Intelligent Analysis Technologies for Encrypted Traffic: Current Status, Advances, and Challenges
-
摘要: 加密流量分析是保障网络安全的关键技术之一,该文系统探讨了其核心应用与主流技术。特征工程基于统计和行为特征刻画流量模式,深度学习则采用卷积神经网络、循环神经网络与图神经网络等架构自动提取深层特征,例如,改进的多尺度卷积神经网络在ISCXVPN2016数据集上的分类准确率达到86.77%。Transformer凭借其强大的特征捕捉能力,进一步推动了该领域发展,如融合掩码自动编码器的流量Transformer方法在相同数据集上的分类准确率达98.07%。此外,联邦学习在保护隐私的同时实现对流量的高精度分类,已有案例验证,其模型精度与集中式学习相比,差距可缩小至0.8%。多模态特征融合技术通过综合流量异构特征提升模型效能,成功将多分类任务的准确率与F1分数分别提升至93.75%和91.95%。生成式模型则有效解决数据稀缺问题,如基于扩散模型方法所生成的流量在包大小和间隔等关键特征上,与真实流量的相似度相较基线模型提升达到43.4%和39.02%。文章最后总结了当前挑战,并展望了未来方向。
-
关键词:
- 加密流量 /
- 特征工程 /
- 深度学习 /
- Transformer /
- 联邦学习
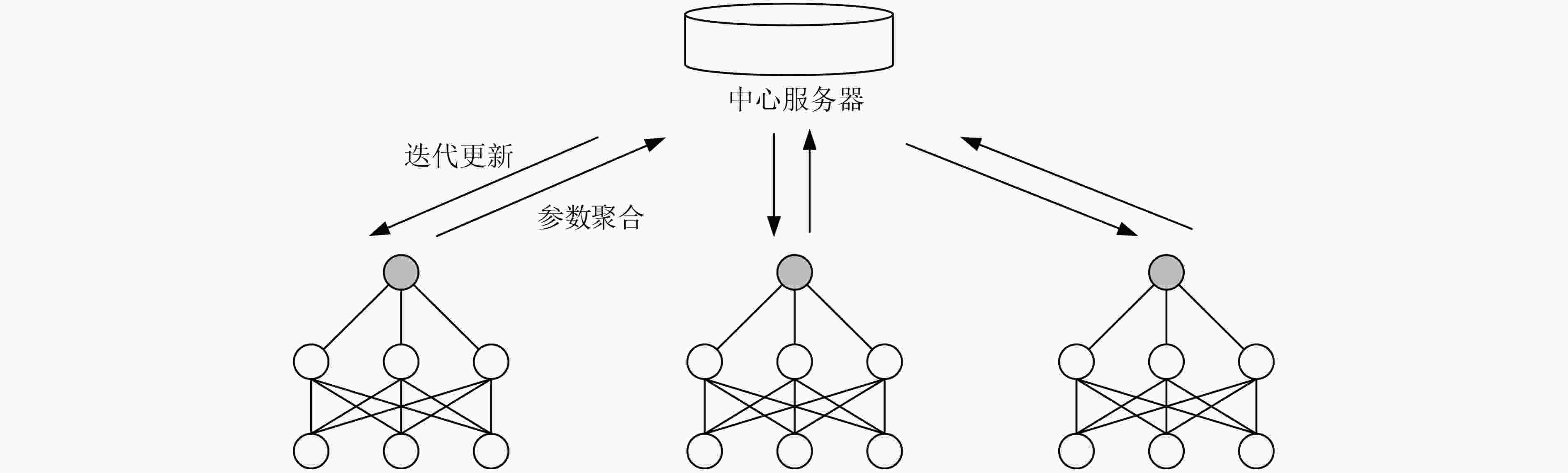
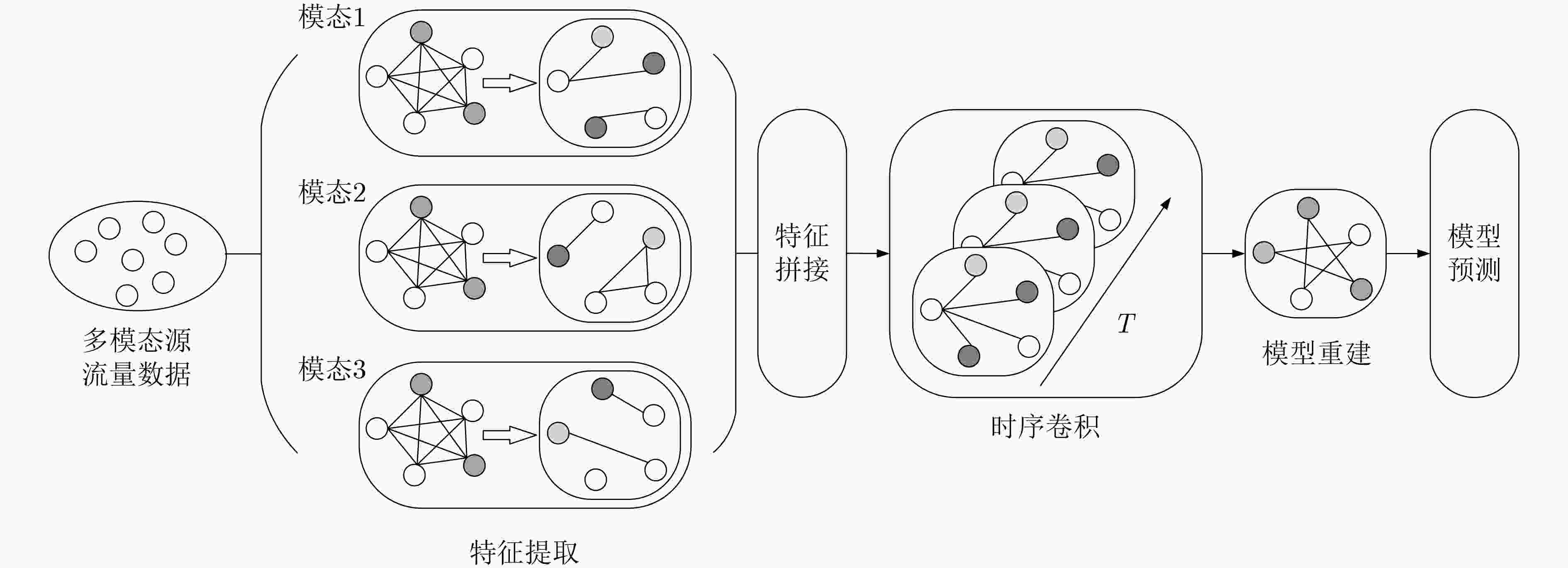
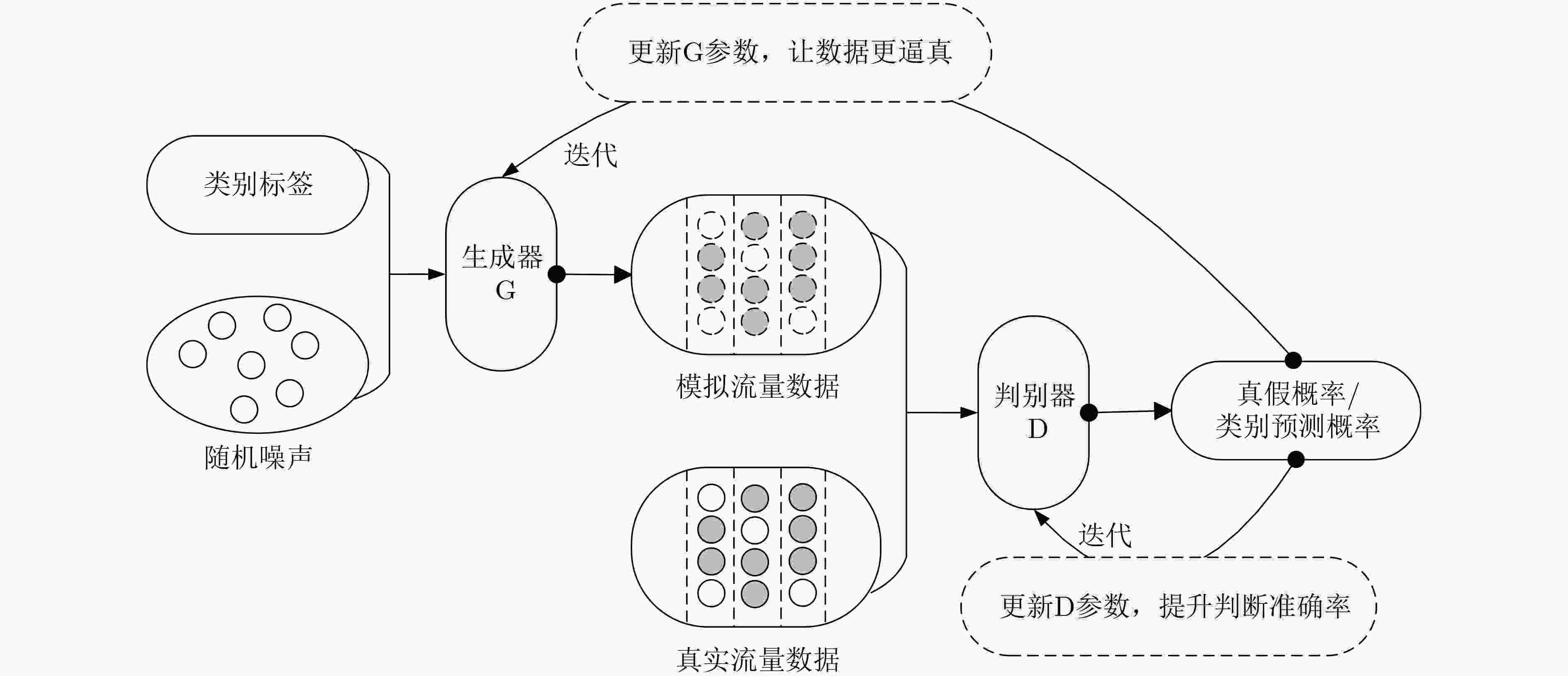
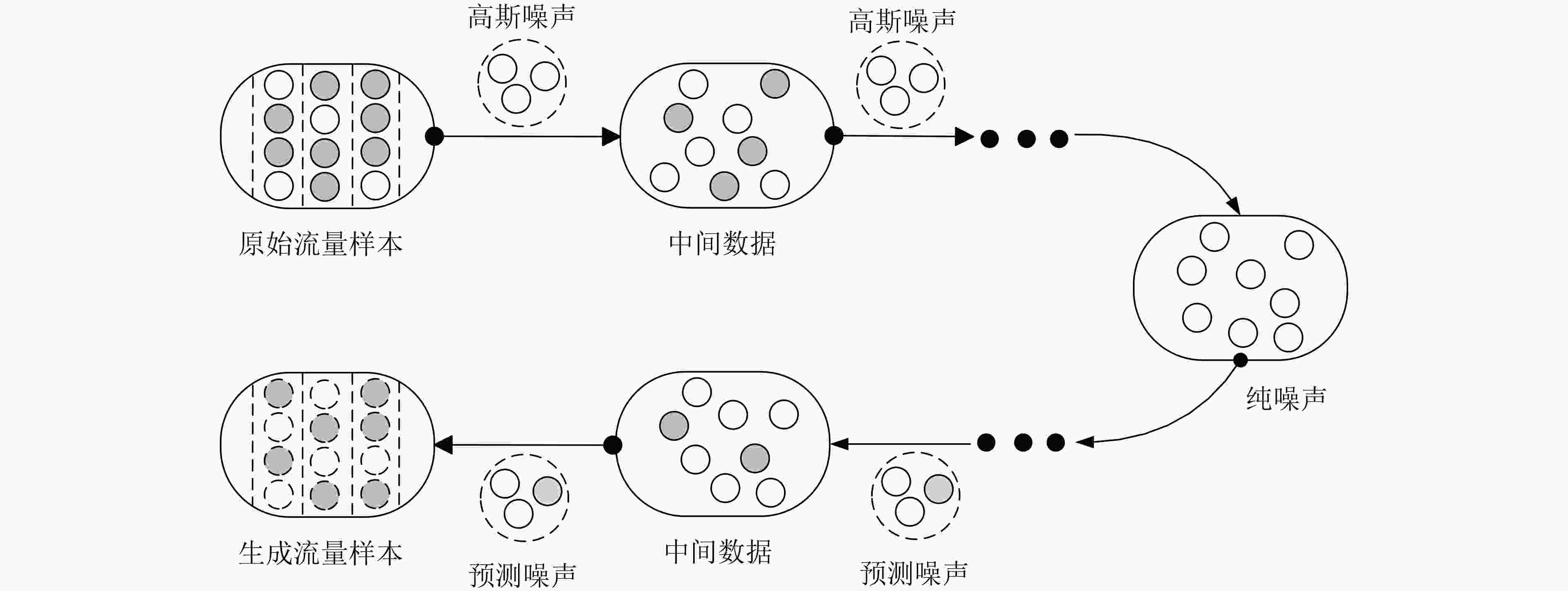
Abstract:Significance Encrypted traffic enables secure and reliable data transmission, yet introduces challenges to network security. These include the covert spread of malicious attacks, reduced effectiveness of security tools, and increased network resource overhead. Encrypted traffic analysis technologies are therefore essential. Traditional port filtering and deep packet inspection are inadequate in increasingly complex network environments. Intelligent encrypted traffic analysis integrates feature engineering, deep learning, Transformer architectures, federated learning, multimodal feature fusion, and generative models. These approaches address network security management from multiple perspectives. They support efficient detection of hidden attacks, improve network resource allocation, balance system security and privacy protection, enhance security defenses, and strengthen user experience. Progress Intelligent encrypted traffic analysis technologies provide new methods for network security. (1) Feature engineering: (a) Statistical features: Basic statistical features of encrypted traffic, such as packet size, count, arrival time, and rate, are selected through feature selection techniques so that the processed data reflect internal traffic characteristics. (b) Behavioral features: Observation and analysis of network traffic identify behavioral patterns such as access frequency and protocol usage habits. (2) Deep learning methods: (a) Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): Convolution and pooling layers automatically extract local features from encrypted traffic and capture key information. An improved multi-scale CNN achieves 86.77% accuracy on the ISCXVPN2016 dataset. (b) Recurrent Neural Network (RNN): RNNs process time-series data through memory units and capture long-term dependencies, enabling analysis of temporal features such as connection duration and traffic trends. (c) Graph Neural Network (GNN): GNNs are suited to relational data and model the graph structures of encrypted traffic to identify potential node relationships. (d) Transformer architectures: With parallel processing and support for long sequences, attention mechanisms capture long-distance dependencies. A traffic Transformer method using masked autoencoders reaches 98.07% accuracy on the ISCXVPN2016 dataset. (3) Other advanced methods: (a) Federated learning: Participants train a shared global model by exchanging sub-model parameters rather than raw traffic data, which protects privacy and improves performance. Reported results show performance gaps relative to centralized learning reduced to 0.8%. (b) Multimodal feature fusion: Features extracted from multiple traffic modalities are fused into a unified representation to build a comprehensive analysis architecture. This integration of heterogeneous features improves model performance, raising accuracy and F1-score for multitask classification to 93.75% and 91.95%. (c) Generative model-driven methods: Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) and diffusion models learn real traffic distributions to generate synthetic samples, which mitigate data scarcity and class imbalance. Diffusion-based traffic generation increases similarity to real traffic in packet size and inter-arrival time by up to 43.4% and 39.02% compared with baseline models. Conclusions This paper explains the necessity of intelligent encrypted traffic analysis technologies and summarizes key methods and related research. Remaining challenges include: (1) Network complexity: Modern networks are heterogeneous and dynamic, using diverse encryption algorithms and producing inconsistent traffic structures that traditional rules do not adapt to. Network adjustments and behavior changes also shift traffic features over time, which complicates analysis. (2) Insufficient model robustness: Encrypted traffic features depend strongly on environment. Accuracy decreases after model migration, and models remain sensitive to non-ideal inputs and adversarial examples, which affect model decisions. (3) Privacy protection and compliance: Encrypted traffic carries sensitive information, and conventional analysis risks exposing original features. Even metadata can be associated with identities, which complicates compliance with anonymization requirements. Prospects Future work may focus on: (1) Dynamic adaptability: Full-link adaptive mechanisms that integrate multi-dimensional information may support dynamic context awareness. Incremental learning frameworks may help models respond in real time to feature drift. Genetic algorithms and reinforcement learning may also support dynamic detection strategies. (2) Anti-attack capability: A comprehensive protection system that includes adversarial sample detection, model defense, and attack traceability may be established by designing monitoring modules and applying adversarial training. (3) Privacy protection and compliance: Differential privacy can be applied by adding controlled noise during feature extraction or to model parameters. Homomorphic encryption may support analytical tasks directly on ciphertext. (4) Synergy between reverse engineering and Explainable AI (XAI): Reverse engineering may deepen protocol analysis and enhance the quality of inputs for XAI, and XAI may improve model transparency. This supports closed-loop optimization between protocol analysis and model interpretation. -
Key words:
- Encrypted traffic /
- Feature engineering /
- Deep learning /
- Transformer /
- Federated learning
-
表 1 各种分析方法对比总结
方法 核心关键技术 适用性与创新点 挑战与不足 基于统计
特征提取加密流量的统计特征(如数据包大小、时间间隔、流量速率等)进行分析 简单高效,适用于实时分析;
能够捕捉流量的全局统计特性依赖人工特征,难以适应复杂变化;
对新型攻击适应性不足;特征提取过程
易丢失时序与上下文信息基于行为
特征对用户或应用的行为模式(如访问频率、通信模式、流量突发性等)进行分析 能够检测未知攻击,适用于APT检测 需大量历史数据建立基线;对变化敏感,可能导致误报;难以区分正常行为
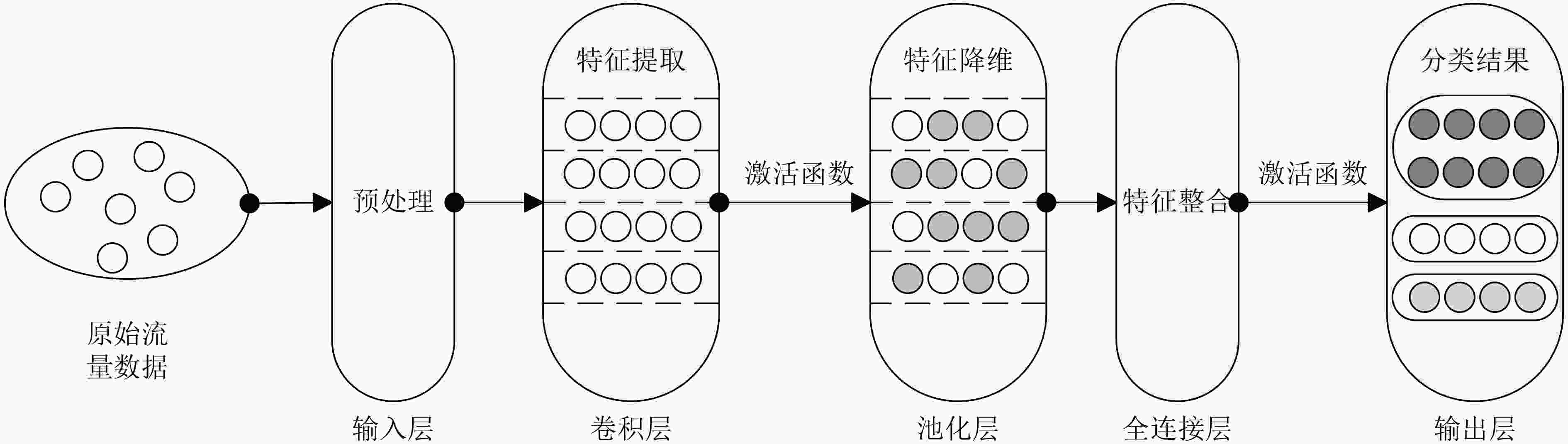
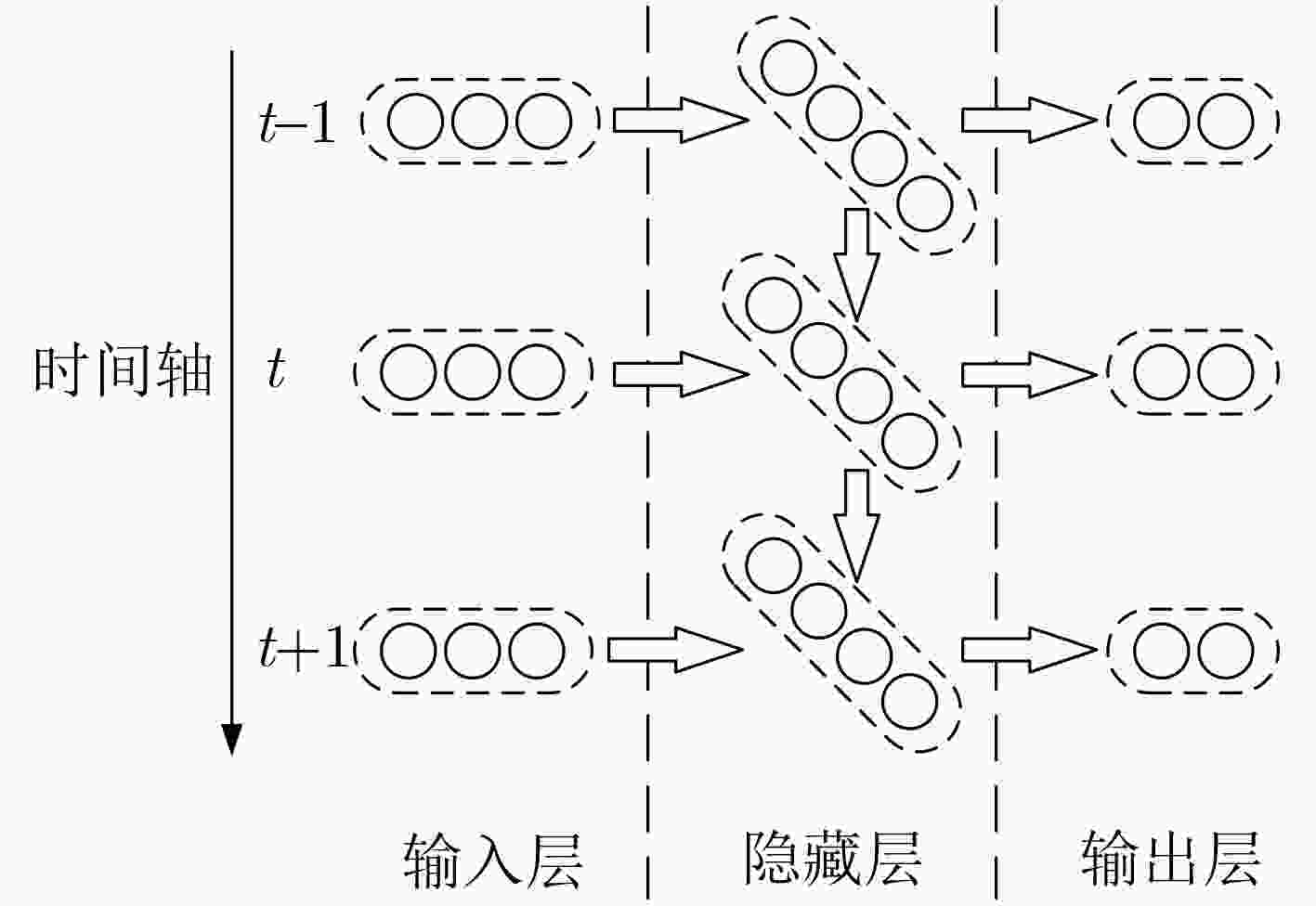
与伪装的恶意流量基于CNN 利用CNN从加密流量的原始数据(如字节序列或图像化表示)中自动提取局部特征 能够自动学习特征,减少对人工设计的依赖;在流量分类和异常检测中表现优异 对时序特征的捕捉能力有限;需要大量标注数据进行训练;模型的可解释性较差 基于RNN 利用RNN及变体(如LSTM、GRU)捕捉流量时序特征,适用于分析时间依赖关系 能够有效处理流量的时序信息,
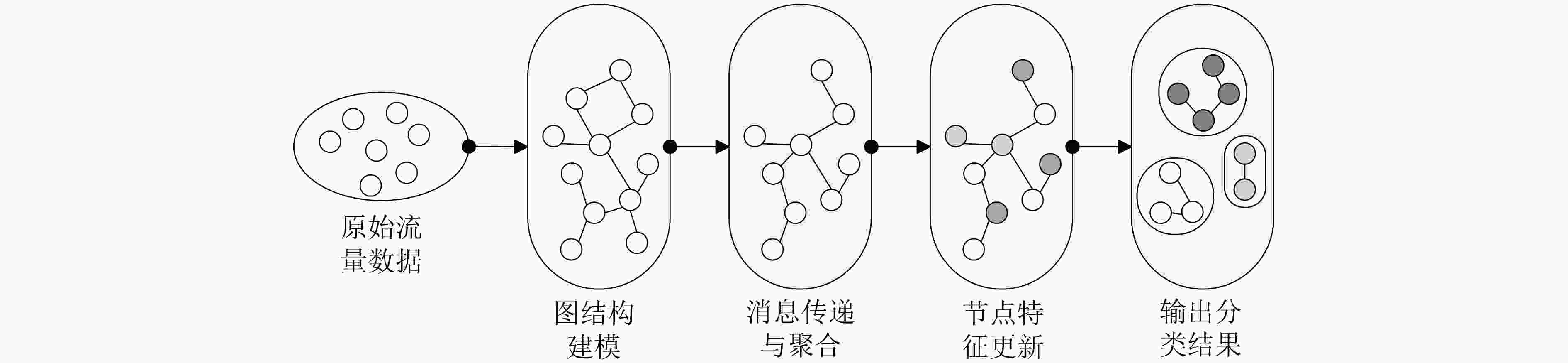
适用于检测长时间跨度的攻击行为训练过程计算复杂度高,难以处理大规模数据;对长距离依赖的捕捉能力有限;容易过拟合,泛化性较差 基于GNN 利用GNN对网络流量中的拓扑结构进行
建模,捕捉节点(如IP地址、设备)
之间的关系能够分析网络流量的全局结构特征,
适用于检测分布式攻击对大规模网络的计算开销较大;需要高质量的图结构数据;模型训练和推理
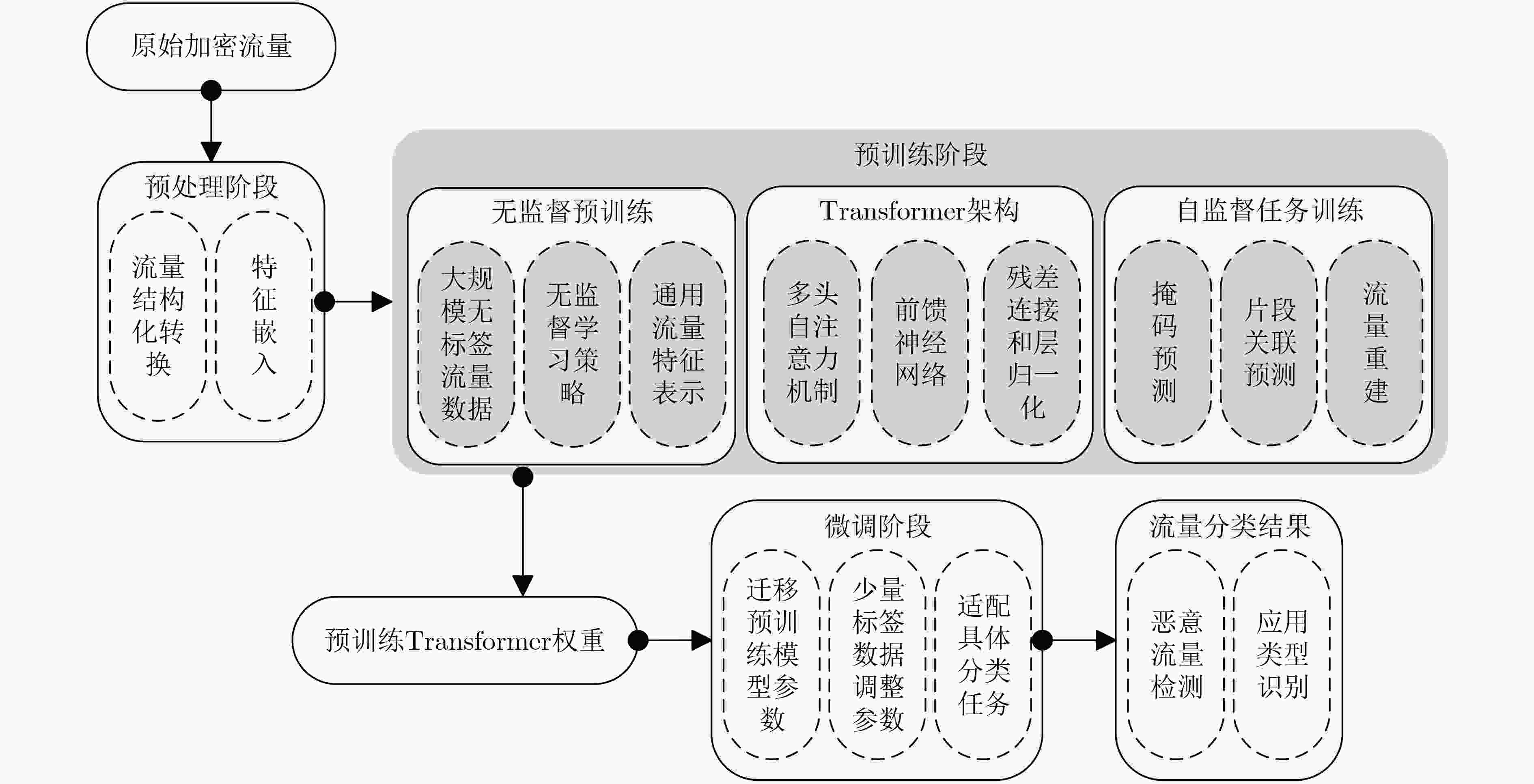
效率较低基于Transformer 利用Transformer的自注意力机制捕捉加密流量的全局上下文依赖关系 能够处理长序列数据,适用于复杂
加密流量的分类和异常检测计算复杂度高,对硬件资源要求较高;需大量标注数据训练;对局部特征捕捉能力有限;自注意力机制对短序列流量存在冗余计算问题 联邦学习
范式通过分布式设备在本地训练模型,
并聚合模型参数以实现全局优化,
同时保护数据隐私支持隐私保护的分布式学习,
适用于多节点协同分析通信开销较大,影响效率;对非独立同分布数据的适应性较差;需解决模型聚合中的安全性和一致性问题 多模态特征
融合整合网络流量、DNS日志、用户行为
等多源数据,通过多模态融合技术
提升分析的全面性能够从多维度捕捉加密流量的特征,
提高分析的准确性和鲁棒性数据异构性导致特征对齐和融合难度较大;对计算资源和存储资源的需求较高 基于GAN 利用生成器生成模拟加密流量,判别器区分真假流量,通过对抗训练学习流量
分布与特征解决数据标注难、类不平衡问题;适用于异常检测、数据增强与未知模式探索 训练不稳定,易模式崩溃;对超参数敏感,需大量计算资源;生成流量
细粒度特征与真实流量有差异基于DM 通过正向扩散加噪、反向扩散去噪,生成与真实数据分布一致的样本 对罕见或新型异常检测效果好;
有融合多模态加密流量数据的潜力迭代多、计算成本高、耗时久;
对超参数敏感,难以快速收敛 -
[1] XU Junfeng, LIN Weiguo, and FAN Wenqing. APT encrypted traffic detection method based on two-parties and multi-session for IoT[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13234, 2023. [2] YI Tao, CHEN Xingshu, LI Qindong, et al. An anomaly behavior characterization method of network traffic based on Spatial Pyramid Pool (SPP)[J]. Computers & Security, 2024, 141: 103809. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2024.103809. [3] ALMUHAMMADI S, ALNAJIM A, and AYUB M. QUIC network traffic classification using ensemble machine learning techniques[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(8): 4725. doi: 10.3390/app13084725. [4] LUXEMBURK J, HYNEK K, ČEJKA T, et al. CESNET-QUIC22: A large one-month QUIC network traffic dataset from backbone lines[J]. Data in Brief, 2023, 46: 108888. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2023.108888. [5] ZUO Ming, GUO Changyong, XU Haiyan, et al. METC: A hybrid deep learning framework for cross-network encrypted DNS over HTTPS traffic detection and tunnel identification[J]. Information Fusion, 2025, 121: 103125. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2025.103125. [6] JUNG W K and KWAK B I. MTL-DoHTA: Multi-task learning-based DNS over HTTPS traffic analysis for enhanced network security[J]. Sensors, 2025, 25(4): 993. doi: 10.3390/s25040993. [7] ALZIGHAIBI A R. Detection of DoH traffic tunnels using deep learning for encrypted traffic classification[J]. Computers, 2023, 12(3): 47. doi: 10.3390/computers12030047. [8] AFZAL A, HUSSAIN M, SALEEM S, et al. Encrypted network traffic analysis of secure instant messaging application: A case study of signal messenger app[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(17): 7789. doi: 10.3390/app11177789. [9] ALSERHANI F. Analysis of encrypted network traffic for enhancing cyber-security in dynamic environments[J]. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 38(1): 2381882. doi: 10.1080/08839514.2024.2381882. [10] DONG Wenqi, YU Jing, LIN Xinjie, et al. Deep learning and pre-training technology for encrypted traffic classification: A comprehensive review[J]. Neurocomputing, 2025, 617: 128444. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.128444. [11] MILLER K M, LUKIC K, and SKIERA B. The impact of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) on online tracking[J]. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 2025: S0167811625000229. doi: 10.1016/j.ijresmar.2025.03.002. [12] OCELÍK V, KOLK A, and IRION K. Shifting battlegrounds: Corporate political activity in the general data protection regulation[J]. Academy of Management Proceedings, 2023, 2023(1): 208bp. doi: 10.5465/AMPROC.2023.208bp. [13] SCHÄGE S. TOPAS2-pass key exchange with full perfect forward secrecy and optimal communication complexity[J]. Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 2024, 92(10): 3085–3124. doi: 10.1007/s10623-024-01429-3. [14] LEE C D and CHEN T H. New secure and practical E-mail protocol with perfect forward secrecy[J]. Symmetry, 2021, 13(7): 1144. doi: 10.3390/sym13071144. [15] FAN Qing, CHEN Jianhua, SHOJAFAR M, et al. SAKE*: A symmetric authenticated key exchange protocol with perfect forward secrecy for industrial internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(9): 6424–6434. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3145584. [16] CHEN Fangjie, BAI Jingpeng, and GAO Weihan. Research on encrypted traffic detection based on key features[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 1786–1793. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3347806. [17] SHEKHAWAT A S, DI TROIA F, and STAMP M. Feature analysis of encrypted malicious traffic[J]. Expert Systems with Applications: An International Journal, 2019, 125(C): 130–141. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.01.064. [18] ZHENG Xianchun and LI Hui. Identification of malicious encrypted traffic through feature fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 80072–80080. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3279120. [19] PATHMAPERUMA M H, RAHULAMATHAVAN Y, DOGAN S, et al. Deep learning for encrypted traffic classification and unknown data detection[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(19): 7643. doi: 10.3390/s22197643. [20] WU Hao, ZHANG Xi, and YANG Jufeng. Deep learning-based encrypted network traffic classification and resource allocation in SDN[J]. Journal of Web Engineering, 2021, 20(8): 2319–2334. doi: 10.13052/jwe1540-9589.2085. [21] CHEN Xuyang, HAN Lu, ZHAN Dechuan, et al. MIETT: Multi-instance encrypted traffic transformer for encrypted traffic classification[C]. The 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, USA, 2025: 15922–15929. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v39i15.33748. [22] ZHAN Mingming, YANG Jin, JIA Dongqing, et al. EAPT: An encrypted traffic classification model via adversarial pre-trained transformers[J]. Computer Networks, 2025, 257: 110973. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2024.110973. [23] WANG Zixuan, MIAO Cheng, XU Yuhua, et al. Trusted encrypted traffic intrusion detection method based on federated learning and autoencoder[J]. China Communications, 2024, 21(8): 211–235. doi: 10.23919/JCC.ja.2022-0392. [24] LIU Wei, CUI Wentao, SHE Wei, et al. Encrypted network traffic detection based on Blockchain and federated learning[C]. 2024 4th International Conference on Blockchain Technology and Information Security (ICBCTIS), Wuhan, China, 2024: 139–144. doi: 10.1109/ICBCTIS64495.2024.00030. [25] ZENG Yong, WANG Zhe, GUO Xiaoya, et al. Social networks based robust federated learning for encrypted traffic classification[C]. ICC 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Communications, Rome, Italy, 2023: 4937–4942. doi: 10.1109/ICC45041.2023.10279778. [26] WANG Xiangbin, YUAN Qingjun, WANG Yongjuan, et al. Combine intra- and inter-flow: A multimodal encrypted traffic classification model driven by diverse features[J]. Computer Networks, 2024, 245: 110403. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2024.110403. [27] LIU Ming, YANG Qichao, WANG Wenqing, et al. Semi-supervised encrypted malicious traffic detection based on multimodal traffic characteristics[J]. Sensors, 2024, 24(20): 6507. doi: 10.3390/s24206507. [28] DAI Jianbang, XU Xiaolong, and XIAO Fu. GLADS: A global-local attention data selection model for multimodal multitask encrypted traffic classification of IoT[J]. Computer Networks, 2023, 225: 109652. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2023.109652. [29] MENG Xuying, LIN Chungang, WANG Yequan, et al. NetGPT: Generative pretrained transformer for network traffic[EB/OL]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2304.09513, 2023. [30] ACETO G, CIUONZO D, MONTIERI A, et al. MIMETIC: Mobile encrypted traffic classification using multimodal deep learning[J]. Computer Networks, 2019, 165: 106944. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2019.106944. [31] WANG Tongze, XIE Xiaohui, WANG Wenduo, et al. NetMamba: Efficient network traffic classification via pre-training unidirectional mamba[C]. 2024 IEEE 32nd International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP), Charleroi, Belgium, 2024: 1-11. doi: 10.1109/ICNP61940.2024.10858569. [32] 付钰, 刘涛涛, 王坤, 等. 基于机器学习的加密流量分类研究综述[J]. 通信学报, 2025, 46(1): 167–191. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2025006.FU Yu, LIU Taotao, WANG Kun, et al. Survey of research on encrypted traffic classification based on machine learning[J]. Journal on Communications, 2025, 46(1): 167–191. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2025006. [33] VU L, VAN TRA D, and NGUYEN Q U. Learning from imbalanced data for encrypted traffic identification problem[C]. The Seventh Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2016: 147–152. doi: 10.1145/3011077.3011132. [34] VAN EDE T, BORTOLAMEOTTI R, CONTINELLA A, et al. FlowPrint: Semi-supervised mobile-app fingerprinting on encrypted network traffic[C]. 2020 Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2020. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2020.24412. [35] REZAEI S and LIU Xin. Deep learning for encrypted traffic classification: An overview[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(5): 76–81. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2019.1800819. [36] PARK J T, SHIN C Y, BAEK U J, et al. User behavior detection using multi-modal signatures of encrypted network traffic[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 97353–97372. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3311889. [37] SUBAHI A and THEODORAKOPOULOS G. Detecting IoT user behavior and sensitive information in encrypted IoT-app traffic[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(21): 4777. doi: 10.3390/s19214777. [38] WANG Jibao, CAO Zigang, KANG Cuicui, et al. User behavior classification in encrypted cloud camera traffic[C]. 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/GLOBECOM38437.2019.9013558. [39] CONTI M, MANCINI L V, SPOLAOR R, et al. Analyzing android encrypted network traffic to identify user actions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(1): 114–125. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2478741. [40] ZHAI Liang, ZHENG Qiuhua, ZHANG Xu, et al. Identification of private ICS protocols based on raw traffic[J]. Symmetry, 2021, 13(9): 1743. doi: 10.3390/sym13091743. [41] MA Ruolong and QIN Sujuan. Identification of unknown protocol traffic based on deep learning[C]. 2017 3rd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2017: 1195–1198. doi: 10.1109/CompComm.2017.8322732. [42] 顾伟, 行鸿彦, 侯天浩. 基于网络流量时空特征和自适应加权系数的异常流量检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(6): 2647–2654. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230825.GU Wei, XING Hongyan, and HOU Tianhao. Abnormal traffic detection method based on traffic spatial-temporal features and adaptive weighting coefficients[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(6): 2647–2654. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230825. [43] IKRAM S T and CHERUKURI A K. Improving accuracy of intrusion detection model using PCA and optimized SVM[J]. CIT. Journal of Computing and Information Technology, 2016, 24(2): 133–148. doi: 10.20532/cit.2016.1002701. [44] KOCH R, GOLLING M, and RODOSEK G D. Behavior-based intrusion detection in encrypted environments[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(7): 124–131. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6852093. [45] FU Chuanpu, LI Qi, and XU Ke. Detecting unknown encrypted malicious traffic in real time via flow interaction graph analysis[C]. 2023 Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2023. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2023.23080. [46] FU Chuanpu, LI Qi, SHEN Meng, et al. Frequency domain feature based robust malicious traffic detection[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2023, 31(1): 452–467. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2022.3195871. [47] MIAO Gongxun, WU Guohua, ZHANG Zhen, et al. Boosting encrypted traffic classification using feature-enhanced recurrent neural network with angle constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2025, 11(4): 1760–1771. doi: 10.1109/TBDATA.2024.3484674. [48] OEUNG P and SHEN Fuke. Imbalanced internet traffic classification using ensemble framework[C]. 2019 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2019: 37–42. doi: 10.1109/ICOIN.2019.8717977. [49] QING Yuqi, YIN Qilei, DENG Xinhao, et al. Low-quality training data only? A robust framework for detecting encrypted malicious network traffic[C]. 2024 Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, San Diego, USA, 2024. doi: 10.14722/ndss.2024.23081. [50] HE Hongye, YANG Zhiguo, and CHEN Xiangning. PERT: Payload encoding representation from transformer for encrypted traffic classification[C]. 2020 ITU Kaleidoscope: Industry-Driven Digital Transformation (ITU K), Ha Noi, Vietnam, 2020: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/ITUK50268.2020.9303204. [51] FU Chuanpu, LI Qi, XU Ke, et al. Point cloud analysis for ML-based malicious traffic detection: Reducing majorities of false positive alarms[C]. The 2023 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2023: 1005–1019. doi: 10.1145/3576915.3616631. [52] ZHOU Guangmeng, GUO Xiongwen, LIU Zhuotao, et al. TrafficFormer: An efficient pre-trained model for traffic data[C]. 2025 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, USA, 2025: 1844–1860. doi: 10.1109/SP61157.2025.00102. [53] CUI Susu, HAN Xueying, DONG Cong, et al. MVDet: Encrypted malware traffic detection via multi-view analysis[J]. Journal of Computer Security, 2024, 32(6): 533–555. doi: 10.3233/JCS-230024. [54] OH C, HA J, and ROH H. A survey on TLS-encrypted malware network traffic analysis applicable to security operations centers[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 12(1): 155. doi: 10.3390/app12010155. [55] CUI Susu, DONG Cong, SHEN Meng, et al. CBSeq: A channel-level behavior sequence for encrypted malware traffic detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18: 5011–5025. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2023.3300521. [56] SHAPIRA T and SHAVITT Y. FlowPic: A generic representation for encrypted traffic classification and applications identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2021, 18(2): 1218–1232. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2021.3071441. [57] HOROWICZ E, SHAPIRA T, and SHAVITT Y. A few shots traffic classification with mini-FlowPic augmentations[C]. The 22nd ACM Internet Measurement Conference, Nice, France, 2022: 647–654. doi: 10.1145/3517745.3561436. [58] HOROWICZ E, SHAPIRA T, and SHAVITT Y. Self-supervised traffic classification: Flow embedding and few-shot solutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2024, 21(3): 3054–3067. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2024.3366848. [59] WANG Wei, ZHU Ming, ZENG Xuewen, et al. Malware traffic classification using convolutional neural network for representation learning[C]. 2017 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Da Nang, Vietnam, 2017: 712–717. doi: 10.1109/ICOIN.2017.7899588. [60] HOLASOVA E, BLAZEK P, FUJDIAK R, et al. Exploring the power of convolutional neural networks for encrypted industrial protocols recognition[J]. Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks, 2024, 38: 101269. doi: 10.1016/j.segan.2023.101269. [61] PENG Quan, FU Xingbing, LIN Fei, et al. Multi-scale convolutional neural networks optimized by elite strategy dung beetle optimization algorithm for encrypted traffic classification[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2025, 264: 125729. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125729. [62] YU Lancan, YUAN Jianting, ZHENG Jin, et al. A model of encrypted network traffic classification that trades off accuracy and efficiency[J]. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 2025, 33(1): 11. doi: 10.1007/s10922-024-09892-y. [63] ABBAS S, ALSUBAI S, OJO S, et al. An efficient deep recurrent neural network for detection of cyberattacks in realistic IoT environment[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2024, 80(10): 13557–13575. doi: 10.1007/s11227-024-05993-2. [64] SONG Zhuoxue, ZHAO Ziming, ZHANG Fan, et al. I2RNN: An incremental and interpretable recurrent neural network for encrypted traffic classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2024, 19(1): 1–14. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2023.3245411. [65] REN Xinming, GU Huaxi, and WEI Wenting. Tree-RNN: Tree structural recurrent neural network for network traffic classification[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 167: 114363. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114363. [66] HUOH T L, LUO Yan, LI Peilong, et al. Flow-based encrypted network traffic classification with graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2023, 20(2): 1224–1237. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2022.3227500. [67] HAN Xinbo, XU Guizhong, ZHANG Meng, et al. DE-GNN: Dual embedding with graph neural network for fine-grained encrypted traffic classification[J]. Computer Networks, 2024, 245: 110372. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2024.110372. [68] SHEN Meng, ZHANG Jinpeng, ZHU Liehuang, et al. Accurate decentralized application identification via encrypted traffic analysis using graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 2367–2380. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3050608. [69] JUNG I S, SONG Y R, JILCHA L A, et al. Enhanced encrypted traffic analysis leveraging graph neural networks and optimized feature dimensionality reduction[J]. Symmetry, 2024, 16(6): 733. doi: 10.3390/sym16060733. [70] LI Zhiyuan, ZHAO Hongyi, ZHAO Jingyu, et al. SAT-Net: A staggered attention network using graph neural networks for encrypted traffic classification[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2025, 233: 104069. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2024.104069. [71] LIN Xinjie, XIONG Gang, GOU Gaopeng, et al. ET-BERT: A contextualized datagram representation with pre-training transformers for encrypted traffic classification[C]. The ACM Web Conference 2022, Lyon, France, 2022: 633–642. doi: 10.1145/3485447.3512217. [72] HANG Zijun, LU Yuliang, WANG Yongjie, et al. Flow-MAE: Leveraging masked AutoEncoder for accurate, efficient and robust malicious traffic classification[C]. The 26th International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions and Defenses, Hong Kong, China, 2023: 297–314. doi: 10.1145/3607199.3607206. [73] ZHAO Ruijie, ZHAN Mingwei, DENG Xianwen, et al. Yet another traffic classifier: A masked Autoencoder based traffic transformer with multi-level flow representation[C]. The 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, USA, 2023: 5420–5427. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v37i4.25674. [74] FEDORCHENKO E, NOVIKOVA E, and SHULEPOV A. Comparative review of the intrusion detection systems based on federated learning: Advantages and open challenges[J]. Algorithms, 2022, 15(7): 247. doi: 10.3390/a15070247. [75] SANON S P, REDDY R, LIPPS C, et al. Secure federated learning: An evaluation of homomorphic encrypted network traffic prediction[C]. 2023 IEEE 20th Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, USA, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/CCNC51644.2023.10060116. [76] MARCILLO P, SUNTAXI G, and HERNÁNDEZ-ÁLVAREZ M. A privacy-preserving scheme for a traffic accident risk level prediction system[J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(21): 9876. doi: 10.3390/app14219876. [77] NOVIKOVA E, DOYNIKOVA E, and GOLUBEV S. Federated learning for intrusion detection in the critical infrastructures: Vertically partitioned data use case[J]. Algorithms, 2022, 15(4): 104. doi: 10.3390/a15040104. [78] JIN Zhiping, DUAN Ke, CHEN Changhui, et al. FedETC: Encrypted traffic classification based on federated learning[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(16): e35962. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35962. [79] YIN Ziwei, LI Kun, and BI Hongjun. Trusted multi-domain DDoS detection based on federated learning[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(20): 7753. doi: 10.3390/s22207753. [80] LIN Peng, YE Kejiang, HU Yishen, et al. A novel multimodal deep learning framework for encrypted traffic classification[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 2023, 31(3): 1369–1384. doi: 10.1109/TNET.2022.3215507. [81] ACETO G, CIUONZO D, MONTIERI A, et al. DISTILLER: Encrypted traffic classification via multimodal multitask deep learning[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2021, 183/184: 102985. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2021.102985. [82] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139–144. doi: 10.1145/3422622. [83] YUAN Xinyu, QIAO Yan, WEI Zhenchun, et al. Diffusion models meet network management: Improving traffic matrix analysis with diffusion-based approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2025, 22(2): 1259–1275. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2025.3527442. [84] YANG Ling, ZHANG Zhilong, SONG Yang, et al. Diffusion models: A comprehensive survey of methods and applications[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023, 56(4): 105. doi: 10.1145/3626235. [85] WANG Pan, WANG Zixuan, YE Feng, et al. ByteSGAN: A semi-supervised generative adversarial network for encrypted traffic classification in SDN edge gateway[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 200: 108535. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2021.108535. [86] ILIYASU A S and DENG Huifang. Semi-supervised encrypted traffic classification with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 118–126. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962106. [87] MAO Jiaming, ZHANG Mingming, CHEN Mu, et al. Semisupervised encrypted traffic identification based on auxiliary classification generative adversarial network[J]. Computer Systems Science and Engineering, 2021, 39(3): 373–390. doi: 10.32604/csse.2021.018086. [88] SIVAROOPAN N, BANDARA D, MADARASINGHA C, et al. NetDiffus: Network traffic generation by diffusion models through time-series imaging[J]. Computer Networks, 2024, 251: 110616. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2024.110616. [89] ZHANG Shiyuan, CHAI Haoye, LI Yong, et al. PacketDiff: A flow guided diffusion model for network packet trace generation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2025, 12(18): 38804–38819. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2025.3587658. [90] JIANG Xi, LIU Shinan, GEMBER-JACOBSON A, et al. NetDiffusion: Network data augmentation through protocol-constrained traffic generation[J]. The ACM on Measurement and Analysis of Computing Systems, 2024, 8(1): 11. doi: 10.1145/3639037. [91] HAYDEN B, WALSH T, and BARTON A. Defending against deep learning-based traffic fingerprinting attacks with adversarial examples[J]. ACM Transactions on Privacy and Security, 2025, 28(1): 1. doi: 10.1145/3698591. [92] ABOLFATHI M, INTURI S, BANAEI-KASHANI F, et al. Toward enhancing web privacy on HTTPS traffic: A novel SuperLearner attack model and an efficient defense approach with adversarial examples[J]. Computers & Security, 2024, 139: 103673. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2023.103673. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
