Kepler’s Laws Inspired Single Image Detail Enhancement Algorithm
-
摘要: 近年来,基于残差学习的单幅图像细节增强算法备受关注,其通过更新残差层来拟合图像细节层,并与原图像线性叠加实现图像细节增强。然而,此更新过程使用的方法是贪心算法,极易使系统陷入局部最优解,进而限制了系统性能。鉴于此,受行星运动规律的启发,该研究将残差更新类比为行星空间位置的动态调整,借鉴开普勒定律,通过计算确定行星的全局最优位置,进而实现残差层的精准更新。具体而言,将输入图像分块,对每个原始图像块,将其候选图像块视为“行星”,最佳匹配块视为“恒星”。通过计算每个“行星”与原始图像块之间的差异、“行星”的速度和“恒星”的引力,更新“行星”和“恒星”的位置,直至“恒星”的位置达到收敛状态,确定全局最佳匹配块的位置。实验结果显示,该研究提出的算法在视觉效果及量化评估方面均优于当前方法。值得一提的是,在BSDS200数据集4倍增强因子的结果中,该研究提出的方法比当前流行方法QWLS的量化指标PSNR和SSIM分别高出1.51 dB和
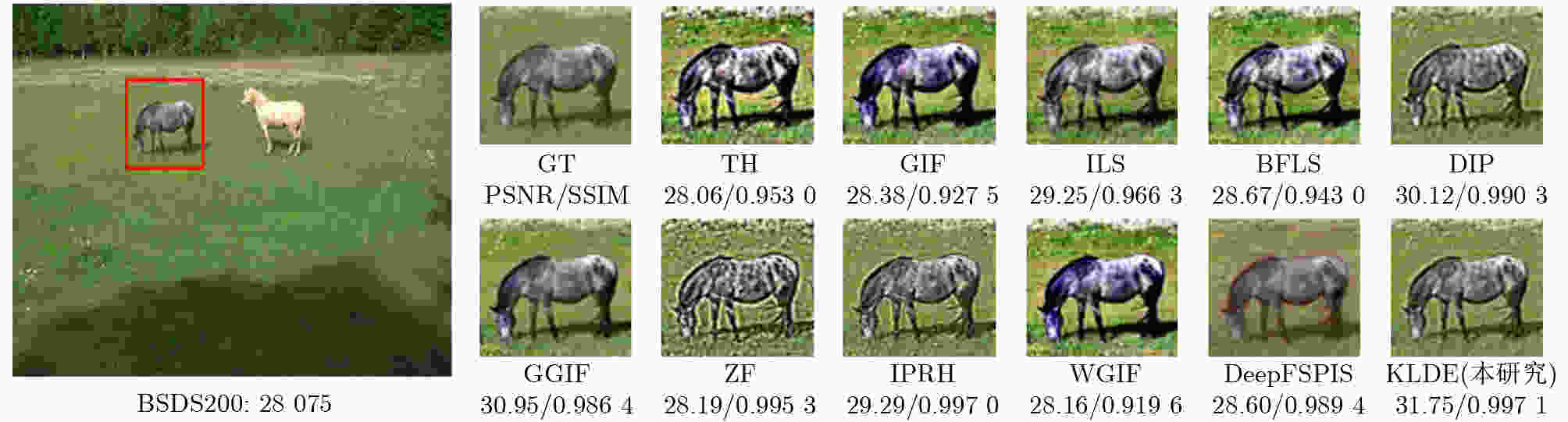
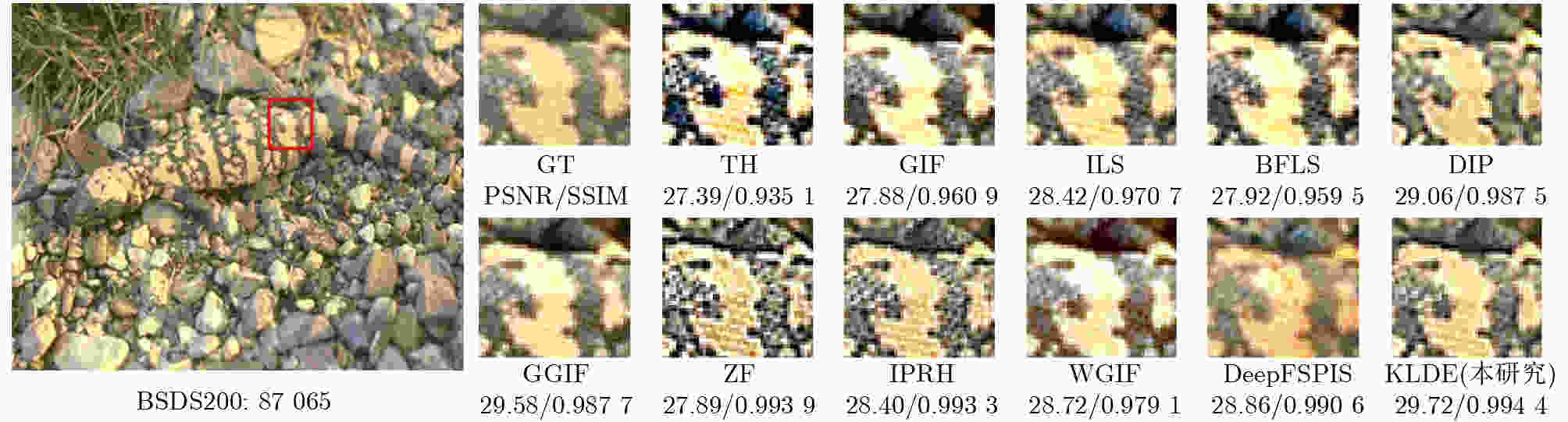
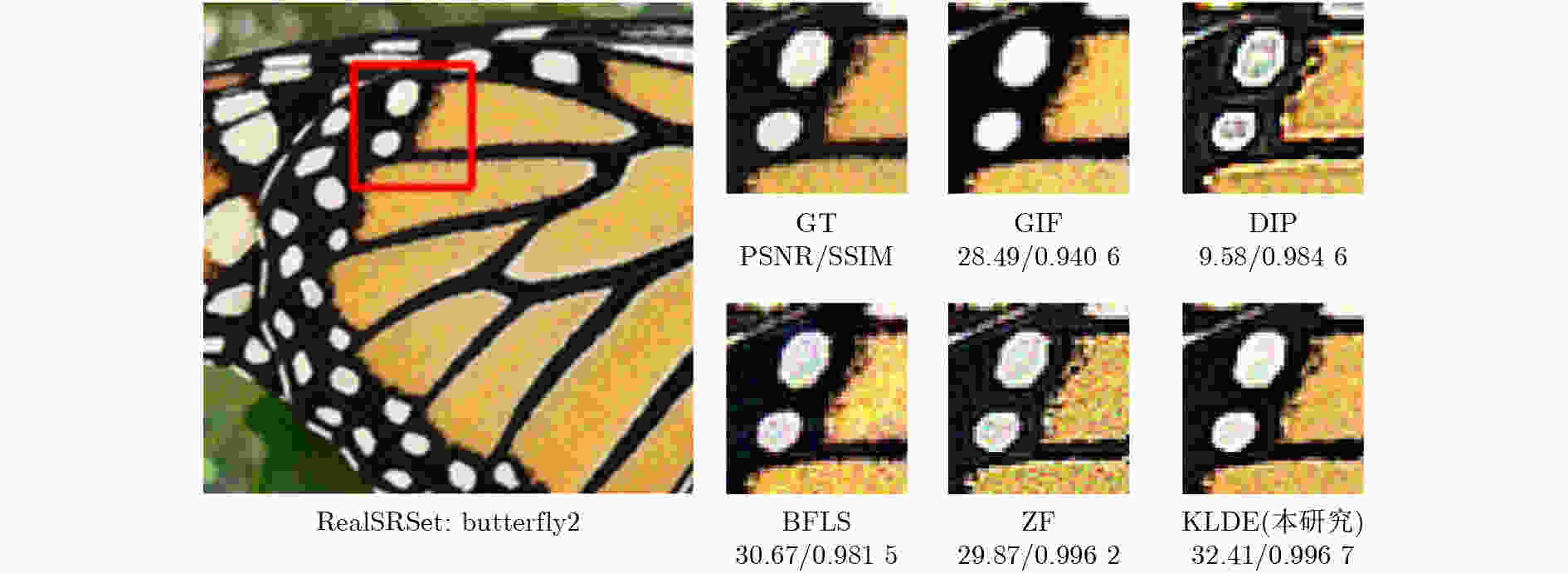
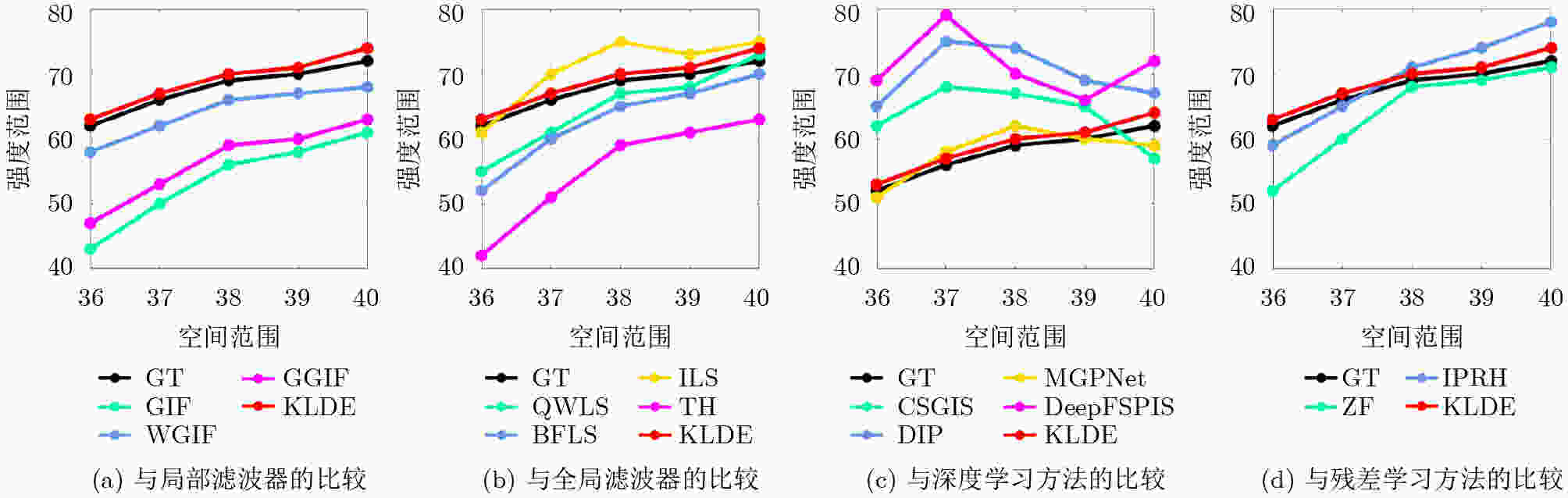
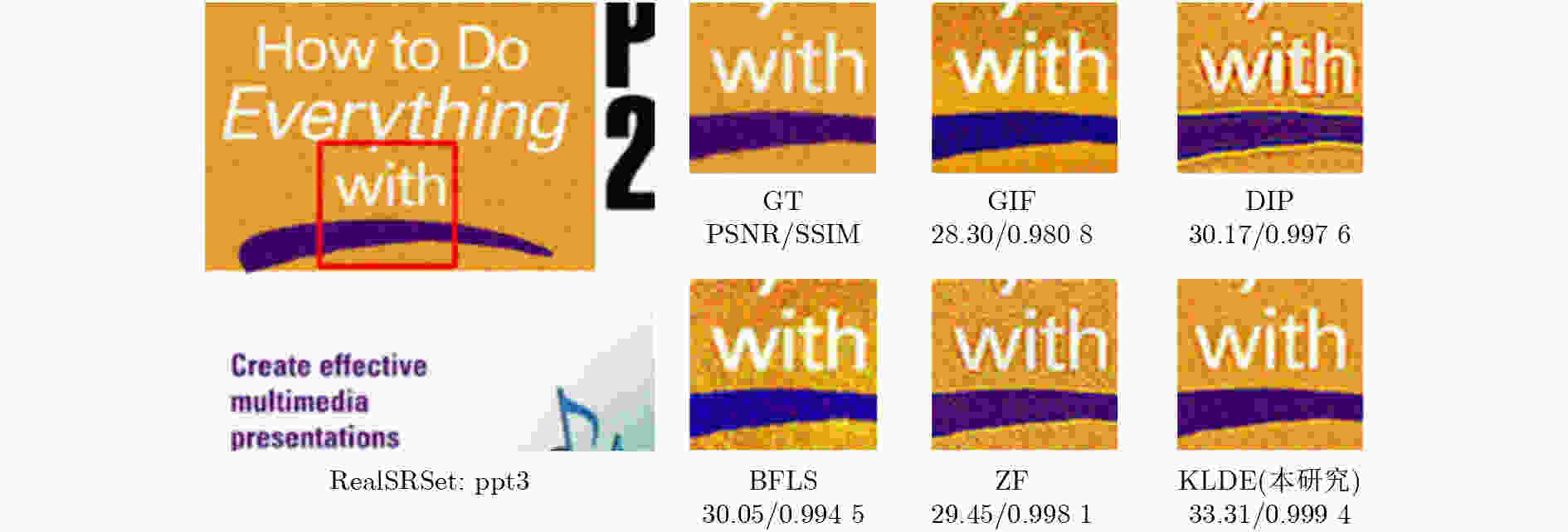
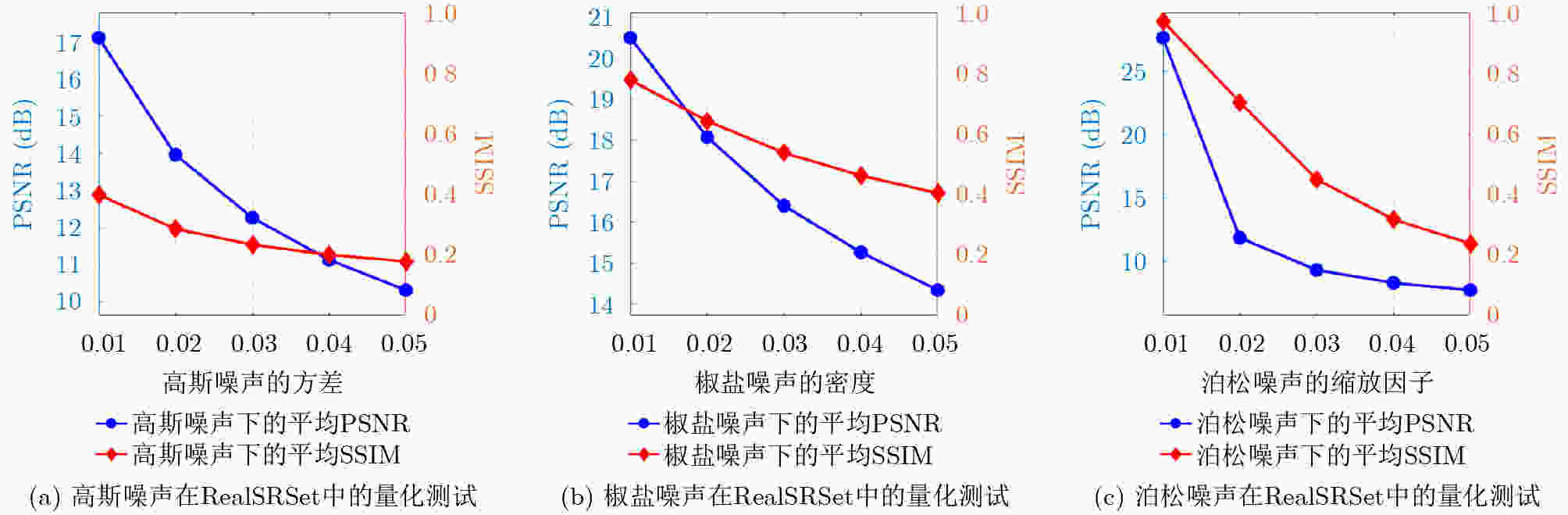
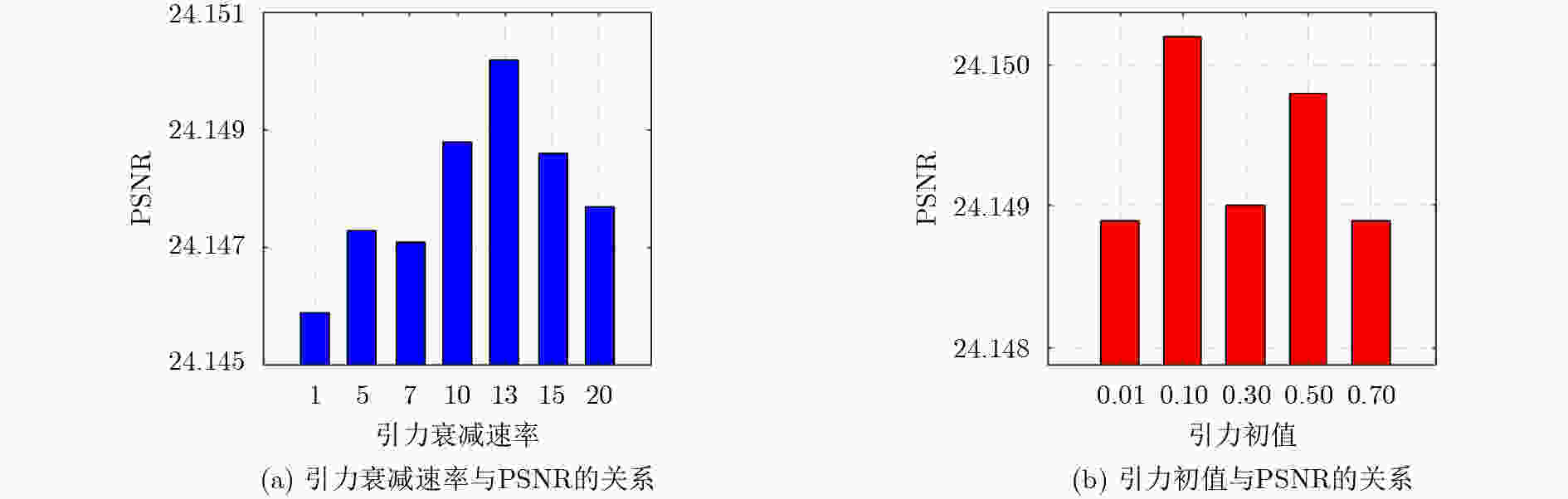
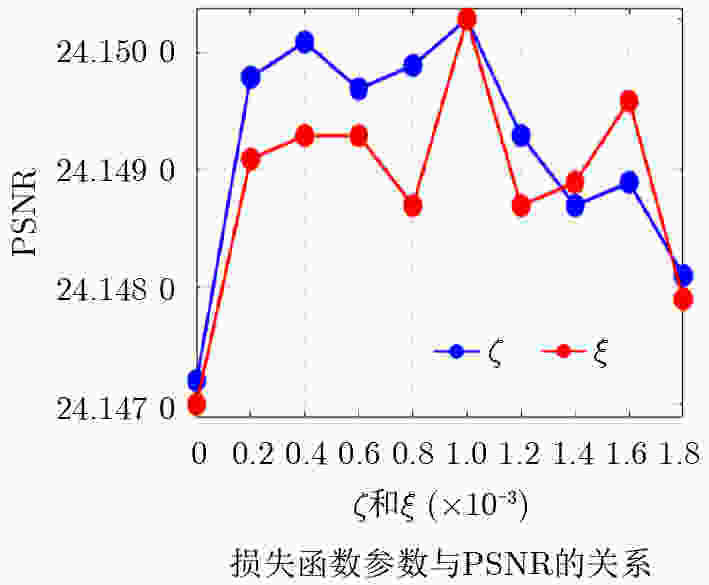
0.041 3 ,彰显了该研究算法的优越性。Abstract:Objective Single-image detail enhancement based on residual learning has received extensive attention in recent years. In these methods, the residual layer is updated by using the similarity between the residual layer and the detail layer, and it is then combined linearly with the original image to enhance image detail. This update process is a greedy algorithm, which tends to trap the system in local optima and limits overall performance. Inspired by Kepler’s laws, the residual update is treated as the dynamic adjustment of planetary positions. By applying Kepler’s laws and computing the global optimal position of the planets, precise updates of the residual layer are achieved. Methods The input image is partitioned into multiple blocks. For each block, its candidate blocks are treated as “planets”, and the best matching block is treated as a “star”. The positions of the “planets” and the “star” are updated by computing the differences between each “planet” and the original image block until the positions converge, which determines the location of the global optimal matching block. Results and Discussions In this study, 16 algorithms are tested on three datasets at two magnification levels ( Table 1 ). The test results show that the proposed algorithm achieves strong performance in both PSNR and SSIM evaluations. During detail enhancement, compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm shows stronger edge preservation capability (Fig. 7 ). However, it is not robust to noise (Fig. 8 –Fig. 10 ), and the performance of the enhanced images continues to decline as noise intensity increases (Fig. 11 ). Both the initial gravitational constant and the gravitational attenuation rate constant present a fluctuating trend, meaning they increase first and then decrease (Fig. 12 ). When the gradient loss and texture loss weights are set to 0.001, the KLDE system achieves its best performance (Fig. 13 ).Conclusions This study proposes a single-image detail enhancement algorithm inspired by Kepler’s laws. By treating the residual update process as the dynamic adjustment of planetary positions, the algorithm applies Kepler’s laws to optimize residual layer updates, reduces the tendency of greedy search to reach local optima, and achieves more precise image detail enhancement. Experimental results show that the algorithm performs better than existing methods in visual effects and quantitative metrics and produces natural enhancement results. The running time remains relatively long because the iterative update of candidate blocks and the calculation of parameters such as gravity form the main computational bottleneck. Future work will focus on optimizing the algorithm structure to reduce unnecessary searches and improve system efficiency. The algorithm does not require training and achieves strong performance, which indicates potential value in high-precision offline image enhancement scenarios. -
表 1 增强因子为2和4时在基准数据集下的指标对比
模型 增强因子 RealSRSet[32] BSDS200[33] T91[34] PSNR(dB) SSIM PSNR(dB) SSIM PSNR(dB) SSIM WLS(TOG 1992)[15] ×2 20.16 0.8235 17.74 0.7439 18.63 0.7693 GIF(TPAMI 2013)[8] 24.45 0.8908 23.89 0.8344 23.82 0.8444 WGIF(TIP 2015)[9] 25.66 0.8867 27.91 0.8816 24.85 0.8517 GGIF(TIP 2015)[10] 27.35 0.9256 27.41 0.8865 26.95 0.8955 ZF(ICCV 2017)[30] 20.65 0.7731 22.56 0.7966 24.09 0.9237 BFLS(TCSVT 2020)[36] 22.51 0.8318 23.06 0.7965 21.63 0.7659 ILS(TOG 2020)[17] 26.16 0.8761 25.09 0.8313 23.48 0.8093 DIP(IJCV 2020)[38] 23.00 0.7970 23.75 0.7657 25.87 0.8232 IPRH(JEI 2020)[31] 26.30 0.9147 24.97 0.8629 28.48 0.9102 TH(TPAMI 2022)[37] 20.70 0.7872 21.32 0.7620 21.43 0.7616 DeepFSPIS(ACM MM 2022)[39] 26.13 0.8640 27.05 0.8640 25.67 0.8260 CSGIS(CGF 2022)[40] 24.50 0.8340 25.32 0.8355 25.18 0.8216 PTF(TOG 2023)[35] 18.43 0.7365 19.12 0.7116 18.76 0.6939 MGPNet(SPL 2024)[41] 20.56 0.6953 23.38 0.8430 21.18 0.7489 QWLS(IJCV 2024)[18] 24.54 0.8894 26.83 0.9099 27.50 0.9153 KLDE(本研究) 31.20 0.9718 28.59 0.9344 32.32 0.9626 WLS(TOG 1992)[15] ×4 - - - - - - GIF(TPAMI 2013)[8] 19.53 0.7638 18.71 0.6637 18.73 0.6862 WGIF(TIP 2015)[9] 20.87 0.7781 22.54 0.7517 19.77 0.7081 GGIF(TIP 2015)[10] 22.09 0.8294 21.90 0.7517 21.53 0.7699 ZF(ICCV 2017)[30] 16.60 0.6038 18.07 0.6218 19.36 0.6081 BFLS(TCSVT 2020)[36] 18.70 0.6982 18.07 0.6174 16.95 0.5898 ILS(TOG 2020)[17] 21.10 0.7491 19.81 0.6636 18.49 0.6432 DIP(IJCV 2020)[38] 19.69 0.6988 21.16 0.6860 22.71 0.7285 IPRH(JEI 2020)[31] 21.47 0.8039 20.14 0.7105 23.30 0.7782 TH(TPAMI 2022)[37] 16.72 0.6354 16.77 0.5786 16.91 0.5822 DeepFSPIS(ACM MM 2022)[39] 20.88 0.7220 21.59 0.7030 20.47 0.6510 CSGIS(CGF 2022)[40] 19.16 0.6651 19.82 0.6523 19.77 0.6344 PTF(TOG 2023)[35] 15.09 0.5777 15.17 0.5244 14.89 0.5080 MGPNet(SPL 2024)[41] 16.86 0.5422 19.47 0.7070 18.02 0.6018 QWLS(IJCV 2024)[18] 20.27 0.7721 21.83 0.7906 22.88 0.7950 KLDE(本研究) 25.87 0.9181 23.34 0.8319 26.84 0.8921 注:黑色加粗字体为每列最优值,加下划线字体为每列次优值 表 2 MOS比较
表 3 数据集RealSRSet上增强因子为4时运行时间比较
模型 平均运行时间(s) PSNR(dB) GIF(TPAMI 1992)[8] 0.04 19.53 WGIF(TIP 2015)[9] 0.08 20.87 GGIF(TIP 2015)[10] 0.08 22.09 ZF(ICCV 2017)[30] 0.04 16.60 BFLS(TCSVT 2020)[36] 0.52 18.70 ILS(TOG 2020)[17] 0.44 21.10 DIP(IJCV 2020)[38] 4.01 19.69 IPRH(JEI 2020)[31] 0.03 21.47 TH(TPAMI 2022)[37] 0.39 16.72 DeepFSPIS(ACM MM 2022)[39] 0.52 20.88 CSGIS(CGF 2022)[40] 0.16 19.16 PTF(TOG 2023)[35] 7.64 15.09 MGPNet(SPL 2024)[41] 0.21 16.86 QWLS(IJCV 2024)[18] 0.39 20.27 KLDE(本研究) 13.29 25.87 注:黑色加粗字体为本研究算法 -
[1] 徐少平, 熊明海, 周常飞. 利用近清图像空间搜索的深度图像先验降噪模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(11): 4229–4235. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240114.XU Shaoping, XIONG Minghai, and ZHOU Changfei. Deep image prior denoising model using relatively clean image space search[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(11): 4229–4235. doi: 10.11999/JEIT240114. [2] 程德强, 袁航, 钱建生, 等. 基于深层特征差异性网络的图像超分辨率算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(3): 1033–1042. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230179.CHENG Deqiang, YUAN Hang, QIAN Jiansheng, et al. Image super-resolution algorithms based on deep feature differentiation network[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(3): 1033–1042. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230179. [3] LI Feng, BAI Huihui, and ZHAO Yao. Detail-preserving image super-resolution via recursively dilated residual network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 358: 285–293. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.05.042. [4] ZHAO Mo, CAO Gang, HUANG Xianglin, et al. Hybrid transformer-CNN for real image denoising[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 1252–1256. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2022.3176486. [5] CAO Gang, TIAN Huawei, YU Lifang, et al. Acceleration of histogram-based contrast enhancement via selective downsampling[J]. IET Image Processing, 2018, 12(3): 447–452. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2017.0789. [6] NARENDRA P M. A separable median filter for image noise smoothing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1981, PAMI-3(1): 20–29. doi: 10.1109/tpami.1981.4767047. [7] TOMASI C and MANDUCHI R. Bilateral filtering for gray and color images[C]. Sixth International Conference on Computer Vision (IEEE Cat. No. 98CH36271), Bombay, India, 1998: 839–846. doi: 10.1109/iccv.1998.710815. [8] HE Kaiming, SUN Jian, and TANG Xiaoou. Guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(6): 1397–1409. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.213. [9] LI Zhengguo, ZHENG Jinghong, ZHU Zijian, et al. Weighted guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(1): 120–129. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2371234. [10] KOU Fei, CHEN Weihai, WEN Changyun, et al. Gradient domain guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 4528–4539. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2468183. [11] CHENG Jun, LI Zhengguo, GU Zaiwang, et al. Structure-preserving guided retinal image filtering and its application for optic disk analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(11): 2536–2546. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2838550. [12] SUN Zhonggui, HAN Bo, LI Jie, et al. Weighted guided image filtering with steering kernel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 500–508. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2928631. [13] TAN Ailing, LIAO Hongping, ZHANG Bozhi, et al. Infrared image enhancement algorithm based on detail enhancement guided image filtering[J]. The Visual Computer, 2023, 39(12): 6491–6502. doi: 10.1007/s00371-022-02741-6. [14] LI Jun, HAN Yuxuan, GAO Yin, et al. An enhance relative total variation with BF model for edge-preserving image smoothing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(10): 5420–5432. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3255208. [15] RUDIN L I, OSHER S, and FATEMI E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1992, 60(1/4): 259–268. doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F. [16] XU Li, YAN Qiong, XIA Yang, et al. Structure extraction from texture via relative total variation[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2012, 31(6): 139. doi: 10.1145/2366145.2366158. [17] LIU Wei, ZHANG Pingping, HUANG Xiaolin, et al. Real-time image smoothing via iterative least squares[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2020, 39(3): 28. doi: 10.1145/3388887. [18] LIU Wei, ZHANG Pingping, QIN Hongxing, et al. Fast global image smoothing via quasi weighted least squares[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2024, 132(12): 6039–6068. doi: 10.1007/s11263-024-02105-8. [19] HE Lei, XIE Yongfang, XIE Shiwen, et al. Iterative self-guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(8): 7537–7549. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3374758. [20] LI Siyuan, LIU Yuan, ZENG Jiafu, et al. Image smoothing method based on global gradient sparsity and local relative gradient constraint optimization[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 15152. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65886-5. [21] SASAKI T, BANDOH Y, and KITAHARA M. Sparse regularization based on reverse ordered weighted L1-norm and its application to edge-preserving smoothing[C]. ICASSP 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Korea, 2024: 9531–9535. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10448119. [22] QI Huiqing, LI Fang, CHEN Peng, et al. Edge-preserving image restoration based on a weighted anisotropic diffusion model[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2024, 184: 80–88. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2024.06.007. [23] XU Li, REN J S J, YAN Qiong, et al. Deep edge-aware filters[C]. The 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning - Volume 37, Lille, France, 2015: 1669–1678. [24] LIU Sifei, PAN Jinshan, and YANG M H. Learning recursive filters for low-level vision via a hybrid neural network[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision – ECCV 2016, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 560–576. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46493-0_34. [25] FAN Qingnan, YANG Jiaolong, HUA Gang, et al. A generic deep architecture for single image reflection removal and image smoothing[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 3258–3267. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2017.351. [26] YANG Yang, TANG Ling, YAN Tao, et al. Parameterized L0 image smoothing with unsupervised learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2024, 8(2): 1938–1951. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3359060. [27] ZHANG Feng, TIAN Ming, LI Zhiqiang, et al. Lookup table meets local laplacian filter: Pyramid reconstruction network for tone mapping[C]. Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, USA, 2023: 2510. [28] QI Huiqing, TAN Shengli, and LUO Xiaoliu. Self-supervised dual generative networks for edge-preserving image smoothing[C]. ICASSP 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Korea, 2024: 7215–7219. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP48485.2024.10448288. [29] KIM D, PARK J, JUNG J, et al. Lens distortion correction and enhancement based on local self-similarity for high-quality consumer imaging systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2014, 60(1): 18–22. doi: 10.1109/tce.2014.6780920. [30] TAO Xin, ZHOU Chao, SHEN Xiaoyong, et al. Zero-order reverse filtering[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 222–230. doi: 10.1109/iccv.2017.33. [31] JIANG He, ASAD M, HUANG Xiaolin, et al. Learning in-place residual homogeneity for single image detail enhancement[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2020, 29(4): 043016. doi: 10.1117/1.jei.29.4.043016. [32] ZHANG Kai, LIANG Jingyun, VAN GOOL L, et al. Designing a practical degradation model for deep blind image super-resolution[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, Canada, 2021: 4771–4780. doi: 10.1109/iccv48922.2021.00475. [33] ARBELÁEZ P, MAIRE M, FOWLKES C, et al. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(5): 898–916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.161. [34] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision -- ECCV 2014, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 184–199. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_13. [35] ZHANG Qing, JIANG Hao, NIE Yongwei, et al. Pyramid texture filtering[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2023, 42(4): 110. doi: 10.1145/3592120. [36] LIU Wei, ZHANG Pingping, CHEN Xiaogang, et al. Embedding bilateral filter in least squares for efficient edge-preserving image smoothing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(1): 23–35. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2890202. [37] LIU Wei, ZHANG Pingping, LEI Yinjie, et al. A generalized framework for edge-preserving and structure-preserving image smoothing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(10): 6631–6648. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3097891. [38] DMITRY U, VEDALDI A, and VICTOR L. Deep image prior[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(7): 1867–1888. doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01303-4. [39] LI Mingjia, FU Yuanbin, LI Xinhui, et al. Deep flexible structure preserving image smoothing[C]. The 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 2022: 1875–1883. doi: 10.1145/3503161.3547857. [40] WANG Jie, WANG Yongzhen, FENG Yidan, et al. Contrastive semantic-guided image smoothing network[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2022, 41(7): 335–346. doi: 10.1111/cgf.14681. [41] HE Xuyi, QUAN Yuhui, XU Yong, et al. Image smoothing via multiscale global perception[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024, 31: 411–415. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2024.3354549. -





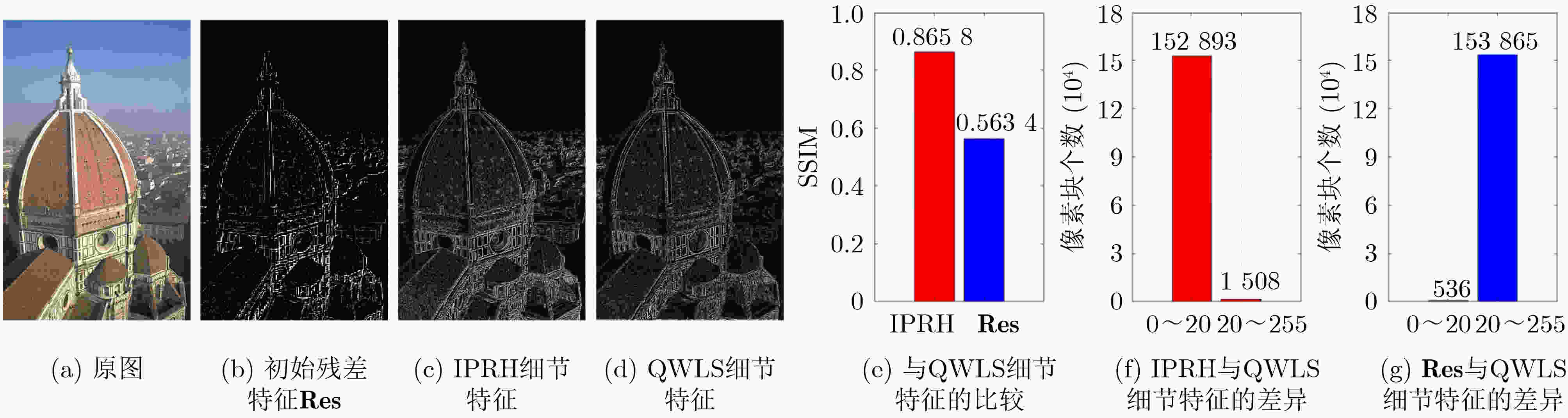
 下载:
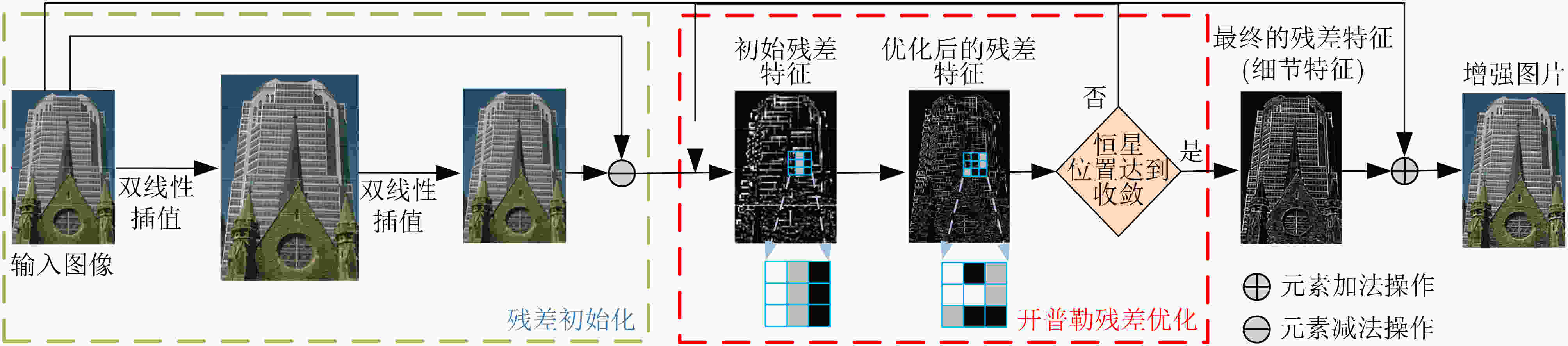
下载:
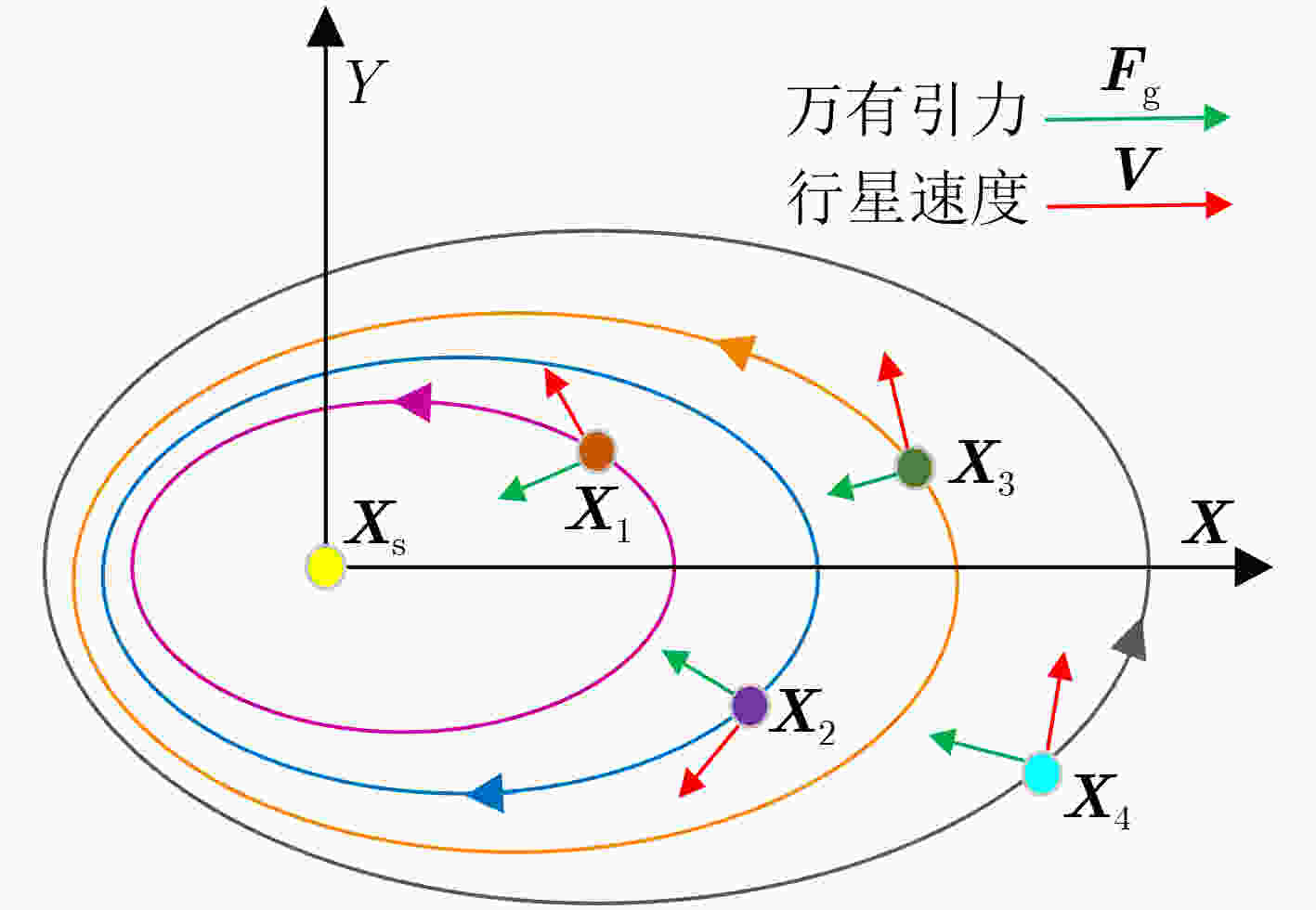






 下载:
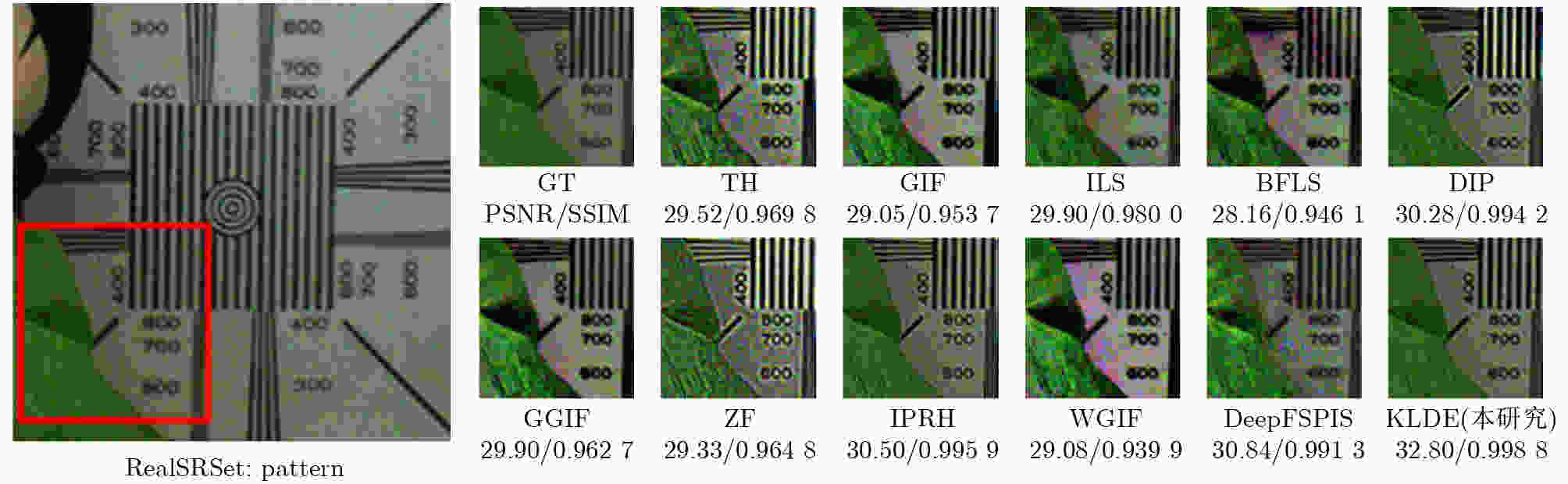
下载:
