Data-Driven Secure Control for Cyber-Physical Systems under Denial-of-Service Attacks: An Online Mode-Dependent Switching-Q-Learning Strategy
-
摘要: 基于学习策略和切换系统理论,该文研究了拒绝服务(DoS)攻击下未知信息物理系统(CPSs)的安全分析与控制问题。考虑到攻击能量有限性,采用攻击频率和持续时间来描述DoS攻击。特别地,不同于现有的安全学习方法,该文利用切换系统理论提出了一种在线模态依赖的切换-Q-学习控制新算法及相应的数据驱动安全评估新准则。首先,将休眠和活跃DoS攻击下的未知CPSs分别转化为一类含有稳定和不稳定子系统的未知切换系统。随后设计了一种新颖的在线模态依赖的切换-Q-学习算法,进而获得数据驱动的最优安全控制增益。同时通过约束子系统阶段和切换阶段的能量函数,提出了一种具有攻击频率和持续时间约束的数据驱动安全评估准则。最后通过网络化轮式机器人系统的对比实验验证了该方法的高效性和优越性。Abstract:
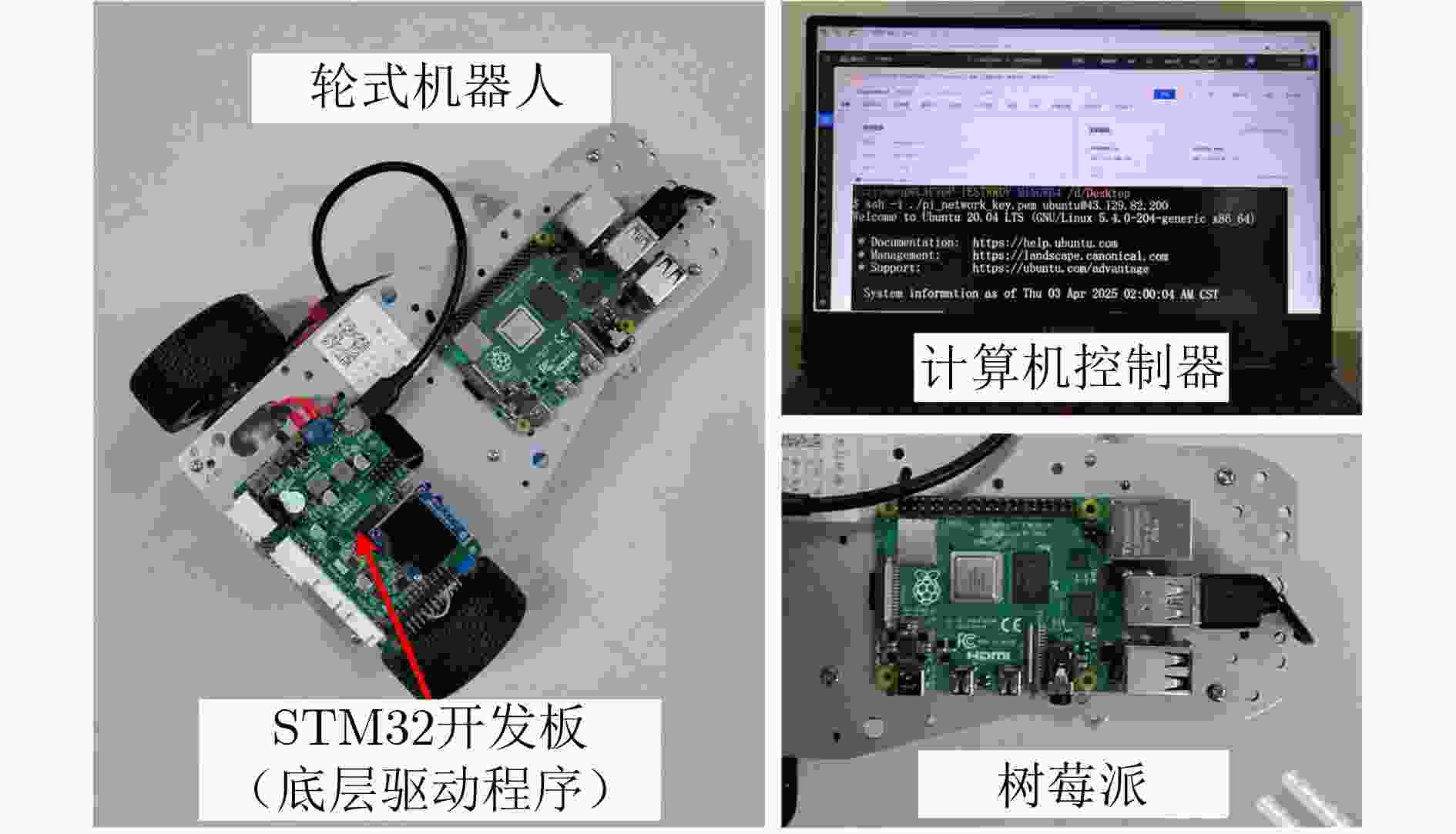
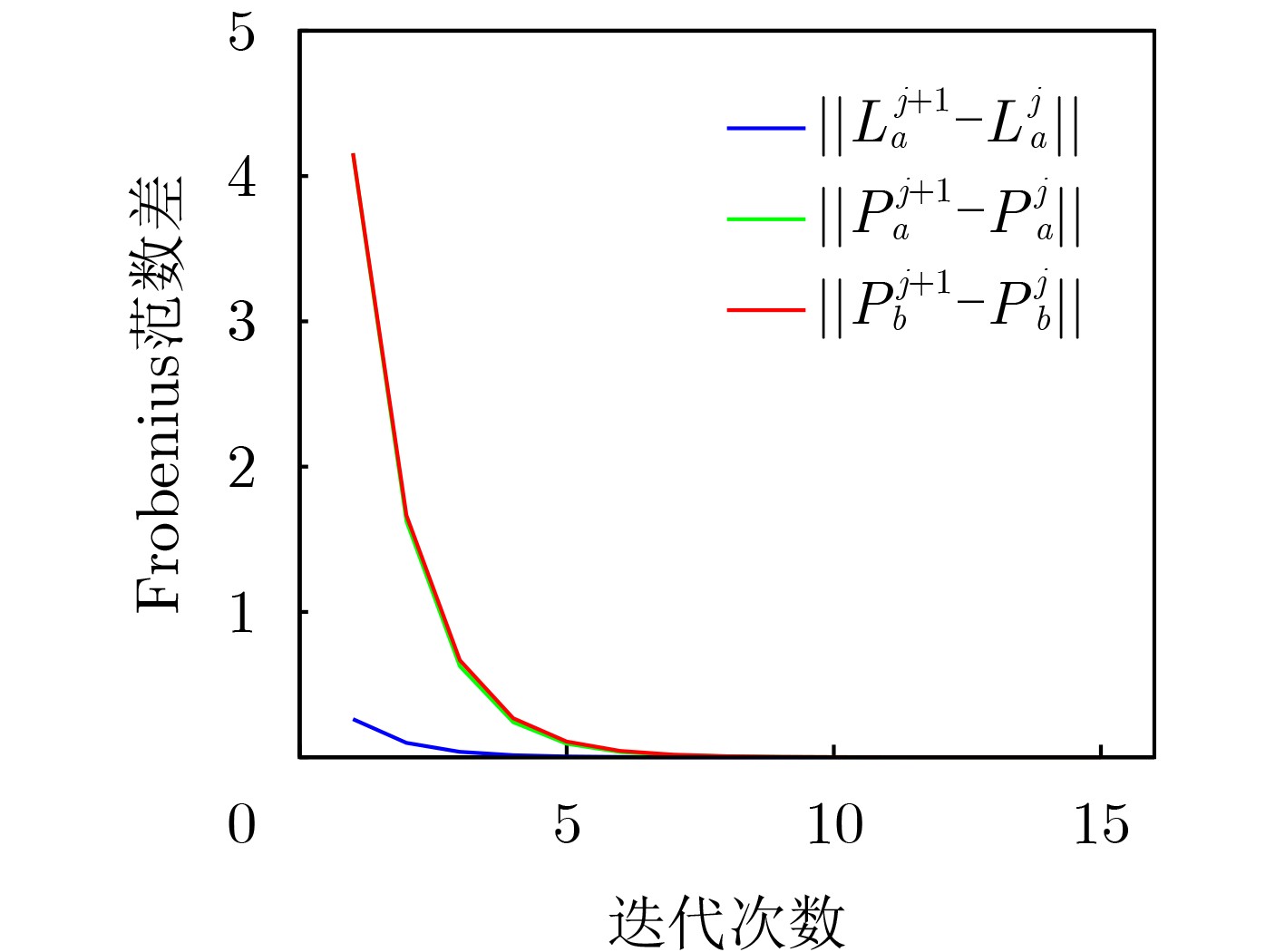
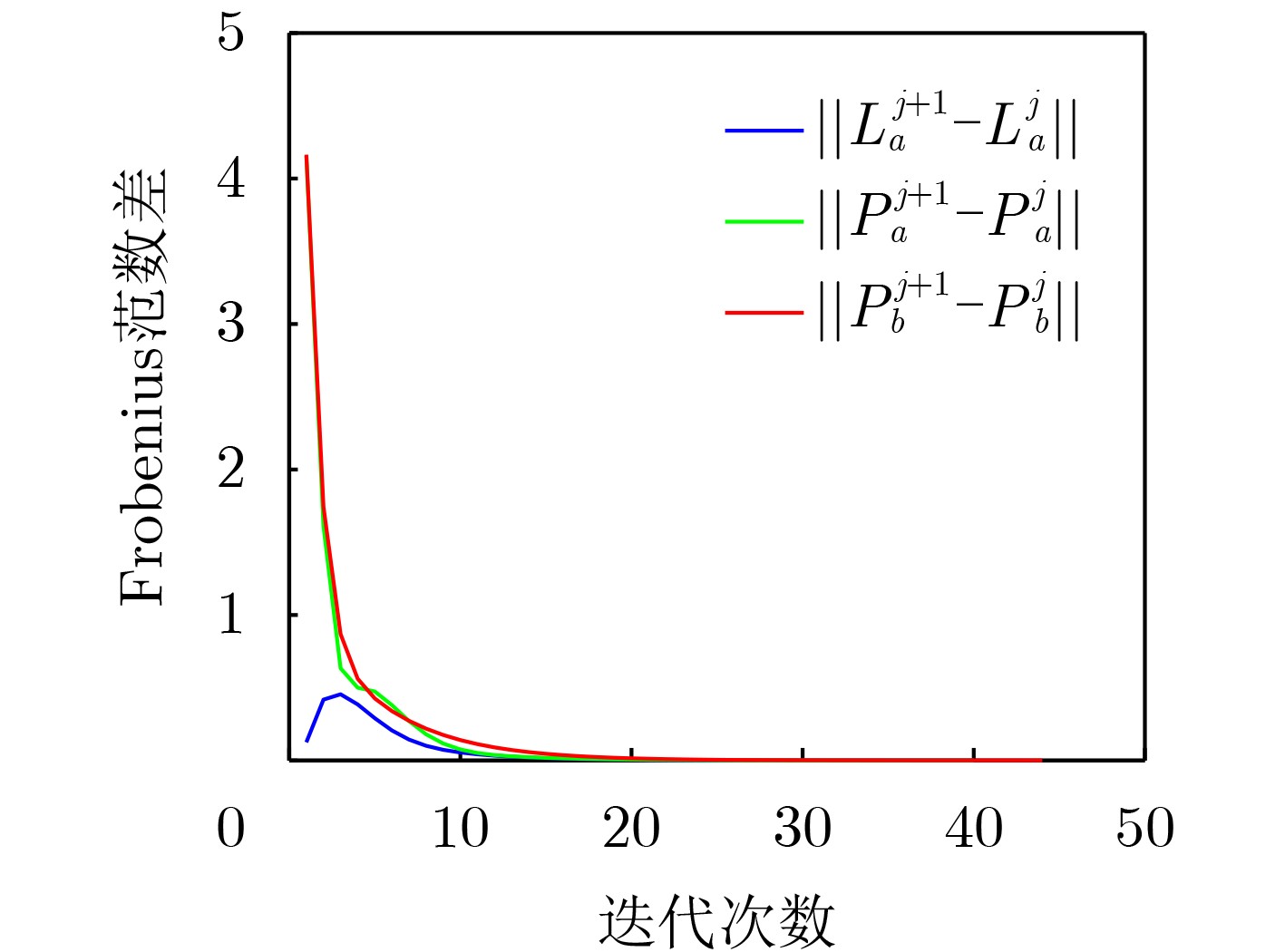
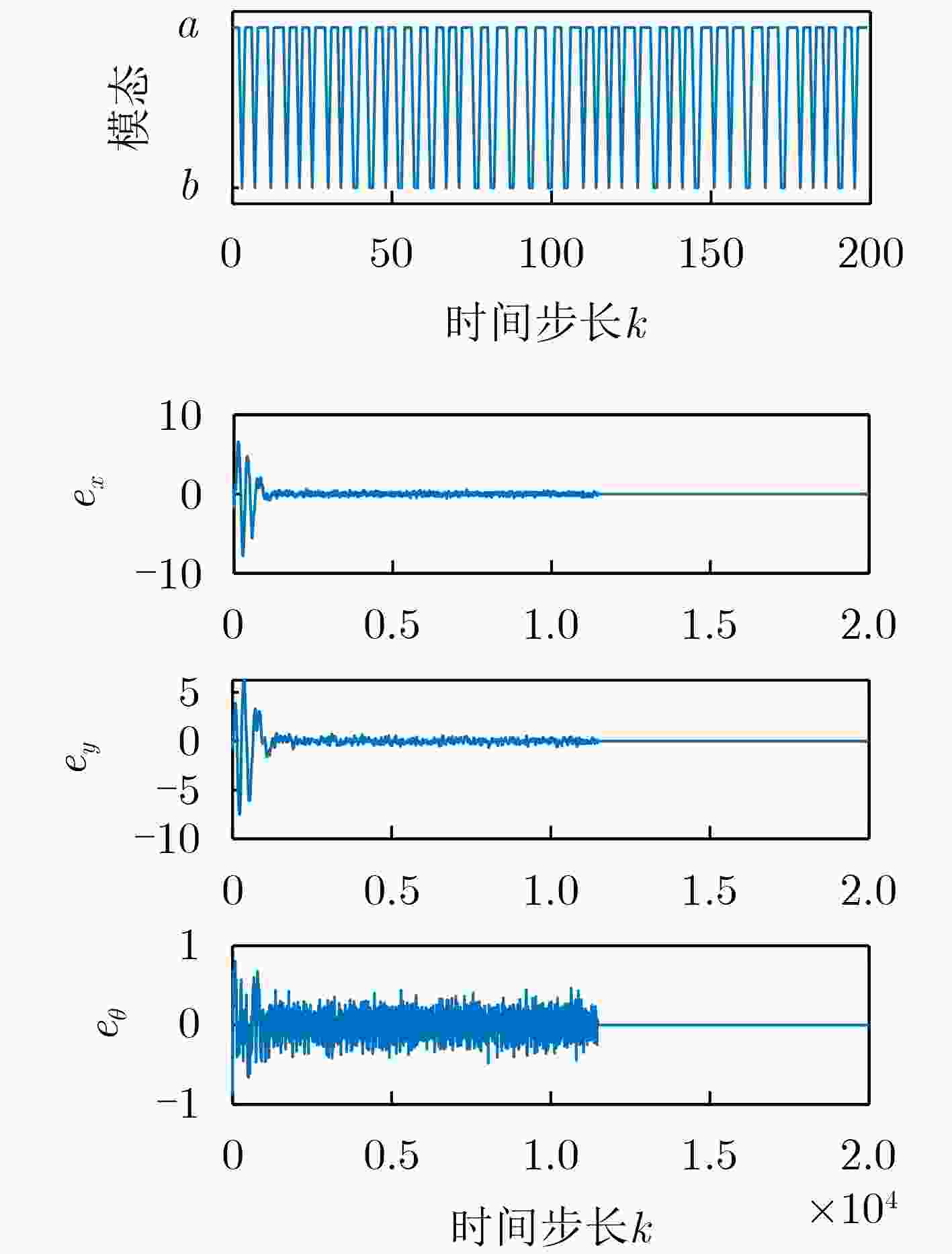
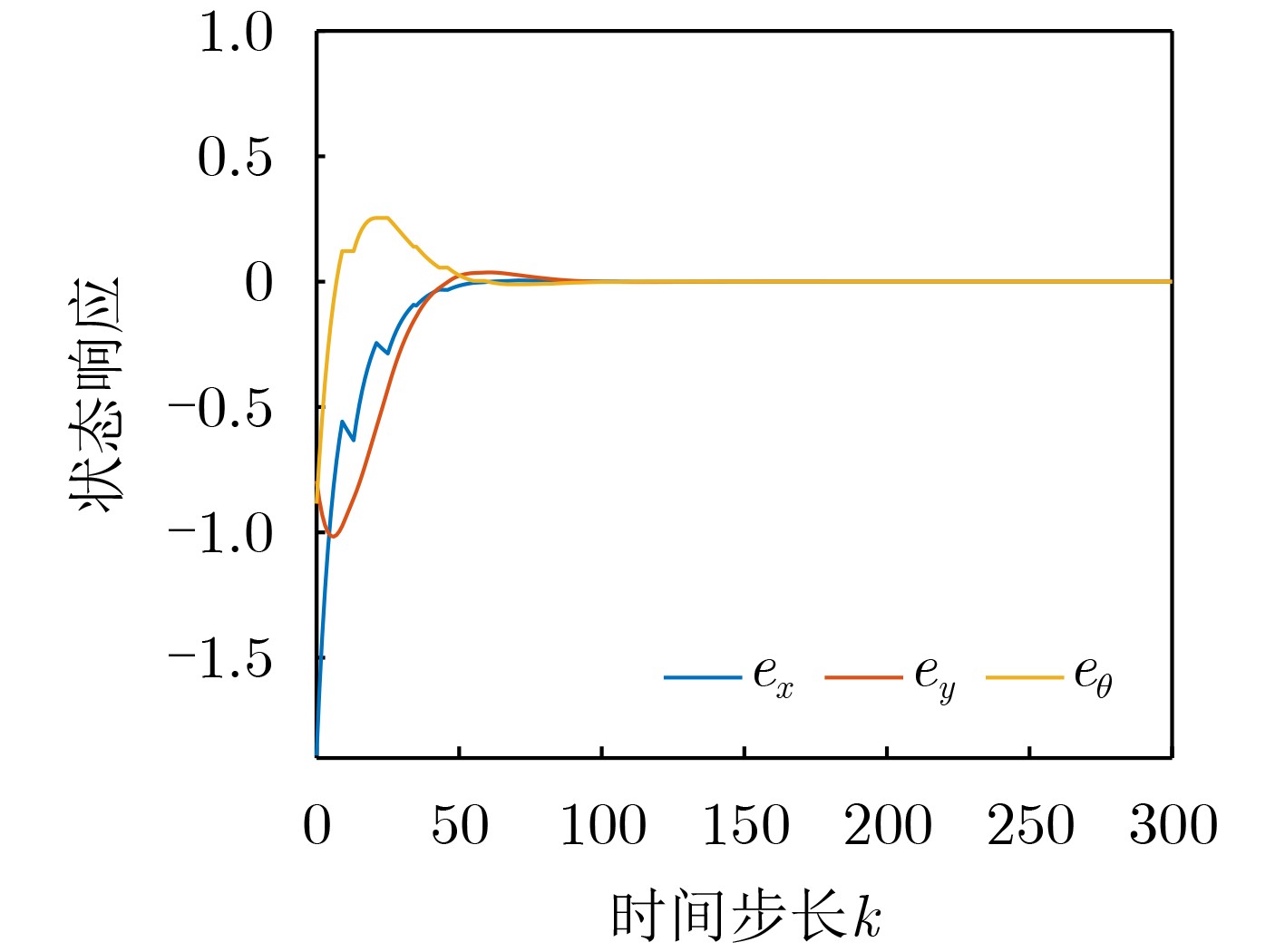
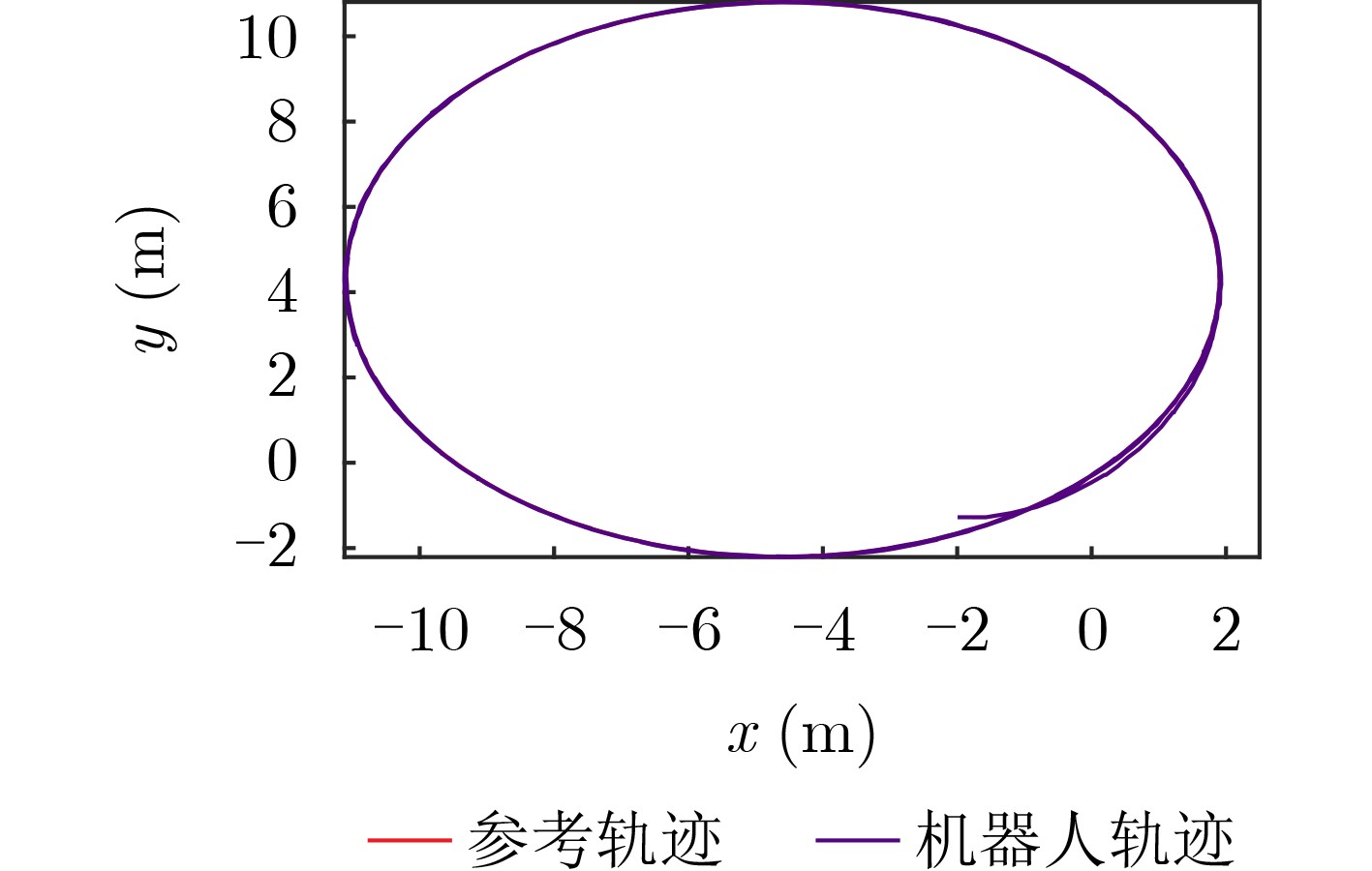
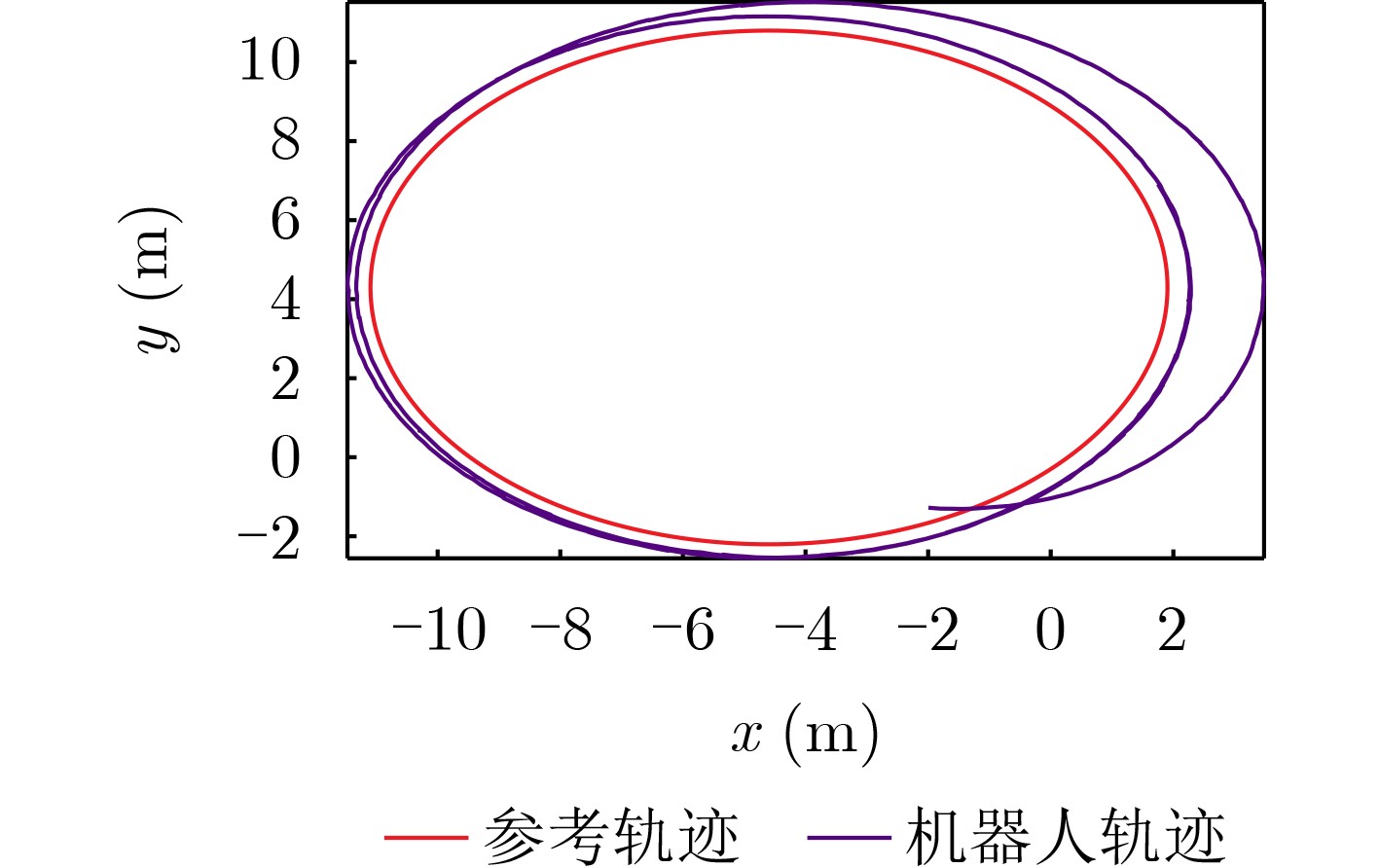
Objective The open network architecture of cyber-physical systems (CPSs) enables remarkable flexibility and scalability, but it also renders CPSs highly vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Particularly, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks have emerged as one of the predominant threats, which can cause packet loss and reduce system performance by directly jamming channels. On the other hand, CPSs under dormant and active DoS attacks can be regarded as dual-mode switched systems with stable and unstable subsystems, respectively. Therefore, it is worth exploring how to utilize the switched system theory to design a secure control approach with high degrees of freedom and low conservatism. However, due to the influence of complex environments such as attacks and noises, it is difficult to model practical CPSs exactly. Currently, although a Q-learning-based control method demonstrates potential for handling unknown CPSs, the significant research gap exists in switched systems with unstable modes, particularly for establishing the evaluable stability criterion. Therefore, it remains to be investigated for unknown CPSs under DoS attacks to apply switched system theory to design the learning-based control algorithm and evaluable security criterion. Methods An online mode-dependent switching-Q-learning strategy is presented to study the data-driven evaluable criterion and secure control for unknown CPSs under DoS attacks. Initially, the CPSs under dormant and active DoS attacks are transformed into switched systems with stable and unstable subsystems, respectively. Subsequently, the optimal control problem of the value function is addressed for the model-based switched systems by designing a new generalized switching algebraic Riccati equation (GSARE) and obtaining the corresponding mode-dependent optimal security controller. Furthermore, the existence and uniqueness of the GSARE’s solution are proved. In what follows, with the help of model-based results, a data-driven optimal security control law is proposed by developing a novel online mode-dependent switching-Q-learning control algorithm. Finally, through utilizing the learned control gain and parameter matrices from the above algorithm, a data-driven evaluable security criterion with the attack frequency and duration is established based on the switching constraints and subsystem constraints. Results and Discussions In order to verify the efficiency and advantage of the proposed methods, comparative experiments of the wheeled robot are displayed in this work. Firstly, compare the model-based result (Theorem 1) and the data-driven result (Algorithm 1) as follows: From the iterative process curves of control gain and parameter matrices ( Fig. 2 andFig. 3 ), it can be observed that the optimal control gain and parameter matrices under threshold errors can all be successfully obtained from both the model-based GSARE and the data-driven algorithm. Meanwhile, the tracking errors of CPSs can converge to 0 by utilizing the above data-driven controller (Fig. 5 ), which ensures the exponential stability of CPSs and verifies the efficiency of our proposed switching-Q-learning algorithm. Secondly, it is evident from learning process curves (Fig.4) that although the initial value of the learned control gain is not stabilizable, the optimal control gain can still be successfully learned to stabilize the system from Algorithm 1. This result significantly reduces conservatism compared to existing Q-learning approaches, which take stabilizable initial control gains as the learning premise. Thirdly, compare the data-driven evaluable security criterion in Theorem 2 of this work and existing criteria as follows: While the switching parameters learned from Algorithm 1 do not satisfy the popular switching constraint to obtain the model dwell-time, by utilizing the evaluable security criterion proposed in this paper, the attack frequency and duration are obtained based on the new switching constraints and subsystem constraints. Furthermore, it is seen from the comparison of the evaluable security criteria (Tab.1 ) that our proposed evaluable security criterion is less conservative than the existing evaluable criteria. Finally, the learned optimal controller and the obtained DoS attack constraints are applied to the tracking control experiment of a wheeled robot under DoS attacks, and the result is compared with existing results via Q-learning controllers. It is evident from the tracking trajectory comparisons of the robot (Fig.6 andFig.7 ) that the robot enables significantly faster and more accurate trajectory tracking with the help of our proposed switching-Q-learning controller. Therefore, the efficiency and advantage of the proposed algorithm and criterion in this work are verified.Conclusions Based on the learning strategy and the switched system theory, this study presents an online mode-dependent switching-Q-learning control algorithm and the corresponding evaluable security criterion for the unknown CPSs under DoS attacks. The detailed results are provided as follows: (1) By representing the unknown CPSs under dormant and active DoS attacks as unknown switched systems with stable and unstable subsystems, respectively, the security problem of CPSs under DoS attacks is transformed into a stabilization problem of the switched systems, which offers high design freedom and low conservatism. (2) A novel online mode-dependent switching-Q-learning control algorithm is developed for unknown switched systems with unstable modes. Through the comparative experiments, the proposed switching-Q-learning algorithm effectively increases the design freedom of controllers and decreases conservatism over existing Q-learning algorithms. (3) A new data-driven evaluable security criterion with the attack frequency and duration is established based on the switching constraints and subsystem constraints. It is evident from the comparative criteria that the proposed criterion demonstrates significantly reduced conservatism over existing evaluable criteria via single subsystem constraints and traditional model dwell-time constraints. -
1 在线模态依赖的切换-Q-学习控制算法
1:设定初始值$ {\boldsymbol{L}}_a^0 $、$ {\boldsymbol{\mathcal{P}}}_i^0 $、$ {\boldsymbol{P}}_i^0 $和$j = 0$,其中$i \in \{ a,b\} $. 2:设定学习误差阈值$ \varepsilon _i^{} $ 3:执行策略更新(32) 4:执行策略评估(31) 5:如果 $ \Vert {{\boldsymbol{P}}}_{i}^{j+1}-{{\boldsymbol{P}}}_{i}^{j}\Vert \lt {\epsilon}_{i} $,那么 6: 输出参数矩阵$ {\boldsymbol{P}}_i^{j + 1} $和最优控制增益$ {\boldsymbol{L}}_a^{j + 1} $ 7:否则 8: $j = j + 1$ 9: 返回步骤3 10:结束判断 表 1 本文与文献[24]的数据驱动安全评估准则比较
本文定理2 (基于本文算法1) 文献[24]推论1(基于[24]中算法1) 切换参数: ${\mu _a} = 1.04$、 ${\mu _b} = 1.74$ 无
子系统参数: ${\eta _a} = 0.8$、 $ {\eta _b} = 1.55 $ $ {\mu _1}{\text{ = 0}}{\text{.11}} $、$ {\mu _2}{\text{ = 18}}{\text{.5}} $
攻击约束: ${\tau _{\text{F}}} = {\text{10}}{\text{.26}}$、${\tau _{\text{D}}} = 4$ $\tau \ge 6$(${\text{T}} = 6$下) -
[1] 杨挺, 刘亚闯, 刘宇哲, 等. 信息物理系统技术现状分析与趋势综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3393–3406. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211135.YANG Ting, LIU Yachuang, LIU Yuzhe, et al. Review on cyber-physical system: Technology analysis and trends[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3393–3406. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211135. [2] 杨光红, 芦安洋, 安立伟. 网络攻击下的信息物理系统安全状态估计研究综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(8): 2093–2105. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2023.0885.YANG Guanghong, LU Anyang, and AN Liwei. A survey on secure state estimation of cyber-physical systems under cyber attacks[J]. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(8): 2093–2105. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2023.0885. [3] LU Kangdi and WU Zhengguang. Resilient event-triggered load frequency control for cyber-physical power systems under DoS attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2023, 38(6): 5302–5313. doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2022.3229667. [4] OBAYYA M, AL-WESABI F N, ALABDAN R, et al. Artificial intelligence for traffic prediction and estimation in intelligent cyber-physical transportation systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2024, 70(1): 1706–1715. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2023.3320513. [5] 李云鹏, 张立宪, 韩岳江, 等. 基于模型预测控制的子母式无人机编队飞行控制方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(2): 312–326. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240405.LI Yunpeng, ZHANG Lixian, HAN Yuejiang, et al. Model predictive control-based formation flight control method for composite UAVs[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(2): 312–326. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240405. [6] LANGNER R. Stuxnet: Dissecting a cyberwarfare weapon[J]. IEEE Security & Privacy, 2011, 9(3): 49–51. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2011.67. [7] KHAN S. Distributed sensors, computation and AI for automation, protection and maintenance of power grid[C]. Proceedings of the 2022 18th International Computer Engineering Conference, Cairo, Egypt, 2022: 130–135. doi: 10.1109/ICENCO55801.2022.10032522. [8] XU Hang, BARBOT S, and WANG Teng. Remote sensing through the fog of war: Infrastructure damage and environmental change during the Russian-Ukrainian conflict revealed by open-access data[J]. Natural Hazards Research, 2024, 4(1): 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.nhres.2024.01.006. [9] WANG Zhe, ZHANG Heng, YANG Chaoqun, et al. Improved zero-dynamics attack scheduling with state estimation[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2025, 12(2): 472–474. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2024.124737. [10] ZHAO Rui, ZUO Zhiqiang, SHI Yang, et al. DoS and stealthy deception attacks for switched systems: A cooperative approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(7): 4396–4410. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3321248. [11] DE PERSIS C and TESI P. Input-to-state stabilizing control under denial-of-service[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(11): 2930–2944. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2416924. [12] SU Lei and YE Dan. Observer-based output feedback control for cyber-physical systems under randomly occurring packet dropout and periodic DoS attacks[J]. ISA Transactions, 2019, 95: 58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.05.008. [13] TAN Wen, HOU Zhongsheng, and LI Yuanxin. Data-driven containment control for unknown MIMO nonlinear MASs under aperiodic DoS attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 7762–7772. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3469153. [14] DEBRUHL B and TAGUE P. Digital filter design for jamming mitigation in 802.15. 4 communication[C]. Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks, Lahaina, USA, 2011: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCCN.2011.6006020. [15] SHI Ting, SHI Peng, and CHAMBERS J. Dynamic event-triggered model predictive control under channel fading and denial-of-service attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(4): 6448–6459. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2023.3325534. [16] YUAN Yuan, YUAN Huanhuan, GUO Lei, et al. Resilient control of networked control system under DoS attacks: A unified game approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2016, 12(5): 1786–1794. doi: 10.1109/TII.2016.2542208. [17] SAEEDI M, ZAREI J, RAZAVI-FAR R, et al. Event-triggered adaptive optimal fast terminal sliding mode control under denial-of-service attacks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(2): 2684–2692. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3073816. [18] ZHU Yanzheng and ZHENG Weixing. Observer-based control for cyber-physical systems with periodic DoS attacks via a cyclic switching strategy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(8): 3714–3721. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2953210. [19] WU Chengwei, WU Ligang, LIU Jianxing, et al. Active defense-based resilient sliding mode control under denial-of-service attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 237–249. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2917373. [20] SHEN Hao, LIU Xinmiao, MA Qian, et al. Observer-based control for interval type-2 fuzzy systems under PDT-based DoS attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 55(6): 3780–3790. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2025.3547320. [21] WANG Fuxing, LONG Yue, and LI Tieshan. Thruster fault detection for unmanned marine vehicles under DoS attacks: An asynchronous switched method[C]. Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Information Science and Technology, Chengdu, China, 2024: 554–559. doi: 10.1109/ICIST63249.2024.10805417. [22] 华和安, 方勇纯, 钱辰, 等. 基于线性滤波器的四旋翼无人机强化学习控制策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3407–3417. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210251.HUA He’an, FANG Yongchun, QIAN Chen, et al. Reinforcement learning control strategy of quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles based on linear filter[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3407–3417. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210251. [23] REN Yan, ZHANG Heng, YANG Wei, et al. Transferable adversarial attack against deep reinforcement learning-based smart grid dynamic pricing system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(6): 9015–9025. doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3379645. [24] YIN Liyuan, XU Lezhong, HOU Fusheng, et al. Security analysis and control under periodic DoS attacks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(5): 8473–8484. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3319703. [25] LIU Jinliang, DONG Yanhui, ZHA Lijuan, et al. Reinforcement learning-based tracking control for networked control systems with DoS attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 4188–4197. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2024.3376250. [26] GAO Weinan, DENG Chao, JIANG Yi, et al. Resilient reinforcement learning and robust output regulation under denial-of-service attacks[J]. Automatica, 2022, 142: 110366. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110366. [27] LI Hao, CHEN Hua, and ZHANG Wei. On model-free reinforcement learning for switched linear systems: A subspace clustering approach[C]. Proceedings of the 2018 56th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Monticello, USA, 2018: 123–130, doi: 10.1109/ALLERTON.2018.8635985. [28] CHEN Hua, ZHANG Linfang, and ZHANG Wei. Optimal control inspired Q-learning for switched linear systems[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 American Control Conference (ACC), Denver, USA, 2020: 4003–4010. doi: 10.23919/ACC45564.2020.9147818. [29] ZHANG Xuewen, WANG Yun, XIA Jianwei, et al. Optimal tracking control for discrete-time modal persistent dwell time switched systems based on Q-learning[J]. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 2023, 44(6): 3327–3341. doi: 10.1002/oca.3040. [30] SUN Jiayue, ZHANG Huaguang, WANG Yingchun, et al. Optimal tracking control of switched systems applied in grid-connected hybrid generation using reinforcement learning[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(15): 9363–9374. doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-05696-2. [31] WU Jiacheng, LIAN Bosen, SU Hongye, et al. Data-driven weighted $\tiny{H_\infty }$ control of persistent dwell time switched systems with optimal disturbance attenuation guaranteed[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 8162–8173. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3480449. [32] ZHAI Lijing and VAMVOUDAKIS K G. Data-based and secure switched cyber-physical systems[J]. Systems & Control Letters, 2021, 148: 104826. doi: 10.1016/j.sysconle.2020.104826. [33] ZHANG Wei, ABATE A, HU Jianghai, et al. Exponential stabilization of discrete-time switched linear systems[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2526–2536. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.07.018. [34] AL-TAMIMI A, LEWIS F L, and ABU-KHALAF M. Model-free Q-learning designs for linear discrete-time zero-sum games with application to H-infinity control[J]. Automatica, 2007, 43(3): 473–481. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.09.019. [35] FEI Zhongyang, SHI Shuang, and SHI Peng. Analysis and Synthesis for Discrete-Time Switched Systems: A Quasi-Time-Dependent Method[M]. Cham: Springer, 2020: 23–25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-25812-2. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
