Multi-UAV RF Signals CNN|Triplet-DNN Heterogeneous Network Feature Extraction and Type Recognition
-
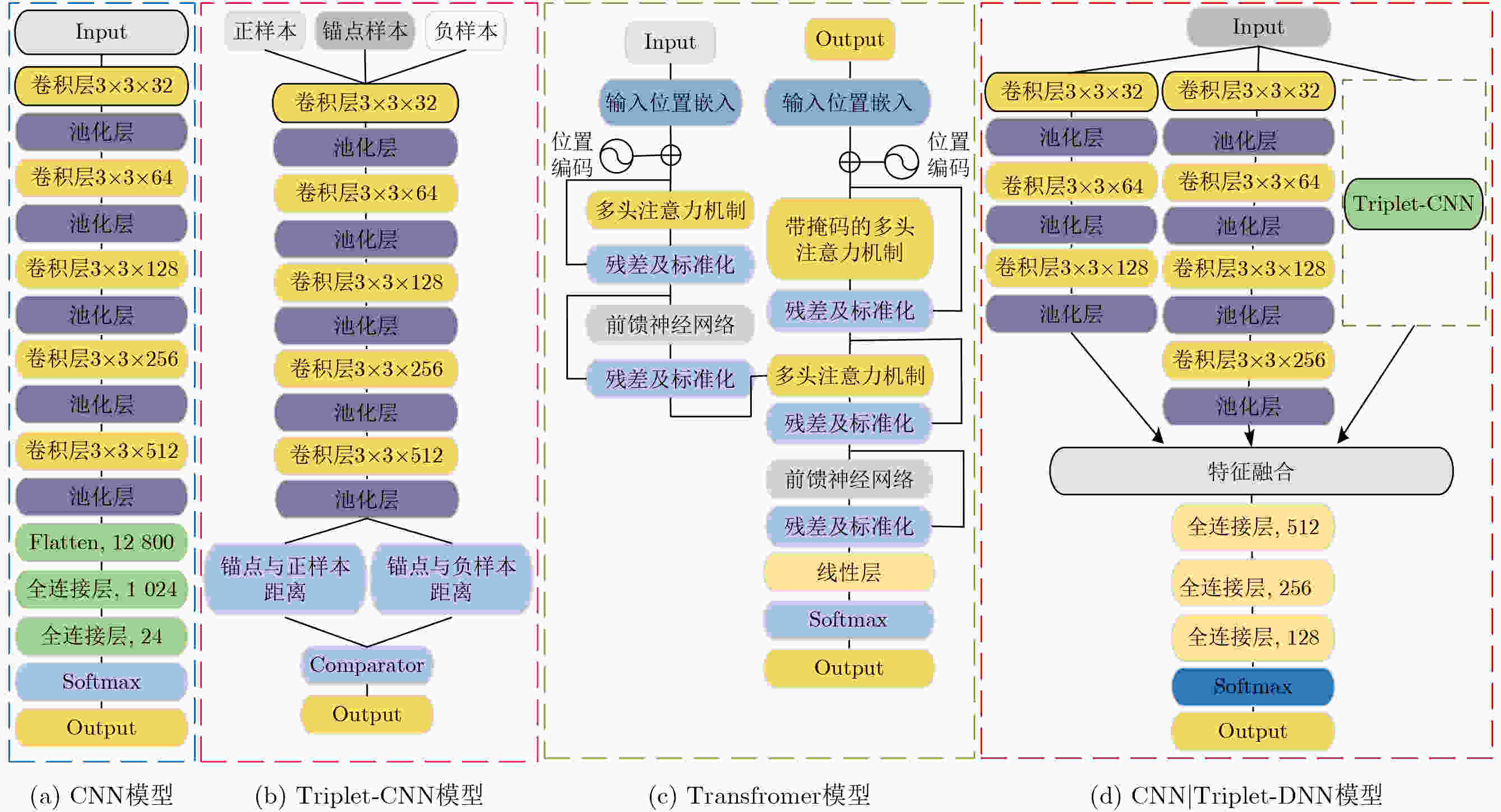
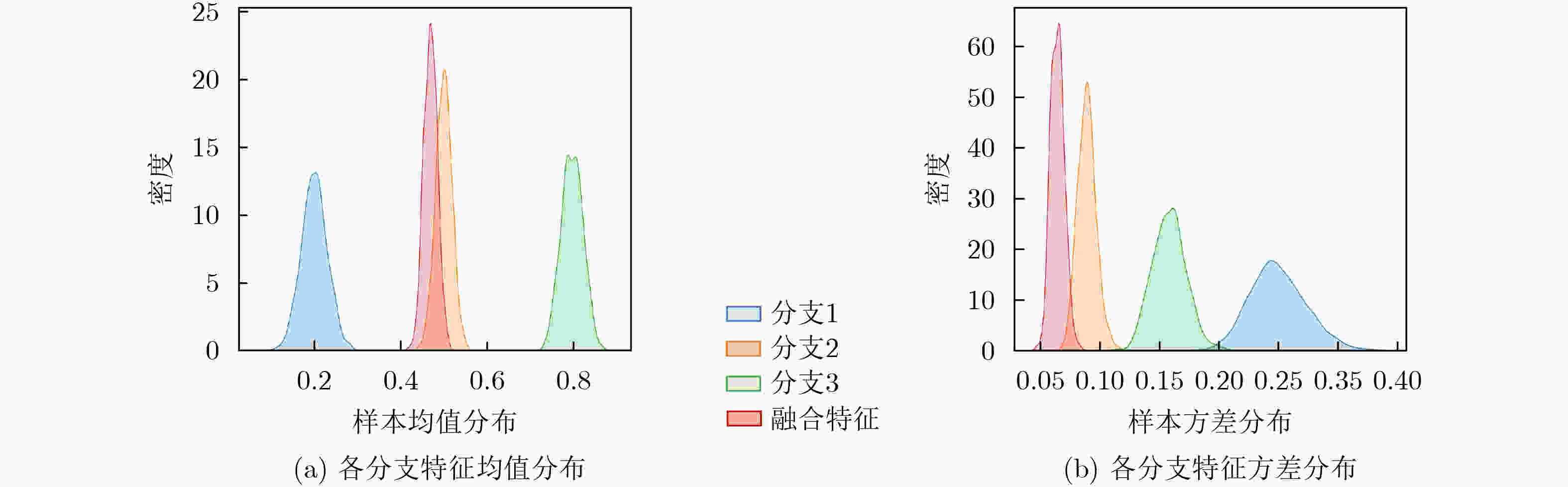
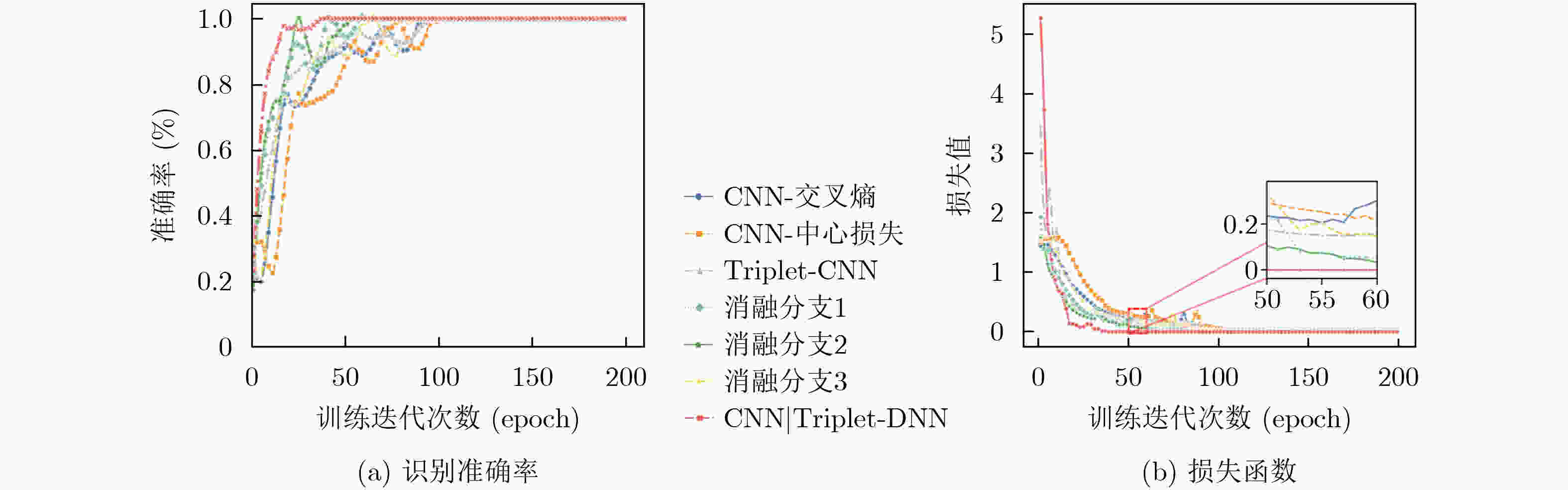
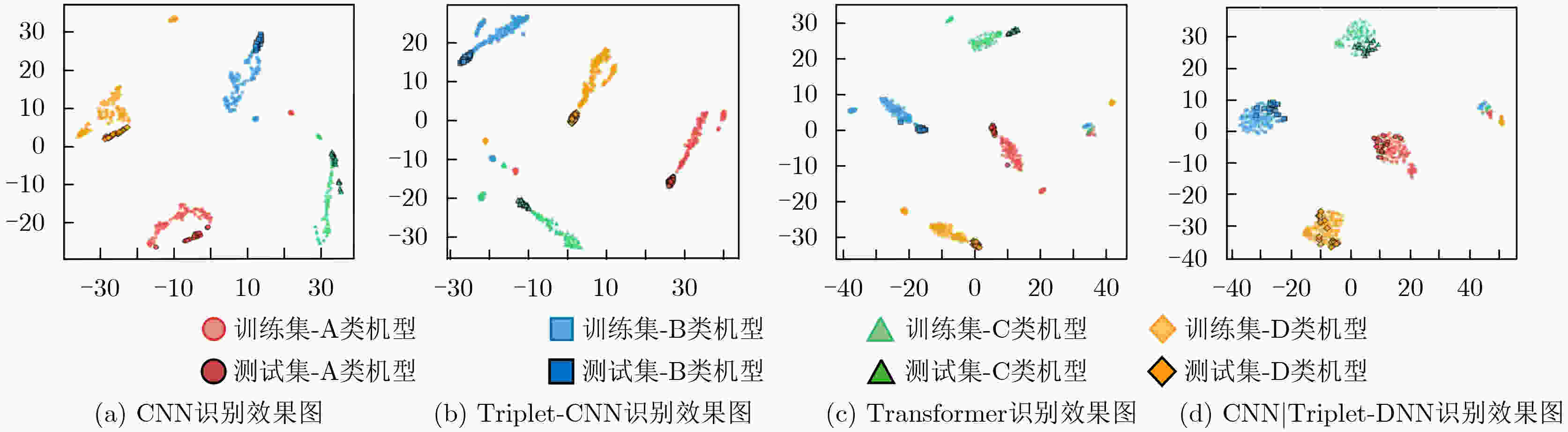
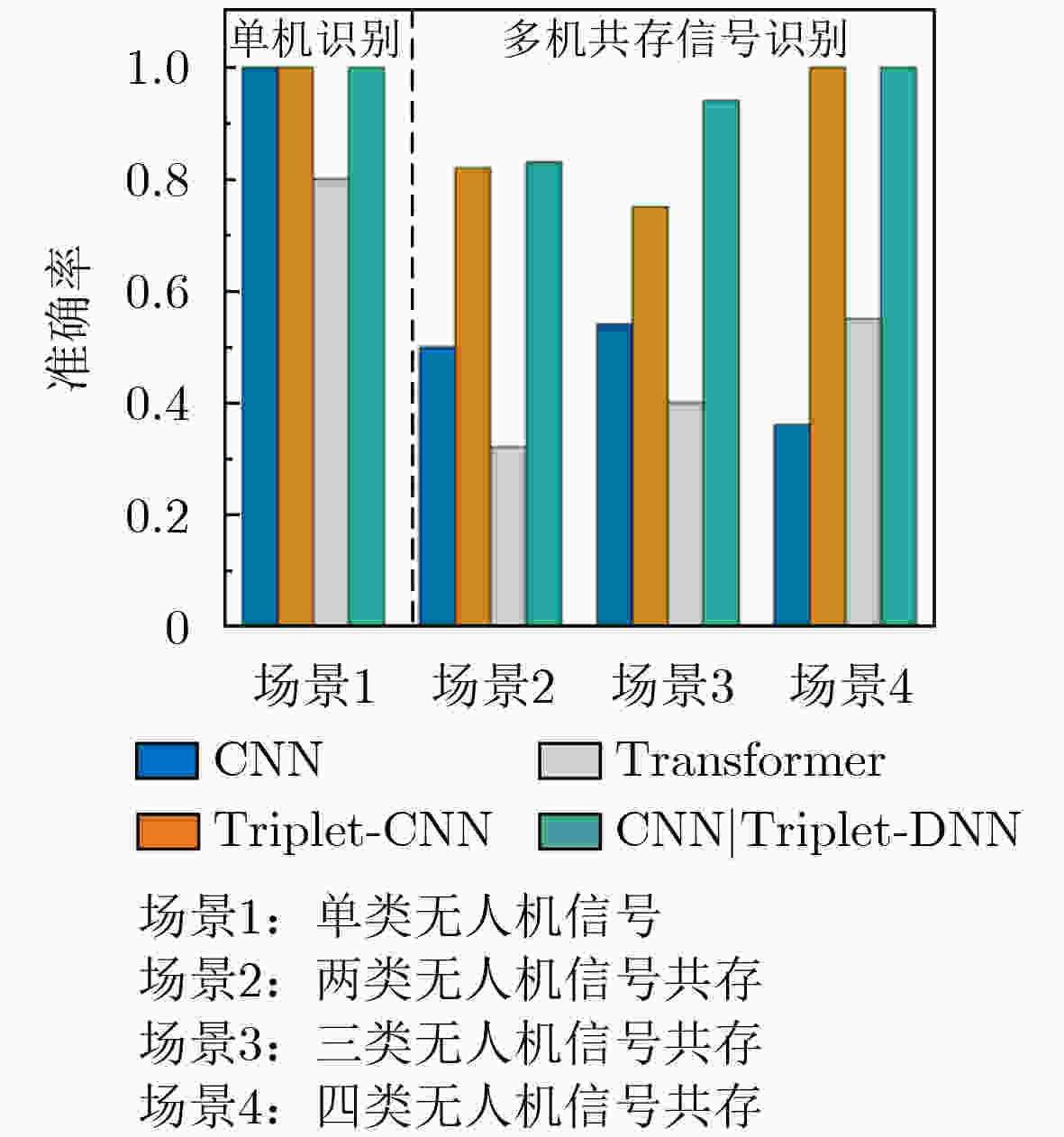
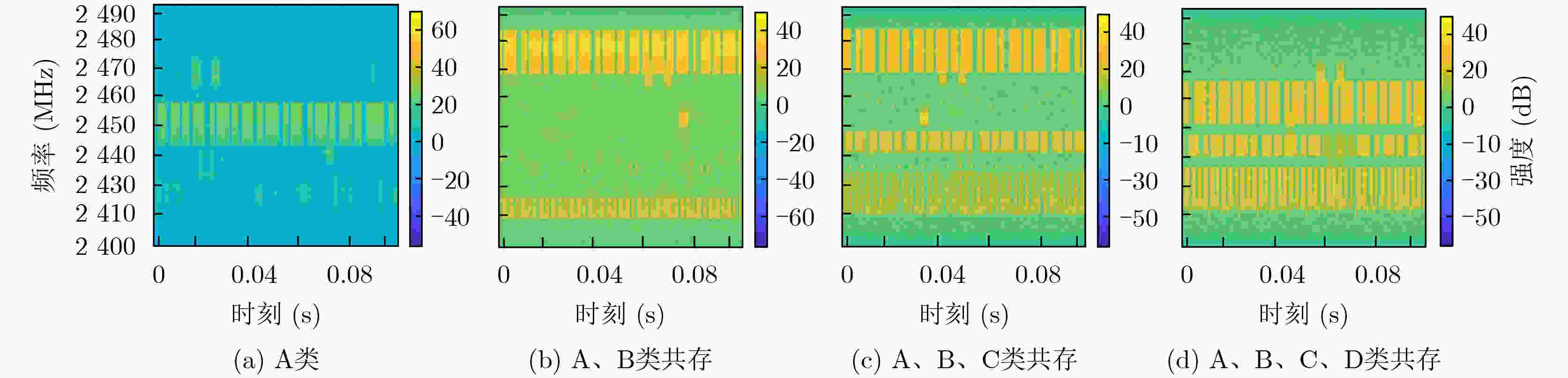
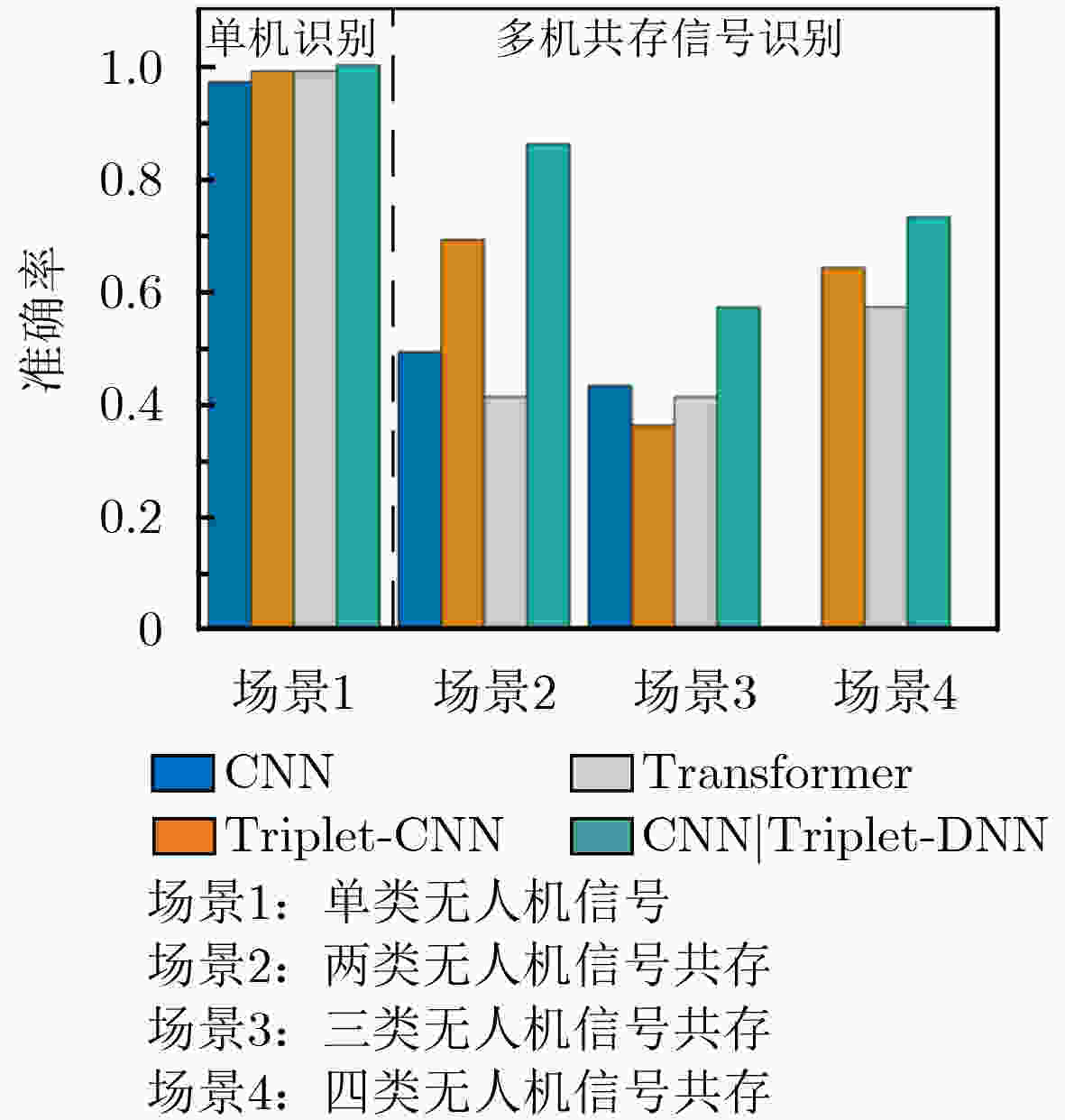
摘要: 随着无人机技术的广泛应用,多机共存场景中机型识别对空域管理与黑飞无人机反制具有重要意义。针对射频(RF)信号的特征提取与机型识别需求,该文提出CNN|Triplet-DNN异构网络模型。该模型采用不同深度卷积层与三元组(Triplet)结合的三分支结构,通过交叉熵、中心及三元组损失的动态协同,从分类准确性、类内聚集性和类间分离性三个角度,提取并融合时频图的异构多层特征;进一步利用深度神经网络(DNN)增强特征的非线性拟合能力,提升机型的识别准确率。基于DroneRFa数据集进行消融实验,验证了模型分支设计的有效性;通过叠加DroneRFa中单无人机信号模拟4类及以下多机共存场景,CNN|Triplet-DNN模型的机型识别准确率达83%~100%;在实飞实验中,该模型对2~4类共存场景中的机型识别准确率分别为86%, 57%和73%。与CNN, Triplet-CNN和Transformer模型相比,CNN|Triplet-DNN模型的识别性能更优。
-
关键词:
- 多无人机共存 /
- 机型识别 /
- CNN|Triplet-DNN模型 /
- RF信号 /
- 时频图
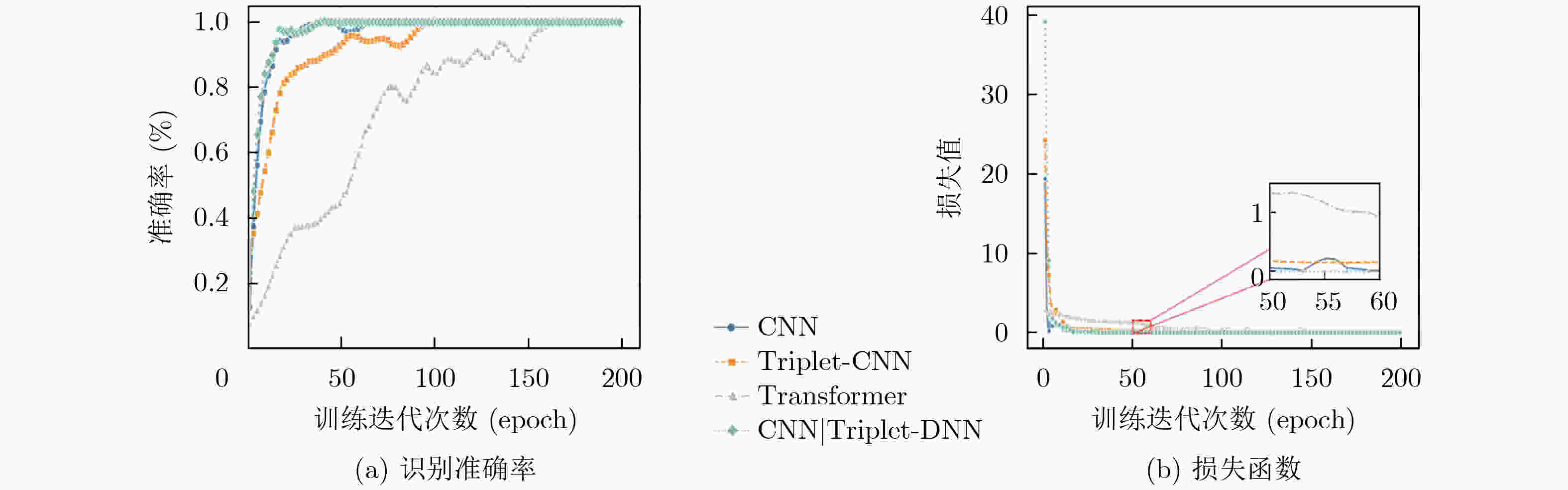
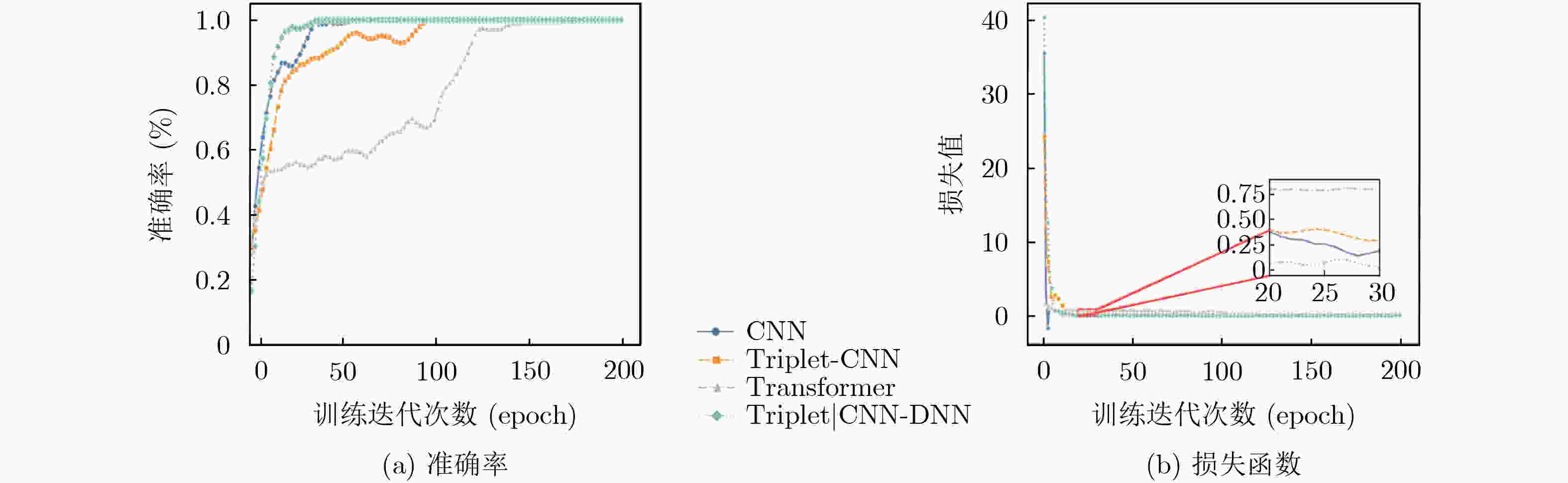
Abstract:Objective This study addresses the detection requirements of simultaneous Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) operations. The strategy is based on extracting model-specific information features from Radio Frequency (RF) time-frequency spectra. A CNN|Triplet-DNN heterogeneous network is developed to optimize feature extraction and classification. The method resolves the problem of identifying individual UAV models within coexisting RF signals and supports efficient multi-UAV management in complex environments. Methods The CNN|Triplet-DNN architecture uses a parallel-branch structure that integrates a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and a Triplet Convolutional Neural Network (Triplet-CNN). Branch 1 employs a lightweight CNN to extract global features from RF time-frequency diagrams while reducing computational cost. Branch 2 adds an enhanced center-loss function to strengthen feature discrimination and address ambiguous feature boundaries under complex conditions. Branch 3, based on a Triplet-CNN framework, applies Triplet Loss to capture local and global features of RF time-frequency diagrams. The complementary features from the three branches are fused and processed through a fully connected DNN with a Softmax activation function to generate probability distributions for UAV signal classification. This structure improves UAV type recognition performance. Results and Discussions RF signals from the open-source DroneRFa dataset were superimposed to simulate multi-UAV coexistence, and real-world drone signals were collected through controlled flights to build a comprehensive signal database. (1) Based on single-UAV RF time-frequency diagrams from the open-source dataset, ablation experiments ( Fig. 7 ) were conducted on the three-branch CNN|Triplet-DNN structure to validate its design, and each model was trained. (2) The simulated multi-UAV coexistence dataset was used for identification tasks to evaluate recognition performance under coexistence conditions. Results (Fig. 10 ) show that recognition accuracy for four or fewer UAV types ranges from 83% to 100%, confirming the effectiveness of the CNN|Triplet-DNN model. (3) Each model was trained using the flight dataset and then applied to real multi-UAV coexistence identification. The CNN|Triplet-DNN achieved recognition accuracies of 86%, 57%, and 73% for two, three, and four UAV types, respectively (Fig. 13 ). Comparison with the CNN, Triplet-CNN, and Transformer models shows that the CNN|Triplet-DNN has stronger generalizability. All models exhibited performance degradation on real-world data relative to the open-source dataset, mainly because drones dynamically adjust communication frequency bands, which reduces recognition performance under coexistence scenarios.Conclusions A CNN|Triplet-DNN heterogeneous network is proposed for identifying RF signals emitted by multiple UAVs. The three-branch structure and backpropagation algorithm improve the extraction of discriminative aircraft-model features, and the DNN enhances model generalization. Experiments using open-source datasets and real flight scenarios verify the method’s effectiveness and practical value. Future work will address dataset expansion, model optimization for dynamic frequency-band adaptation, and improved recognition under complex coexistence conditions. -
表 1 各层网络模型的训练效果指标
网络深度 准确率 精确率 召回率 F1分数 训练时间(s) 全部参数(个) 3 0.8947 0.8220 0.8947 0.8511 57.49 10,654,192 4 0.8974 0.8235 0.8953 0.8521 52.72 2,728,496 5 0.9447 0.9737 0.9473 0.9509 48.86 1,196,720 6 0.8947 0.8202 0.8947 0.8511 47.75 557,872 表 2 四类无人机具体参数
无人机型号 标记类 起飞重量(g) 最大飞行速度(m/s) 图传技术协议 图传信号带宽(MHz) 大疆精灵4 Pro A 1,375 20 OcuSync 2.0 15~20 大疆经纬Matrice 4 B 1,219 21 OcuSync 4.0 5~40 大疆御3 C 895 21 OcuSync 3.0+ 5~10 道通智能EVO Lite D 835 18 Autel SkyLink 5~10 -
[1] RAHMAN M S, KHALIL I, and ATIQUZZAMAN M. Blockchain-powered policy enforcement for ensuring flight compliance in drone-based service systems[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(1): 116–123. doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.2000219. [2] SHAN Lin, MIURA R, MATSUDA T, et al. Vehicle-to-vehicle based autonomous flight coordination control system for safer operation of unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(11): 669. doi: 10.3390/drones7110669. [3] 赵慎, 诸皓冉, 周超, 等. 声学探测无人机中的麦克风立体阵列优化设计[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2025, 39(5): 155–165. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2407714.ZHAO Shen, ZHU Haoran, ZHOU Chao, et al. Optimization design of microphone array for acoustic detection drones[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2025, 39(5): 155–165. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2407714. [4] CAI Zhenxin, WANG Yu, JIANG Qi, et al. Toward intelligent lightweight and efficient UAV identification with RF fingerprinting[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(15): 26329–26339. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3395466. [5] MAGANAHALLI G M, MARUTHI A, UTTARKAR C, et al. Neural network-based classification of unmanned aerial vehicle flight modes using convolution and transfer learning[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2025, 3278(1): 020025. doi: 10.1063/5.0262989. [6] FENG Junhao, TANG Xiaogang, ZHANG Binquan, et al. A lightweight deep learning RF fingerprint recognition method[C]. The 4th International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering, Shenzhen, China, 2022: 452–457. doi: 10.1109/CISCE55963.2022.9851177. [7] LI Chaoqun, WANG Jinming, WANG Wenyan, et al. RF-based on feature fusion and convolutional neural network classification of UAVs[C]. The IEEE 8th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2022: 1899–1904. doi: 10.1109/ICCC56324.2022.10065895. [8] 周景贤, 李希娜. 基于改进卷积神经网络和射频指纹的无人机检测与识别[J]. 计算机应用, 2024, 44(3): 876–882. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023030299.ZHOU Jingxian and LI Xina. UAV detection and recognition based on improved convolutional neural network and radio frequency fingerprint[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2024, 44(3): 876–882. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023030299. [9] 晏行伟, 孔令轩, 刘坤, 等. 基于MobileNet-DOA的无人机射频信号识别方法[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2025, 23(1): 57–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2025.01.006.YAN Xingwei, KONG Lingxuan, LIU Kun, et al. Drone radio frequency signal identification method based on MobileNet-DOA[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2025, 23(1): 57–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2025.01.006. [10] 曾政智, 周嘉伟, 罗正华. 同频段混合信号中的无人机信号盲检测识别[J]. 电讯技术, 2020, 60(6): 689–694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2020.06.013.ZENG Zhengzhi, ZHOU Jiawei, and LUO Zhenghua. Blind detection and recognition of UAV signal in mixed signal in same frequency band[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2020, 60(6): 689–694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2020.06.013. [11] SAZDIĆ-JOTIĆ B, POKRAJAC I, BAJČETIĆ J, et al. Single and multiple drones detection and identification using RF based deep learning algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 187: 115928. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115928. [12] XU Chengtao, CHEN Bowen, LIU Yongxin, et al. RF fingerprint measurement for detecting multiple amateur drones based on STFT and feature reduction[C]. 2020 Integrated Communications Navigation and Surveillance Conference (ICNS), Herndon, USA, 2020: 4G1. doi: 10.1109/ICNS50378.2020.9223013. [13] ZHANG Jiangfan, ZHANG Yan, SHI Zhiguang, et al. Unmanned aerial vehicle object detection based on information-preserving and fine-grained feature aggregation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(14): 2590. doi: 10.3390/rs16142590. [14] 张萌, 李响, 张经纬. 基于图像偏移角和多分支卷积神经网络的旋转不变模型设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(12): 4522–4528. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240417.ZHANG Meng, LI Xiang, and ZHANG Jingwei. Design of rotation invariant model based on image offset angle and multibranch convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(12): 4522–4528. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240417. [15] ZHENG Yunfei, ZHANG Xuejun, WANG Shenghan, et al. Convolutional neural network and ensemble learning-based unmanned aerial vehicles radio frequency fingerprinting identification[J]. Drones, 2024, 8(8): 391. doi: 10.3390/drones8080391. [16] CHA B R and VAIDYA B. Enhancing human activity recognition with Siamese networks: A comparative study of contrastive and triplet learning approaches[J]. Electronics, 2024, 13(9): 1739. doi: 10.3390/electronics13091739. [17] SINGH G, STEFENON S F, and YOW K C. The shallowest transparent and interpretable deep neural network for image recognition[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 13940. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92945-2. [18] 俞宁宁, 毛盛健, 周成伟, 等. DroneRFa: 用于侦测低空无人机的大规模无人机射频信号数据集[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(4): 1147–1156. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230570.YU Ningning, MAO Shengjian, ZHOU Chengwei, et al. DroneRFa: A large-scale dataset of drone radio frequency signals for detecting low-altitude drones[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(4): 1147–1156. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230570. [19] HAN Jia, YU Zhiyong, YANG Jian, et al. Real-world UAV recognition based on radio frequency fingerprinting with transformer[J]. IET Communications, 2025, 19(1): e70004. doi: 10.1049/cmu2.70004. [20] ROMAN-RANGEL E and MARCHAND-MAILLET S. Inductive t-SNE via deep learning to visualize multi-label images[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 81: 336–345. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2019.01.015. -





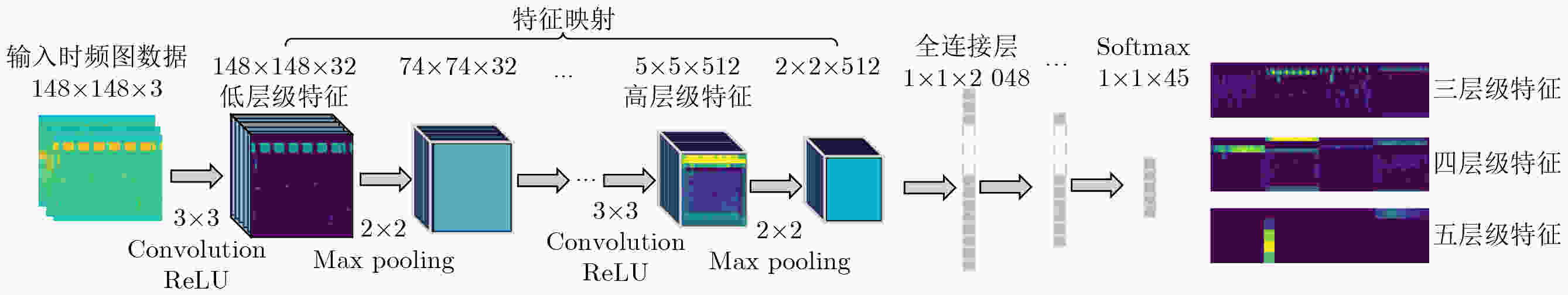
 下载:
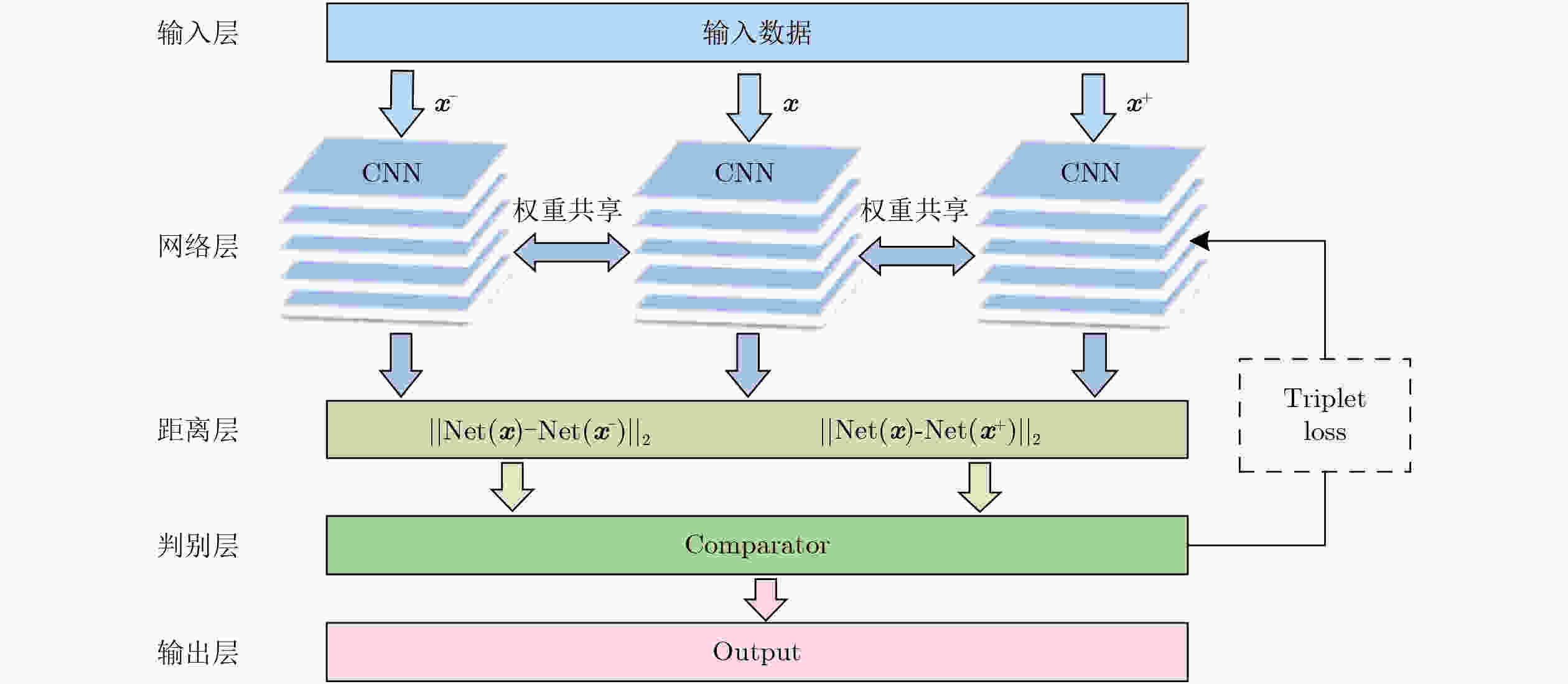
下载:
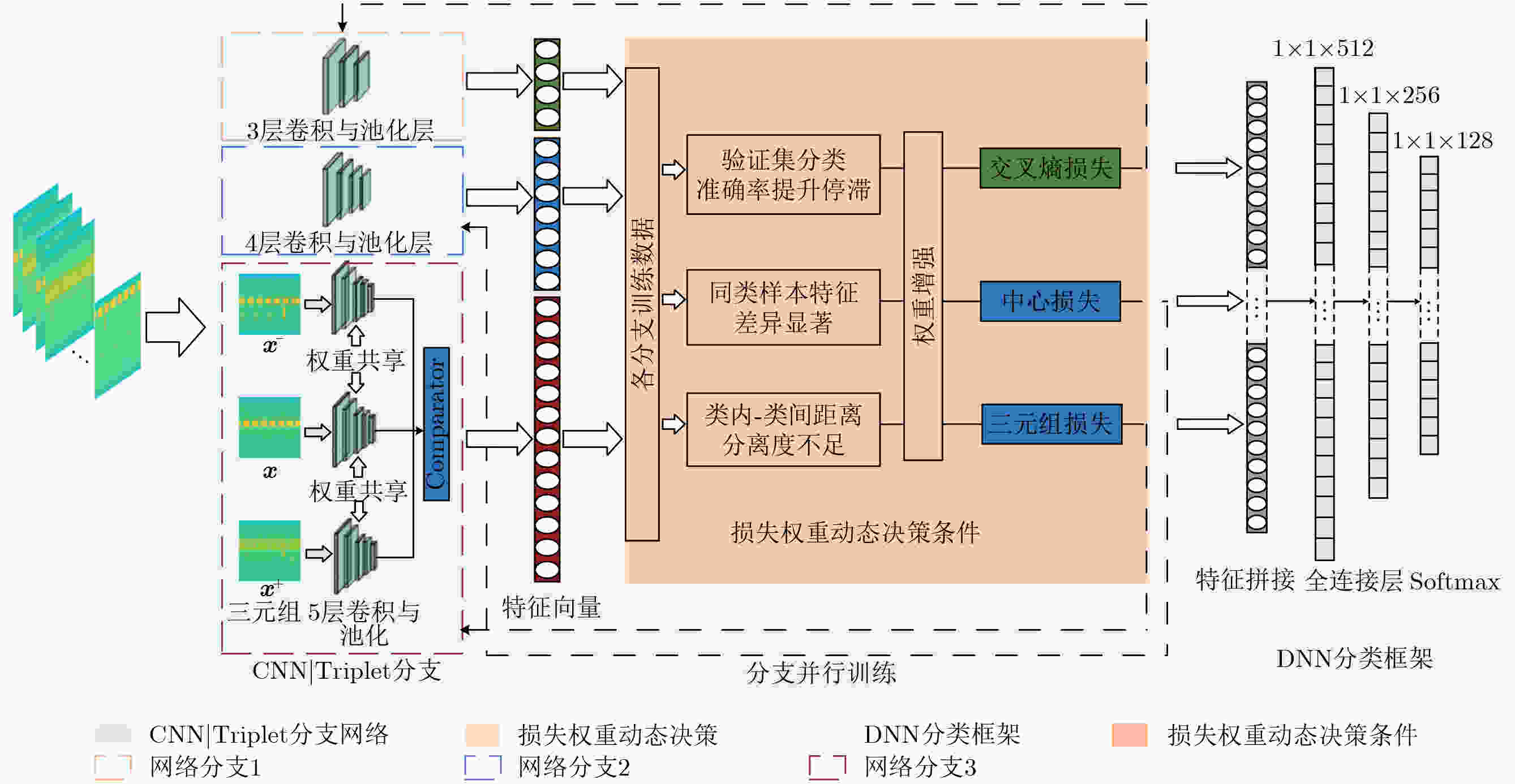
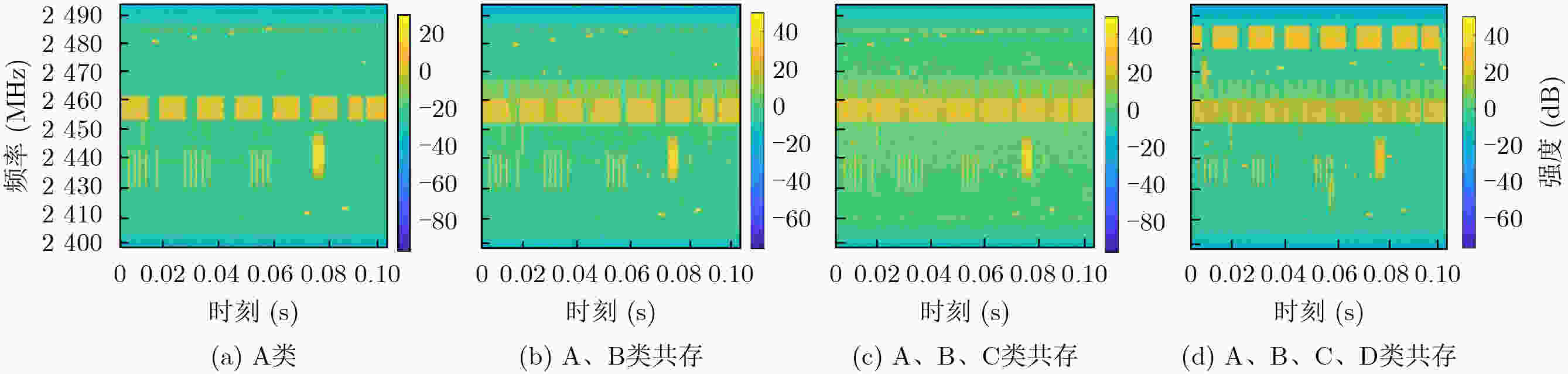


 下载:
下载:
