warning and key decision-making and protects lives and property. Current mainstream methods show loss of local details, limited representation of conditional information, and weak adaptability in complex regions. This study proposes a PredUMamba model based on a diffusion model. The model introduces a Mamba block with an adaptive zigzag scanning mechanism that extracts key local detail information and reduces computational complexity. A multi-scale spatiotemporal correlation attention module is also designed to enhance interactions across spatiotemporal hierarchies and to achieve a comprehensive representation of conditional information. In addition, a radar echo dataset tailored for complex regions is constructed for the southern Anhui mountainous area to evaluate the model's ability to predict sudden and extreme rainfall. This work provides an intelligent solution and theoretical support for precipitation nowcasting. Methods The PredUMamba model adopts a two-stage diffusion network. In the first stage, a frame-by-frame Variational AutoEncoder (VAE) is trained to map precipitation data from pixel space to a low-dimensional latent space. In the second stage, a diffusion network is built on the encoded latent space. An adaptive zigzag Mamba module with a spatiotemporal alternating scanning strategy is proposed. Sequential scanning is performed within rows and turn-back scanning is performed between rows. This design captures detailed precipitation-field features while maintaining low computational complexity. A multi-scale spatiotemporal correlation attention module is further introduced on temporal and spatial scales. On the temporal scale, adaptive convolution kernels and attention-based convolution layers extract local and global information. On the spatial scale, a lightweight correlation attention mechanism aggregates spatial information and strengthens historical conditional information representation. A radar dataset for the southern Anhui mountainous area is constructed to evaluate model adaptability in complex terrain. Results and Discussions The adaptive zigzag Mamba module and multi-scale spatiotemporal correlation attention module strengthen the model's ability to capture intrinsic spatiotemporal dependencies. They extract conditional information more accurately and yield prediction results closer to real conditions. Experiments show that PredUMamba achieves the best performance across all indicators on the Southern Anhui Mountain Area and Shanghai radar datasets. On the SEVIR dataset, FVD, CSI_pool4, and CSI_pool16 outperform other methods, and CSI and CRPS achieve competitive results. Visualization results further show that PredUMamba does not produce temporal blurring ( Fig. 4 ). This indicates stronger stability and clear advantages in detail generation and motion-trend prediction. The model preserves edge details aligned with real precipitation fields and maintains accurate motion patterns.Conclusions This study proposes an innovative PredUMamba model based on a diffusion network architecture. Model performance is improved through a Mamba module with an adaptive zigzag scanning mechanism and a multi-scale spatiotemporal correlation attention module. The adaptive zigzag module captures fine-grained spatiotemporal features and reduces computational complexity. The multi-scale attention module strengthens historical conditional information extraction through temporal dual-branch processing and a lightweight spatial correlation mechanism, enabling joint representation of local and global features. A radar dataset for the southern Anhui mountainous area is also constructed to validate model applicability in complex terrain. The dataset covers precipitation under various terrain conditions and supports extreme rainfall prediction. Comparative experiments on the constructed dataset and on public datasets show that PredUMamba achieves the best results on the southern Anhui mountainous area and Shanghai datasets. On the SEVIR dataset, FVD, CSI_pool4, and CSI_pool16 outperform other methods, and CRPS and CSI achieve competitive results. As this work focuses on a data-driven forecasting approach, future research will integrate physical-condition constraints to improve interpretability and enhance prediction accuracy for small- and medium-scale convective systems. -
Key words:
- Precipitation nowcasting /
- Diffusion model /
- State-space model /
- Radar echo /
- Multi-scale
-
表 2 PredUMamba和其他方法在皖南山区雷达数据集上对比实验结果
模型 参数(M) FVD POD CSI CSI-pool4 CSI-pool16 ConvLSTM[22] 14.0 / 0.369 0.288 0.320 0.369 PredRNN[29] 46.6 / 0.420 0.302 0.333 0.373 Earthformer[16] 15.1 780.1 0.414 0.311 0.345 0.381 VideoGPT[30] 99.6 446.2 0.398 0.278 0.330 0.440 LDM[12] 438.6 407.3 0.426 0.306 0.343 0.446 Prediff[8] 220.5 246.0 0.438 0.321 0.368 0.498 本文PredUMamba 180.0 236.6 0.456 0.327 0.384 0.517 表 1 PredUMamba和其他方法在SEVIR数据集上对比实验结果
模型 参数(M) FVD CRPS CSI CSI-pool4 CSI-pool16 ConvLSTM [22] 14.0 659.7 0.033 0.400 0.445 0.513 PredRNN [29] 46.6 663.5 0.030 0.407 0.449 0.503 Earthformer [16] 15.1 690.7 0.030 0.410 0.456 0.500 VideoGPT [30] 99.6 261.6 0.038 0.365 0.434 0.579 LDM [12] 438.6 133.0 0.028 0.358 0.402 0.552 Prediff [8] 220.5 120.0 0.024 0.402 0.462 0.624 本文PredUMamba 180.0 85.7 0.025 0.408 0.480 0.646 表 3 PredUMamba和其他方法在上海雷达数据集上对比实验结果
模型 参数(M) FVD POD CSI CSI-pool4 CSI-pool16 ConvLSTM[22] 14.0 / 0.277 0.187 0.214 0.243 PredRNN[29] 46.6 / 0.280 0.201 0.221 0.248 Earthformer[16] 15.1 663.1 0.298 0.213 0.236 0.259 VideoGPT[30] 99.6 488.6 0.266 0.181 0.215 0.287 LDM [12] 438.6 349.2 0.243 0.169 0.201 0.280 Prediff[8] 220.5 185.7 0.304 0.211 0.243 0.327 本文PredUMamba 180.0 129.3 0.313 0.228 0.268 0.361 表 4 PredUMamba不同模块在SEVIR数据集上的消融实验
Mamba模块 STCA 参数(M) FVD CRPS CSI CSI-pool4 CSI-pool16 ViM AZM × × × 438.6 133.0 0.028 0.358 0.402 0.552 √ × × 168.1 103.0 0.026 0.381 0.451 0.621 × √ × 172.0 116.0 0.026 0.401 0.462 0.628 × × √ 450.5 114.2 0.027 0.361 0.423 0.581 √ × √ 177.0 94.8 0.026 0.389 0.467 0.616 × √ √ 180.0 85.0 0.025 0.408 0.480 0.646 -
[1] 李海, 冯开泓, 杨文恒, 等. 机载双极化气象雷达多种降水粒子回波仿真方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(8): 2945–2954. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220830.LI Hai, FENG Kaihong, YANG Wenheng, et al. Study on simulation method of precipitation particle echo of airborne dual-polarization weather radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(8): 2945–2954. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220830. [2] 周康辉, 郑永光, 杨波, 等. 强对流天气客观临近预报技术进展和展望[J]. 气象学报, 2025, 83(3): 798–812. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2025.20240106.ZHOU Kanghui, ZHENG Yongguang, YANG Bo, et al. Objective nowcasting of severe convective weather: Technological progress and outlook[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2025, 83(3): 798–812. doi: 10.11676/qxxb2025.20240106. [3] 朱平, 李生辰, 王振会, 等. 青藏高原东部暴雨云团局地强降水响应特征[J]. 遥感学报, 2014, 18(2): 405–431. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20143069.ZHU Ping, LI Shengchen, WANG Zhenhui, et al. Characteristics of rainstorm cloud clusters to local heavy precipitation over the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2014, 18(2): 405–431. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20143069. [4] 刘西川, 宋堃, 高太长, 等. 复杂大气条件对微波传播衰减的影响研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(1): 181–188. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170253.LIU Xichuan, SONG Kun, GAO Taichang, et al. Research on the effect of complex atmospheric condition on microwave propagation attenuation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(1): 181–188. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170253. [5] BAILEY L P, CLARE M A, HUNT J E, et al. Highly variable deep-sea currents over tidal and seasonal timescales[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2024, 17(8): 787–794. doi: 10.1038/s41561-024-01494-2. [6] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canda, 2014: 2672–2680. [7] VAN DEN OORD A, KALCHBRENNER N, VINVALS O, et al. Conditional image generation with PixelCNN decoders[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 4797–4805. [8] GAO Zhihan, SHI Xingjian, HAN Boran, et al. PreDiff: Precipitation nowcasting with latent diffusion models[C]. The 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2023: 3439. [9] GONG Junchao, BAI Lei, YE Peng, et al. CasCast: Skillful high-resolution precipitation nowcasting via cascaded modelling[C]. The 41st International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2024: 633. [10] LING Xudong, LI Chaorong, QIN Fengqing, et al. RNDiff: Rainfall nowcasting with condition diffusion model[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2025, 160: 111193. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2024.111193. [11] 李云, 杨松林, 邢智童, 等. 多尺度特征注意力网络下的卫星信号识别研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(6): 1792–1802. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250126.LI Yun, YANG Songlin, XING Zhitong, et al. Study on satellite signal recognition with multi-scale feature attention network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(6): 1792–1802. doi: 10.11999/JEIT250126. [12] ROMBACH R, BLATTMANN A, LORENZ D, et al. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA 2022: 10684–10695. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01042. [13] CHEN Lei, CAO Yuan, MA Leiming, et al. A deep learning-based methodology for precipitation nowcasting with radar[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2020, 7(2): e2019EA000812. doi: 10.1029/2019EA000812. [14] VEILLETTE M S, SAMSI S, and MATTIOLI C J. SEVIR: A storm event imagery dataset for deep learning applications in radar and satellite meteorology[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 1846. [15] PALMER T N, SHUTTS G J, HAGEDORN R, et al. Representing model uncertainty in weather and climate prediction[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2005, 33: 163–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.33.092203.122552. [16] GAO Zhihan, SHI Xingjian, WANG Hao, et al. Earthformer: Exploring space-time transformers for earth system forecasting[C]. The 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 25390–25403. [17] TANG Yujin, QI Lu, XIE Fei, et al. Video prediction transformers without recurrence or convolution[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.04733, 2024. [18] ZHANG Yuchen, LONG Mingsheng, CHEN Kaiyuan, et al. Skilful nowcasting of extreme precipitation with NowcastNet[J]. Nature, 2023, 619(7970): 526–532. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06184-4. [19] LEINONEN J, HAMANN U, NERINI D, et al. Latent diffusion models for generative precipitation nowcasting with accurate uncertainty quantification[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.12891, 2023. [20] GAO Zhangyang, TAN Cheng, WU Lirong, et al. SimVP: Simpler yet better video prediction[C]. The 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 3170–3180. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00317. [21] SHI Xingjian, GAO Zhihan, LAUSEN L, et al. Deep learning for precipitation nowcasting: A benchmark and a new model[C]. The 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017. [22] SHI Xingjian, CHEN Zhourong, WANG Hao, et al. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[C]. The 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 802–810. [23] ZHU Lianghui, LIAO Bencheng, ZHANG Qian, et al. Vision mamba: Efficient visual representation learning with bidirectional state space model[C]. The 41st International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2024: 2584. [24] CHEN Hongruixuan, SONG Jian, HAN Chengxi, et al. ChangeMamba: Remote sensing change detection with spatiotemporal state space model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4409720. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3417253. [25] XU Xiongxiao, CHEN Canyu, LIANG Yueqing, et al. SST: Multi-scale hybrid mamba-transformer experts for time series forecasting[C]. The 34th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Seoul Republic of Korea, 2024: 3655–3665. [26] KINGMA D P, WELLING M. Auto-encoding variational bayes[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014. [27] LARVOR G and BERTHOMIER L. MeteoNet: An open reference weather dataset for AI by Météo-France[C]. The 101st Annual AMS Meeting 2021, Online, 2021. [28] LOSHCHILOV I and HUTTER F. Fixing weight decay regularization in Adam[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101, 2017. [29] WANG Yunbo, WU Haixu, ZHANG Jianjin, et al. PredRNN: A recurrent neural network for spatiotemporal predictive learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(2): 2208–2225. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3165153. [30] YAN W, ZHANG Yunzhi, ABBEEL P, et al. VideoGPT: Video generation using VQ-VAE and transformers[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.10157, 2021. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
