Design of Efficient ORBGRAND Decoders with Parity-Check Constraint
-
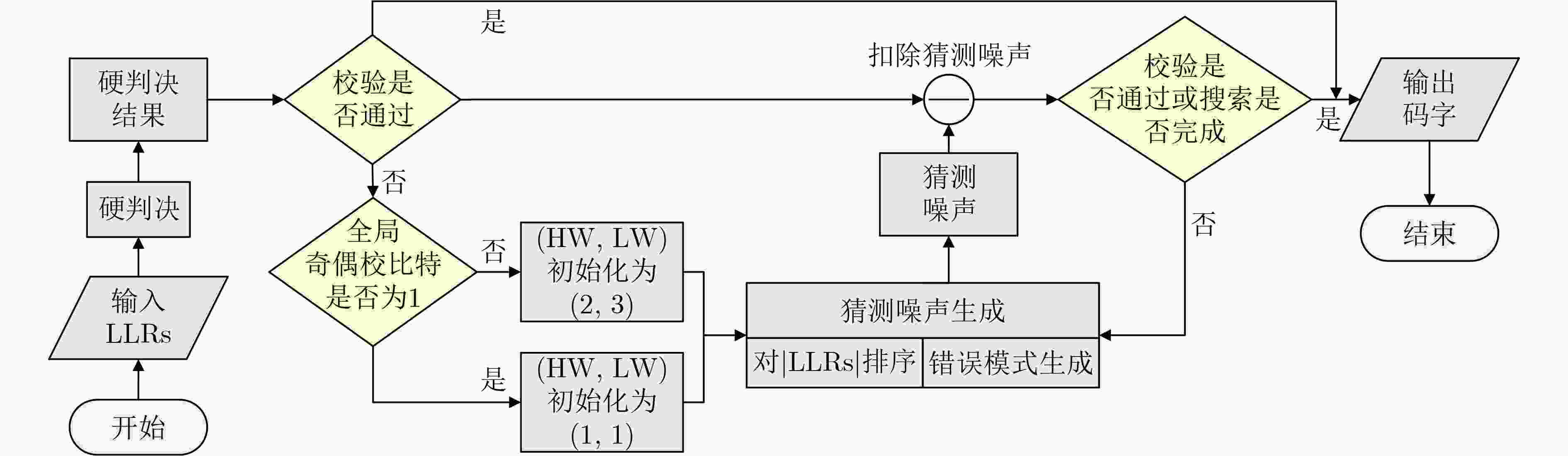
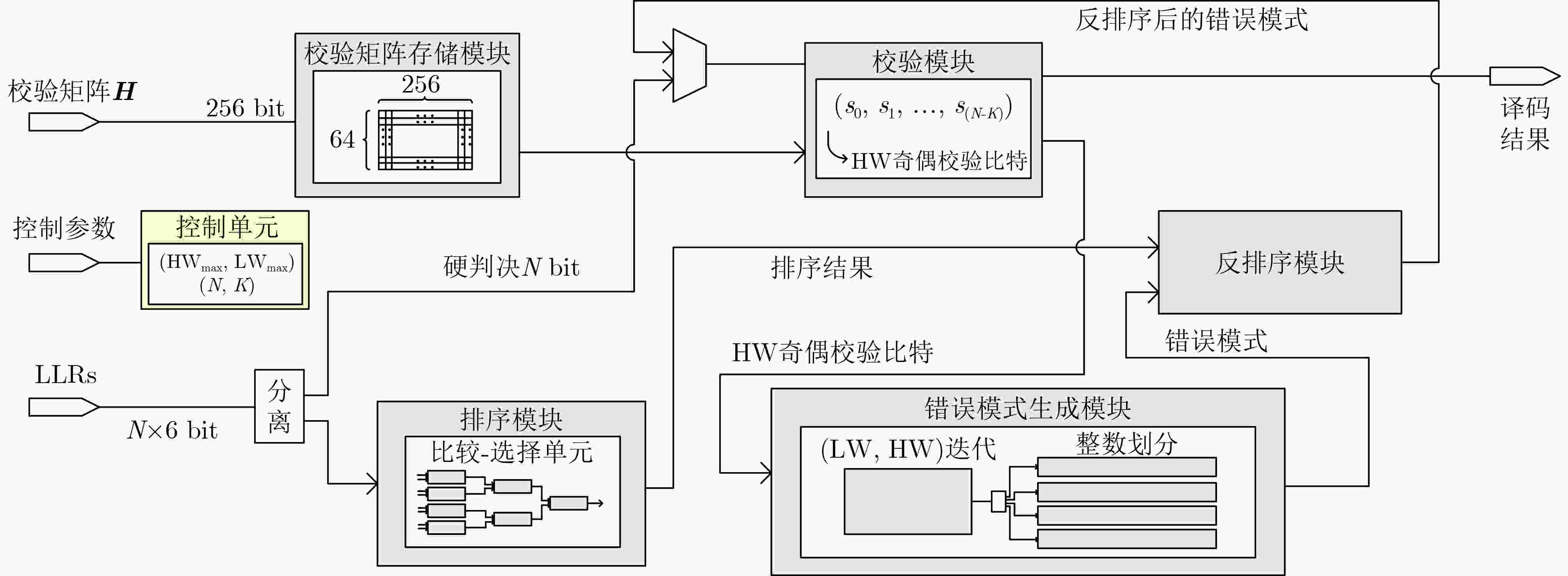
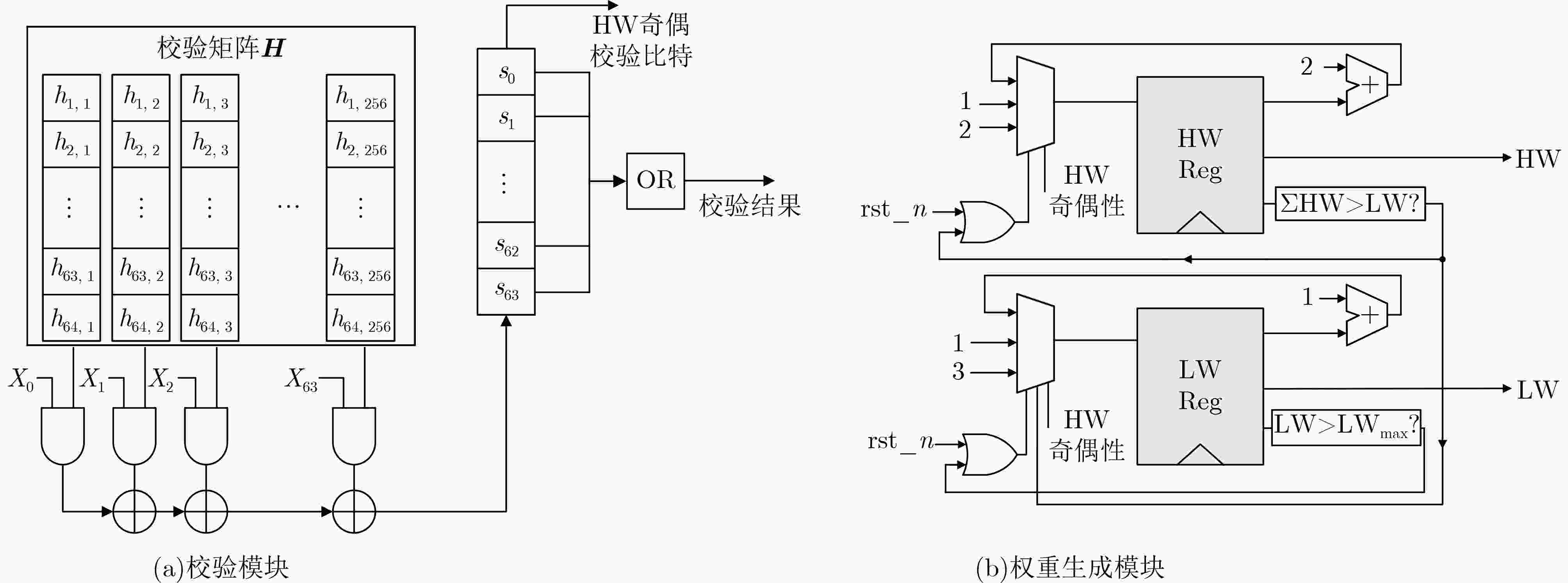
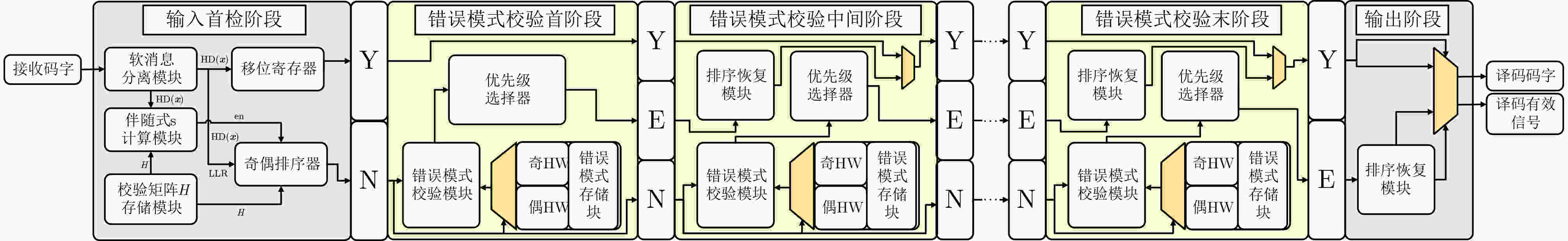
摘要: 有序可靠位猜测随机加性噪声译码(ORBGRAND)凭借其平均时延短和通用性等优点受到广泛关注。然而,目前ORBGRAND算法和硬件实现仍然面临挑战,如最差时延长和吞吐率受限等。为了改善上述问题,该文提出将特殊的编码校验关系融入现有串行和展开架构的ORBGRAND译码器以提升硬件效率。针对串行架构,利用全局奇偶校验比特控制逻辑重量和汉明重量(HW)的迭代过程,跳过部分无效错误模式的生成与校验过程;针对展开架构,根据全局奇偶校验比特将错误模式按照HW奇偶性进行分类存储与测试。采用现有文献中的归一化方法处理后的硬件实现结果表明,所提优化的串行架构译码器吞吐率提升了80.9%,面积效率提升了48.1%;所提优化的展开架构译码器吞吐率提升了584%,面积效率提升了
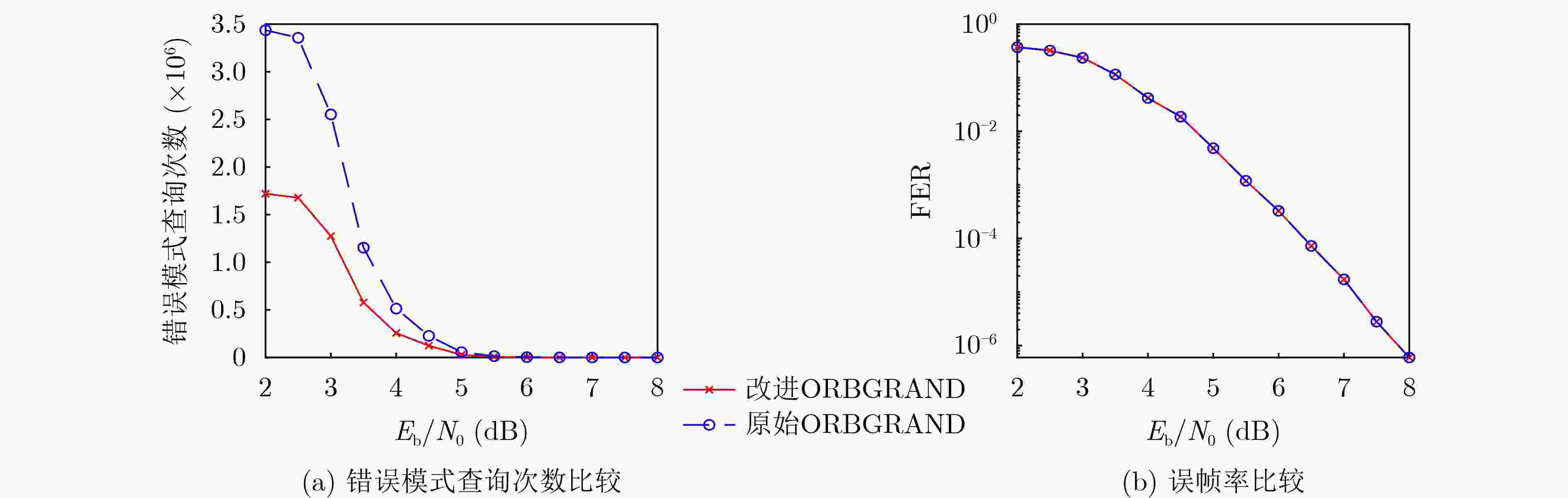
1223 %。Abstract:Objective Ordered Reliability Bits Guessing Random Additive Noise Decoding (ORBGRAND) is a universal channel decoding algorithm characterized by its simple principles, strong decoding performance, low average latency, and hardware-friendly implementation. Since its proposal, ORBGRAND has attracted considerable attention as a promising alternative to traditional decoding methods. By combining ordered reliability bits with a noise-guessing strategy, it achieves near Maximum-Likelihood Decoding (MLD) performance while avoiding prohibitive resource overhead. However, challenges remain: its worst-case latency and limited throughput restrict practical use in high-speed communication systems. To address these gaps, this work proposes improved ORBGRAND serial and unrolled hardware architectures that incorporate a special parity-check constraint. Methods This study proposes incorporating a specific parity-check constraint into serial and unrolled ORBGRAND architectures. In the serial architecture, the global parity-check bit is used to control the iteration of Hamming Weight (HW) and Logistic Weight (LW), enabling the decoder to skip the generation and verification of invalid error patterns. In the unrolled architecture, error patterns are separately pre-stored and queried according to the global parity-check bit. This design significantly enhances the hardware efficiency of ORBGRAND decoders. Results and Discussions The improved serial and unrolled ORBGRAND decoders with the global parity-check constraint are implemented and compared with their original counterparts. Simulation results for a tested code indicate that the parity-check constraint preserves the decoding performance of conventional ORBGRAND, while reducing the average number of error pattern queries by 50% in the low to medium Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) range. The architectures are synthesized using Synopsys Design Compiler with TSMC 28 nm technology. The serial ORBGRAND architecture achieves an operating frequency of 400 MHz, delivering a throughput of 33.1 Gbps at SNR = 8 dB. The implementation occupies 0.18 mm2 of area, yielding an area efficiency of 183.9 Gbps/mm2. Compared with the prior art, the serial design increases throughput by 80.9% and area efficiency by 48.1%. The unrolled architecture achieves a throughput of 110.6 Gbps and an area efficiency of 3.97 Gbps/mm2, corresponding to improvements of 584% in throughput and 1223 % in area efficiency relative to the prior art.Conclusions The ORBGRAND algorithm offers a promising approach for high-performance decoding in communication systems by combining high parallelism with near MLD performance. The specific parity-check constraint filters out invalid error patterns, significantly reducing the number of error pattern queries in serial and unrolled ORBGRAND architectures, without compromising performance. The serial and unrolled architectural implementations achieve notable gains in throughput and area efficiency compared with original designs. Integrating ORBGRAND with parity-check constraints thus represents a significant advancement, providing a more efficient solution for pratical communication applications. Future work will focus on further optimization of these architectures and their adaptation to diverse communication standards. In particular, the exploration of additional coding contraints may further extend the applicability of the approach. -
表 1 本文所提串行架构译码器综合结果及其与文献[13]的比较
本工作串行
架构现有串行
架构[13]实现类型 综合 综合 测试的编码方案 CA-Polar CA-Polar 码率 240/256 240/256 工艺 (nm) 28 40 供电电压 (V) 0.9 1.0 频率 (MHz) 400 180 延迟 (ns) 7.25 18.75 面积 (mm2) 0.18 0.3 吞吐率 (Gbps) 33.1 12.8 面积效率 (Gbps/mm2) 183.9 42.6 目标 FER 10–7 10–7 面积@(28nm, 0.9V) (mm2) 0.18 0.15 频率@(28nm, 0.9V) (MHz) 400 257 延迟@(28nm, 0.9V) (ns) 7.25 13.11 吞吐率@(28nm, 0.9V) (Gbps) 33.1 18.3 面积效率@(28nm, 0.9V) (Gbps/mm2) 183.9 124.2 注:归一化:面积:$ {S}^{2} $,频率:$ 1/S $,延迟:$ S $,吞吐率:$ 1/S $,面积效率:$ 1/{S}^{3} $,$ {S} $ 为目标工艺/当前工艺。 表 2 本文所提展开架构译码器综合结果及其与文献[16]的比较
本工作展开架构 现有展开架构[16] A B C D 实现类型 综合 综合 综合 综合 测试的编码方案 CA-Polar CA-Polar CA-Polar CA-Polar 码率 105/128 105/128 105/128 105/128 工艺 (nm) 28 28 7 7 供电电压 (V) 0.9 0.9 0.5 0.5 单阶段存储数/单阶段校验数 1024 /512512/256 512/512 256/256 译码周期 10 18 18 34 频率 (MHz) 616 1053 616 701 延迟 (cc)-(ns) 17-25.49 25-22.75 25-40.58 41-58.49 面积 (mm2) 24.51 27.82 3.38 3.70 吞吐率 (Gbps) 64.68 110.57 64.68 73.61 面积效率 (Gbps/mm2) 2.64 3.97 19.13 19.89 面积@(28nm, 0.9V) (mm2) 24.51 27.82 54.08 59.20 频率@(28nm, 0.9V) (MHz) 616 1053 154 175 延迟@(28nm, 0.9V) (ns) 25.49 22.75 162.32 233.96 吞吐率@(28nm, 0.9V) (Gbps) 64.68 110.57 16.17 18.40 面积效率@(28nm, 0.9V) (Gbps/mm2) 2.64 3.97 0.30 0.31 注:归一化:面积:$ {S}^{2} $,频率:$ 1/S $,延迟:$ S $,吞吐率:$ 1/S $,面积效率:$ 1/{S}^{3} $,$ {S} $为目标工艺/当前工艺。 -
[1] DUFFY K R, LI Jiange, and MÉDARD M. Capacity-achieving guessing random additive noise decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2019, 65(7): 4023–4040. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2019.2896110. [2] DUFFY K R, YUAN Peihong, GRIFFIN J, et al. Soft-output guessing codeword decoding[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2025, 29(2): 328–332. doi: 10.1109/lcomm.2024.3516486. [3] MILLWARD J A, DUFFY K R, RANGASWAMY M, et al. Enhancing guessing random additive noise decoding using channel estimation[C]. 2024 IEEE 25th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Lucca, Italy, 2024: 676–680. doi: 10.1109/SPAWC60668.2024.10694171. [4] WAN Li and ZHANG Wenyi. Approaching maximum likelihood decoding performance via reshuffling ORBGRAND[C]. 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Athens, Greece, 2024: 31–36. doi: 10.1109/ISIT57864.2024.10619402. [5] YUAN Peihong, MÉDARD M, GALLIGAN K, et al. Soft-output (SO) GRAND and iterative decoding to outperform LDPC codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2025, 24(4): 3386–3399. doi: 10.1109/twc.2025.3530880. [6] BLANC L D, HERRMANN V, REN Yuqing, et al. A GRANDAB decoder with 8.48 gbps worst-case throughput in 65nm CMOS[C]. 2024 IEEE European Solid-State Electronics Research Conference (ESSERC), Bruges, Belgium, 2024: 685–688. doi: 10.1109/ESSERC62670.2024.10719587. [7] DUFFY K R and MÉDARD M. Guessing random additive noise decoding with soft detection symbol reliability information - SGRAND[C]. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Paris, France, 2019: 480–484. doi: 10.1109/ISIT.2019.8849297. [8] DUFFY K R, MÉDARD M, and AN Wei. Guessing random additive noise decoding with symbol reliability information (SRGRAND)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(1): 3–18. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3114315. [9] DUFFY K R, AN Wei, and MÉDARD M. Ordered reliability bits guessing random additive noise decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 4528–4542. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2022.3203251. [10] CONDO C, BIOGLIO V, and LAND I. High-performance low-complexity error pattern generation for ORBGRAND decoding[C]. 2021 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Madrid, Spain, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GCWkshps52748.2021.9682165. [11] JI Chao, YOU Xiaohu, ZHANG Chuan, et al. Efficient ORBGRAND implementation with parallel noise sequence generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2025, 33(2): 435–448. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2024.3466474. [12] ABBAS S M, JALALEDDINE M, TSUI C Y, et al. Improved step-GRAND: Low-latency soft-input guessing random additive noise decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2025, 33(4): 1028–1041. doi: 10.1109/tvlsi.2025.3529637. [13] RIAZ A, YASAR A, ERCAN F, et al. A sub-0.8-pJ/bit universal soft-detection decoder using ORBGRAND[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2025, 60(7): 2645–2659. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2024.3502240. [14] ABBAS S M, TONNELLIER T, ERCAN F, et al. High-throughput and energy-efficient VLSI architecture for ordered reliability bits GRAND[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2022, 30(6): 681–693. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2022.3153605. [15] XIAO Jiayu, ZHOU Yangcan, SONG Suwen, et al. A low-latency and area-efficient ORBGRAND decoder for polar codes[C]. 2023 4th Information Communication Technologies Conference (ICTC), Nanjing, China, 2023: 10–15. doi: 10.1109/ICTC57116.2023.10154861. [16] CONDO C. A fixed latency ORBGRAND decoder architecture with LUT-aided error-pattern scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(5): 2203–2211. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2022.3150583. [17] ABBAS S M, JALALEDDINE M, and GROSS W J. List-GRAND: A practical way to achieve maximum likelihood decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2023, 31(1): 43–54. doi: 10.1109/tvlsi.2022.3223692. [18] GEISELHART M, KRIEG F, CLAUSIUS J, et al. 6G: A welcome chance to unify channel coding?[J]. IEEE BITS the Information Theory Magazine, 2023, 3(1): 67–80. doi: 10.1109/MBITS.2023.3322974. [19] TATARIA H, SHAFI M, MOLISCH A F, et al. 6G wireless systems: Vision, requirements, challenges, insights, and opportunities[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(7): 1166–1199. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2021.3061701. [20] GE Yingmeng, JI Zhenhao, HUANG Yongming, et al. Automatic hybrid-precision quantization for MIMO detectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2023, 71: 1039–1052. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2023.3240511. [21] GIARD P, BALATSOUKAS-STIMMING A, MULLER T C, et al. PolarBear: A 28-nm FD-SOI ASIC for decoding of polar codes[J]. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2017, 7(4): 616–629. doi: 10.1109/jetcas.2017.2745704. [22] HU Shuai, HAN Kaining, WANG Fujie, et al. Hybrid stochastic LDPC decoder with fully correlated stochastic computation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(9): 3643–3654. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2022.3179282. [23] PENG Guiqiang, LIU Leibo, ZHOU Sheng, et al. A 1.58 Gbps/W 0.40 Gbps/mm2 ASIC Implementation of MMSE Detection for 128×864 -QAM massive MIMO in 65 nm CMOS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2018, 65(5): 1717–1730. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2017.2754282. [24] ZHANG Qichen, CHEN Yun, LI Shixian, et al. A high-performance stochastic LDPC decoder architecture designed via correlation analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2020, 67(12): 5429–5442. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2020.3003457. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
