Spatio-Temporal Constrained Refined Nearest Neighbor Fingerprinting Localization
-
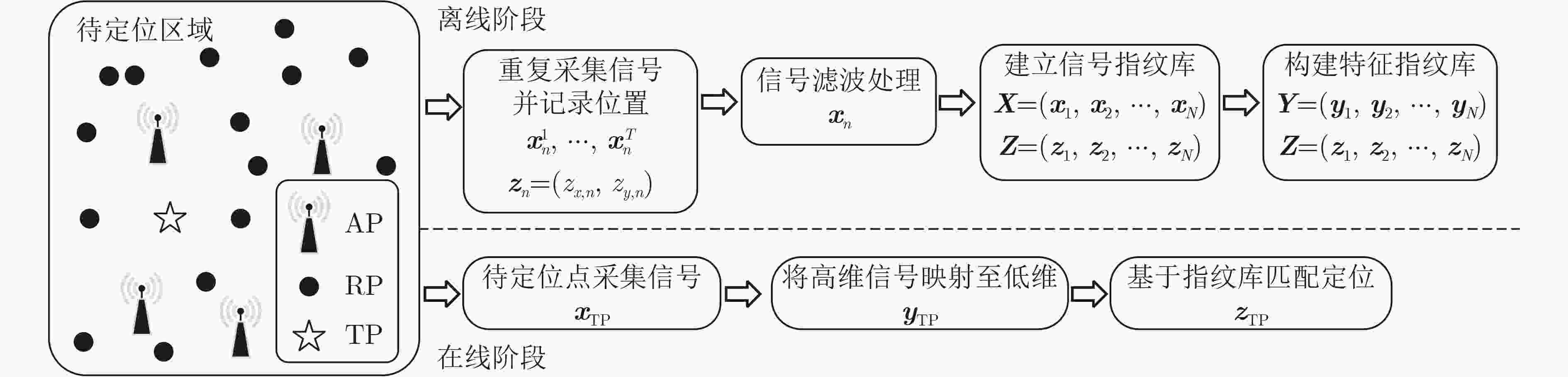
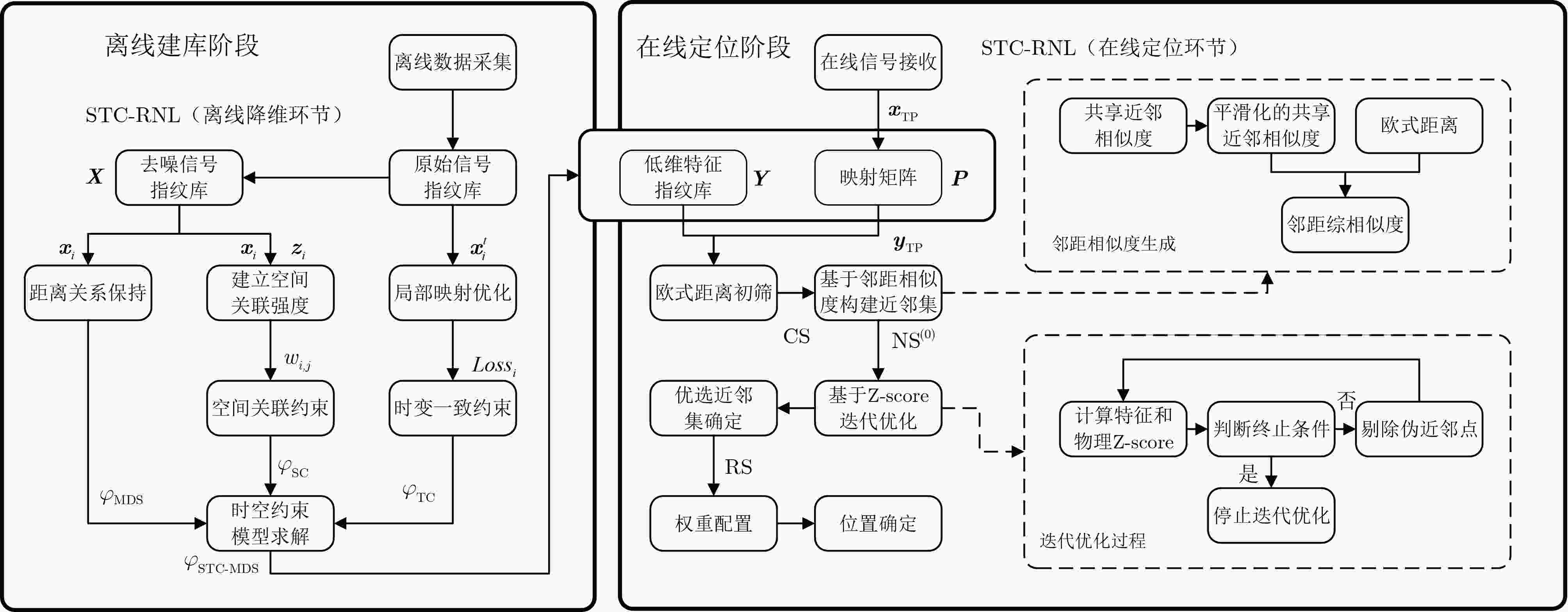
摘要: 针对室内指纹定位中降维技术导致的信号与物理空间的几何关联弱化、信号时变引起的在线映射偏差以及定位过程中伪近邻点干扰等问题,该文提出时空约束下优选近邻指纹定位算法。在离线降维建库阶段,引入空间关联约束,依据参考点间的物理距离调节低维特征空间结构,加强低维特征与物理坐标的耦合关系;同时设计时变一致约束,促使同一位置不同时刻的指纹在映射后的低维空间中保持聚集,以提升高维信号到低维特征的映射稳定性。在在线定位阶段,融合共享近邻相似度和欧氏距离生成邻距相似度,据此构建近邻集,进而采用基于Z-score阈值的迭代优化策略,分析内部相似度分布并剔除伪近邻点,保障近邻质量和定位精度。实验结果表明,所提算法在实测数据集上平均定位误差较基准方法降低至少12.42%,在公开数据集上降低至少7.08%,且在相同误差范围内的累计概率更高。Abstract:
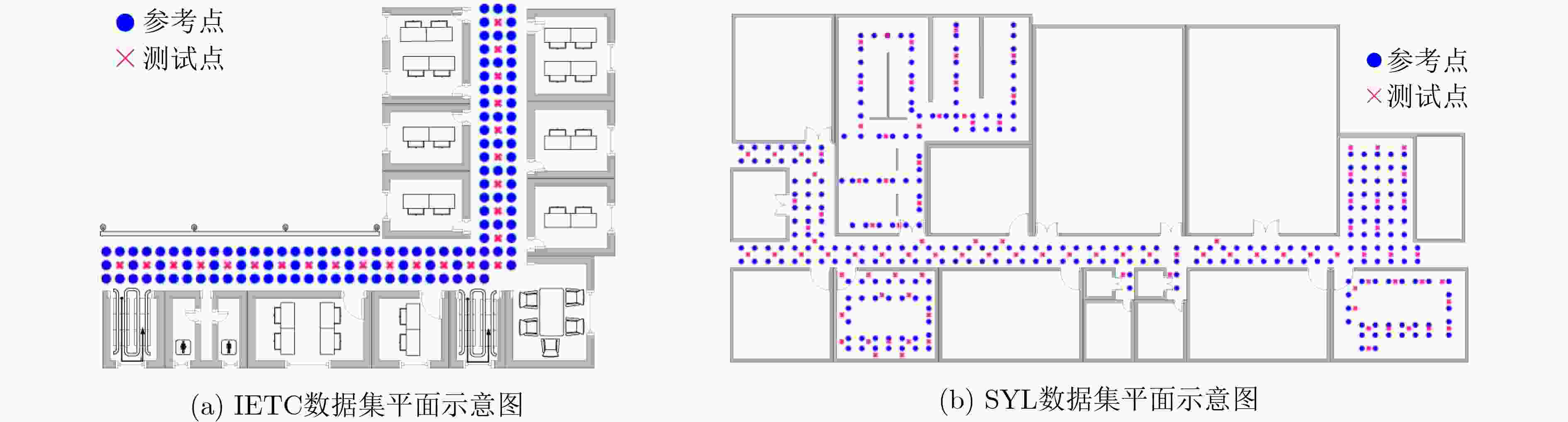
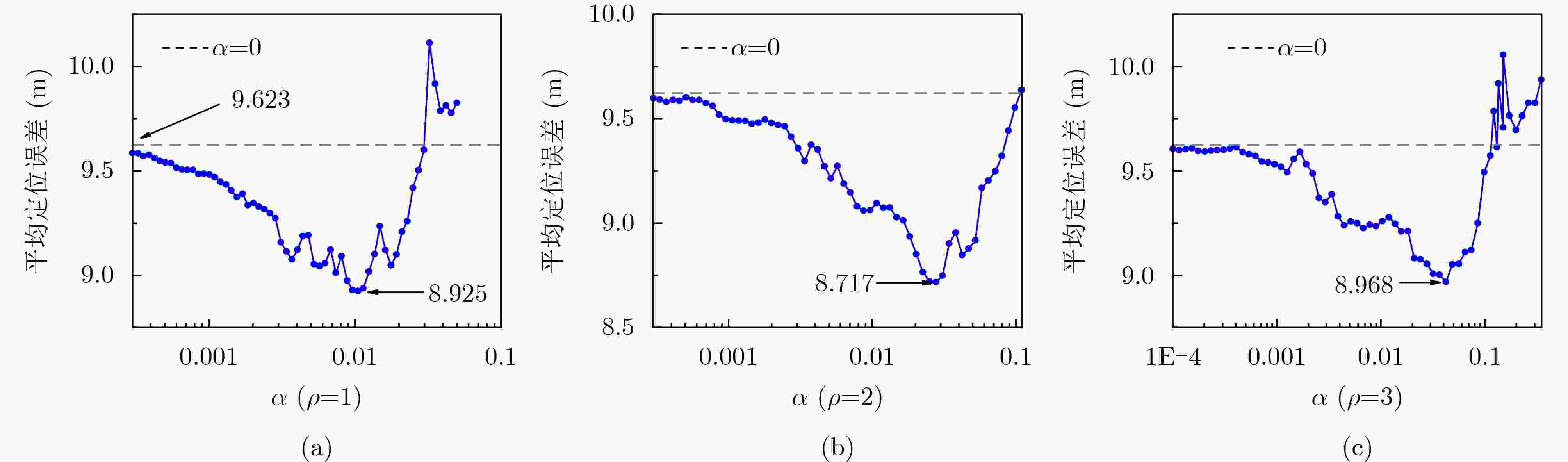
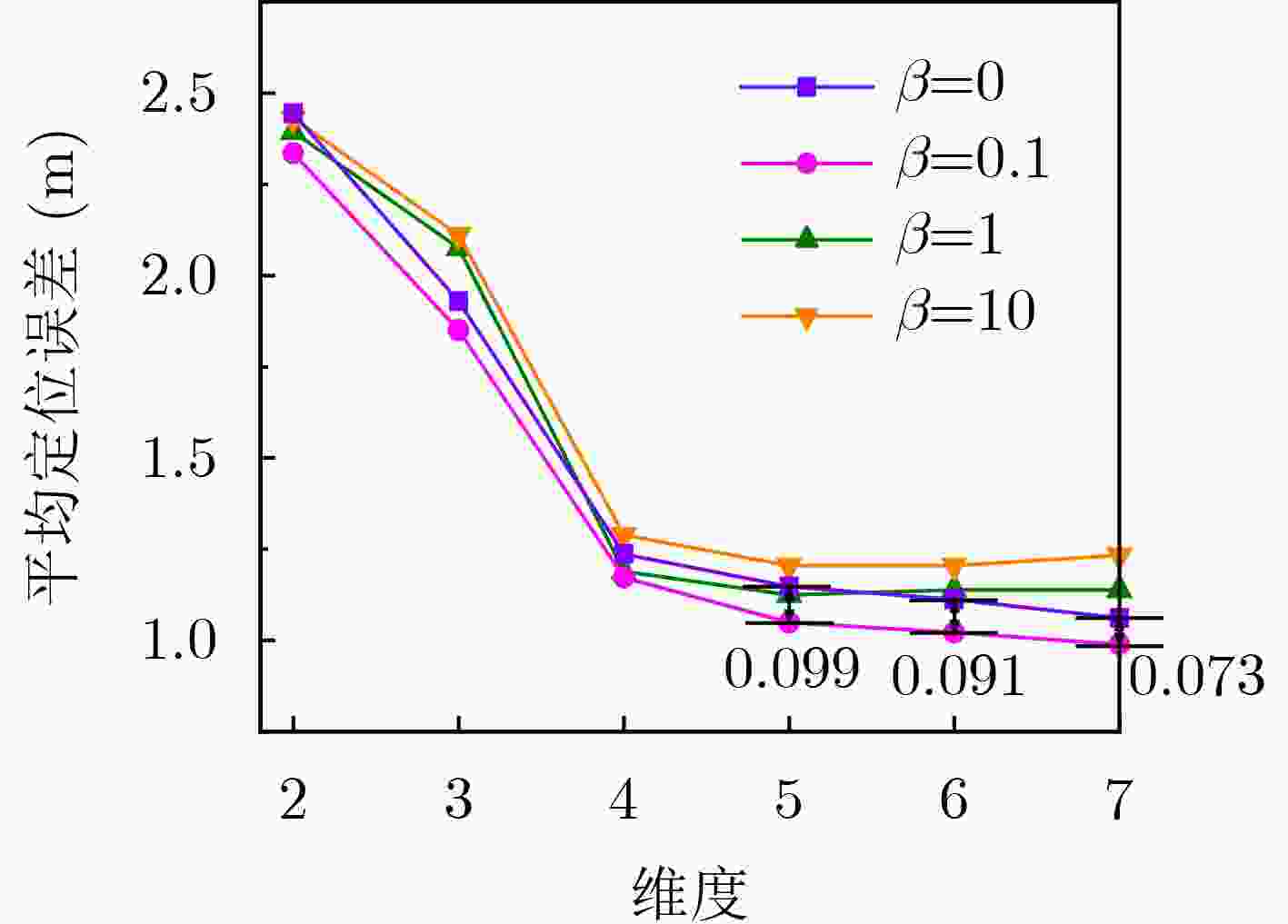
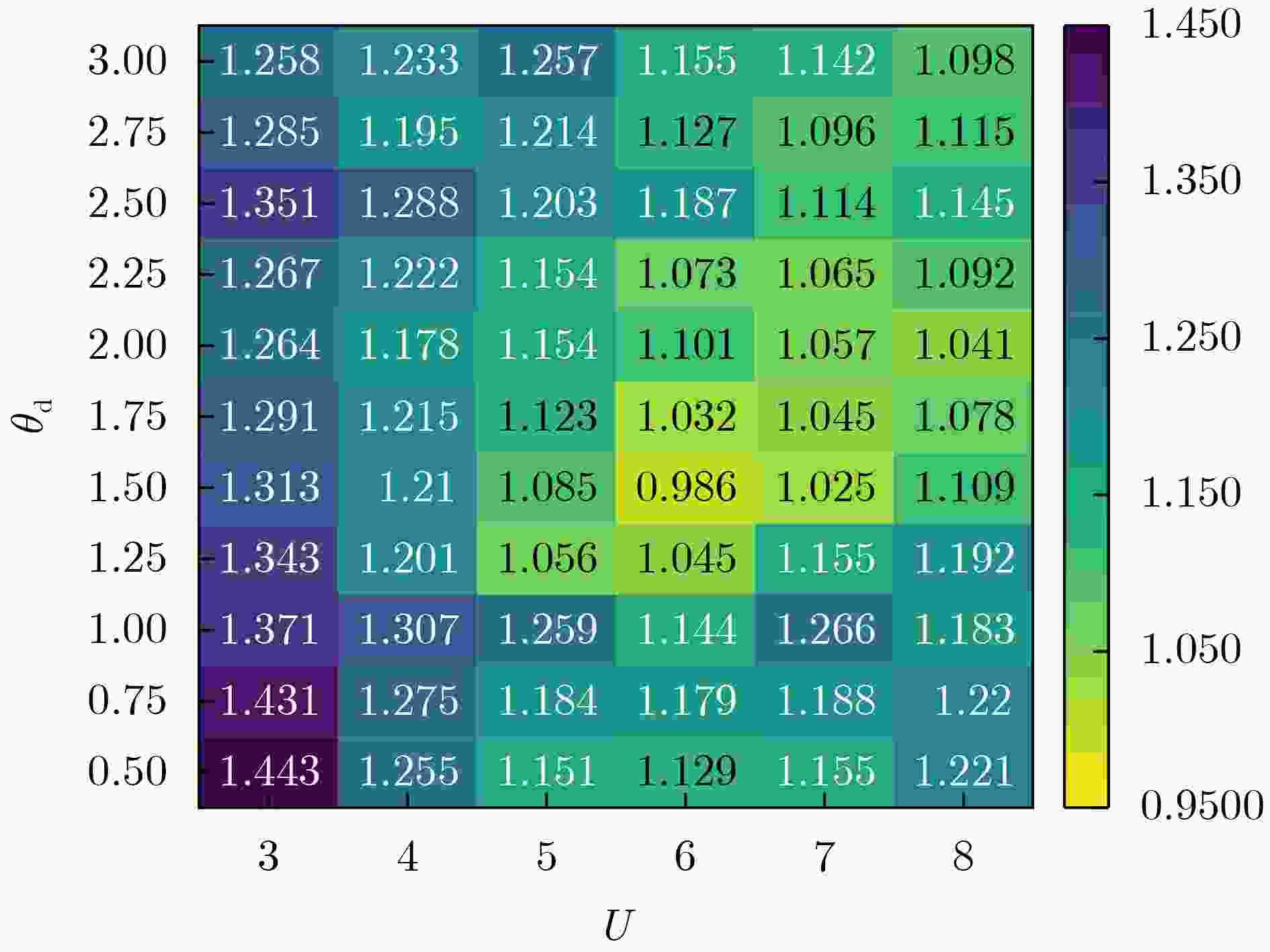
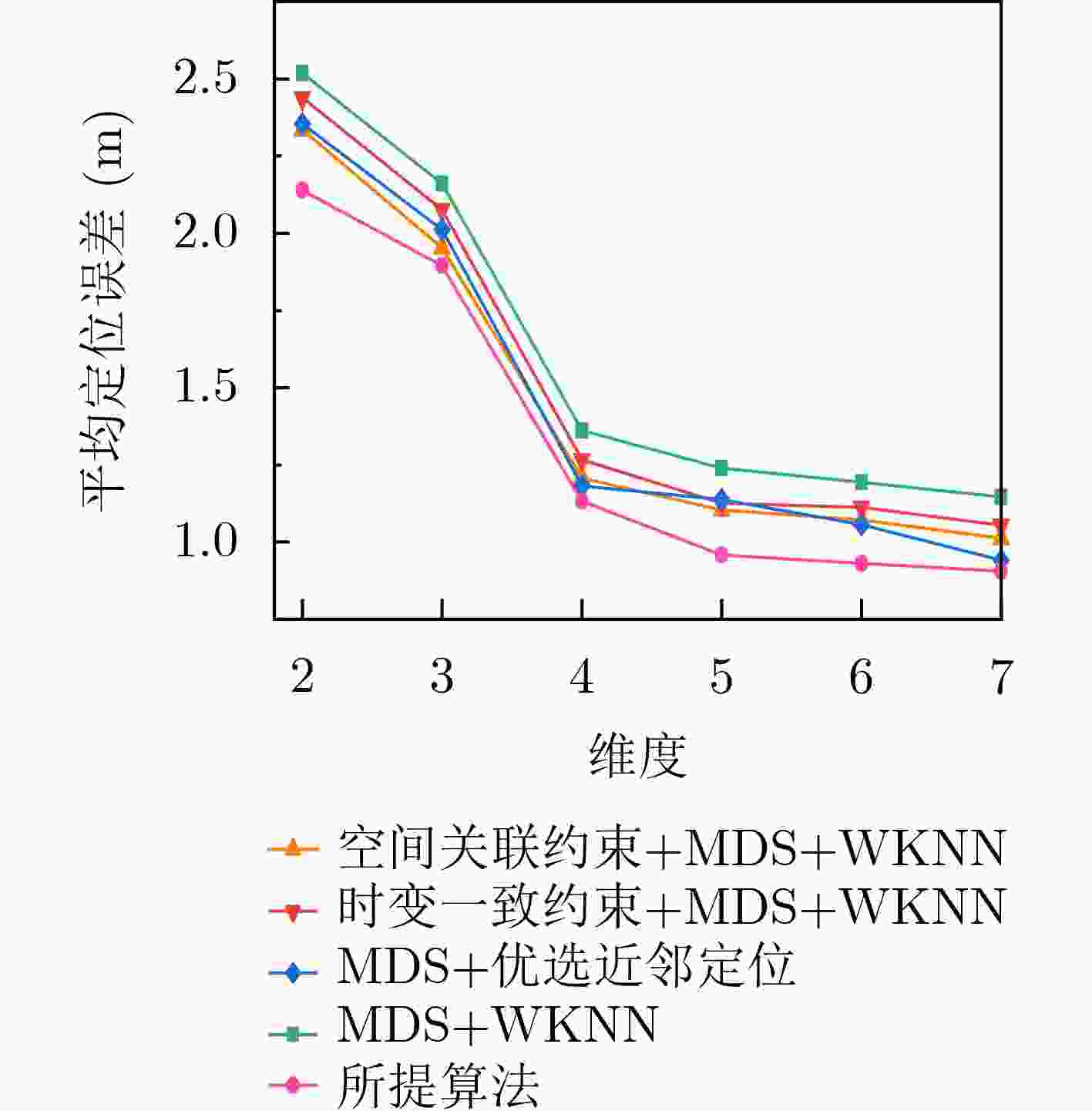
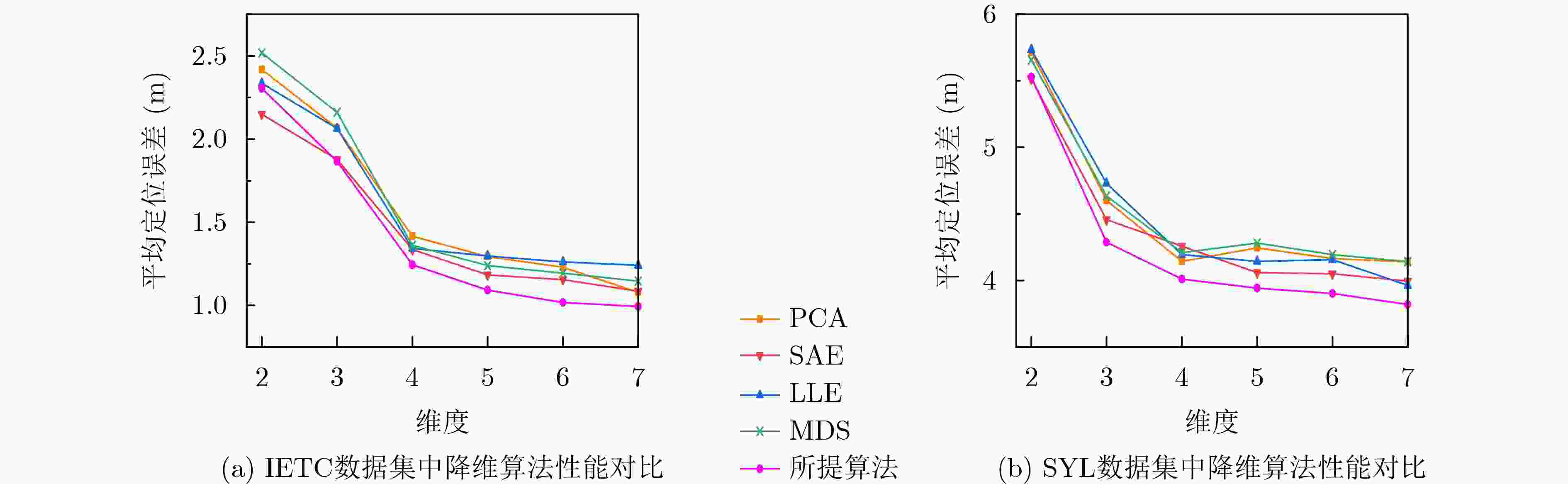
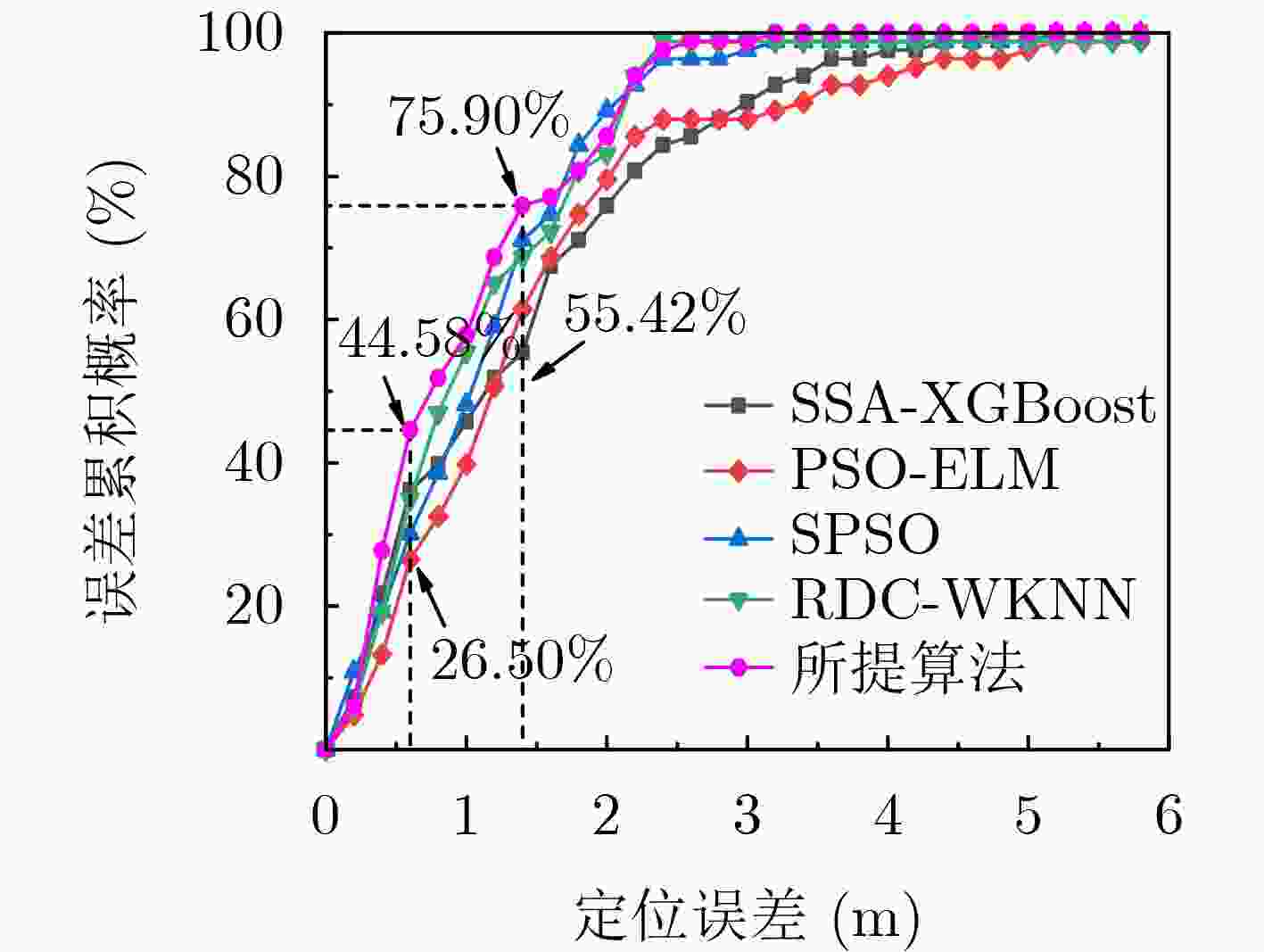
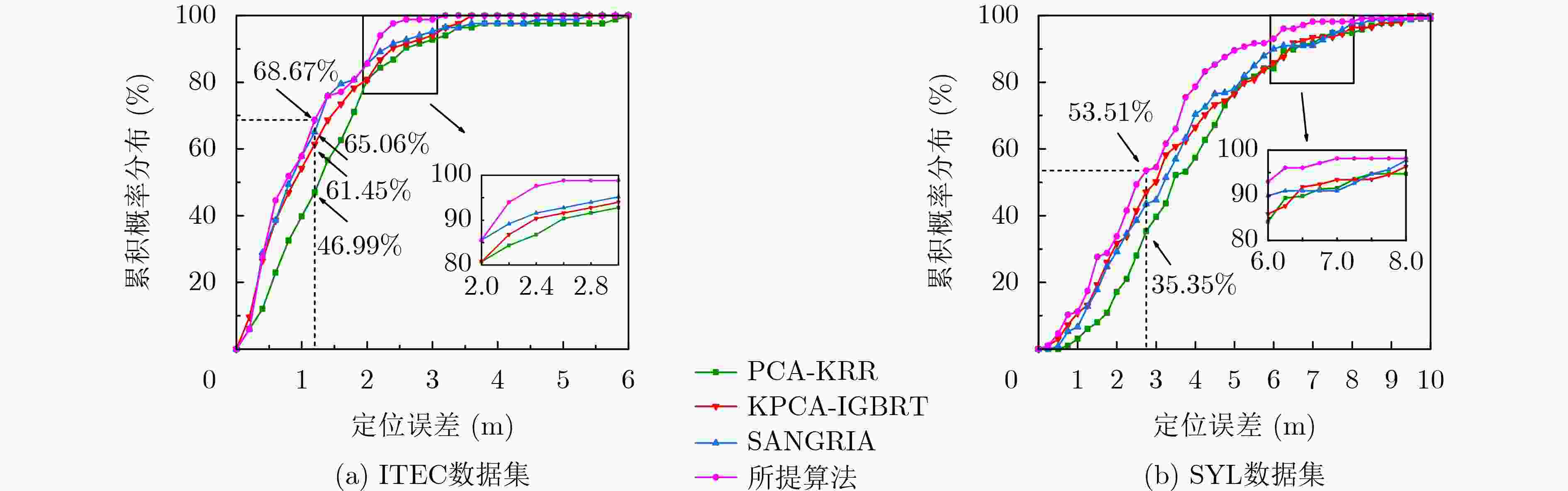
Objective Indoor fingerprint-based localization faces three key challenges. First, Dimensionality Reduction (DR), used to reduce storage and computational costs, often disrupts the geometric correlation between signal features and physical space, which reduces mapping accuracy. Second, signal features present temporal variability caused by human movement or environmental changes. During online mapping, this variability introduces bias and distorts similarity between target and reference points in the low-dimensional space. Third, pseudo-neighbor interference persists because environmental noise or imperfect similarity metrics lead to inaccurate neighbor selection and skew position estimates. To address these issues, this study proposes a Spatio-Temporal Constrained Refined Nearest Neighbor (STC-RNL) fingerprinting localization algorithm designed to provide robust, high-accuracy localization under complex interference conditions. Methods In the offline phase, a robust DR framework is constructed by integrating two constraints into a MultiDimensional Scaling (MDS) model. A spatial correlation constraint uses physical distances between reference points and assigns stronger associations to proximate locations to preserve alignment between low-dimensional features and the real layout. A temporal consistency constraint clusters multiple temporal signal samples from the same location into a compact region to suppress feature drift. These constraints, combined with the MDS structure-preserving loss, form the optimization objective, from which low-dimensional features and an explicit mapping matrix are obtained. In the online phase, a progressive refinement mechanism is applied. An initial candidate set is selected using a Euclidean distance threshold. A hybrid similarity metric is then constructed by enhancing shared-neighbor similarity with a Sigmoid-based strategy, which truncates low and smooths high similarities, and fusing it with Euclidean distance to improve discrimination of true neighbors. Subsequently, an iterative Z-score-based filtering procedure removes reference points that deviate from local group characteristics in feature and coordinate domains. The final position is estimated through a similarity-weighted average over the refined neighbor set, assigning higher weights to more reliable references. Results and Discussions The performance of STC-RNL is assessed on a private ITEC dataset and a public SYL dataset. The spatio-temporal constraints enhance the robustness of the mapping matrix under noisy conditions ( Table 2 ). Compared with baseline DR methods, the proposed module reduces mean localization error by at least 6.30% in high-noise scenarios (Fig. 9 ). In the localization stage, the refined neighbor selection reduces pseudo-neighbor interference. On the ITEC dataset, STC-RNL achieves an average error of 0.959 m, improving performance by 9.61% to 33.68% compared with SSA-XGBoost and SPSO (Table 1 ). End-to-end comparisons show that STC-RNL reduces the average error by at least 12.42% on ITEC and by at least 7.08% on SYL (Table 2 ), and its CDF curves demonstrate faster convergence and higher precision, especially within the 1.2 m range (Fig. 10 ). These results indicate that the algorithm maintains high stability and accuracy with a lower maximum error across datasets.Conclusions The STC-RNL algorithm addresses structural distortion and mapping bias found in traditional DR-based localization. By jointly optimizing offline feature embedding with spatio-temporal constraints and online neighbor selection with progressive refinement, the coupling between signal features and physical coordinates is strengthened. The main innovation lies in a synergistic framework that ensures only high-confidence neighbors contribute to the final estimate, improving accuracy and robustness in dynamic environments. Experiments show that the model reduces average localization error by 12.42%$ \sim $32.80% on ITEC and by 7.08%$ \sim $13.67% on SYL relative to baseline algorithms, while achieving faster error convergence. Future research may incorporate nonlinear manifold modeling to further improve performance in heterogeneous access point environments. -
表 1 不同定位算法性能比较(m)
定位算法 平均定位误差 最小值 最大值 SSA-XGBoost 1.340 0.049 4.750 PSO-ELM 1.446 0.082 6.182 SPSO 1.102 0.050 5.064 RDC-WKNN 1.061 0.097 7.039 所提算法 0.959 0.047 3.121 表 2 整体算法性能对比(m)
数据集 定位算法 平均定位误差 最小值 最大值 标准差 ITEC PCA-KRR 1.427 0.053 5.861 1.075 KPCA-IGBRT 1.129 0.028 3.478 0.904 SANGIRA 1.095 0.010 5.288 0.966 所提算法 0.959 0.047 3.121 0.727 SYL PCA-KRR 4.259 0.652 45.636 4.477 KPCA-IGBRT 4.002 0.118 48.163 4.943 SANGIRA 3.957 0.211 50.927 4.963 所提算法 3.677 0.058 40.950 4.570 -
[1] FARAHSARI P S, FARAHZADI A, REZAZADEH J, et al. A survey on indoor positioning systems for IoT-based applications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(10): 7680–7699. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3149048. [2] YANG Yang, CHEN Mingzhe, BLANKENSHIP Y, et al. Positioning using wireless networks: Applications, recent progress, and future challenges[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2024, 42(9): 2149–2178. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2024.3423629. [3] WANG He, WANG Qitong, HUANG Leilei, et al. A PCA acceleration algorithm for WiFi sensing and its hardware implementation[C]. 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Singapore, Singapore, 2024: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS58744.2024.10557859. [4] SONG Qianwen, GUO Songtao, LIU Xing, et al. CSI amplitude fingerprinting-based NB-IoT indoor localization[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(3): 1494–1504. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2782479. [5] YAO Bin, LI Wen, WEI Dongyan, et al. Topology construction based on indoor crowdsourcing data using manifold learning: Evaluation of algorithms and key parameters[C]. 2021 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, loret de Mar, Spain, 2021: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/IPIN51156.2021.9662627. [6] AYINLA S L, AZIZ A A, and DRIEBERG M. SALLoc: An accurate target localization in WiFi-enabled indoor environments via SAE-ALSTM[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 19694–19710. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3360228. [7] YANG Haifeng, ZHANG Yongbo, HUANG Yuliang, et al. WKNN indoor location algorithm based on zone partition by spatial features and restriction of former location[J]. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 2019, 60: 101085. doi: 10.1016/j.pmcj.2019.101085. [8] SHEN Qiang and CUI Yinghua. WiFi fingerprint correction for indoor localization based on distance metric learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(21): 36167–36177. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3462759. [9] WANG Guanzhong, ZHANG Dongheng, ZHANG Tianyu, et al. Learning domain-invariant model for WiFi-based indoor localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(12): 13898–13913. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3438454. [10] ZHENG Jin, LI Kailong, and ZHANG Xing. Wi-Fi fingerprint-based indoor localization method via standard particle swarm optimization[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(13): 5051. doi: 10.3390/s22135051. [11] 刘志平, 李桂南, 余航, 等. 正则化距离准则的Wi-Fi位置指纹室内定位方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2017, 42(12): 185–189,194. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2017.12.031.LIU Zhiping, LI Guinan, YU Hang, et al. A regularized-distance rule method for Wi-Fi fingerprinting indoor positioning[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(12): 185–189,194. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2017.12.031. [12] WALTER M J, WALKER D J, and CRAVEN M J. Visualizing population dynamics to examine algorithm performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2022, 26(6): 1501–1510. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2022.3157143. [13] SUN Liping, BAO Shuting, CI Shang, et al. Differential privacy-preserving density peaks clustering based on shared near neighbors similarity[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 89427–89440. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2927308. [14] BI Jingxue, WANG Yunjia, YU Baoguo, et al. Supplementary open dataset for WiFi indoor localization based on received signal strength[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2022, 3(1): 25. doi: 10.1186/s43020-022-00086-y. [15] 冷腾飞, 苏圣超. 基于子区域切分与SSA-XGBoost的室内定位方法[J]. 传感技术学报, 2024, 37(5): 833–840. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2024.05.013.LENG Tengfei and SU Shengchao. Indoor localization method based on subspace segmentation and SSA-XGBoost[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2024, 37(5): 833–840. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2024.05.013. [16] QIU Wanqing, ZHANG Qingmiao, ZHAO Junhui, et al. Improved PSO-extreme learning machine algorithm for indoor localization[J]. China Communications, 2024, 21(5): 113–122. doi: 10.23919/JCC.fa.2022-0011.202405. [17] 张贺娜, 乐燕芬, 施伟斌. 基于特征降维的核岭回归室内定位算法[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2020, 41(10): 83–91. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2006576.ZHANG Hena, LE Yanfen, and SHI Weibin. Kernel ridge regression based indoor location algorithm using feature reduction[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2020, 41(10): 83–91. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J2006576. [18] 李新春, 房梽斅, 张春华. 基于KPCA和改进GBRT的室内定位算法[J]. 传感技术学报, 2019, 32(3): 430–437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2019.03.019.LI Xinchun, FANG Zhixiao, and ZHANG Chunhua. Indoor positioning algorithm based on KPCA and improved GBRT[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2019, 32(3): 430–437. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1699.2019.03.019. [19] GUFRAN D, TIKU S, and PASRICHA S. SANGRIA: Stacked autoencoder neural networks with gradient boosting for indoor localization[J]. IEEE Embedded Systems Letters, 2024, 16(2): 142–145. doi: 10.1109/LES.2023.3279017. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
