Multi-code Deep Fusion Attention Generative Adversarial Networks for Text-to-Image Synthesis
-
摘要: 文本生成图像是一项极具挑战的跨模态任务,其核心在于生成与文本描述高度一致、细节丰富的高质量图像。当前基于生成对抗网络的方法多依赖单一噪声输入,导致生成图像细粒度不足;同时,单词级特征利用不充分,也制约了文本与图像之间的语义对齐精度。为此,该文提出一种多码深度特征融合生成对抗网络(mDFA-GAN)。该方法通过设计多噪声输入生成器与多码先验融合模块,提升生成图像的细节表现力;在生成器中引入多头注意力机制,从多角度对齐单词与图像子区域,增强语义一致性;此外,提出多码先验融合损失以稳定训练过程。在CUB和COCO数据集上的实验结果表明,所提方法在IS与FID评价指标上均优于当前主流生成对抗网络方法,能够生成更逼真、细节更丰富、语义一致性更强的图像。Abstract:
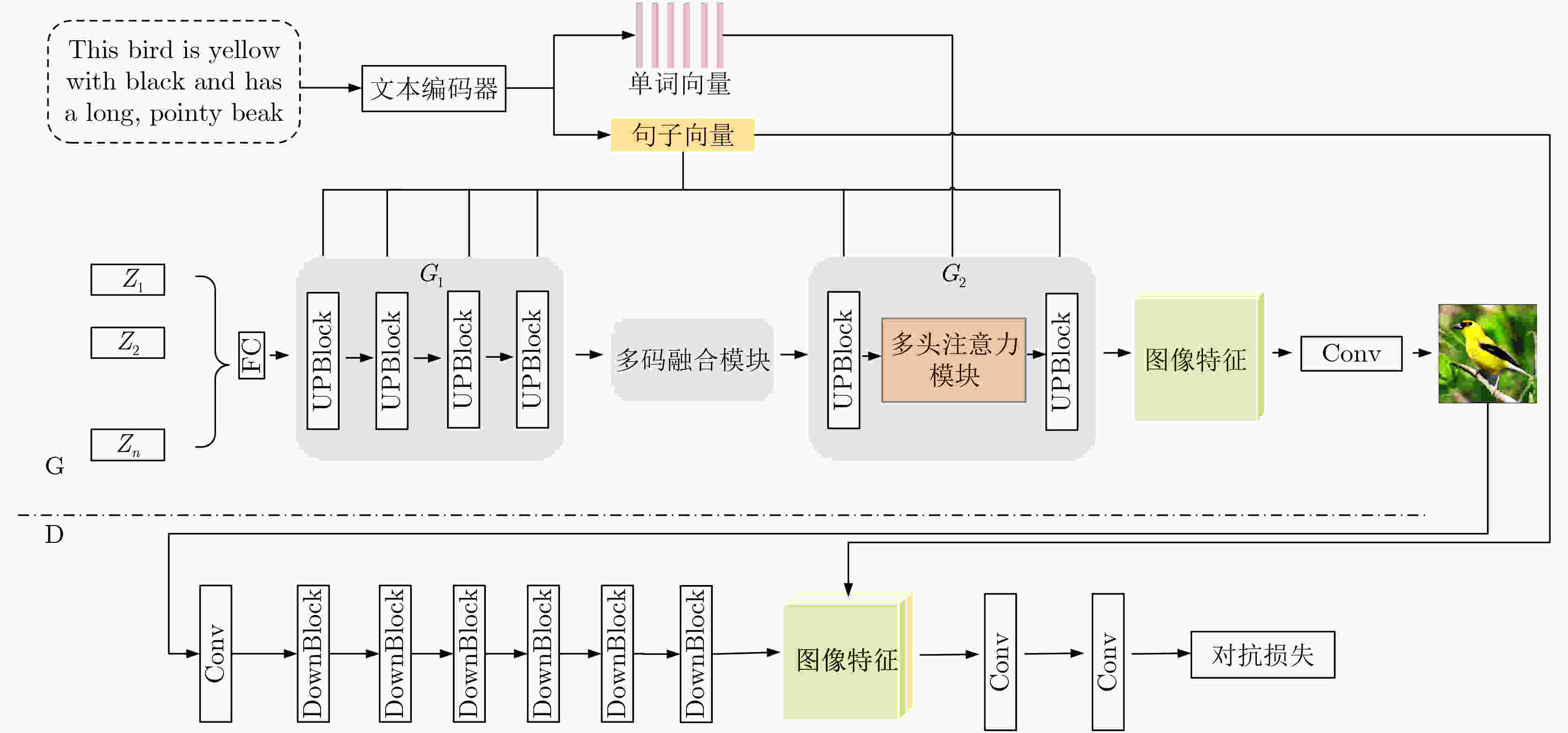
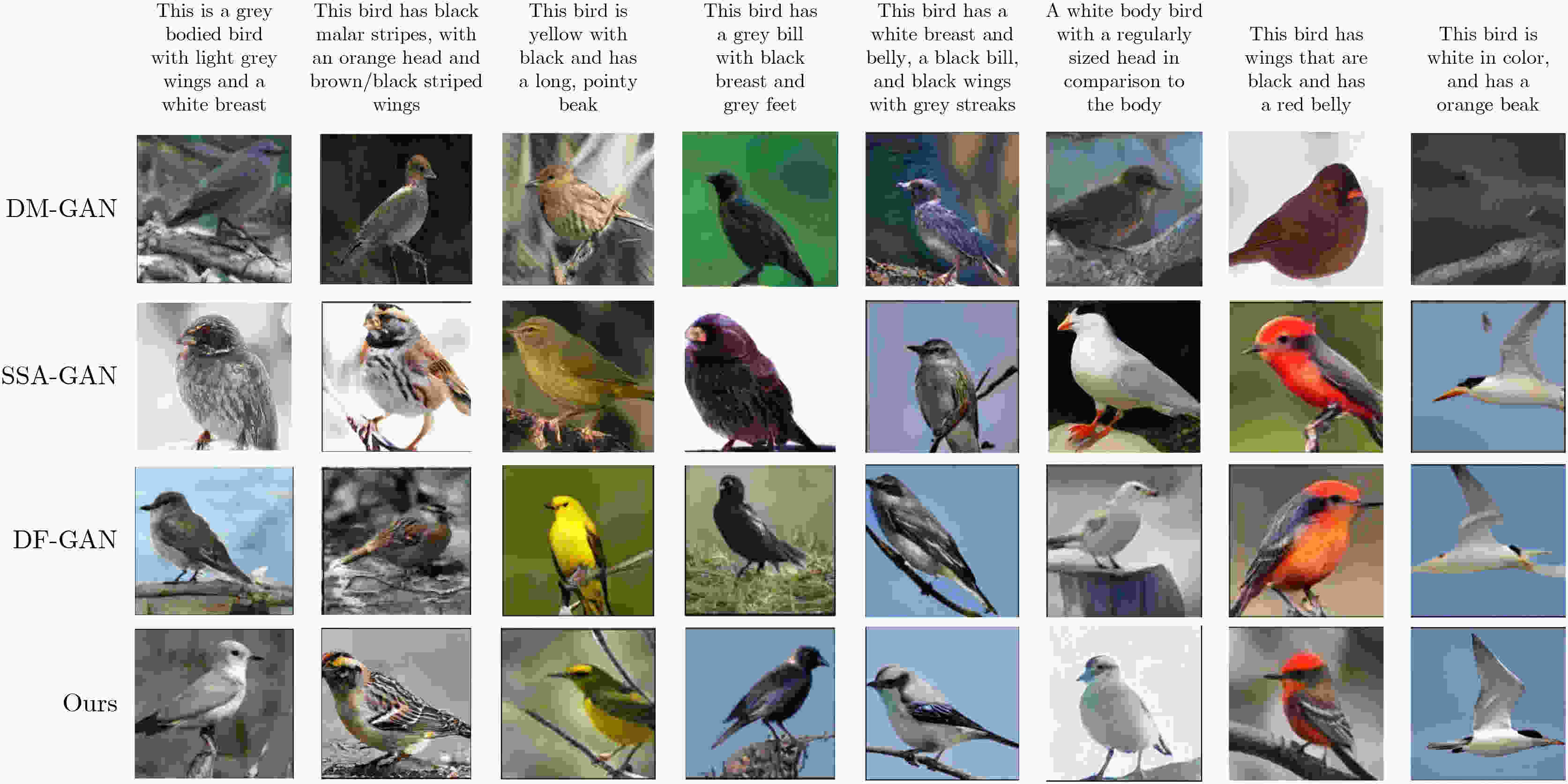
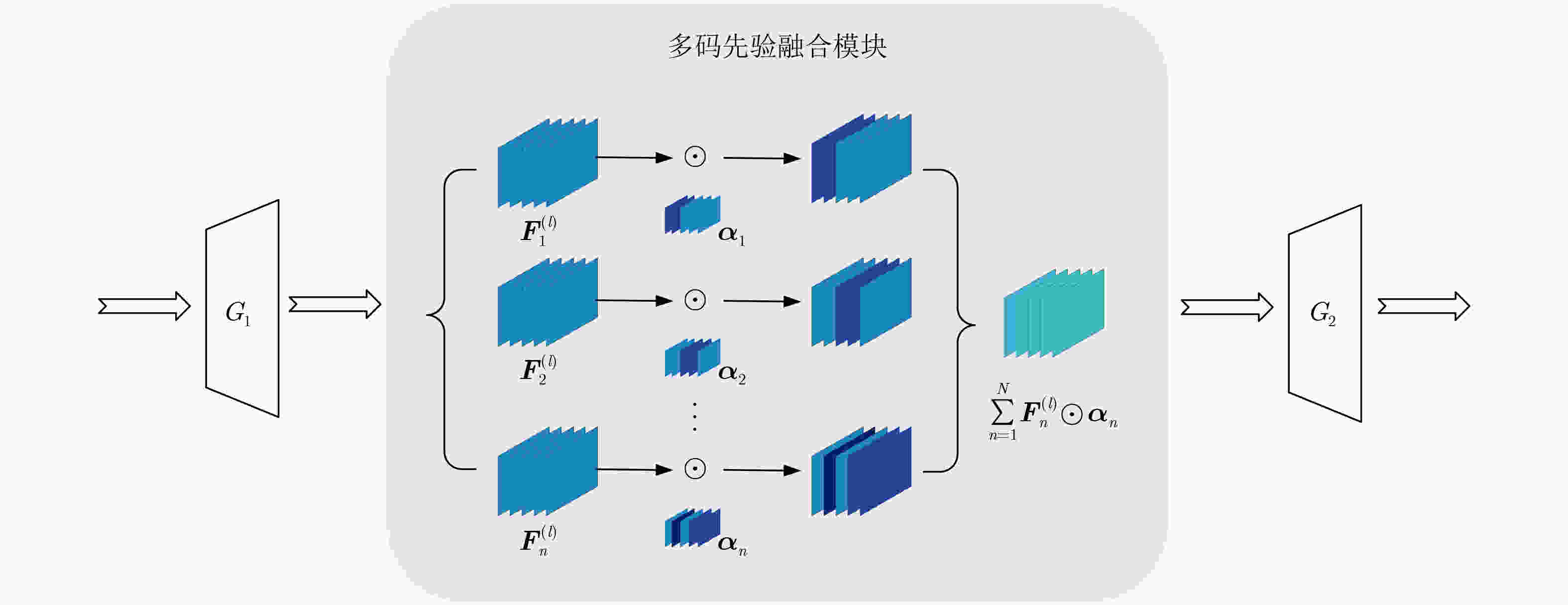
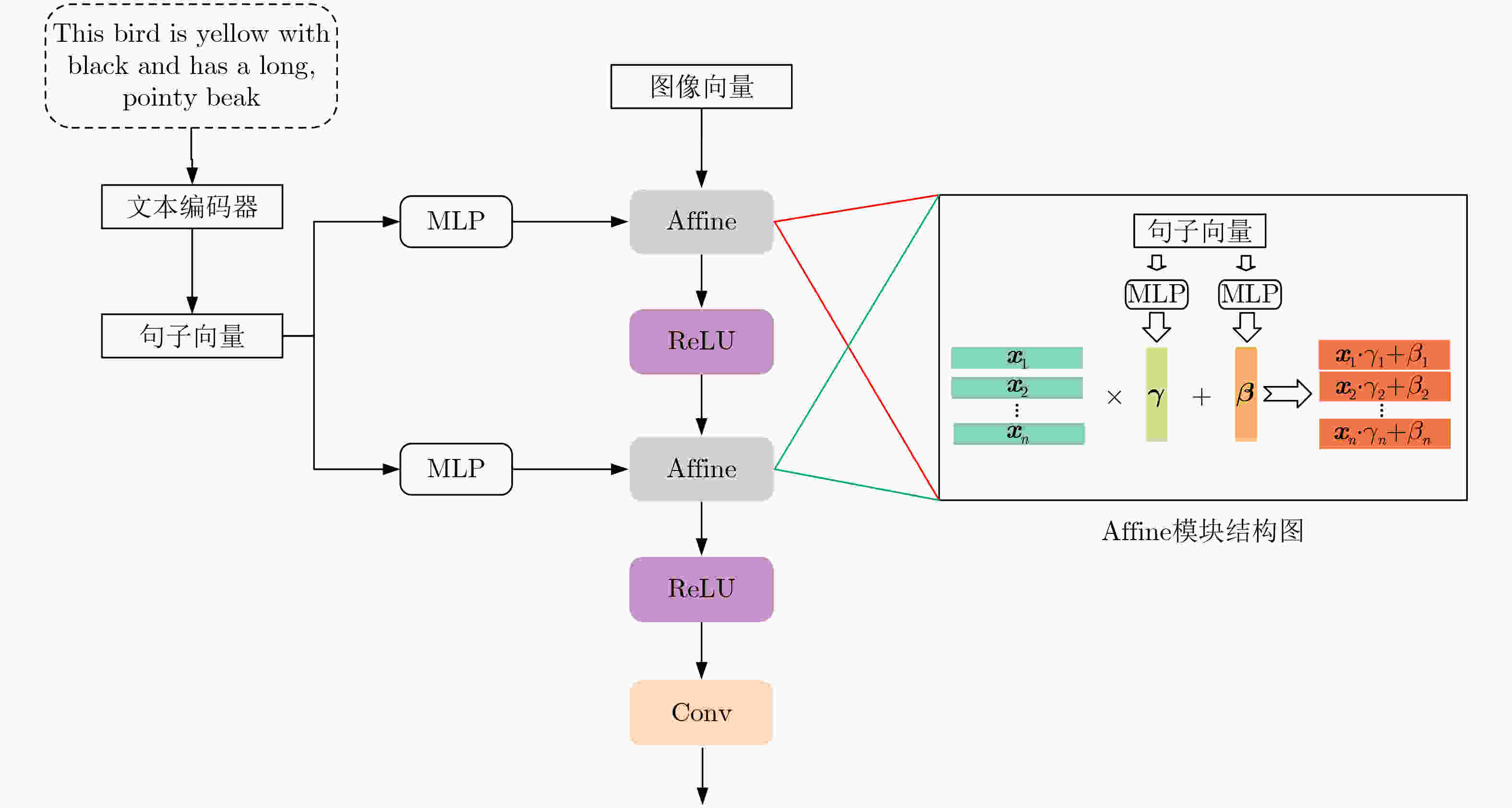
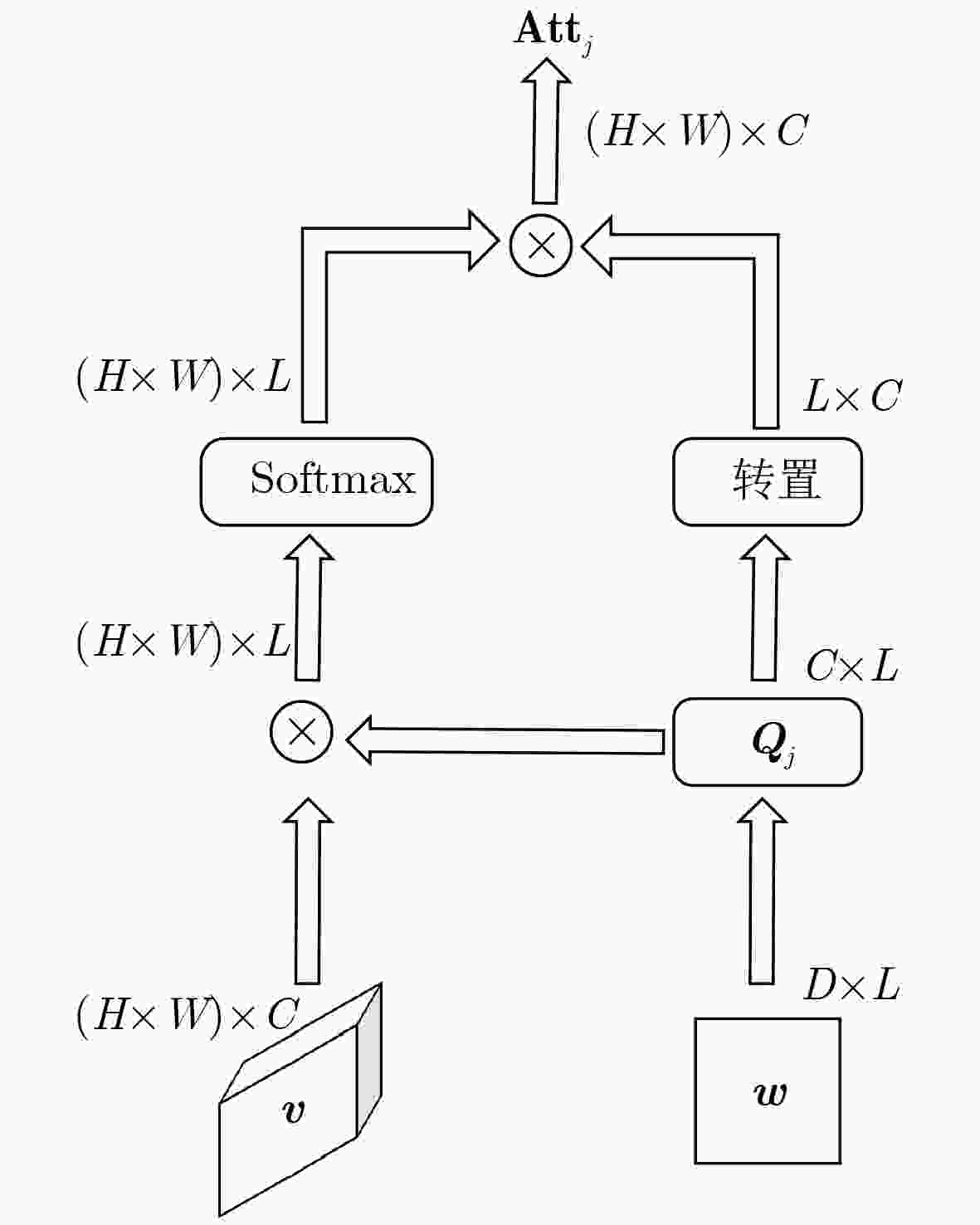
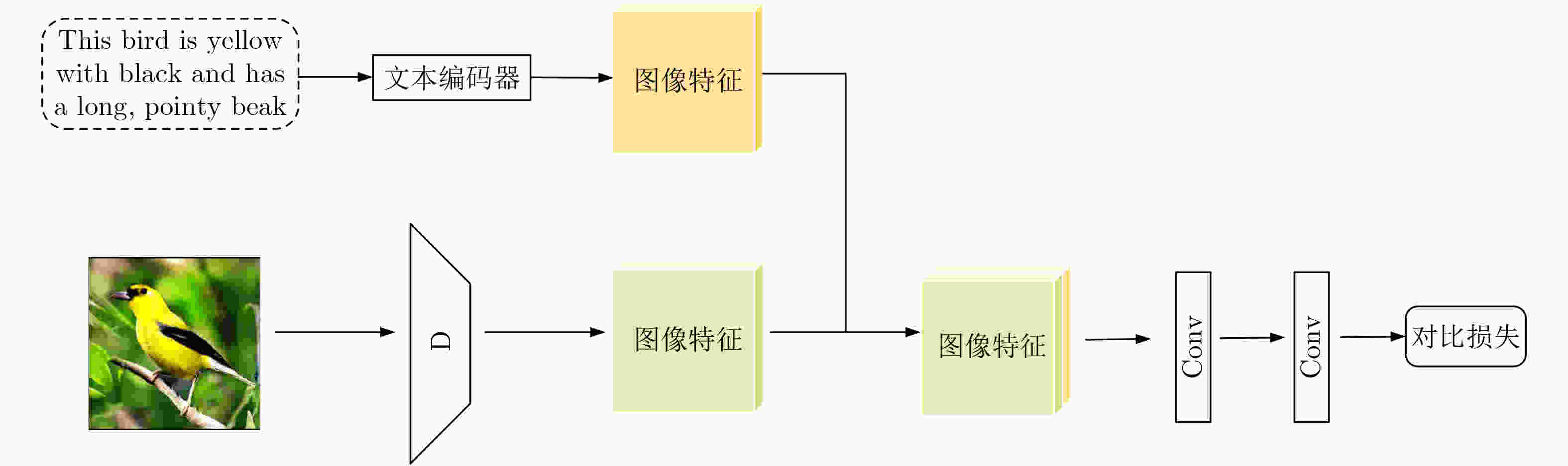
Objective Text-to-image synthesis is a core task in multimodal artificial intelligence and aims to generate photorealistic images that accurately correspond to natural language descriptions. This capability supports a wide range of applications, including creative design, education, data augmentation, and human-computer interaction. However, simultaneously achieving high visual fidelity and precise semantic alignment remains challenging. Most existing Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) based methods condition image generation on a single latent noise vector, which limits the representation of diverse visual attributes described in text. Therefore, generated images often lack fine textures, subtle color variations, or detailed structural characteristics. In addition, although attention mechanisms enhance semantic correspondence, many approaches rely on single-focus attention, which is insufficient to capture the complex many-to-many relationships between linguistic expressions and visual regions. These limitations result in an observable discrepancy between textual descriptions and synthesized images. To address these issues, a novel GAN architecture, termed Multi-code Deep Feature Fusion Attention Generative Adversarial Network (mDFA-GAN), is proposed. The objective is to enhance text-to-image synthesis by enriching latent visual representations through multiple noise codes and strengthening semantic reasoning through a multi-head attention mechanism, thereby improving detail accuracy and textual faithfulness. Methods An mDFA-GAN is proposed. The generator incorporates three main components. First, a multi-noise input strategy is adopted, in which multiple independent noise vectors are used instead of a single latent noise vector, allowing different noise codes to capture different visual attributes such as structure, texture, and color. Second, a Multi-code Prior Fusion Module is designed to integrate these latent representations. This module operates on intermediate feature maps and applies learnable channel-wise weights to perform adaptive weighted summation, producing a unified and detail-rich feature representation. Third, a Multi-head Attention Module is embedded in the later stages of the generator. This module computes attention between visual features and word embeddings across multiple attention heads, enabling each image region to attend to multiple semantically relevant words and improving fine-grained cross-modal alignment. Training is conducted using a unidirectional discriminator with a conditional hinge loss combined with a Matching-Aware zero-centered Gradient Penalty (MA-GP) to enhance training stability and enforce text-image consistency. In addition, a multi-code fusion loss is introduced to reduce variance among features derived from different noise codes, thereby promoting spatial and semantic coherence. Results and Discussions The proposed mDFA-GAN is evaluated on the CUB-200-2011 and MS COCO datasets. Qualitative results, as illustrated in ( Fig. 6 ) and (Fig. 7 ), indicate that the proposed method generates images with accurate colors, fine-grained details, and coherent complex scenes. Subtle textual attributes, such as specific plumage patterns and object shapes, are effectively captured. Quantitative evaluation demonstrates state-of-the-art performance. An Inception Score (IS) of 4.82 is achieved on the CUB-200-2011 dataset (Table 1 ), reflecting improved perceptual quality and semantic consistency. Moreover, the lowest Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) values of 13.45 on CUB-200-2011 and 16.50 on MS COCO are obtained (Table 2 ), indicating that the generated images are statistically closer to real samples. Ablation experiments confirm the contribution of each component. Performance degrades when either the Multi-code Prior Fusion Module or the Multi-head Attention Module is removed (Table 3 ). Further analysis identifies that setting the number of noises to 3 is the optimal configuration (Table 4 ). In terms of efficiency, the model achieves an inference time of 0.8 seconds per image (Table 5 ), maintaining the efficiency advantage of GAN-based methods.Conclusions A novel text-to-image synthesis framework, mDFA-GAN, is proposed to address limited fine-grained detail representation and insufficient semantic alignment in existing GAN-based methods. By decomposing the latent space into multiple noise codes and adaptively fusing them, the model enhances its capacity to generate detailed visual content. The integration of multi-head cross-modal attention enables more accurate and context-aware semantic grounding. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate that mDFA-GAN achieves state-of-the-art performance, as evidenced by improved IS and FID scores and high-quality visual results. Ablation studies further validate the necessity and complementary effects of the proposed components. The framework provides both an effective solution for text-to-image synthesis and useful architectural insights for future research in multimodal representation learning. -
表 1 在CUB数据集上与前沿算法相比IS得分情况表
方法 Inception Score(IS)↑ StackGAN++ 4.04±0.06 AttnGAN 4.36±0.03 DM-GAN 4.47±0.19 DR-GAN 4.66±0.15 DF-GAN 4.61±0.12 SSA-GAN 4.70±0.08 本文 4.82±0.10 表 2 在CUB数据集和COCO数据集上与前沿算法相比FID得分情况表
方法 CUB-FID↓ COCO-FID↓ StackGAN++ 15.30 81.59 AttnGAN 23.98 35.49 DM-GAN 16.09 32.64 DR-GAN 14.96 27.80 DF-GAN 14.81 19.32 SSA-GAN 15.61 19.37 Cogview - 27.10 LDM-8 - 23.31 本文 13.45 16.50 表 3 模型组成部分的消融实验
组成部分 CUB-FID↓ COCO-FID↓ 基线模型 多码融合模块 多头注意力 √ - - 14.81 19.32 √ √ - 14.21 17.94 √ - √ 13.75 17.19 √ √ √ 13.45 16.50 表 4 噪声n的数量选择实验
FID n 1 2 3 4 5 CUB-FID↓ 14.21 13.67 13.45 13.65 13.70 COCO-FID↓ 17.94 16.95 16.50 16.86 16.90 表 5 推理速度对比(s)
方法 DF-GAN Stable Diffusion DALLE2 本文 推理速度 0.5 1.4 2 0.8 -
[1] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139–144. doi: 10.1145/3422622. [2] TAO Ming, TANG Hao, WU Fei, et al. DF-GAN: A simple and effective baseline for text-to-image synthesis[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 16494–16504. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01602. [3] XU Tao, ZHANG Pengchuan, HUANG Qiuyuan, et al. AttnGAN: Fine-grained text to image generation with attentional generative adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1316–1324. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00143. [4] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [5] XUE A. End-to-end Chinese landscape painting creation using generative adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 3862–3870. doi: 10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00391. [6] SHAHRIAR S. GAN computers generate arts? A survey on visual arts, music, and literary text generation using generative adversarial network[J]. Displays, 2022, 73: 102237. doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2022.102237. [7] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967–5976. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.632. [8] ALOTAIBI A. Deep generative adversarial networks for image-to-image translation: A review[J]. Symmetry, 2020, 12(10): 1705. doi: 10.3390/sym12101705. [9] XIA Weihao, YANG Yujiu, XUE Jinghao, et al. TEDIGAN: Text-guided diverse face image generation and manipulation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2256–2265. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00229. [10] KOCASARI U, DIRIK A, TIFTIKCI M, et al. StyleMC: Multi-channel based fast text-guided image generation and manipulation[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2022: 3441–3450. doi: 10.1109/WACV51458.2022.00350. [11] SAHARIA C, CHAN W, CHANG H, et al. Photorealistic text-to-image diffusion models with deep language understanding[C]. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2023: 15679–15689. [12] ZHANG Han, XU Tao, LI Hongsheng, et al. StackGAN: Text to photo-realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5908–5916. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.629. [13] ZHANG Han, XU Tao, LI Hongsheng, et al. StackGAN++: Realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(8): 1947–1962. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2856256. [14] LIAO Wentong, HU Kai, YANG M Y, et al. Text to image generation with semantic-spatial aware GAN[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 18166–18175. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01765. [15] TAO Ming, BAO Bingkun, TANG Hao, et al. GALIP: Generative adversarial CLIPs for text-to-image synthesis[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 14214–14223. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01366. [16] LU Cheng, ZHOU Yuhao, BAO Fan, et al. DPM-Solver++: Fast solver for guided sampling of diffusion probabilistic models[J]. Machine Intelligence Research, 2025, 22(4): 730–751. doi: 10.1007/s11633-025-1562-4. [17] DING Ming, YANG Zhuoyi, HONG Wenyi, et al. CogView: Mastering text-to-image generation via transformers[C]. Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 19822–19835. [18] ROMBACH R, BLATTMANN A, LORENZ D, et al. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 10674–10685. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01042. [19] ZHAO Liang, HUANG Pingda, CHEN Tengtuo, et al. Multi-sentence complementarily generation for text-to-image synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 8323–8332. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3297769. [20] DEVLIN J, CHANG Mingwei, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), Minneapolis, USA, 2019: 4171–4186. doi: 10.18653/v1/N19-1423. [21] LI Bowen, QI Xiaojuan, LUKASIEWICZ T, et al. Controllable text-to-image generation[C]. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 185. [22] RUAN Shulan, ZHANG Yong, ZHANG Kun, et al. DAE-GAN: Dynamic aspect-aware GAN for text-to-image synthesis[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 13940–13949. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01370. [23] ZHANG L, ZHANG Y, LIU X, et al. Fine-grained text-to-image synthesis via semantic pyramid alignment[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, Canada, 2023: 23415–23425. [24] CHEN J, LIU Y, WANG H, et al. Improving text-image semantic consistency in generative adversarial networks via contrastive learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 5102–5113. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2024.3356781. [25] DENG Zhijun, HE Xiangteng, and PENG Yuxin. LFR-GAN: Local feature refinement based generative adversarial network for text-to-image generation[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and Applications, 2023, 19(5): 207. doi: 10.1145/358900. [26] YANG Bing, XIANG Xueqin, KONG Wangzeng, et al. DMF-GAN: Deep multimodal fusion generative adversarial networks for text-to-image synthesis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 6956–6967. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2024.3358086. [27] WANG Z, ZHOU Y, SHI B, et al. Advances in controllable and disentangled representation learning for generative models[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2023, 131(5): 1245–1263. doi: 10.1007/s11263-023-01785-y. [28] YUAN M and PENG Y. T2I-CompBench: A comprehensive benchmark for open-world compositional text-to-image generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(5): 2754–2769. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3330805. [29] SALIMANS T, GOODFELLOW I, ZAREMBA W, et al. Improved techniques for training GANs[C]. Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 2234–2242. [30] HEUSEL M, RAMSAUER H, UNTERTHINER T, et al. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium[C]. Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6629–6640. [31] TAN Hongchen, LIU Xiuping, YIN Baocai, et al. DR-GAN: Distribution regularization for text-to-image generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(12): 10309–10323. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3165573. [32] WAH C, BRANSON S, WELINDER P, et al. The Caltech-UCSD birds-200–2011 dataset[R]. CNS-TR-2010-001, 2011. [33] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. Proceedings of 13th European Conference on Computer Vision -- ECCV 2014, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10602-1_48. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
