An EEG Emotion Recognition Model Integrating Memory and Self-attention Mechanisms
-
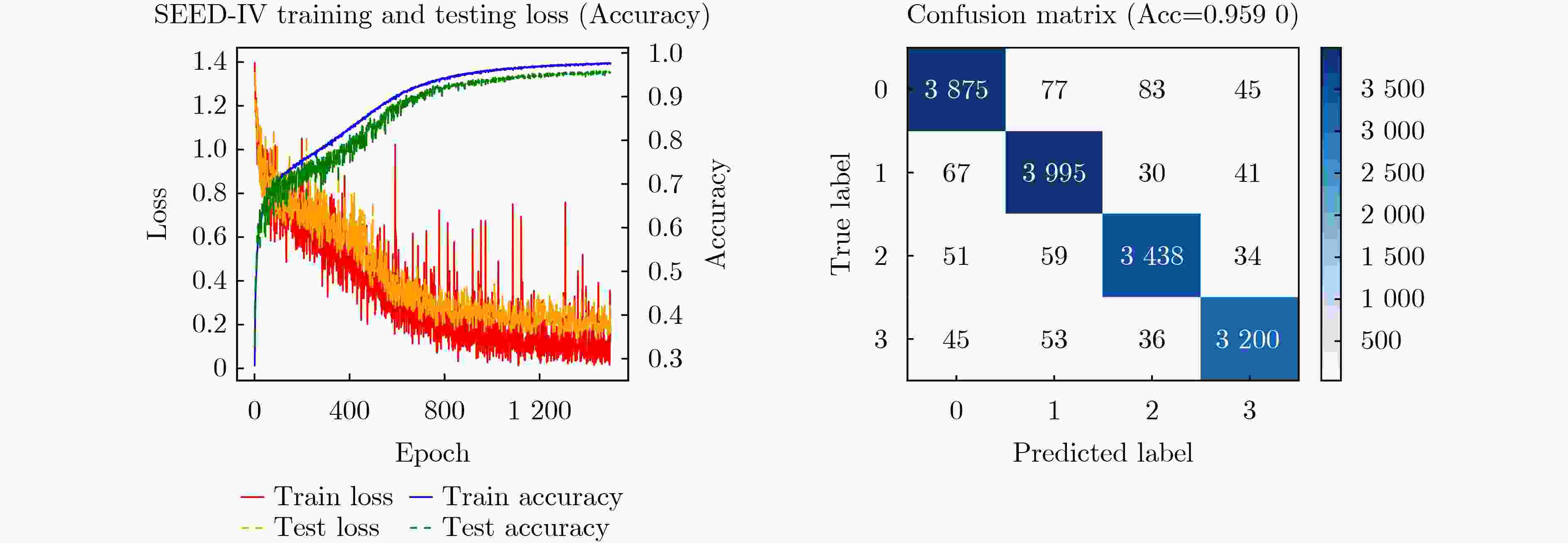
摘要: 脑电图(EEG)作为一种非侵入式的神经信号获取手段,蕴含丰富的情感和认知信息,在脑科学研究与情感识别中具有广泛应用。当前Transformer在脑电图情绪识别中虽具备良好的全局建模能力,但其多头自注意力机制忽略了脑电图是由大脑活动产生的数据,会有遗忘效应,人在当前时刻会对其它时刻产生的状态产生遗忘,而目前的Transformer仅关注当前时刻与其它时刻相关性大小,忽略了遗忘效应,限制了模型在脑电图情绪识别中的作用。因此,亟需设计一种兼顾相关性大小与遗忘效应的脑电图情绪识别模型,该文提出一种融合记忆力遗忘机制和自注意力机制的脑电情感识别模型(MSA),在兼顾相关性大小的同时注入符合人类遗忘机制的遗忘机制,在几乎不增加额外参数和计算量的情况下提升模型的性能。该模型首先利用聚合卷积神经网络(ACNN)聚合各通道的时空特征,再借助MSA结构建模全局依赖关系和记忆关系。再通过分类头得出最终分类结果。在DEAP二分类任务中,MSA模型在效价和唤醒维度上分别获得98.87%与98.30%的分类准确率;在SEED三分类任务中达到97.64%的分类准确率,在SEED-IV四分类任务中获得95.90%的准确率,均优于现有主流方法。实验结果验证了所提模型在多类别情感识别任务中的有效性与鲁棒性。
-
关键词:
- 脑电图 /
- 情感识别 /
- 记忆力 /
- Transformer /
- 脑机接口
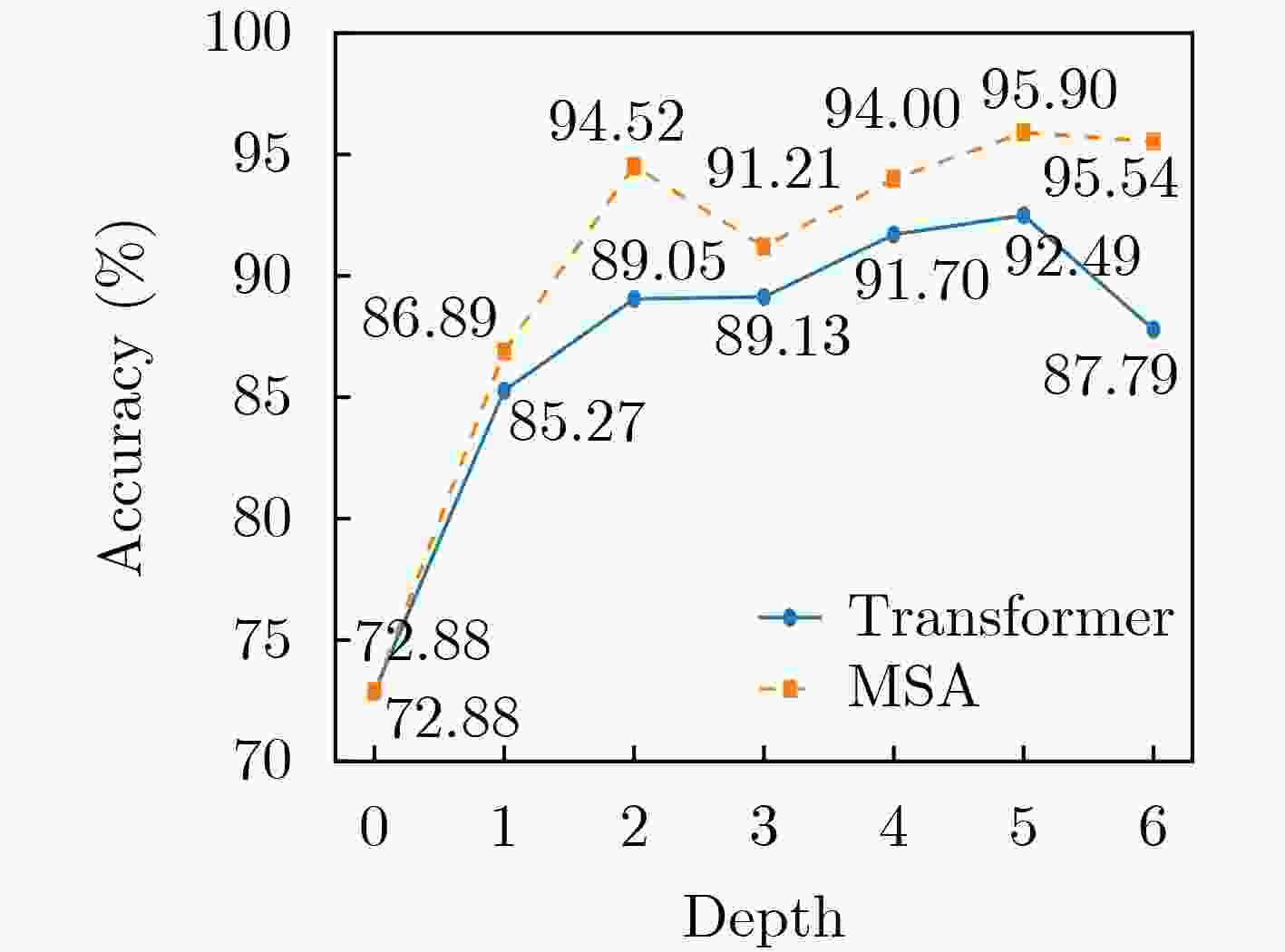
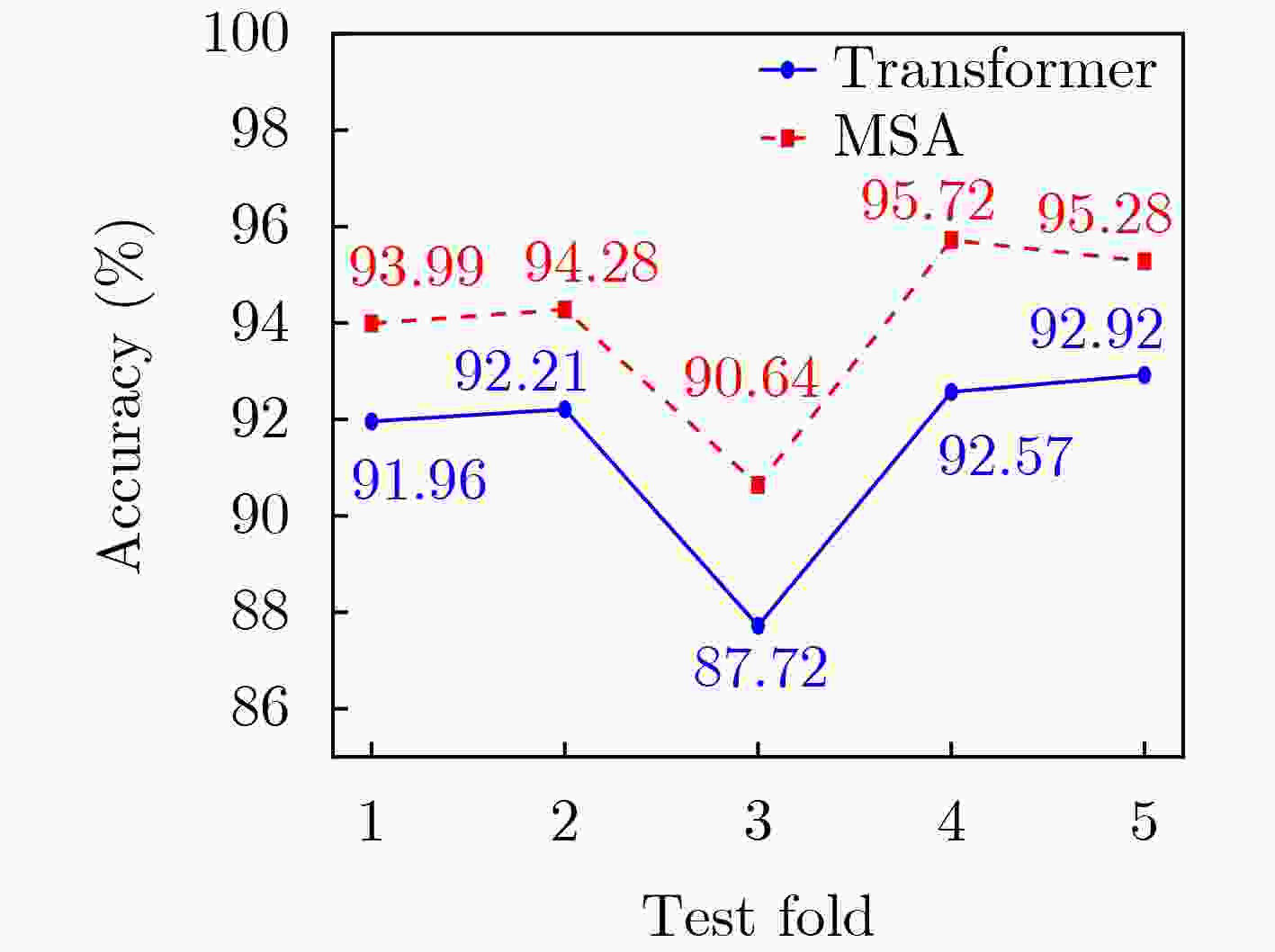
Abstract:Objective ElectroEncephaloGraphy (EEG) is a noninvasive technique for recording neural signals and provides rich emotional and cognitive information for brain science research and affective computing. Although Transformer-based models demonstrate strong global modeling capability in EEG emotion recognition, their multi-head self-attention mechanisms do not reflect the characteristics of brain-generated signals that exhibit a forgetting effect. In human cognition, emotional or cognitive states from distant time points gradually decay, whereas existing Transformer-based approaches emphasize temporal relevance only and neglect this forgetting behavior. This limitation reduces recognition performance. Therefore, a model is designed to account for both temporal relevance and the intrinsic forgetting effect of brain activity. Methods A novel EEG emotion recognition model, termed Memory Self-Attention (MSA), is proposed by embedding a memory-based forgetting mechanism into the standard self-attention framework. The MSA mechanism integrates global semantic modeling with a biologically inspired memory decay component. For each attention head, a memory forgetting score is learned through two independent linear decay curves to represent natural attenuation over time. These scores are combined with conventional attention weights so that temporal relationships are adjusted by distance-aware forgetting behavior. This design improves performance with a negligible increase in model parameters and computational cost. An Aggregated Convolutional Neural Network (ACNN) is first applied to extract spatiotemporal features across EEG channels. The MSA module then captures global dependencies and memory-aware interactions. The refined representations are finally passed to a classification head to generate predictions. Results and Discussions The proposed model is evaluated on several benchmark EEG emotion recognition datasets. On the DEAP binary classification task, classification accuracies of 98.87% for valence and 98.30% for arousal are achieved. On the SEED three-class task, an accuracy of 97.64% is obtained, and on the SEED-IV four-class task, the accuracy reaches 95.90%. These results ( Figs. 3 ~5 ,Tables 3 ~5 ) exceed those of most mainstream methods, indicating the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed approach across different datasets and emotion classification settings.Conclusions An effective and biologically informed method for EEG-based emotion recognition is presented by incorporating a memory forgetting mechanism into a Transformer architecture. The proposed MSA model captures both temporal correlations and forgetting characteristics of brain signals, providing a lightweight and accurate solution for multi-class emotion recognition. Experimental results confirm its strong performance and generalizability. -
表 1 标准自注意力机制MHSA与MSA的参数量与计算量对比
MHSA MSA 增量分析与说明 参数量 3$d_{{\mathrm{emb}}}^2 $+$d_{{\mathrm{emb}}}^2 $ 3$d_{{\mathrm{emb}}}^2 $+$d_{{\mathrm{emb}}}^2 $+4H 仅增加4H个可学习参数(随头数线性增长,4个参数/头) 计算量 O(H⋅N2⋅dk) O(H⋅N2⋅dk)+ O(H⋅N2) 增加一项加法广播,计算开销极小 参数占比 - $ \dfrac{4H}{3{\mathrm{d}}_{\text{emb}}^{2}+{\mathrm{d}}_{\text{emb}}^{2}}=\dfrac{H}{{\mathrm{d}}_{\text{emb}}^{2}}\approx 0 $ 与嵌入维度相比可忽略 计算开销占比 - $ \dfrac{1}{d_{\mathrm{k}}}=\dfrac{H}{d_{\mathrm{emb}}}\approx0 $ 与嵌入维度相比可忽略 表 2 预处理后的DEAP, SEED和SEED-IV数据集
数据集 数据格式 总样本数 训练样本数 测试样本数 DEAP 32×384 20480 16384 4096 SEED 62×400 76140 60912 15228 SEED-IV 62×400 75645 60516 15129 表 3 DEAP数据集实验结果(%)
表 4 SEED数据集实验结果(%)
-
[1] DOLAN R J. Emotion, cognition, and behavior[J]. Science, 2002, 298(5596): 1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.1076358. [2] FRANTZIDIS C A, BRATSAS C, PAPADELIS C L, et al. Toward emotion aware computing: An integrated approach using multichannel neurophysiological recordings and affective visual stimuli[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 2010, 14(3): 589–597. doi: 10.1109/TITB.2010.2041553. [3] ZHANG Tong, ZHENG Wenming, CUI Zhen, et al. A deep neural network-driven feature learning method for multi-view facial expression recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2016, 18(12): 2528–2536. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2016.2598092. [4] LIU Zhentao, XIE Qiao, WU Min, et al. Speech emotion recognition based on an improved brain emotion learning model[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 309: 145–156. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.005. [5] BRITTON J C, PHAN K L, TAYLOR S F, et al. Neural correlates of social and nonsocial emotions: An fMRI study[J]. NeuroImage, 2006, 31(1): 397–409. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.11.027. [6] ZHANG Tong, WANG Xuehan, XU Xiangmin, et al. GCB-Net: Graph convolutional broad network and its application in emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2022, 13(1): 379–388. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2019.2937768. [7] ZHENG Weilong, ZHU Jiayi, and LU Baoliang. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from EEG[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2019, 10(3): 417–429. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2712143. [8] ALARCÃO S M and FONSECA M J. Emotions recognition using EEG signals: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2019, 10(3): 374–393. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2017.2714671. [9] LI Xiang, SONG Dawei, ZHANG Peng, et al. Emotion recognition from multi-channel EEG data through convolutional recurrent neural network[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Shenzhen, China, 2016: 352–359. doi: 10.1109/BIBM.2016.7822545. [10] CHEN Jingxia, JIANG D M, and ZHANG Y N. A hierarchical bidirectional GRU model with attention for EEG-based emotion classification[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 118530–118540. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2936817. [11] DU Xiaobing, MA Cuixia, ZHANG Guanhua, et al. An efficient LSTM network for emotion recognition from multichannel EEG signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2022, 13(3): 1528–1540. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2020.3013711. [12] PARK H J and FRISTON K. Structural and functional brain networks: From connections to cognition[J]. Science, 2013, 342(6158): 1238411. doi: 10.1126/science.1238411. [13] SONG Tengfei, ZHENG Wenming, SONG Peng, et al. EEG emotion recognition using dynamical graph convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2020, 11(3): 532–541. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2018.2817622. [14] YE Weishan, ZHANG Zhiguo, TENG Fei, et al. Semi-supervised dual-stream self-attentive adversarial graph contrastive learning for cross-subject EEG-based emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2025, 16(1): 290–305. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2024.3433470. [15] LI Yang, ZHENG Wenming, CUI Zhen, et al. A novel neural network model based on cerebral hemispheric asymmetry for EEG emotion recognition[C]. The 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1561–1567. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2018/216. [16] LI Yang, WANG Lei, ZHENG Wenming, et al. A novel Bi-hemispheric discrepancy model for EEG emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2021, 13(2): 354–367. doi: 10.1109/TCDS.2020.2999337. [17] SONG Tengfei, ZHENG Wenming, LIU Suyuan, et al. Graph-embedded convolutional neural network for image-based EEG emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2022, 10(3): 1399–1413. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2021.3087174. [18] LIU Shuaiqi, ZHAO Yingying, AN Yanling, et al. GLFANet: A global to local feature aggregation network for EEG emotion recognition[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2023, 85: 104799. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.104799. [19] SONG Yonghao, ZHENG Qingqing, LIU Bingchuan, et al. EEG conformer: Convolutional transformer for EEG decoding and visualization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2023, 31: 710–719. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2022.3230250. [20] DU Yuxiao, DING Han, WU Min, et al. MES-CTNet: A novel capsule transformer network base on a multi-domain feature map for electroencephalogram-based emotion recognition[J]. Brain Sciences, 2024, 14(4): 344. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14040344. [21] 张学军, 王天晨, 王泽田. 基于多域信息融合的卷积Transformer脑电情感识别模型[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2024, 39(6): 1543–1552. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2024.06.021.ZHANG Xuejun, WANG Tianchen, and WANG Zetian. Convolutional Transformer EEG emotion recognition model based on multi-domain information fusion[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2024, 39(6): 1543–1552. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2024.06.021. [22] ZHANG Yong, JI Xiaomin, and ZHANG Suhua. An approach to EEG-based emotion recognition using combined feature extraction method[J]. Neuroscience Letters, 2016, 633: 152–157. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.09.037. [23] JENKE R, PEER A, and BUSS M. Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from EEG[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2014, 5(3): 327–339. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2014.2339834. [24] CHEN Kun, CHAI Shulong, CAI Mincheng, et al. A novel 3D feature fusion network for EEG emotion recognition[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2025, 102: 107347. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2024.107347. [25] KOELSTRA S, MUHL C, SOLEYMANI M, et al. DEAP: A database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2012, 3(1): 18–31. doi: 10.1109/T-AFFC.2011.15. [26] ZHENG Weilong and LU Baoliang. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Autonomous Mental Development, 2015, 7(3): 162–175. doi: 10.1109/TAMD.2015.2431497. [27] ZHENG Weilong, LIU Wei, LU Yifei, et al. EmotionMeter: A multimodal framework for recognizing human emotions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(3): 1110–1122. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2797176. [28] LI Rui, REN Chao, LI Chen, et al. SSTD: A novel spatio-temporal demographic network for EEG-based emotion recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2023, 10(1): 376–387. doi: 10.1109/TCSS.2022.3188891. [29] LI Rui, REN Chao, GE Yiqing, et al. MTLFuseNet: A novel emotion recognition model based on deep latent feature fusion of EEG signals and multi-task learning[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023, 276: 110756. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110756. [30] CHEN Kun, JING Huchuan, LIU Quan, et al. A novel caps-EEGNet combined with channel selection for EEG-based emotion recognition[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2023, 86: 105312. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2023.105312. [31] LIN Kai, ZHANG Linhang, CAI Jing, et al. DSE-Mixer: A pure multilayer perceptron network for emotion recognition from EEG feature maps[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2024, 401: 110008. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2023.110008. [32] CHEN Kun, RUAN Wenhao, LIU Quan, et al. A novel deep learning model combining 3DCNN-CapsNet and hierarchical attention mechanism for EEG emotion recognition[J]. Neural Networks, 2025, 186: 107267. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2025.107267. [33] ZHONG Peixiang, WANG Di, MIAO Chunyan, et al. EEG-based emotion recognition using regularized graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2022, 13(3): 1290–1301. doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2020.2994159. [34] YANG Lijun, WANG Yixin, OUYANG Rujie, et al. Electroencephalogram-based emotion recognition using factorization temporal separable convolution network[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 133: 108011. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.108011. [35] LI Ming, YU Peng, and SHEN Yang. A spatial and temporal transformer-based EEG emotion recognition in VR environment[J]. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 2025, 19: 1517273. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1517273. [36] XIAO Guowen, SHI Meng, YE Mengwen, et al. 4D attention-based neural network for EEG emotion recognition[J]. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 2022, 16(4): 805–818. doi: 10.1007/s11571-021-09751-5. [37] LIU Jiyao, WU Hao, ZHANG Li, et al. Spatial-temporal transformers for EEG emotion recognition[C]. The 6th International Conference on Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Birmingham, UK, 2023: 116–120. doi: 10.1145/3571560.3571577. [38] LI Menghang, QIU Min, KONG Wanzeng, et al. Fusion graph representation of EEG for emotion recognition[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(3): 1404. doi: 10.3390/s23031404. [39] LI Cunbo, TANG Tian, PAN Yue, et al. An efficient graph learning system for emotion recognition inspired by the cognitive prior graph of EEG brain network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(4): 7130–7144. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2024.3405663. -





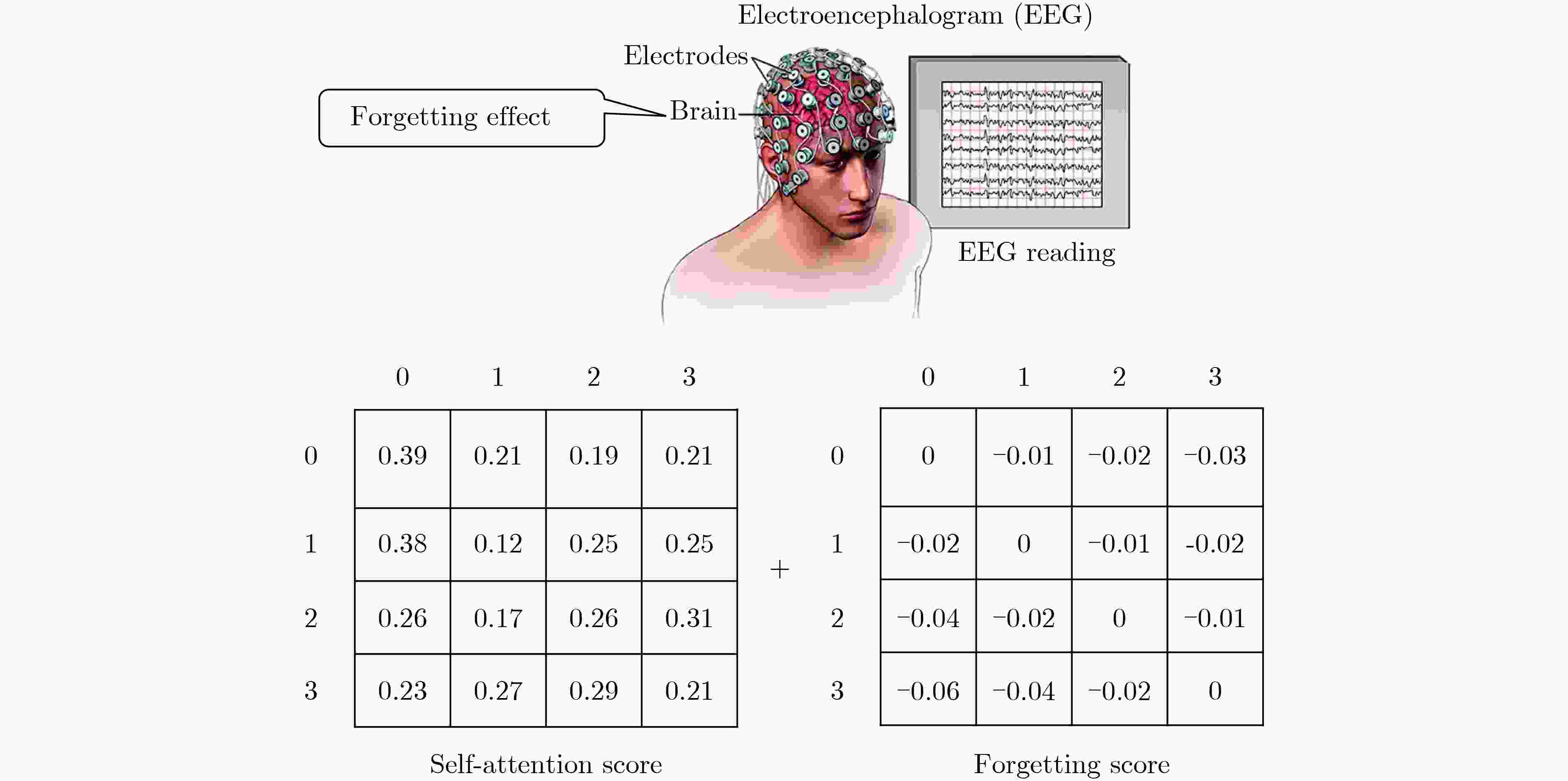
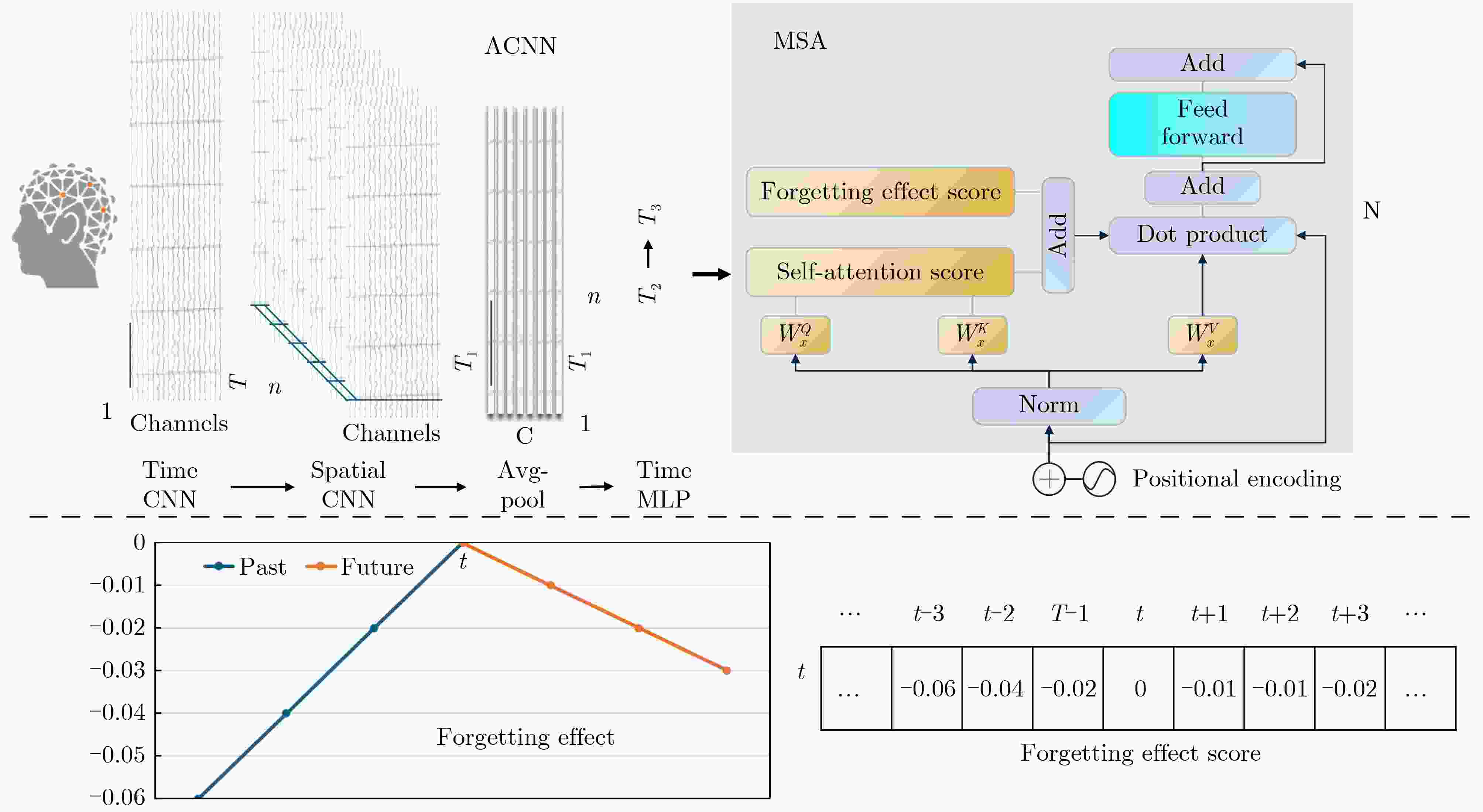
 下载:
下载:
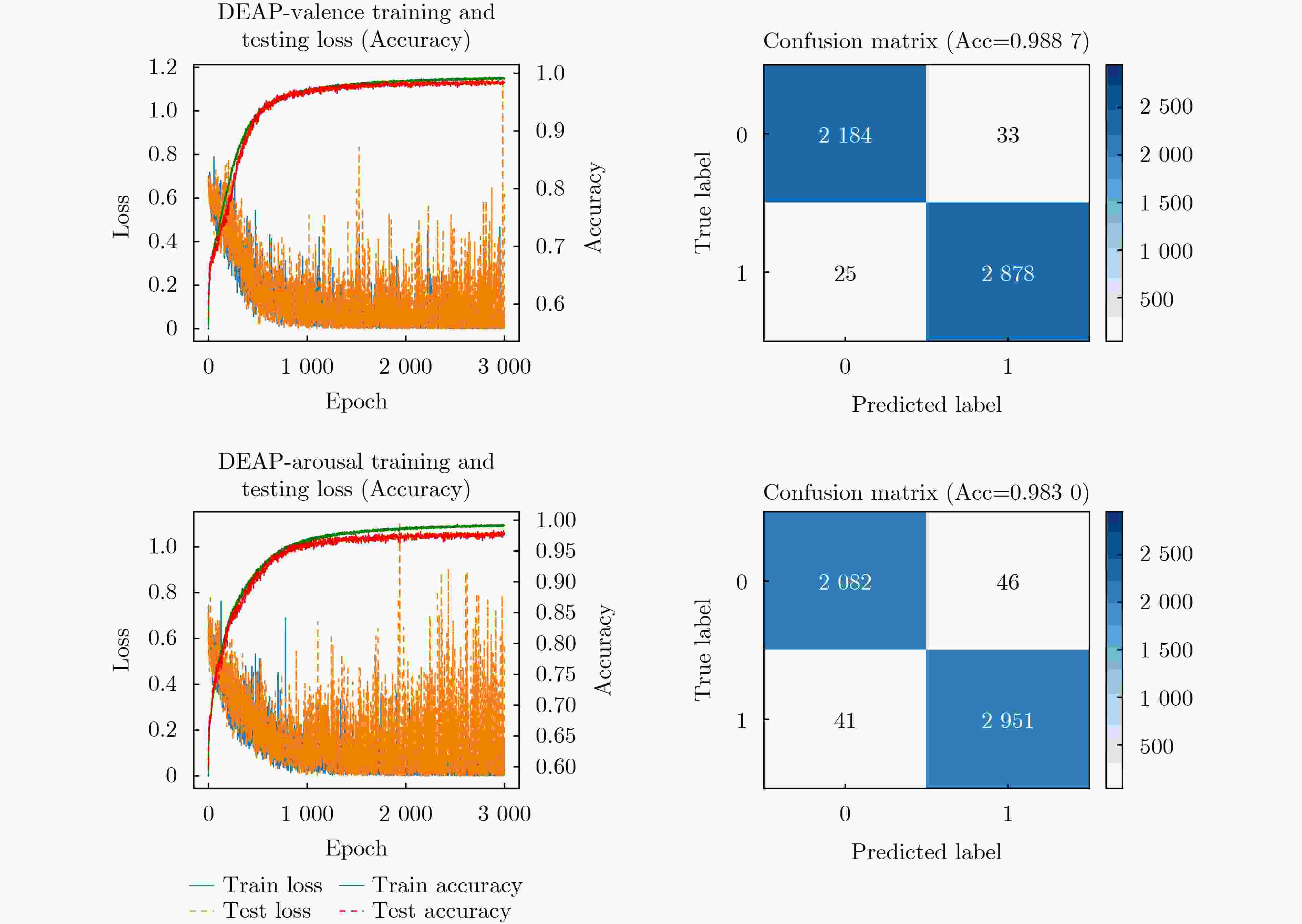
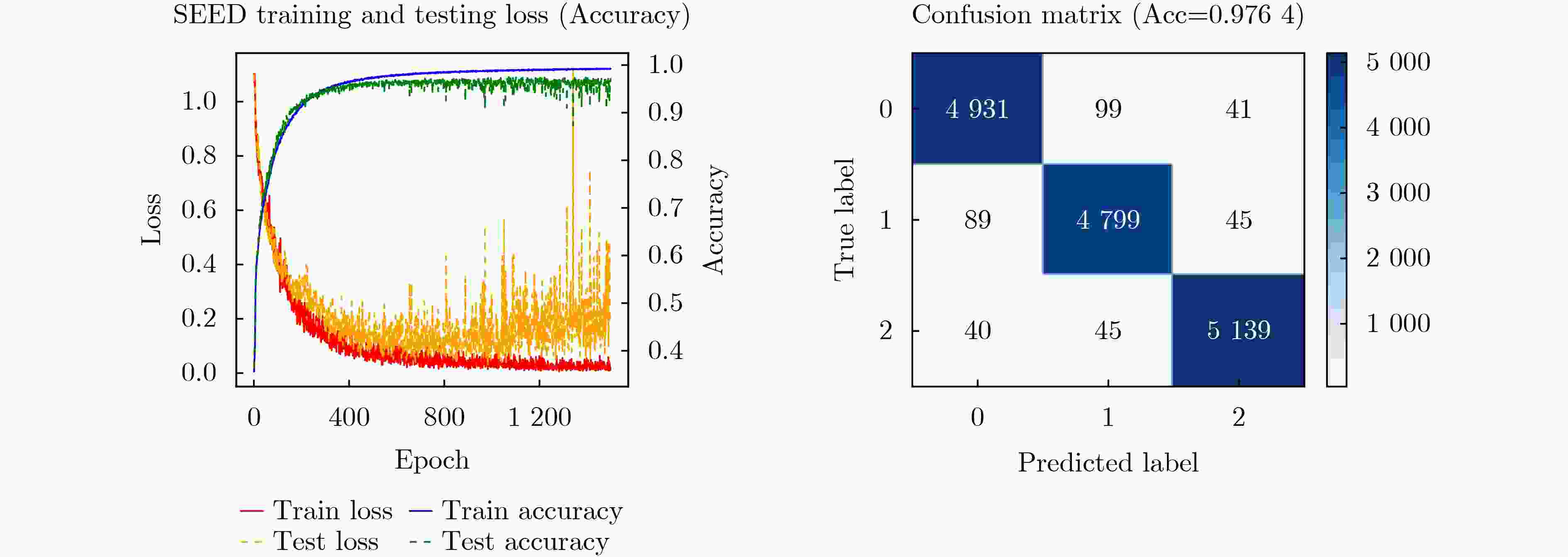


 下载:
下载:
