Vision Enabled Multimodal Integrated Sensing and Communications: Key Technologies and Prototype Validation
-
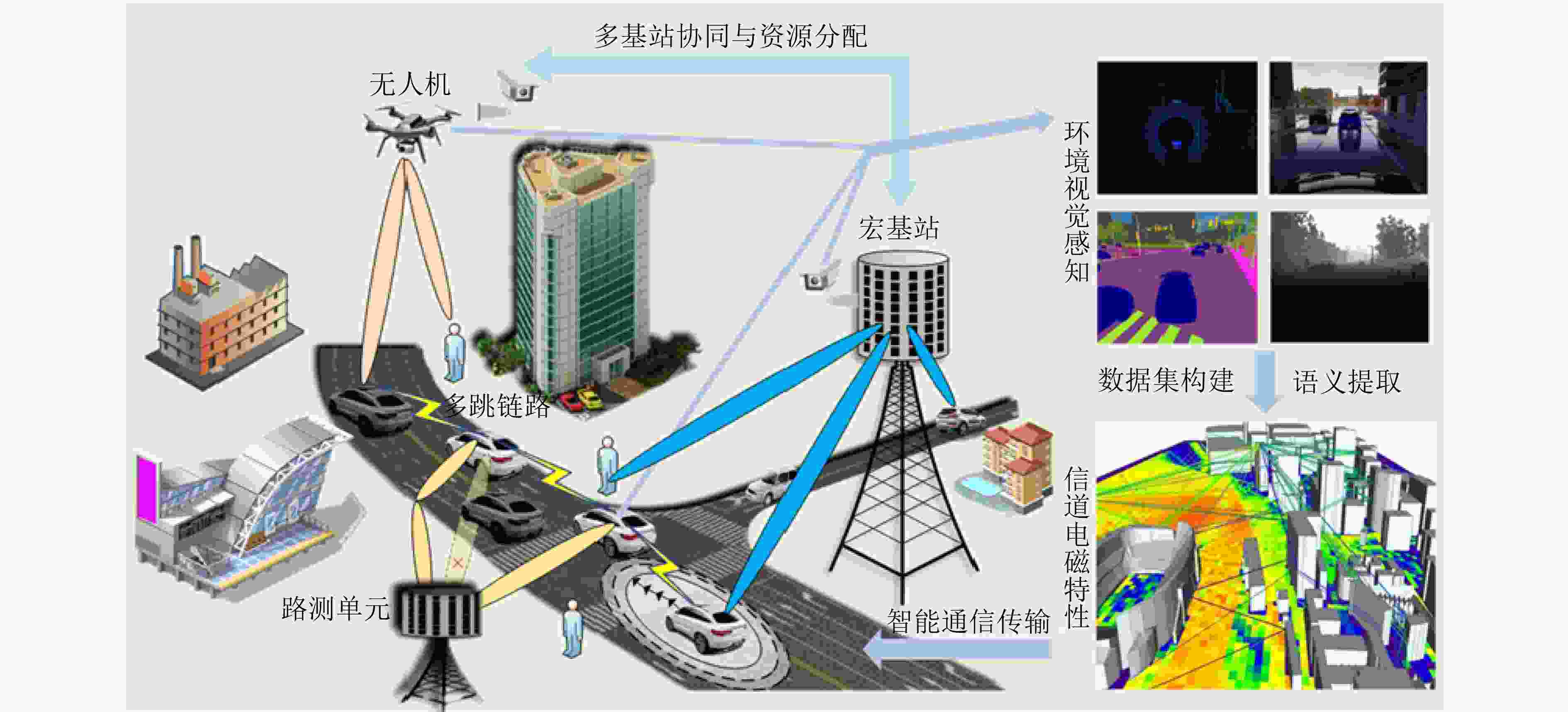
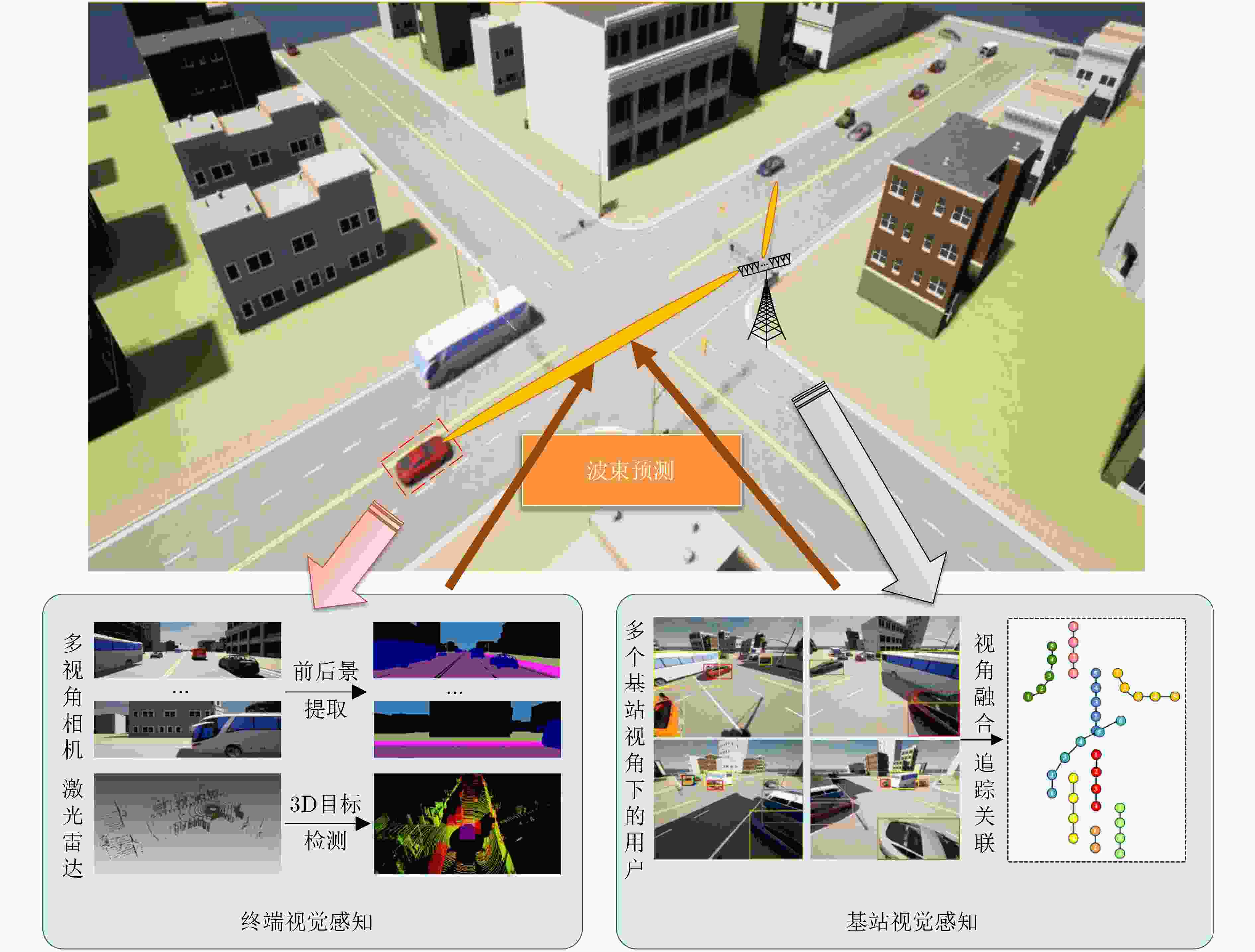
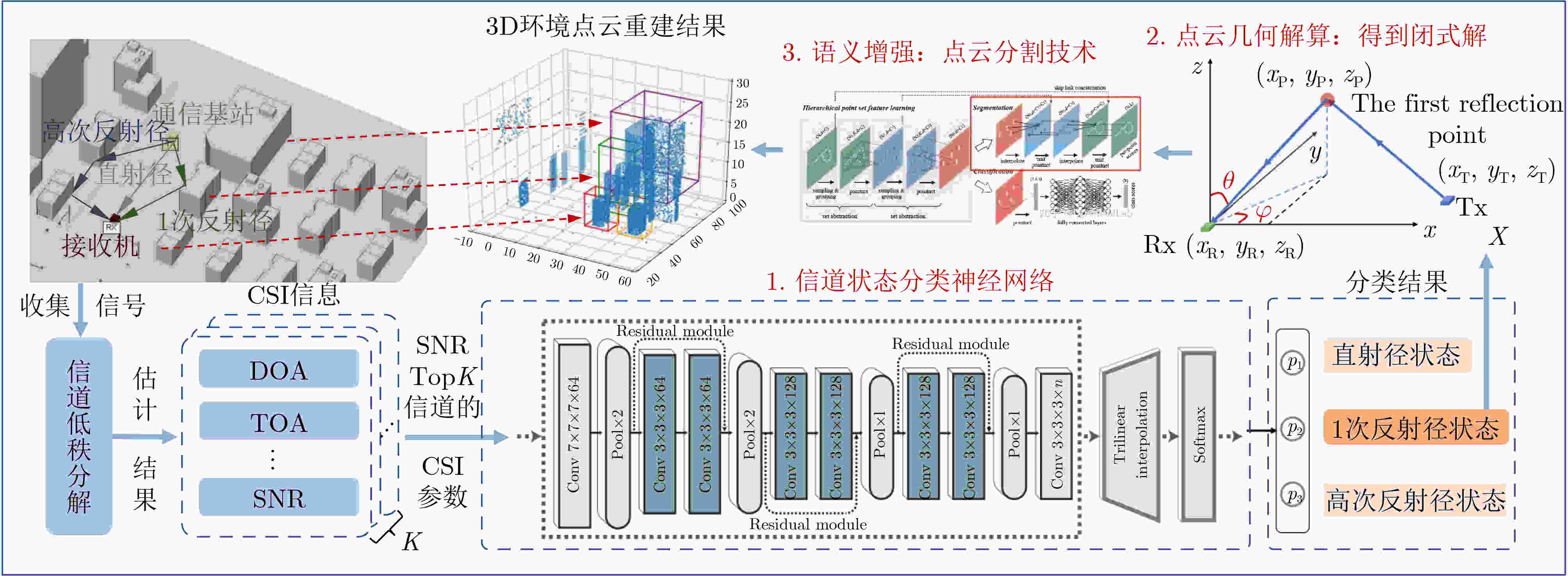
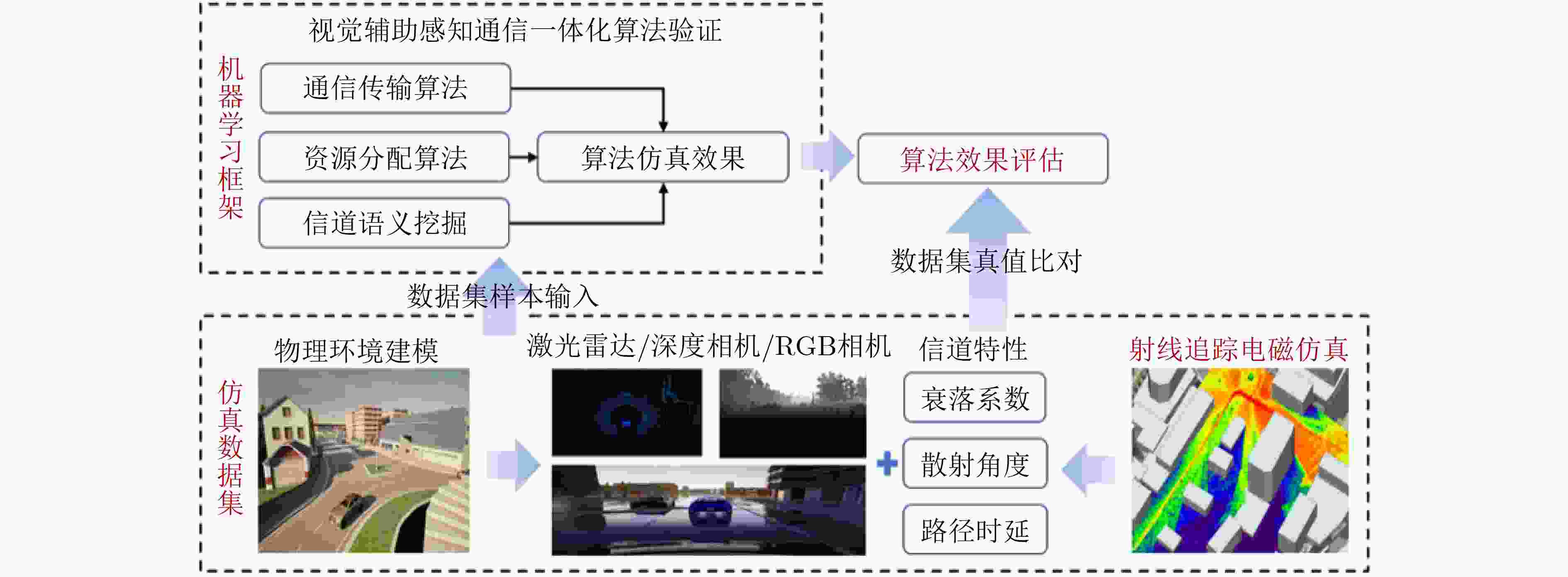
摘要: 面向6G系统的通信感知一体化(ISAC)技术具备感知物理世界的能力。视觉可以感知环境进而辅助通信,同样无线信号可以辅助突破视觉感知的局限。该文首先探明环境视觉与无线通信的内在关联机理,进而阐述基于视觉感知辅助通信的算法,包括波束预测、遮挡预判和多基站多用户的资源调度分配方法;然后基于无线信号辅助视觉感知,探索基于无线信号辅助视觉的环境感知,提出静态环境重建和动态目标感知方法,从而辅助恶劣天气、不良光照等非理想条件下的鲁棒感知;形成一套完整的融合视觉的多模态无线通信感知一体化理论和技术方法。同时,进行了软硬件仿真测试与原型平台验证。实验结果表明,具备视觉支持的多模态ISAC系统的应用潜力巨大。Abstract:
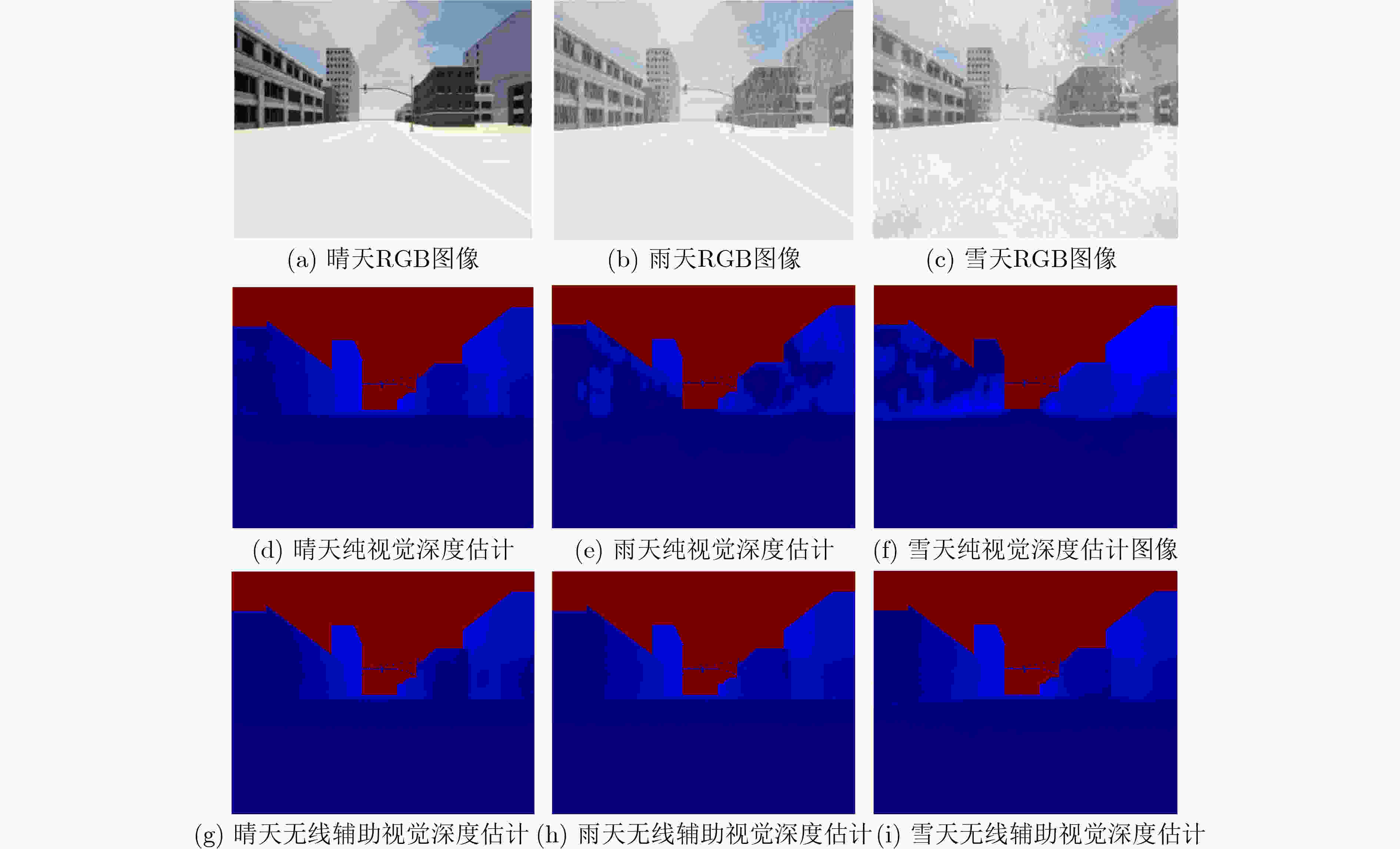
Objective Integrated Sensing And Communications (ISAC) is regarded as a key enabling technology for Sixth-Generation mobile communications (6G), as it simultaneously senses and monitors information in the physical world while maintaining communication with users. The technology supports emerging scenarios such as low-altitude economy, digital twin systems, and vehicle networking. Current ISAC research primarily concentrates on wireless devices that include base stations and terminals. Visual sensing, which provides strong visibility and detailed environmental information, has long been a major research direction in computer science. This study proposes the integration of visual sensing with wireless-device sensing to construct a multimodal ISAC system. In this system, visual sensing captures environmental information to assist wireless communications, and wireless signals help overcome limitations inherent to visual sensing. Methods The study first explores the correlation mechanism between environmental vision and wireless communications. Key algorithms for visual-sensing-assisted wireless communication are then discussed, including beam prediction, occlusion prediction, and resource scheduling and allocation methods for multiple base stations and users. These schemes demonstrate that visual sensing, used as prior information, enhances the communication performance of the multimodal ISAC system. The sensing gains provided by wireless devices combined with visual sensors are subsequently explored. A static-environment reconstruction scheme and a dynamic-target sensing scheme based on wireless-visual fusion are proposed to obtain global information about the physical world. In addition, a “vision-communication” simulation and measurement dataset is constructed, establishing a complete theoretical and technical framework for multimodal ISAC. Results and Discussions For visual-sensing-assisted wireless communications, the hardware prototype system constructed in this study is shown in ( Fig. 6 ) and (Fig. 7 ), and the corresponding hardware test results are presented in (Table 1 ). The results show that visual sensing assists millimetre-wave communications in performing beam alignment and beam prediction more effectively, thereby improving system communication performance. For wireless-communication-assisted sensing, the hardware prototype system is shown in (Fig. 8 ), and the experimental results are shown in (Fig. 9 ) and (Table 2 ). The static-environment reconstruction obtained through wireless-visual fusion shows improved robustness and higher accuracy. Depth estimation based on visual and communication fusion also presents strong robustness in rainy and snowy weather, with the RMSE reduced by approximately 50% compared with pure visual algorithms. These experimental results indicate that vision-enabled multimodal ISAC systems present strong potential for practical application.Conclusions A multimodal ISAC system that integrates visual sensing with wireless-device sensing is proposed. In this system, visual sensing captures environmental information to assist wireless communications, and wireless signals help overcome the inherent limitations of visual sensing. Key algorithms for visual-sensing-assisted wireless communication are examined, including beam prediction, occlusion prediction, and resource scheduling and allocation for multiple base stations and users. The sensing gains brought by wireless devices combined with visual sensors are also analysed. Static-environment reconstruction and dynamic-target sensing schemes based on wireless-visual fusion are proposed to obtain global information about the physical world. A “vision-communication” simulation and measurement dataset is further constructed, forming a coherent theoretical and technical framework for multimodal ISAC. Experimental results show that vision-enabled multimodal ISAC systems present strong potential for use in 6G networks. -
表 1 视觉辅助通信波束验证结果(%)
未来33 ms 未来66 ms 未来99 ms 未来132 ms 场景1 场景2 场景3 所有 场景1 场景2 场景3 所有 场景1 场景2 场景3 所有 场景1 场景2 场景3 所有 被遮挡准确率 94.3 95.4 97.7 95.5 88.1 92.4 95.4 91.8 82.2 92.0 93.2 90.5 76.8 90.3 95.7 88.2 不被遮挡准确率 98.9 99.1 99.3 99.1 98.7 98.8 99.6 99.1 97.9 98.1 98.2 98.1 98.5 98.5 96.3 98.0 准确率 98.3 98.2 99.3 98.6 97.8 96.7 99.3 97.7 96.9 96.2 97.7 96.8 96.3 95.8 96.3 96.1 表 2 无线融合视觉深度估计算法与纯视觉算法指标对比
天气 RMSE RMSELOG MAE MAELOG AbsRel SqRel DELTAL1 DELTAL2 DELTAL3 仅用
视觉雨天 10.70 0.45 2.13 0.56 0.29 15.71 0.4978 0.7998 0.9020 雪天 18.56 0.99 3.25 0.93 0.72 26.35 0.1469 0.3256 0.4316 晴天 5.97 0.45 1.68 0.50 0.26 12.99 0.6358 0.9479 0.9803 视觉融合
无线信号雨天 6.35 0.22 1.49 0.38 0.17 13.88 0.8091 0.9489 0.9860 雪天 7.99 0.37 1.79 0.48 0.30 18.90 0.7003 0.8598 0.9301 晴天 5.61 0.19 1.21 0.32 0.14 13.15 0.9052 0.9709 0.9914 -
[1] MASCHIETTI F, GESBERT D, DE KERRET P, et al. Robust location-aided beam alignment in millimeter wave massive MIMO[C]. 2017 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, Singapore, 2017: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2017.8254901. [2] MUPPIRISETTY L S, CHARALAMBOUS T, KAROUT J, et al. Location-aided pilot contamination avoidance for massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(4): 2662–2674. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2800038. [3] DESTINO G and WYMEERSCH H. On the trade-off between positioning and data rate for mm-wave communication[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Paris, France, 2017: 797–802. doi: 10.1109/ICCW.2017.7962756. [4] GAO Jiabao, ZHONG Caijun, and ZHANG Zhaoyang. Location-aided deep learning-based channel estimation for hybrid massive MIMO systems[C]. 2021 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Changsha, China, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/WCSP52459.2021.9613576. [5] CHEN Xuhong, LU Jiaxun, LIU Shanyun, et al. Location-aided umbrella-shaped massive MIMO beamforming scheme with transmit diversity for high speed railway communications[C]. 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 2016: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTCSpring.2016.7504325. [6] CHOWDHURY M Z, SHAHJALAL M, AHMED S, et al. 6G wireless communication systems: Applications, requirements, technologies, challenges, and research directions[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2020, 1: 957–975. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2020.3010270. [7] CUI Yuanhao, LIU Fan, JING Xiaojun, et al. Integrating sensing and communications for ubiquitous IoT: Applications, trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(5): 158–167. doi: 10.1109/MNET.010.2100152. [8] GAO Feifei, LIN Bo, BIAN Chenghong, et al. FusionNet: Enhanced beam prediction for mmWave communications using sub-6 GHz channel and a few pilots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(12): 8488–8500. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3110301. [9] WU Shunyao, CHAKRABARTI C, and ALKHATEEB A. LiDAR-aided mobile blockage prediction in real-world millimeter wave systems[C]. 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Austin, USA, 2022: 2631–2636. doi: 10.1109/WCNC51071.2022.9771651. [10] XU Weihua, GAO Feifei, JIN Shi, et al. 3D scene-based beam selection for mmWave communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(11): 1850–1854. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3005983. [11] DEMIRHAN U and ALKHATEEB A. Radar aided 6G beam prediction: Deep learning algorithms and real-world demonstration[C]. 2022 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Austin, USA, 2022: 2655–2660. doi: 10.1109/WCNC51071.2022.9771564. [12] KLAUTAU A, GONZÁLEZ-PRELCIC N, and HEATH R W. LIDAR data for deep learning-based mmWave beam-selection[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(3): 909–912. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2899571. [13] DIAS M, KLAUTAU A, GONZÁLEZ-PRELCIC N, et al. Position and LIDAR-aided mmWave beam selection using deep learning[C]. 2019 IEEE 20th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Cannes, France, 2019: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/SPAWC.2019.8815569. [14] MASHHADI M B, JANKOWSKI M, TUNG T Y, et al. Federated mmWave beam selection utilizing LIDAR data[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(10): 2269–2273. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3099136. [15] JIANG Shuaifeng, CHARAN G, and ALKHATEEB A. LiDAR aided future beam prediction in real-world millimeter wave V2I communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2023, 12(2): 212–216. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3219409. [16] SALEHI B, REUS-MUNS G, ROY D, et al. Deep learning on multimodal sensor data at the wireless edge for vehicular network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(7): 7639–7655. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3170733. [17] CHARAN G, ALRABEIAH M, and ALKHATEEB A. Vision-aided 6G wireless communications: Blockage prediction and proactive handoff[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(10): 10193–10208. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3104219. [18] XU Weihua, GAO Feifei, ZHANG Jianhua, et al. Deep learning based channel covariance matrix estimation with user location and scene images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(12): 8145–8158. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3107947. [19] ALRABEIAH M, HREDZAK A, and ALKHATEEB A. Millimeter wave base stations with cameras: Vision-aided beam and blockage prediction[C]. 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring), Antwerp, Belgium, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTC2020-Spring48590.2020.9129369. [20] KODA Y, NAKASHIMA K, YAMAMOTO K, et al. Handover management for mmWave networks with proactive performance prediction using camera images and deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(2): 802–816. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2961655. [21] CHARAN G, ALRABEIAH M, and ALKHATEEB A. Vision-aided dynamic blockage prediction for 6G wireless communication networks[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCWorkshops50388.2021.9473651. [22] NISHIO T, OKAMOTO H, NAKASHIMA K, et al. Proactive received power prediction using machine learning and depth images for mmWave networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(11): 2413–2427. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2933763. [23] KODA Y, PARK J, BENNIS M, et al. Communication-efficient multimodal split learning for mmWave received power prediction[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(6): 1284–1288. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2978824. [24] TIAN Yu and WANG Chenwei. Vision-aided beam tracking: Explore the proper use of camera images with deep learning[C]. 2021 IEEE 94th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Fall), Norman, USA, 2021: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/VTC2021-Fall52928.2021.9625195. [25] AHN Y, KIM J, KIM S, et al. Toward intelligent millimeter and terahertz communication for 6G: Computer vision-aided beamforming[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2023, 30(5): 179–186. doi: 10.1109/MWC.007.2200155. [26] WU Shunyao, ALRABEIAH M, CHAKRABARTI C, et al. Blockage prediction using wireless signatures: Deep learning enables real-world demonstration[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2022, 3: 776–796. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2022.3162591. [27] DING Ruijin, XU Weihua, YUAN Wanmai, et al. Vision-aided blockage avoidance in UAV-assisted V2X communications[Z]. arXiv: 2207.12991, 2022. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2207.12991. [28] CHARAN G, HREDZAK A, and ALKHATEEB A. Millimeter wave drones with cameras: Computer vision aided wireless beam prediction[C]. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Rome, Italy, 2023: 1896–1901. doi: 10.1109/ICCWorkshops57953.2023.10283784. [29] XU Weihua, ZHAO Chuanbin, and GAO Feifei. Angle domain channel-based camera pose correction for vision-aided ISAC systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2024, 13(8): 2080–2084. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2024.3401408. [30] CHEN Quan, ZHU Hai, YANG Lei, et al. Edge computing assisted autonomous flight for UAV: Synergies between vision and communications[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2021, 59(1): 28–33. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2000501. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
