Considering Workload Uncertainty in Strategy Gradient-based Hyper-heuristic Scheduling for Software Projects
-
摘要: 该文围绕软件项目开发过程中存在的不确定因素,建立一种考虑任务工作量不确定性的多目标软件项目调度模型。该模型采用非对称三角区间二型模糊数描述工作量的不确定性。为了提高不确定环境下的决策质量,提出一种基于策略梯度的超启发式算法求解该模型。该算法将强化学习中的一种策略梯度算法(即Actor-Critic算法)作为高层策略,根据算法的当前运行状态选择合适的低层启发式策略。同时引入优先经验回放法,以利用历史经验信息更新网络参数,加快收敛速度并降低学习成本。将所提算法与6种代表性算法在12个人工合成算例和3个实例上进行了对比。实验结果表明,所提算法在不确定调度环境中能够搜索到一组收敛性和多样性更好的非支配解。Abstract:
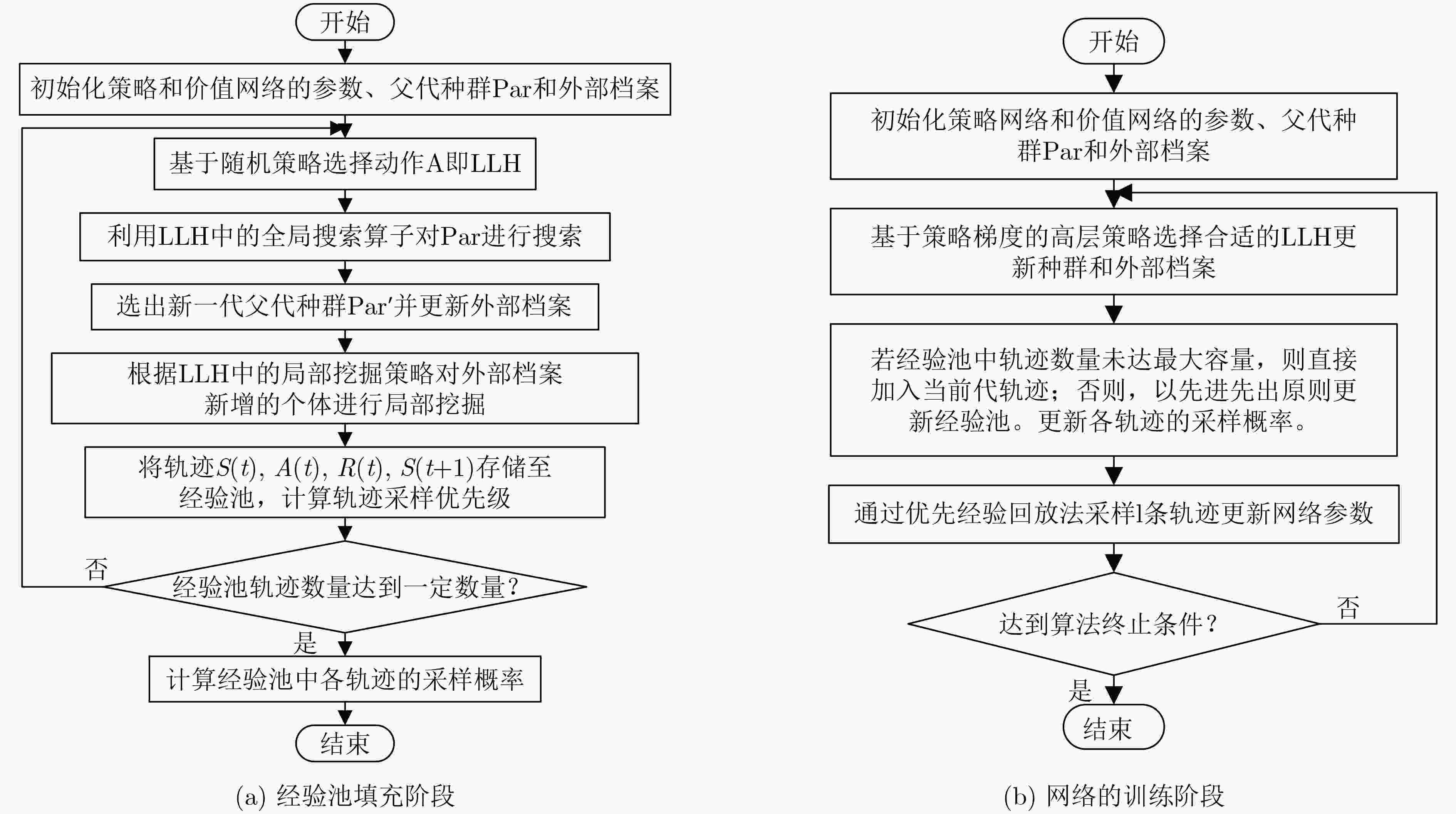
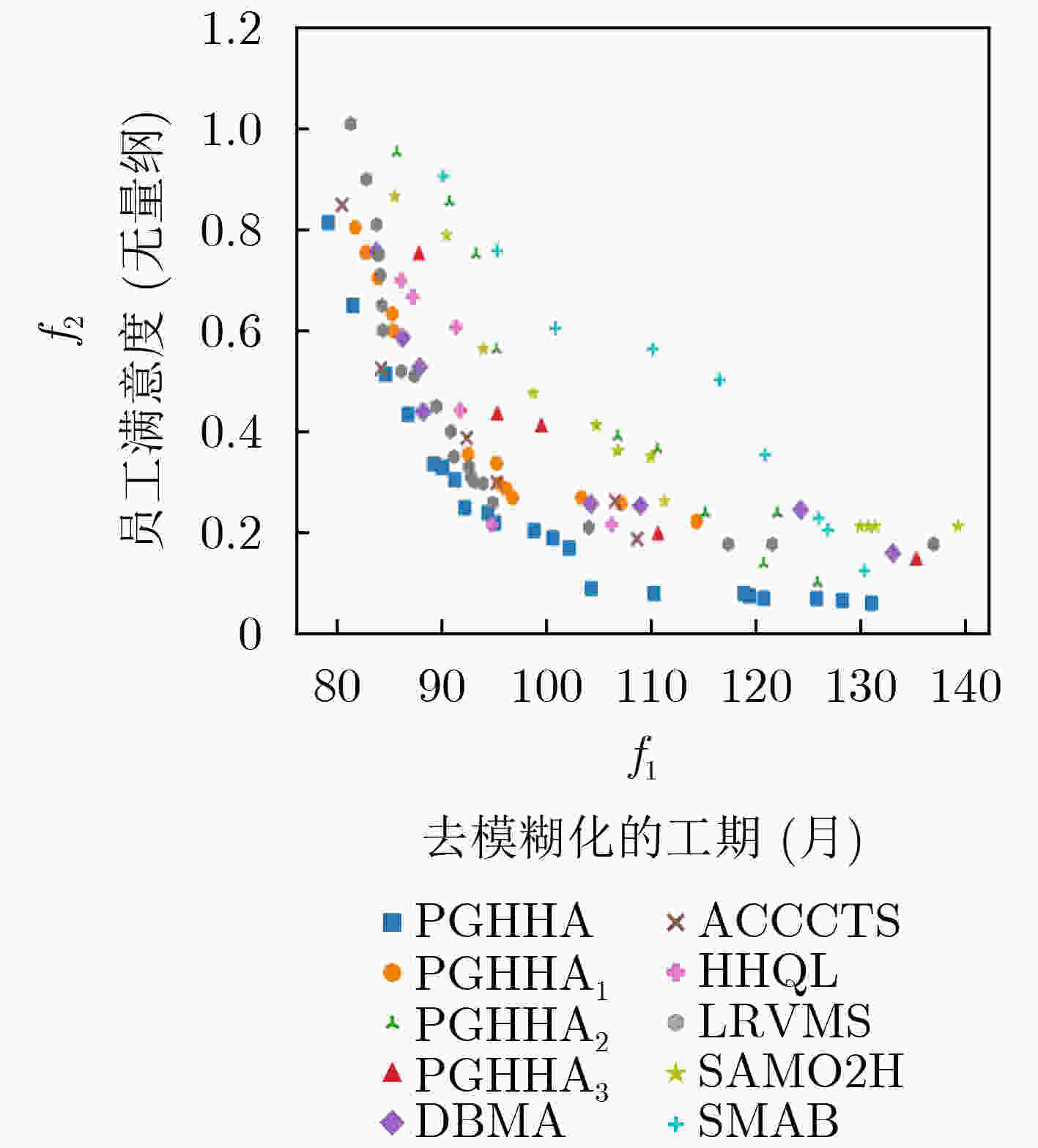
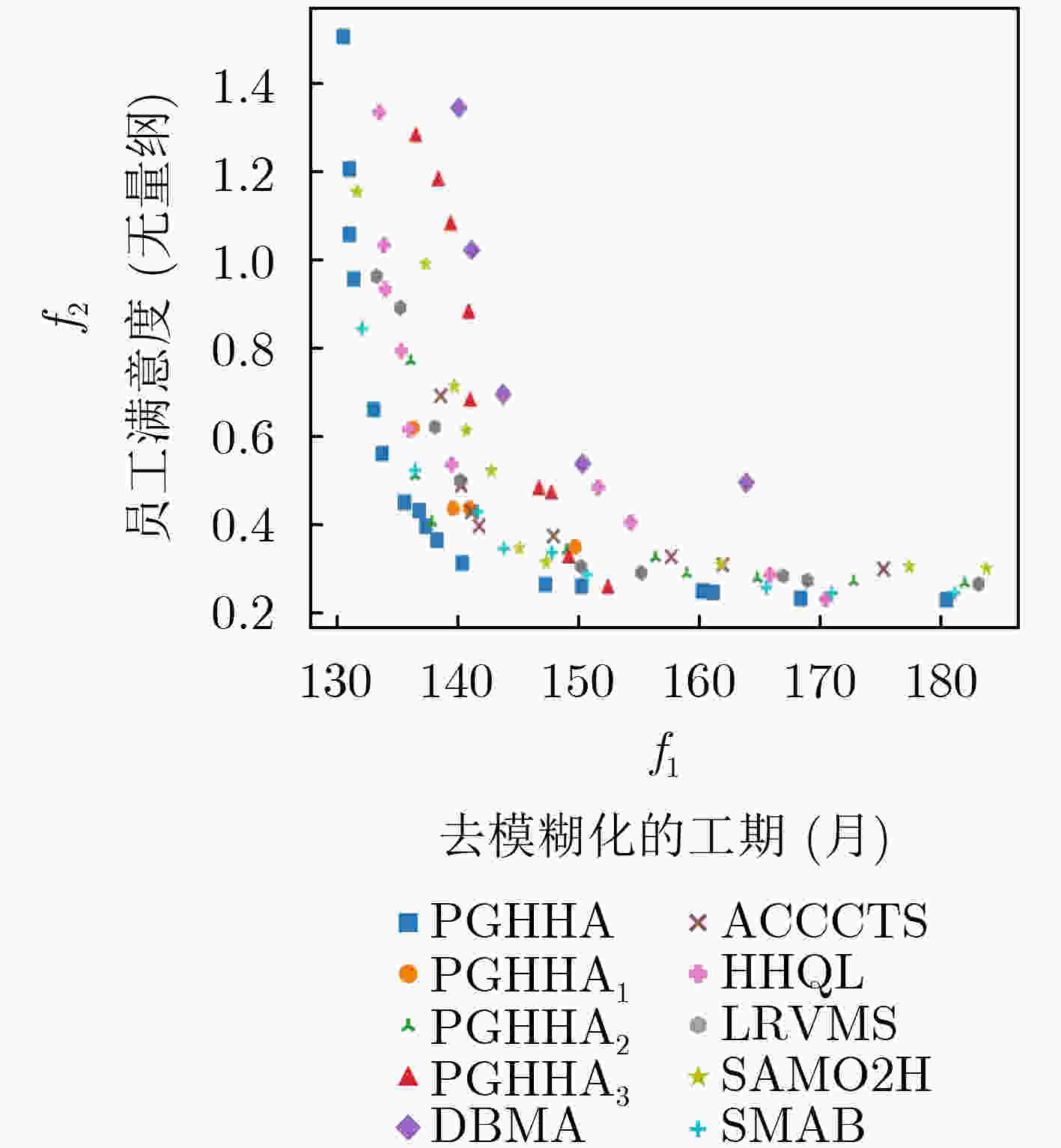
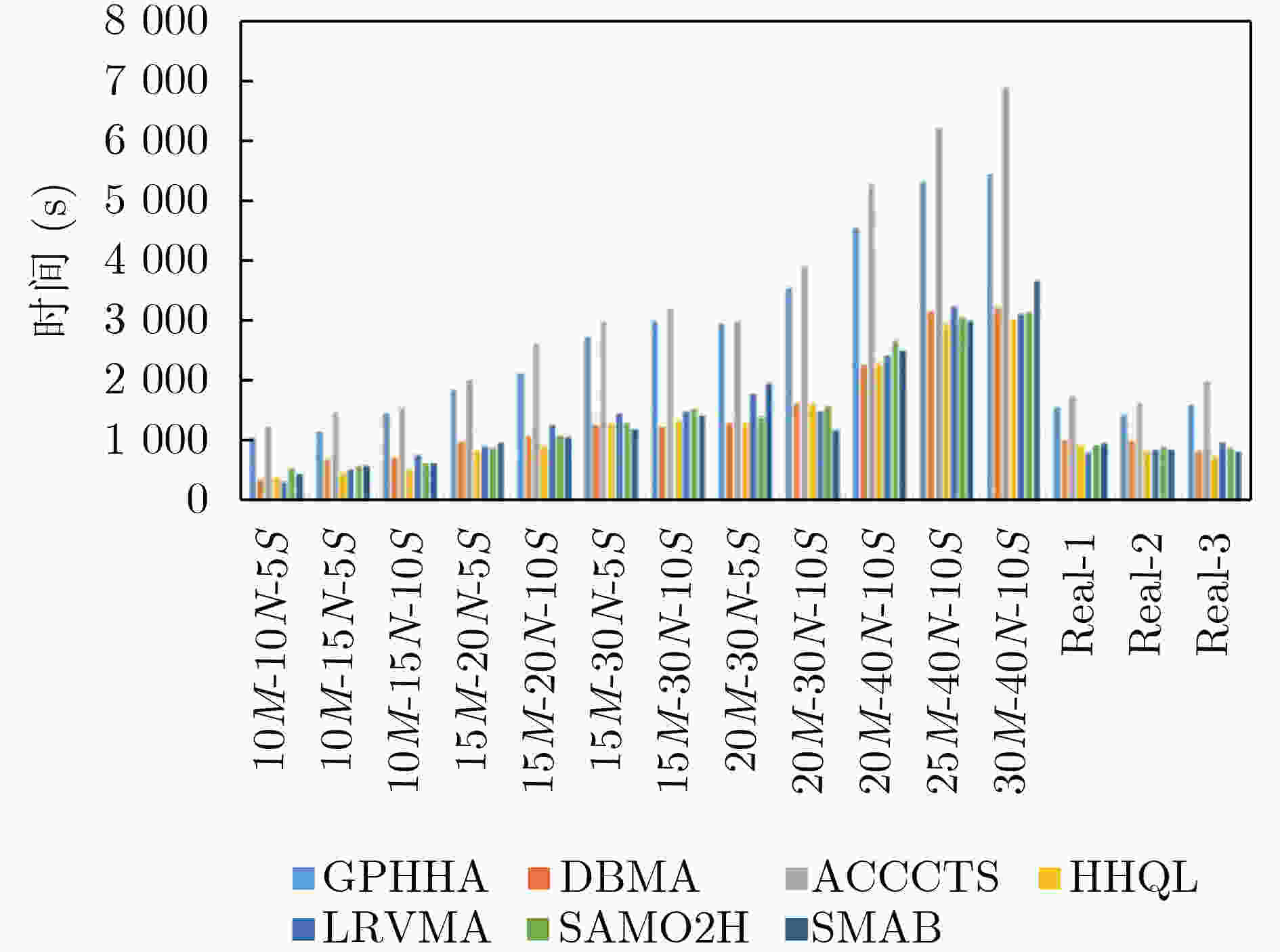
Objective The Software Project Scheduling Problem (SPSP) is essential for allocating resources and arranging tasks in software development, and it affects economic efficiency and competitiveness. Deterministic assumptions used in traditional models overlook common fluctuations in task effort caused by requirement changes or estimation deviation. These assumptions often reduce feasibility and weaken scheduling stability in dynamic development settings. This study develops a multi-objective model that integrates task effort uncertainty and represents it using asymmetric triangular interval type-2 fuzzy numbers to reflect real development conditions. The aim is to improve decision quality under uncertainty by designing an optimization method that shortens project duration and increases employee satisfaction, thereby strengthening robustness and adaptability in software project scheduling. Methods A Policy Gradient-based Hyper-Heuristic Algorithm (PGHHA) is developed to solve the formulated model. The framework contains a High-Level Strategy (HLS) and a set of Low-Level Heuristics (LLHs). The High-Level Strategy applies an Actor-Critic reinforcement learning structure. The Actor network selects appropriate LLHs based on real-time evolutionary indicators, including population convergence and diversity, and the Critic network evaluates the actions selected by the Actor. Eight LLHs are constructed by combining two global search operators, the matrix crossover operator and the Jaya operator with random jitter, with two local mining strategies, duration-based search and satisfaction-based search. Each LLH is configured with two neighborhood depths (V1=5 and V2=20), determined through Taguchi orthogonal experiments. Each candidate solution is encoded as a real-valued task-employee effort matrix. Constraints including skill coverage, maximum dedication, and maximum participant limits are applied during optimization. A prioritized experience replay mechanism is introduced to reuse historical trajectories, which accelerates convergence and improves network updating efficiency. Results and Discussions Experimental evaluation is performed on twelve synthetic cases and three real software projects. The algorithm is assessed against six representative methods to validate the proposed strategies. HyperVolume Ratio (HVR) and Inverted Generational Distance (IGD) are used as performance indicators, and statistical significance is examined using Wilcoxon rank-sum tests with a 0.05 threshold. The findings show that the PGHHA achieves better convergence and diversity than all comparison methods in most cases. The quantitative improvements are reflected in the summarized values ( Table 5 ,Table 6 ). The visual distribution of Pareto fronts (Fig. 4 ,Fig. 5 ) shows that the obtained solutions lie below those of alternative algorithms and display more uniform coverage, indicating higher convergence precision and improved spread. The computational cost increases because of neural network training and the experience replay mechanism, as shown inFig. 6 . However, the improvement in solution quality is acceptable considering the longer planning period of software development. Modeling effort uncertainty with asymmetric triangular interval type-2 fuzzy numbers enhances system stability. The adaptive heuristic selection driven by the Actor-Critic mechanism and the prioritized experience replay strengthens performance under dynamic and uncertain conditions. Collectively, the evidence indicates that the PGHHA provides more reliable support for software project scheduling, maintaining diversity while optimizing conflicting objectives under uncertain workload environments.Conclusions A multi-objective software project scheduling model is developed in this study, where task effort uncertainty is represented using asymmetric triangular interval type-2 fuzzy numbers. A PGHHA is designed to solve the model. The algorithm applies an Actor-Critic reinforcement learning structure as the high-level strategy to adaptively select LLHs according to the evolutionary state. A prioritized experience replay mechanism is incorporated to enhance learning efficiency and accelerate convergence. Tests on synthetic and real cases show that: (1) The proposed algorithm delivers stronger convergence and diversity under uncertainty than six representative algorithms; (2) The combination of global search operators and local mining strategies maintains a suitable balance between exploration and exploitation. (3) The use of type-2 fuzzy representation offers a more stable characterization of effort uncertainty than type-1 fuzzy numbers. The current work focuses on a single-project context. Future work will extend the model to multi-project environments with shared resources and inter-project dependencies. Additional research will examine adaptive reward strategies and lightweight network designs to reduce computational demand while preserving solution quality. -
表 1 员工和任务属性
符号 定义 $ {E_i} $ 第i个员工,i=1,2,···,M,M为员工总数 $ E_i^{{\text{maxded}}} $ $ {E_i} $对项目的最大投入度 $ v_i^k $ 员工$ {E_i} $在技能k上的等级,技能等级分为5级,$ v_i^k \in \left\{ {1,2,3,4,5} \right\} $ $ {o_i} $ $ {E_i} $已掌握的技能集合 $ p_i^k $ $ {E_i} $对技能k的熟练度,$ p_i^k \in [0,C] $,C=5 $ {\text{c}}{{\text{o}}_{il}} $ 员工$ {E_i} $和员工$ {E_l} $的合作次数 $ {T_j} $ 第j个任务,j=1,2,···,N,N为任务总数 $ \tilde T_j^{{\text{eff}}} $ $ {T_j} $所需要的模糊工作量,单位是人·月 $ {\text{T\_li}}{{\text{m}}_j} $ $ {T_j} $的最大参与人数 $ T_j^{{\text{ext}}} $ 任务$ {T_j} $的重要程度,$ T_j^{{\text{ext}}} \in \left\{ {1,2,3,4,5} \right\} $ $ {T^{{\text{im}}}} $ 重要任务的集合,由重要程度为5级的任务构成,即$ {T^{{\text{im}}}} = \left\{ {{T_j}|T_j^{{\text{ext}}} = 5,j = 1,2,\cdots,N} \right\} $ $ {\text{re}}{{\text{q}}_j} $ $ {T_j} $所需要的技能集合 $ {H^k} $ 在技能k上骨干员工的集合,由技能等级为4级或5级的员工构成,即$ H^k=\left\{E_i|v_i^k=4,或{{ v}}_i^k=5,i=1,2,\cdots,M\right\} $ 表 2 4种种群状态的划分
$ {S_1} $ $ {S_2} $ $ {S_3} $ $ {S_4} $ $ \Delta {\text{HV}} \gt 0 $ $ \Delta {\text{HV}} \lt 0 $ $ \Delta {\text{HV}} \gt 0 $ $ \Delta {\text{HV}} \le 0 $ $ \Delta {\text{DV}} \gt 0 $ $ \Delta {\text{DV}} \gt 0 $ $ \Delta {\text{DV}} \lt 0 $ $ \Delta {\text{DV}} \le 0 $ 表 3 8种低层启发式策略
LLH1 LLH2 LLH3 LLH4 MCO+SLSS+V1 MCO+SLSS+V2 MCO+DLSS+V1 MCO+DLSS+V2 LLH5 LLH6 LLH7 LLH8 JORJ+SLSS+V1 JORJ+SLSS+V2 JORJ+DLSS+V1 JORJ+DLSS+V2 表 4 20M-40N-10S算例上不同参数的取值结果对比
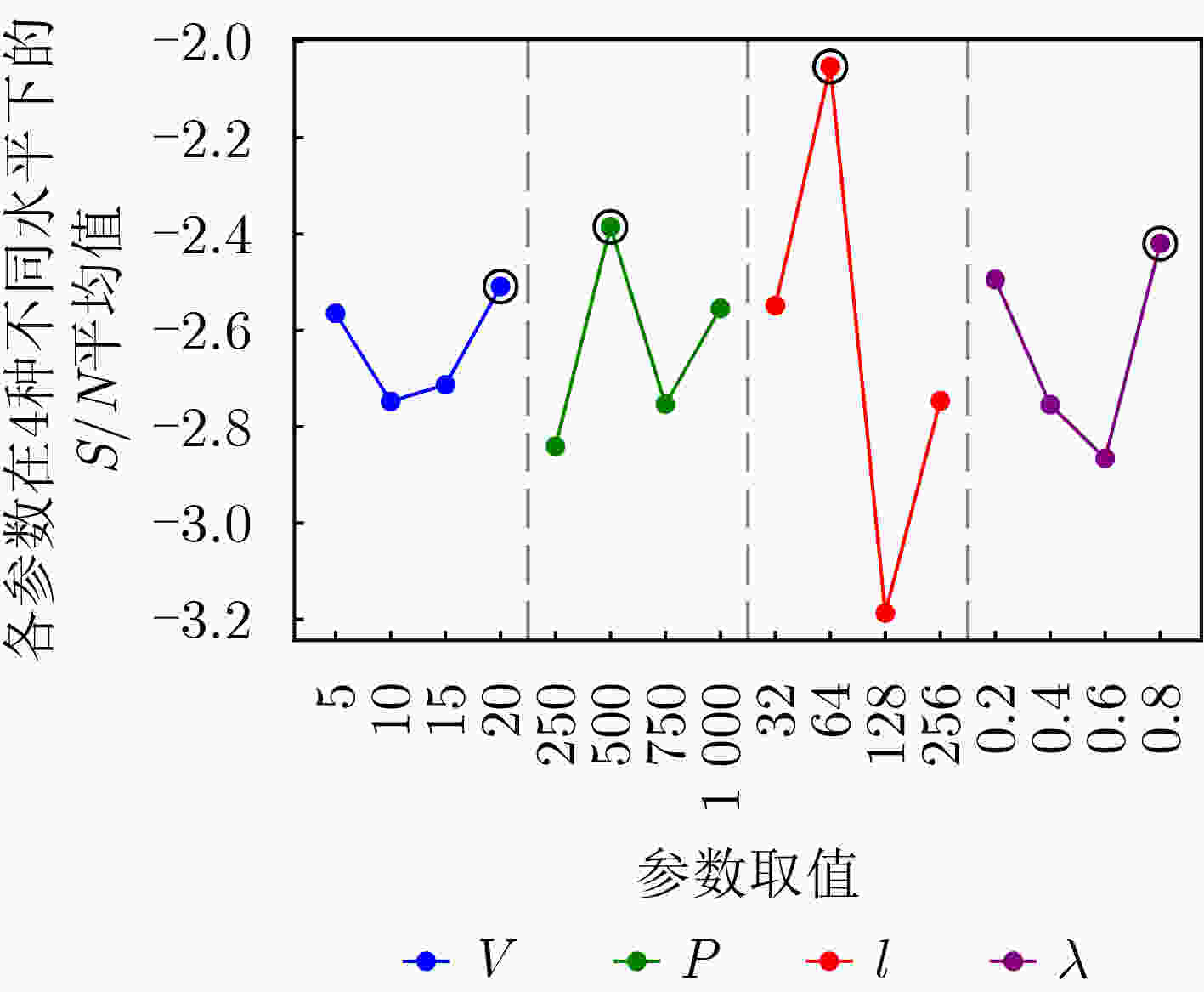
组别 参数 结果 V L l $ \lambda $ S/N 1 5 250 32 0.2 – 2.3655 2 5 500 64 0.4 – 1.7542 3 5 750 128 0.6 – 3.6635 4 5 1000 256 0.8 – 2.4745 5 10 250 64 0.6 – 2.6962 6 10 500 32 0.8 – 2.3946 7 10 750 256 0.2 – 2.7389 8 10 1000 128 0.4 – 3.1599 9 15 250 128 0.8 – 3.1577 10 15 500 256 0.6 – 2.6271 11 15 750 32 0.4 – 2.9583 12 15 1000 64 0.2 – 2.1076 13 20 250 256 0.4 – 3.1444 14 20 500 128 0.2 – 2.7643 15 20 750 64 0.8 – 1.6519 16 20 1000 32 0.6 – 2.4745 表 5 所提算法PGHHA和替换单一策略算法的对比结果
算例 PGHHA PGHHA1 PGHHA2 PGHHA3 HVR IGD HVR IGD HVR IGD HVR IGD 10M-10N-5S 0.99250 0.09220 0.98400 =0.12346 +0.96899 +0.21161 +0.97471 +0.14761 +10M-15N-5S 0.95844 0.05834 0.89655 +0.20335 +0.93145 +0.17469 +0.81489 +0.29439 +10M-15N-10S 0.94790 0.11968 0.87704 +0.26172 +0.92149 +0.18779 +0.80562 +0.29297 +15M-20N-5S 0.98163 0.08262 0.79431 +0.38438 +0.90486 +0.15519 +0.77907 +0.38811 +15M-20N-10S 0.97927 0.11605 0.74462 +0.29048 +0.77350 +0.23512 +0.76558 +0.27590 +15M-30N-5S 0.96563 0.09172 0.74232 +0.23335 +0.79543 +0.24815 +0.69608 +0.31365 +15M-30N-10S 0.97375 0.08377 0.41407 +0.45349 +0.86138 +0.17924 +0.78636 +0.29754 +20M-30N-5S 0.99449 0.04014 0.76834 +0.23783 +0.79635 +0.18083 +0.76224 +0.26607 +20M-30N-10S 0.97315 0.17456 0.49679 +0.46848 +0.57295 +0.37948 +0.76702 +0.24577 +20M-40N-10S 0.87440 0.07848 0.71880 +0.15870 +0.63450 +0.12640 +0.70570 +0.12980 +25M-40N-10S 0.95382 0.09408 0.89277 +0.15278 +0.84310 +0.13515 +0.87307 +0.19490 +30M-40N-10S 0.94910 0.10911 0.89051 +0.18086 +0.86931 +0.17546 +0.89889 +0.18816 +Real-1 0.98426 0.10089 0.78669 +0.31839 +0.79828 +0.30680 +0.76297 +0.35578 +Real-2 0.96564 0.05132 0.84702 +0.12234 +0.86167 +0.09253 +0.83655 +0.17651 +Real-3 0.97003 0.22431 0.94249 +0.37577 +0.96009 =0.32971 +0.92067 +0.29233 ++/–/= 14/0/1 15/0/0 14/0/1 15/0/0 15/0/0 15/0/0 表 6 所提算法的性能验证实验中6种算法的对比结果
算例 PGHHA DBMA ACCCTS HHQL HVR IGD HVR IGD HVR IGD HVR IGD 10M-10N-5S 0.99258 0.09220 0.97294 +0.15199 +0.98768 =0.10607 +0.98235 +0.12064 +10M-15N-5S 0.95844 0.05834 0.82412 +0.22569 +0.88027 +0.16973 +0.84688 +0.20773 +10M-15N-10S 0.94790 0.11968 0.84145 +0.26447 +0.89963 +0.20285 +0.87447 +0.25913 +15M-20N-5S 0.98163 0.08262 0.79265 +0.36254 +0.80773 +0.23642 +0.79295 +0.33822 +15M-20N-10S 0.97927 0.11605 0.74482 +0.31588 +0.77390 +0.23932 +0.75041 +0.24309 +15M-30N-5S 0.96563 0.09172 0.72179 +0.30118 +0.76937 +0.13433 +0.71657 +0.25633 +15M-30N-10S 0.97375 0.08377 0.82710 +0.26013 +0.86548 +0.20556 +0.82900 +0.23633 +20M-30N-5S 0.99449 0.04014 0.77301 +0.23358 +0.80215 +0.17489 +0.79327 +0.18709 +20M-30N-10S 0.97315 0.17456 0.51097 +0.52757 +0.84647 +0.36461 +0.74630 +0.48835 +20M-40N-10S 0.87440 0.07848 0.73501 +0.12918 +0.80785 +0.12685 +0.79785 +0.14953 +25M-40N-10S 0.95382 0.09408 0.89869 +0.14658 +0.93671 +0.10052 =0.90224 +0.09777 =30M-40N-10S 0.94910 0.10911 0.93293 +0.16346 +0.94881 =0.11868 +0.94190 +0.14346 +Real-1 0.98426 0.10089 0.77856 +0.29865 +0.79490 +0.30287 +0.78771 +0.25761 +Real-2 0.96564 0.05132 0.87619 +0.16981 +0.90169 +0.09354 +0.85187 +0.15740 +Real-3 0.97003 0.22431 0.92007 +0.35695 +0.93587 +0.33432 +0.96637 =0.22856 ++/–/= 15/0/0 15/0/0 13/0/2 14/0/1 14/0/1 14/0/1 续表6 算例 LRVMA SMO2H SMAB HVR IGD HVR IGD HVR IGD 10M-10N-5S 0.98428 +0.10658 +0.98795 =0.11816 +0.99009 =0.11218 +10M-15N-5S 0.87415 +0.16099 +0.86120 +0.16605 +0.87402 +0.12515 +10M-15N-10S 0.87242 +0.23220 +0.86701 +0.22302 +0.85549 +0.25300 +15M-20N-5S 0.80580 +0.35287 +0.80364 +0.35751 +0.80681 +0.32411 +15M-20N-10S 0.90308 +0.15268 +0.80479 +0.25375 +0.76270 +0.19806 +15M-30N-5S 0.74572 +0.23613 +0.74964 +0.21988 +0.74641 +0.16522 +15M-30N-10S 0.82229 +0.26220 +0.85177 +0.16454 +0.85042 +0.16622 +20M-30N-5S 0.78010 +0.22599 +0.79598 +0.14746 +0.79434 +0.17365 +20M-30N-10S 0.52278 +0.45390 +0.54351 +0.40593 +0.57787 +0.39774 +20M-40N-10S 0.69624 +0.16358 +0.78799 +0.11185 +0.80452 +0.11378 +25M-40N-10S 0.90800 +0.13031 +0.92778 +0.09934 =0.92141 +0.15109 +30M-40N-10S 0.91817 +0.15803 +0.94147 +0.14479 +0.94544 =0.12199 +Real-1 0.78399 +0.28787 +0.79216 +0.29067 +0.80337 +0.25183 +Real-2 0.85814 +0.17055 +0.85469 +0.11839 +0.86265 +0.04942 =Real-3 0.95563 +0.23613 +0.94699 +0.25314 +0.92067 +0.29233 ++/–/= 15/0/0 15/0/0 14/0/1 14/0/1 13/0/2 14/0/1 -
[1] 中国软件行业协会. 中国软件产业高质量发展报告(2025)[OL]. https://www.csia.org.cn/content/6367.html, 2025.China Software Industry Association. Report on the high-quality development of China’s software industry (2025) [OL]. https://www.csia.org.cn/content/6367.html, 2025. [2] CRAWFORD B, SOTO R, JOHNSON F, et al. A max–min ant system algorithm to solve the software project scheduling problem[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, 41(15): 6634–6645. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.05.003. [3] ALBA E and CHICANO J F. Software project management with GAs[J]. Information Sciences, 2007, 177(11): 2380–2401. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2006.12.020. [4] LI Hongbo, ZHU Hanyu, ZHENG Linwen, et al. Software project scheduling with multitasking[J]. Economic Computation and Economic Cybernetics Studies and Research, 2023, 57(1): 153–170. doi: 10.24818/18423264/57.1.23.10. [5] LI Hongbo, ZHU Hanyu, ZHENG Linwen, et al. Software project scheduling under activity duration uncertainty[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2024, 338(1): 477–512. doi: 10.1007/s10479-023-05343-0. [6] MASMOUDI M and HAÏT A. Project scheduling under uncertainty using fuzzy modelling and solving techniques[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 26(1): 135–149. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2012.07.012. [7] YU Hui, GAO Kaizhou, WU Naiqi, et al. Scheduling multiobjective dynamic surgery problems via Q-learning-based meta-heuristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(6): 3321–3333. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3352522. [8] MAHDAVI A, SHIRAZI B, and REZAEIAN J. Toward a scalable type-2 fuzzy model for resource-constrained project scheduling problem[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 100: 106988. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106988. [9] LI Junqing, LIU Zhengmin, LI Chengdong, et al. Improved artificial immune system algorithm for type-2 fuzzy flexible job shop scheduling problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 29(11): 3234–3248. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3016225. [10] JI Jianjiao, GUO Yinan, GAO Xiaozhi, et al. Q-Learning-Based hyperheuristic evolutionary algorithm for dynamic task allocation of crowdsensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(4): 2211–2224. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3112675. [11] HUANG Yao, GUO Yinan, CHEN Guoyu, et al. Q-learning assisted multi-objective evolutionary optimization for low-carbon scheduling of open-pit mine trucks[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2025, 92: 101778. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2024.101778. [12] 杨潇, 郭一楠, 吉建娇, 等. 异构群智感知PPO多目标任务指派方法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2024, 41(6): 1056–1066. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2023.20950.YANG Xiao, GUO Yinan, JI Jianjiao, et al. PPO multi-objective task allocation method for heterogeneous crowd sensing[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2024, 41(6): 1056–1066. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2023.20950. [13] CHEN Mengjiao, XU Jiyuan, ZHANG Wenyu, et al. A new customer-oriented multi-task scheduling model for cloud manufacturing considering available periods of services using an improved hyper-heuristic algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 269: 126419. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.126419. [14] YANG Jinfeng, XU Hua, CHENG Jinhai, et al. A decomposition-based memetic algorithm to solve the biobjective green flexible job shop scheduling problem with interval type-2 fuzzy processing time[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2023, 183: 109513. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2023.109513. [15] 杨和林, 郑梦婷, 刘帅, 等. 恶意干扰下的无人机辅助边缘计算加权能耗与时延智能优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(7): 2879–2887. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230986.YANG Helin, ZHENG Mengting, LIU Shuai, et al. Intelligent weighted energy consumption and delay optimization for UAV-assisted MEC under malicious jamming[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(7): 2879–2887. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230986. [16] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182–197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017. [17] MINKU L L, SUDHOLT D, and YAO Xin. Improved evolutionary algorithm design for the project scheduling problem based on runtime analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2014, 40(1): 83–102. doi: 10.1109/TSE.2013.52. [18] CHEN Weineng and ZHANG Jun. Ant colony optimization for software project scheduling and staffing with an event-based scheduler[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2013, 39(1): 1–17. doi: 10.1109/TSE.2012.17. [19] CHANG C K, JIANG H Y, DI Yu, et al. Time-line based model for software project scheduling with genetic algorithms[J]. Information and Software Technology, 2008, 50(11): 1142–1154. doi: 10.1016/j.infsof.2008.03.002. [20] SHEN Xiaoning, MINKU L L, MARTURI N, et al. A Q-learning-based memetic algorithm for multi-objective dynamic software project scheduling[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 428: 1–29. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.041. [21] MAHMUD S, ABBASI A, CHAKRABORTTY R K, et al. A self-adaptive hyper-heuristic based multi-objective optimisation approach for integrated supply chain scheduling problems[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 251: 109190. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109190. [22] CIMBALA J M. Taguchi orthogonal arrays[EB/OL]. https://www.me.psu.edu/cimbala/me345web_Fall_2014/Lectures/Taguchi_orthogonal_arrays.pdf, 2025. [23] ZHAO Fuqing, DI Shilu, and WANG Ling. A hyperheuristic with Q-learning for the multiobjective energy-efficient distributed blocking flow shop scheduling problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(5): 3337–3350. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3192112. [24] SHAO Zhongshi, SHAO Weishi, CHEN Jianrui, et al. A feedback learning-based selection hyper-heuristic for distributed heterogeneous hybrid blocking flow-shop scheduling problem with flexible assembly and setup time[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 131: 107818. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107818. [25] WU Xiuli, CONSOLI P, MINKU L, et al. An evolutionary hyper-heuristic for the software project scheduling problem[C]. The 14th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature–PPSN XIV, Edinburgh, UK, 2016: 37–47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-45823-6_4. [26] LI Rui, GONG Wenyin, LU Chao, et al. A learning-based memetic algorithm for energy-efficient flexible job-shop scheduling with type-2 fuzzy processing time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2023, 27(3): 610–620. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2022.3175832. [27] ZHU Lilu, WU Feng, HU Yanfeng, et al. A heuristic multi-objective task scheduling framework for container-based clouds via actor-critic reinforcement learning[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35(13): 9687–9710. doi: 10.1007/s00521-023-08208-6. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
