Edge-Cloud Collaborative Searchable Attribute-Based Signcryption Approach for Internet of Vehicles
-
摘要: 动态开放的网络环境使车联网难免遭受窃听、数据篡改和伪造,传统云计算因高延迟难以满足海量数据的实时性需求,安全性和性能之间固有冲突制约着车联网发展。为了解决上述问题,该文专为车联网设计出边云协同可搜索属性签密方法,可允许授权用户无须解密密文,就能通过云端快速匹配机制高效检索所需信息。利用边缘计算下沉计算能力到网络边缘,协同云服务器、边缘服务器和车载终端设备共同工作。通过属性签密和线性秘密共享机制的融合,实现车联网数据的细粒度访问控制,更好地保障数据的安全性。针对车载设备资源受限问题,将解签密过程中的复杂运算外包给高性能边缘节点处理,减轻了车载终端的运算负担且提升了响应速度,能够很好地适应车联网这种动态的资源受限复杂环境。Abstract:
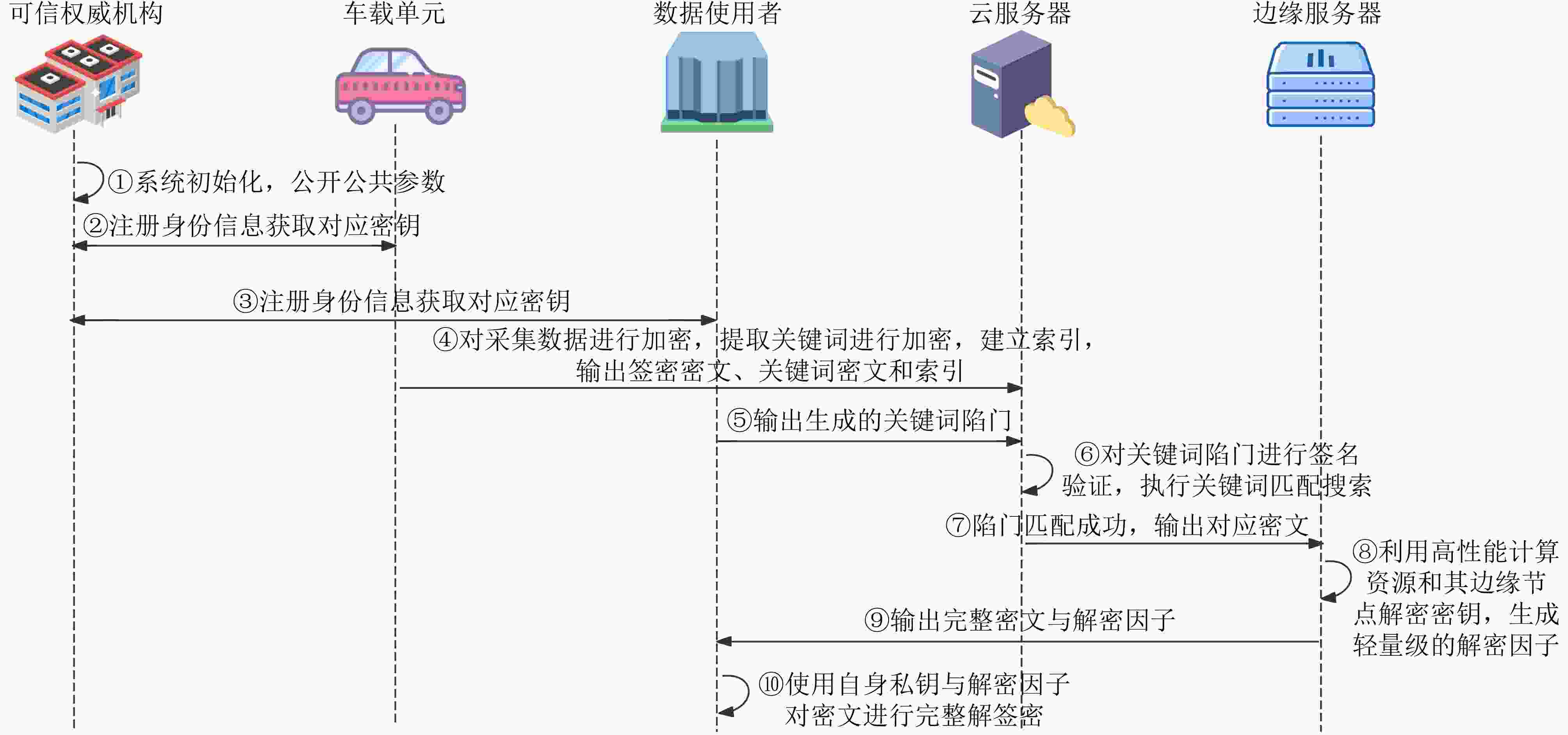
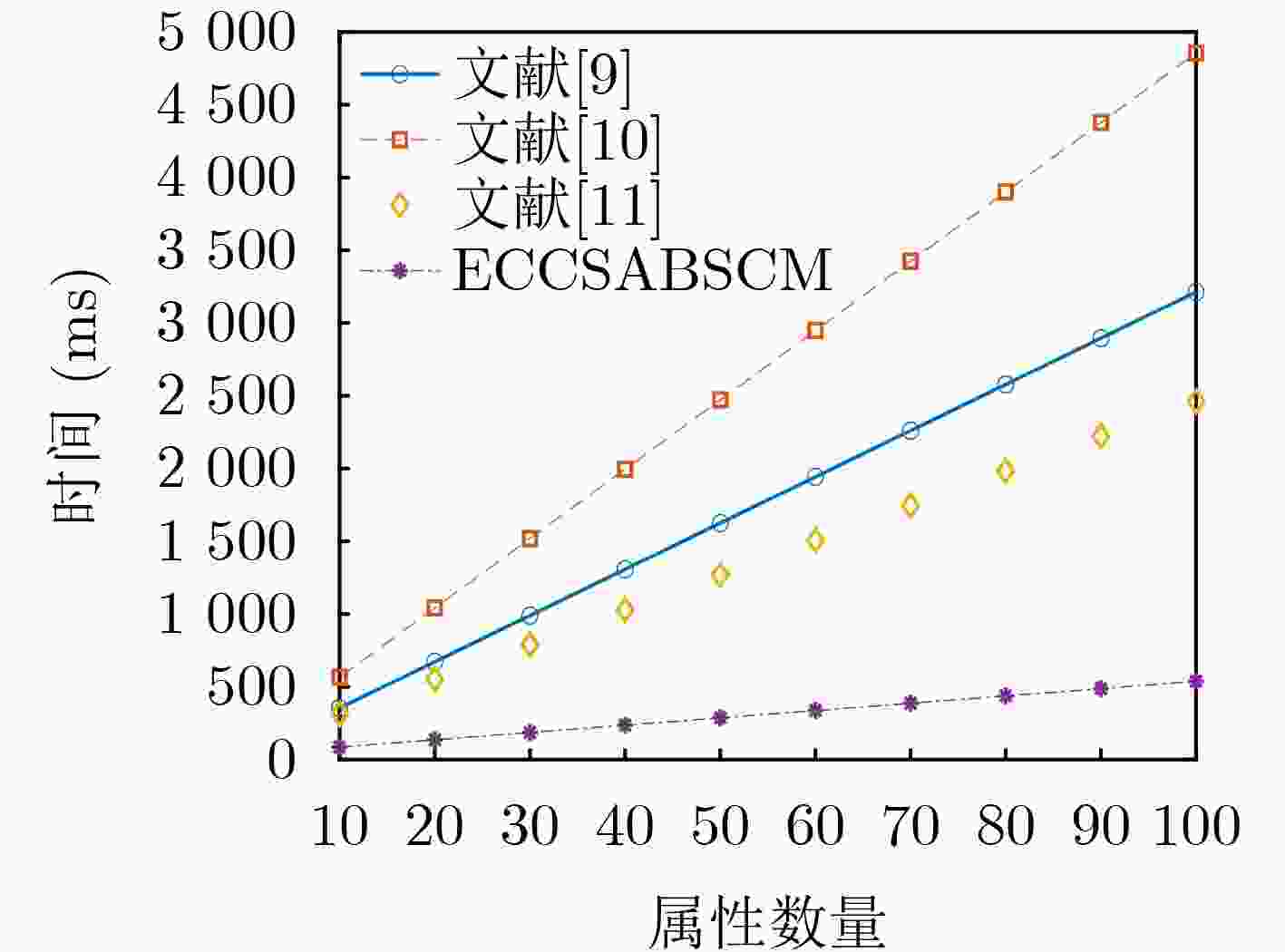
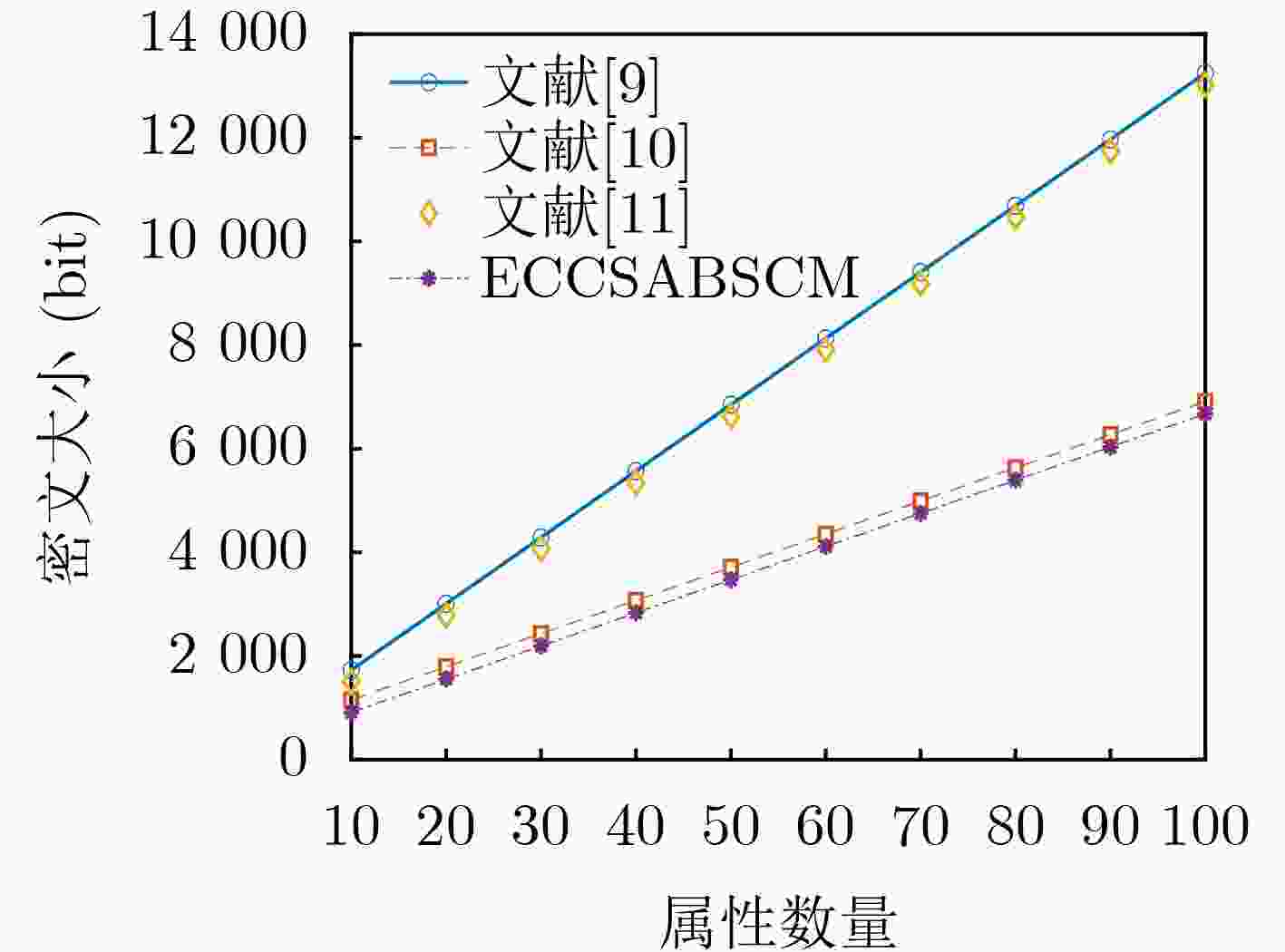
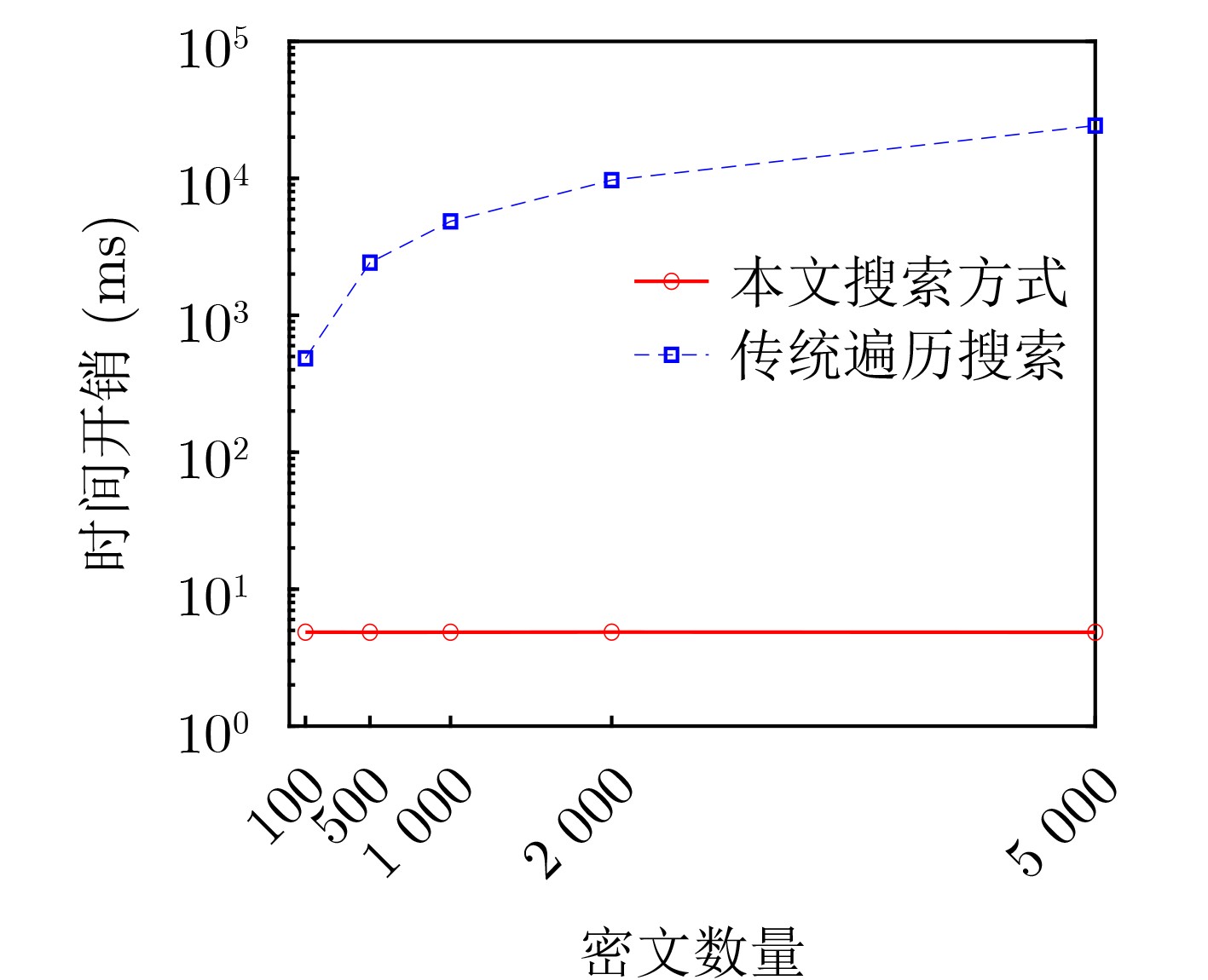
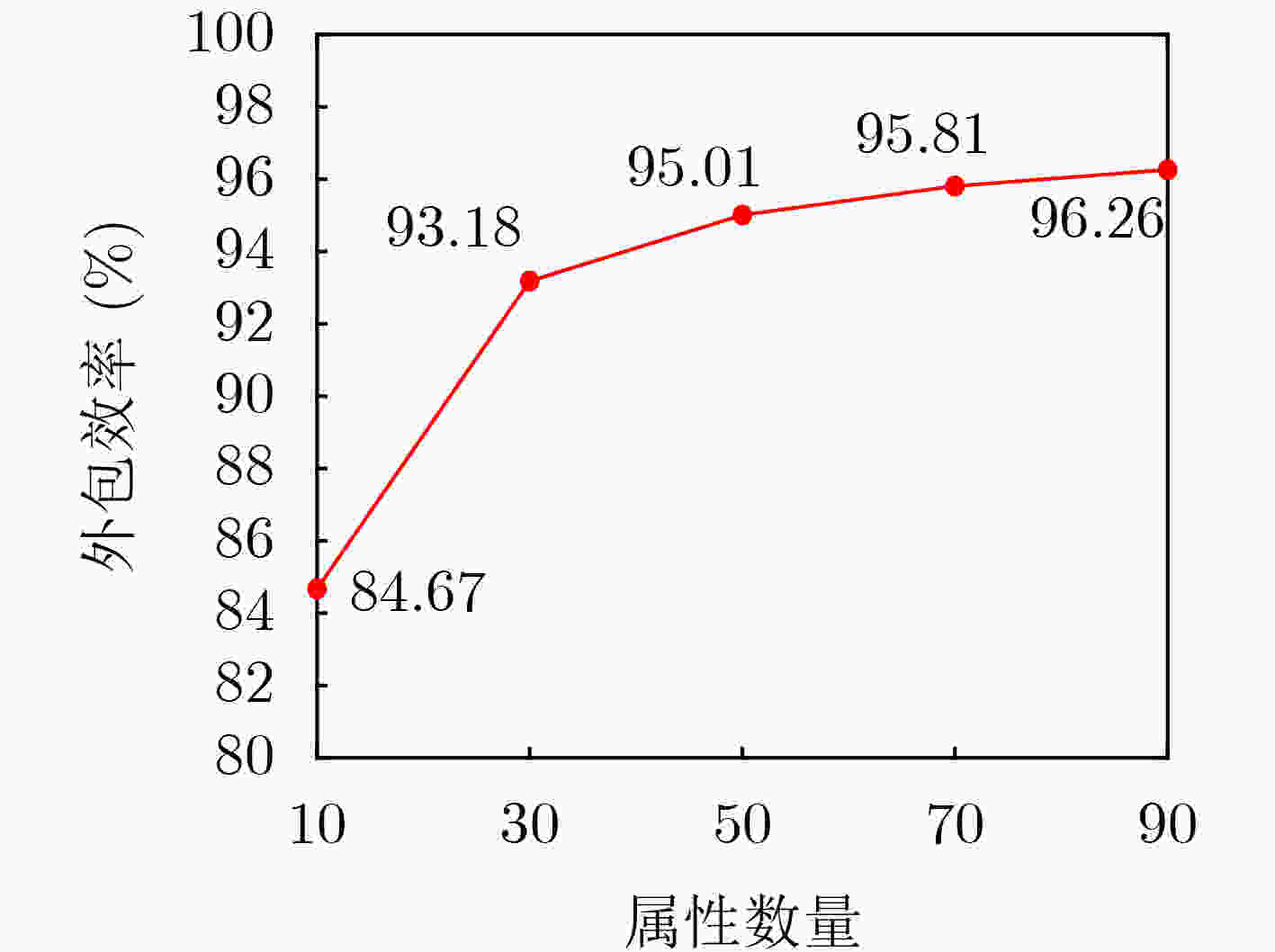
Objective The dynamic and open environment of the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) poses substantial challenges to data security and real-time performance. Large-scale data interactions are vulnerable to eavesdropping, tampering, forgery, and replay attacks. Conventional cloud computing architectures exhibit inherent latency and cannot satisfy millisecond-level real-time requirements in IoV applications, which results in inefficient data transmission and an increased risk of traffic accidents. Therefore, balancing data security and real-time performance represents a critical bottleneck for large-scale IoV deployment. Methods An edge-cloud collaborative searchable attribute-based signcryption method is proposed for IoV applications. A multi-layer architecture is constructed, consisting of cloud servers, edge servers, and in-vehicle terminal devices. Access control is enforced through a hybrid key-policy and ciphertext-policy mechanism derived from attribute-based signcryption and a Linear Secret Sharing Scheme (LSSS). To reduce local decryption overhead, bilinear pairing operations are outsourced to edge nodes. SM9 is adopted for trapdoor generation and signature authentication. The proposed method provides data confidentiality, signature unforgeability, and trapdoor unforgeability. Results and Discussions The proposed method demonstrates superior performance in an IoV edge-cloud collaborative architecture for searchable attribute-based signcryption ( Tables 1 ~5 ). Functional characteristics are summarized in (Table 1 ). (Fig. 2 ) illustrates the variation in total computation time as the number of attributes increases. Although the total time increases slightly, the growth rate remains low. By offloading computation-intensive tasks to edge nodes, the local computational burden on user terminals is substantially reduced. This optimization is quantified by an outsourcing efficiency exceeding 96% (Table 4 ,Fig. 5 ). Instantaneous retrieval is achieved by reducing the search complexity to O(1) through a hash-based index (Fig. 4 ). End-to-end search latency is maintained within an acceptable range for IoV applications (Table 5 ), which confirms suitability for real-time data access. As shown in (Fig. 3 ), with an increasing number of attributes, the ciphertext size variation of the proposed method remains the smallest among the compared schemes.Conclusions The proposed method achieves fine-grained access control, data confidentiality, data integrity, and unforgeability, while maintaining advantages in computational and communication efficiency. Through a computation offloading mechanism, the method effectively addresses resource constraints of on-board devices in dynamic, resource-sensitive, and real-time IoV environments. -
表 2 运算符号说明(ms)
符号及含义 执行一次双线性对操作: $ 1{T}_{\mathrm{p}} $ 执行一次指数操作:$ {1T}_{\mathrm{e}} $ 执行一次乘法操作:$ 1{T}_{\mathrm{m}} $ 执行一次哈希函数操作:$ 1{T}_{\mathrm{h}} $ 耗时 4.843 7.941 0.043 0.003 表 3 计算开销分析
对比方法 总体时间开销 密文大小 文献[9] $ (4+4n){T}_{\mathrm{e}}+3{T}_{\mathrm{m}}+{T}_{\mathrm{h}}+{T}_{\mathrm{p}} $ $ \left(\begin{matrix}2n+7\\ \end{matrix}\right)\left| {G}_{1}\right| $ 文献[10] $ {(6n+10)T}_{\mathrm{e}}+{T}_{\mathrm{m}}+2{T}_{\mathrm{p}}+(3n+2){T}_{\mathrm{h}} $ $ 4\left| {Z}_{p}\right| +6\left| {G}_{1}\right| +\left(n+1\right)\left| {G}_{\mathrm{T}}\right| $ 文献[11] $ {\left(3n+7\right){{T}_{\mathrm{e}}}+3T}_{\mathrm{h}}+(n+5){T}_{\mathrm{m}}+4{T}_{\mathrm{p}} $ $ 2\left| {Z}_{p}\right| +(2n+3)\left| {G}_{1}\right| $ ECCSABSCM $ 2{T}_{\mathrm{e}}+\left(4n+9\right){T}_{\mathrm{m}}+(n+4{)T}_{\mathrm{p}}+(2n+5){T}_{\mathrm{h}} $ $ \left| {Z}_{p}\right| +\left(n+2\right)\left| {G}_{1}\right| +2\left| {G}_{2}\right| $ 表 4 解签密计算任务外包效率分析
属性数量 $ 10 $ $ 30 $ $ 50 $ 70 90 $ {T}_{\mathrm{t}}(\text{ms}) $ 108.71 306.66 504.64 702.63 900.60 $ {T}_{\mathrm{r}}(\text{ms}) $ 16.66 20.92 25.18 29.44 33.70 $ \text{OE}(\% ) $ 84.67 93.18 95.01 95.81 96.26 表 5 端到端搜索延迟构成(ms)
属性数量 $ 10 $ $ 30 $ $ 50 $ 70 90 $ {T}_{\text{Calc}} $ 137.31 337.86 538.43 738.99 939.55 $ {T}_{\text{Comm}} $ 80.00 80.00 80.00 80.00 80.00 $ {T}_{\mathrm{E}2\mathrm{E}} $ 217.31 417.86 618.43 818.99 1019.55 -
[1] LIU Jianhang, XUE Kunlei, MIAO Qinghai, et al. MCVCO: Multi-MEC cooperative vehicular computation offloading[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(1): 813–826. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3299381. [2] HADDAJI A, AYED S, and CHAARI FOURATI L. IoV security and privacy survey: Issues, countermeasures, and challenges[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2024, 80(15): 23018–23082. doi: 10.1007/s11227-024-06269-5. [3] TANG Chaogang, CHEN Wei, ZHU Chunsheng, et al. When cache meets vehicular edge computing: Architecture, key issues, and challenges[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2022, 29(4): 56–62. doi: 10.1109/MWC.202.2100159. [4] QUAN Haoyu, ZHANG Qingmiao, and ZHAO Junhui. Federated learning assisted intelligent IoV mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2025, 9(1): 228–241. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2024.3421357. [5] DAMSGAARD H J, OMETOV A, and NURMI J. Approximation opportunities in edge computing hardware: A systematic literature review[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 55(12): 252. doi: 10.1145/3572772. [6] 董裕民, 张静, 谢昌佐, 等. 云边端架构下边缘智能计算关键问题综述: 计算优化与计算卸载[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 765–776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230390.DONG Yumin, ZHANG Jing, XIE Changzuo, et al. A survey of key issues in edge intelligent computing under cloud-edge-terminal architecture: Computing optimization and computing offloading[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 765–776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230390. [7] DENG Ningzhi, DENG Shaojiang, HU Chunqiang, et al. An efficient revocable attribute-based signcryption scheme with outsourced unsigncryption in cloud computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 42805–42815. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963233. [8] YU Huifang and BAI Xiaoping. Identity-based searchable attribute signcryption in lattice for a blockchain-based medical system[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2024, 25(3): 461–471. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2300248. [9] 牛淑芬, 王卫芳, 董润园, 等. 云边协同下支持等值测试的属性基广播签密方案[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2025, 19(8): 2241–2250. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2410023.NIU Shufen, WANG Weifang, DONG Runyuan, et al. Attribute-based broadcast signcryption scheme with equivalence testing support under cloud-edge collaboration[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2025, 19(8): 2241–2250. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2410023. [10] 牛淑芬, 周思玮, 吕锐曦, 等. 医疗社交网络中基于云计算的属性基签密方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(3): 884–893. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220070.NIU Shufen, ZHOU Siwei, LÜ Ruixi, et al. Attribute-base signcryption scheme based on cloud computing in mobile medical social network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(3): 884–893. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220070. [11] ELTAYIEB N, ELHABOB R, HASSAN A, et al. A blockchain-based attribute-based signcryption scheme to secure data sharing in the cloud[J]. Journal of Systems Architecture, 2020, 102: 101653. doi: 10.1016/j.sysarc.2019.101653. [12] 万云飞, 彭长根, 谭伟杰, 等. 基于国密SM9的边云协同属性基签密方案[J]. 信息安全研究, 2025, 11(2): 115–121. doi: 10.12379/j.issn.2096-1057.2025.02.03.WAN Yunfei, PENG Changgen, TAN Weijie, et al. Edge cloud collaborative attribute-based signcryption scheme based on state secret SM9[J]. Journal of Information Security Research, 2025, 11(2): 115–121. doi: 10.12379/j.issn.2096-1057.2025.02.03. [13] 王惠, 王峥. 工业物联网中基于区块链的属性基签密方案[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2024, 45(10): 2888–2896. doi: 10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2024.10.002.WANG Hui and WANG Zheng. Attribute based signcryption scheme based on blockchain in industrial internet of things[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2024, 45(10): 2888–2896. doi: 10.16208/j.issn1000-7024.2024.10.002. [14] 赖建昌, 黄欣沂, 何德彪, 等. 国密SM9数字签名和密钥封装算法的安全性分析[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2021, 51(11): 1900–1913. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0049.LAI Jianchang, HUANG Xinyi, HE Debiao, et al. Security analysis of SM9 digital signature and key encapsulation[J]. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2021, 51(11): 1900–1913. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0049. [15] QIAO Zirui, CAO Lei, ZHU Yasi, et al. DADD: Direct authentication with vehicles from different domains[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025, 26(10): 16811–16825. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2025.3575535. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
